Science Bowl: Physical Science
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

61 Terms
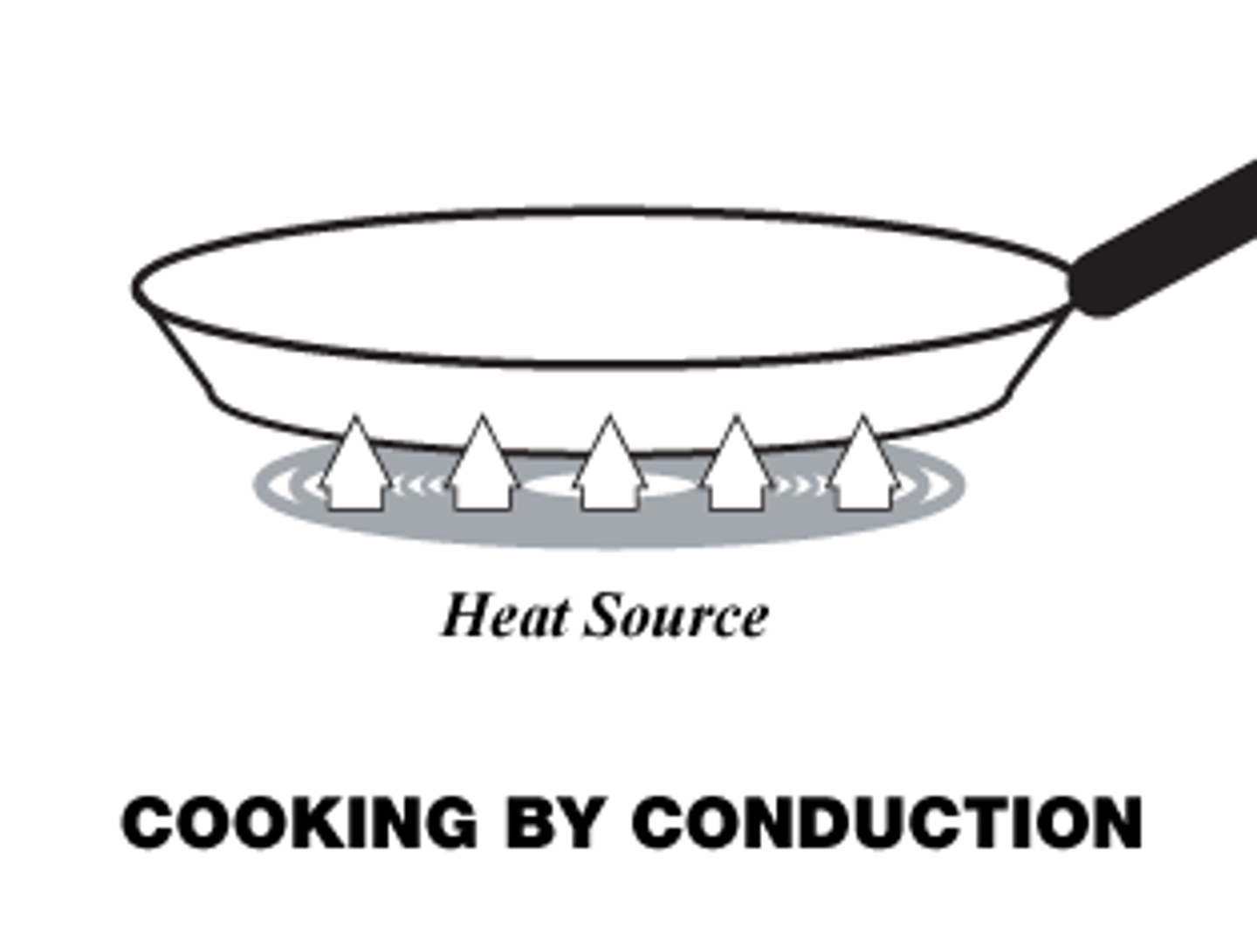
Conduction
Heat transfer through direct contact
