Redox - Yr12 ✅
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
define oxidation state
the number of electrons lost or gained by an atom in a compound compared to the uncombined atom
what is an oxidising agent
electron acceptor
gains electrons and is reduced
reduction in oxidation number (gets more negative)
what is a reducing agent
electron donor
loses electrons and is oxidised
increase in oxidation number (gets more positive)
does an oxidising agent get reduced or oxidised
reduced- by accepting electrons
what are the 10 rules for assigning oxidation states
oxidation state of an uncombined element is zero
oxidation numbers of the elements in a compounds add up to zero
oxidation number of a monoatomic ion is equal to the ionic charge
iin a polyatomic ion the sum of the individual oxidation states of the elements adds up to the charge on the ion
the more electronegative element in a compound is given a negative oxidation state
group 1 metals= +1
group 2 metals = +2
Al always has an oxidation state of +3
H = +1 (except for metal hydrides when its -1 e.g.NaH)
F= -1
O = -2 (except in peroxides H2O2 when its -1 and in compounds with fluorine
Cl, Br, I = -1, expect in compounds with O and F
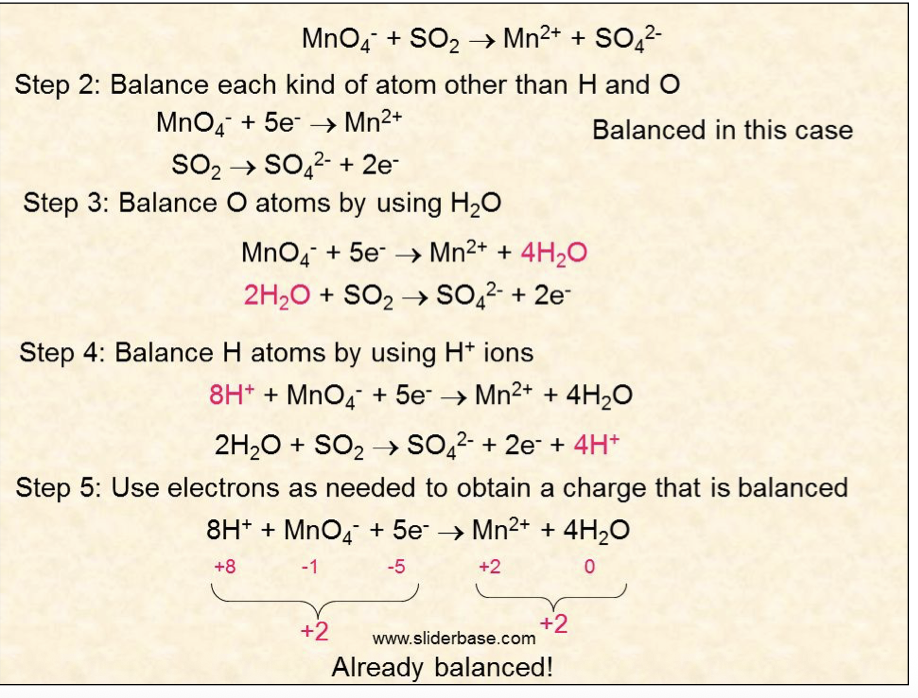
give the useful method which helps to write has equations
balance all species excluding oxygen and hydrogen
balance oxygen using H2O
balance hydrogen using H+ ions
balance charges using e-
see example
when combining half equations, what must you ensure?
the number of electrons is the same of both half equations
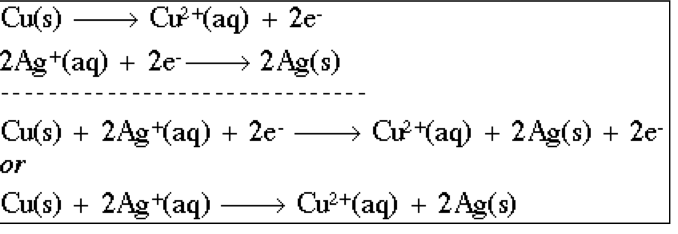
what is oxidation
loss of electrons

what is reduction
gain of electrons
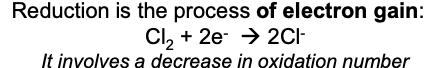
more complex half equations
If the substance that is being oxidised or reduced contains a varying amount of O (eg
MnO4- → Mn2+ ) then the half equations are balanced by adding H+, OH_ ions and H2O.
method to combining half equations
Multiply the half equations to get equal electrons
Add half equations together and cancel electrons and potentially H+
define oxidation
loss of electrons
increase in oxidation state
define reduction
gain of electrons
decrease in oxidation state