Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
What is the product of interphase?
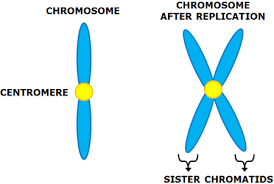
A chromosome that consists of two sister chromatids, connected by a centromere
What is the difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2?
Meiosis 1- homologous chromosomes are separated
Meiosis II - chromatids (each half of a duplicated chromosome) are separated.
Describe the process of crossing over
Homologous chromosomes come together to form bivalents.
Non-sister chromatids wrap around each other and join up at the chiasmata
The chromosomes break up at the chiasmata, and sections of chromosomes swap over between non-sister chromatids.
The swapping over is only between non-sister chromatids.
The final chromatids still have the same genes, but they may have different alleles.
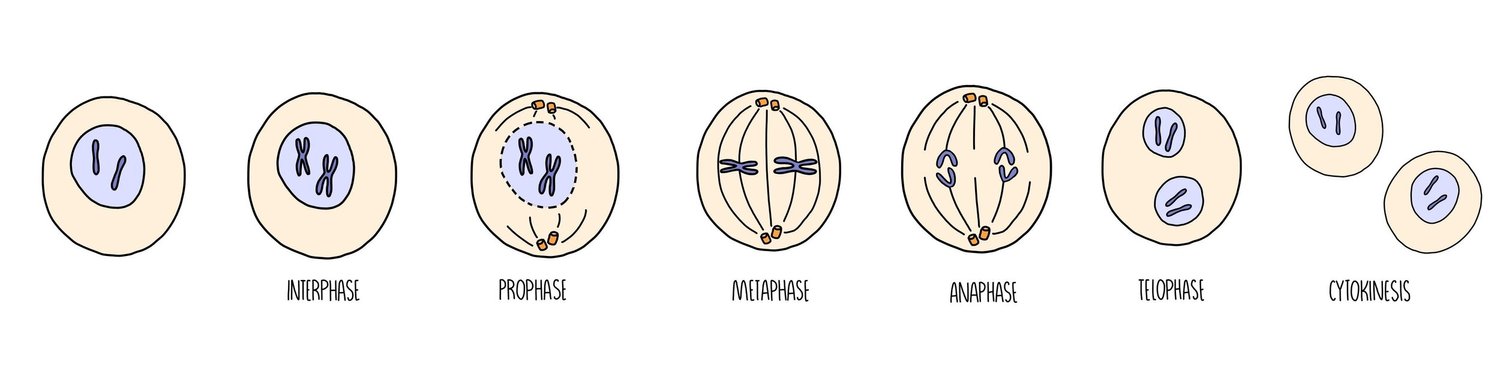
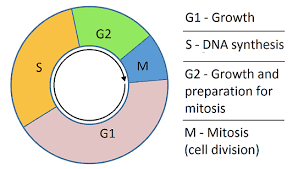
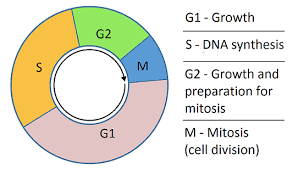
State what the cell cycle is and outline its stages.
Regulated cycle of division with intermediate growth periods.
Interphase
Mitosis or meiosis (nuclear division)
Cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division)
What happens during interphase?
G1 , S and G2 phase
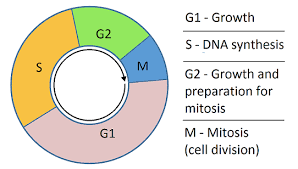
What happens during G1 phase?
Organelles replicate
The cell increases in size.
Protein synthesis
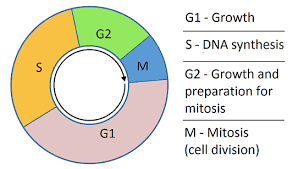
What happens during S phase?
DNA replicates- ready for mitosis
What happens during G2 phase?
Cell keeps growing
Proteins needed for cell division are made
* growth
* cell replacement/ tissue repair
* asexual reproduction
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
Outline what happens during prophase in mitosis
Chromosomes condense, becoming visible.
The chromosomes consist of two identical chromatids called sister chromatids which are joined together at the centromere
Centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell & mitotic spindle fibres form.
The nuclear envelope & nucleolus break down = chromosomes free in cytoplasm.
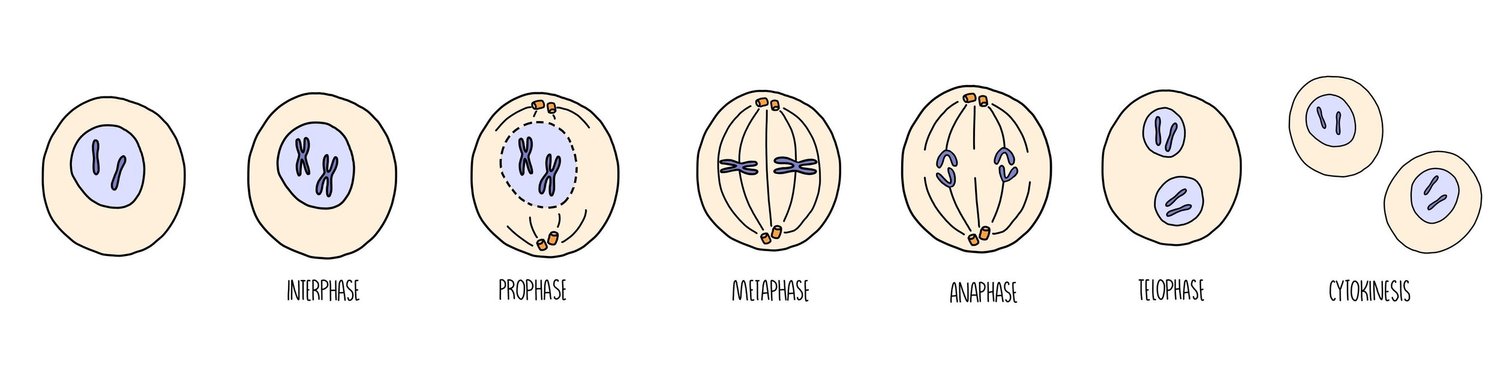
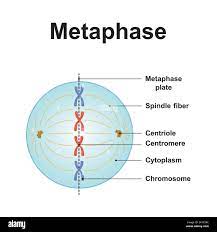
Outline what happens during metaphase in mitosis
Mitotic spindle fibres attach at the centromeres of each chromosome.
The spindle fibres pull the chromosomes, making them line up at the metaphase plate
Outline what happens during anaphase in mitosis
The sister chromatids separate at the centromere (the centromere divides in two)
Spindle fibre begin to shorten
The separated sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle fibres
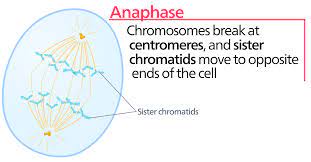
Outline what happens during telophase in mitosis
The chromatids decondense - can be called chromosomes again.
Mitotic spindle breaks down
Nuclear envelopes begin to reform around each set of chromosomes
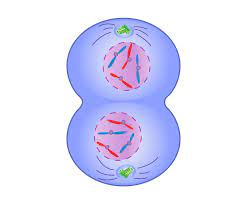
1. .Contractile division of cytoplasm.