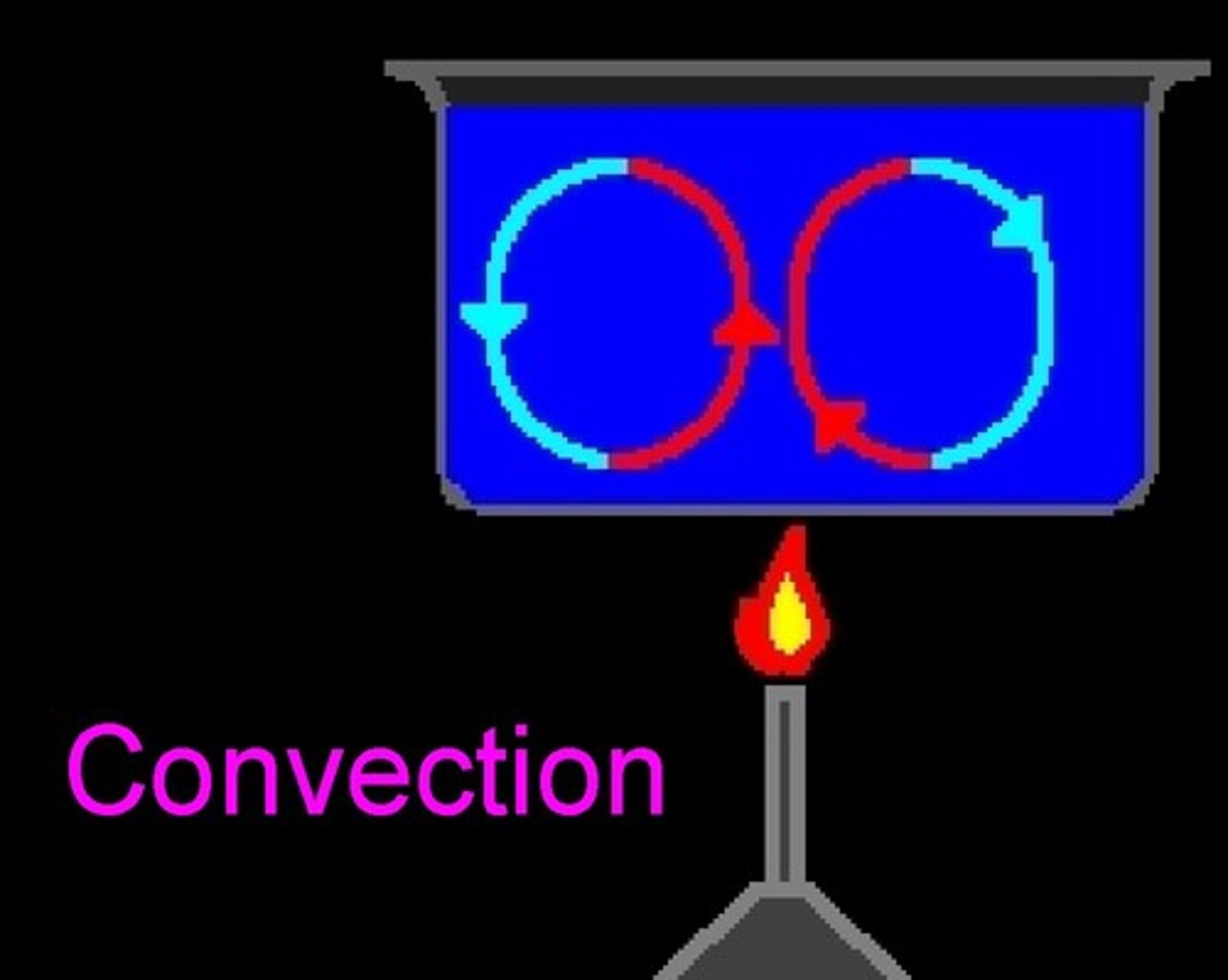
Convection
Heat transfer through fluids (liquids or gases) moving
Radiation
Heat transfer through heat waves

