Final Exam #2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms

Osteoblasts
Function: Build new bone matrix by secreting collagen and minerals.
Importance: Essential for bone growth, healing, and remodeling.
Other Facts: Found on bone surfaces; become osteocytes when trapped in matrix.
Quick Tip: “Blasts Build” — think of them as bone construction workers.
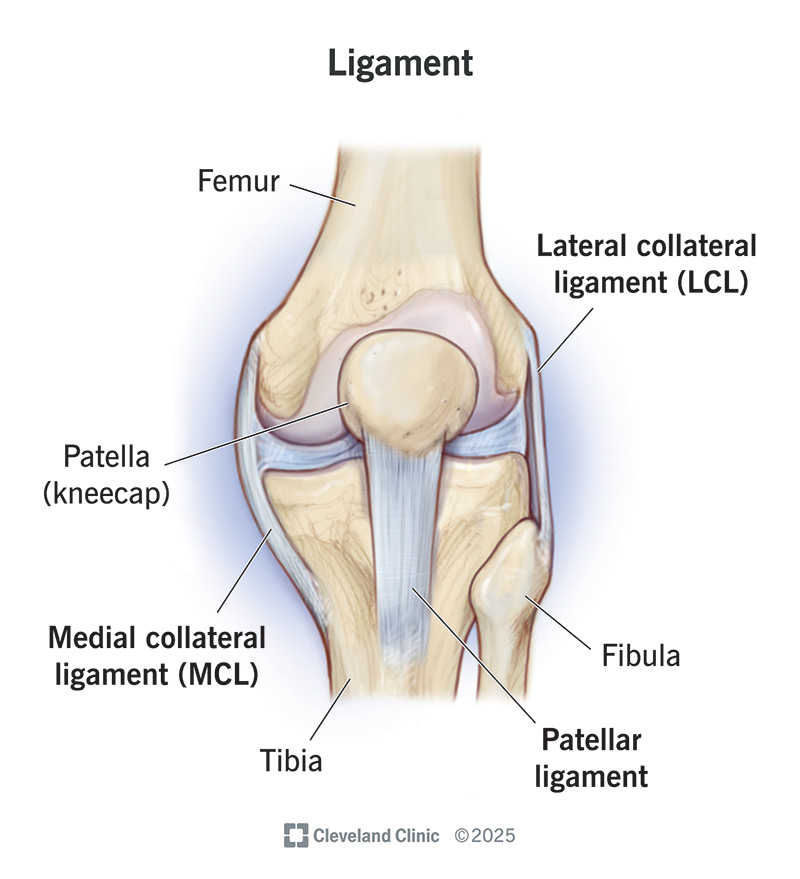
Ligament
Function: Connects bone to bone; stabilizes joints.
Importance: Prevents excessive movement and injury.
Other Facts: Made of dense regular connective tissue; poor blood supply = slow healing.
Quick Tip: “Ligament = Link bones.”
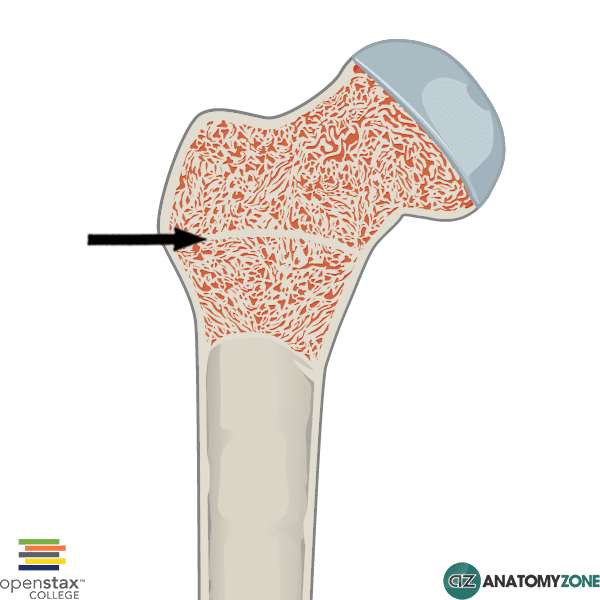
Epiphyseal Plate
Function: Site of longitudinal bone growth during childhood/adolescence.
Importance: Determines future height and bone length.
Other Facts: Located between epiphysis and diaphysis of long bones; becomes epiphyseal line after puberty.
Quick Tip: “Growth plate = growing space.”
Blood Calcium Levels
Function: Supports nerve signaling, muscle contraction, and bone strength.
Importance: Must stay within a narrow range for survival.
Other Facts: Regulated by PTH (raises) and calcitonin (lowers); stored in bones.
Quick Tip: “Calcium = calm nerves + strong bones.”
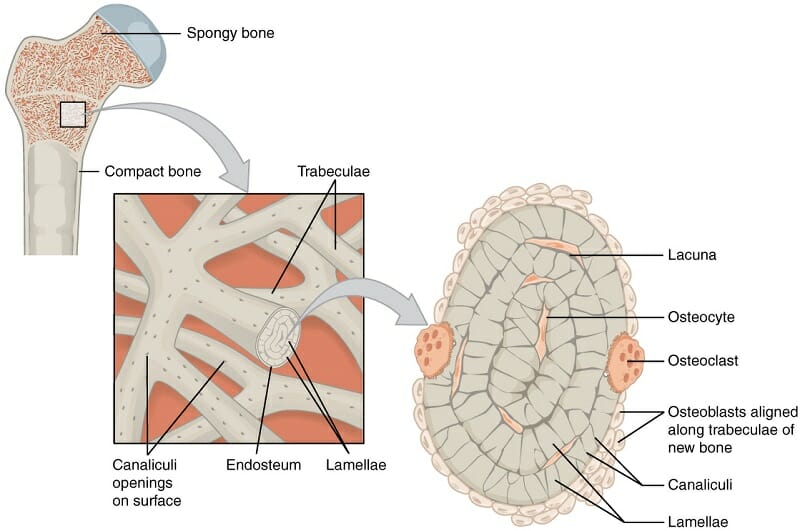
Spongy Bone
Function: Reduces bone weight and absorbs shock.
Importance: Houses red marrow for blood cell production.
Other Facts: Found in epiphyses and flat bones; made of trabeculae.
Quick Tip: “Spongy = shock absorber + blood maker.”
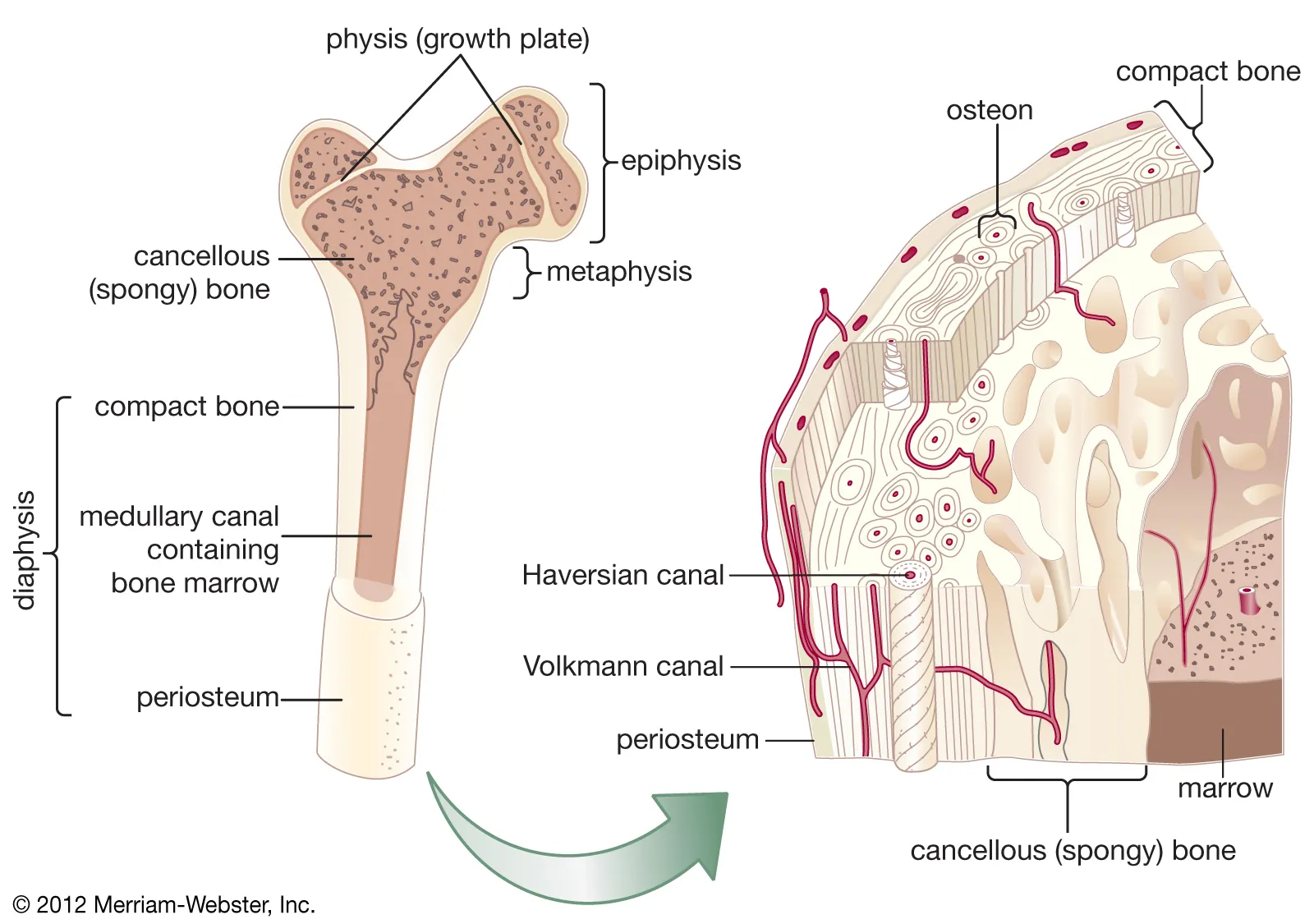
Compact Bone
Function: Provides strength and protection.
