34. Miscellaneous Topics
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
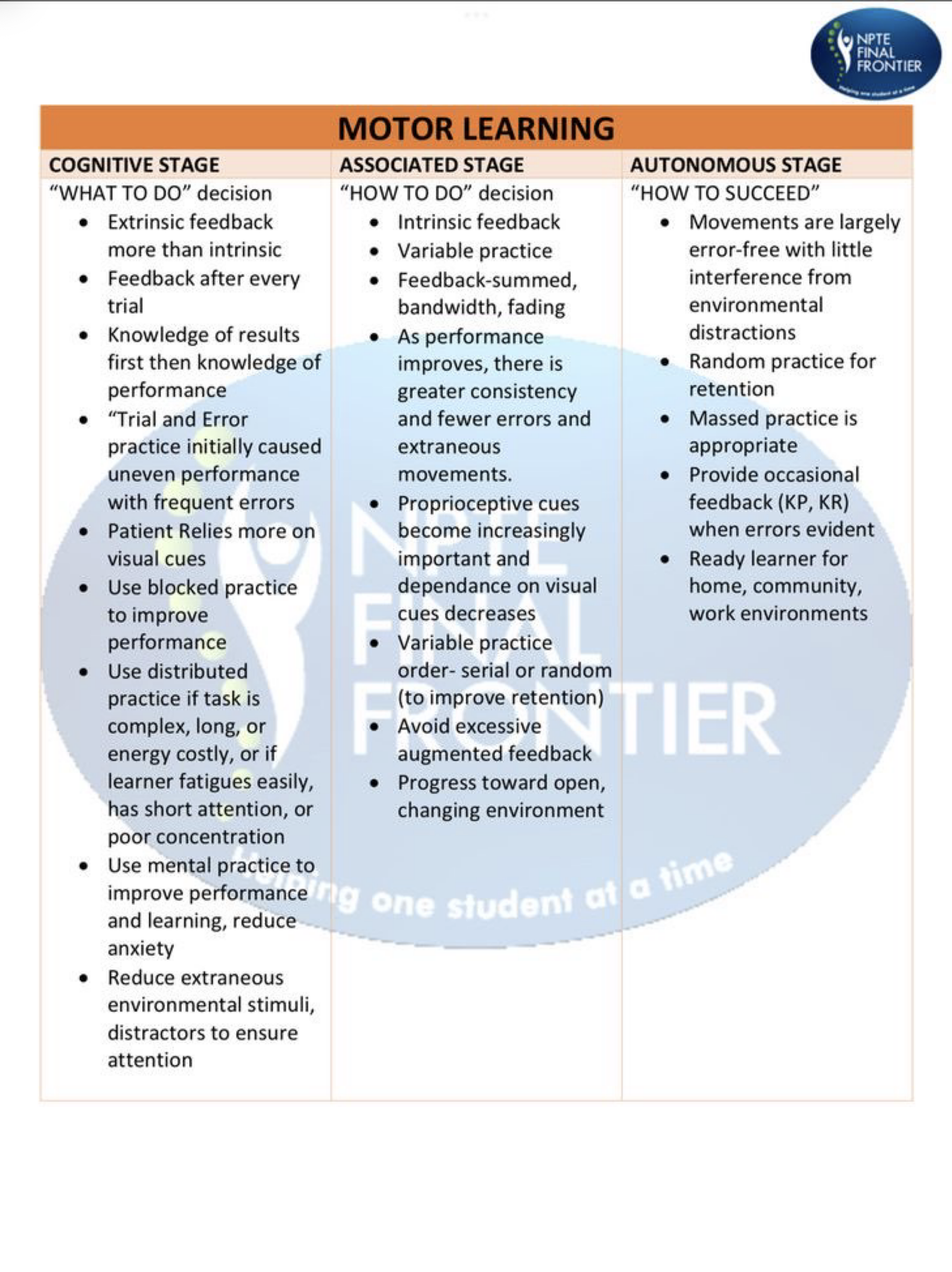
Motor Learning
Motor Learning » Stage 1: Cognitive Stage (Beginning/Novice)
4 Characteristics
Gathering Info
Frequent Errors and Feedback
Cannot Perform Dual Task
Large Gains BUT Inconsistent Performance
Motor Learning » Stage 2: Associative Stage (Intermediate/Practice)
6 Characteristics
» Putting Actions Together «
Practice is Critical
Small Gains BUT Disjointed Performance
Less Cognitive Effort
Begin to Learn What Errors They Are Making
Patient Reflects on Performance
Motor Learning » Stage 3: Autonomus Stage (Advanced/Fine Tuning)
5 Characteristics
Accurate
Consistent
Efficient
Smooth
Recognize when skills are performed INCORRECTLY
Motor Learning occurs as a direct result of what?
