cariology
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
dental caries
an infectious microbiologic disease of the teeth that results in localized dissolution and destruction of calcified tissues
dental caries
ubiquitous process defined as the result of a localized chemical dissolution of the tooth surface caused by acid production by the biofilm exposed frequently to sugar
caries diagnosis
the clinical judgement integrating available information, including the detection and assessment of caries signs (lesions) to determine presence of the disease
caries activity
concept that reflects the mineral balance, in terms of net mineral loss, net mineral gain or stasis over time
active caries
implies caries initiation/progression
inactive caries
implies caries arrest/regression
prognosis of caries
expected course of dental caries
caries free
implies no detectable signs of dental caries
cavity free
implies no detected cavities in dentine
non-cavitated and or micro-cavitated carious lesions
thorough clinical examination of cavity free may reveal the presence of ?
caries care/management/control
actions taken to interfere with mineral loss at all stages of the caries disease
fluoride
non-operative treatments
restoration
operative treatments
caries prevention
inhibition of caries initiation/primary prevention
primary, together with secondary and tertiary
prevention, comprising non-operative and operative treatments
cariogenic
substances or microorganism capable of promoting dental caries
candies, sweets, carbs
example of cariogenic
cariostatic
substances or procedures capable of arresting dental caries
fluoride, chlorhexidine
example of cariostatic
dental biofilm
a consortium of microorganisms that stick to a tooth surface
dental plaque
a clinical term used commonly when referring to the dental biofilm
caries lesion
clinical manifestation of caries disease
non-cavitated
initial lesion development, before cavitation occurs characterized by a change in color, glossiness or surface structure because of demineralization
cavitated
denotes a loss of surface integrity
refers to the total loss of enamel and exposure of the underlying dentin
cavitation denotes the inability to biologically replace the loss of hard tissue
3000 to 5000 BC
when was the first year of dental cream introduced
powdered ashes
oxen hooves
burnt eggshells
pumice
myrrh
dental cream in 3000 - 5000 BC is made up of ?
1873
what year was the first commercially produced toothpaste launched and sold in a jar
1892
what is the year when dr. washington sheffield put toothpaste in a collapsable tube similar to the one we have today
1914
the year when fluoride is added to toothpaste
france and england
were major manufacturers of toothbrushes
second half of 19th century
regular tooth brushing was not a widespread practice until after ?
paleozoic fishes
history of dental caries: 570-250 million years
mesozoic herbivores dinosaurs
245 - 265 million years
prehominines of the eocene
60 - 25 million years
miocenic
25 - 5 million years
pliocenic
5 - 1.6 million years
pleistocenic animals
1.6 - 0.01 million years
5000 BC
a sumerian text from describes a “tooth worm” as the cause of caries
ancient chinese in 2500 BC
earliest theory was the “tooth worm theory”
460 - 357 BC ; hippocrates
_____ proclaimed that disease was due to natural causes and should be treated by means of human reason
…. and in what year?
350 BC ; aristotle
_______ observed figs and sweets caused tooth decay
…. and in what year?
12th century
when did caries is described as holes in the teeth or cavities
bronze and iron age
low caries
sugar cane in the western world in 11th century, increase in caries prevalence
…. what year?
middle ages
caries incidence increased and affected around 20% of the teeth in populations whose food was cooked and included carbohydrates
… what year?
pierre fauchard
known as the father of modern dentistry, was one of the first to proclaim the idea of caries and sugars
w.d. miller; 1890
he found that acid producing bacteria inhabits the mouth and acid dissolved tooth structures
w.d. miller with g.v. black and j.l. williams
researched plaque and basis for explanation of the etiology of caries
fernando e. rodrigez vargaz; 1921
he also found several strains of lactobacilli
killian clarke ; 1924
he found streptococcus mutans in london for which he believed that they were the cause of caries but remained unproven
keyes and fitzgerald ; 1950s
found the cause of caries only after experiments on hamsters
the legend of the worms 5000 BC
what theory?
earliest reference to tooth decay from ancient sumerian text
caries are caused by worms – cause of toothache
early studies
what theory?