Importance: Supports body weight and resists stress.
Other Facts: Dense outer layer of bones; made of osteons.
Quick Tip: “Compact = cortex = strong shell.”
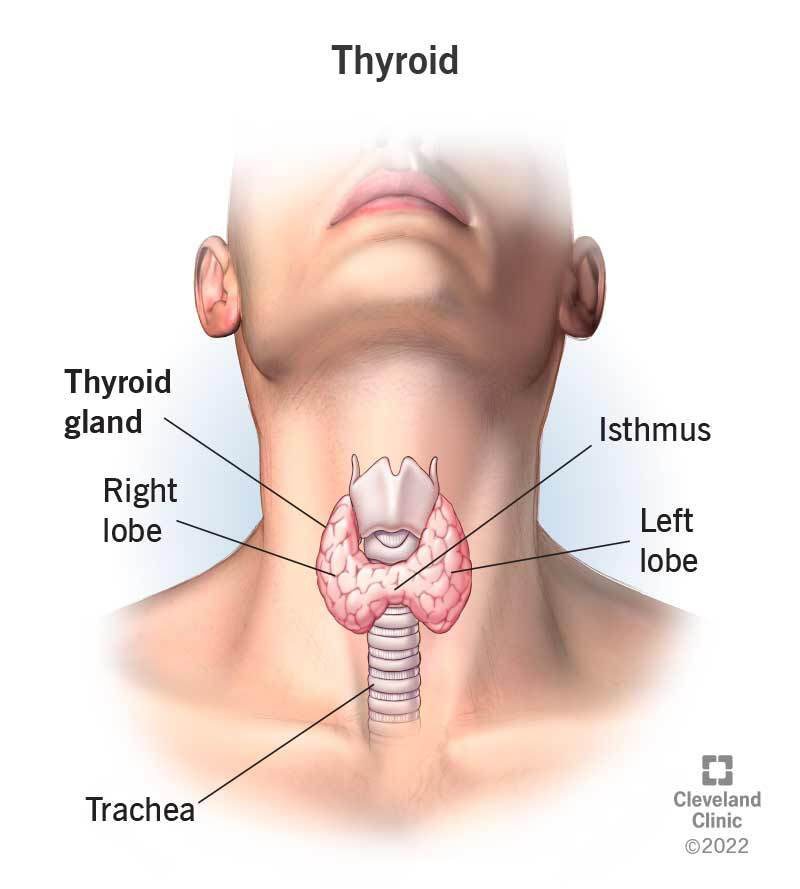
Thyroid
Function: Regulate metabolism, heart rate, tempature, brain development, and growth.
Importance: Crucial for energy balance and development.
Other Facts:
It makes hormones (T3 & T4) that control metabolism — how the body uses energy.
Quick Tip: Think of the thyroid as your body’s “energy thermostat” — it speeds up or slows down processes.
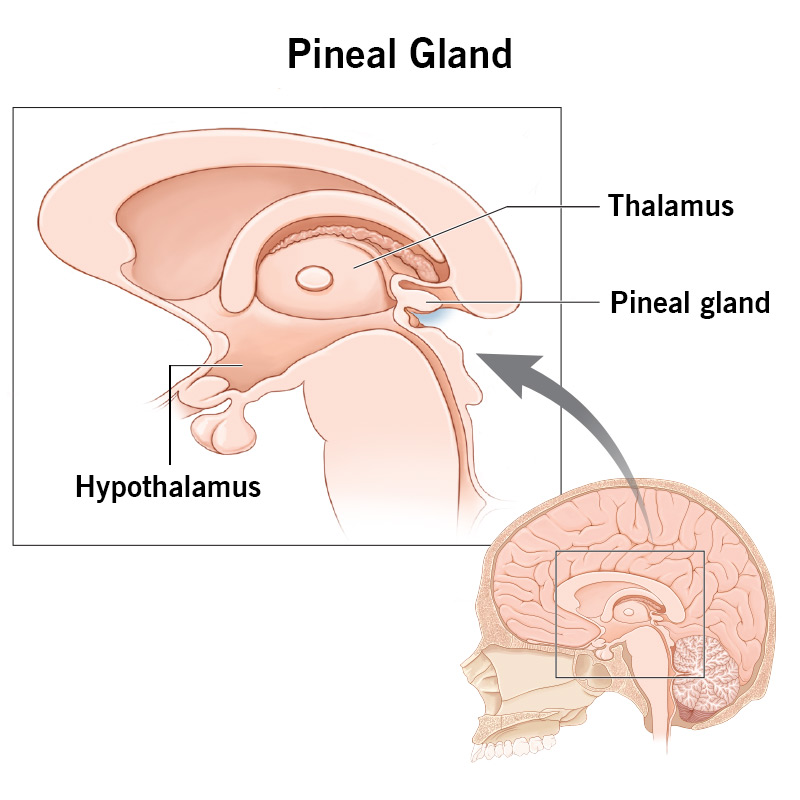
Pineal Gland
Function: Secretes melatonin to regulate sleep-wake cycles.
Importance: Controls circadian rhythm.
Other Facts: Located deep in the brain near the thalamus.
Quick Tip: “Pineal = PM hormone.”
Insulin vs Glucagon
🩸 Insulin
Released by: Pancreas (beta cells).
Function: Lowers blood glucose.
How:
Released when blood sugar is high (after eating).
Helps cells absorb glucose for energy.
Stores extra glucose as glycogen in liver & muscles.
🩸 Glucagon
Released by: Pancreas (alpha cells).
Function: Raises blood glucose.
How:
Released when blood sugar is low (fasting).
Signals liver to break down glycogen → glucose.
Glucose is released into blood.
⚡ Quick Tip
Insulin = “store sugar” (after meals).
Glucagon = “release sugar” (between meals/fasting).
👉 Easy memory: Insulin IN → glucose into cells. Glucagon GONE → glucose released into blood.
Fight or Flight Hormones
Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
Made by: Adrenal medulla
Role: Immediate “boost”
Increases heart rate, blood pressure, breathing.
Mobilizes glucose for quick energy.
Sharpens reflexes and physical readiness.
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline)
Made by: Adrenal medulla
Role: Heightened awareness
Constricts blood vessels → raises blood pressure.
Keeps you alert, focused, and responsive to surroundings.
Cortisol
Made by: Adrenal cortex (not medulla — this is the key correction).
Role: Longer‑term stress support
Maintains blood glucose by releasing stored energy.
Pauses digestion, immunity, and other to focus on survival
Provides “backup fuel” for endurance under stress.
📌 Main takeaway:
Epinephrine + norepinephrine = fast, immediate fight‑or‑flight response (adrenal medulla).
Cortisol = slower, sustained stress support (adrenal cortex).
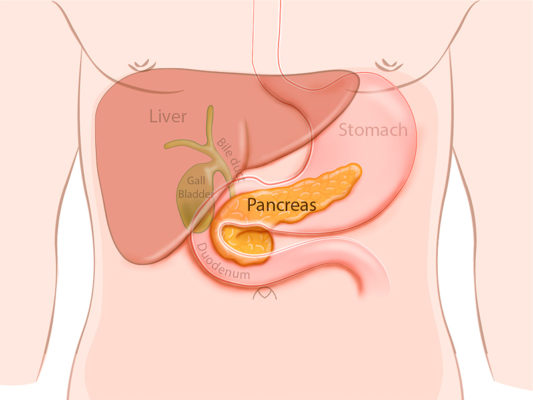
Pancreas
Function: Regulates blood sugar via insulin and glucagon; aids digestion with enzyme secretion.
Importance: Critical for glucose homeostasis and nutrient absorption.
Other Facts: Dual-function gland (endocrine + exocrine); located behind the stomach.
Quick Tip: “Pancreas = sugar switch + digestive helper.”
ADH & Aldosterone
Function:
ADH: Retains water by acting on kidneys.
Aldosterone: Retains sodium, which pulls water with it.
Importance: Maintain blood pressure and fluid balance.
Other Facts: ADH from hypothalamus/pituitary; Aldosterone from adrenal cortex.
Quick Tip: “ADH = Aqua hold, Aldo = Salt saver.”
ADH
Function: Helps kidneys reabsorb water → reduces urine output.
Importance: Prevents dehydration, keeps blood pressure and fluid balance stable.
Other facts:
Made in hypothalamus, released by posterior pituitary.
Also called vasopressin.
Works mainly on kidney tubules.
Quick tip: ADH = “Adds H₂O” back to the body.
Aldosterone
Function: Keeps sodium (Na⁺), gets rid of potassium (K⁺).
Importance: Raises blood pressure, balances salt and water.
Other facts: Made in adrenal gland (cortex).
Quick tip: Aldosterone = “Adds Na⁺” → water follows → ↑ BP.
