Lecture 1 Functional Organization of the Human Body and Control Homeostasis
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
1. Atoms & Molecules
2. Cells
3. Tissues
4. Organs
5. Systems
What 5 units is the organization of the human body?
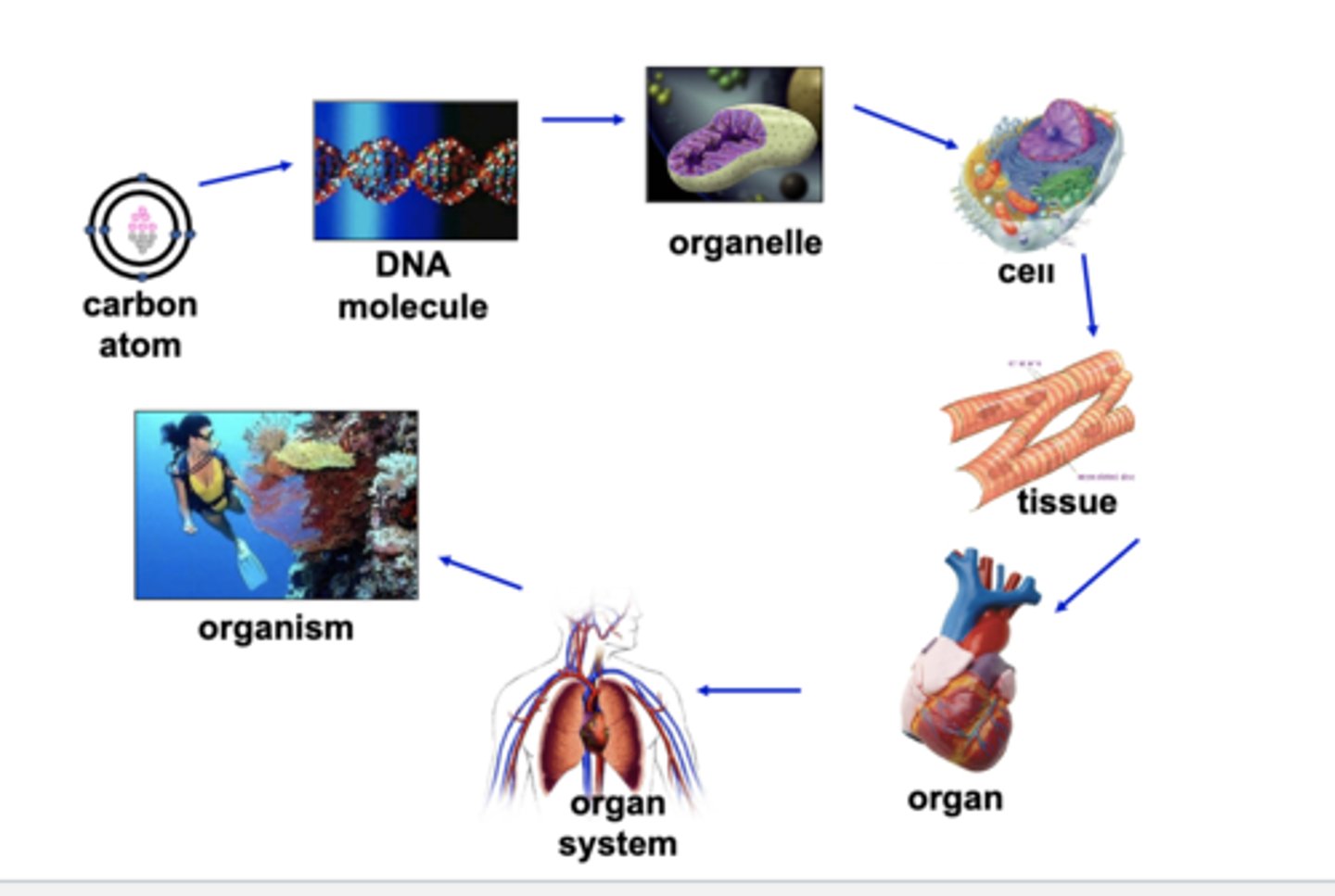
Cell
What is the smallest unit that can carry out life's activities?
Tissue
Group of cells working together to preform a specific job?
Organ
Group off tissues working together to preform a specific job?
Organ system
Group of organs working together to preform a specific job?
Cell;organ system
A organism can be made of ______ or many _____?
Cells
what are the basic building blocks of the body forms tissues , organs , converting nutrients into energy and perform its functions , having hereditary code that controls coping of themselves and processes required substances by cell
Protoplasm
What are the different substances that makes the cell are collectively called?
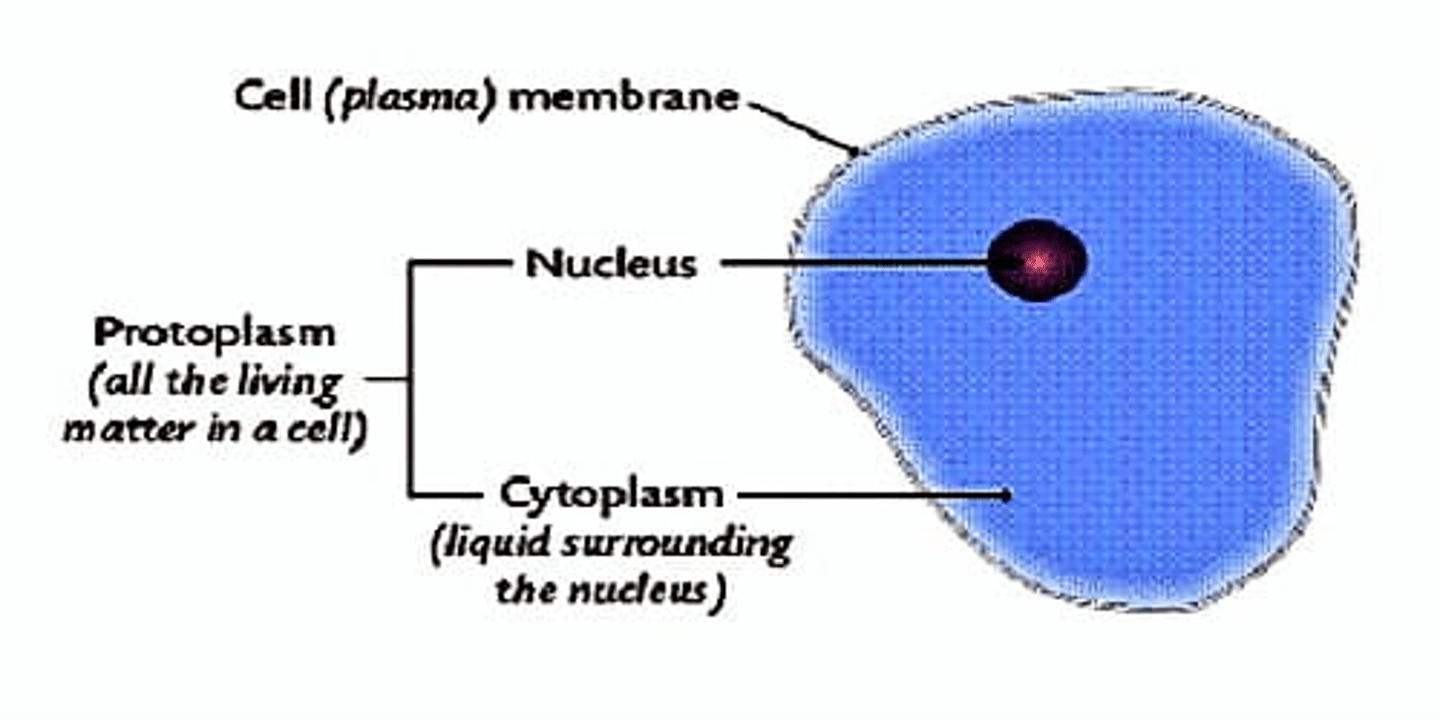
70%-85%
What percentage of water is in the Protoplasm?
(ECF): 142
(ICF): 10
what percentage of Na (ECF) and (ICF) are in the Protoplasm?
(ECF): 103
(ICF): 04
what percentage of Cl (ECF) and (ICF) are in the Protoplasm?
(ECF): 04
(ICF): 140
what percentage of K (ECF) and (ICF) are in the Protoplasm?
(ECF): 2.4
(ICF): 0.0001
what percentage of Ca (ECF) and (ICF) are in the Protoplasm?
10%-20%
What percentage of proteins are in the Protoplasm?
02%
What percentage of Lipids are in the Protoplasm?
01%
What percentage of Carbohydrates are in the Protoplasm?
1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in organisms
3. All cells come from other cells.
What are the 3 characteristics of the cell theory?
Robert Hooke
what scientist took a piece of cork of Spanish Oak and prepared thin slices and observed cells (cellulae) under a microscope?

