NRS 326 (UP) Exam 4: Detoxification and Elimination
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
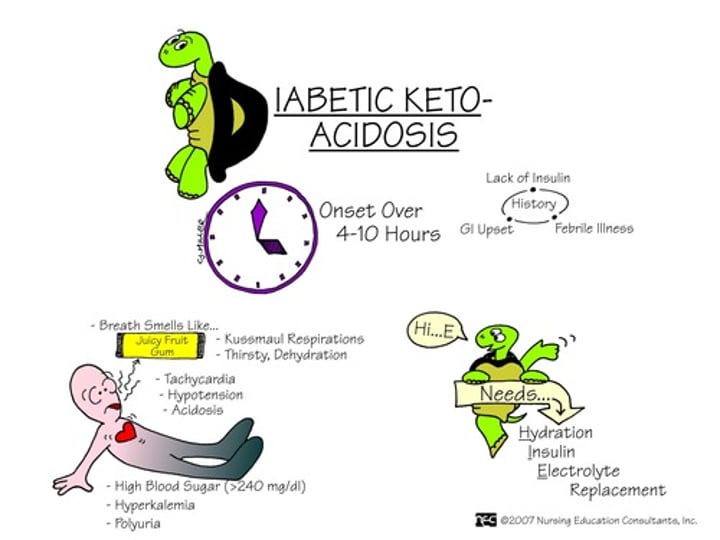
What is DKA?
diabetic ketoacidosis
- occurs in type 1 diabetics
- Too much circulating glucose and not enough insulin in system -> cells breaking down fat into acidic ketone bodies for energy
- This puts the body into a state of acidosis
Risk factors for DKA
a type 1 diabetic who...
- uses expired insulin
- does not use insulin
- injects insulin into scar tissue
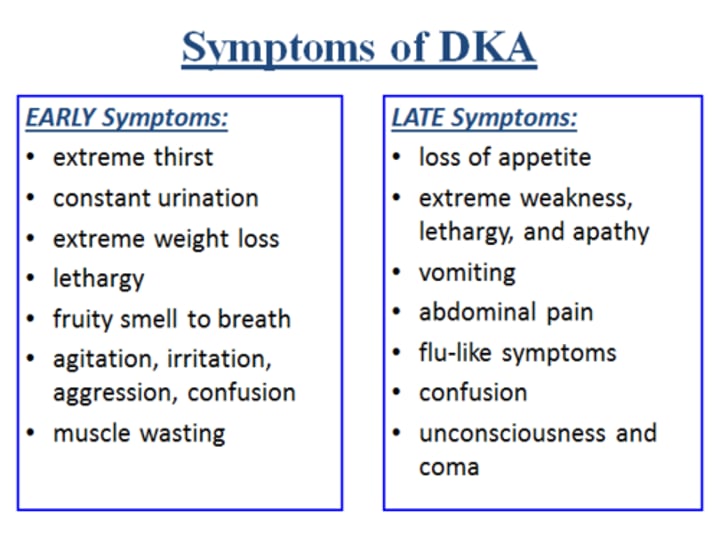
symptoms of DKA
kussmaul respirations,
fruity breath odor (due to exhaled acetone),
delirium/confusion,
abd pain,
N/V,
dehydration,
frequent uriniation (polyuria),
muscle aches,
dry mouth/skin,
excess thirst,
What are Kussmaul respirations?
deep, rapid respirations
characteristic of acidosis
Treatments for DKA
- IV insulin
- IV fluids and electrolytes (maintain hydration and organ function)
- heart attack screening
Definition & Attributes of Elimination
the excretion of waste products from the kidneys (urinary system) and intestines (gastrointestinal system)
Attributes: urinary and bowel elimination
Scope of elimination
incontinence <-> normal <-> retention
what is defecation?
elimination of feces
What is micturition?
emptying of the bladder (urination)
another word for voiding
what is continence?
the ability to control movements of the bowels and bladder
What is anuria?
no urine output
what is oliguria?