\
2. Cell membrane cleavage furrow forms.
\
3. forms 2 daughter cells which are genetically identical to the original cell and each other
What happens during cytokinesis in plants?
Cellulose starts to build up at the equator (the end plate).
Plasma membrane forms in the middle of the end plate resulting in two fully separated plant cells
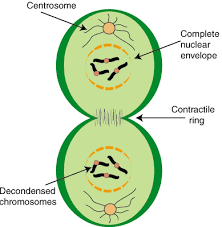
How is the cell cycle regulated?
Checkpoints regulated by cell-signalling proteins
These ensure damaged cells do not progress to next stage of cycle.
Describe what happens during the G1 phase checkpoint
The cell checks that the chemicals needed for replication are present
Chromosomes are checked for damage.
If damage is detected then the cell does not advance into the S phase until repairs have been made
Describe what happens during the S phase checkpoint
Chromosomes are checked to ensure they have been replicated.
If all the chromosomes haven't been successfully replicated then the cell cycle stops
Describe what happens during the G2 phase checkpoint
An additional check for DNA damage occurs after the DNA has been replicated.
The cell cycle will be delayed until any necessary repairs are made
Describe what happens during the M phase checkpoint
The final check- occurs during metaphase
It determines whether the chromosomes are correctly attached to the spindle fibres
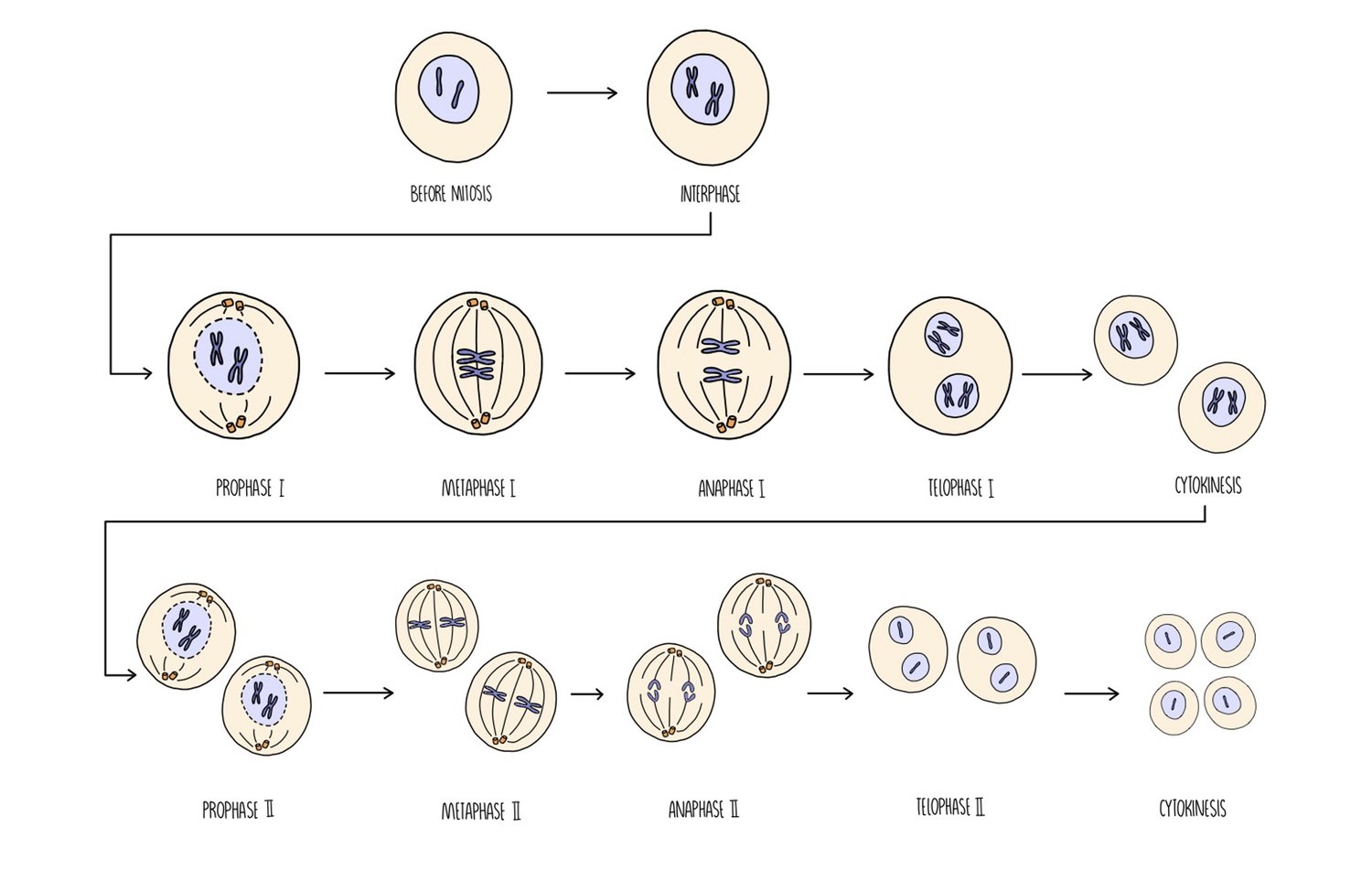
What is meiosis?
A form of cell division where the nucleus divides twice
Produces 4 genetically different haploid cells known as gametes from 1 diploid cell
Describe what happens during meiosis Ⅰ
Its the first division, the reduction division.
The pairs of homologous chromosomes are separated into 2 cells.