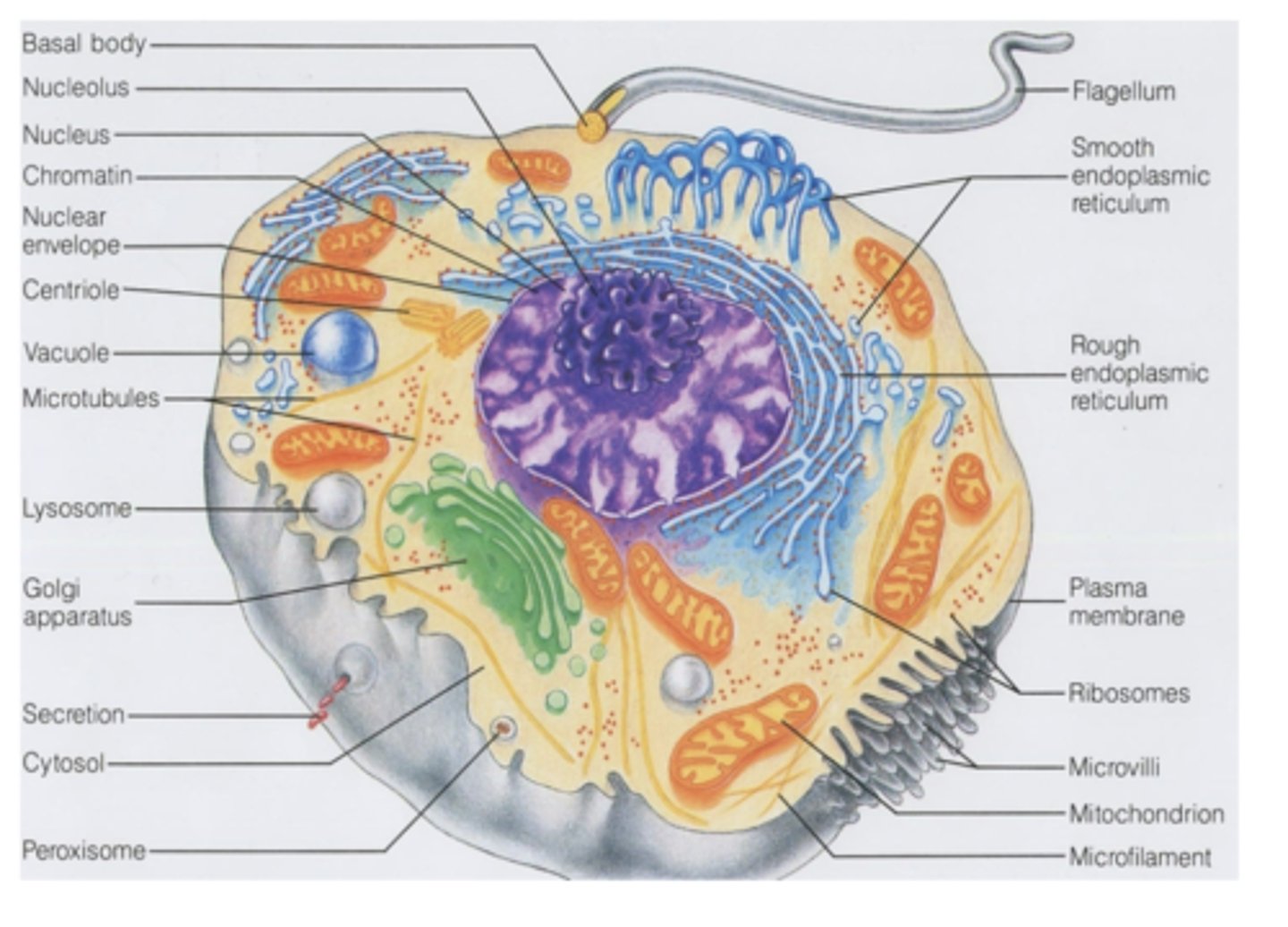
1. Plasma membrane
2. Rough endoplasmic retinaculum (RER)
3. Smooth endoplasimic retinaculum (SER)
4. Golgi apparatus
5. Lysosomes
6. Mitochondria
7. Peroxisomes
What eukaryotic cell organelles are membranous? (7)
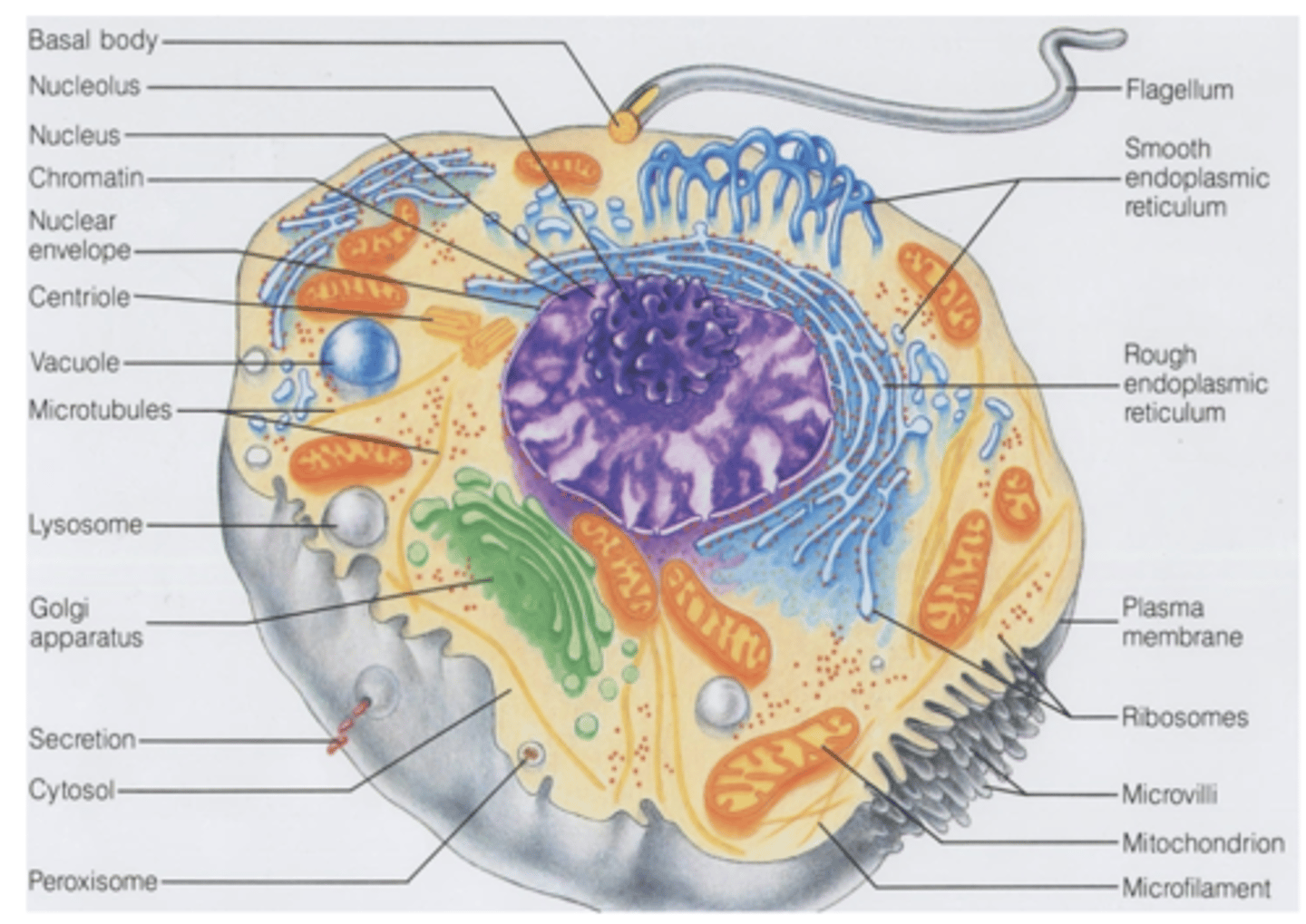
1. Microtubules
2. Filaments
3. Centrioles
4. Ribosomes
5. Proteasomes
What eukaryotic cell organelles are non-membranous? (5)
cell membrane / plasma lemma / bio membrane.
What is the Plasma membrane also called? (3)
Quasi fluid (acts partially like fluid and partially like solid), elastic, pliable & film-likethin partitions over and inside cytoplasm
What kind of fluid is the plasma membrane?
Selectively permeable for solutes but semi permeable for water.
What is the plasma membrane selectively permeable for? what is it semi-permeable for?
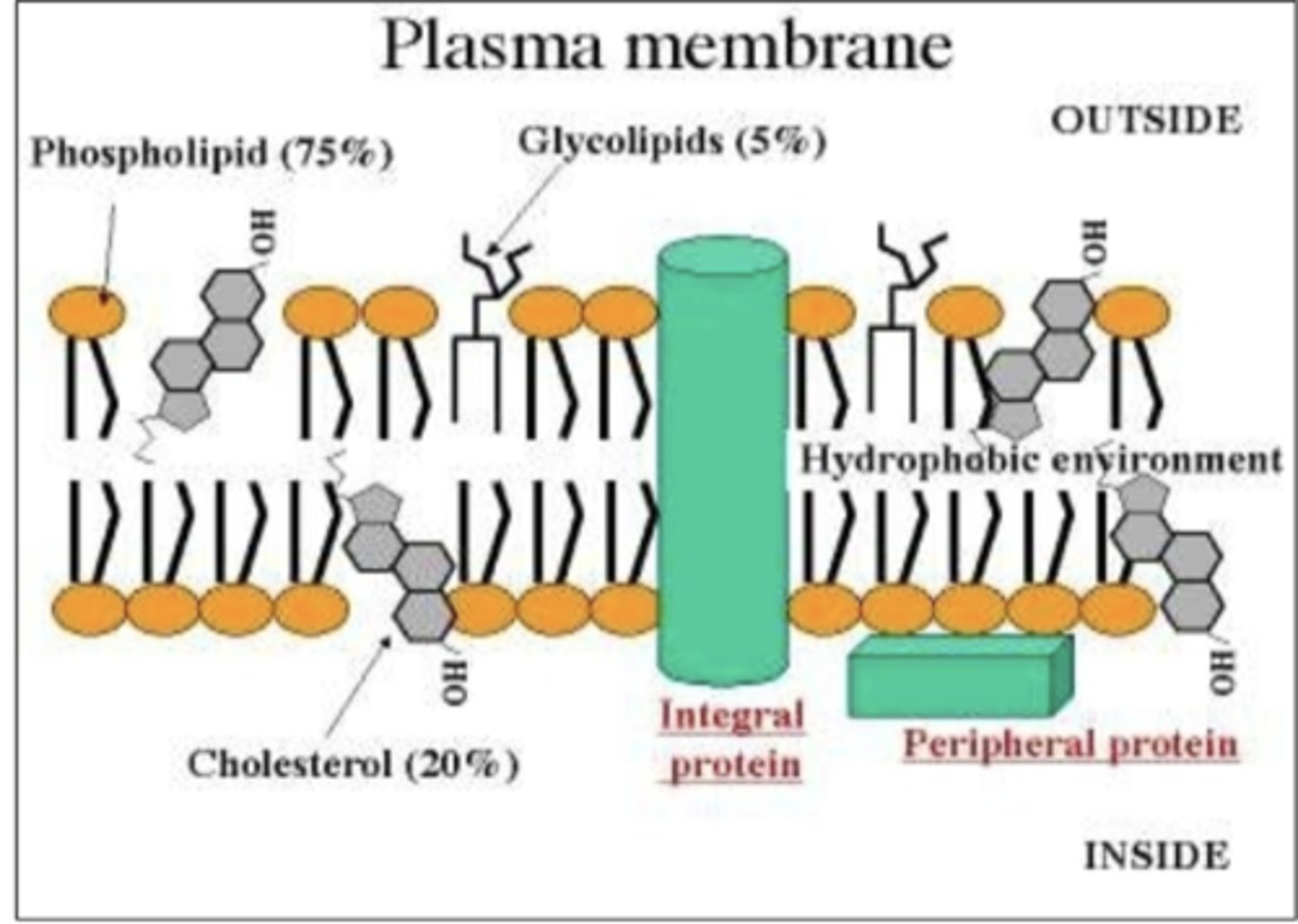
a) Lipids (20-79%)
b) Proteins (20-70%)
c) Carbohydrates (1-5%)
d) Water (20%)
What is the composition of Lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and water of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane has 2 layers (a bilayer) of phospholipids
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
fats withphosphorus attached
What are phospholipids?
at body temperature is like vegetable oil
What is the state of phospholipids at body temperature?
quasi fluid.
The plasma membrane is NOT solid but is
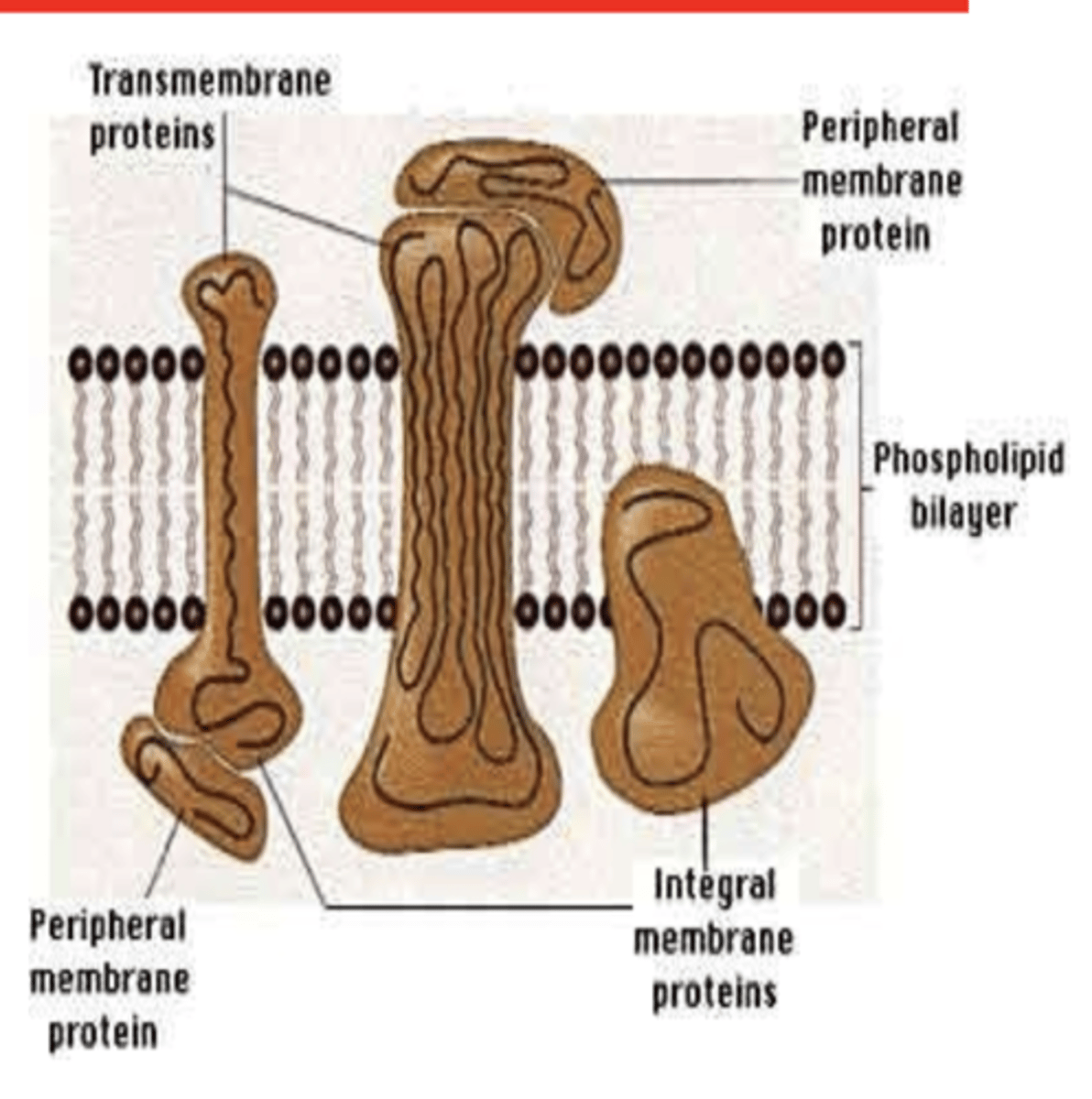
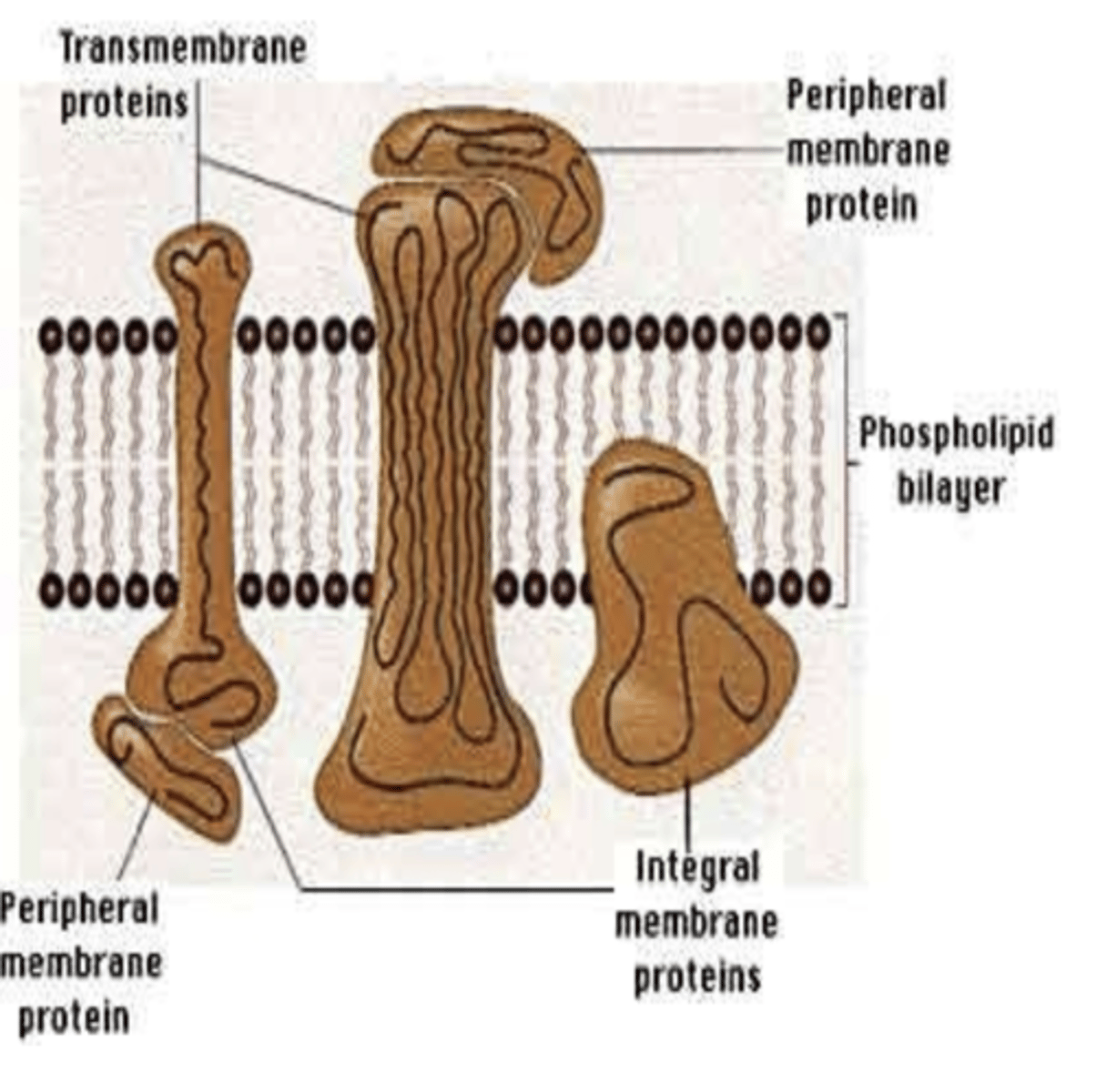
Inside: intrinsic, integral proteins
Outside: extrinsic, peripheral protein
Protein molecules of the plasma membrane occur at places both inside (2) and on outer side of lipid bilayer (2)
Hydrophobic bonds
Integral proteins pass into lipid bilayer & establish what type of bonds with lipid molecules?