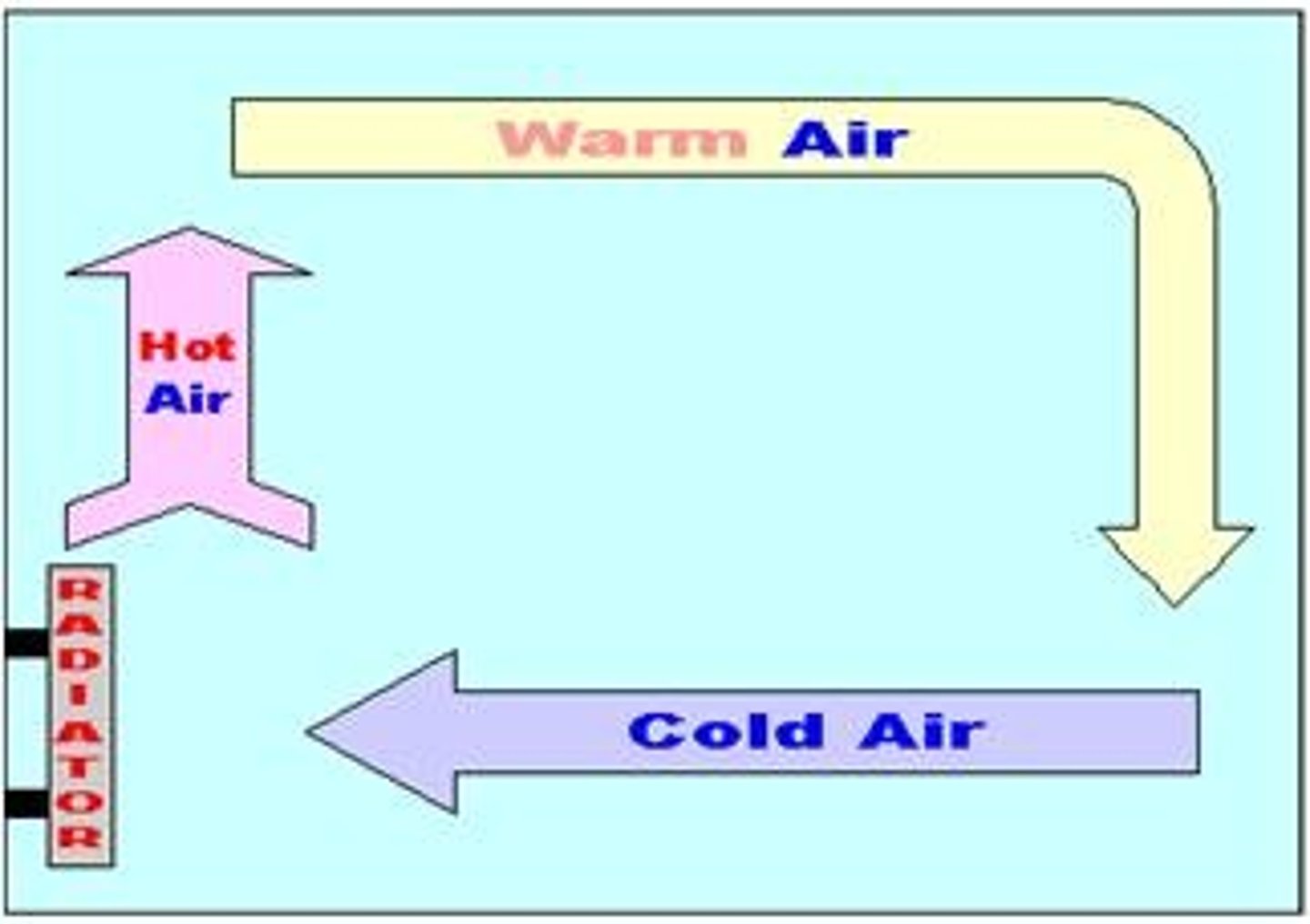
Convection Current
The circular flow of a fluid
Conductor
Something that passes heat well