Each cell only contain one full set of genes instead of 2 = haploid
Crossing over occurs
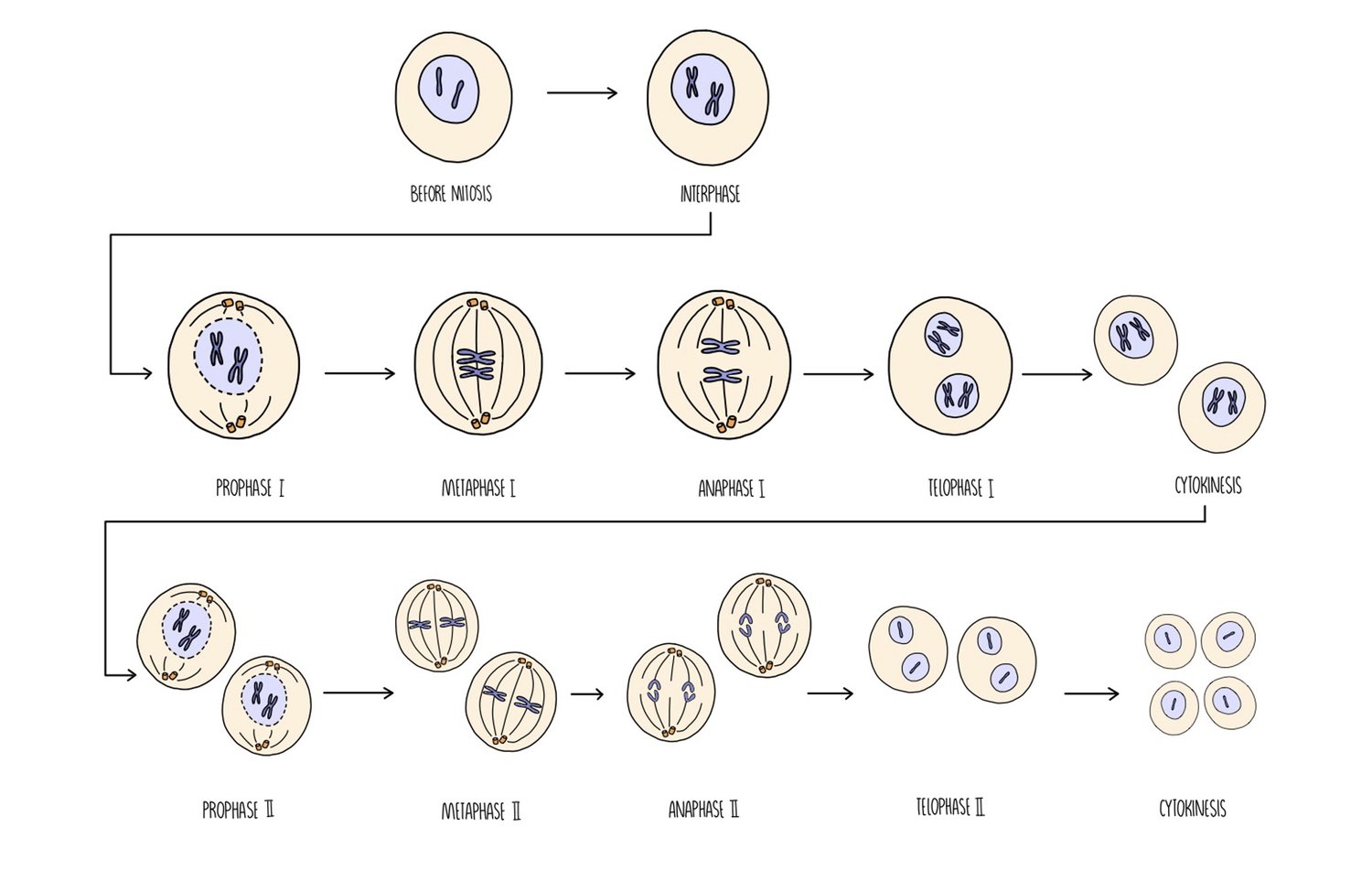
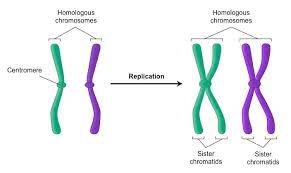
What are homologous chromosomes?
Pair of chromosomes with genes at the same locus.
1 maternal & 1 paternal.
Some alleles may be the same while others are different
What happens during meiosis Ⅱ?
Independent segregation of sister chromatids.
Each cell divides again, producing 4 haploid cells.
\
* Independent assortment (random segregation) of homologous chromosomes & sister chromatids.
\
Result in new combinations of alleles.
\
* Cells produce proteins that determine their structure & function.
What is a stem cell?
Undifferentiated cells that can divide indefinitely and turn into other specific cell types.
Its a renewing source of undifferentiated cells
\
* Pluripotent: can develop into any cell type excluding the placenta and embryo.
\
* Multipotent: can only develop into a few different types of cell.
\
* Unipotent: can only develop into once type of cell.
\
* Drug testing on artificially grown tissues.
\
* Treating neurological diseases e.g. Alzheimer's & Parkinson's.
\
* Researching developmental biology e.g. formation of organs, embryos.
\
* many lysosomes in their cytoplasm- contains digestive enzymes to break down engulfed particles
\
* multilobed nucleus allowing them to move and engulf material more easily
\
* no nucleus- more room for hemoglobin
\
* lots of haemoglobin in cytoplasm to carry oxygen.
\
* Erythrocytes- have a short lifespan & cannot undergo mitosis since they have no nucleus.
\
* Leucocytes, including neutrophils.
tissues that perform specific function →
organs made of several tissue types →
organ systems
\
* Goblet cells secrete mucus- helps to trap dust, dirt and microorganisms - preventing them from entering vital organs where they may cause infection
\
* The layer of cells forms a thin cross-section- shortens the diffusion pathway
\
* It is permeable- allowing for the easy diffusion of gases
\
* Lots of mitochondria to provide energy to swim
\
* The acrosome contains digestive enzymes to enable the sperm to penetrate the surface of the egg
\
* haploid nucleus
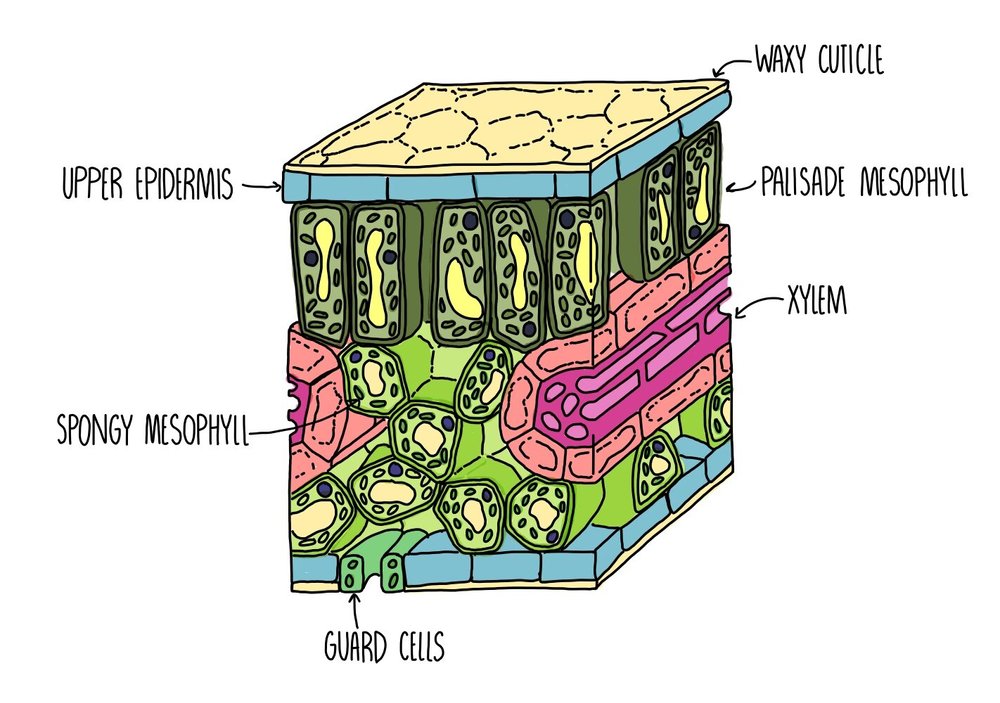
Describe the structure and function of palisade cells
Large number of chloroplasts are present in the cytoplasm - maximise the absorption of light for photosynthesis
The tall and thin shape - allows light to penetrate deeper and for many cells to be densely packed together
Thin walls so CO2 can diffuse easily into the cell
\
* Hair-like projections increase surface area for osmosis / carrier proteins for active transport.
\
* Many mitochondria produce ATP for active transport.
\
* Thin permeable cell wall-shorter diffusion distance for entry of water and ions
\
* Inner cell walls are thicker while the outer cell walls are thinner- The difference in the thickness of the cell walls allows the cell to bend when turgid
\
* The cytoplasm has a high density of chloroplasts and mitochondria.
What are meristems?
Totipotent undifferentiated plant cells
Can develop into various types of plant cell, including xylem vessels & phloem sieve tubes.