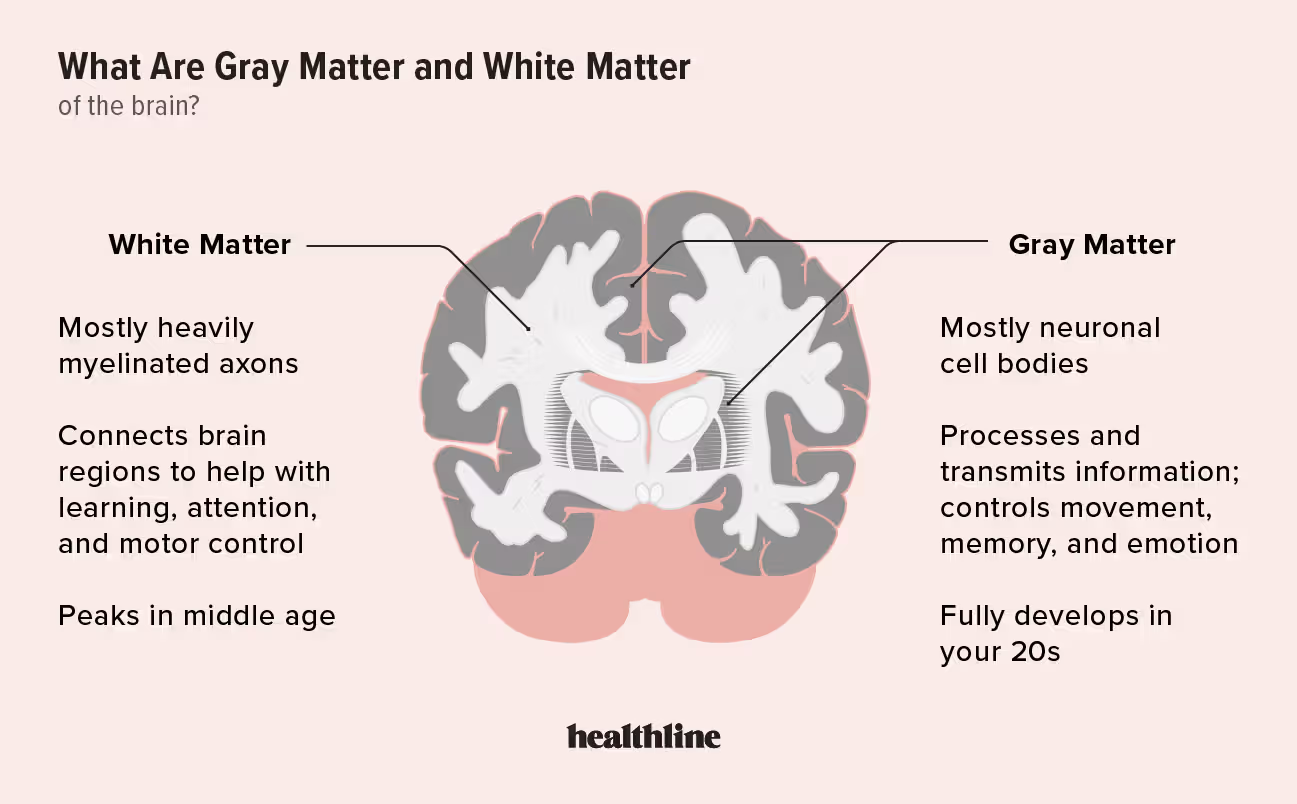
White matter
Function: Transmits signals quickly across brain and spinal cord.
Importance: Enables fast communication between brain regions.
Other Facts: Made of myelinated axons; deeper in brain, outer in spinal cord.
made up mainly of myelinated axons — nerve fibers wrapped in a fatty covering called myelin. The myelin gives white matter its pale color and allows electrical signals to travel quickly and efficiently through the nervous system.
Quick Tip: “White = wires.”
Afferent vs Efferent Neurons
Function:
Afferent: Carry sensory info to CNS.
Efferent: Carry motor commands from CNS.
Importance: Coordinate input and output for body control.
Other Facts: Afferent = dorsal root; Efferent = ventral root.
Quick Tip: “Afferent Arrives, Efferent Exits.”

Axons & Synaptic Knobs
Axon:
Long fiber that carries electrical signals (action potentials) away from the cell body.
Think of it as the “wire” transmitting the impulse.
Synaptic knob (axon terminal):
End of the axon.
Releases neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) into the synaptic cleft.
These neurotransmitters cross to the next neuron (or muscle/gland) and trigger a response.
Main message:
Axon = electrical signal highway.
Synaptic knob = chemical messenger release point.
Importance: Enable neuron-to-neuron communication.
Other Facts: Axons may be myelinated; knobs are at axon terminals.
Easy memory: Axon passes it down, knob passes it on.
Autonomic Nervous System
Function: Controls involuntary functions (heart rate, digestion, breathing).
Importance: Keeps body running without conscious effort.
Other Facts: Includes sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
Quick Tip: “Auto = automatic body control.”
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
Function:
Sympathetic: Activates fight-or-flight.
Parasympathetic: Promotes rest-and-digest.
Importance: Balance stress and recovery.
Other Facts: Sympathetic = thoracolumbar; Parasympathetic = craniosacral.
Quick Tip: “Symp = speed, Para = peace.”
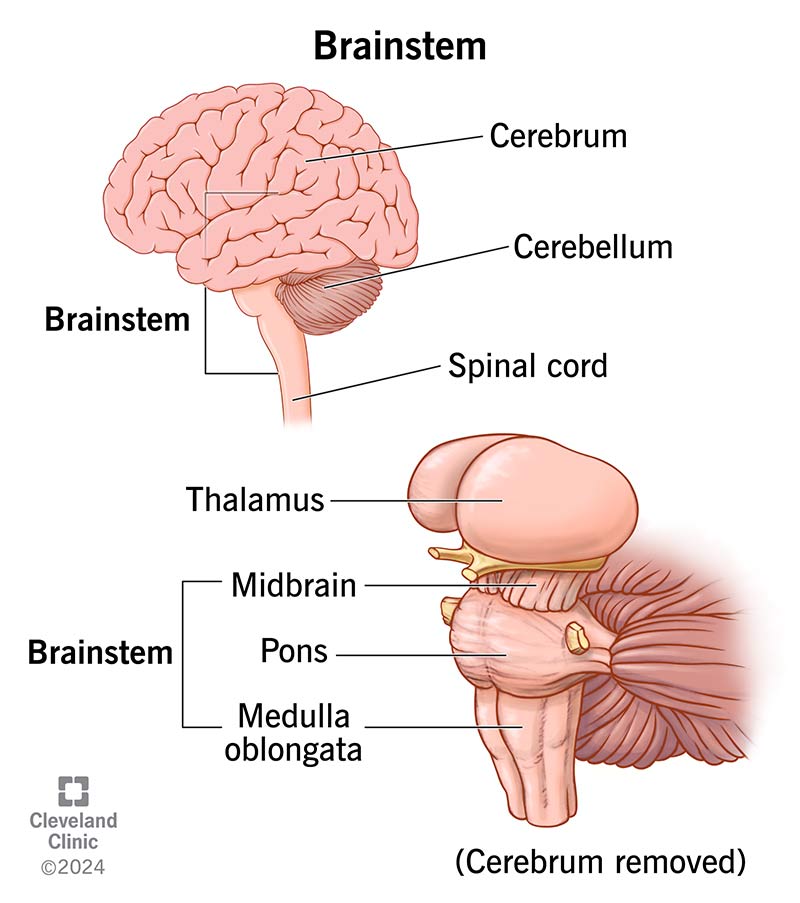
Medulla and Cerebellum
Function:
Medulla: Controls vital signs (breathing, heart rate).
Cerebellum: Coordinates movement and balance.
Importance: Essential for survival and smooth motion.
Other Facts: Both located in hindbrain; medulla = brainstem, cerebellum = posterior.
Quick Tip: “Medulla = monitor, Cerebellum = coordination.”
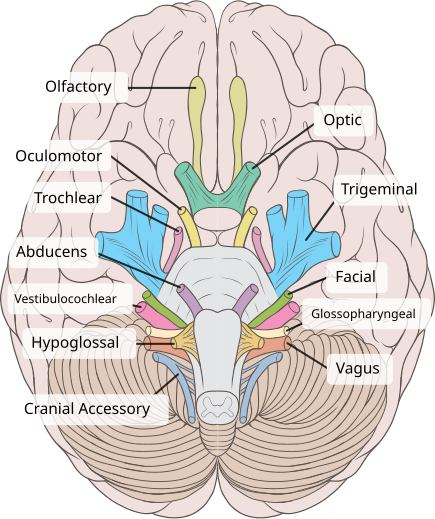
Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
Function: Controls most eye movements, eyelid lifting, and pupil constriction.
Importance: Lets you track objects, open your eyes, and adjust to light.
Other facts:
It’s the 3rd cranial nerve.
Works with CN IV (trochlear) and CN VI (abducens) for full eye movement.
Damage → double vision, drooping eyelid (ptosis), or pupil problems.
Quick tip: Oculomotor = “Moves the eye & more.”