Insulator
Something that DOES NOT transfer heat well

Melting
Solid > Liquid
Gains thermal energy

Freezing
Liquid > Solid
Loses thermal energy

Vaporization
Liquid > Gas
Gains thermal energy

Condensation
Gas > Liquid
Loses thermal energy

Sublimation
Solid > Gas
Gains thermal energy FAST, skips liquid

Deposition
Gas > Solid
Loses thermal energy FAST, skips liquid

Specific Heat
Amount of energy needed to raise temperature

Heat
Transfer of thermal energy from HOT TO COLD substance

Temperature
Kinetic energy, how fast particles are moving

Combustion
Burning of fossil fuels

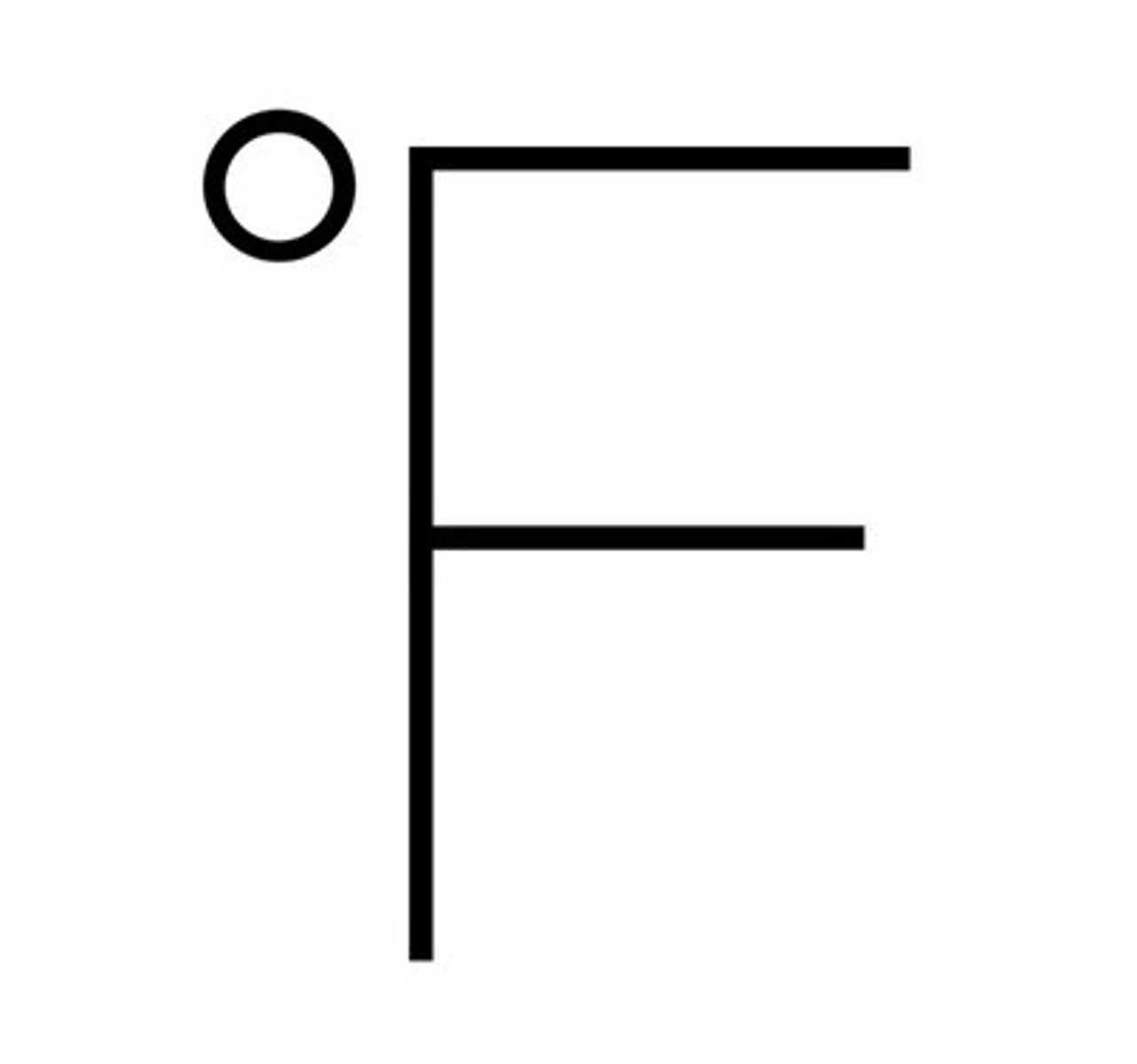
Fahrenheit
'
MURICA
32 F freezing, 212 F boiling
Celsius
Used everywhere else 0 C freezing, 100 C boiling

