Spinal Cord
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Spinal cord (ending)
Elongated part of the CNS extending from the foramen magnum to approximately the L2 vertebral level in adults
Spinal cord segments
31 total segments giving rise to paired spinal nerves: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal
Conus medullaris
Tapered caudal end of the spinal cord
Filum terminale
Thin extension of pia mater anchoring the conus medullaris to the coccyx
Cervical enlargement
Region of the spinal cord (C5–T1) that supplies the upper extremities via the brachial plexus
Lumbosacral enlargement
Region of the spinal cord (L1–S3) that supplies the lower extremities
Spinal meninges
Three protective coverings of the spinal cord: dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater
Dorsal rootlets
Posterior rootlets that carry sensory (afferent) information into the spinal cord
Ventral rootlets
Anterior rootlets that carry motor (efferent) information out of the spinal cord
Dorsal root ganglion
Collection of sensory neuron cell bodies located on the dorsal root
Spinal nerve
Formed by the union of dorsal and ventral roots and contains mixed sensory and motor fibers
Rami
Branches of a spinal nerve that remain mixed and go on to form named peripheral nerves
Dermatome
Area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
Myotome
Group of muscles supplied by a single spinal nerve
Gray matter (spinal cord)
H- or butterfly-shaped central region of the spinal cord containing neuron cell bodies
White matter
Outer region of the spinal cord composed of ascending and descending axon tracts
Dorsal horn
Region of gray matter that receives sensory input
Ventral horn
Region of gray matter containing motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscle
Lateral horn
Gray matter region present from T1–L2 containing sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies
Central canal
CSF-filled channel at the center of the spinal cord
Anterior median fissure
Deep ventral groove separating the anterior white matter
Posterior median sulcus
Shallow dorsal groove separating the posterior white matter
Alar plate
Embryologic dorsal neural tube region that develops into sensory structures
Basal plate
Embryologic ventral neural tube region that develops into motor structures
Ventricular zone derivative
Region that gives rise to spinal gray matter during development
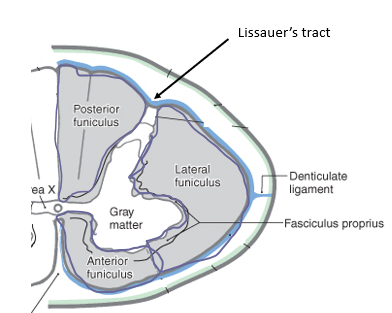
Funiculi
Three major white matter regions of the spinal cord: dorsal, lateral and anterior
Dorsal columns
Ascending tracts that convey fine touch, proprioception, and vibration from the ipsilateral side of the body to the somatosensory cortex
