AQA Biology paper 1
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
aerobic respiration
an exothermic reaction in which glucose is broken down using oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water and release energy for the cells
anaerobic respiration
an exothermic reaction in which glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen to produce lactic acid in animals and ethanol and carbon dioxide in plants and yeast. A small amount of energy is transferred for the cells
exothermic reaction
a reaction that transfers energy to the environment
glycogen
carbohydrate store in animals
lactic acid
the end product of anaerobic respiration in animal cells
oxygen debt
the extra oxygen that must be taken into the body after exercise has stopped to complete the aerobic respiration of lactic acid
Mitochondria
Organelle that is the site of respiration
Responses to exercise
Heart rate increases, Breathing rate increases, glycogen in muscles is converted to glucose
endothermic reaction
a reaction that requires a transfer of energy from the environment
glucose
a simple sugar
limiting factors
limit the rate of a reaction, for example photosynthesis
photosynthesis
the process by which plants make food using carbon dioxide, water, and light
Reactants for photosynthesis
water and carbon dioxide
Products of photosynthesis
glucose and oxygen
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
white blood cells
Blood cells that perform the function of destroying disease-causing microorganisms
Sperm cells
It has a long tail and a streamlined head to help it swim. There are a lot of mitochondria in the cell to provide the energy needed. It also carries enzymes in its head to digest through the egg cell membrane.
light
energy source for photosynthesis
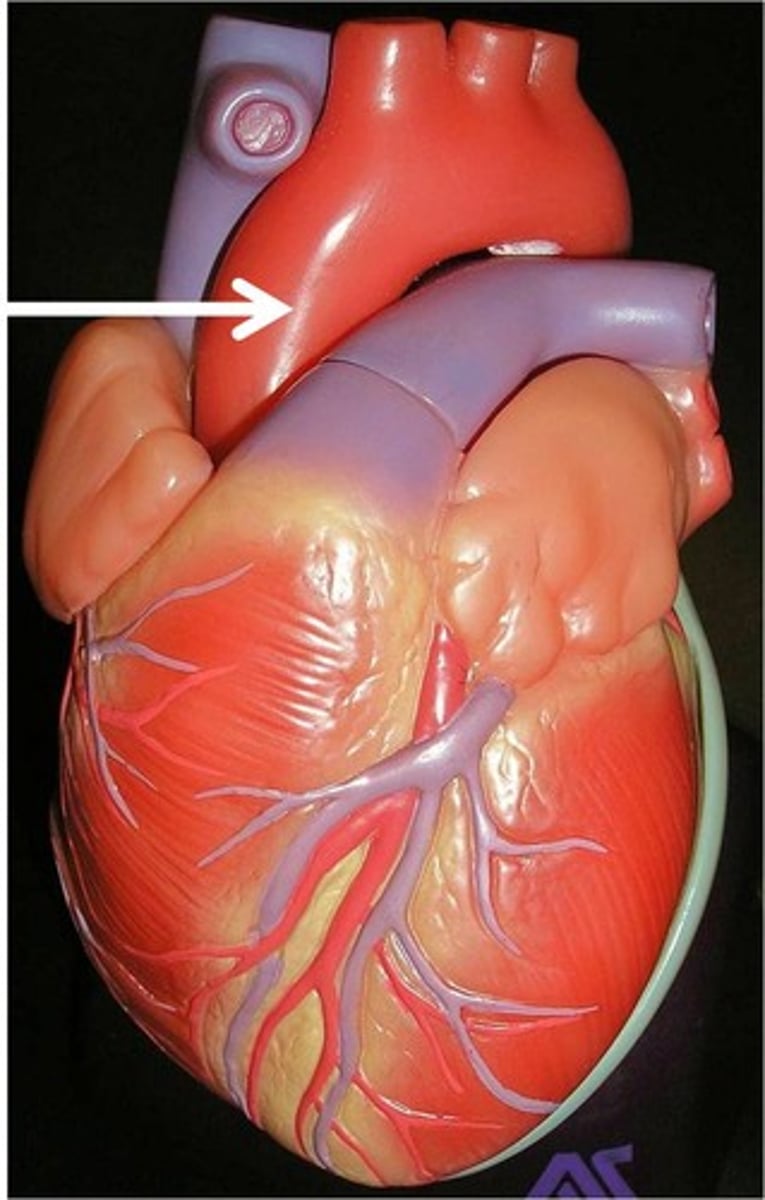
aorta
the artery that leaves the heart from the left ventricle and carries oxygenated blood to the body
arteries
blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. They usually carry oxygenated blood and have a pulse
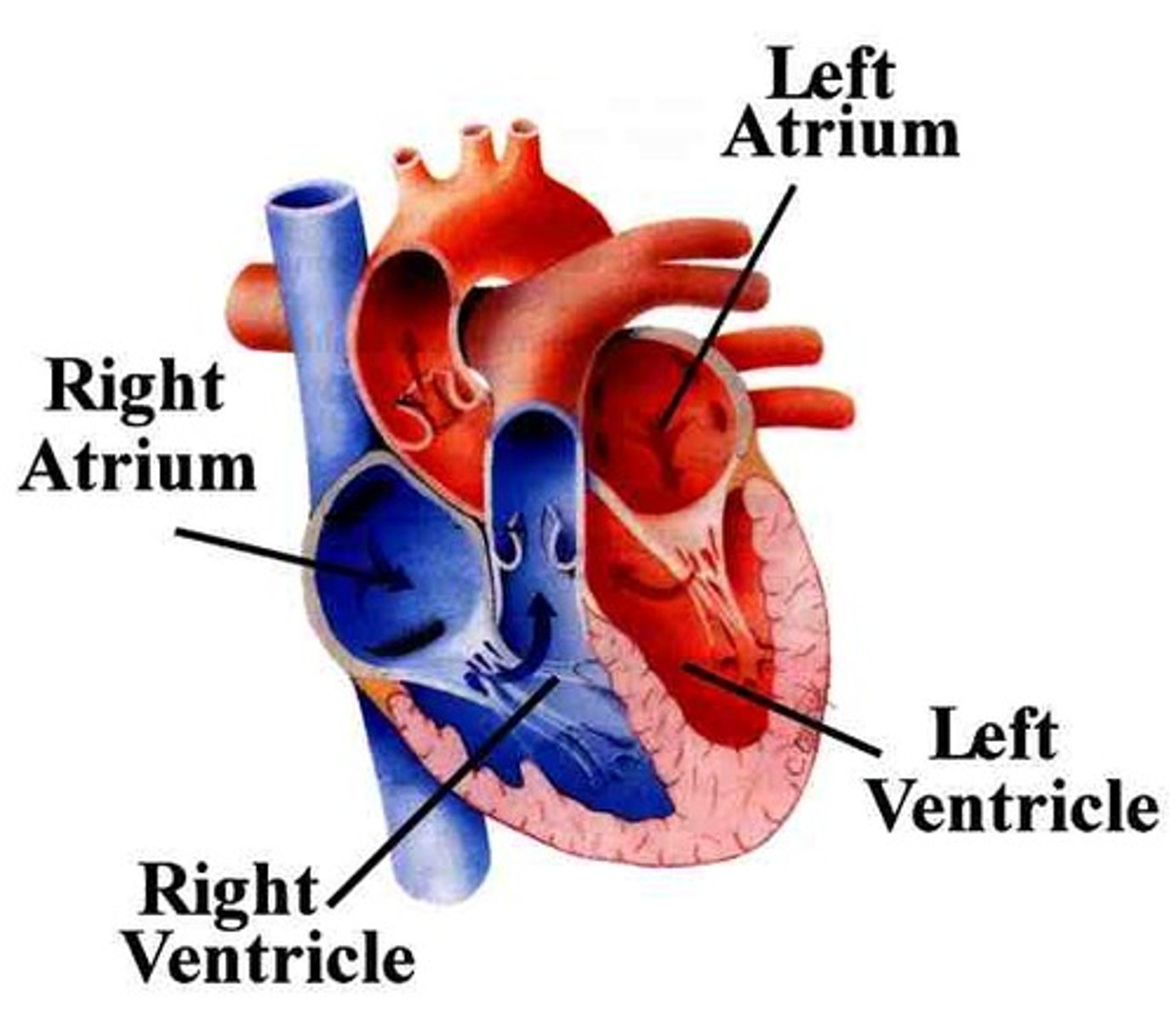
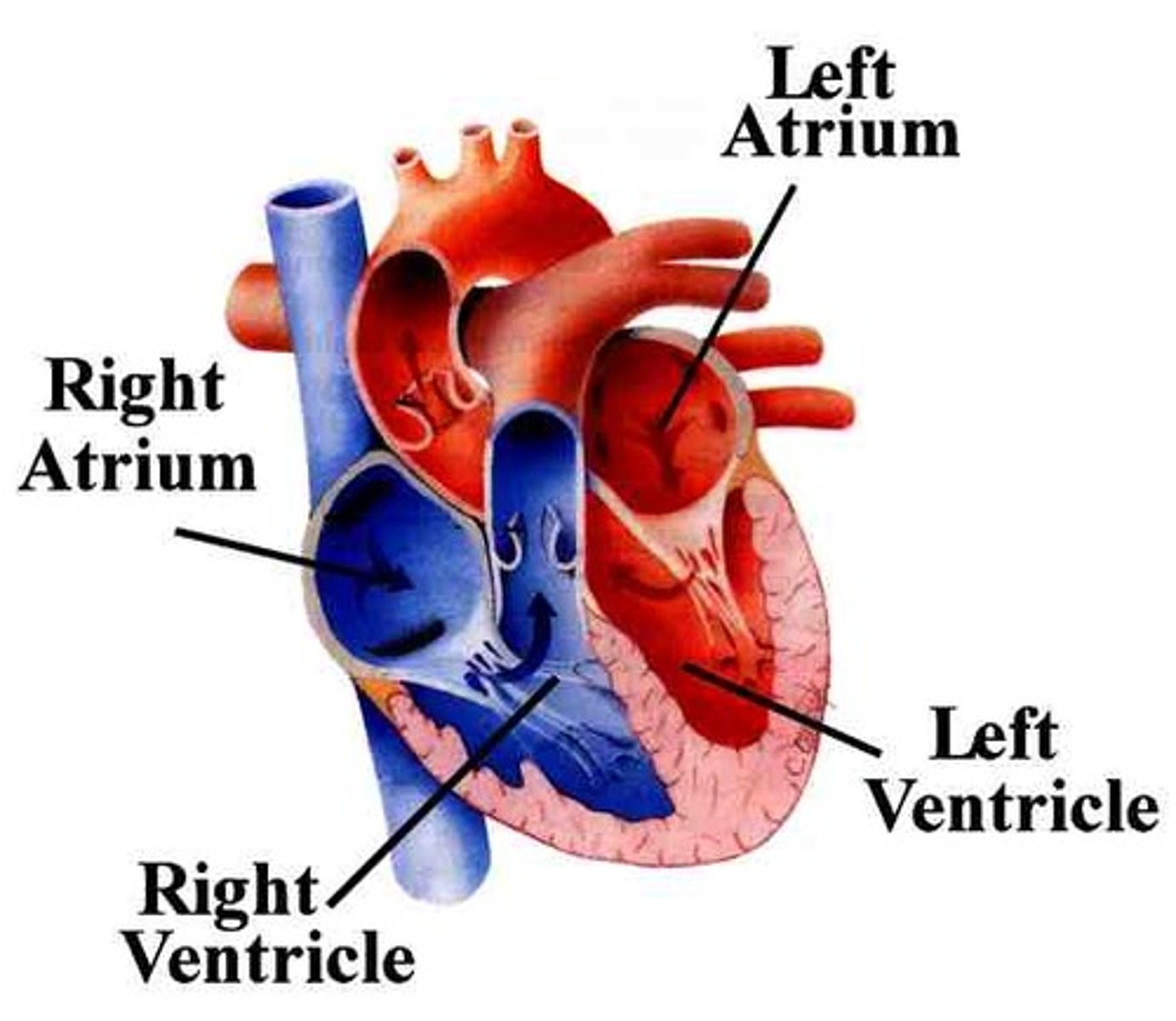
atria
the upper chambers of the heart
capillaries
the smallest blood vessels. They run between individual cells and have a wall that is only one cell thick
coronary arteries
the blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle
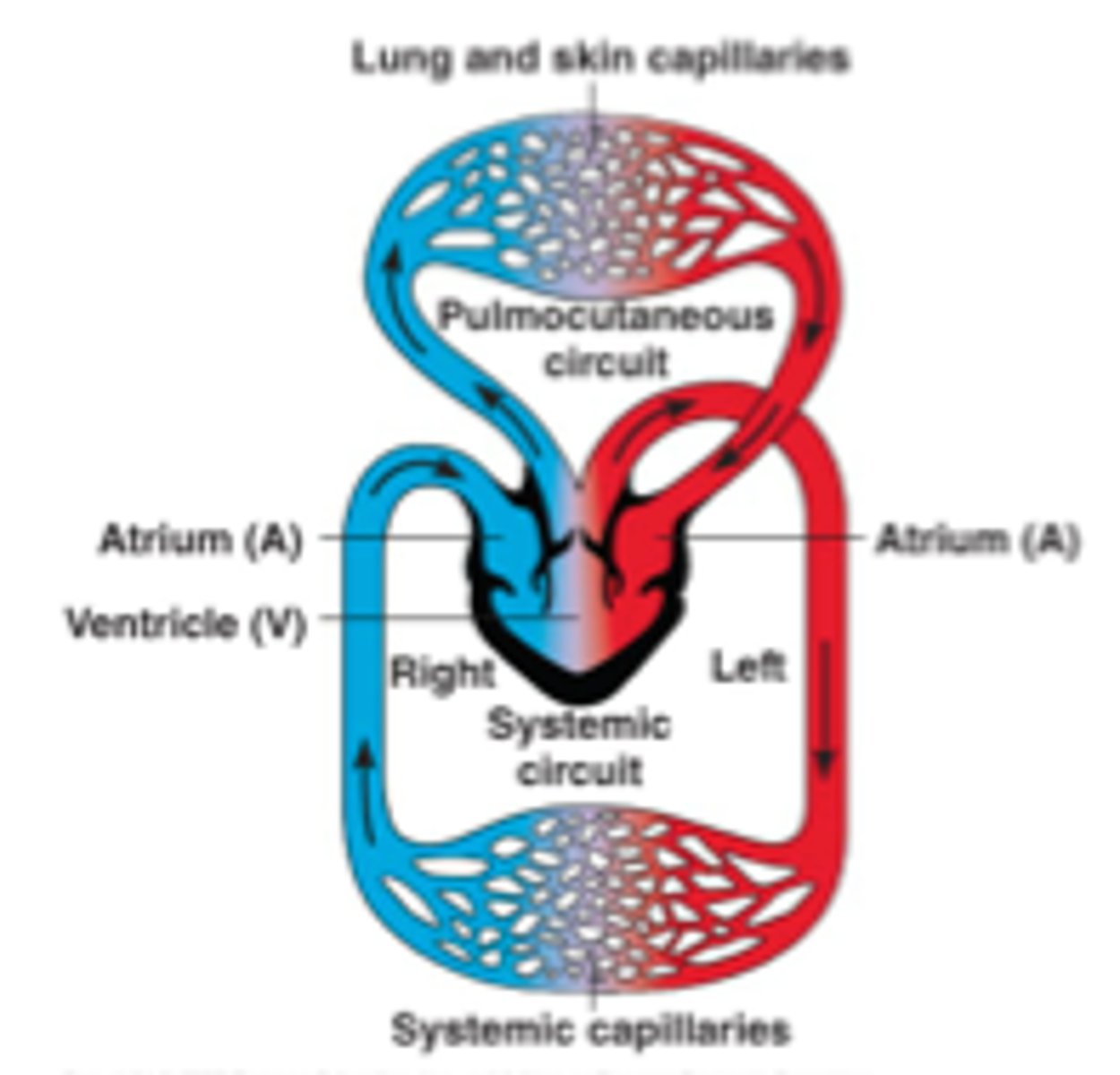
double circulatory system
the circulation of blood from the heart to the lungs is separate from the circulation of blood from the heart to the rest of the body
epidermal
the name given to cells that make up the epidermis or outer layer of an organism
guard cells
surround the stomata in the leaves of plants and control their opening and closing