WHO is practice important for?
How often should feedback be given for Novice Learners?
Practice
Novice Learners at the Cognitive Phase
Frequent Feedback
Cognitive Learning Phase:
What type of practice is BEST for pts in the COGNITIVE learning phase?
BUT can begin ___ practice as they progress
What should the PT allow time for in pts in the Cognitive Learning Phase?
Blocked Practice
Serial Practice
Process the Practice
Associative Learning Phase:
ASSOCIATIVE learners are beginning to develop and hone in what?
What type of practice are ASSOCIATIVE learners?
What should the PT allow time for in pts in the Associative Learning Phase?
Internal Reference of Correctness
Transition from Serial Practice » Random Practice
Reflect on the Performance
What is Blocked Practice?
Example:
Repetition and Practice
Ex: Practice STS 12x from WC
111222333
What is Serial Practice?
Example:
Practice sequence in which different skills are performed in a MIXED ORDER but FIXED FORMAT
Ex: Practice STS 4x from bed, 4x from WC, 4x from couch
123123123
What is Random Practice?
Example:
RP:
Previously constructed plans be abandoned
Processing facilitates learning
Ex: Random order of transfers
1232123
Random Practice is BEST for what 2 types of learners?
Associative Learner » Who has developed a “Reference of Correctness”
Autonomous Learners » Who are highly skilled/expert
What is Mental Practice?
What is Part Task v Whole Task Practice?
Mental:
Having patient review planned movement in their heads PRIOR to completing movement
Part v Whole:
Breaking up the training into portions » practice a portion of the movement
Intrinsic v Extrinsic Feedback:
Define:
Intrinsic Feedback:
Extrinsic Feedback:
AKA:
Rate Given:
Intrinsic:
Patient thinking and performing
Kinesthetic, Visual, Cutaneous, Vestibular, Auditory Feedback of the patient
Extrinsic:
External sources that are supplemental to intrinsic feedback
AKA: Augmented
Rate:
Concurrently, Immediately After, or Delayed
How much feedback should be given as learning progresses for these stages:
Cognitive Level:
Associative Feedback: (4)
Cognitive Level:
Frequent Feedback
Associative Feedback:
LESS OFTEN is more beneficial
DELAYED Feedback is more beneficial than INTERMEDIATE Feedback
Blocked » Random once pts has “Internal Reference of Correctness”
Given when patient performance falls OUTSIDE of acceptable level OR FADING feedback as pt skill level improves

Scoliosis:
At what degree of Scoliosis curvature is a brace effective?
