NEU101 ASU Final Quizlet
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
These fluid filled chambers in the brain were suggestive to ancient peoples that the brain functioned primarily as some kind of fluid pump.
Ventricles
The ____________is the main, front part of the brain while the ___________ is the smaller part of the brain in the back.
cerebrum, cerebellum
Grey matter is made primarily of the __________ of neutrons while the white matter is made primarily from the _________ of neurons.
cell bodies, axons
which of the following terms refer to collections of axons ( or white matter ) ?
Tract, bundle, commissure
T/F Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is an imaging technique that uses MRI.
True
T/F Computer Tomography scans (CT Scans ) do not require exposure to radiation.
False
T/F Position emission Tomography (PET) scans allow observation of patterns of current brain activity, not just anatomy.
True
Sagittal
This image depicts what kind of brain section?
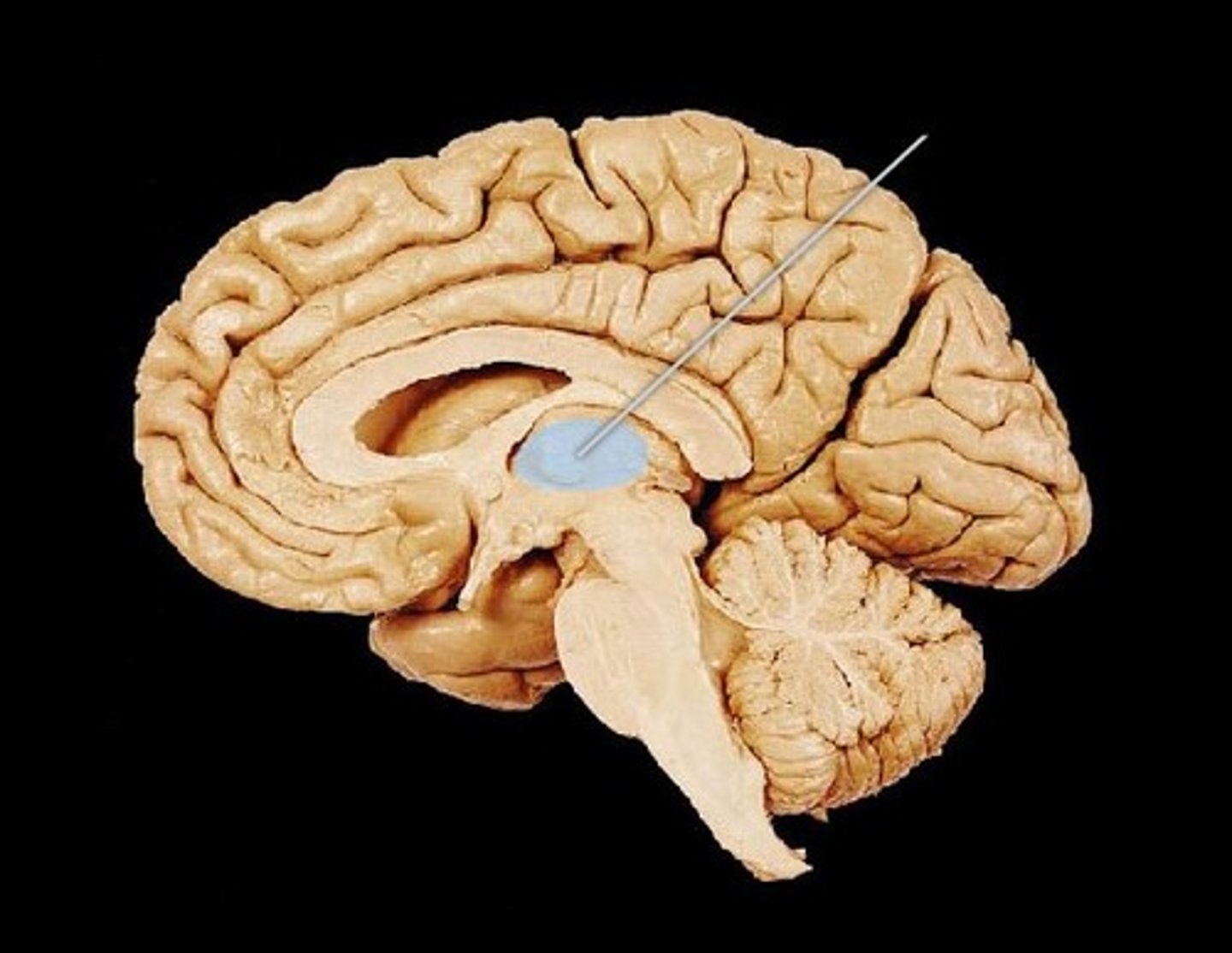
Coronal
This image depicts what kind of brain section?