Tunnel protein or transmembrane proteins
Integral proteins that run through out the lipid bilayer are called?
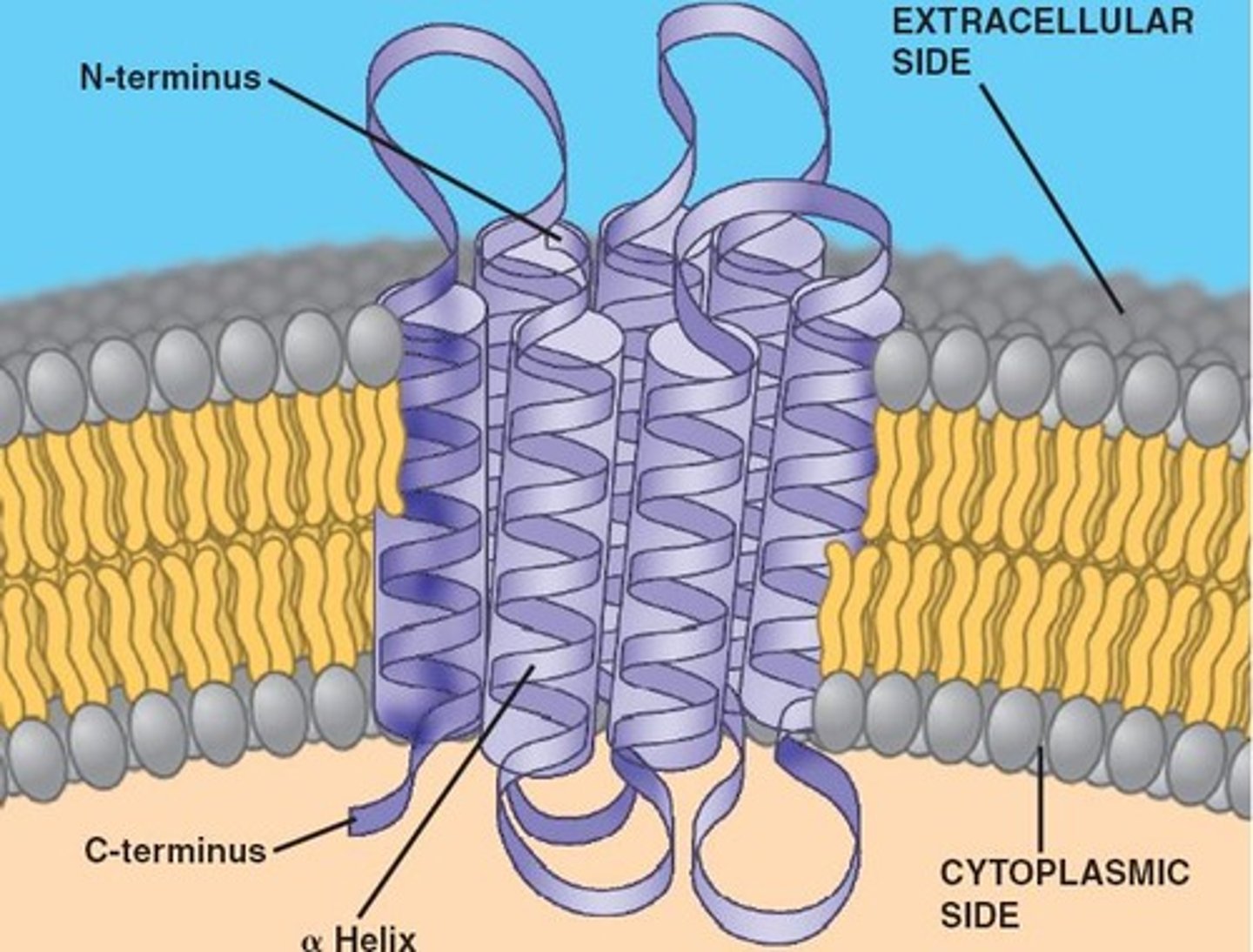
These tunnels form channels for passage of water- and water-solublesubstance which passes selective properties for passage of different ions.
What do tunnel or transmembrane proteins form? What does it allow passage for?
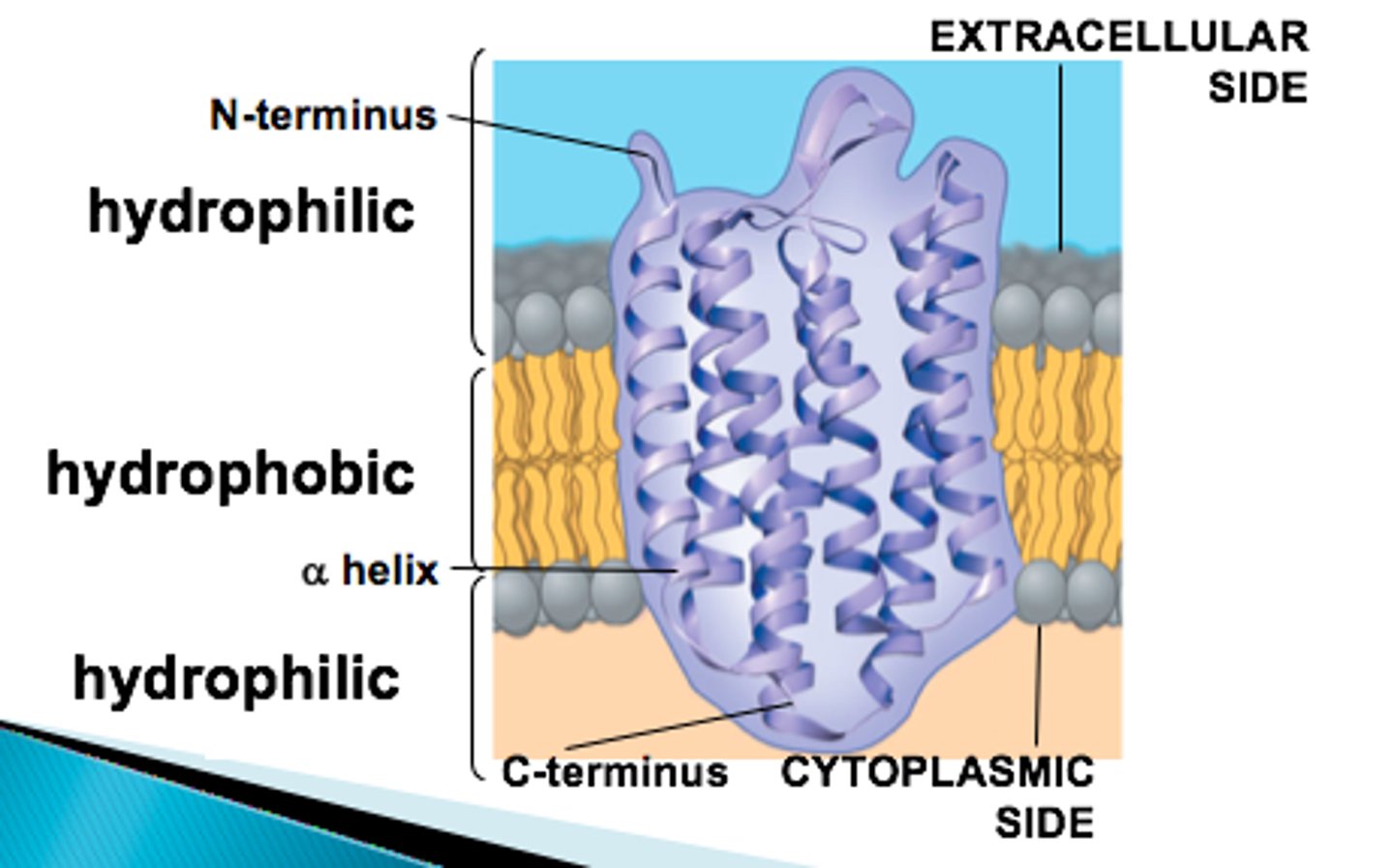
Proteins are held by both polar and non-polar side chains
What are tunnel or transmembrane proteins held by in the plasma membrane?
Extrinsic proteins are attached covalently to phospholipid head or non-covalently to transmembrane protein
What are extrinsic proteins attached covalently to? or non-covalently to in the plasma membrane?
structural & functional specificity to membranes
proteins in the plasma membrane provide?