haemoglobin
the red pigment that carries oxygen around the body in the red blood cells
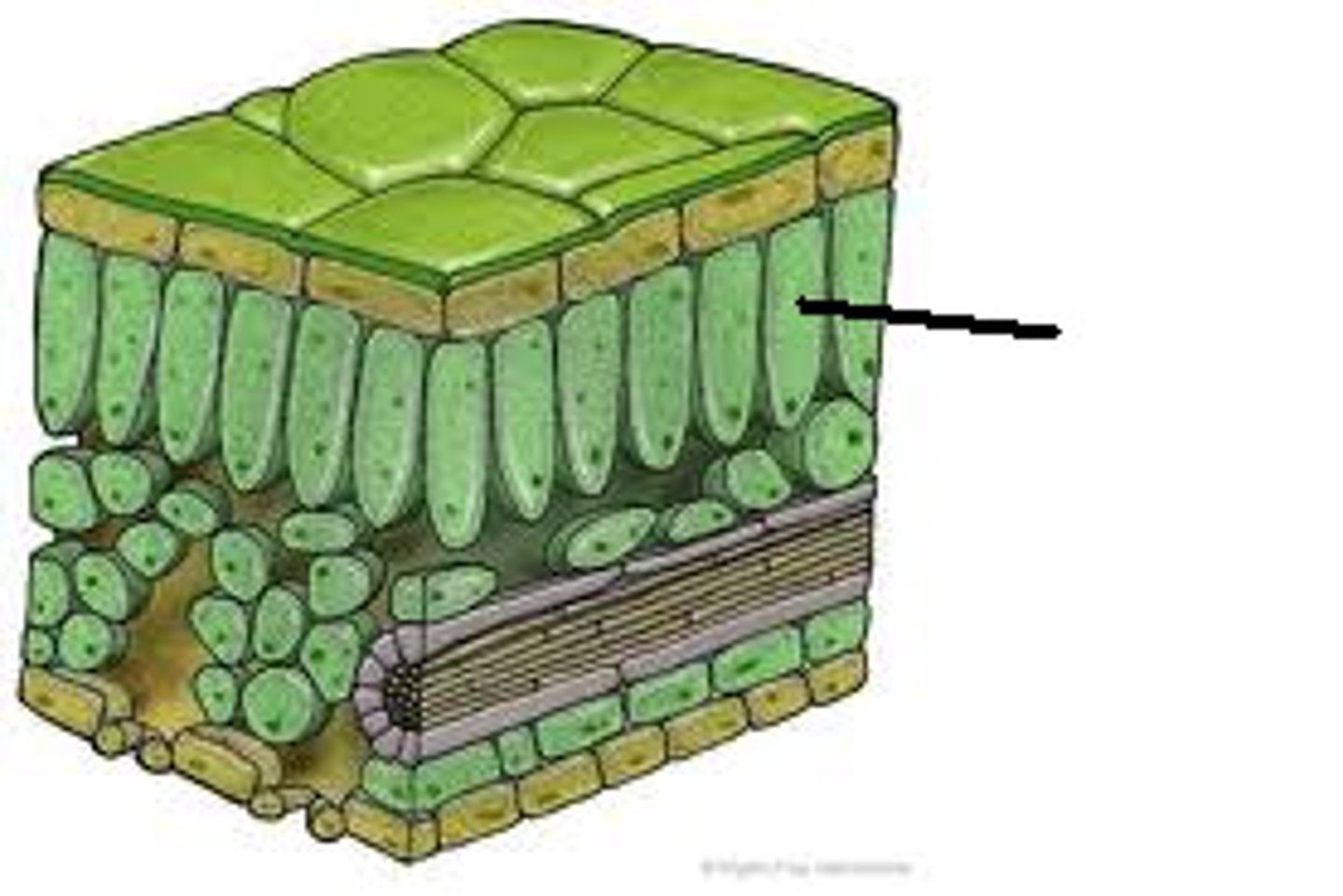
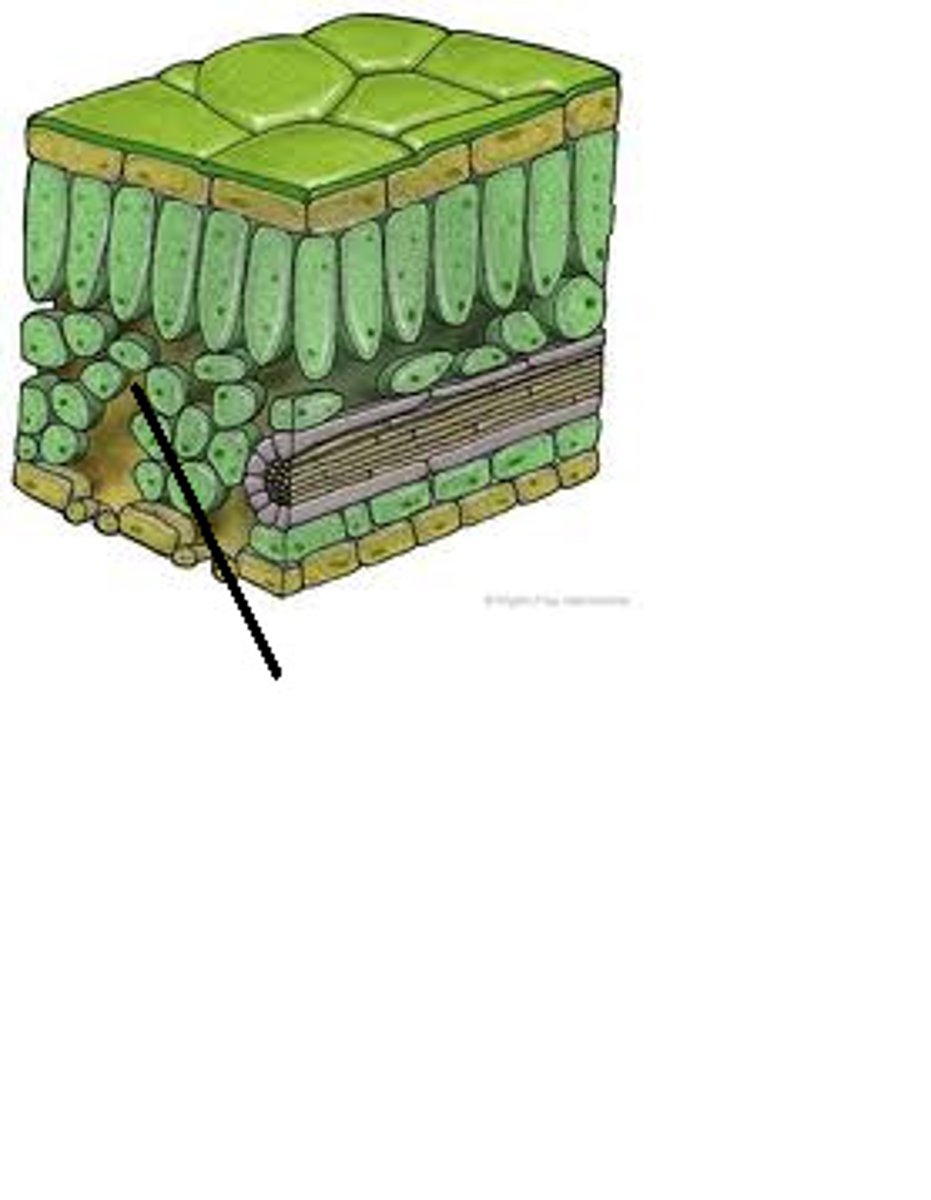
palisade mesophyll
the upper layer of the mesophyll tissue in plant leaves made up of closely packed cells that contain many chloroplasts for photosynthesis
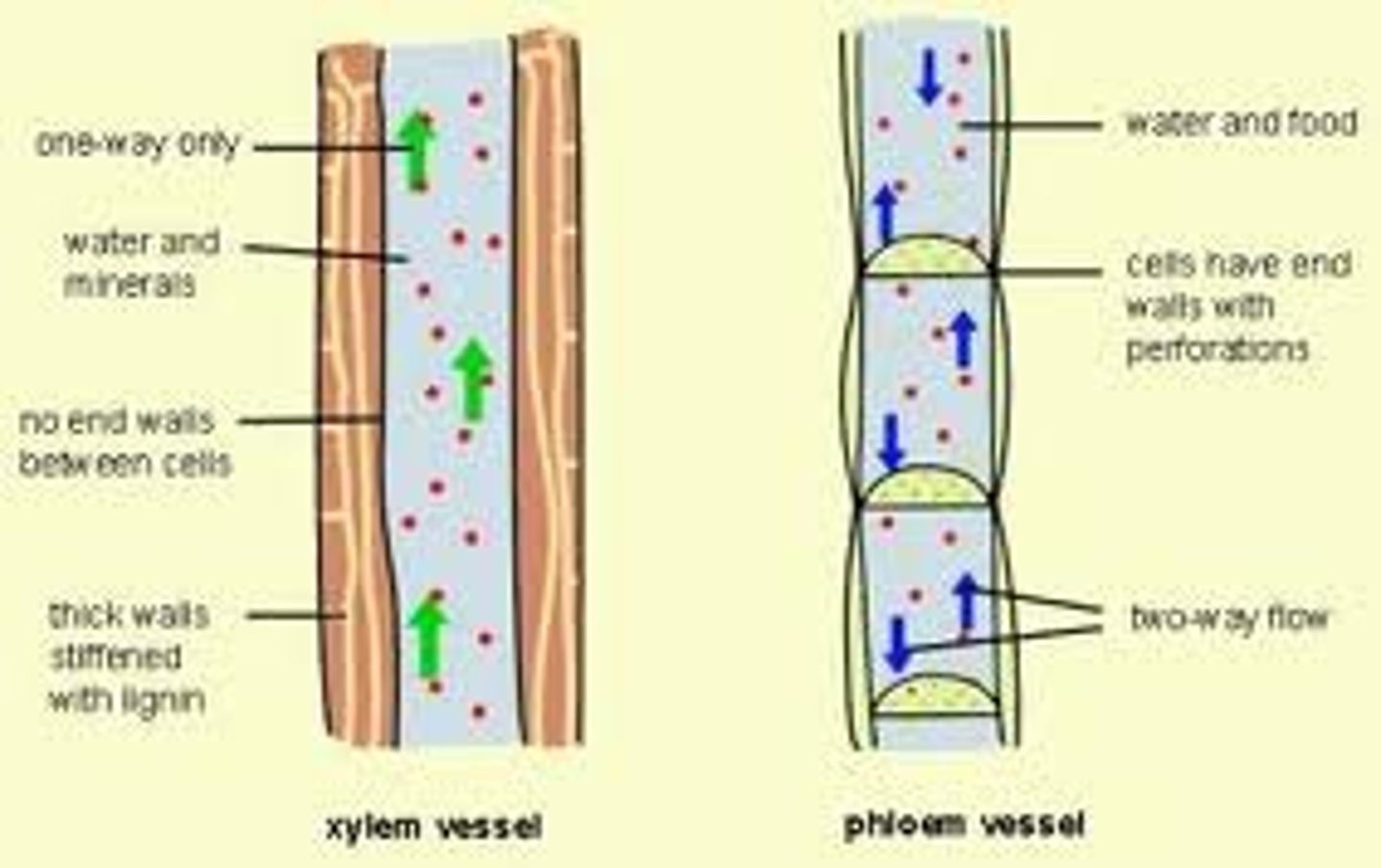
phloem
the living transport tissue in plants that carries dissolved food (sugars) around the plant
plasma
the clear yellow-liquid part of the blood that carries dissolved substances and blood cells around the body
platelets
fragments of cells in the blood that play a vital role in the clotting mechanism of the blood
pulmonary artery
the large blood vessel that takes deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs
pulmonary vein
the large blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left atrium of the heart
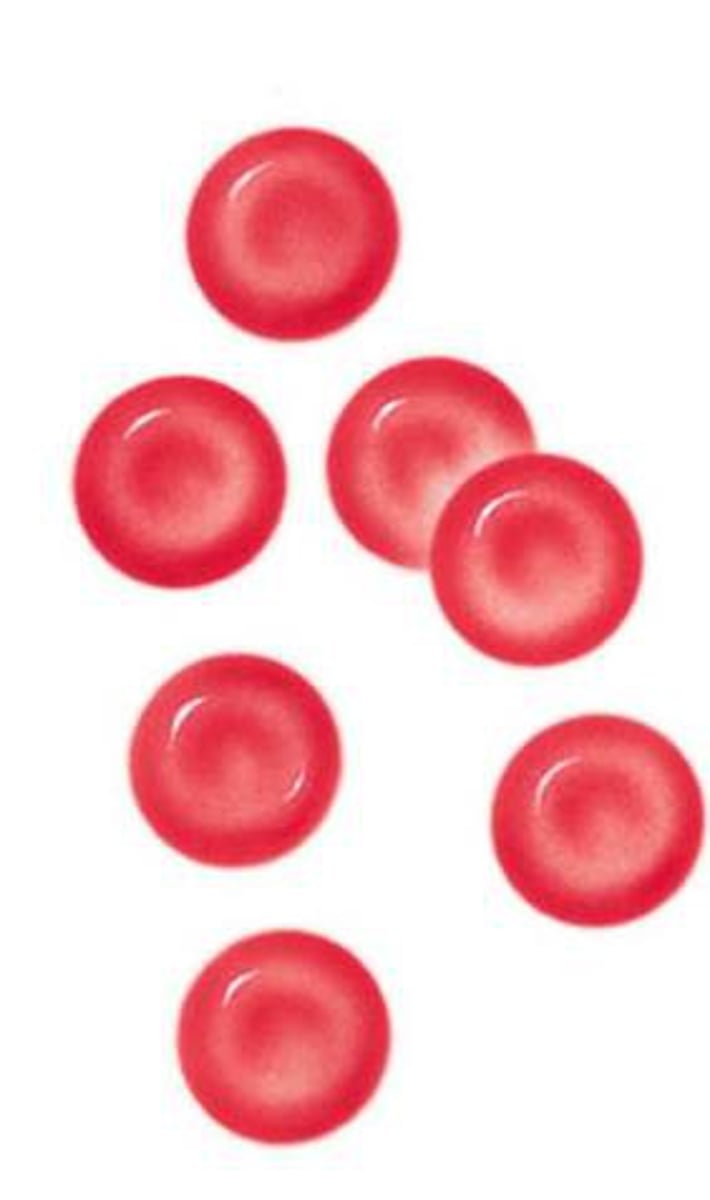
red blood cells
biconcave cells that contain the red pigment haemoglobin and carry oxygen around the body in the blood
spongy mesophyll
the lower layer of mesophyll tissue in plant leaves that contains some chloroplasts and many large air spaces to give a big surface area for the exchange of gases
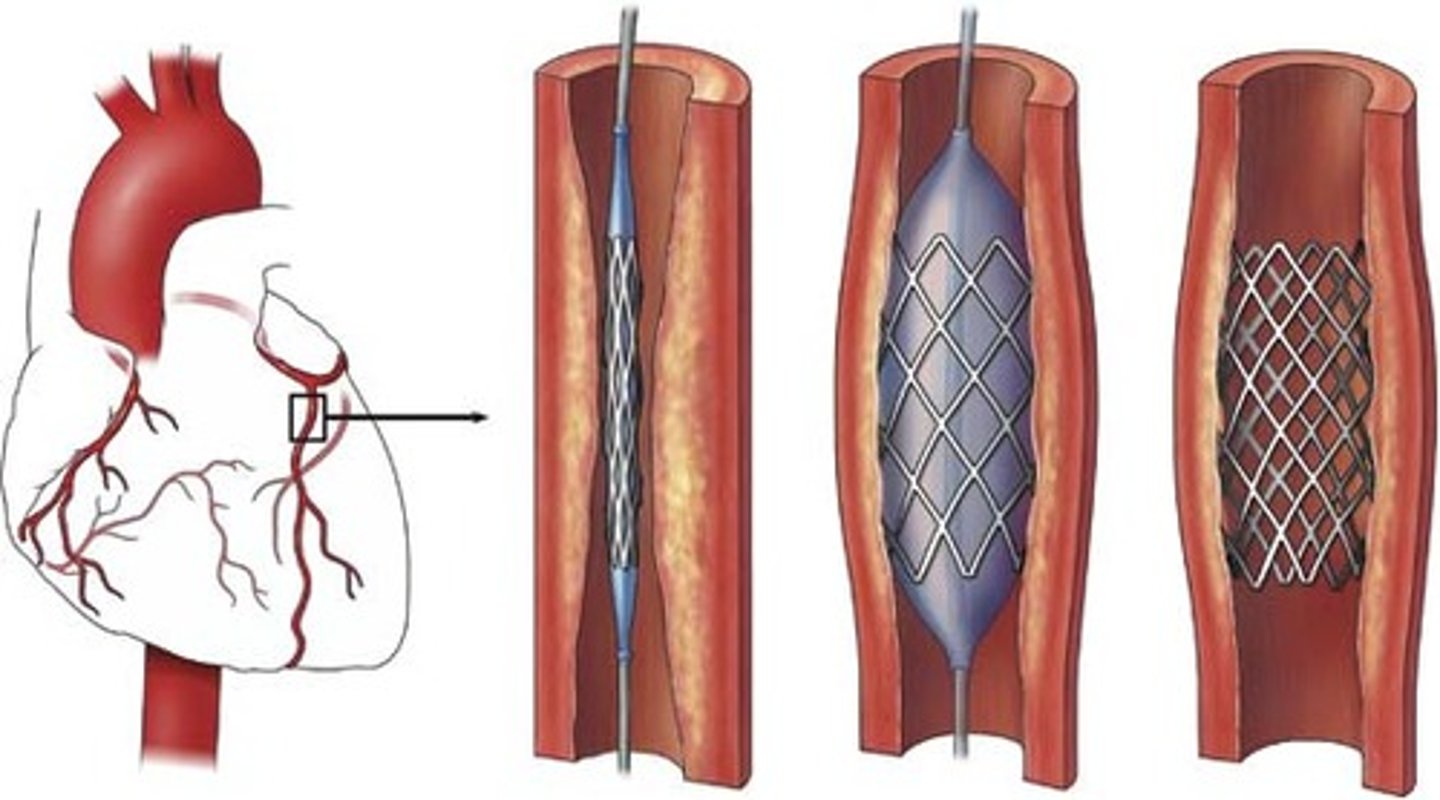
stent