Low urine output; less than 500 cc of urine in 24 hours
what is nocturia?
frequent urination at night
what is dysuria?
painful or difficult urination
what is polyuria?
excessive urination
what is polydipsia?
excessive thirst
what is a colectomy?
removal of part of the colon
- shortens GI tract
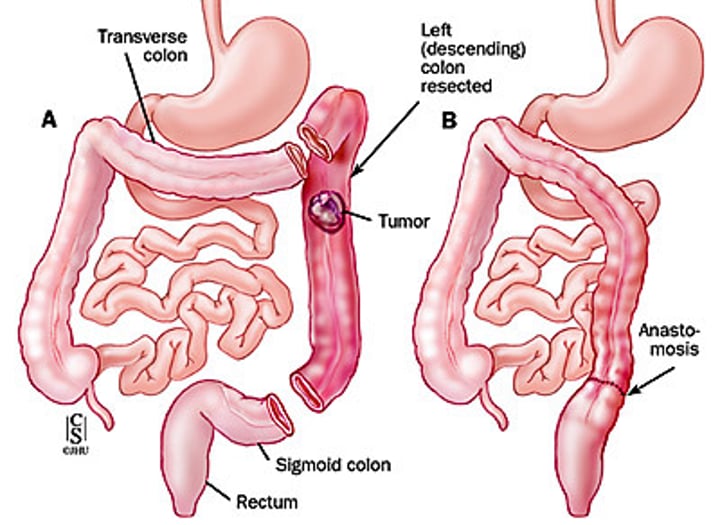
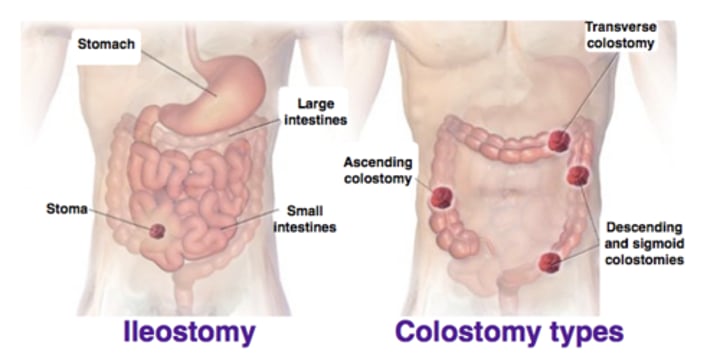
what is an ileostomy or colostomy?
When the end of the small bowel (ileum) or loop of the ileum is brought out onto the right side of the abdominal wall, resulting in a stoma
lifespan considerations for infants/toddlers/children regarding elimination
- lack control over elimination
- around 2 years old; begins to identify urge to pee/poo
lifespan considerations for pregnancy regarding elimination
- increased pressure on bladder (frequent urination, decreased peristalsis, constipation)
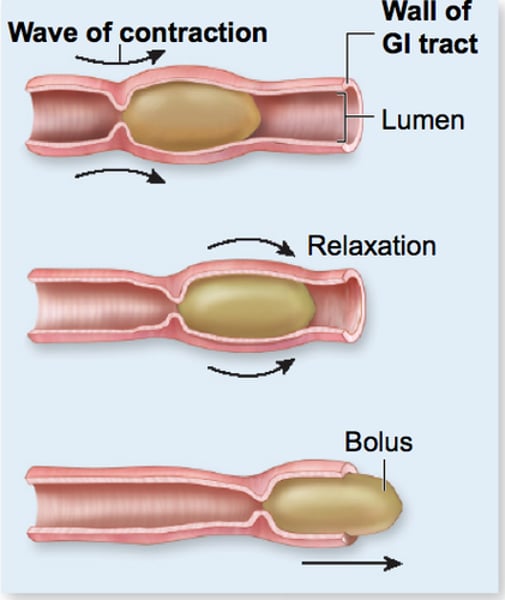
what is peristalsis?
the involuntary constriction and relaxation of the muscles of the intestine or another canal, creating wavelike movements that push the contents of the canal forward.