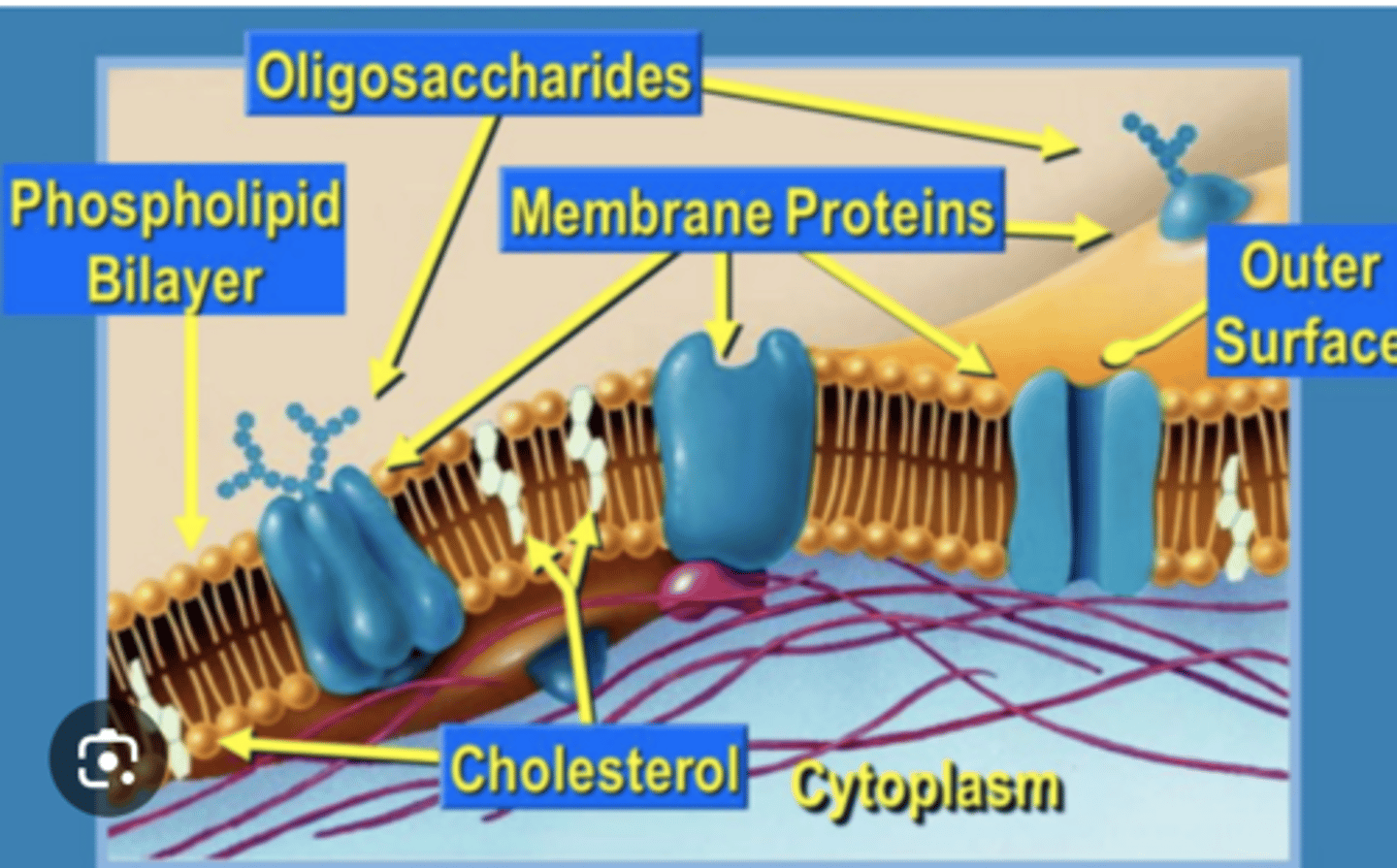
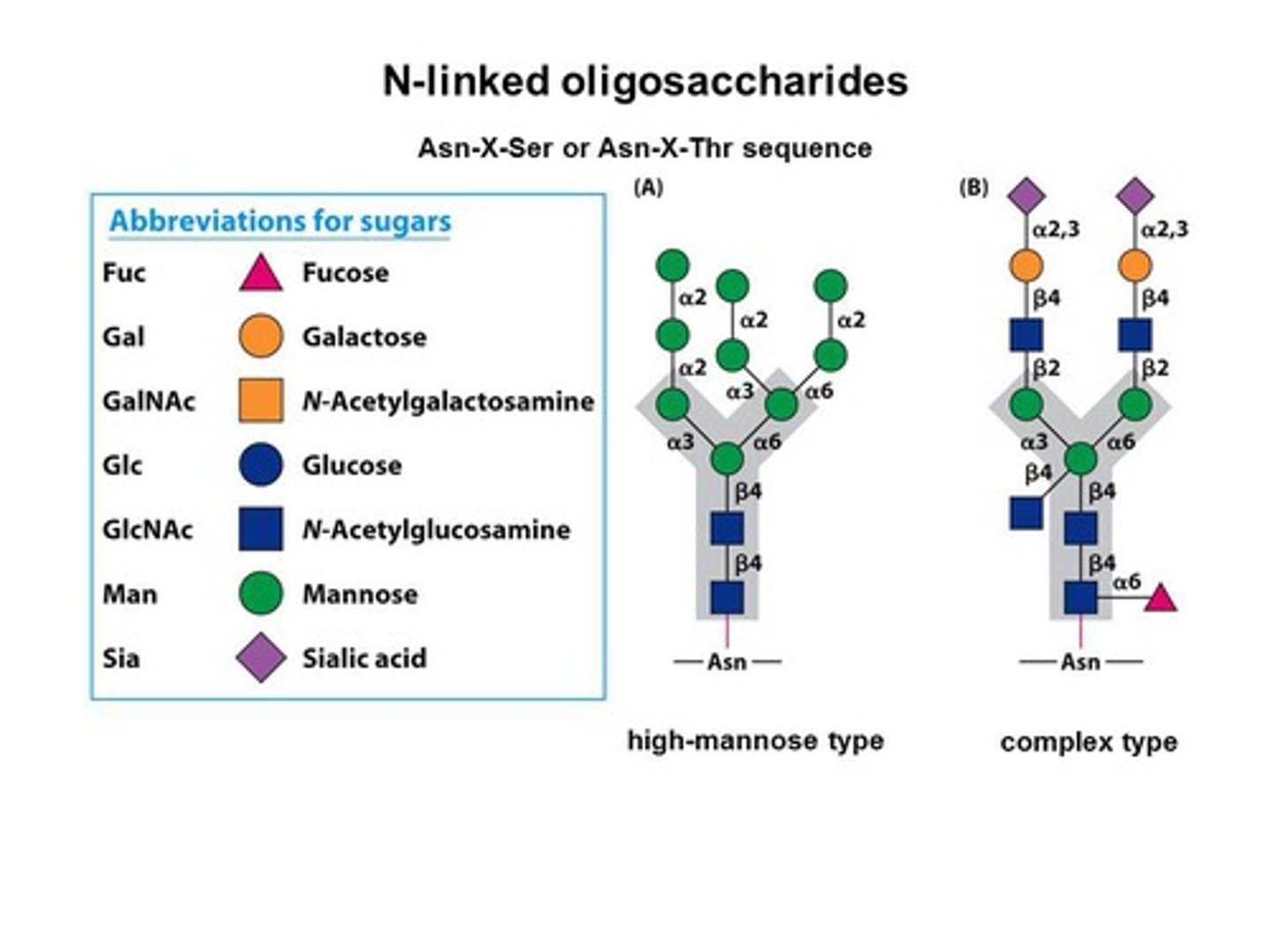
Some lipids & extrinsic proteins present on outer side possess small carbohydrate molecule to form glycolipids & glycoproteins. They constitute glycocalyx or cell coat.
Some lipids & extrinsic proteins present on outer side possess small carbohydrate molecule to form what? what do they constitute to form?
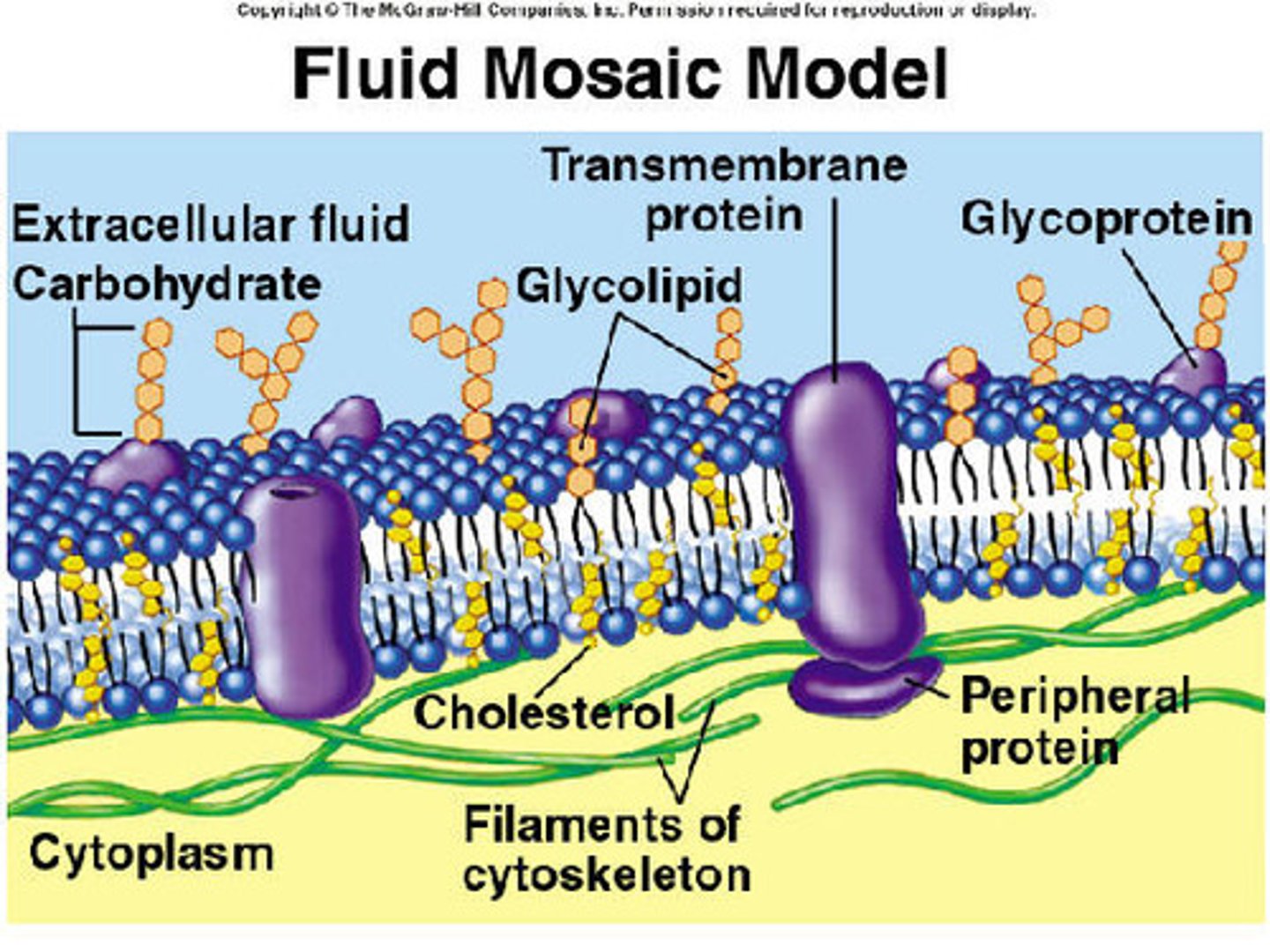
a) Recognition centers
b) Sites of attachments
c) Antigens
d) Provide negative charge to outer surface.
What do conjugated oligosaccharides function as? (4)
amphipathic
i.e.: they posses both hydrophilic & nonpolar hydrophobic ends
Lipid molecules are
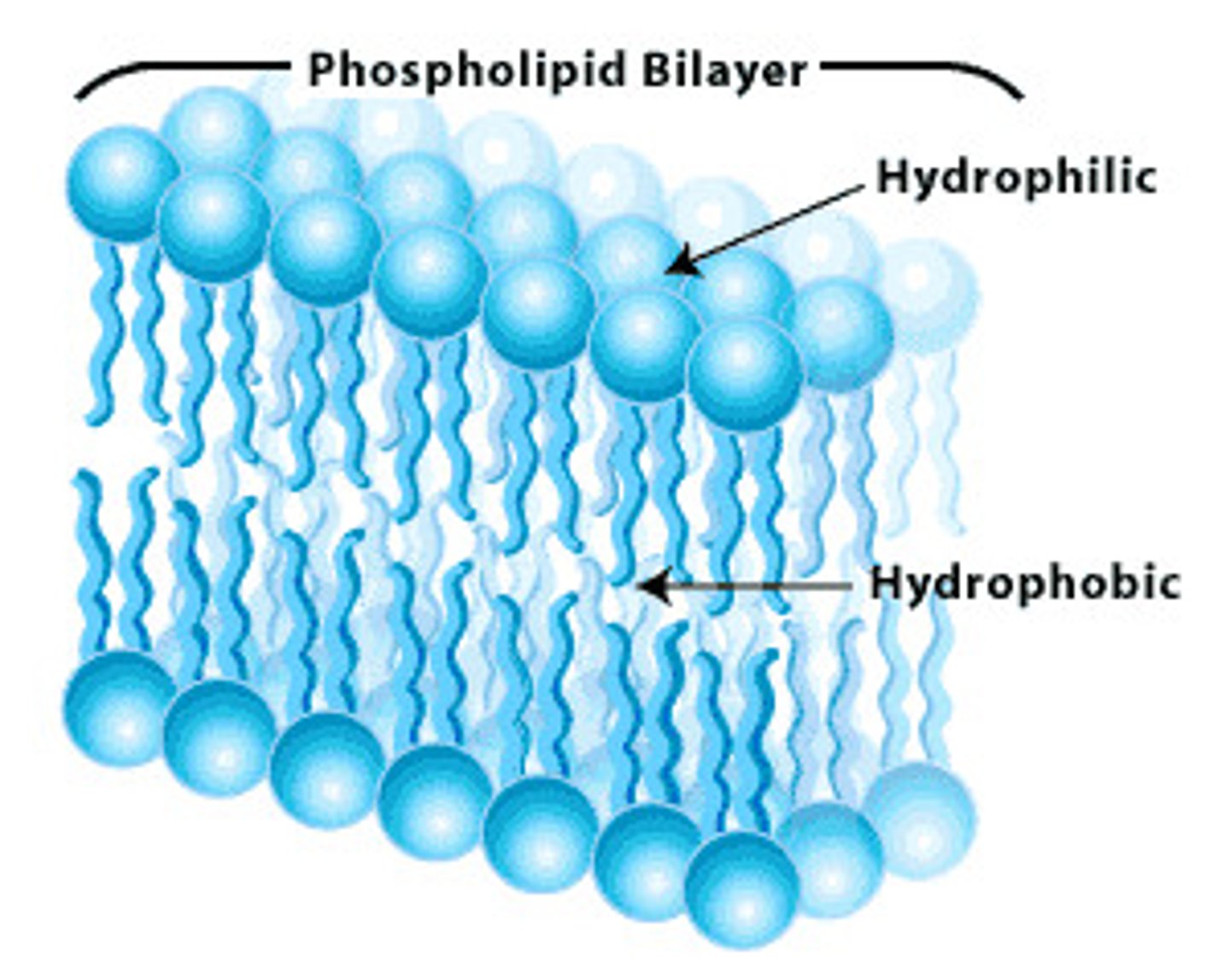
Hydrophilic region is the head
Hydrophobic part contains 2 tails of fatty acids.
