The Rest of the Course (after Midterm 2)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
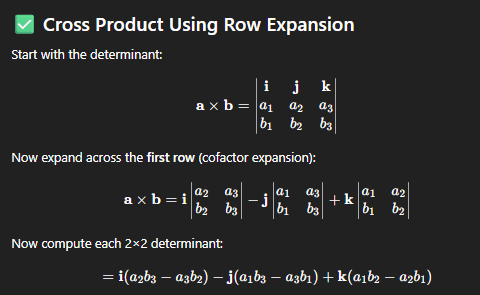
cross product formula using cofactor row expansion
don’t forget the minus sign written before the j (vertical component of the vector)
rmbr: ai + bj + ck = (a, b, c)
formula for the curl of a vector field
remember: ∇ × F (order is important)
expand the top row via cofactor determinant expansion

curl of a vector field F = (P, Q, R): input and output
computing the curl gives you another vector field
the input of a curl = any point in space
the output of a curl = a vector where the direction is the axis that the point is “spinning around” and the magnitude is how fast it is spinning
curl of a vector field: defn
curl measures the infinitesimal circulation per unit area at a point
imagine a tiny closed loop around a point in a vector field, computer the circulation (line integral of the vector field around that loop), divide by the area of the loop, and shrink the loop to size → 0, and the vector that you get is the curl at that point

right hand rule for curl

right hand rule for stokes theorem

the curl of a gradient, which is a type of vector field, is equal to ___
zero.
gives criterion for determining whether a vector field is the gradient of some function
so if you are given some vector field F, and you compute the curl with ∇ × F and it eqiuals to 0, then F = the gradient of some function and you can use the
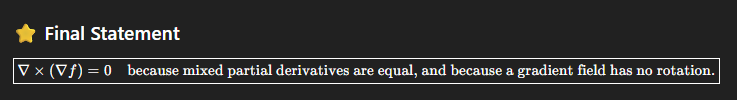
formula for the divergence of a vector field (in 2D)
just remember this dot product: DIV(F) = ∇ ⋅ F

formula for the divergence of a vector field (in 3D)
or just remember: DIV(F) = ∇ ⋅ F

divergence of a vector field: defn
the computation of the divergence gives you a real number, not a vector
if you imagine the vector field as a pool of water, divergence at a point tells you whether water is spreading out (called a source) or converging in (sink)
if divergence result at some point = positive → source
negative → sink
zero → neither source or sink
what is the computation of the divergence of a curl of a vector field equal to?
ZERO.
∇⋅ (∇ × F) = 0, because the dot product between perpen vecs = 0, and ∇ is perpen to (∇ × F) by defn of cross product
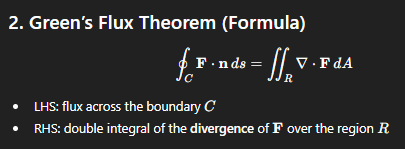
formula for green’s flux theorem
so instead of computing the left hand side, you can compute the right hand side IF green’s flux theorem applies, and the equation just becomes a normal double integral
this theorem is only for 2D
R = D = domain
(∇ ⋅ F) = DIV(F)
criterion for the green’s flux theorem
the curve C that bounds the domain D just be a simple closed curve (it doesn’t cross itself)
C must be positively oriented (when traversed counterclockwise, D is always on your left)
D should be simply connected. if there are holes, it must be computed separately
what is the formula for flux of a parametric surface
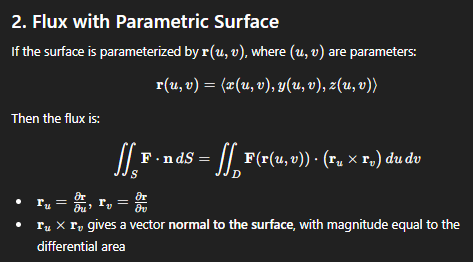
flux of a surface: defn

formula for the normal vector in the flux formula
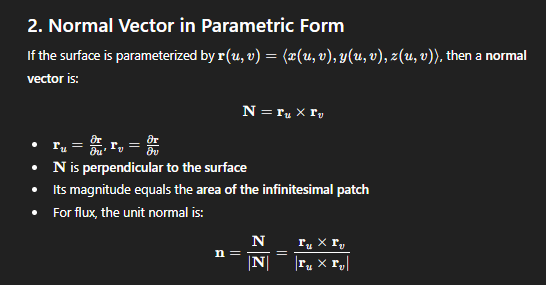
if you have a tangent vector <a,b>, what would the normal vector be?
n = <b, -a>
only works for vectors that only have two components
if a curve is negatively oriented, what should you do?
include a minus sign in the formula
formula to find the unit normal
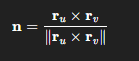
formula to finding the area of a surface

formula for integrating a function over a surface
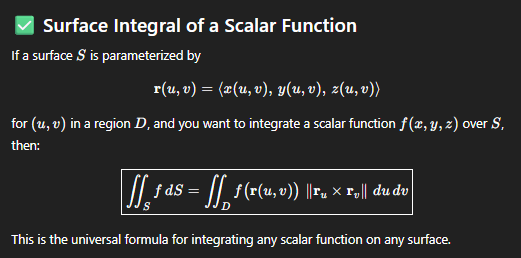
if you were given the parametrization of a cylinder → (Rcosθ, Rsinθ, z), how do you make it a surface
make one of the variables a fixed number
the most common is to make R into a fixed number → if R = 2, then you’d get the surface parametrization of r(u,v) = (2cos(u), 2sin(u), v) where u = θ and v = z….
formula for integrating a vector field over a surface

a shortcut when computing the integral of a vector field over a surface
for when u = F (vector field)
and v and w are the partial derivs of the parametrization of the surface

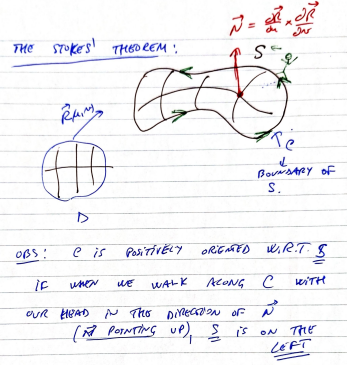
formula for stokes theorem
turns a complicated line integral into a simpler to compute surface integral
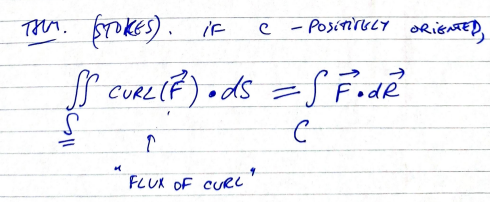
criterion for applying stokes theorem
when you look from the direction of the normal vector, you must walk around the boundary counterclockwise
formula for divergence theorem
this theorem makes it so you don’t have to compute a complicated surface integral, and you just have to compute a regular triple integral by treating the surface as the boundary of some volume
best for surfaces with hard corners, like a cube
the surface must be a CLOSED SMOOTH surface
the normal vec (n) must be pointing outwards out of the surface. if it’s pointing inwards, you have to apply -1 to the integral