(process of digestion to elimination)
lifespan considerations for older adults regarding elimination
- decreased renal function
- less urine production
- bladder capacity decreases
- decreased peristalsis
- incontinence is NOT a normal finding, even though it may be common
what is incontinence? what can it lead to?
involuntary release of urine/feces
can lead to: skin breakdown/damages, changes in activity, changes in social relationships
what is retention? what can it lead to?
difficulty/inability to eliminate urine/feces
can lead to: discomfort/pain, backflow of urine into ureters/kidneys (infection risk), feces can become impacted
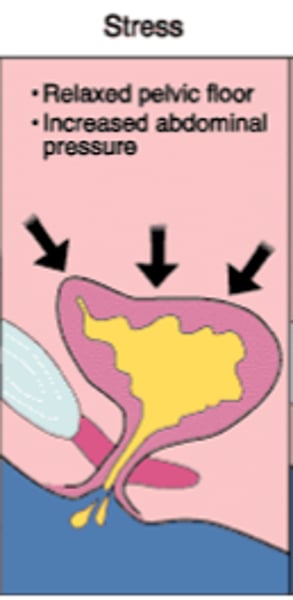
what is stress incontinence?
The loss or leaking of urine during increased abdominal pressure from things such as exercise, sneezing, laughing, coughing, or when lifting something heavy.
- due to weak pelvic floor muscles, common postpartum
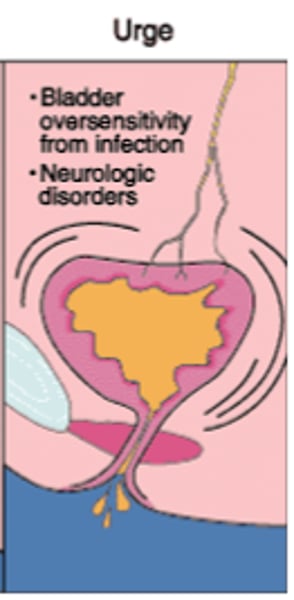
what is urge incontinence?
Overactive bladder- the loss of urine as soon as you feel the urge to go to the bathroom
- due to involuntary bladder contraction, common in UTIs
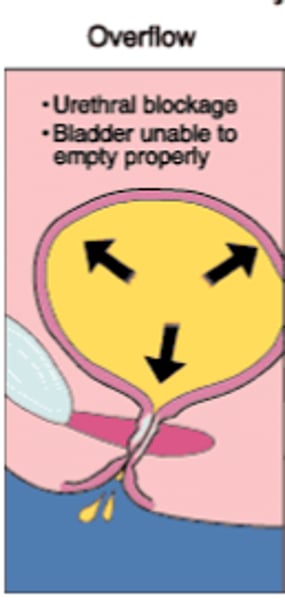
what is overflow incontinence?
Leakage due to inability of the bladder to empty itself correctly (thus causing bladder to fill up to max capacity)
- caused by a urethral blockage & lack of detrusor activity, common in BPH
- may require catheterization
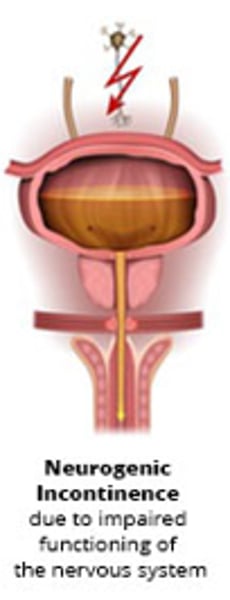
what is neurogenic incontinence?
random voiding/retention due to disturbed function of the nervous system
- common in spinal cord injuries
- may require catheterization
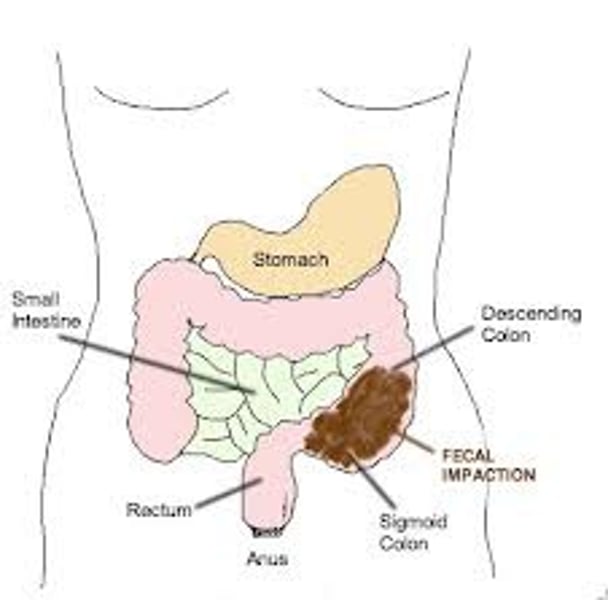
What is fecal impaction?