What is the hydrophobic and hydrophilic region of lipids?
Hydrophobic tail usually occur towards the center of membrane resulting information of a lipid bilayer
The hydrophobic tail of lipids usually occur towards what of the membrane? what does this form?
polar and non-polar
Proteins can posses both ______ and ______ side chains
outer side
the polar hydrophilic linkages of proteins face the
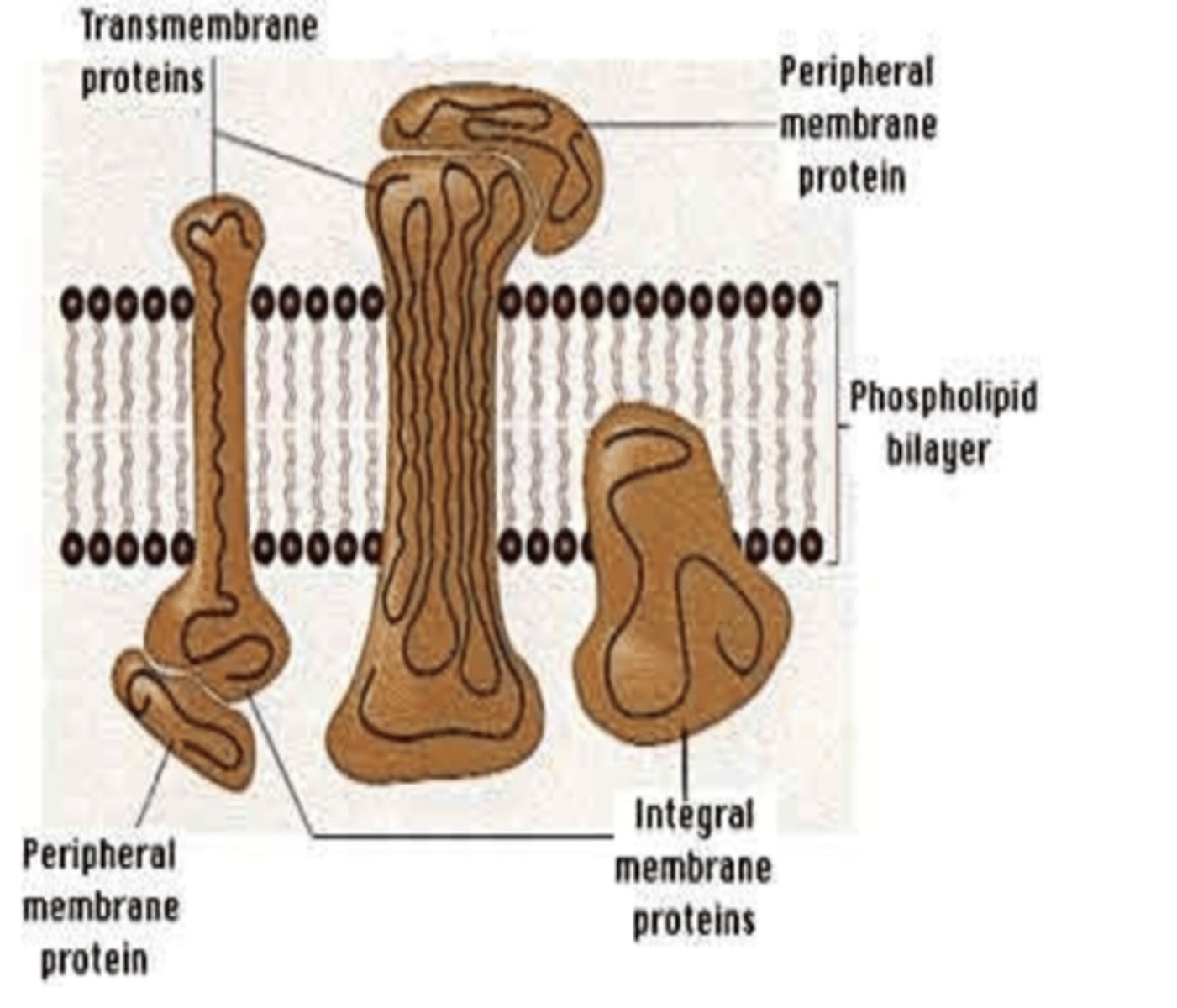
kept folded inside or used to established connections with hydrophobic part of lipids.
the non-polar hydrophobic linkages of proteins are either where in the plasma membrane? (2)
Oligosaccharides
e.g.hexose, fucose, hexoamine, sialic acid
Carbohydrates are branched or unbranched ________.
1. Compartmentalization
2. Protection from injury
3. Providing organic connections between adjacent cells (plasmodesmata & gapjunctions)
4. Providing selective permeability barrier
5. Transporting solutes
6. Responding to external stimuli
7. Energy transduction
8. Secretory, excretory & waste products thrown out by exocytosis.
What are the functions of the cell membrane? (8)
rods, spheres or filamentous bodies
In electron micrographs of cells the mitochondria appears as what?
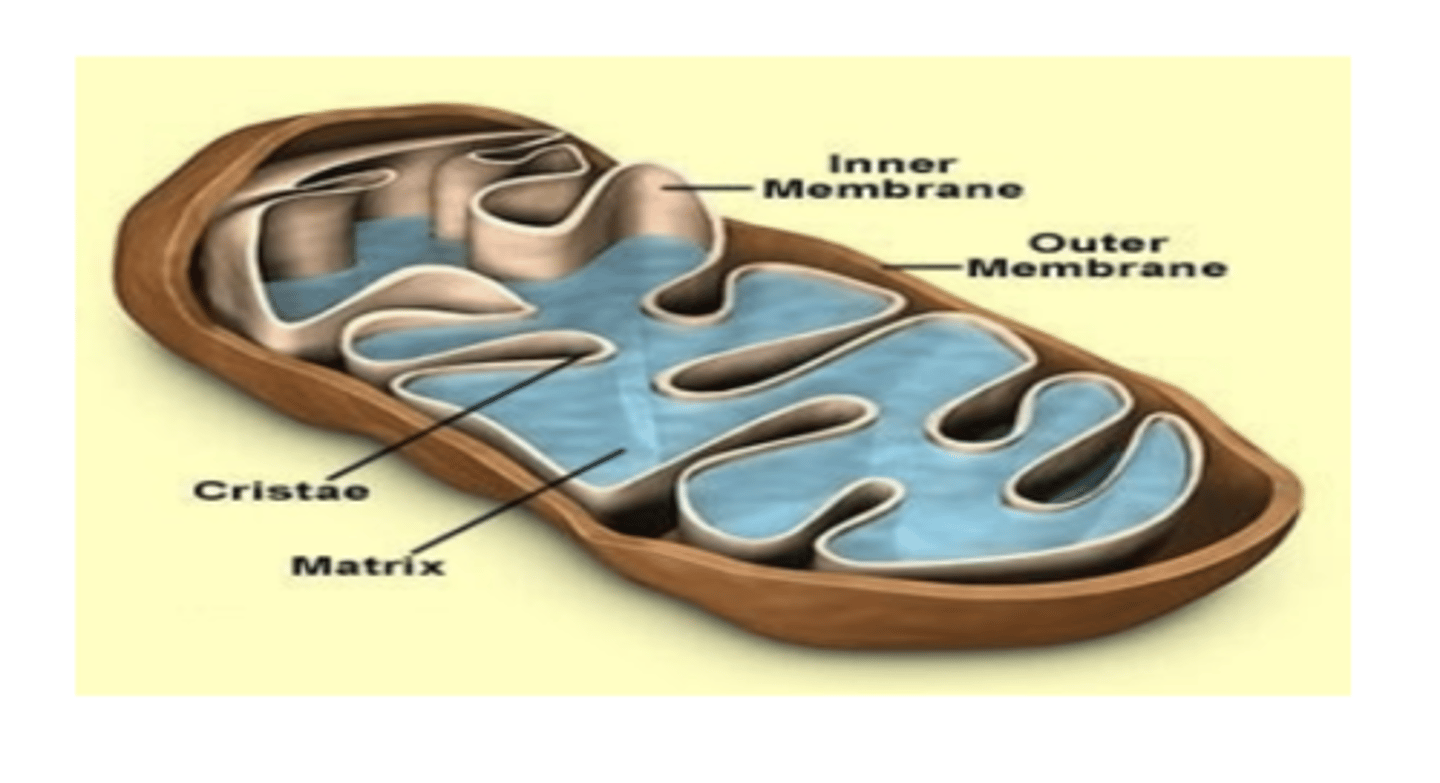
Inner membrane convolutes into cristae ,and this increases its surface area
The inner membrane of the mitochondria convolutes into what? What does this increase?
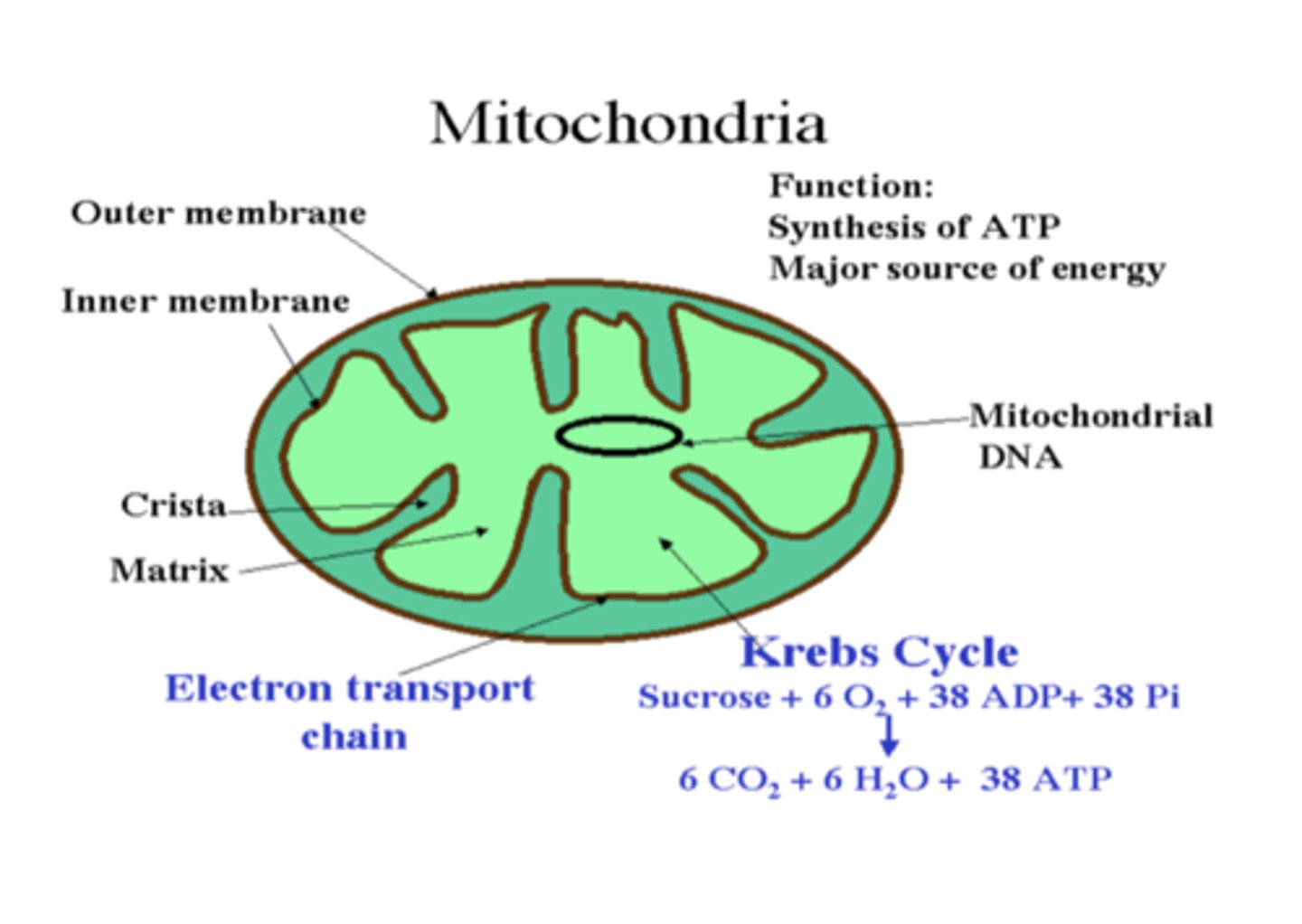
electron transport system
The inner membrane of the mitochondria contains components of the?
it is impermeable to most ions including H, Na, ATP, GTP, CTP etc and to large molecules
What is the inner membrane of the mitochondria impermeable to?
special carriers
e.g. adenine nucleotidecarrier(ATP -ADP transport)
• Complex II i.e. Succinatedehydrogenase
• Complex V i.e. ATP synthase complex.