a metal mesh placed in a blocked or partially blocked artery. They are used to open up the blood vessel by the inflation of a tiny balloon
translocation
the movement of sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant through the phloem
transpiration
the loss of water vapour from the leaves of plants through the stomata when they are opened to allow gas exchange for photosynthesis. It involves evaporation from the surface of the cells and diffusion through the stomata
veins
blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. They usually carry deoxygenated blood and have valves to prevent the backflow of blood
vena cava
the large vein that brings deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart
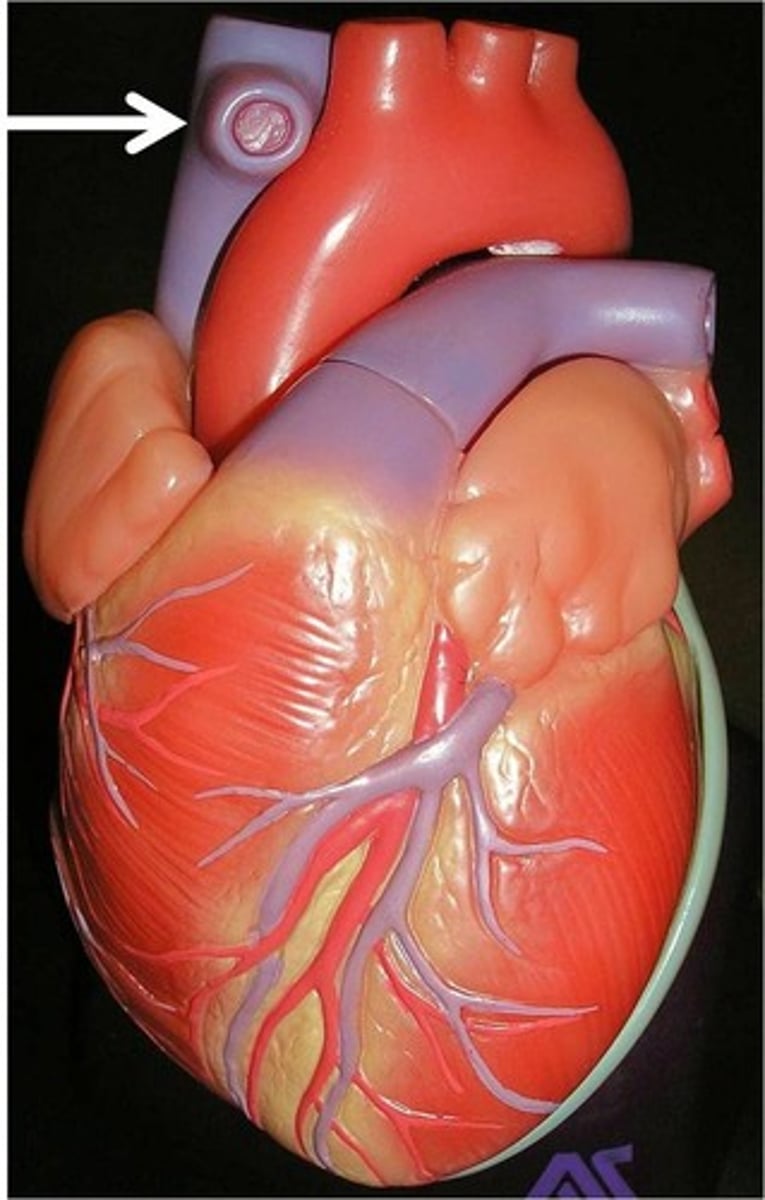
ventricles
chambers of the heart that contract to force blood out of the heart
white blood cells
blood cells involved in the immune system of the body. They engulf pathogens and make antibodies and antitoxins

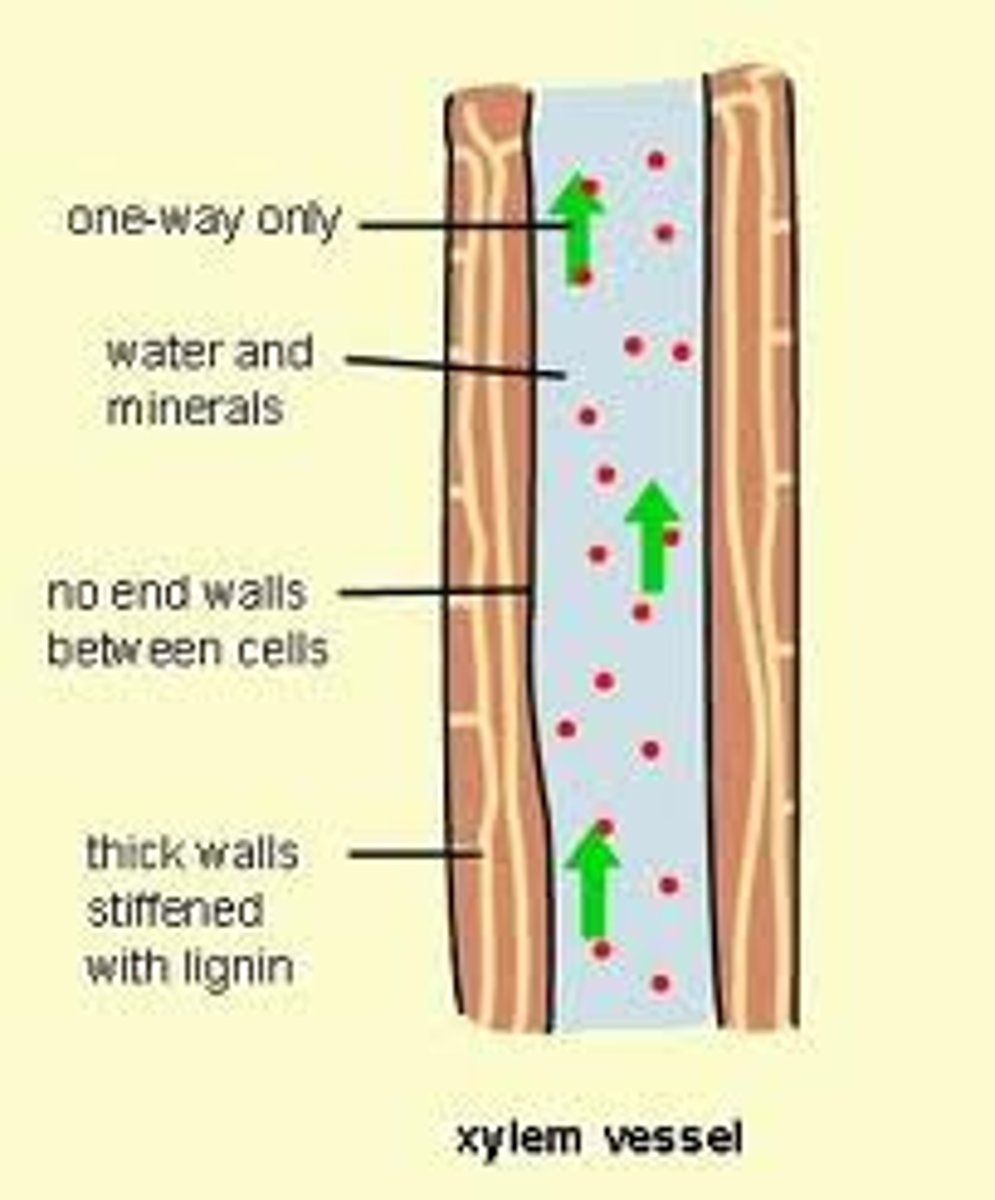
xylem
the non-living transport tissue in plants that transports water from the roots to the leaves and shoots
active site
the site on an enzyme where the reactants bind
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
amylase
enzyme that speeds up the digestion of starch into sugars
bile
neutralises stomach acid to give a high pH for the enzymes from the pancreas and small intestine to work well. It is not an enzyme