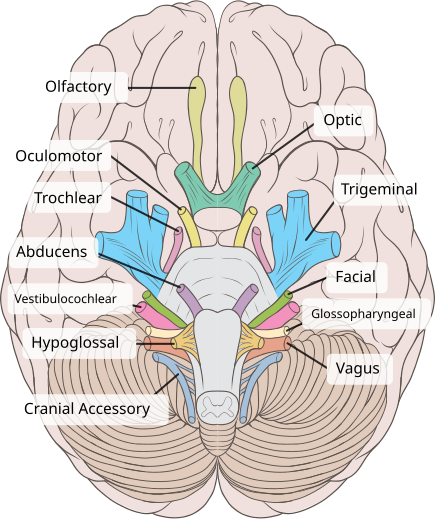
Olfactory (CN I)
Function: Sense of smell.
Importance: Detects odors → linked to taste and memory.
Other facts: First cranial nerve; damage can cause loss of smell (anosmia).
Quick tip: Olfactory = “Odor finder.”
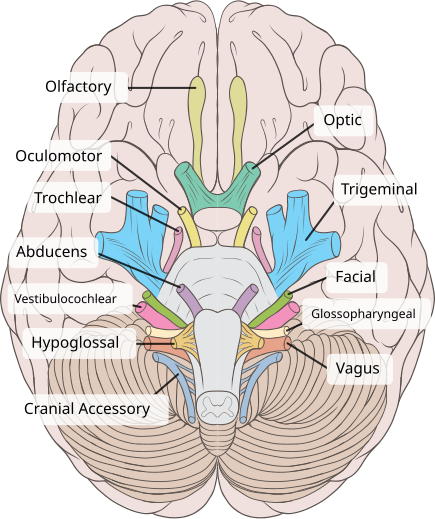
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII)
Function: Hearing (cochlear) + balance (vestibular).
Importance: Lets you hear sounds and stay upright.
Other facts: Eighth cranial nerve; damage can cause hearing loss, dizziness, vertigo.
Quick tip: Vestibulocochlear = “Volume + Balance.”
Afferent
Function: Carry signals into the CNS (brain/spinal cord).
Importance: Bring sensory info (touch, pain, vision, sound).
Sensory signals travel through afferent fibers
Other facts: Think “incoming messages.”
Quick tip: Afferent = “Arrive” at CNS.
Efferent
Function: Carry signals out from the CNS to muscles/glands.
Importance: Control movement and responses (motor output).
Motor signals carry through efferent fibers
Other facts: Think “outgoing commands.”
Quick tip: Efferent = “Exit” the CNS.
Track of a sensory and motor neuron path when a sensory receptor is activated by a stimulus nail
1: afferent
2: ascending
3: brain
4: descending
5: efferent
6: muscle contracts
Primary Motor & Sensory Cortex
Function:
Motor Cortex: Controls voluntary movement.
Sensory Cortex: Processes touch, temperature, pain.
Importance: Enables body control and sensory awareness.
Other Facts:
Primary Motor located in Frontal lobe
Sensory Cortex located in Parietal lobe
Quick Tip: “Motor = motion, Sensory = sensation.”
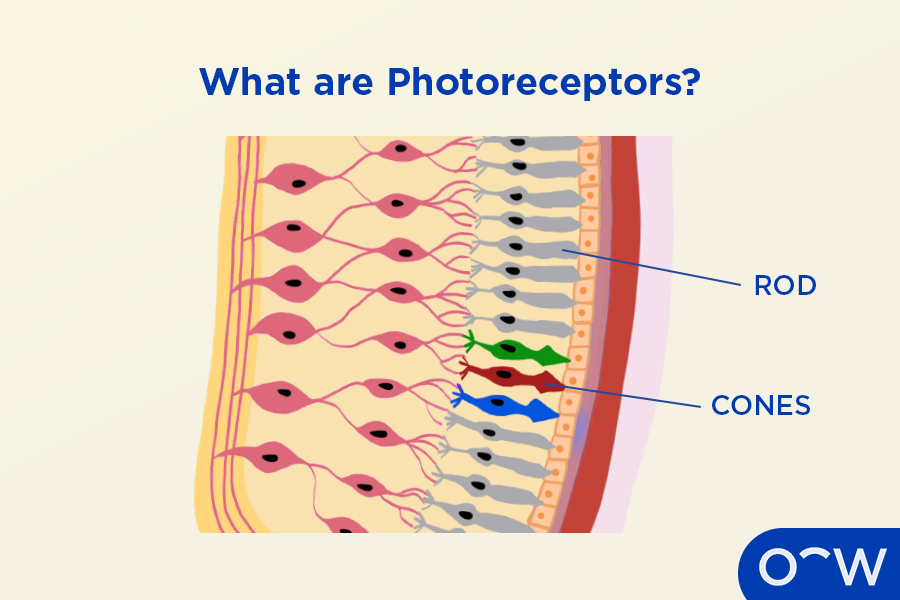
Photoreceptors
Function: Detect light and convert it to neural signals.
Importance: Enable vision.
Other Facts:
Rods = dim light, peripheral vision.
Cones = color and sharp detail.
Located in retina.
Quick Tip: “Rods = night, Cones = color.”
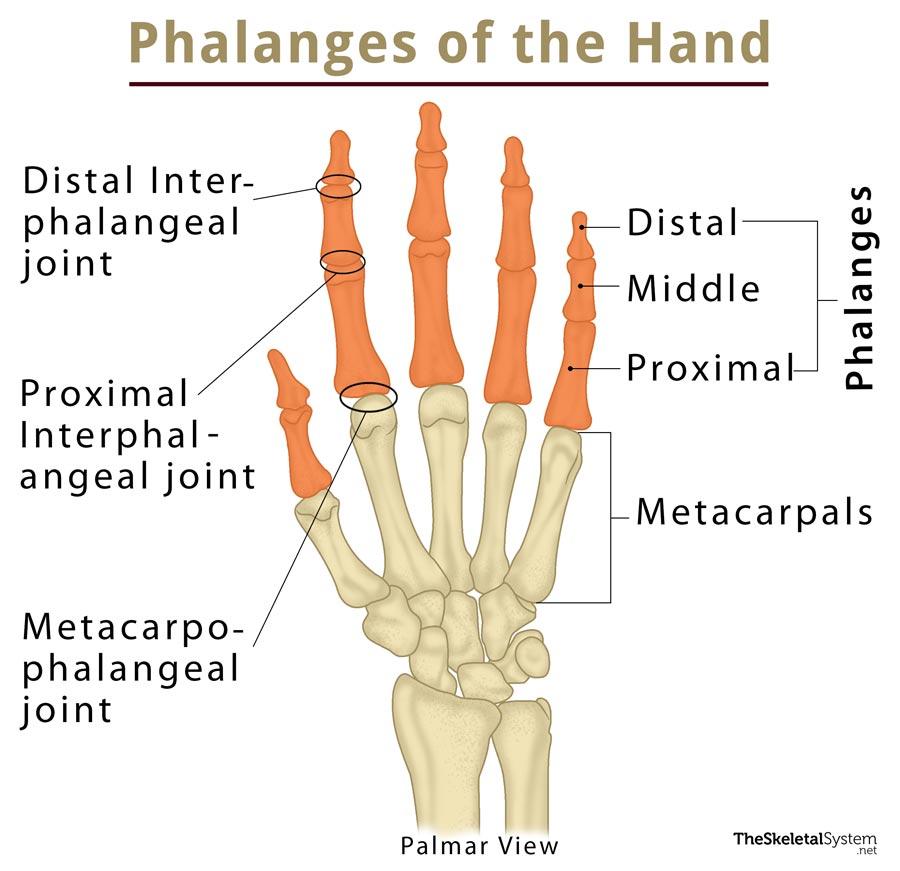
Phalanges (Digits)
Function: Allow fine motor control and grasping.
Importance: Essential for hand and foot movement.
Other Facts: 14 per hand/foot (proximal, middle, distal); thumbs/big toes lack middle phalanx.
Thumb has two
Rest of fingers have 3
Quick Tip: “Phalanges = finger bones.”
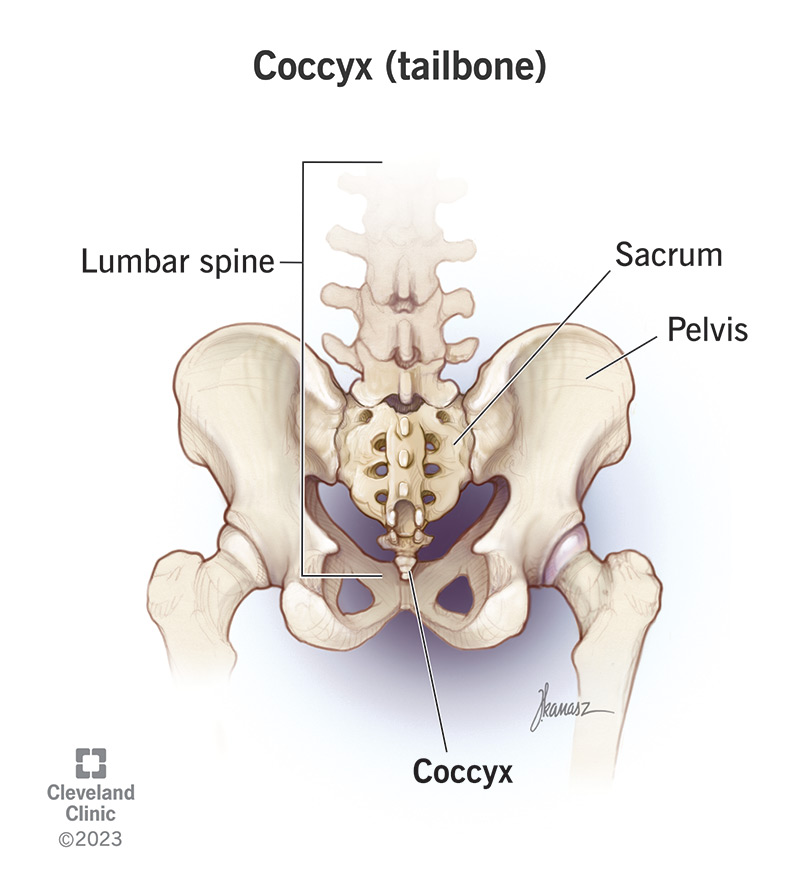
Tailbone (Coccyx)
Function: Provides attachment for ligaments, tendons, and pelvic floor muscles.