prolonged retention or an accumulation of fecal material that forms a hardened mass in the rectum or colon that cannot be expelled by muscle contraction
- typically must be manually removed
What is a fecal occult blood test?
Simplest screening test for colorectal cancer
Detects blood in fecal matter
Positive result requires follow up with a colonoscopy
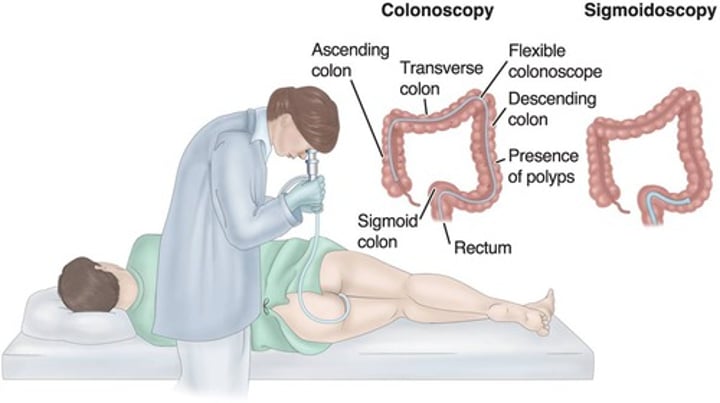
What is a colonoscopy?
Visualization of colon using a flexible scope.
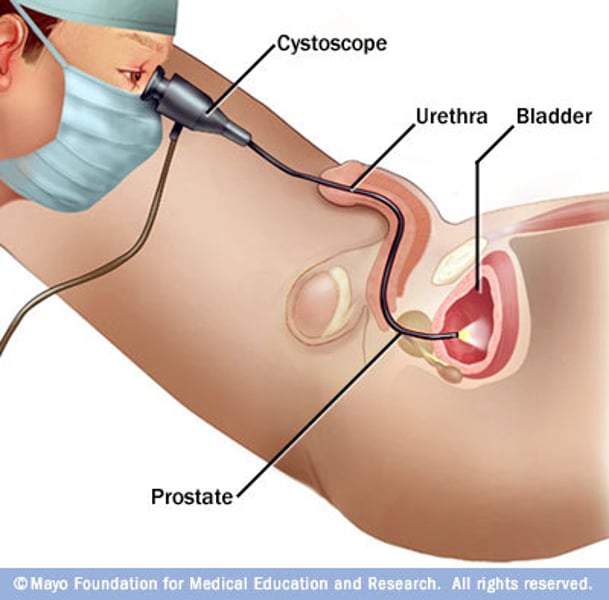
what is a cystoscopy?
visual examination of the urinary bladder using a cystoscope
what is a bladder scan?
hand-held ultrasound device, which can perform a quick, easy and non-invasive scan of the bladder
- calculates bladder volume
what is a post void residual (PVR)?
the amount of urine remaining in the bladder immediately after voiding
categories of laxatives
surfactant (stool softener), fiber/bulk forming agents, bowel stimulants, osmotic laxatives
What are surfactant laxatives?
"stool softeners" (Docusate Sodium)
- increases the amount of water in your feces, making them softer and easier to pass

what are fiber/bulk-forming agents?
Psyllium & Metamucil
- increases the weight of stool by adding fiber and increasing water content in feces
- makes it easier to push the stool out

what are bowel stimulants?
Bisacodyl & Senna
- causes bowel to contract and push out feces
- takes 6-12 hours to work, so it is recommended to take before bed
- most commonly abused laxative

what are osmotic laxatives?
Polyethylene Glycol (Miralax) & Milk of Magnesia
- draws water into the intestines to help move feces along

What are anti-diarrheals?
