BIOL 117 WEEK 1 VOCABULARY + CONCEPTS
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Content: 1.1-1.2, 1.9, 2.1-2.4, 3.8-3.13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
physiology
the study of how living organisms function; ranges from the study of individual molecules to the complex processes that depend on the integrated funcitons of many organs in the body
pathophysiology
study of disease states (physiological dysfunction)
cells
the simplest structural units into which a complex multicellular organism can be divided and still retain the functions characteristic of life
cell differentiation
formation of four general types of specialized cells: muscle cells, neurons, epithelial cells, and connective-tissue cells
muscle cells
generate the mechanical activities that produce force and movement; 3 types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
neurons
initiate and conduct electrical signals
epithelial cells
form barriers/selectively secrete and absorb ions and organic molecules; basolateral surface rests on a basement membrane
connective-tissue cells
connect, anchor, and support the structures of the body; form the extracellular matrix (consists of fibers like collagen, elastin)
tissues
aggregates of differential cells with similar properties; correspond to the four general types of specialized cells (muscle, nervous, epithelial/epithelium, connective)
organs
composed of two or more of the four kinds of tissues (many contain multiple, small, similar functional units
organ system
group of organs that perform an overall function
skeletal muscle (cells + tissue)
attached through other structures to bones, produce movements of the limbs/trunk, also attached to skin; voluntary contraction
cardiac muscle (cells + tissue)
found only in the heart, generate force that causes the heart to contract/pump blood into ciruclation; involuntary muscle
smooth muscle (cells + tissue)
make up part of the walls of many of the tubes in the body, contraction decreases the diameter/shortens the length of these tubes; involuntary muscle
neurons
provide the major means of controlling the activities of other cells
nervous tissue
a collection of neurons (e.g. brain or spinal cord)
nerve
neuron extension which carries the signals from many neurons between the nervous system/other parts of the body
epithelial cells
characterized/named according to their unique shapes
cuboidal (cube-shaped)
columnar (elongated)
squamous (flattened)
ciliated
epithelia
located at surfaces that cover the body or individual organs; line inner surfaces of tubular and hollow structures
simple epithelium
single-cell-thick tissue
stratified epithelium
thicker tissue, numerous layers of cells
basement membrane
anchors the tissue, extracellular protein layer where epithelial cells rest on
basolateral side
the side anchored to the basement membrane
apical side
opposite side, faces the interior of a structure
tight junctions
cells are held together along their lateral surfaces by these extracellular barriers (selective) which regulate the exchange of molecules
loose connective tissue
connective tissue cells and fibers underlying most epithelial layers
dense connective tissue
tough, rigid tissue that makes up tendons/ligaments (other examples include bone, cartilage, and adipose)
extracellular matrix (ECM)
a mixture of proteins: polysaccharides (chains of sugar molecules) and sometimes minerals; provides sacffold for cellular attachments and transmits info in the form of chemical messengers to cells to regulate
what does the ECM regulate?
activity, migration, growth, and differentiation
fibers
some proteins of ECM; insoluble proteins including rope-like collagen fibers and rubberband-like elastin fibers; others are a mix of non fibrous proteins that contain carbohydrate
collagen
1/3 of all bodily proteins
organs (arragnement)
arranged in various proportions and patterns (sheets, tubes, layers, bundles, and strips); do not function in a vacuum they function together
functional units
small, similar subunits many organs are comprised of, perform function of the organ
circulatory system
major organs or tissues: heart, blood vessels, blood
primary functions: transport of blood throughout the body