carbohydrases
enzymes that speed up the breakdown of carbohydrates into simple sugars
carbohydrates
molecules that contain only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They provide the energy for the metabolism and are found in foods such as rice, potatoes, and bread
denatured
the breakdown of the molecular structure of a protein so it no longer functions
differentiate
the process where cells become specialised for a particular function
digestive system
organ system where food is digested and absorbed
enzymes
biological catalysts, usually proteins
fatty acids
part of the structure of a lipid molecule
glycerol
part of the structure of a lipid molecule
lipase
enzymes that speed up the breakdown of lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
lipids
include fats and oils and are found in foods such as butter, olive oil, and crisps. They are made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
organ
an aggregation (collection ) of different tissues working together to carry out specific functions
organ system
a group of organs that work together to carry out specific functions and form organisms
proteases
enzymes that speed up the breakdown of proteins into amino acids
proteins
molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen and are made of long chains of amino acids. They are used for building the cells and tissues of the body and to form enzymes
simple sugars
small carbohydrate units, for example glucose
tissue
a group of specialised cells with a similar structure and function
adult stem cells
stem cells that are found in adults that can differentiate and form a limited number of cells
cell cycle
the three-stage process of cell division in a body cell that involves mitosis and results in the formation of two identical daughter cells
cloning
the production of identical offspring by asexual reproduction
differentiate
the process where cells become specialised for a particular function
embryonic stem cells
stem cells from an early embryo that can differentiate to form the specialised cells of the body
mitosis
part of the cell cycle where one set of new chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell forming two identical nuclei during cell division
stem cells
undifferentiated cells with the potential to form a wide variety of different cell types
therapeutic cloning
a process where an embryo is produced that is genetically identical to the patient so the cells can then be used in medical treatments
How many chromosomes in the human genome?
23 pairs
Where are stem cells found in plants?
Meristems in roots and stems
benign tumours
growths of abnormal cells that are contained in one area, usually within a membrane, and do not invade other tissues