25-45 degrees

Heart Murmurs:
Murmur =
Sounds occurring between S1 and S2 =
Sounds occurring between S2 and S1 =
Correct: 1
Murmur = Turbulent blood flow within heart or great vessels
Sounds occurring between S1 and S2 = Systolic Murmurs
Sounds occurring between S2 and S1 = Diastolic Murmur
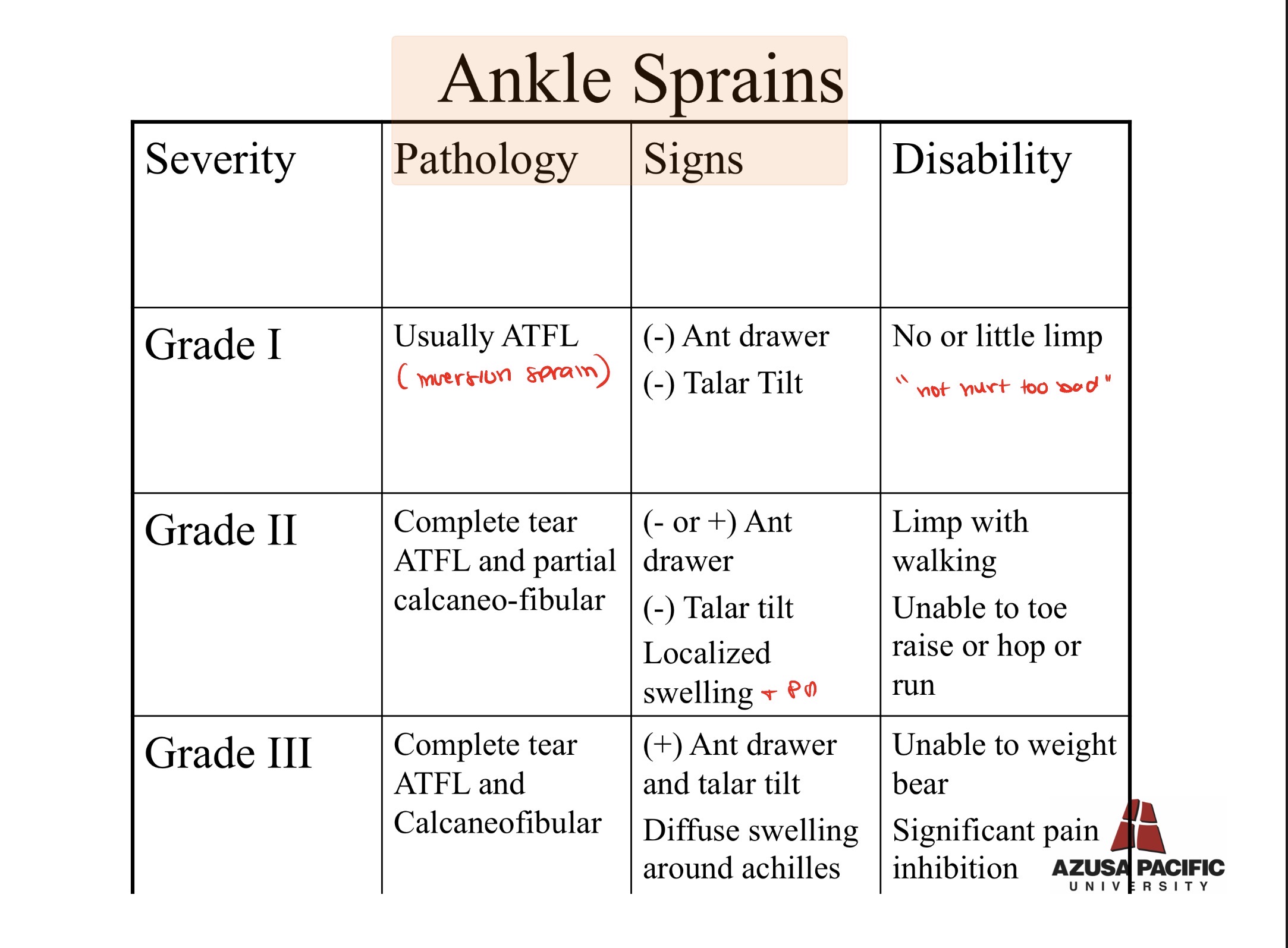
Ankle Sprain Grades:
Grades 1-3:
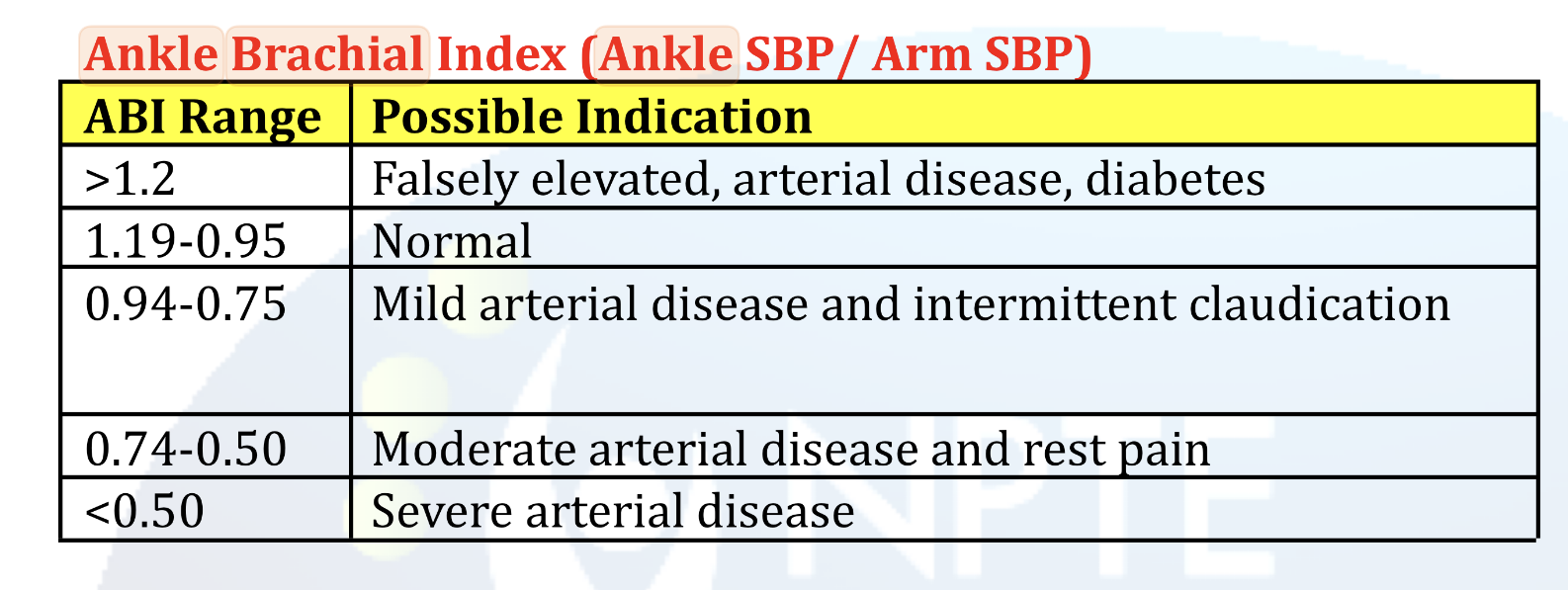