pierre fauchard was one of the first people to cite sugar as the possible cause of caries
in 1890s W.D. miller – world's first oral microbiologist said he believed bacteria in the mouth could dissolve tooth structures
miller and dental pioneers G.V. black and J.L. williams researched plaque and investigated the causes of dental caries
w.d. miller
world's first oral microbiologist
endogenous theory: humoral theory
what theory?
the relative proportion of the 4 elemental fluid of the body determines the person’s physical and mental constitution
4 elemental fluids of the body:
1. blood
2. phlegm
3. black bile
4. yellow bile
which corresponds to 4 humors-sanguine, phlegmatic, melancholic, and choleric, respectively
any imbalance in these humors causes disease including caries
1. blood
2. phlegm
3. black bile
4. yellow bile
humors:
sanguine
phlegmatic
melancholic
choleric
4 elemental fluids of the body? and humors that corresponds
endogenous theory: vital theory
what theory?
was advanced towards the end of the 18th century which postulated that tooth decay originated like bone gangrene, from within the tooth itself
physicians of the middle ages – teeth are the integral part of the body (celsus, galen)
hippocrates
celsus
galen
avicenna
people in VITAL THEORY
exogenous theory: chemical (acid) theory
what theory?
caries starts on the enamel surface, where food putrified and acquired sufficient dissolving power
nitric
citric
sulfuric
what are the acids formed by the decomposition of food in saliva?
parmley and robertson in 1819
people in CHEMICAL (ACID) THEORY
exogenous theory: parasitic (septic) theory
what theory?
dubos (1954) postulated that microorganisms can have toxic and destructive effects on tissues
early microscopic observation of scrapings from teeth and of the carious lesions by antoni
van leeuwenhoek (1632 – 1732) indicated that microorganisms were associated with the carious process
erdl described filamentous organisms in the membrane removed from teeth
ficinus (1847) attributed dental caries to “DENTICOLAE” for decay related microorganisms
ficinus in 1847
he attributed dental caries to “DENTICOLAE” for decay related microorganisms
denticolae
ficinus attributed dental caries to ? for decay related microorganisms
decalcifation of tissues
dissolution of softened residue
dental decay is a chemico-parasitic process consists of two stages:
acids produced from microorganisms of the mouth
acids derived from the fermentation of starch and sugar lodged in the retaining center of the teeth
the blend of two previous theories in chemico-parasitic theory
1. did not explain sub-surface demineralization
2. failed to justify rampant caries
3. did not explain caries in impacted tooth
4. phenomenon of arrested caries if not explained
5. smooth surface caries is not accounted in this theory
limitations of chemico-parasitic theory
exogenous theory: proteolytic theory
what theory?
proposed that organic and protein elements were the initial pathway of invasion by microorganisms
gottlieb (1944) stated that instead of decalcification of inorganic part, the initial action was due to the proteolytic enzymes attacking the lamellae, rod sheaths, tufts and walls of tubules (i.e. organic component)
enamel
enamel rod sheath
enamel lamellae
pathways for microorganism invasion through:
no sufficient evidence to the claim that the initial attack on enamel is proteolytic
in experimental studies caries occurs even in the absence of proteolytic microorganisms
drawbacks of PROTEOLYTIC THEORY
exogenous theory: proteolysis-chelation theory
what theory?
simultaneous microbial degradation of the organic components (hence, proteolysis) and the dissolution of the minerals of the tooth by chelation
chelate results from combining an inorganic metal ion with at least two electron-rich functional groups in a single organic molecule
it considers dental caries to be bacterial destruction where the initial attack is essentially on the organic components of enamel
the breakdown products of this organic matter have chelating properties and thereby dissolve the minerals in enamel
exogenous theory: sucrose-chelation theory
what theory?
eggers-luna (1967) proposed that sucrose itself can cause dissolution of enamel by forming an ionized calcium saccharate
calcium saccharates and calcium complexing intermediates requires inorganic phosphate which is subsequently removed from the enamel by phosphorylating enzymes
ionized calcium saccharate
eggers-luna proposed that sucrose itself can cause dissolution of enamel by forming an ?
streptococcus mutans ; 1924
clark isolated streptococci from human carious lesion, and named ?