Importance: Helps support sitting posture and balance.
Other facts:
Small, triangular bone at the very end of the spine.
Made of 3–5 fused vertebrae.
Can be painful if injured (coccydynia).
Quick tip: Coccyx = “Tiny end bone” → supports sitting.
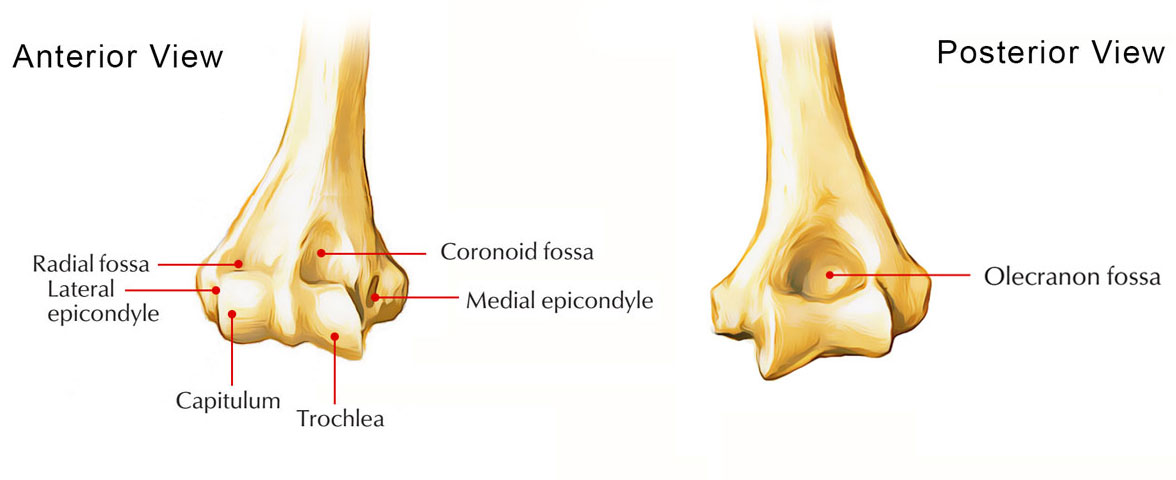
Olecranon Fossa
Function: Receives olecranon process during elbow extension.
Importance: Allows full arm straightening.
Other Facts: Located on posterior distal humerus.
articulates with the olecranon process of the ulna
Quick Tip: “Olecranon = elbow socket.”

Cribriform Plate
Function: Allows olfactory nerves to pass from nose to brain.
Importance: Enables sense of smell.
Other Facts: Part of ethmoid bone; perforated structure.
Quick Tip: Think of it like a strainer: the little holes let smell signals travel up into the brain.
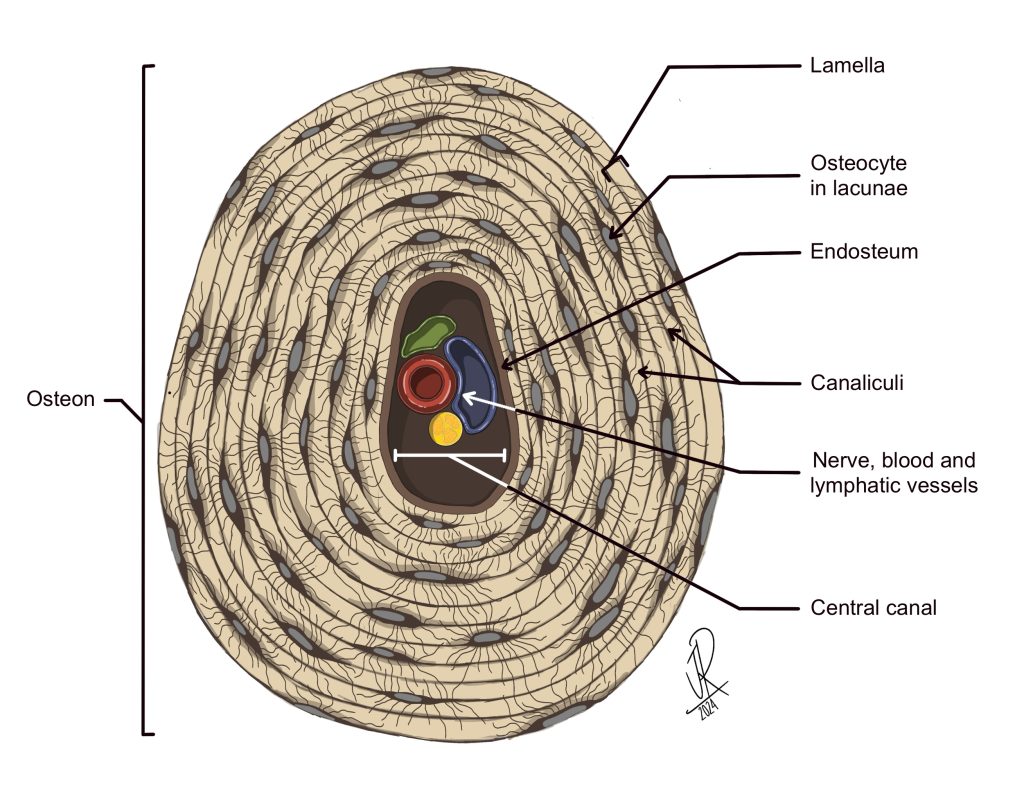
Central canal of Osteons
Function: Carries blood vessels and nerves through compact bone.
Importance: Supplies nutrients and removes waste → keeps bone cells alive.
Other facts:
Found at the center of each osteon (the structural unit of compact bone).
Surrounded by concentric rings of bone tissue (lamellae).
Quick tip: Central canal = “Bone’s highway” → blood & nerves run through.
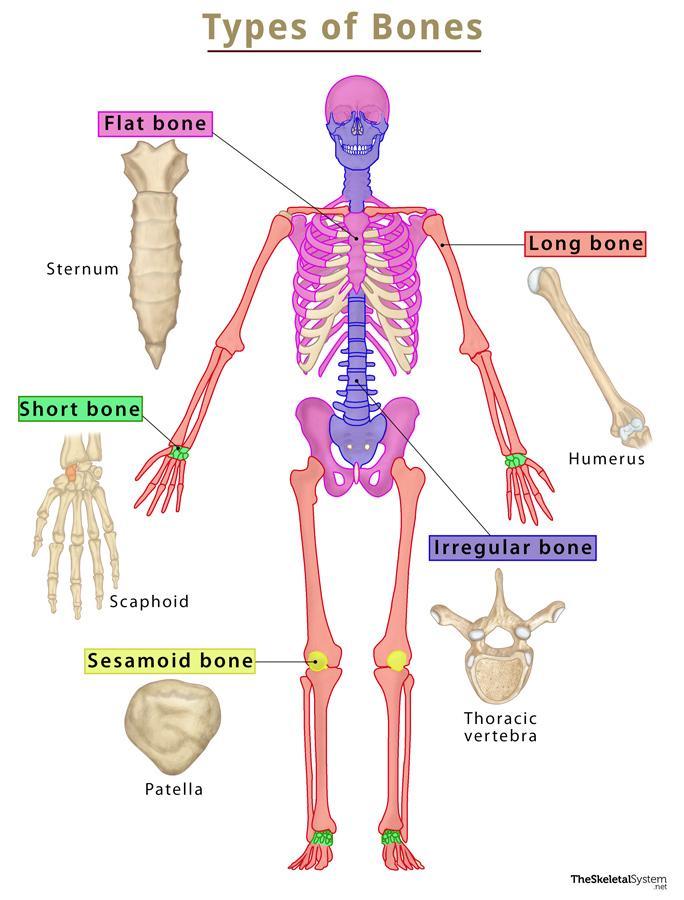
Short Bones
Function: Provide support and stability with little movement.
Importance: Help absorb shock and distribute forces.
Other facts:
Cube‑shaped, about equal length and width.
Found mostly in wrists and ankles.
Examples:
Carpals (wrist bones)
Tarsals (ankle bones)
Quick tip: Short bones = “Small cubes for support.”