Loperamide
- decreases absorption of fluid into the intestines, which slows down the frequency of defecation

it is important to drink a full glass of water when taking laxatives, especially ____________________ laxatives because:
these form a gel when mixed with water that helps "slide" the feces out, so if not enough water is in the system then it can make constipation worse
____________ are the preferred first-line laxative in order to prevent abuse
stool softeners
do not chew or crush this laxatives:
bisacodyl
- needs to be delayed release or else it will not work properly
_________ may discolor urine to a brown/red color
Senna
Contraindications for all laxatives
acute surgical abdomen
fecal impaction/bowel obstruction
severe abdominal pain
cramps
appendicitis
ulcerative colitis
caution uses for all laxatives
- pregnancy/lactation: talk with provider before using (stool softeners generally safe)
- Avoid milk of magnesium & sodium phosphate if patient has a kidney issue
why is it important to not give laxatives to someone with a bowel obstruction/fecal impaction?
- can cause bowel perforation, fluid imbalance, worsened constipation (feces now trapped behind "wall")
assessments needed before giving a laxative
abdominal assessment
when was last BM? what was it like (color, consistency, amount)
assessments needed before giving anti-diarrheal agents
abdominal assessment
stool assessment
IxO
when was last BM? what was stool like (color, consistency, amount?)
anti-diarrheals should never be:
crushed or chewed
act of cholinergics on urinary retention:
Bethanechol
Helps promote bladder emptying
Treats urinary retention/overflow incontinence
act of anticholingerics on urinary incontinence
Oxybutynin
Helps decrease bladder spasms
inhibits contractions and sudden urge to void (treats urge and reflex incontinence)
What is blood urea nitrogen (BUN)? Normal levels?
amount of urea in the blood
Normal: 8-20 mg/dl
- if high: indicates an issue with the liver (cannot turn urea into ammonia
What is serum creatinine? Normal levels?
levels of creatinine in blood
Normal: 0.6-1.3 mg/dl
- If high: indicates an issue with the kidneys (cannot eliminate creatinine in urine)
What is GFR? Normal levels?
Glomerular filtration rate; volume of fluid that filters into Bowman's capsule per minute
- >60 ml/min: ideal
- >90 ml/min: TRUE normal
a GFR of ________ indicates kidney failure, and a GFR from ___________ indicates kidney disease
<15 ml/min
15-60 ml/min
an elevated BUN and elevated serum creatinine indicates:
azotemia
What is azotemia/uremia?
increase in nitrogenous waste products in blood (urea and creatinine)
- issue with kidneys
what is creatinine clearance?
test for kidney function
- measures the levels of creatinine in the urine vs the blood and compares to see how well the kidneys are excreting creatine
- high = decreased kidney function
what is serum ammonia?
measures the levels of ammonia in the blood
- if high: means liver is not processing ammonia properly, and probably has an issue
what are ALT/AST tests?
measures of liver function
- if both elevated: decreased liver function
- if only AST elevated: alcohol, tylenol or statins in system
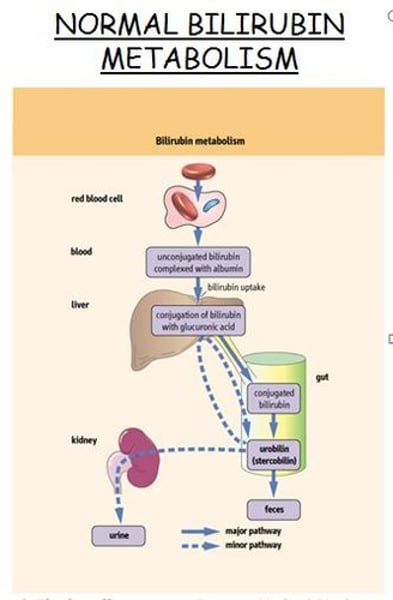
What is bilirubin?
a orange-yellow pigment formed in the liver by the breakdown of hemoglobin and excreted in bile (feces eventually) and urine
- high serum bilirubin: indicates improper liver function
definition of detoxification? attributes?
the removal of toxic substances from the human organism to promote homeostasis
attributes: hepatic & renal
scope of detox
impaired detox (waste accumilation) <-- normal function
what is nitrogenous waste?
by-products of nitrogen
urea, ammonia and creatinine
detoxification relies on the _____ and _____ to process and eliminate waste
kidneys, liver
How is urea produced?
