Psych 253 - Lecture 6: Attitudes, Behaviour, and Persuasion pt.1
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Attitudes
Evaluations of people, objects, and ideas.
Where do attitudes come from? - Nature/Nurture

asked both identical and paternal twins and found that identical twins tends to have more similar attitudes, suggesting genetic component
Mere Exposure Effect
• Robert Zajonc (1968): Attitudinal Effects of Mere Exposure
• Mere Exposure Hypothesis: People come to have positive attitudes toward those stimuli to which they are frequently exposed - (the more you see something the more you like it)
• IV: # of times different “Turkish words” were shown to participants (something unfamiliar to them with no bias)
• DV: ratings of whether these words meant good or bad things (on a continuous scale)
Showed the words different amount of times
Measure:
Sometimes people can tell what words in other languages mean simply by the sound of the word. Please indicate with a check mark along the scale whether each of the following Turkish words sounds like something good or bad to you.
nansoma
good :___:___:___:___:___:___:___: bad
kadirga
good :___:___:___:___:___:___:___: bad
enanwol
good :___:___:___:___:___:___:___: bad
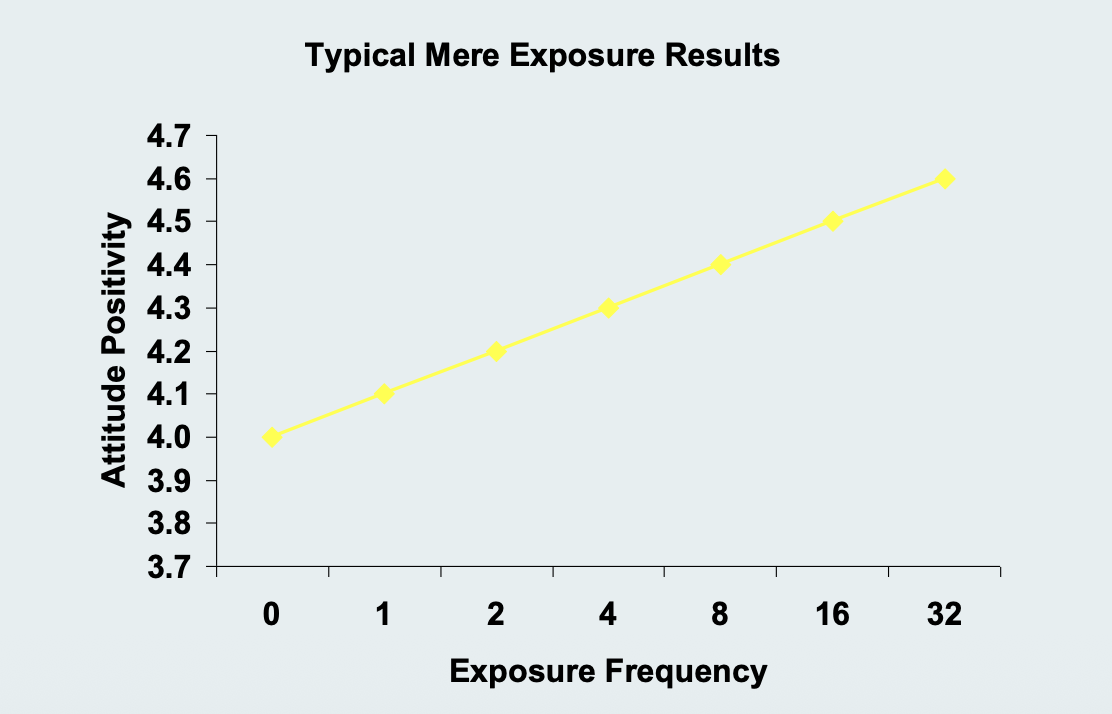
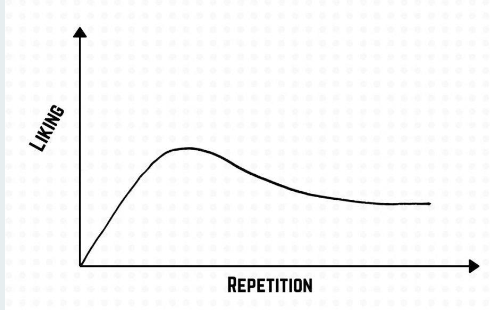
Mere Exposure Effect - Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis of 268 mere exposure effect studies
• Found evidence for the mere exposure effect, but with a few caveats and
modifications:
• Did not find mere exposure for auditory stimuli, only visual stimuli
• Children had much larger mere exposure effects than adults
• Pattern of results is curved; liking does not just continue to go up with more exposures, which makes sense
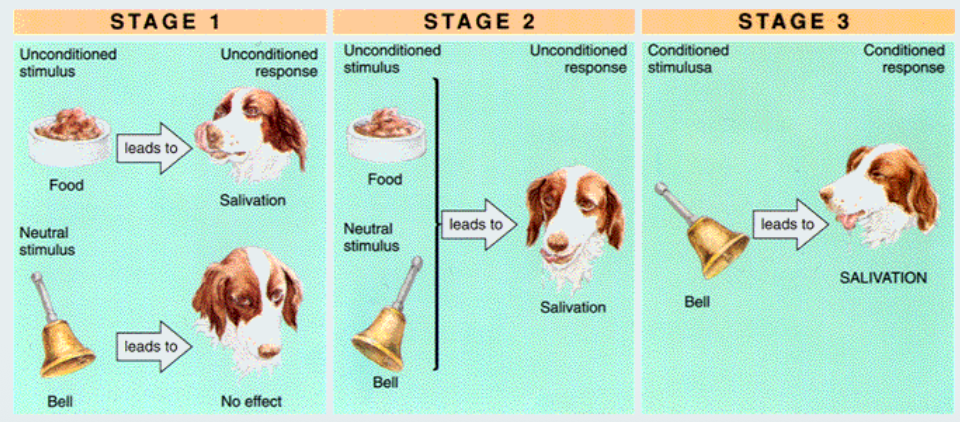
Classical Conditioning
A stimulus that elicits an emotional response is paired
with a neutral stimulus
Neutral stimulus takes on the emotional properties of
the first stimulus
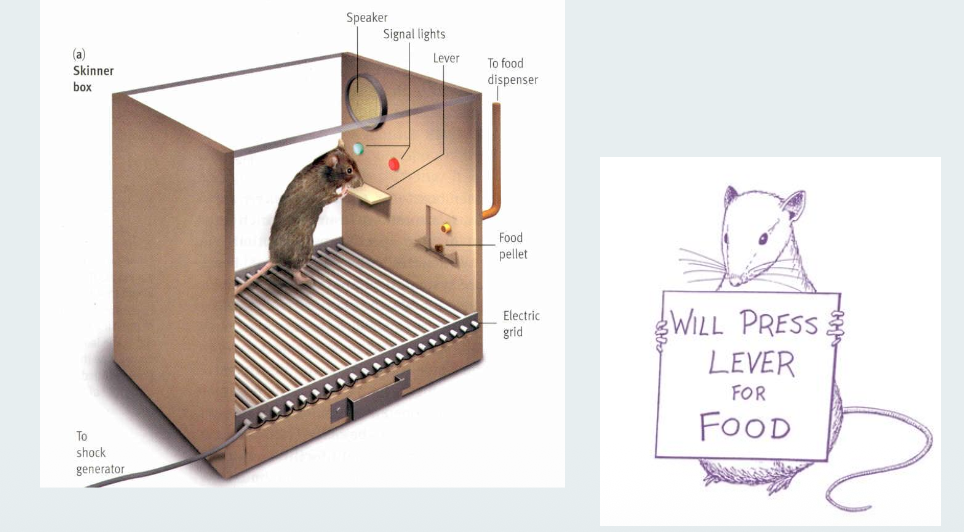
Operant Conditioning
Freely chosen behaviors increase or decrease when followed by reinforcement or punishment.
