ch15.1 - neurobiology of stress (background)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
something to cheer you up if you’re stressed today:)

who popularized the use of the term “stress”
Hans Selye
Selye’s stress definition
the rate of all wear and tear caused by life (negative emotions)
connection made by Selye between stress and disease
general adaptation syndrome
phases of general adaptation syndrome
alarm reaction
adaptation stage (appropriate responses and homeostatic balance)
exhaustion stage (occurs when there’s prolonged stress → ⬆susceptibility to disease)
better definition of stress
body’s multisystem response to a challenge that overwhelms response mechanisms
stress activates two physiological systems in the body:
sympathetic NS
hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
sympathetic NS is the ____ that prepares us for emergencies.
fight or flight response
HPA
produces endocrine changes to help us adapt (releases hormones and stuff). predominates if stress is prolonged
when is HPA activated
when info is conveyed into PVH
PVH activates
HPA axis
CRF (corticotropin releasing factor)
peptide synthesized by neurons in PVH
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
secreted into bloodstream by cells in anterior pituitary
click to reveal PVH and its peptides/hormones
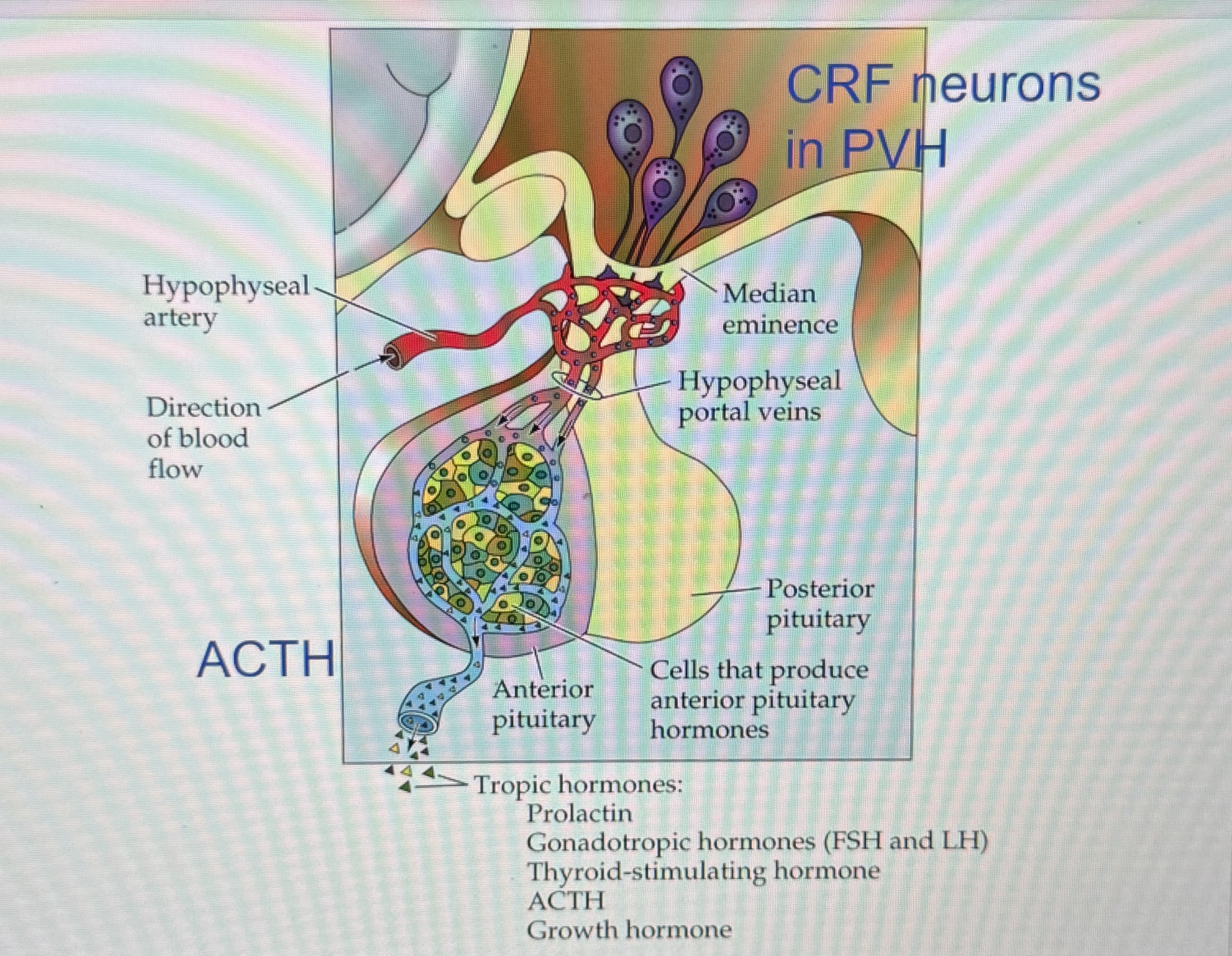