- ammonia is the product of leftover amino acids in the intestines
- the liver takes ammonia and turns it into urea using enzymes
- Ammonia is then transferred to the kidneys via the bloodstream for excretion in urine
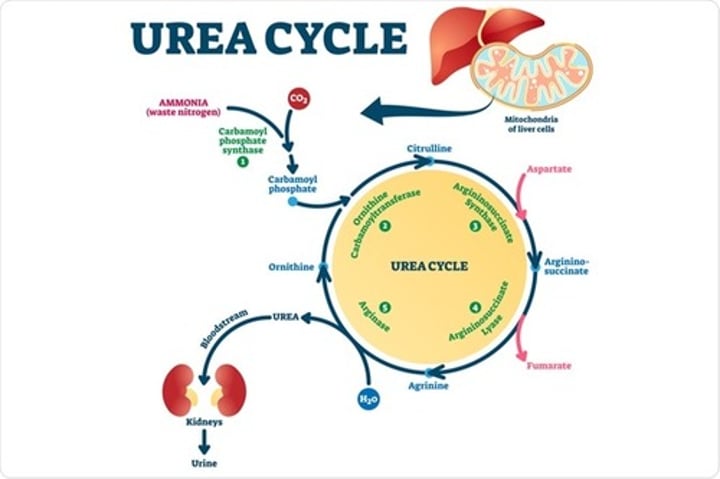
how is creatinine produced?
via muscle metabolism/normal muscle breakdown
- excreted by kidneys with urea
CKD can also cause:
hyperkalemia
metabolic acidosis
lifespan considerations for infants/toddlers/children regarding detoxification
- possible jaundice at birth due to immature hepatic system
- child dosing of meds and some meds contraindicated
lifespan considerations for older adults regarding detoxification
- organ function begins to decline at ~40 years
- increased risk of medication issues (nephro & hepatotoxicity)
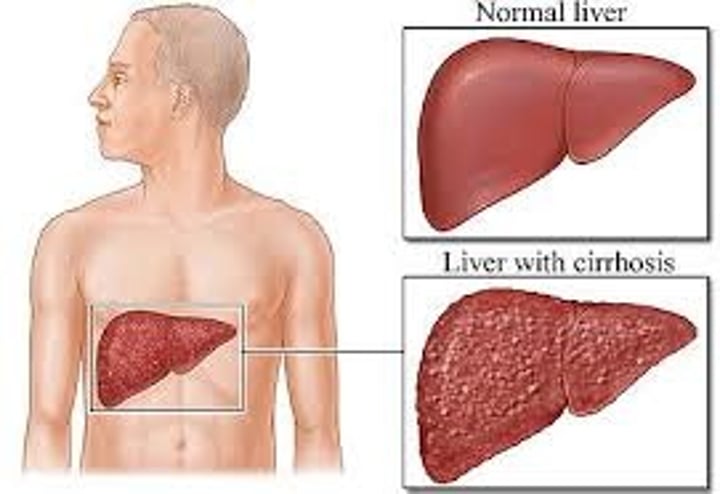
What is cirrhosis?
scarring/hardening of the liver
- decreases liver function
what is liver hepatitis?
inflammatory (and possibly infectious) disease of the liver
- can occur from alcohol abuse (alcohol hepatitis)
what is chronic kidney disease?
progressive loss of renal function that affects nearly all organ systems
- gradual nephron destruction
examples of chronic conditions that can effect liver and kidney functions:
Diabetes (#1 cause)
Heart failure
Improper medication use (ibuprofen=nephrotoxic, acetaminophen=hepatotoxic)
Chronic alcohol use (liver)
________ is very toxic to the brain because...
ammonia
- easily crosses the blood brain barrier and causes neuron dysfunction (hepatic encepalopathy)
what is hepatic encephalopathy
The loss of brain function when a damaged liver doesn't remove toxins (ammonia) from the blood.