For transport of the inner membrane of the mitochondria what is present?
permeable to most ions and molecules which can move from the cytosol to inter membranous space.
The outer membrane of the mitochondria is
The ER is the largest organelle inthe cell
What is the largest organelle in the cell?
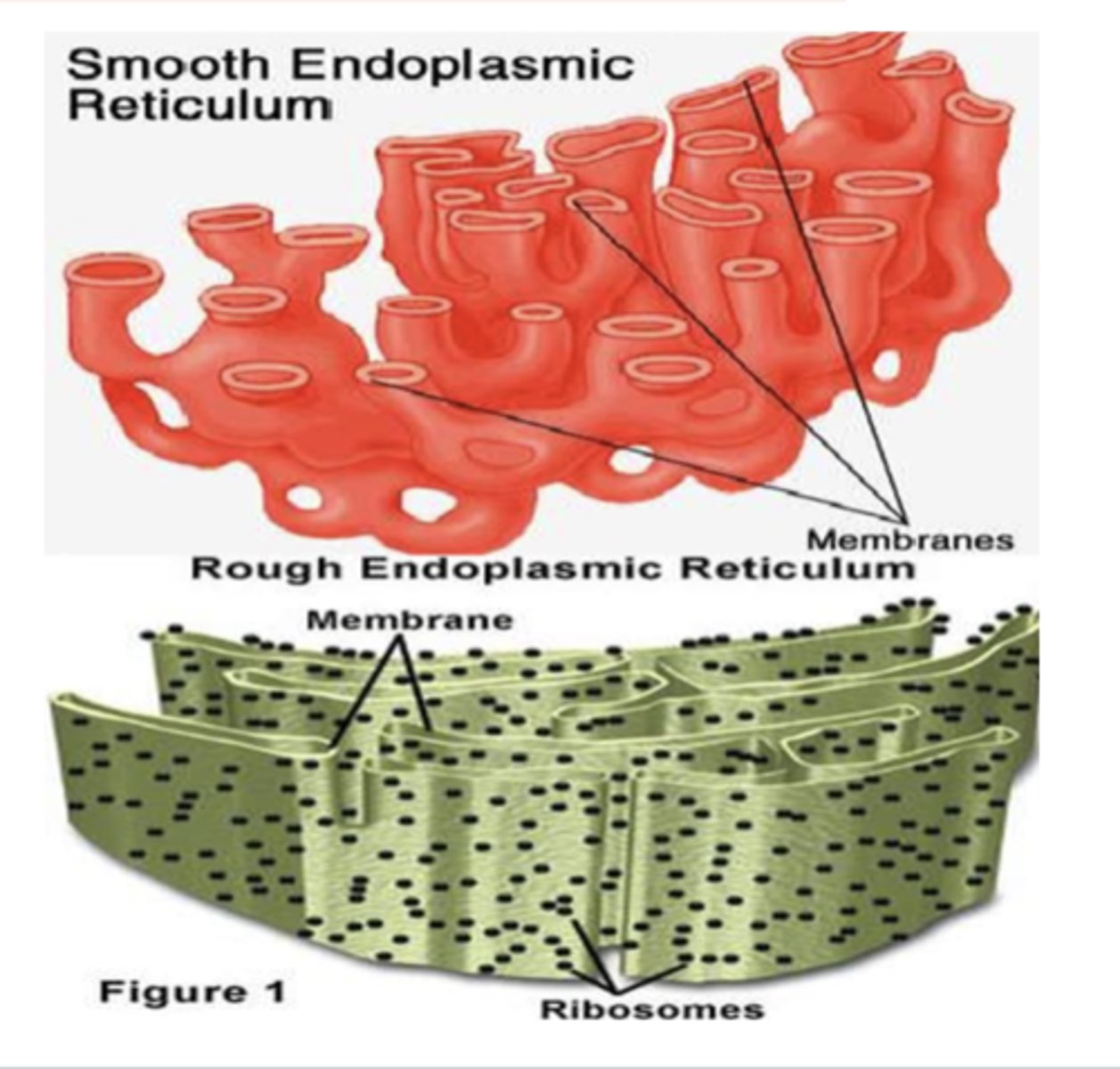
Endoplasmic retinaculum
Where is the major site of protein synthesis, transport, protein folding, lipid and steroid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism and calcium storage take place in the cell?
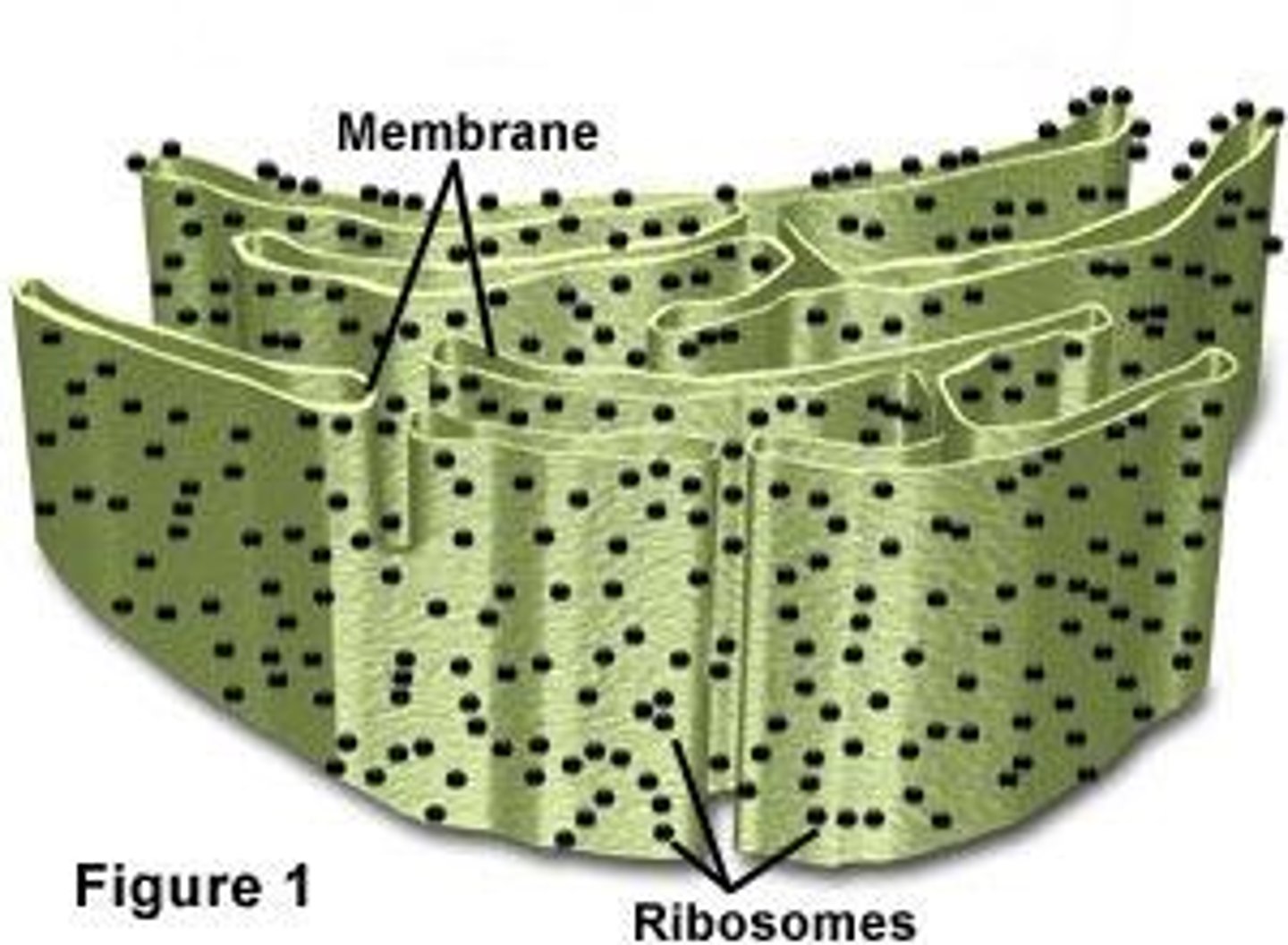
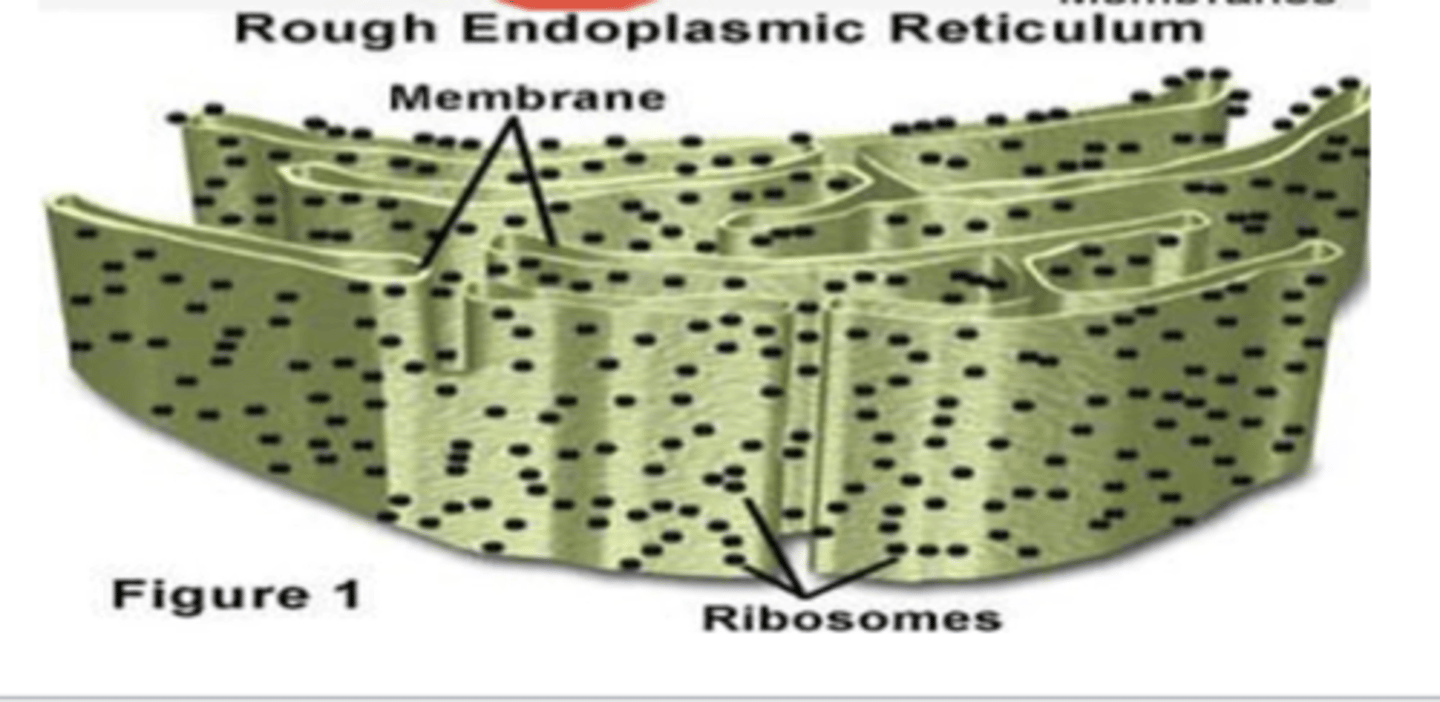
Protein synthesis
- Plasma membrane
- Membranous organelles
- Secretion (by exocytosis
Glycosylation, some post-translational modification, and assembly of multichain proteins
What is the function of the rough ER? (4)