cancer
the common name for a malignant tumour, formed as a result of changes in cells that lead to uncontrolled growth and division
carcinogens
agents that cause cancer or significantly increase the risk of developing cancer
correlation
an apparent link or relationship between two factors
ionising radiation
has enough energy to cause ionisation in the materials it passes through, which in turn can make them biologically active and may result in mutation and cancer
malignant tumours
invade neighbouring tissues and spread to different parts of the body in the blood where they form secondary tumours. They are also known as cancers
tumour
a mass of abnormally growing cells that forms when the cells do not respond to the normal mechanisms that control growth and when control of the cell cycle is lost
clinical trials
test potential new drugs on healthy and patient volunteers
placebo
a medicine that does not contain the active drug being tested, used in clinical trials of new medicines
preclinical testing
is carried out on a potential new medicine in a laboratory using cells, tissues, and live animals
communicable disease
disease caused by pathogens that can be passed from one organism to another
microorganisms
organisms that are usually single-celled and can only be seen using a microscope . They include bacteria, fungi, viruses and protists
mutation
a change in the genetic material of an organism
non-communicable diseases
are not infectious and cannot be passed from one organism to another
pathogens
microorganisms that cause disease
sexually transmitted disease (STD)
transmitted from an infected person to an uninfected person by unprotected sexual contact
vaccine
dead or inactive pathogenic material used in vaccination to develop immunity to a disease in a healthy person
virus
pathogens that are much smaller than bacteria and can only reproduce inside living cells of other organisms
Muscle cells
These cells are long (so that they have space to contract) and contain lots of mitochondria to generate the energy needed for contraction
Alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
Bronchi
two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
gas exchange
process of taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide
Root hair cells
Cells on the surface of plant roots which grow into long "hairs" that stick out into the soil. This gives the plant a big surface area for absorbing water and mineral ions from the soil.
Cellulose
a carbohydrate composed of many monomers.
Magnification
Image size/actual size
Bacteria
don't have a true nucleus instead they have a single circular strand of DNA that floats freely in the cytoplasm
bacteria
Don't have chloroplasts or mitochondria