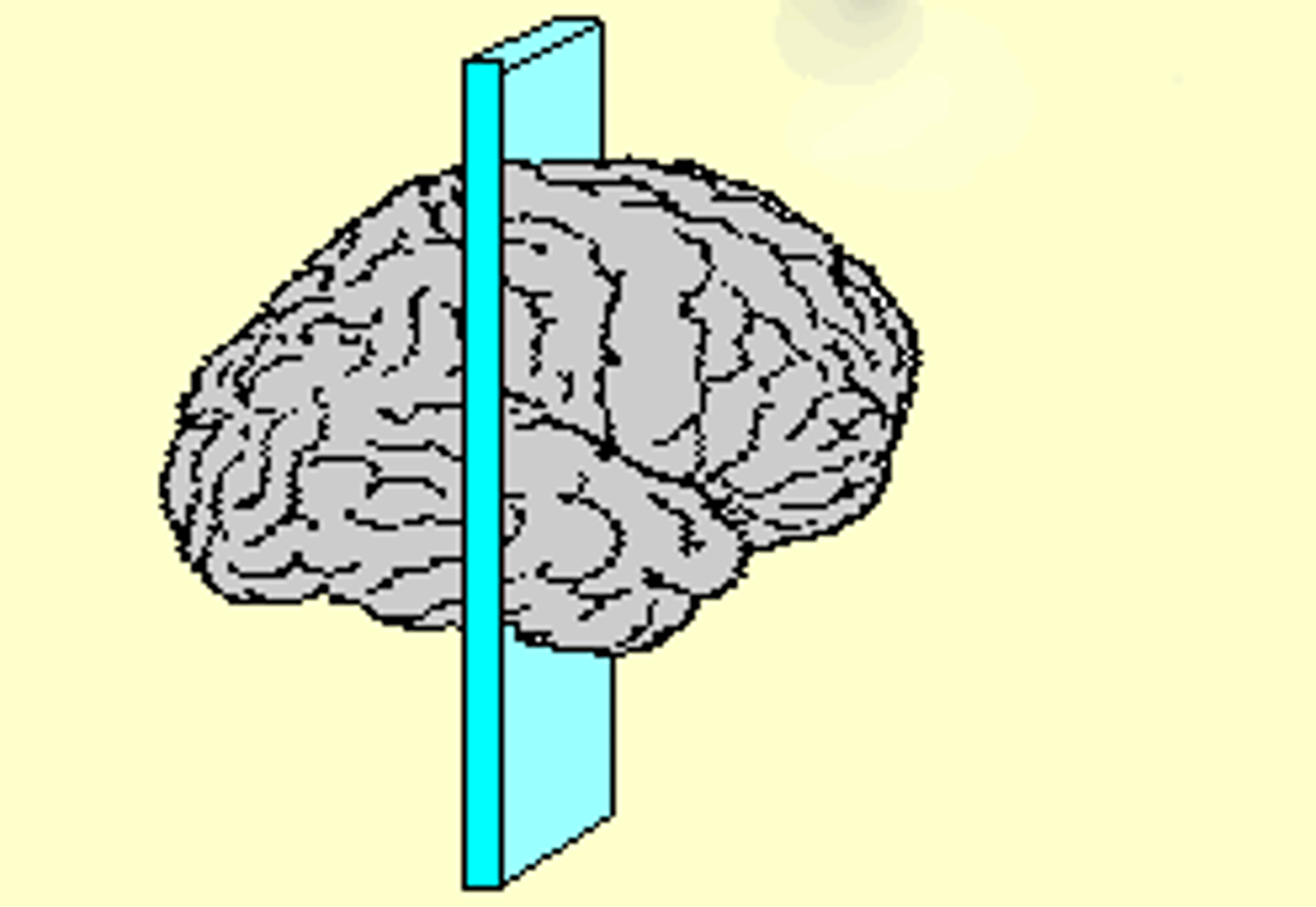
your eyes are _______ to your ears, but _______ to your nose
medial, lateral
Your right eye and right ear are:
ipsilateral
which of the following layers of the meninges is closest to your skull? (farthest from the brain itself)
anterior/rostral
which of the following atomical structures are part of the central nervous system (CNS)
brain, spinal cord
Latin for "little brain"
cerebellum
the biggest part of the brain
cerebrum
controls vital functions like breathing and consciousness:
brain stem
the right half of this structure connects to the right side of the body:
cerebellum
is divided in half by the sagittal fissure
cerebral hemispheres
Spinal nerves carry _________ information from the body to the brain through the ________ of the spinal cord and carry _______ information from the brain to the body through the __________
afferent, dorsal root
efferent, ventral root
T/F the autonomic nervous system ( ANS) is the same thing as the visceral PNS ( peripheral nervous system)
false
Feeling and control of your skin and arm/leg muscles is handled by your __________ which feeling and control of the muscles in your heart and intestines is handled by your ___________.
somatic pns, visceral pns
cerbral spinal fluid (CSF) is produced by the:
ventricles
Which of these three layers of the neural plate develop to become the entire nervous system?
ectoderm
Prosensephalon
forebrain
Mesencephalon
midbrain
Rhombencelphalon
hindbrain
which part of the developing brain hold the pre-cursors to eyes?
forebrain
the hindbrain develops into which structures?