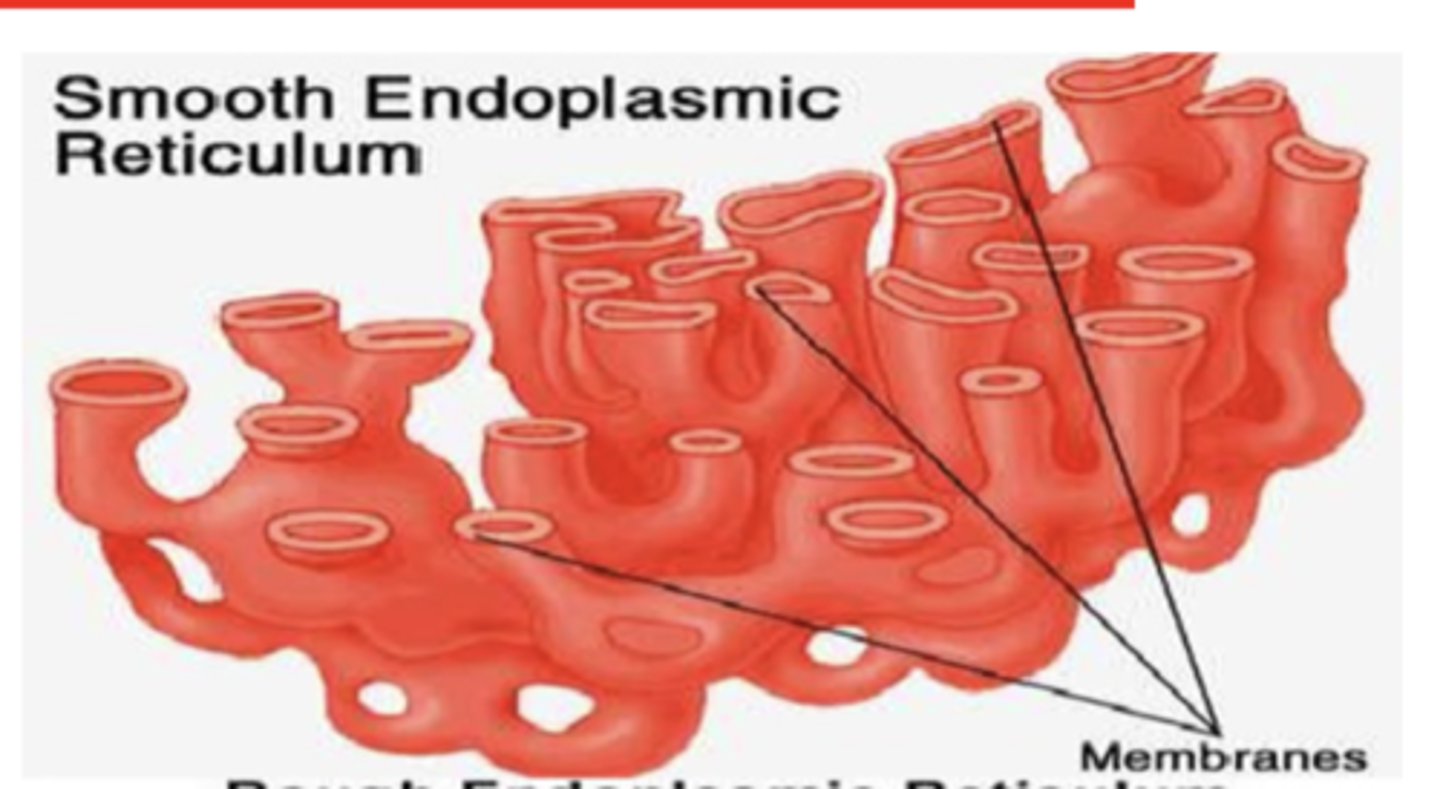
Functions depend on cellular specialization
1. Synthesis of phospholipids and steroids for plasma membrane. Extensive in cells that secrete steroid hormones: Leydig cells, adrenal cortex cells.
2. Detoxification of harmful exogenous molecules (alcohol, barbiturates,etc.): liver cells.
3. Calcium sequestration and release:muscle cells (sarcoplasmic reticulum)
What is the function of the smooth ER? (3)
Tiny granules composed of RNA and proteins they synthesize of proteins.
What are ribosomes? What are they composed of (2)? what do they synthesize?
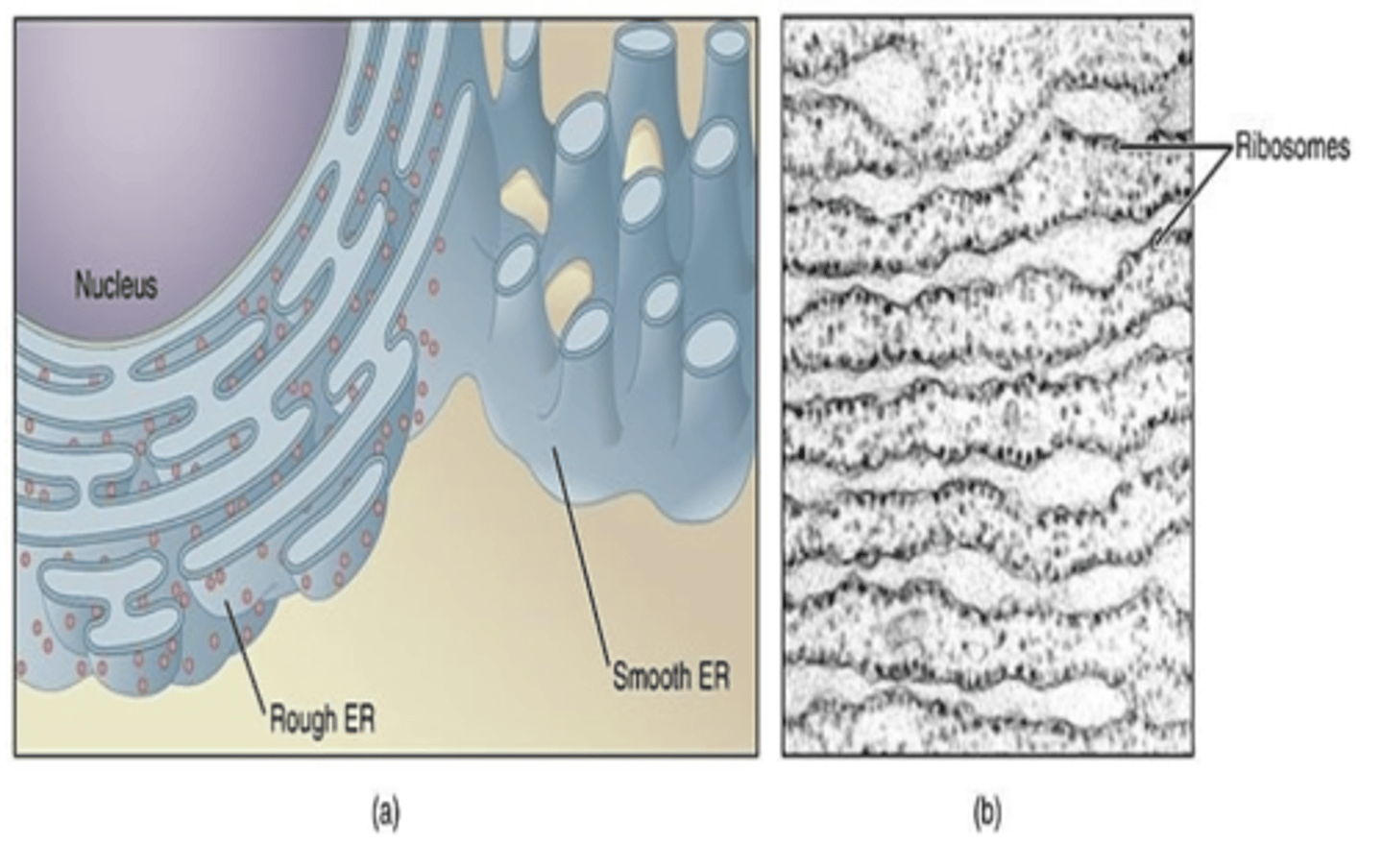
bulk membrane lipid biogenesis
occurs in the endomembrane compartment that includes the ER and Golgi apparatus.
The ER is a site of what? where does it occur? What does it include (2)?
major store of intracellular Ca 2+
What is the ER a major storage of?