… and in what year?
keyes ; 1960
? showed that “caries-free” hamsters develop dental caries only when caged together with “caries-active” hamsters – infectious and transmissible
…and in what year?
mutans streptococci (MS)
the bacteria previously referred to as S. mutans are seven distinct species now called ?
mutans streptococci (MS)
are the principal etiological agents of dental caries
acidogenic theory (chemico-parasitic theory)
the most widely accepted theory to date
HOST
MICROBIAL FLORA
SUBSTRATE
TIME
dental caries is a multifactorial disease with interplay of factors: factors of caries formation
microflora
show selectively on the tooth surface they prefer
streptococcus mutans play a vital role
lactic acid formers which easily colonize on tooth surface
dental plaque
adherent deposit of bacteria and their products which form on all tooth surface
protection of bacteria
trapping nutrients
favorable conditions of diff bacterial species
exchange of genetic material of diff species
microorganism in biofilm show 4 distinct characteristics to survive under difficult situations:
STRUCTURE and COMPOSITION
MORPHOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS
POSITION
tooth factors
fluoride
disturbances in formation or calcification of dental tissues
tooth factors: structure and composition
presence of deep, narrow occlusal fissures or buccal or lingual pits
tooth factors: morphologic characteristics of tooth
MISALIGNED
OUT OF POSITION
ROTATED
tooth factors: position
mand and max first molars
mand and max second molars
most susceptible permanent teeth to caries