pons, medulla, cerebellum
T/F the mesencephalon develops from the mesoderm
false
T/F the olfactory bulb is proportionally larger in rats than humans.
true
T/F the neocortex is found only in humans
true
this structure consists of white matter which connects the two hemispheres.
corpus callosum
hypothalamus:
ANS
Amygdala
fear
thalamus:
sensory
Basal Ganglia
primal
Most parts of the neocortex have this many layers:
6
T/F different parts of the neocortex have distinct cytoarchitecture
true
Nissal stain changes the color of _________ while Golgi stains changes the color of ________
cell bodies, entire neurons
watery potassium-rich fluid inside cells
cytosol
membrane enclosed structures
organelles
responsible for cellular respiration
mitocondria
responsible for protein synthesis
ribosomes
responsible for sorting proteins
golgi apparatus
mitocondria convert_______to______
ADP, ATP
neurons typically only have one _________ but many ________
axon, dendrites
T/F axons can survive alone if they are cut from their cell body
false
_________have relatively short axons that don't extend beyond the general vicinity of the neuron's soma while__________ have long axons that can extend almost all the way across the brain.
Golgi type 2, Golgi type 1
Axons separate from the soma of a cell at the _____ and extend for some length before they end at the ____. Occasionally, axons branch in what is known as an ____
axon hillock, axon terminal, axon collateral
T/F there is no rough endoplasmic reticulum in axons
true
axon terminals contain mitocondria
true
what is the node of Ranvier?
region where the axonal membrane is exposed
which protein provides the "legs" for retrograde transport
dynein
what is the most important function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
site of protein synthesis
what does the mitochondria inhale?
pyruvic acid
Identify the protein that helps anterograde transport move materials from the soma to the terminal.
kinesin
this part of the cytoskeleton is relatively large, runs longitudinally down neurons, and consists of tubulins stuck together like pearls on a string.
microtubules
this part of the cytoskeleton is about the same thickness as the cell membrane and are found throughout the neuron ( but especially in neurites ) and are made of two thin strands of actin.
microfilaments
this part of the cytoskeleton consist of multiple subunits that are wound together into a rope-like structure, making them mechanically very strong.
neurofilaments
long stretches of DNA are missing or duplicated
gene copy number variations
topographical errors where a single protein is abnormal or missing
mutations
small changes in DNA are analogous to misspelling a word
single nucleotide polymorphis
T/F DNA never leaves the nucleus of a cell
true
astrocytes:
regulate chemical content
Oligodendrocytes:
wrap myelin around axons
Microglia
remove debris and dead cells
T/F the protein composition of the membrane of axons is basically the same as that of the membrane of the cell's soma
false
one gene has been deleted:
knockout
genes have been introduced and overexpressed
transgenic
a native gene is replaced with a modified version
knock-in
T/F All ribosomes are attached at rough ER.
false
_______occurs in the nucleus of a cell while _______ occurs in the rough ER
transcription, translation
proteins made of a single chain of amino acids:
polypeptides
connect amino acids into a chain
peptide bonds
a variable set of structures that contributes to the differences in amino acids:
R group
when a chain coils into a spiral configuration
alpha helix
which of the following are cations?
Na+, K+,Ca^2+
what is the advantage of the phospholipid bilayer arrangement?
isolated cytosol from extracellular fluid
what determines the differences between amino acids?
properties of R Groups
identify the term used to represent a change in the membrane potential from the normal resting value to a less negative value
depolarization
Which factor other than the ionic concentration gradient determines the equilibrium potential for an ion?
selective ionic permeability
how does the sodium-potassium pump help maintain the resting membrane potential?
pumps K+ ions in and Na+ ions out
what is the meaning of an ion's equilibrium potential?
electrical potential difference exactly balances an ionic concentration gradient
which of the following factors determines the ion selectivity of specific ion channels?
nature of the R groups lining ion channel
which type of glia cells help to regulate the amount of potassium in extracellular fluid?
astrocytes
T/F ions are approximately the same size as electrons
false
K+
potassium
Na+
sodium
Ca++
calcium
Cl-
chloride
T/F large changes in membrane potential require large changes in ionic concentration?
false
T/F it is possible for ions to interact electrostatically with ions that are on the opposite side of the cell membrane
true
T/F it is possible to calculate the equilibrium potential for an ion if the concentration difference across the membrane is known
true
the resting membrane potential of a typical neuron is about -65mV. What does this mean about the relative charge of the inside and outside of a cell?
the inside of the cell is more negatively charged than the outside
an action potential starts with the cell at resting potential them the __________ then the ________ then the _________ before it returns again to resting potential
rising phase, overshoot, undershoot
T/F some action potentials are more powerful than others
false
what is an oscilloscope and how is it used to study neural activity?
a sophisticated voltmeter that displays signals in graphical form
How is the patch-clamp method used to understand ion channels?
allows a study of the ionic currents passing through individual ion channels
what is the relationship between action potential conduction velocity and axonal diameter?
action potential conductivity velocity increases with increasing axonal diameter
how long does an action potential last from the beginning of the rising phase to the end of a falling phase?
2 msec