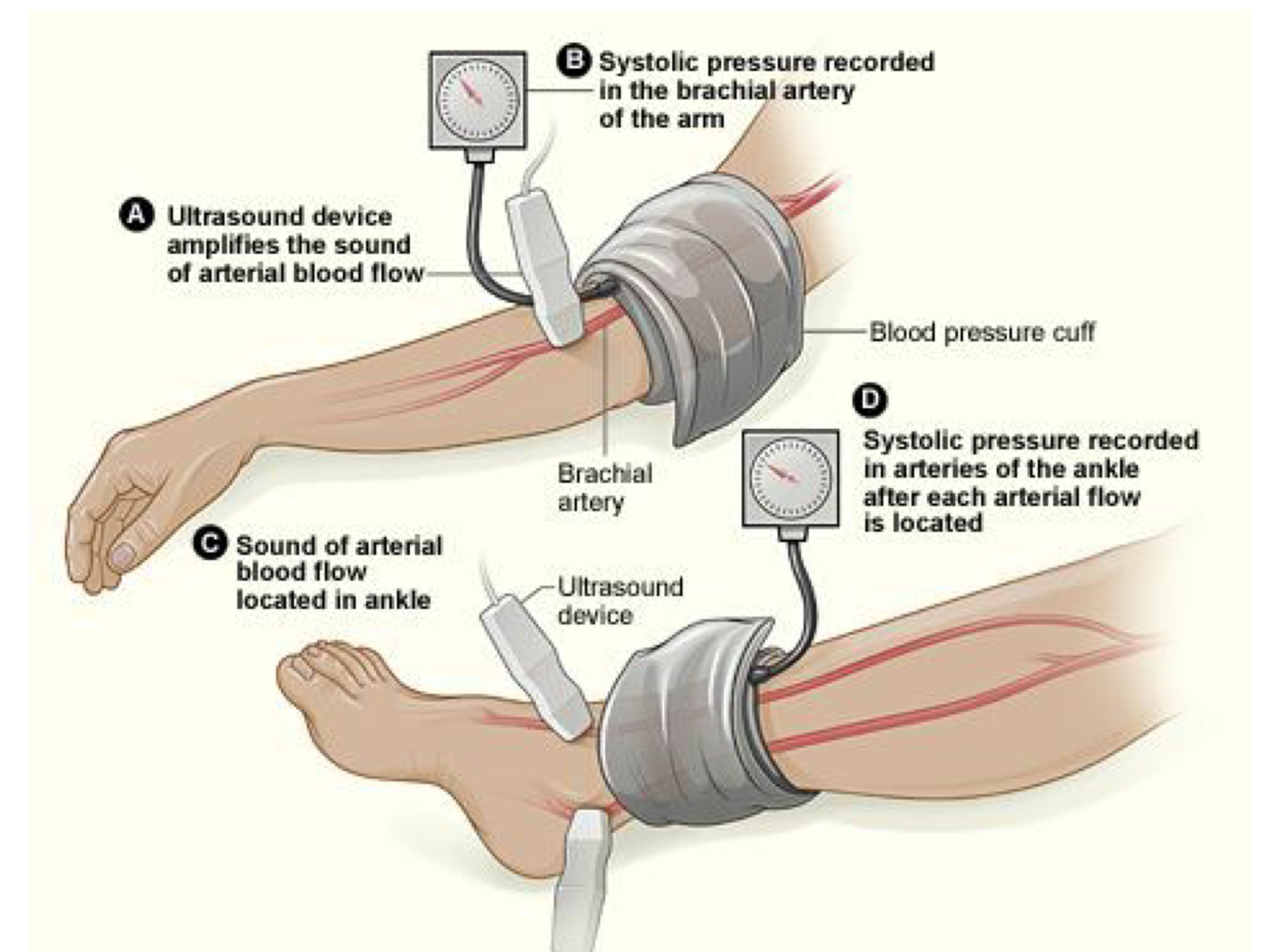
Ankle Brachial Index (Ankle SBP / Arm SBP)
Purpose:
To distinguish…
Compares…
Uses Doppler at what 2 arteries?
Compression Therapy is CONTRAINDICATED for what ABI?
Purpose:
To distinguish LE Neurogenic vs Vascular Claudication Pain
Compares:
Ratios of SBP of Arms and Legs
L Leg Systolic / Highest Brachial BP
R Leg Systolic / Highest Brachial BP
Doppler:
Posterior Tibial Artery
Dorsalis Pedis Artery