Describe the structure of a vascular bundle.
Cambium (meristematic tissue)
Phloem tissue
Xylem tissue
\
* No top and bottom walls between cells- forms continuous hollow tubes- water is drawn upwards towards the leaves by transpiration
\
* Cells are essentially dead, without organelles or cytoplasm, to allow free movement of water
\
* Outer walls are thickened with a substance called lignin- strengthens the tubes- helps support the plant
form a tube to transport sucrose in the dissolved form of sap.
\
* Companion cells:
involved in ATP production for active loading of sucrose into sieve tubes.
\
About cartilage
Type of connective tissue found in joints
Shapes and supports the ears, nose and windpipe
Formed when chondroblasts secrete an extracellular matrix which they become trapped inside
What is erythropoiesis?
Its when new erythrocytes are constantly being formed from bone marrow stem cells
maintains the red blood cell count in the blood
What changes occur to adapt the original stem cell to become an erythrocyte
The cell changes into a biconcave shape: this shape has a larger surface area- more oxygen can be absorbed through the cell surface
Building up of haemoglobin in the cytoplasm: haemoglobin is the pigment that binds with oxygen
The ejection of the nucleus: creates more room in the cytoplasm for haemoglobin, increasing the oxygen-carrying capacity
An elastic membrane: this allows erythrocytes to change shape and therefore squeeze through narrow capillaries
\
* Granules accumulate (these are lysosomes that contain hydrolytic enzymes)
What cells differentiate to form xylem and phloem?
Cambium- is a meristem which undifferentiated tissue in a plant that has the ability to give rise to new cells
\
* deposit lignin in their cell walls
\
* lose their end cell walls
\
* develop sieve plates (located at ends of the cells)
\
Smooth: walls of blood vessels and intestines.
\
Skeletal: attached to incompressible skeleton by tendons.
When does cytokinesis usually begin?
Begins in anaphase
Ends in telophase
Its a separate process to mitosis
What happens during prophase 1 ?
DNA condenses and becomes visible as chromosomes
Chromosomes arrange themselves into homologous pairs (bivalents)
Crossing over of non sister chromatids occurs at chiasmata.
Centrioles start moving to opposite ends of the cell forming spindle fibres
Nuclear envelope breaks down and nucleolus disappears
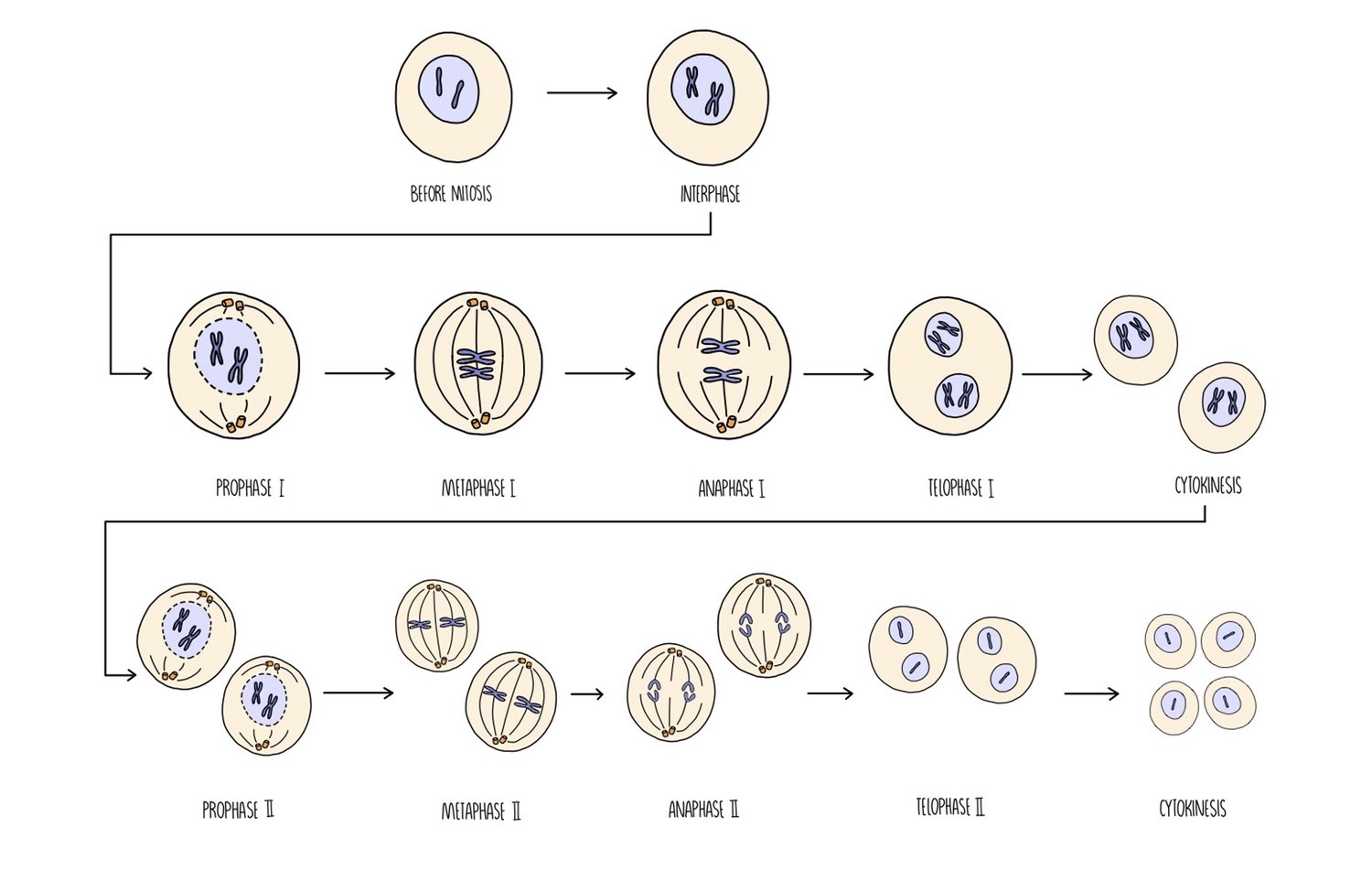
What happens during Metaphase 1?