mand canines and incisors
least likely to develop lesions
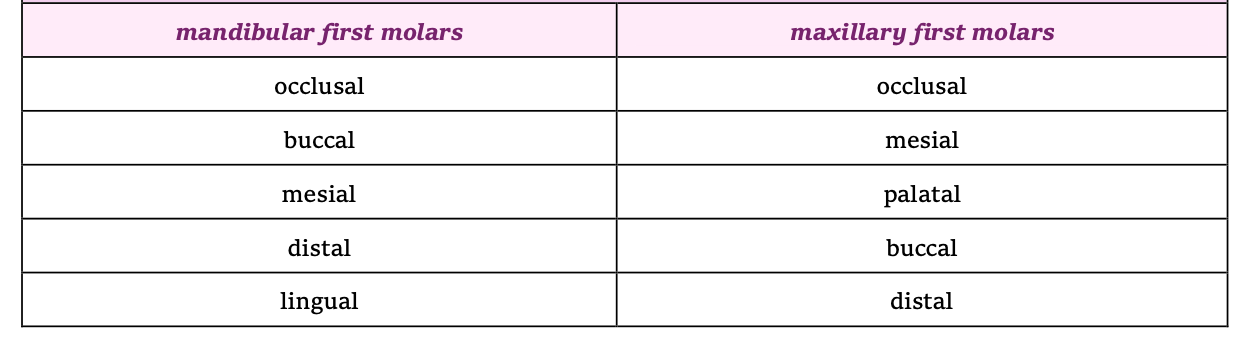
surface of teeth prone to decay
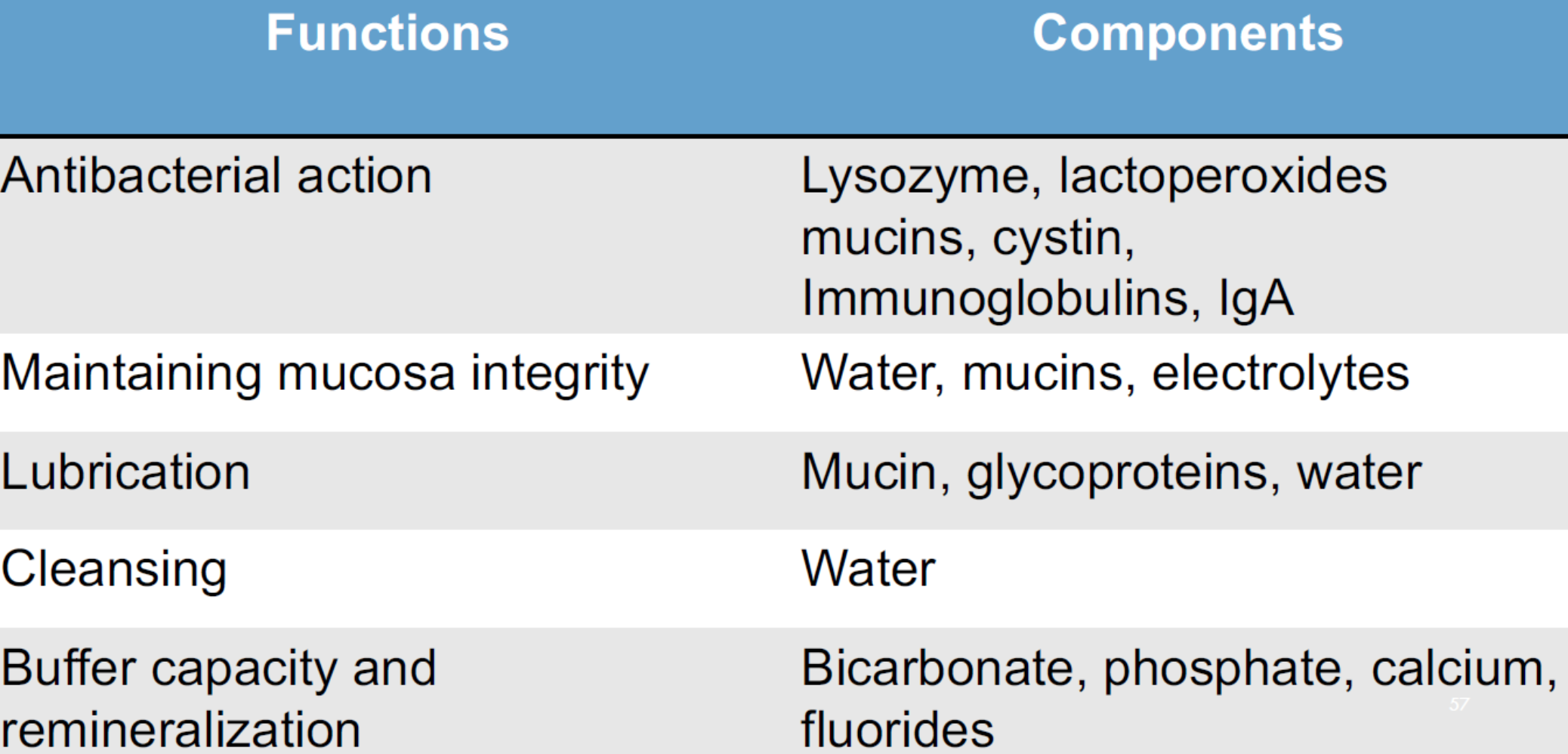
saliva factor and components
saliva
important natural defense mechanism against dissolution of teeth
fluoride
calcium
phosphate
composition of saliva
5.5 pH or lower
pH of saliva
dental caries salivary gland aplasia
lack in salivary flow-more prone to ??
thick and ropy
watery
viscosity of saliva
lysosome (n-acetylmuramide glycanohydrolassae)
can lyse many cariogenic and noncariogenic streptococci
salivary peroxidase system
inactivates many bacterial enzymes of the glycotic pathway and inhibit their growth by preventing cells from accumulating lysine and glutamic acid for essential growth
1. drugs can cause xerostomia
2. diuretics, beta blockers, tricyclic antidepressants
3. antihistamine, anticonvulsants, and antipsychotics, oral morphine
4. greater likelihood of taking these drugs as patients age which explains the correlations of xerostomia with age
5. radiotherapy
medication and treatment that affects salivary flow
1. physical factors (quality of diet)
2. nature of carbohydrate content
3. local factors (carbs, vitamin, fluoride content)
diet and nutritional factors
vitamin a (deficiency)
has definite effects on developing teeth - vitamin
vitamin d
necessary for the normal development of the teeth, malformation, particularly enamel hypoplasia - vitamin
disturbance to calcium and phosphorus
during tooth development may lead to enamel hypoplasia and defects in dentin - vitamin