digestive system
major organs or tissues: mouth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, anus, pancreas, liver, gallbladder
primary functions: digestion and absorption of nutrients and water; elimination of wastes
endocrine system
major organs or tissues: all glands/organs secreting hormones: pancreas, testes, ovaries, hypothalamus, kidneys, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, stomach, small intestine, liver, adipose tissue, heart, and pineal gland; and endocrine cells in other organs
primary functions: regulation and coordination of many activities in the body, including growth, metabolism, reproduction, blood pressure, water and electrolyte balance, and others
immune system
major organs or tissues: white blood cells and their organs of production
primary functions: defense against pathogens
integumentary system
major organs or tissues: skin
primary functions: protection against injury and dehydration; defense against pathogens; regulation of body temperature
lymphatic system
major organs or tissues: lymph vessels, lymph nodes
primary functions: collection of extracellular fluid for return to blood; participation in immune defenses; absorption of fats from digestive system
musculoskeletal system
major organs or tissues: cartilage, bone, ligaments, tendons, joints, skeletal muscles
primary functions: support, protection, and movement of the body; production of blood cells
nervous system
major organs or tissues: brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves and ganglia, sense organs
primary functions: regulation and coordination of many activities in the body, including most of those regulated by the endocrine system; detection of and response to changes in the internal and external environments; states of consciousness; learning; memory; emotion; others
reproductive system
major organs or tissues: males → testes, penis, and associated ducts and glands
females → ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands
primary functions: males → production of sperm; transfer of sperm to female
female → production of eggs; provision of a nutritive environment for the developing embryo and fetus; nutrition of the infant
respiratory system
major organs or tissues: nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
primary functions: exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen; regulation of hydrogen ion concentration in the body fluids
urinary system
major organs or tissues: kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
primary functions: regulation of plasma composition through controlled excretion of ions, water, and organic wastes
general principles of physiology
homeostasis is essential for health and survival
the functions of organ systems are coordinated with each other
most physiological functions are controlled by multiple regulatory systems, often working in opposition
information flow between cells, tissues, and organs is an essential feature of homeostasis/allows for integration of physiological processes
controlled exchange of materials occurs between compartments and across cellular membranes
physiological processes are dictated by the laws of chemistry and physics
physiological processes require the transfer and balamce of matter and energy
structure is a determinant of/has coevolved with function
atoms
units of matter that form all chemical substances
chemical element
each type of atom
components of atoms
protons
neutrons
electrons
atomic number
each chemical element contains a unique and specific number of protons; distinguishes one atom from another
atomic mass
indicates an atom’s mass relative to the mass of other atoms, unit is a dalton (d)
isotopes
have identical numbers of protons, differ in the number of neutrons they contain
radioisotopes
unstable isotopes, spontaneously emit energy/release components of the atom itself aka radiation
PET (positron emission tomography) scans
special imaging technique, used to detect how much of the radioactive glucose appears in different organs
gram atomic mass
amount of the element (in g) equal to the numerical value of its atomic mass
ion
certain atoms may gain/lose one or more electrons, acquire a net electrical charge
