Lecture 8: Substitution and Income Effects of a Price Change
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is the definition of an ordinary good?
As their price falls, their demand will rise
What is the total effect of a price change made up of?
Pure price (substitution) effect and income effect
What is the definition of the pure price (substitution) effect?
As the good becomes cheaper relative to other goods, we demand more of it
What is the definition of the income effect?
As the price of a good falls, we have more money in our pockets to buy more of all goods
What does the sign of the total effect depend on?
Depends on the sign of the substitution and income effect
If the signs are different, the sign of the total effect depends on the magnitude of the two effects
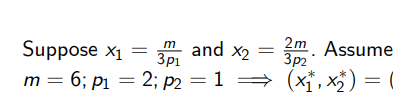
How do we calculate the original and new optimal consumption bundle given: (pictured) and that p1 changes to p’1 = 1? What is the total effect of the change in price?
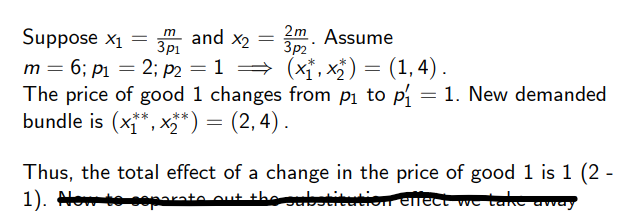
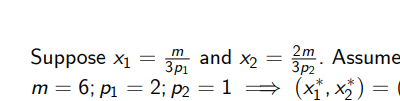
Calculate the original level of utility given: (pictured)
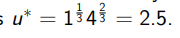
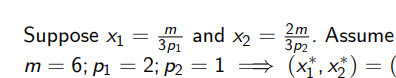
Given (pictured), what is the level of income required to achieve a utility of 2.5 at p’1?
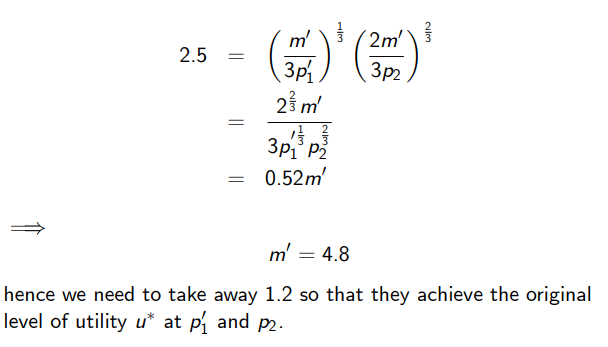
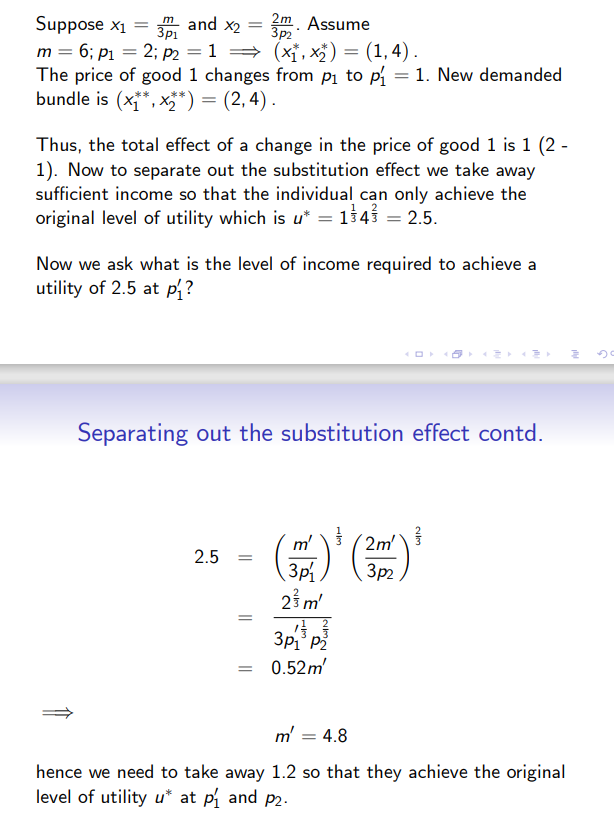
How do we calculate the intermediate bundle given (pictured)?


What are the values of the TE, SE and IE?

