Darwin and modern synthsis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Transmutation
pre-Darwin
Ideas for the altering of one species into another
Promotes by Lamarck and Darwins grandpa
Darwin aboard the Beagle
1831→ Beagle set sail from Plymouth
Visited Galápagos Islands
Collected finch species on different islands
found that different species had adapted to different habitats
Darwins insights from finches
confirmed they were different species, not variations of mainland birds
But, the islands were recently volcanic
1845→ seeing the diversity of structure in one small, intimately related group, concluded that they evolved from a common ancestor and isolating different islands gave way to different species
Malthus populations
→ huge growth potential, but resources are limited = a struggle for existence
1798→ “a population unchecked increases exponentially, whereas food supply grows only arithmetically”
Other ideas that lead to the theory of origin of species
pigeon fanciers used artificial selection to make many kinds of pigeon
Wallace- had a idea called ‘evolution by natural selection’
Wallace/Darwins paper = 1858/59
Natural selection
→ organisms with advantageous traits survive and reproduce, passing traits onto offspring, so evolution occurs over time
‘survival of the fittest’
Fitness = differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype e.g. bigger tails
Darwins 4 postulates of natural selection
Individuals within species are variable
Some variables are passed onto offspring
In most generations, more offspring are produced than can survive
Survival and reproduction are not random, individuals with the highest reproductive success have the most favourable variations
produces ‘descent with modification’
Moth example of natural selection
1811→ 100% ‘typica’ peppered moths
1895→ 98% ‘melanic’
due to tree bark becoming darker, so moths with darker wings survived and reproduced = phenotypic change
Blending inheritance
Darwin believed in ‘blended inheritance’
cells that derived from all other parts of parents bodied (soma cells) could not transmit from parents to offspring
Mendel published his pea studies in 1865, discovered in 1900
It was found (in animals only) to be true, the only hereditary substance was in germ cells
Modern synthesis
Neo-Darwinism evolution:
→an understanding of mechanisms of inheritance combined with Darwin’s concept of Natural Selection
•Evolution = in “terms of changes in allele and gene frequencies over time” and the average action of selection on genotypes.
•Individuals are the units of selection that survive and reproduce, or don’t…
•The only continuity is therefore the transmission of alleles
Altruism
Altruistic behavior = no survival or reproductive advantage to the adult
selection operates on alleles in relation to their average contribution to their own transmission through their action on the individual
Same alleles are present in close relatives
‘Lay down my life fro 2 brothers or 8 cousins’
4 postulates updated

HW equation applications
→ expected relationship between allele frequencies and genotype frequencies
Applications:
if we know allele frequencies, HW equilibrium can be used to calculate the expected phenotype frequencies
If we know phenotypic frequencies, HW can be used to calculate expected allele frequencies/genotypes
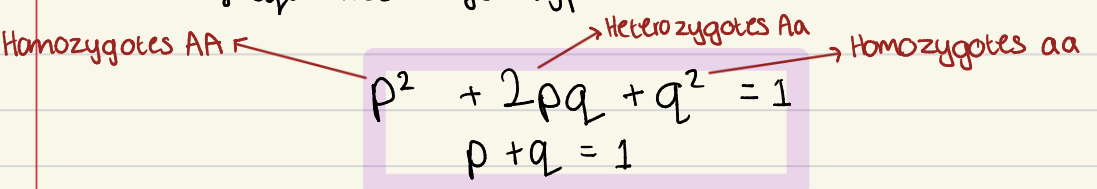
Genetic drift in large/small populations
Small (18 people)
by chance an allele could be transmitted to a high proportion of offspring
If another allele is ‘lost’/extinguished, the allele becomes fixed
Large (100 people)
Allele frequencies change more slowly

Founder effect & bottlenecks
Founder effect→ loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a small no. Of individuals
Population bottleneck→ sharp reduction in the size of a population over several generations = loss of genetic diversity
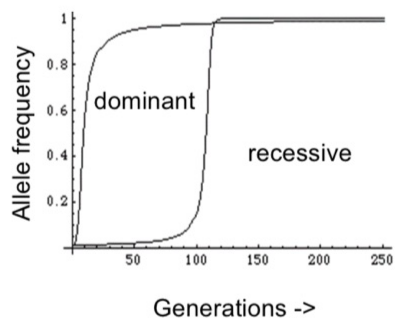
Spread of an allele with selective advantage
an allele has a selective advantage when it makes the organims more likely to survive/reproduce
There must always exist another allele at the same locus which gives a selective disadvantage
Evolution in prokaryotes
many pathogenic bacteria have evolved resistance to the main classes of antibiotics
Multi-drug resistant bacteria have abused untreatable infections
Conjunction→ plasmids can pass between different species by horizontal gene transfer through a sex pilus (attachment)
Transformation→ bacteria can take up free DNA and integrate it
Transduction→ transfer DNA through phases