symptoms of serum ammonia excess
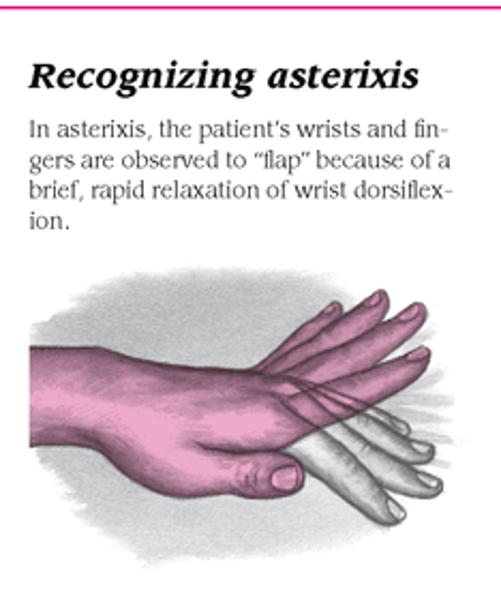
asterixis, personality changes, agitation, restlessness, impaired judgement, slurred speech, incoherence, confusion, disorientation
- think: ammonia excess is an issue of the liver; and all these symptoms are what a "drunk person acts like" (besides asterixis)
what is asterixis?
flapping tremor
symptoms of uremia/azotemia
(urea & creatinine excess)
early: nausea, apathy, weakness, fatigue
late: mental status changes, decline in cell/organ function
What is gynecomastia?
Abnormal breast enlargement in males
- can be a side effect of liver cirrhosis (liver cannot process estrogen for excretion, builds up on system causing "breasts")
normal functions of the liver:
medication breakdown
metabolism of foods (glucose --> glycogen)
production of clotting factors/storage of vitamin K+
bile secretion
if liver is impaired: medications can become more toxic, glucose will not be turned into glycogen (hyperglycemia), bleeding risks, and gray stool/jaundice (bilirubin & iron buildup)
What is bile composed of?
Bile salts, cholesterol, bilirubin, lecithin, water
normal functions of the kidneys:
elimination of urine
balance of electrolytes
balance of acid-base
if kidneys are impaired: urea/creatinine buildup in blood, electrolytes and fluids will be improperly retained/excreted
tests for kidney function:
BUN, serum creatinine, creatinine clearance, GFR
tests for liver function
serum ammonia, ALT/AST
What is dialysis?
method of removing waste products from the body when the kidneys/liver cannot (removes urea and creatinine and fluid, and balances electrolytes/acids and bases)
- can be used in treatment of CKD, but is required in end stage renal disease
- can also be used in liver cirrhosis to remove ammonia (usually only used during hepatic encephalopathy flares)
- types: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
dialysis uses ______ and _____ to filter blood
diffusion
osmosis
what is hemodialysis?
artificial kidney machine (dialyzer) removes waste products from the blood
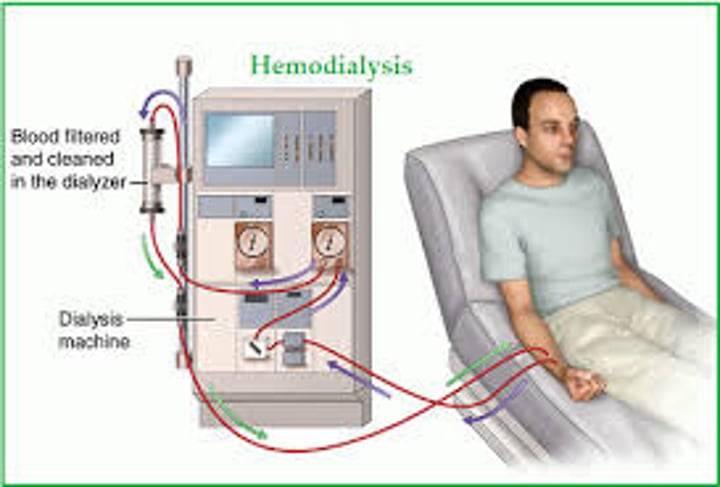
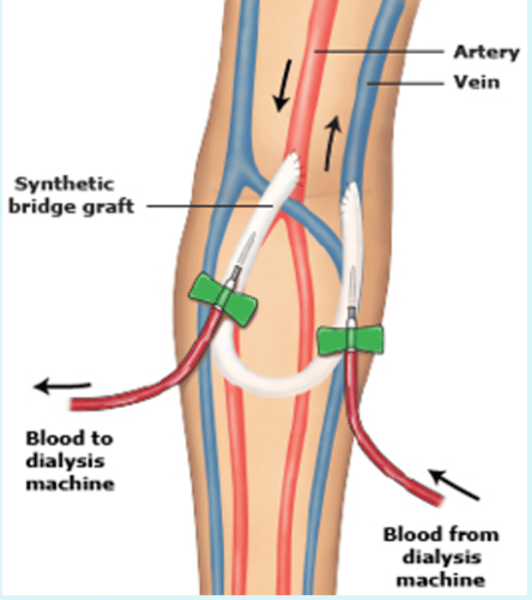
what is a fistula?