The homologous pairs of chromosomes line up across the centre of the cell
Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibres by their centromeres
The maternal and paternal chromosomes in each pair position themselves independently of the others
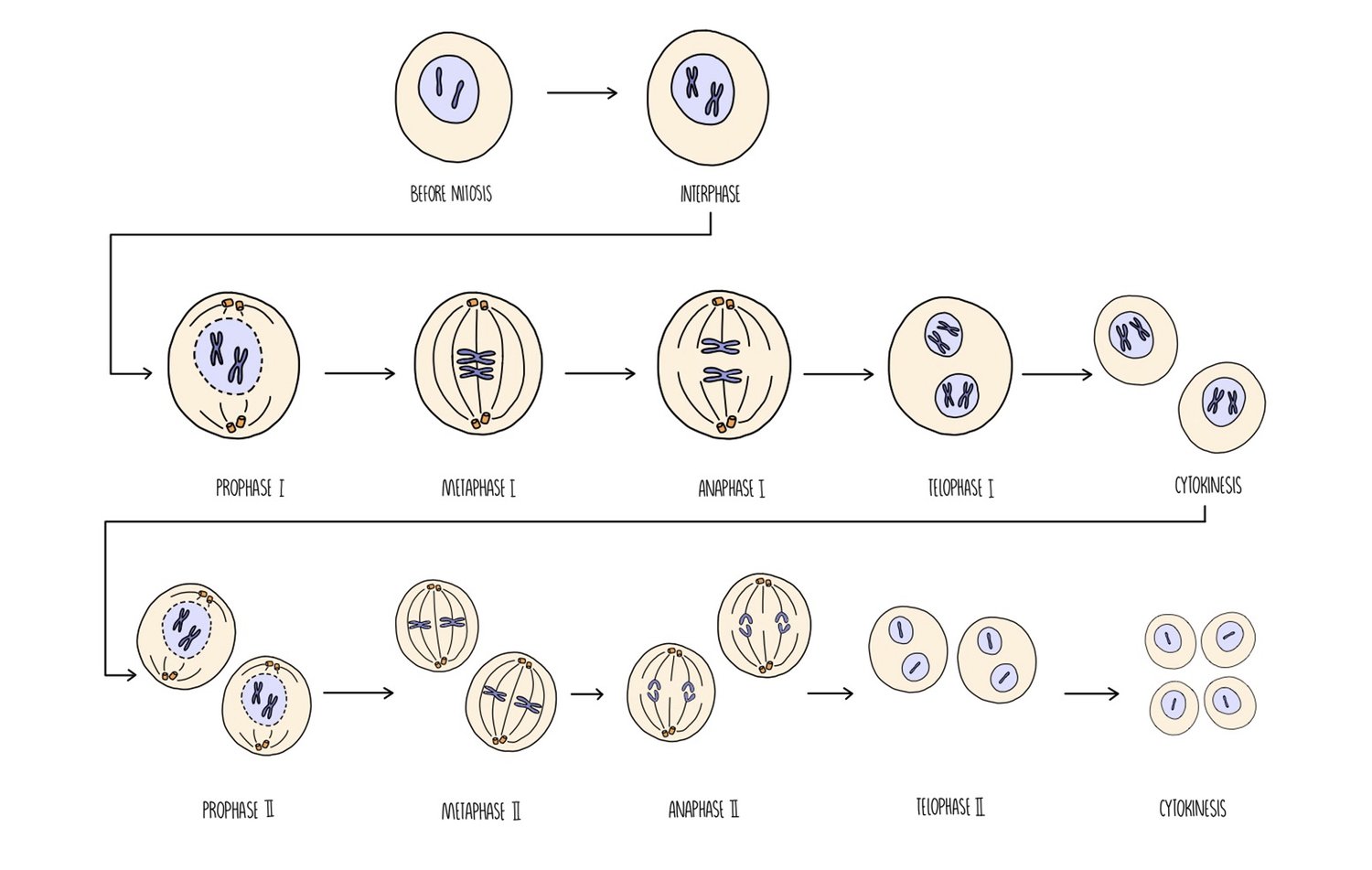
What happens during Anaphase 1 ?
Spindle fibres contract separating the homologous pairs
Centromeres do not divide- sister chromatids of each chromosome remain attached to one another and don't come apart
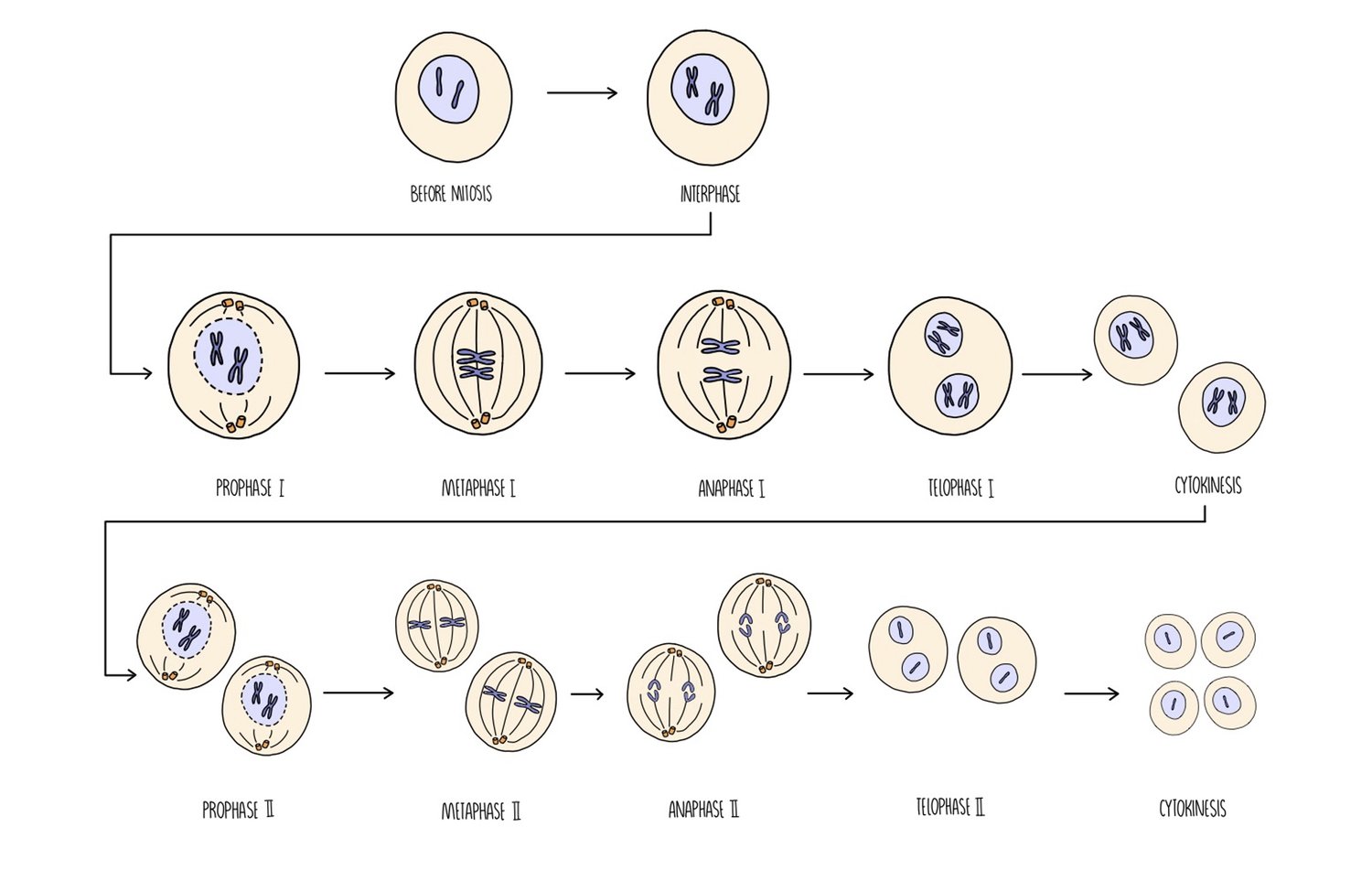
What happens during Telophase 1 during ?
Chromosomes assemble at each pole
Nuclear envelope re forms around the two groups of chromosomes
Chromosomes decondense.