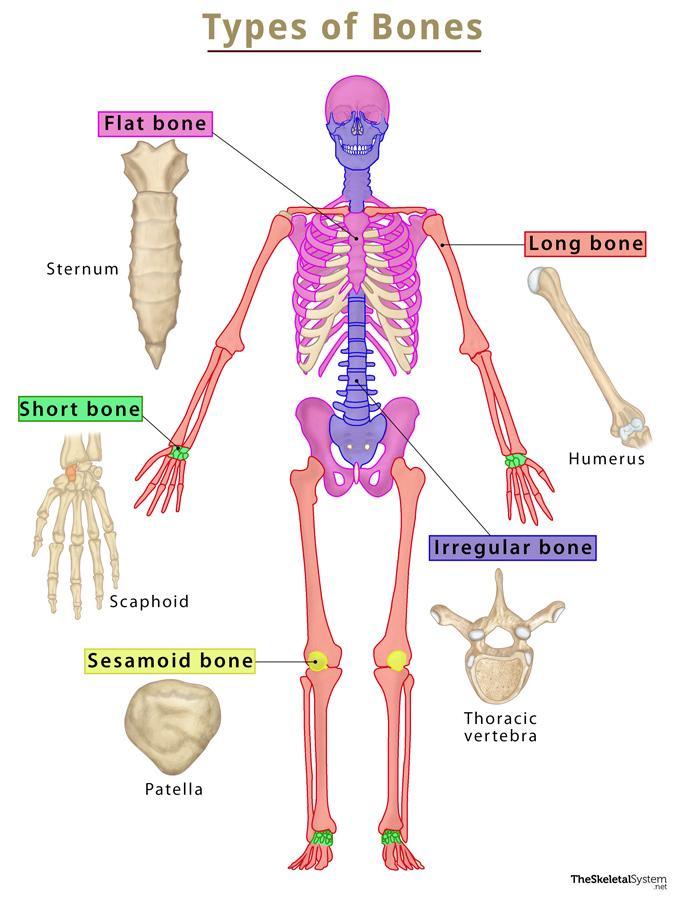
Irregular Bones
Function: Protect nervous tissue, provide anchor points for muscles, and support body structure.
Importance: Their complex shapes fit special roles (not long, short, or flat).
Other facts:
Odd shapes, don’t fit into other bone categories.
Often have projections, curves, or holes.
Examples:
Vertebrae (spinal bones)
Sacrum
Mandible (jaw bone)
Quick tip: Irregular = “Odd shapes for special jobs.”
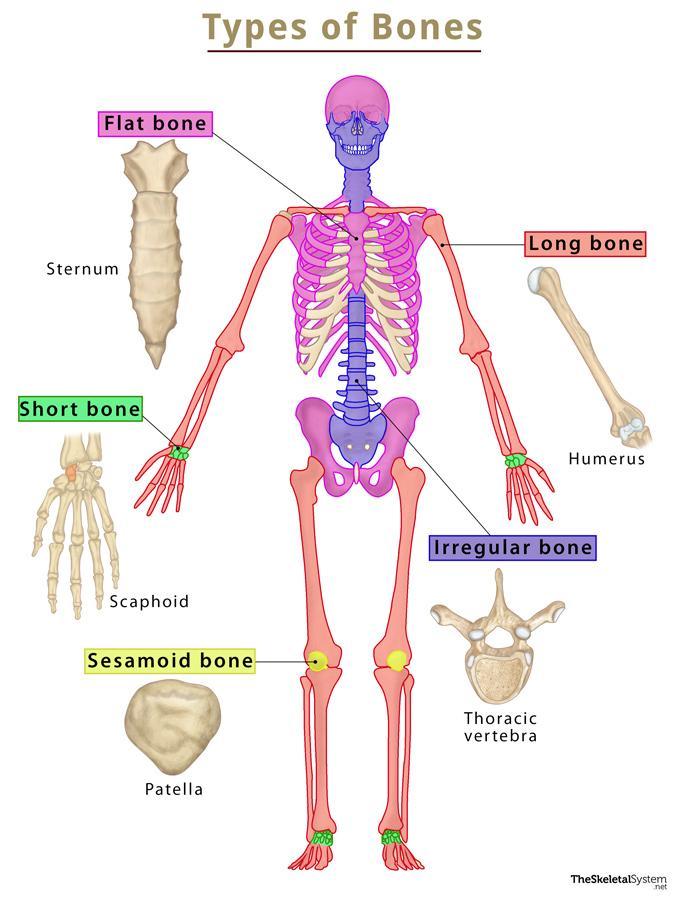
Flat Bones
Function: Protect internal organs + provide broad surfaces for muscle attachment.
Importance: Strong but thin → shield vital structures.
Other facts:
Usually curved, flat, and thin.
Made of spongy bone sandwiched between compact bone.
Examples:
Skull bones (frontal, parietal, occipital)
Sternum (breastbone)
Ribs
Scapula (shoulder blade)
Quick tip: Flat bones = “Protective plates.”
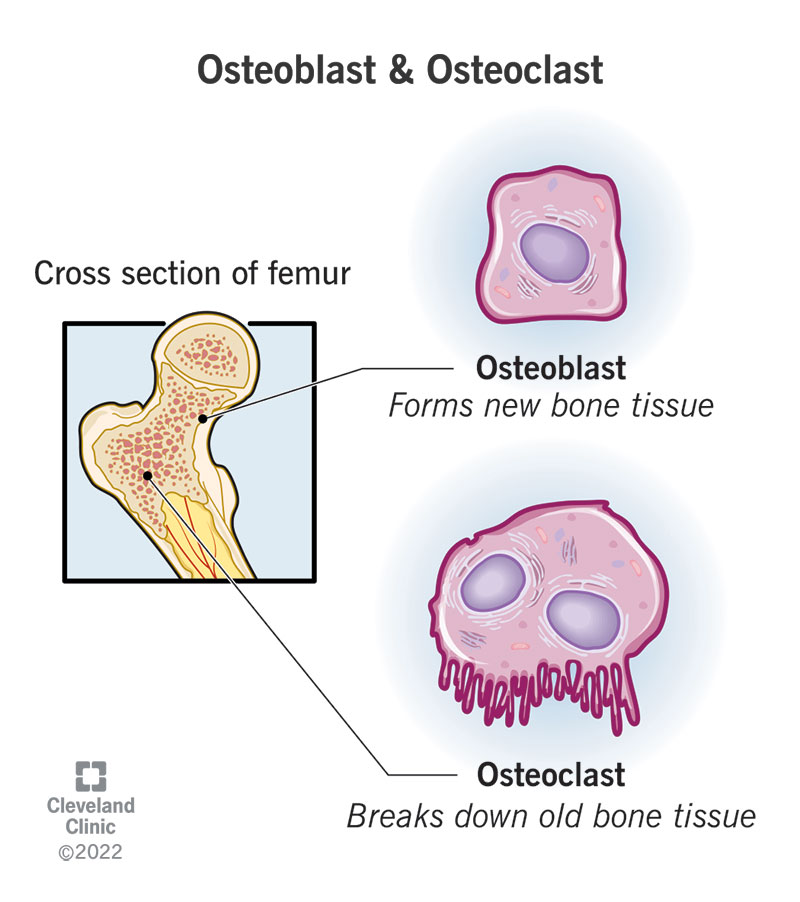
Osteoclast
Function: Break down bone tissue, releasing calcium into the blood.
Importance: Critical for bone remodeling and calcium homeostasis.
Other Facts: Large, multinucleated cells; found on bone surfaces.
Quick Tip: “Clasts Crush.”

Endosteum
Function: Inner lining of bone; contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Importance: Key in bone growth, repair, and remodeling.
Other Facts: Lines medullary cavity and canals of osteons.
Quick Tip: “Endo = inside lining.”
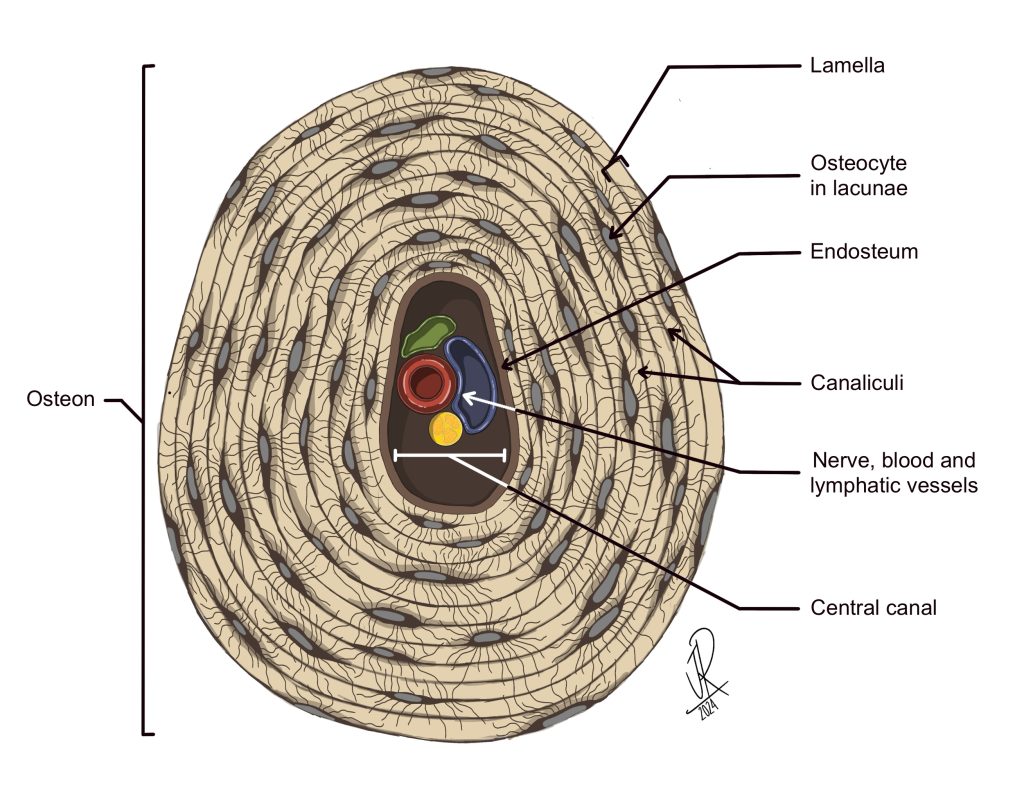
Osteons
Function: Structural units of compact bone; provide strength and nutrient delivery.