ACTH role
tells adrenal gland to release cortisol (glucocorticoid hormone)
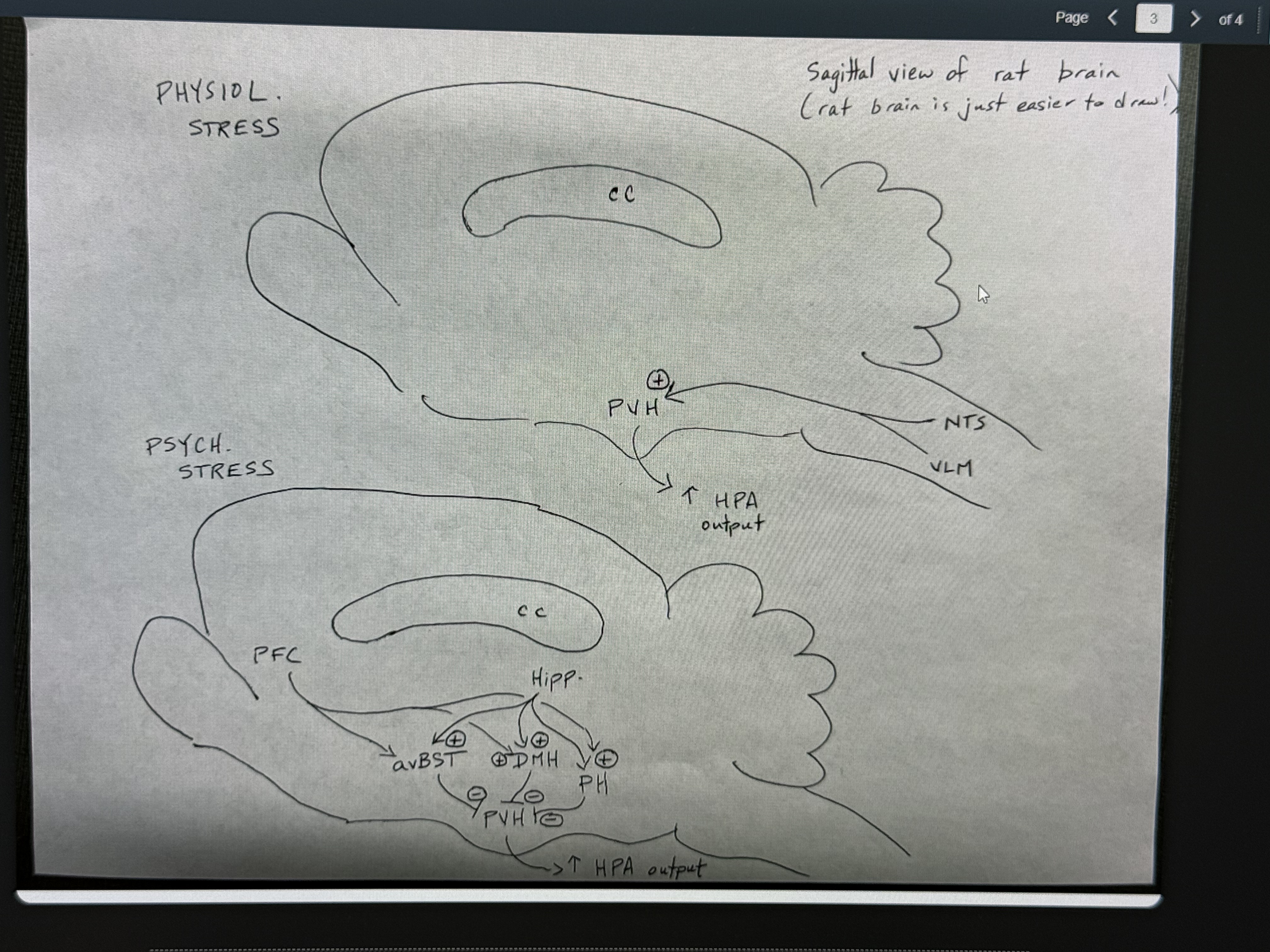
two types of stress that lead to different PVH pathways
physiological stress
psychological stress
physiological stress (blood loss, low O2, etc)
brain stem projects to PVH from nucleus of solitary tract/ ventrolateral medulla
psychological stress (predator exposure. public speaking)
pathways more sensory (relayed to limbic regions like hippoc/ prefrontal cortex by avBST). indirect to PVH.
in psychological stress, inputs over PVH are _____ and release “ _____”, to prevent over activation (but HPA⬆)
inhibitory/ breaks
physiological/ psychological stress diagram
cortisol is
primary stress hormone
4 things cortisol does in response to threats from environment
⬆blood sugar (activates glucose metabolism)
breaks down fats and proteins (for energy)
inhibits immune function (like inflammation)
does cognitive adjustments
what does cortisol do when stressor subsides (i.e: you escape a bear)?
cortisol feeds back ontem brain and shuts OFF HPA axis response
steps of how glucocorticoid receptors work (4)
CORT diffuses and enters cell through plasma membrane
binds to glucocorticoid receptor (GR), CORT-GR forms dimer
activated dimer translocates to nucleus
binds to DNA to alter gene expression
click to reveal glucocorticoid diagram