Kelvin
Used in science, 273 more than Celsius
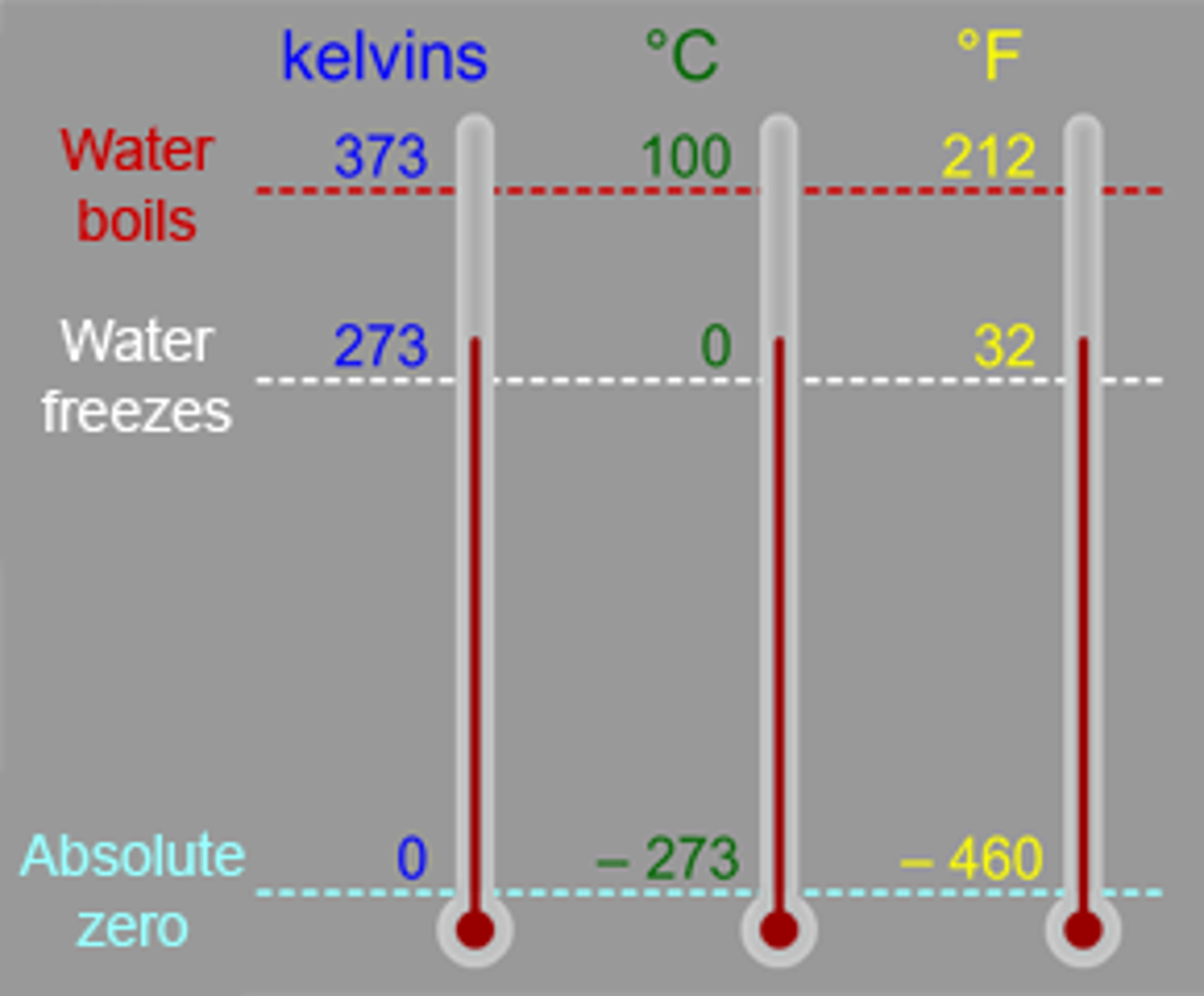
Absolute Zero
Coldest possible temp, no more energy can be removed

Thermal Expansion
Things expand when heated

Melting/Freezing Point
32 F liquid freezes or solid melts

Boiling Point
212 F liquid boils

Evaporation
Liquid becomes gas on SURFACE

Boiling
Liquid becomes gas UNDER SURFACE

Thermal Energy
Total particles in substance
Motion
The state in which one objects distance from another is changing
Meter
Basic SI unit of length
Speed
Distance an object travels in a certain time
Velocity
Speed in a given direction
Acceleration
Rate at which velocity changes
Newton
Measures a force
Force
Push or pull on an object
Net Force
Overall or total force on an object
Balanced Forces
Equal forces acting in opposite directions
Unbalanced Forces
Changes an objects motion due to a nonzero total force
Inertia
Tendency of object to continue doing what it already was
Mass
Amount of matter in object
Momentum
Mass x velocity
Friction
Force a surface exerts on an object when they rub together
Gravity
Force that pulls objects toward each other based on their weight and distance
Weight
How strongly gravity forces you down to Earth
Density
Mass of a substance contained in its volume
Buoyant Force
Upward force acting on an object submerged
Input Force
Force you put in
Output Force
Force the machine puts out
Work
When a force moves an object
Joule
Measures work and energy
Efficiency
How productive a machine is. Output divided by input
Lever
Straight object that pivots to do work
Screw
Inclined plane wrapped around central cylinder
Inclined Plane
Flat surface with one end higher than the other
Fulcrum
Fixed point a lever rotates around
Power
How quickly work is done, measured in watts
Energy
Ability to do work
Elastic Energy
Energy of objects stretched or compressed
Gravitational Energy
Energy of objects with mass and height
Electrical Energy
Energy of electrical moving charges
Nuclear Energy
Energy stored in nucleus of an atom
Potential Energy
Energy that is stored, many different types
Kinetic Energy
Energy an object has when it's moving