Importance: Organize bone into concentric rings for durability.
Other Facts: Each osteon has a central canal with blood vessels/nerves.
Quick Tip: “Osteon = bone donut.”

SAM Pathway
Stressor detected
The hypothalamus in the brain senses danger or stress.
Sympathetic nervous system activated
Hypothalamus sends signals down the sympathetic nerves.
Adrenal medulla stimulated
The sympathetic nerves directly stimulate the adrenal medulla (inner part of adrenal glands).
Hormone release
Adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) are secreted into the bloodstream.
Body-wide effects
Heart rate ↑
Blood pressure ↑
Breathing rate ↑ (bronchioles dilate)
Glucose released from liver for energy
Digestion ↓ (energy diverted to muscles)
⚡ Quick Tip:
SAM = Sympathetic → Adrenal Medulla → Adrenaline surge.
Activates fight-or-flight response.
Think: “Sprint Away Mechanism” → fast, short‑term stress response.
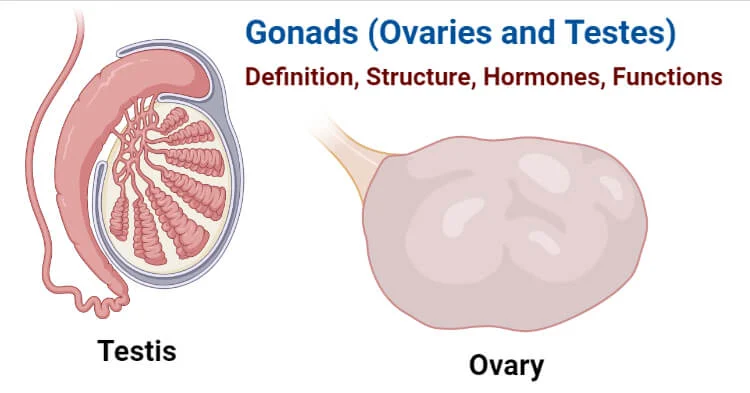
Gonad
Function:
Ovaries: Estrogen, progesterone.
Testes: Testosterone.
Importance: Control reproduction, secondary sex characteristics.
Other Facts: Regulated by pituitary hormones (LH, FSH).
Quick Tip: “Gonads = gender hormones.”
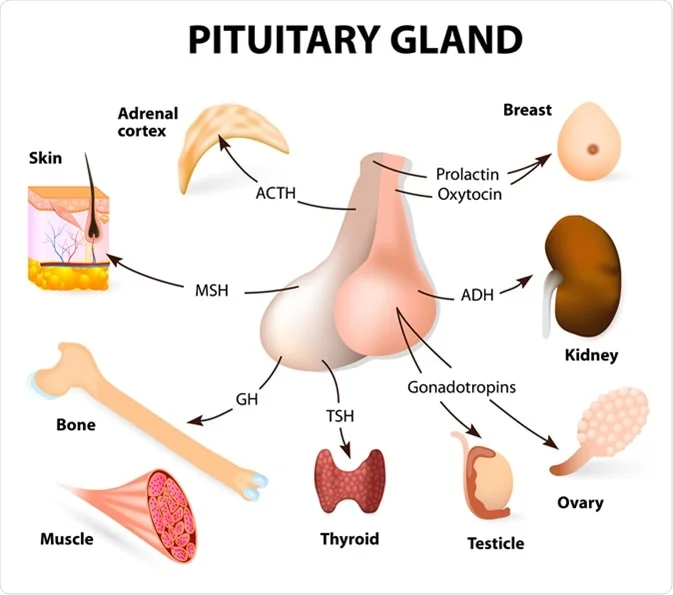
Pituitary Gland Hormone
Anterior Pituitary:
GH: Growth of bones, muscles, metabolism
TSH: Stimulates thyroid
ACTH: Stimulates adrenal cortex (cortisol)
FSH: Egg & sperm production
LH: Ovulation & testosterone
PRL: Milk production
Posterior Pituitary:
ADH: Water reabsorption, fluid balance
Oxytocin: Labor contractions, milk release
⚡ Quick Tip:
Anterior = Makes hormones
Posterior = Stores & releases hypothalamus hormones
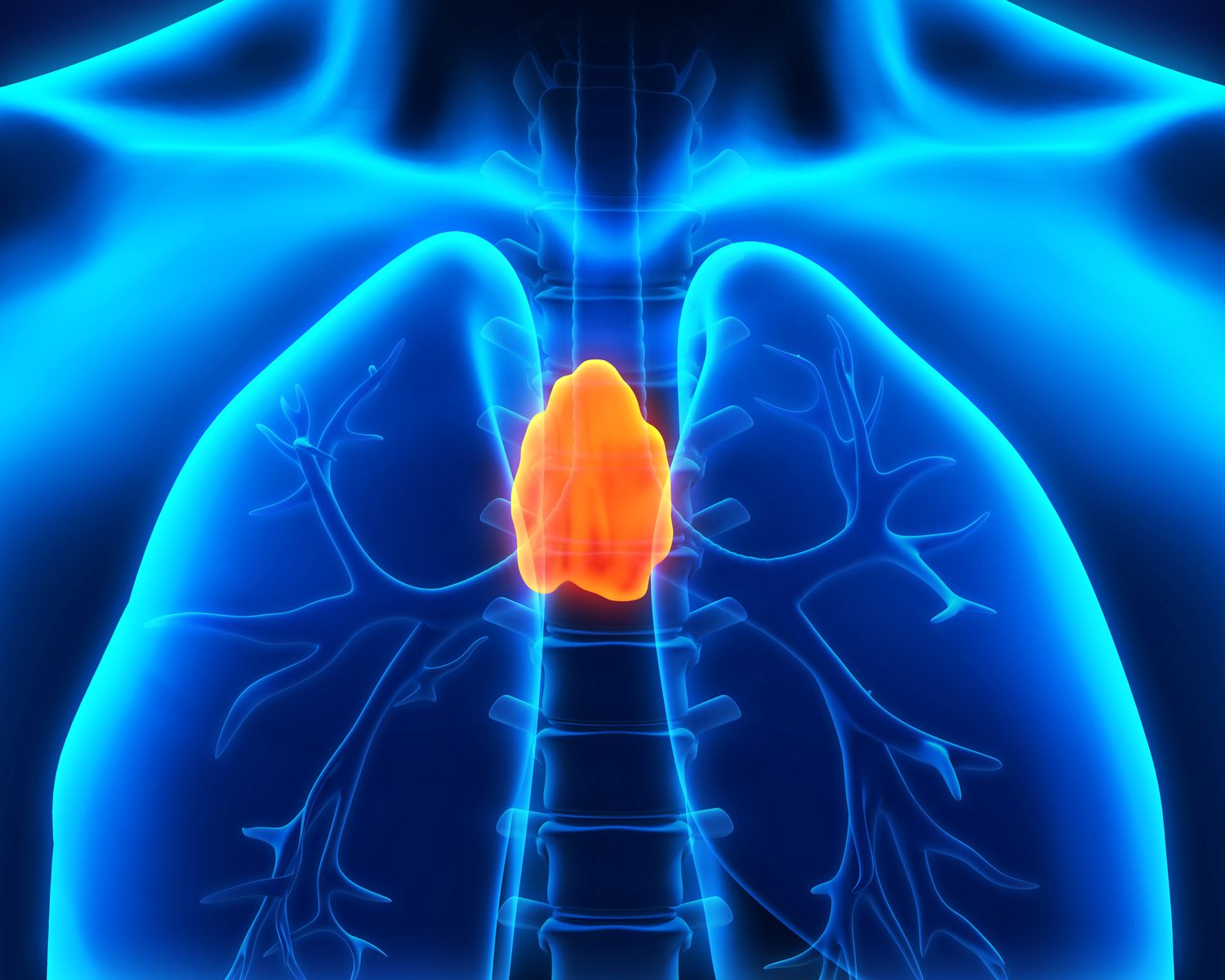
Thymus Hormone
Thymosin: Helps T cells grow and mature → “Immune coach.”
Thymopoietin: Guides T cells to become specialized → “Trainer for identity.”
Thymulin: Fine‑tunes T cell function (needs zinc) → “Immune tuner.”
📌 Memory trick: Thymus = school for T cells
Coach = Thymosin
Teacher = Thymopoietin
Principal = Thymulin
ACTH
Function: Stimulates adrenal cortex to release cortisol.
Importance: Helps body respond to stress, regulates metabolism and blood pressure.
Other facts: Made in anterior pituitary, controlled by hypothalamus (CRH).
A type of pituitary gland hormone
Quick tip: ACTH = “Adrenal Cortex Trigger Hormone.”
ADH
Function: Promotes water reabsorption in the kidneys → reduces urine output.
Importance: Helps maintain blood pressure and fluid balance.
Other facts: Made in the hypothalamus, stored and released by the posterior pituitary.
A type of pituitary gland hormone
Quick tip: ADH = “Always Decreases H2O loss.”