cations
net positive charge
anions
net negative charge
electrolytes
ionic forms of mineral elements
4 of the body’s essential elements
C - carbon
H - hydrogen
O - oxygen
N - nitrogen
molecules
formed by linking atoms together by chemical bonds
covalent bond
formed between two atoms that share a pair of electrons
polar covalent bond: one atom attracts the bonding e- more than the other atom of the pair
nonpolar covalent bond: formed between two atoms of similar electronegativities
ionic bond
strong bond between cations and anions; readily breaks in water
hydrogen bond
weak electrical attraction between H and O or N in different molecules/between different regions of one molecule (molecular shapes can be altered by the rotation of their atoms aorund covalent bonds
ionic molecules
molecules containing atoms that have ionized; common ionized groups include carboxyl groups (-COOH) / amino groups (-NH2)
electronegativity
measure of an atom’s ability to attact e- in a covalent bond
strong acids
hydrochloric acid and other acids that are completely ionized in solution
weak acids
do not completely ionize in solution
classes of organic molecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
carbohydrates
polar macromolecules consisting of monosaccharides (e.g. glucose), disaccharides (e.g. sucrose), and polysaccharides (e.g. glycogen, a polymer of glucose)
lipids
nonpolar molecules including triglycerides, phospholipids, fatty acids, and steroids
proteins
comprised of 20 different amino acids bound together by peptide bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another
primary structure → amino acid sequence
secondary structure → beta-pleated sheets and alpha helices
tertiary structure → three-dimensional conformation (the final shape of a protein)
quaternary structure → multiple polypeptide chains bound together
nucleic acids
polymers of nucleotides (include DNA and RNA), responsible for the storage, expression, and transmission of genetic information
major categories and functions of proteins
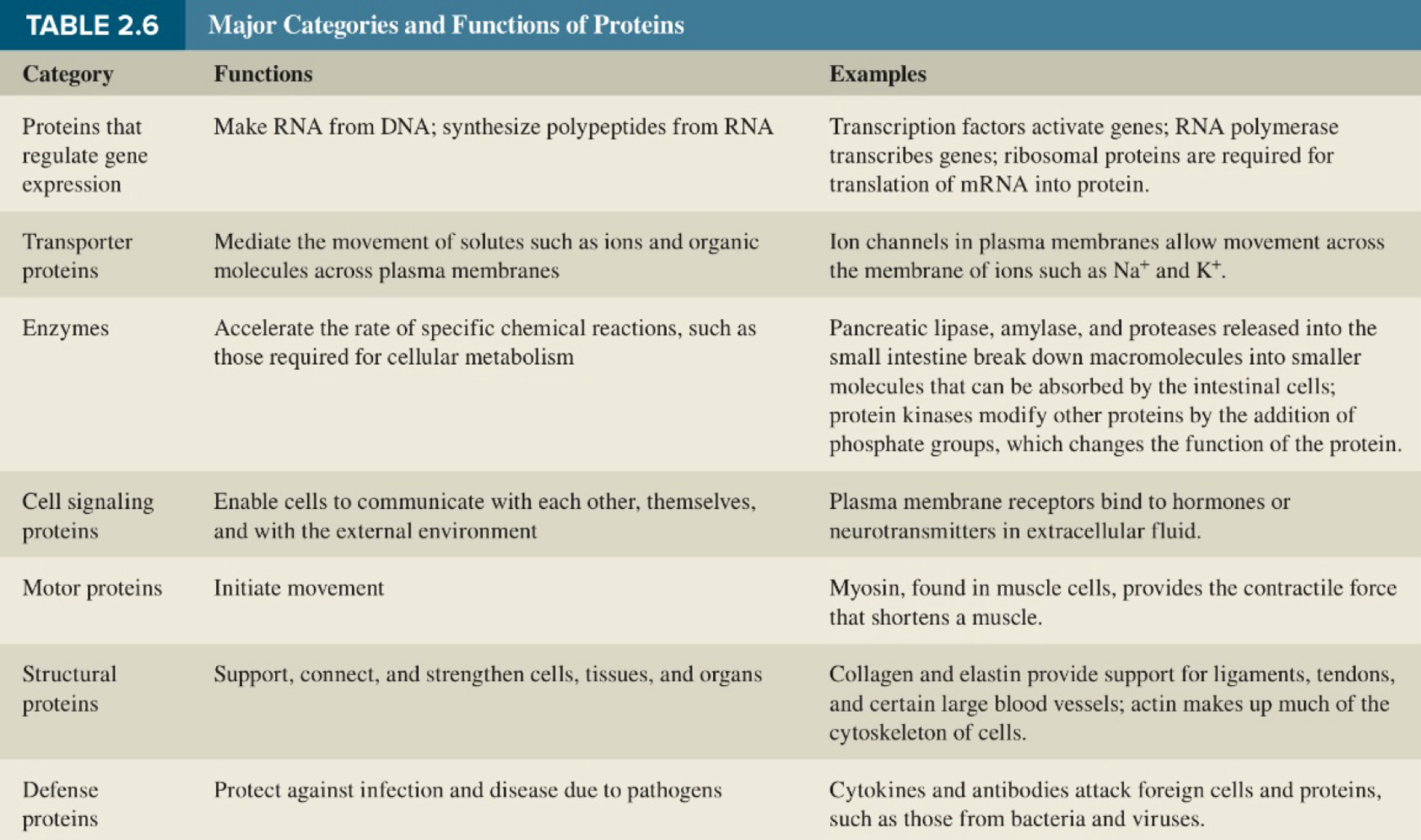
ligand
any molecule (including a protein) that binds to proteins
binding states
regions in a protein with shapes typically complementary to the ligand; site of ligand bonding
chemical specificity
the likelihood of a particular protein binding only one ligand at its ligand-binding site
affinity
the strength of ligand-protein binding
saturation
fraction of total binding sites of a protein that are occupied by ligands
competition
occurs when more than one ligand is able to bind to the same binding site of a particular protein (typically with different affinities)
allosteric proteins
possess both a functional site and a regulatory site
protein kinase
enzymes that catalyze the addition of a phosphate group to side chains of certain amino acids in a protein (covalent modulation)
metabolism
synthesis (anabolism) and breakdown (catabolism) of organic molecules req. for cell function
activation energy
required to initiate the breaking of chemical bonds in a reaction; is usually acquired through collisions between molecules
catalysts
increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy
temperature
higher temp means increased reaction rate
reversible reaction
reaction that can proceed in either direction
enzymes
proteins that catalyze nearly all chemical reactions in the body; they act on substrates (reactants) to generate products and aren’t consumed by the reaction
cofactors
molecules or elements required in small concentrations by some enzymes for full activity
rates of enzyme-mediated reactions can be increased by
increase in: temperature, substrate conc. enzyme conc and enzyme activity
enzyme activity
altered by allosteric or covalent activation/inhibition; a given enzyme may have several regulatory sites
metabolic pathway
sequence of enzyme-mediated reactions leading to formation of a particular product
rate-limiting reaction
enzyme-catalyzed step that determines rate of product formation in a metabolic pathway
end-product inhibition
occurs when the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as a modulator molecule, inhibiting the rate-limiting enzyme’s ability