Animal cell undergoes cytokinesis
Cleavage furrow forms
The cytoplasm divides
2 haploid daughter cells are produced
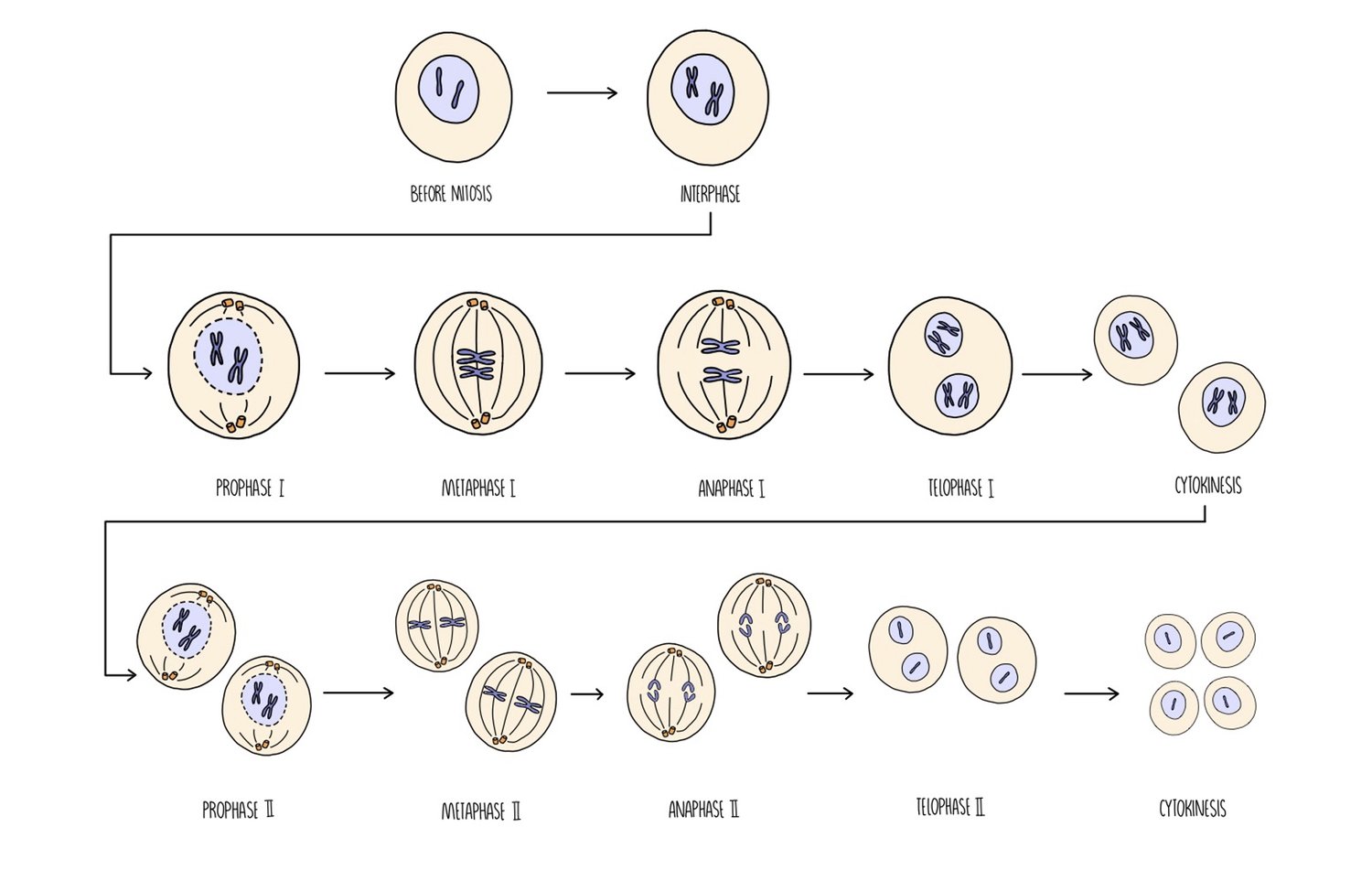
What happen during Prophase 2?
The chromosomes condense and coils and become visible again.
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrioles move to opposite poles - spindles formation begins.
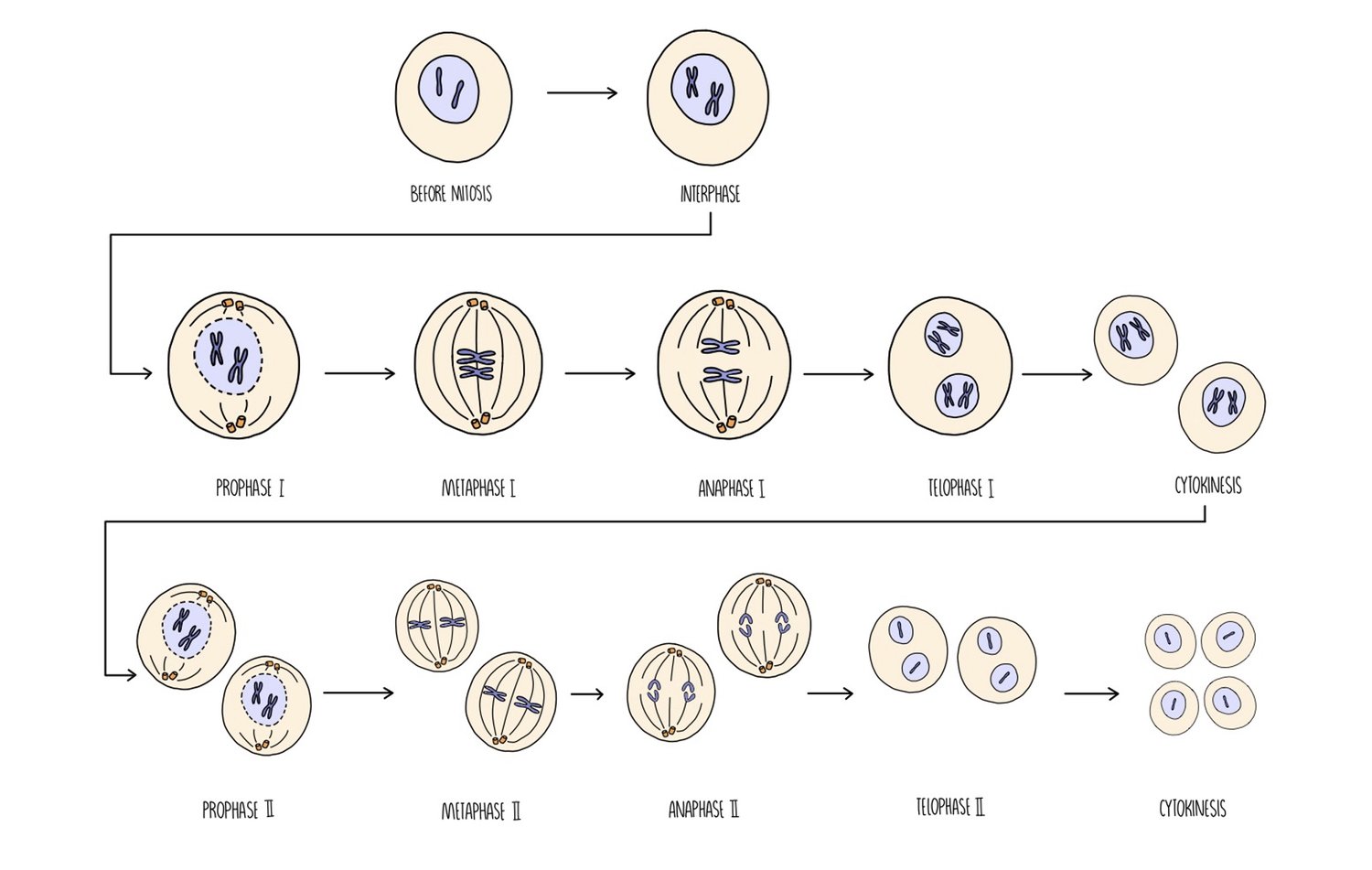
What happens during Metaphase 2?