Positive/Negative Reinforcement, Positive/Negative Punishment
Persuasion (2)
Persuasion is the process by which a message induces change in beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors
We will discuss central and peripheral routes to persuasion
Central routes employ direct, relevant, logical message; requires controlled processing to be effective
Peripheral routes rely on superficial cues that have little to do with logic (does this remind you of something?)
Ethical ways to persuade people video - rewatch and complete notes and know examples
Reciprocity - Obligation to give when you receive For the mint study, just remember that for the DV of tipping, the IV order of effects is: 1 mint + another mint “just for you > 2 mints > 1 mint
be the first to give and make it personizlied and…
Scarcity - People want more of those things there are less of Changing perceived scarcity is enough to change people’s attitudes toward products Also a big part of art’s value, as well as various collectible items
Authority - Follow the lead of credible, knowledgable experts
when receptionist told customer how qualified realtors were before transferring, more people signed up with them
Pitfalls: expertise in one domain can be mistaken for expertise in others: e.g., “I’m a doctor” Or, authority can be faked with signals like degrees or uniforms
Consistency - Looking for, and asking for commitments that can be made
Foot-in-the-door refers to a small initial commitment that is then escalated with larger requests
People asked (versus not asked; IV) to put a small “drive safely” card in their window more likely to agree to put up a large yard sign (DV)
Liking - Prefer to say yes to people they like
People like those that are similar to us, those who pay us compliments, and those who cooperate with us
Straightforward; related to impression management strategies Also: part of using athletes and celebrities to hawk products
Consensus - People will look to the actions of others to determine their own
Saying that “a high percentage of people do this” is a good strategy for persuading people to do a given behavior
Tied to do the idea of social norms (Prentice & Paluck)