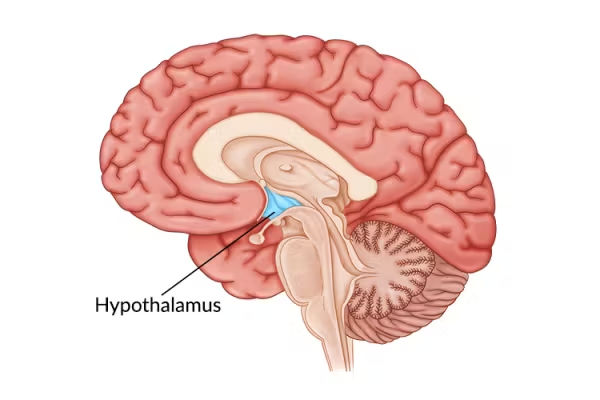
Hypothalamus
Function: Regulates hunger, thirst, temperature, circadian rhythm, and pituitary gland.
Importance: Maintains homeostasis.
Other Facts: Located below thalamus; links nervous and endocrine systems.
Quick Tip: “Hypothalamus = homeostasis hub.”
Hormones
Function: Chemical messengers that regulate body functions.
Importance: Coordinate growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress.
Other Facts: Travel via blood; act on target cells with receptors.
Quick Tip: “Hormones = body’s text messages.”
Adrenaline
Function: Increases heart rate, blood pressure, and energy.
Importance: Key in fight-or-flight response.
Other Facts: Secreted by adrenal medulla.
Quick Tip: “Adrenaline = action fuel.”
Oxytocin
Function: Stimulates uterine contractions, milk letdown, and bonding.
Importance: Vital in childbirth and social connection.
Other Facts: Produced in hypothalamus, released by pituitary.
Quick Tip: “Oxytocin = cuddle hormone.”
LH
Function:
Triggers ovulation in females
stimulates testosterone in males.
Importance: Essential for fertility and reproduction.
Other Facts: Secreted by anterior pituitary.
Quick Tip: “LH = love hormone.”
Type I Diabetes
Function issue: The pancreas cannot produce insulin because immune cells destroy the insulin‑producing beta cells.
Importance: Without insulin, glucose cannot enter cells → blood sugar stays high.
Other facts:
Usually develops in childhood or adolescence.
Requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Autoimmune condition.
Quick tip: Type 1 = “No insulin made.” → Hyposecretion.
Type II Diabetes
Function issue: The pancreas makes insulin, but the body’s cells don’t respond properly (insulin resistance).
Importance: Glucose cannot enter cells efficiently → blood sugar stays high.
Other facts:
Often linked to lifestyle factors (diet, weight, activity).
More common in adults, but rising in children too.
May be managed with lifestyle changes, oral meds, or insulin if needed.
Quick tip: Type II = “Cells ignore insulin.” → Hyposensitivity.
Hormones that regulate blood calcium
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): Raises blood calcium by pulling calcium from bone and increasing absorption.
Calcitonin: Lowers blood calcium by storing calcium in bone.
Vitamin D (Calcitriol): Helps absorb calcium from food in the intestines.
Quick tip:
PTH = Pulls calcium Higher
Calcitonin = Calcium in bone
Vitamin D = Dietary calcium booster
Hydrophilic Hormones
Definition: Water‑loving, cannot cross cell membrane.
Action: Bind to surface receptors → use second messengers (like cAMP).
Examples: Insulin, epinephrine, peptide hormones.
Effect: Fast, short‑term response.
Quick tip: Hydrophilic = “Surface signalers.”
Hydrophobic Hormones
Definition: Water‑fearing, lipid‑soluble, cross cell membrane easily.
Action: Bind to intracellular receptors → change gene expression.
Examples: Steroids (cortisol, estrogen, testosterone), thyroid hormones.
Effect: Slow, long‑lasting response.
Quick tip: Hydrophobic = “Gene regulators.”
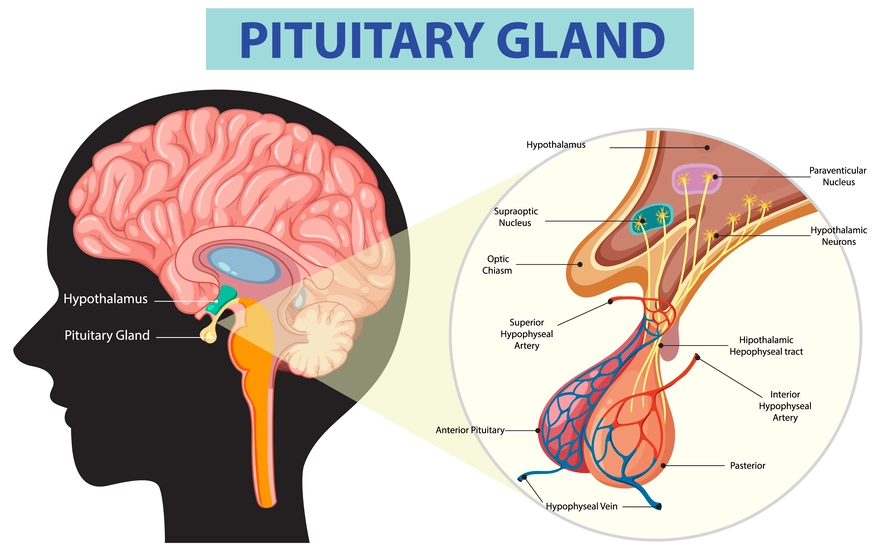
Pituitary gland
Function: Master gland that controls growth, metabolism, reproduction, stress, and water balance.
Importance: Directs other endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenal, gonads).
Other facts: Has two parts — anterior (makes hormones) and posterior (stores/releases hypothalamus hormones).
Quick tip: Pituitary = “Boss gland.”
Temporal Lobe
Function: Processes sound, language, and memory.
Importance: Essential for communication and recognition.
Other Facts: Located on sides of brain; houses auditory cortex.
Quick Tip: “Temporal = tunes + talk.”
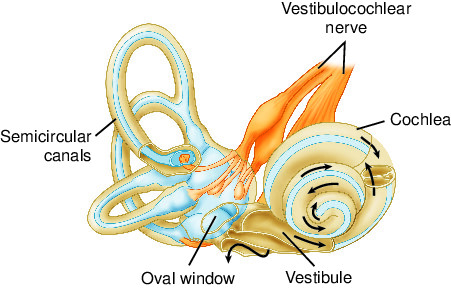
Cochlea
Function: Converts sound waves into electrical signals.
Importance: Enables hearing.
Other Facts: Spiral-shaped structure in inner ear; contains hair cells.
Quick Tip: “Cochlea = sound converter.”
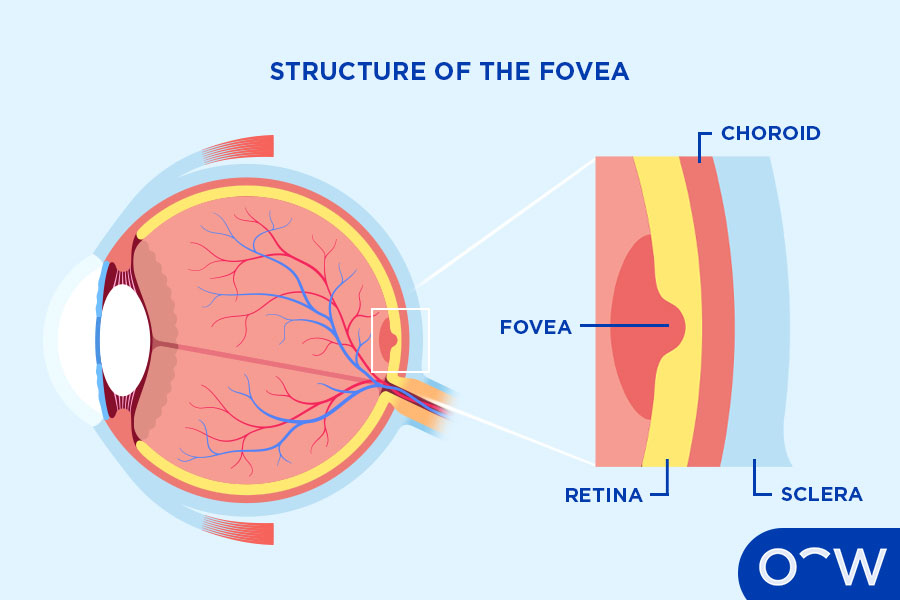
Fovea Centrails and Occipital Lobe
Function:
Fovea Centralis: Sharpest vision, high cone density.
Occipital Lobe: Processes visual information.
Importance: Together enable clear, detailed vision.
Other Facts: Fovea in retina; occipital lobe at back of brain.
Quick Tip: “Fovea = focus, Occipital = optic processor.”
Proprioceptors
Function: Specialized receptors that detect stretch, tension, and joint position.
Importance: Provide feedback to the nervous system to adjust movements in real time.
Found in:
Muscle spindles → in muscles, sense stretch.
Golgi tendon organs → in tendons, sense tension.
Joint receptors → in ligaments/capsules, sense position.
Quick tip: Proprioceptors = “Sensors for body awareness.”
Proprioception
Function: Sense of body position, movement, and balance without needing to look.
Importance: Essential for coordination, posture, and smooth movement.
Other facts: Sometimes called the “sixth sense”; lets you touch your nose with eyes closed.
Quick tip: Proprioception = “Body’s GPS.”