Individual chromosomes assemble on the centre (metaphase plate)
Attached to spindle fibre by the centromere
Due to crossing over, the chromatids are not identical
Independent assortment and more genetic variation is produced.
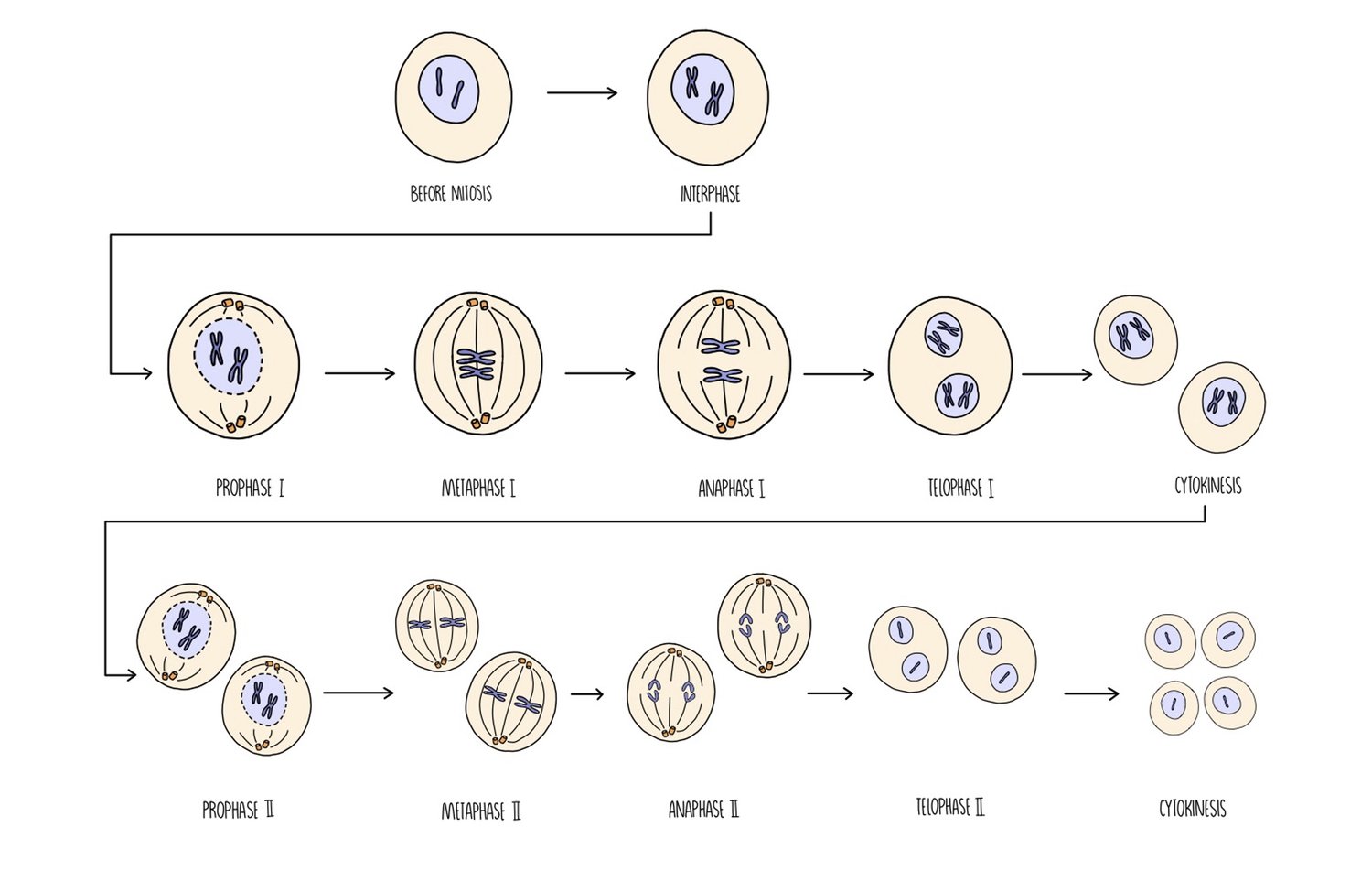
What happens in anaphase 2?
Centromeres divide
Sister chromatids of the individual chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles
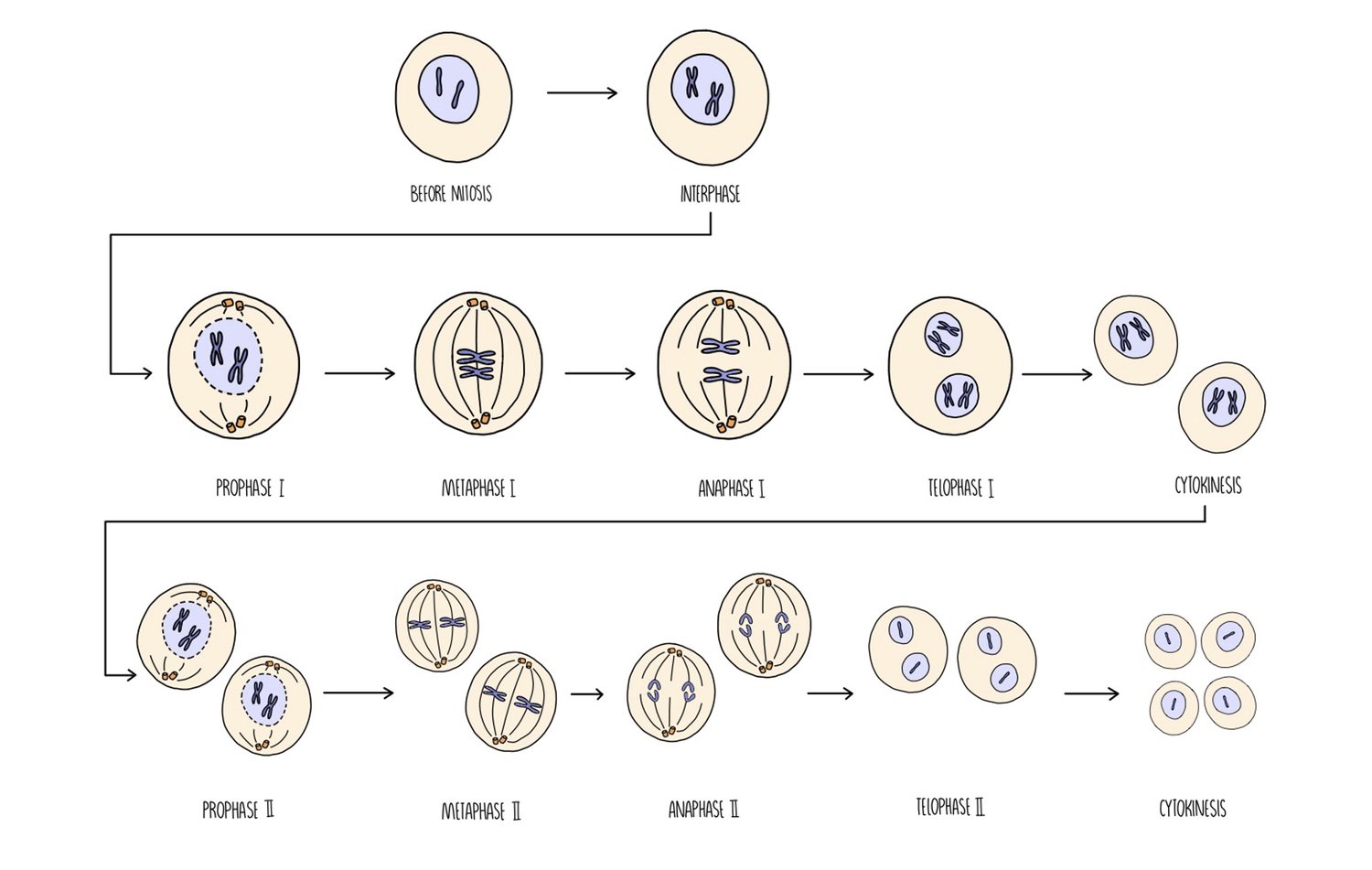
Telophase 2
The chromatids decondense- become chromosomes again
Nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes and the nucleolus becomes visible.