artificial connections of veins
- if fistula is working properly during hemodialysis, you should be able to feel a "thrill"
- auscultate to hear the "bruit"
What is peritoneal dialysis?
uses lining of abdomen (peritoneal membrane) to filter blood
- catheter in abdomen surgically placed
- Dialysate put in through catheter to push materials to peritoneal membrane to filter
- if drainage is cloudy: could indicate infection
what is dialysate made of?
potassium, chloride, magnesium, glucose, HC03-
pros and cons of hemodialysis
Pros: effective, "hands off" (the patient does not have to do anything), good for critical issues, less infection risk
Cons: Must have transport and access to clinic, 4 hours 3x weekly, fluid/diet restrictions, needles, clotting and bleeding risks, hypotension and hypovolemia risks
pros and cons of peritoneal dialysis
Pros: 20-30 mins, no needles, can be done from home
Cons: 4x daily, risk for peritonitis/infection, no days off, increased loss of protein, increased glucose levels, leftover fluid in abdomen can impact body image
what is peritonitis?
inflammation of the peritoneal cavity
- can be a result of infection (peritoneal dialysis)
what is lactulose?
osmotic laxative
- mainly used to decrease ammonia production and trap ammonia in the GI tract for excretion via feces
- can also be used to treat constipation
side effects of lactulose
diarrhea, cramping, frequent loose stools
______ may be a life-long medication in patients with liver failure
lactulose
What are varices?
dilated veins caused by liver cirrhosis
- scarring causes a backflow of blood into veins, keeping them dilated and enlarged
- can "pop" and cause severe internal bleeding
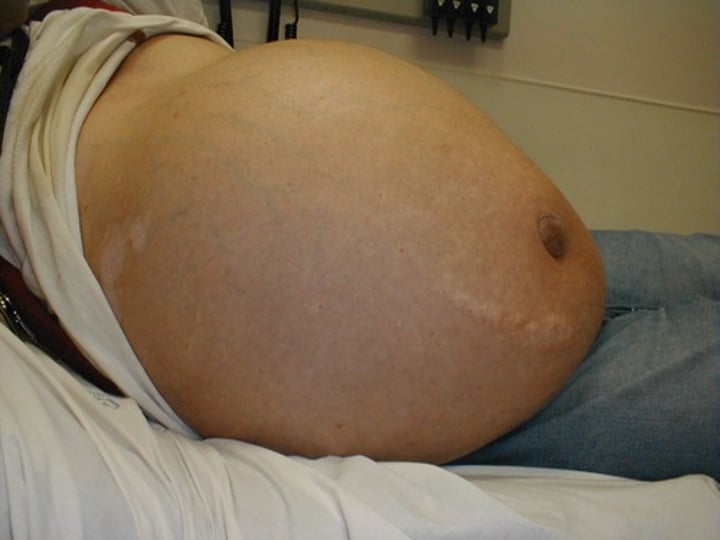
What are ascites?
the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, causing abdominal swelling.
- obstructed blood flow to liver due to cirrhosis causes a decrease in protein production by the liver, and there is less protein available to keep fluid in vasculature (resulting in ascites)