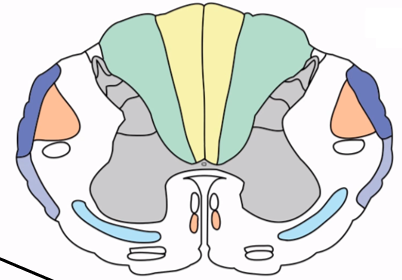
Fasciculus gracilis
Dorsal column tract carrying sensory information from the legs (YELLOW) ipsilaterally to the primary somatosensory area
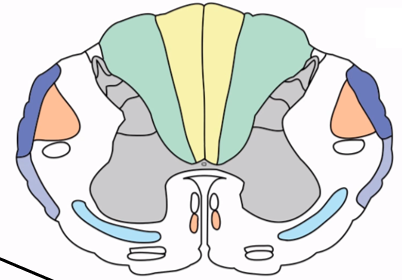
Fasciculus cuneatus
Dorsal column tract carrying sensory information from the arms (GREEN) ipsilaterally to the primary somatosensory area
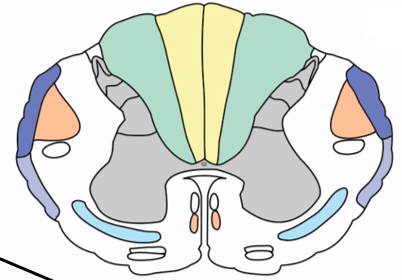
Spinothalamic tract
Ascending tract conveying pain, temp, crude touch, contralateral to the primary somatosensory area (TEAL)
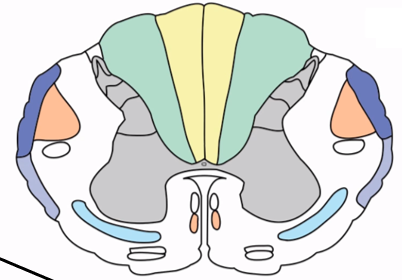
Lissauer’s tract
Region where pain and temperature fibers ascend or descend one to two levels before crossing
Spinocerebellar tracts
Ascending tracts conveying unconscious proprioceptive information ipsilaterally to the cerebellum (DARK BLUE/GREY)
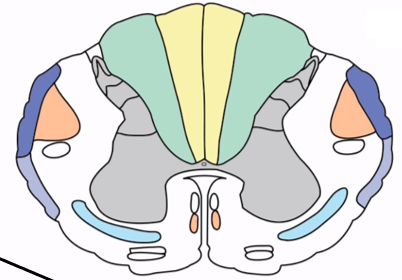
Corticospinal tract
Descending motor pathway controlling voluntary movement (ORANGE)
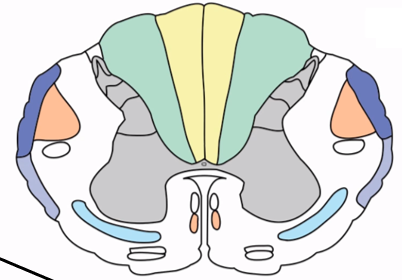
Lateral corticospinal tract
Major corticospinal pathway (80-90%) that decussates in the caudal medulla and controls limb movement
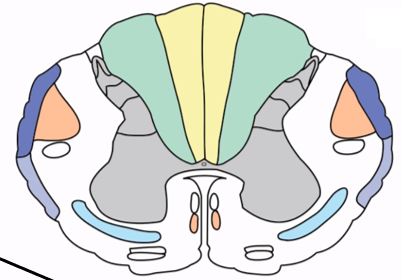
Ventral corticospinal tract
Minor corticospinal pathway (10-20%) that decussates in the spinal cord and controls trunk muscles
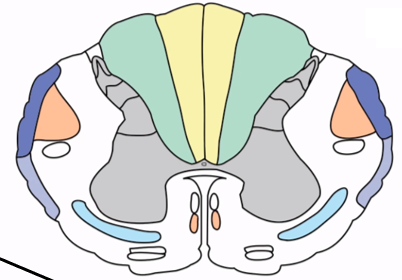
Upper motor neuron
Neuron originating in the cortex that influences lower motor neurons
Lower motor neuron
Neuron in the ventral horn whose axon innervates skeletal muscle
Anterior spinal artery
Single artery from the vertebral artery supplying the anterior two-thirds of the spinal cord including motor tracts (symptoms of problem- lose muscle)
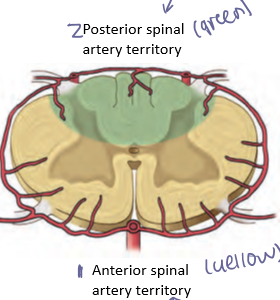
Posterior spinal arteries
Paired arteries from the vertebral arteries/PICAs supplying the dorsal columns of the spinal cord (symptoms of problem- lose sensation)
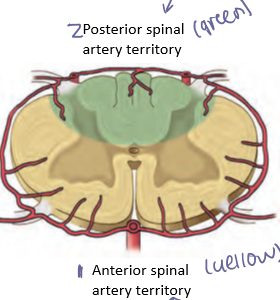
Artery of Adamkiewicz
Major radicular artery supplying the lumbosacral enlargement
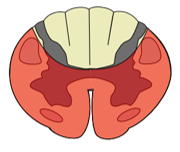
Anterior spinal artery syndrome
Ischemic injury causing bilateral motor paralysis and loss of pain and temperature with preserved dorsal column function
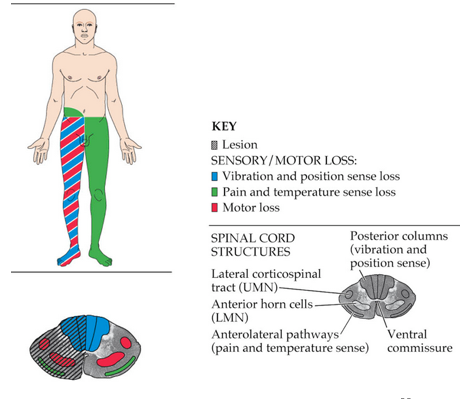
Brown-Sequard syndrome
Hemicord lesion causing ipsilateral motor weakness and loss of proprioception with contralateral loss of pain and temperature
Spinal reflex
Involuntary stereotyped response mediated by a spinal circuit
Reflex arc
Pathway consisting of receptor, sensory neuron, integration, motor neuron, and effector
Monosynaptic reflex
Reflex involving a single synapse such as the patellar reflex
Polysynaptic reflex
Reflex involving multiple synapses such as the withdrawal reflex