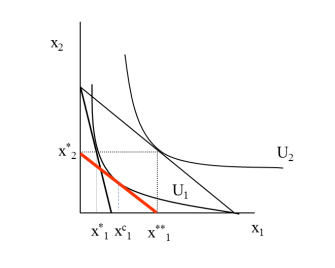
How do we show the TE, IE and SE diagrammatically?
What is the equation for the TE (uncompensated response) of the demand for good 1 when its price changes from p1 to p’1 using the Marshallian demand curves?
Difference in demand as a result of the price change in good 1 from p1 to p’1
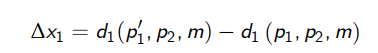
What is the equation for the SE (Compensated response) of the demand for good 1 when its price changes from p1 to p’1 using the Marshallian demand curves?
The effect on demand due to a change in the price of good 1 from p1 to p’1 and a simultaneous change in income from m to m’
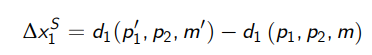
What is the equation for the IE (Compensated response) of the demand for good 1 when its price changes from p1 to p’1 using the Marshallian demand curves?
The effect on demand due to a change in income from m’ to m given the price of good 1 (p’1)
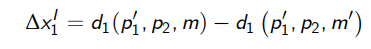
What type of good do we normally interpret x2 as when assessing TE, SE and IE?
x2 = numeraire good; allows us to interpret the variable on the y-axis as expenditure on all other goods
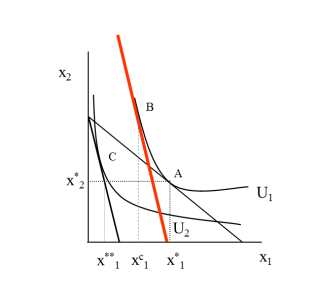
How can we explain this diagram regarding TE, SE and IE?

What sign does the SE always have?
Negative (technically non-positive)
If a good has a positive (negative) IE, what type of good is it?
Normal (inferior)
To derive the entire demand schedule (for all prices) we solve what optimisation problem?
Expenditure Minimisation Problem (EMP)
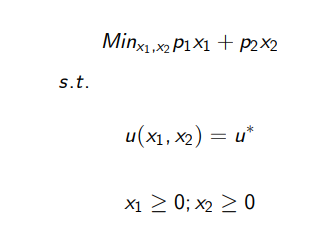
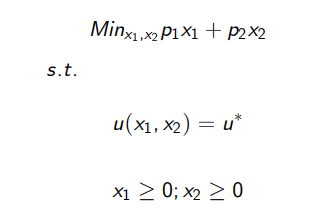
What are the generic solutions to the EMP?

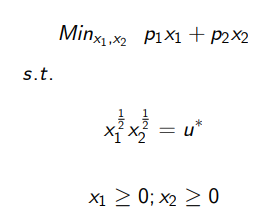
Solve this EMP (FOC and SOC)

How can we show the SE using the Hicksian demand curve?
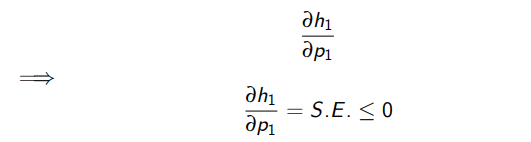
What does the theory of duality tell us?
The solutions to UMP and EMP are equivalent as long as certain conditions hold
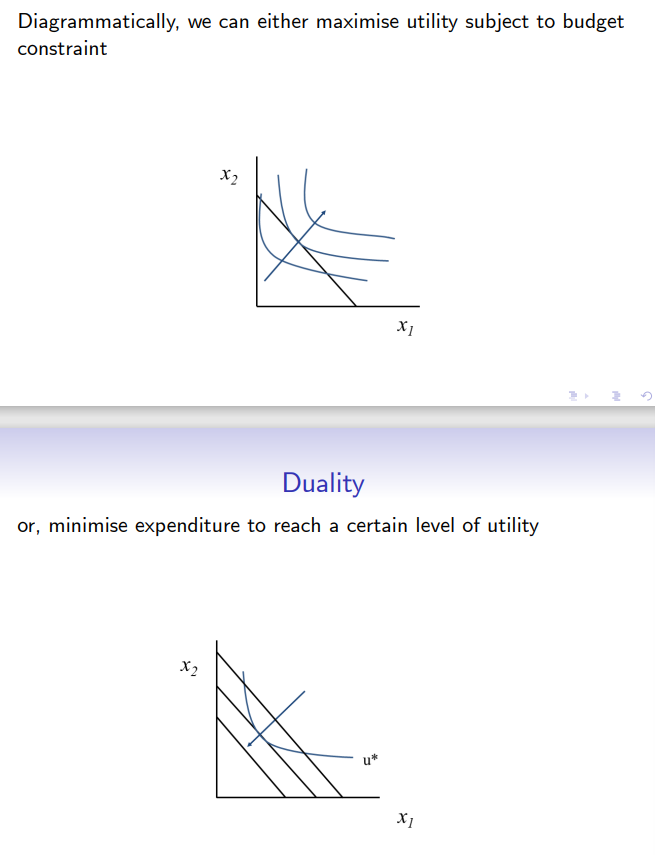
What is the first condition for duality (solutions to UMP and EMP being equivalent)?
The minimised expenditure required to reach a certain level of utility should equal the income level, m in the budget constraint of the UMP
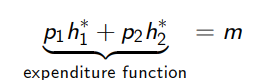
What is the second condition for duality (solutions to UMP and EMP being equivalent)?
The maximum utility obtained from the utility maximisation problem is equal to the target level of utility in the expenditure minimisation problem
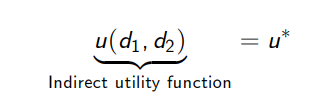
How do we show equivalence between Marshallian and Hicksian demand curves where i = 1, 2?

Show that the Marshallian and Hicksian demand curves are equivalent for this example