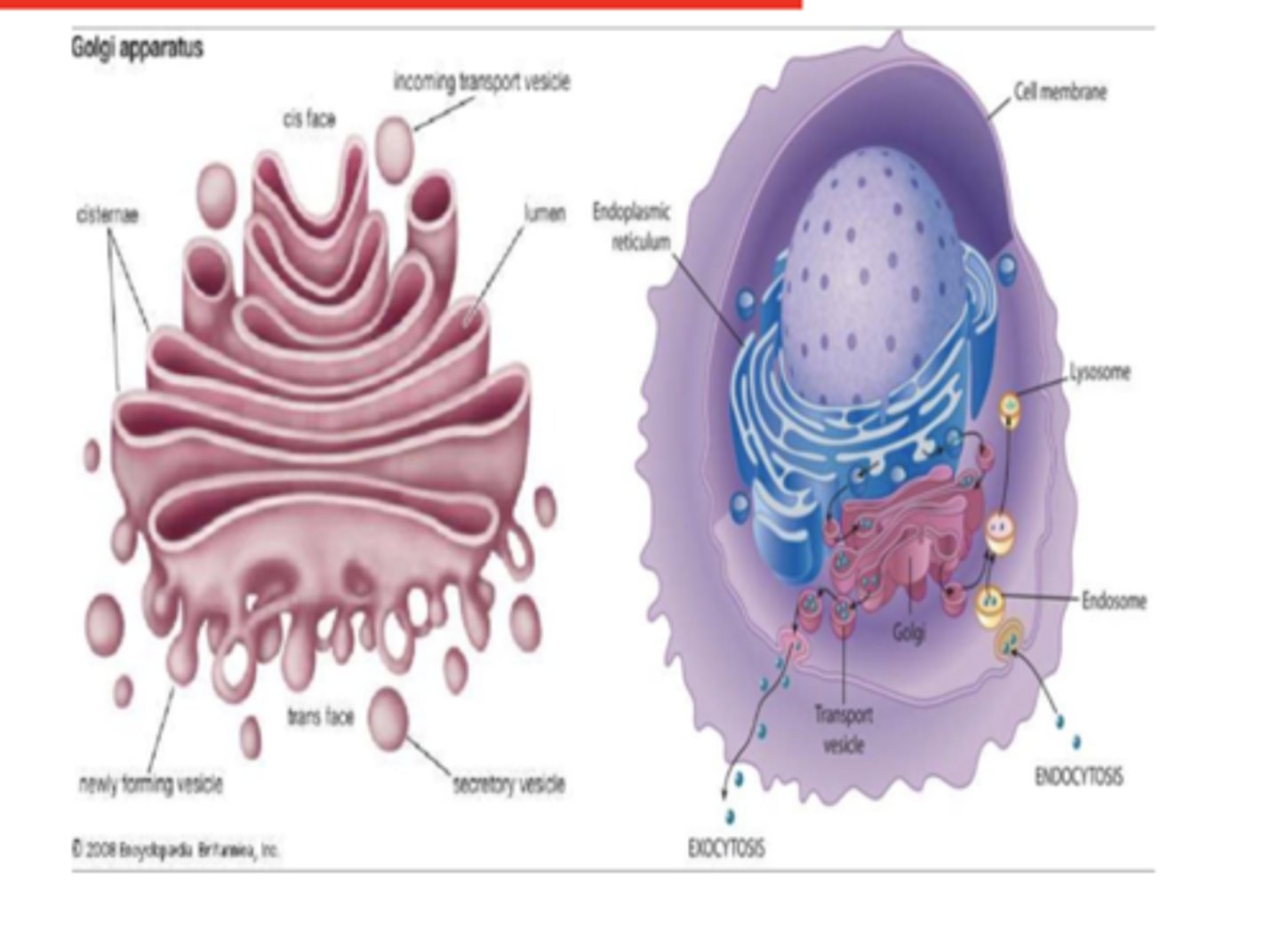
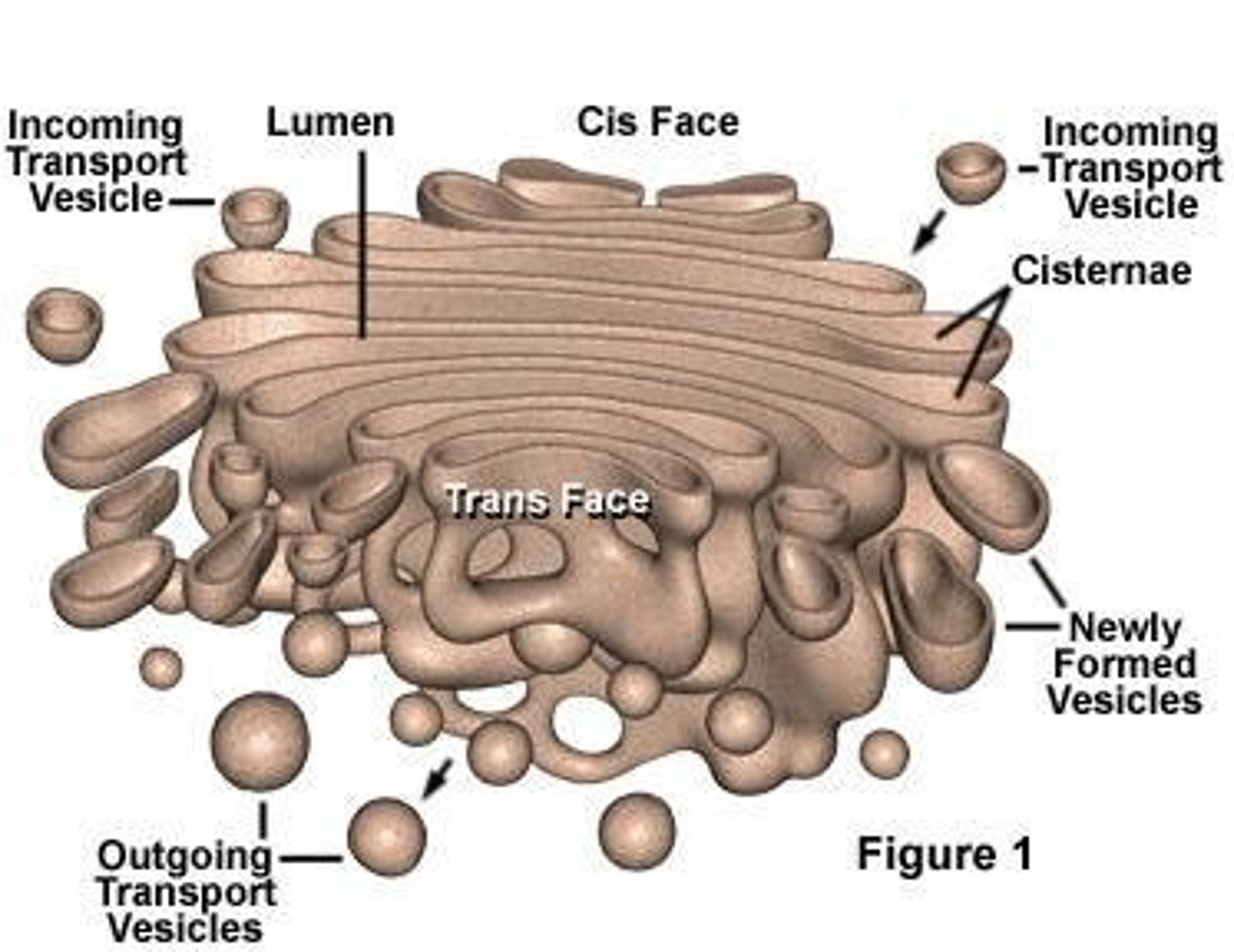
1. Terminal process of post-translational modification of RER-synthesized proteins
2. Packaging and distribution of proteins from RER.
What are the functions of the Golgi apparatus? (2)
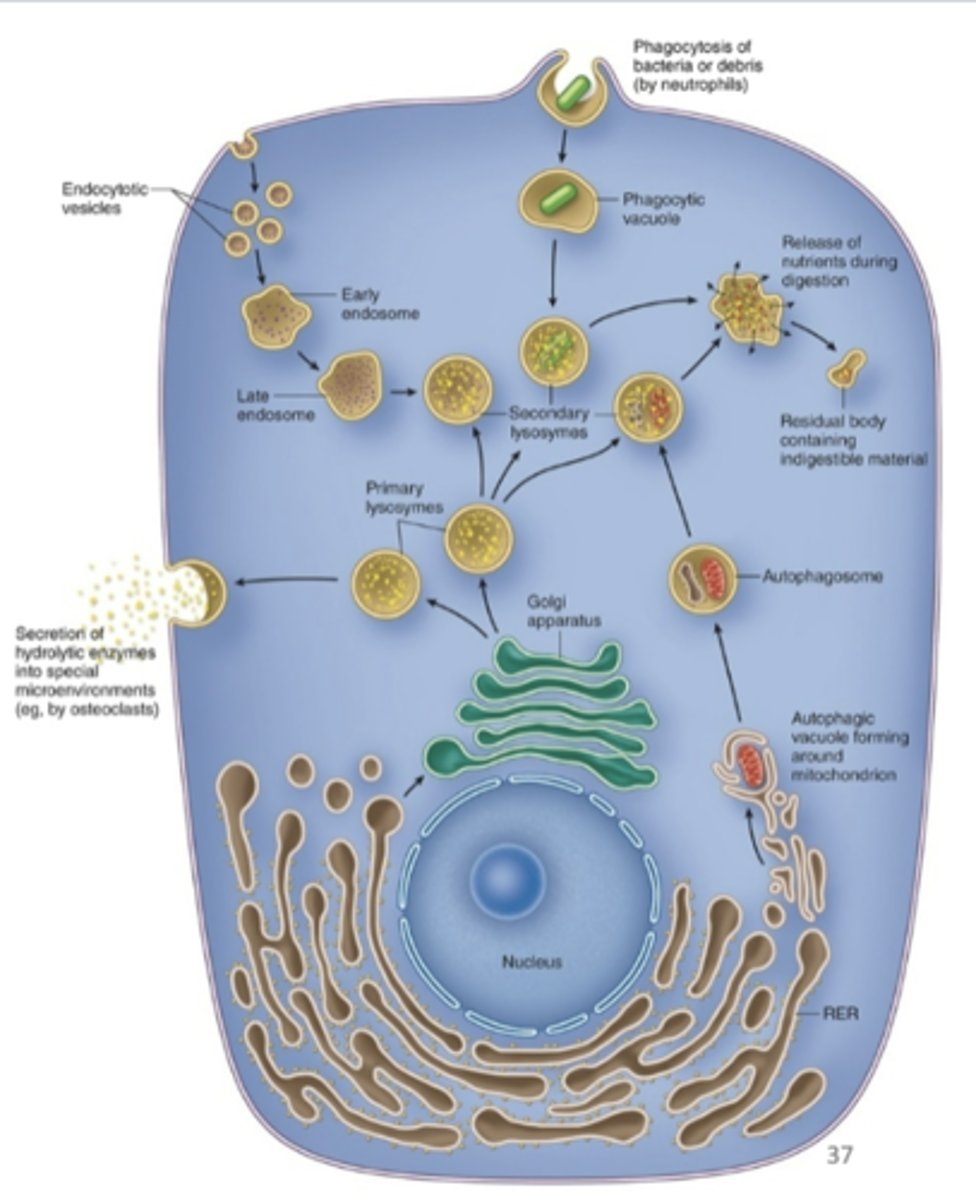
1. Cellular digestion of extracellular material
2. Release of nutrients
3. Autophagy.
4. Secretion of hydrolytic enzymes
What is the function of the Lysomes? (4)
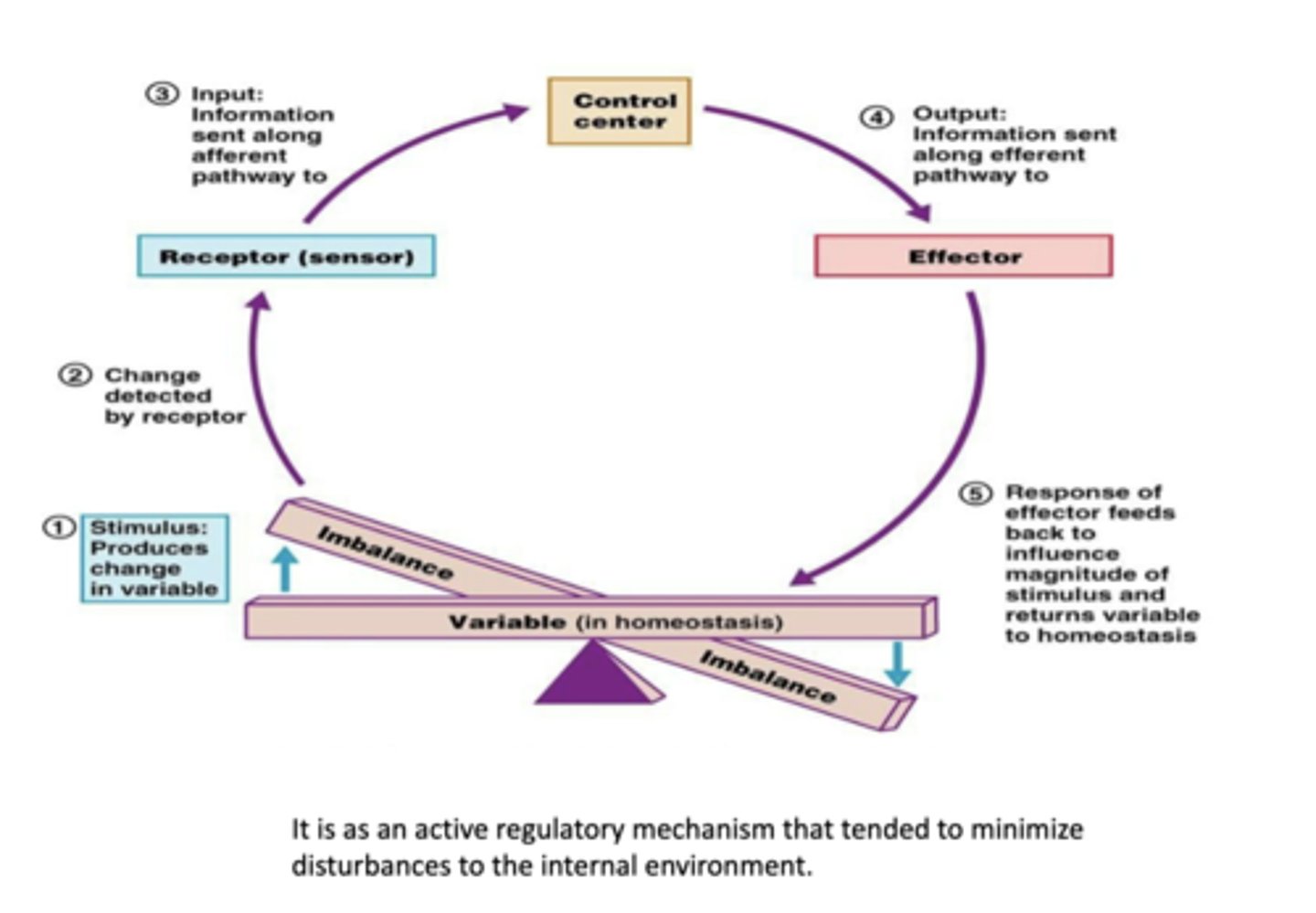
The body uses negative feedback loops and, less often, positive feedback loops to maintain or restore homeostasis.
The body uses what to maintain or restore homeostasis?
1. sensor
2. a control center
3. an effector
What do feedback loops involve? (3)
The world outside of the body and its “state.” The state or conditions in the outside world can determine the state of many internal properties of the organism
What is the external environment?
The internal environment is the extracellular fluid compartment. This is the environment in which the bodys cells live. It is what Bernard meant by the "internal milieu".
What is the internal environment?
The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment by an organism in the face of a changing external environment and varying internal activity using negative feedback mechanisms to minimize an error signal.
What is Homeostasis?
Negative feedback
a. Maintains Homeostasis
b. Acts like a thermostat
1. Set point
2. Disturbance
c. Returns factor (variable) to mean valued.
d. Effectiveness of system = Gain
What are the regulatory methods used by the human body? What does it do? (4)
NO!
Homeostatic regulation is a constant, continuous process and does not ordinarily operate as an on/off switch that results in an all-or-none response.
Do homeostatic mechanisms operate like an on/off switch?
means that systems must work together to support human life.
What is interdependence mean?
is a disordered or incorrectly functioning organ, part, structure, or system of the body
Causes of disease:
1. Genetic or developmental errors
2. Infection
3. Poisons
4. Nutritional deficiencies or imbalance
5. Toxicity
6. Unfavorable environmental factors
What is a Disease?
Signs of disease are objective; they can be measured.
ex: Fever, HPB, Rash
What are signs of a disease?

Symptoms of disease are subjective. Symptoms can’t be observed by another person; but a person that is ill experiences them.
ex: Dizziness, Pain, Blurry vision
What are symptoms of a disease?