Cytokinesis results in the division of cells forming 4 daughter cells.
Cells are haploid because of the reduction division.
Cells will be genetically different from each other and the parent cell
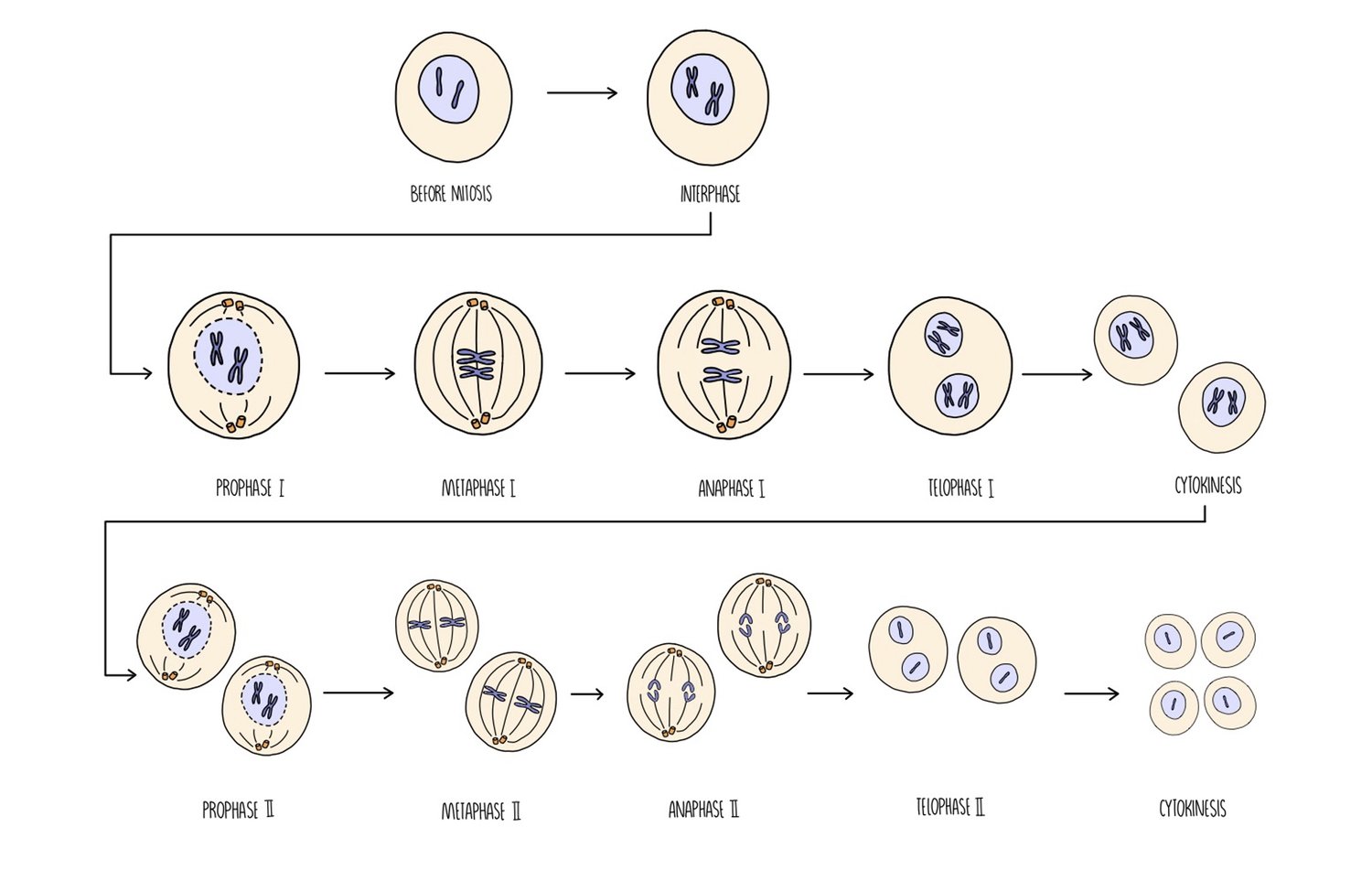
What is the significance of meiosis in life cycles?
Produces haploid cells
Produces genetic variation by independent assortment and crossing over.
\
* When turgid, stoma opens;
\
* when flaccid, stoma closes.
\
* Walls are thickened by spirals of cellulose.
* companion (cell)
When does the formation of the spindle apparatus occur?
Prophase I
When do the chromosomes get pulled to opposite poles?
Anaphase I
Explain why meiosis needs to have twice as many stages as mitosis.
To halve chromosome number
To separate homologous pairs (of chromosomes) and sister chromatids
\
* so both (daughter) cells receive a full copy
Explain what is meant by a homologous pair of chromosomes
One maternal and one paternal
Carry same genes
Pair up in meiosis
Similar length
State what is meant by the term tissue.
A group of specialised cells working together to perform a particular function
* short (diffusion) pathway
* secrete mucus
\
* just behind tip of shoot
\
* vascular bundle
\
* bud
\
* It will carry out the function indefinitely and not enter the cell cycle
Why might a cell leave a cycle (temporarily or permanently)
Differentiation
Damaged DNA = cell arrest
Get older = more cells
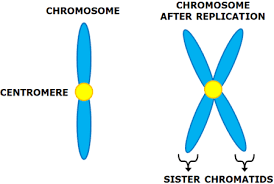
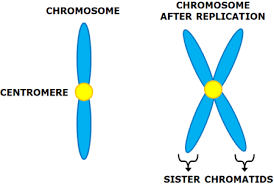
\
* During prophase 1 of meiosis = genetic variation
Independent assortment
The production of different combinations of alleles in daughter cells
Its caused due to the random alignment of homologous pairs along the equator
Each chromosome is inherited randomly and independent of other chromosomes
Results in genetic variation
What is a Zygote?
The initial diploid cell formed when 2 gametes are joined by the means of sexual reproduction