Contra:
< 0.80 ABI
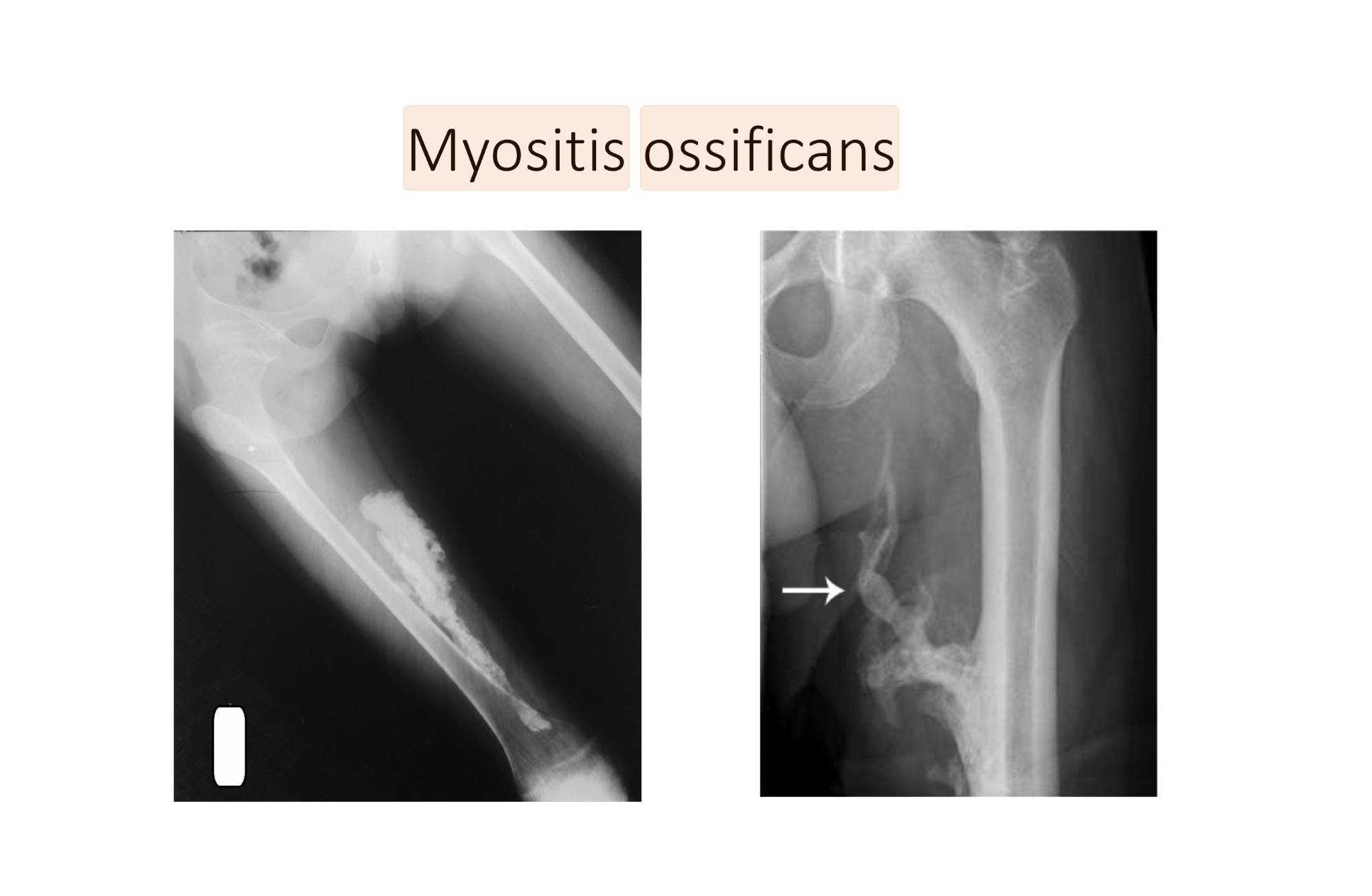
Myositis Ossificans:
Widespread ossification of __ __.
Episodes of _ and _ _ _.
Tissues can __
How can Myositis Ossificans occur? (3)
3 MC sites
Tx: (2)
Connective Tissue
Eposides of Fever or Soft Tissue Inflammation
Harden
How:
Often in Early Childhood or after trauma
Maybe from massage or STM TOO EARLY in rehab
Lack of RICE after injury
Muscles:
Quads
Brachialis
Deltoid
Tx:
Ice in fully stretched positions
STOP MASSAGING AND USING HEAT
Metabolic Equivalent:
1 MET =
Convenient Method for standardizing…
Light Intensity:
Moderate Intensity:
Vigorous Intensity:
1 MET = Relative Oxygen Consumption at REST
Standardizing » Intensity of Activities
Light Intensity: 1.6-2.9 METS
Moderate Intensity: 3.0-5.9 METS
Walk, Run, LE/Arm Cycling (~3.5)
Vigorous Intensity: ≥ 6.0 METS
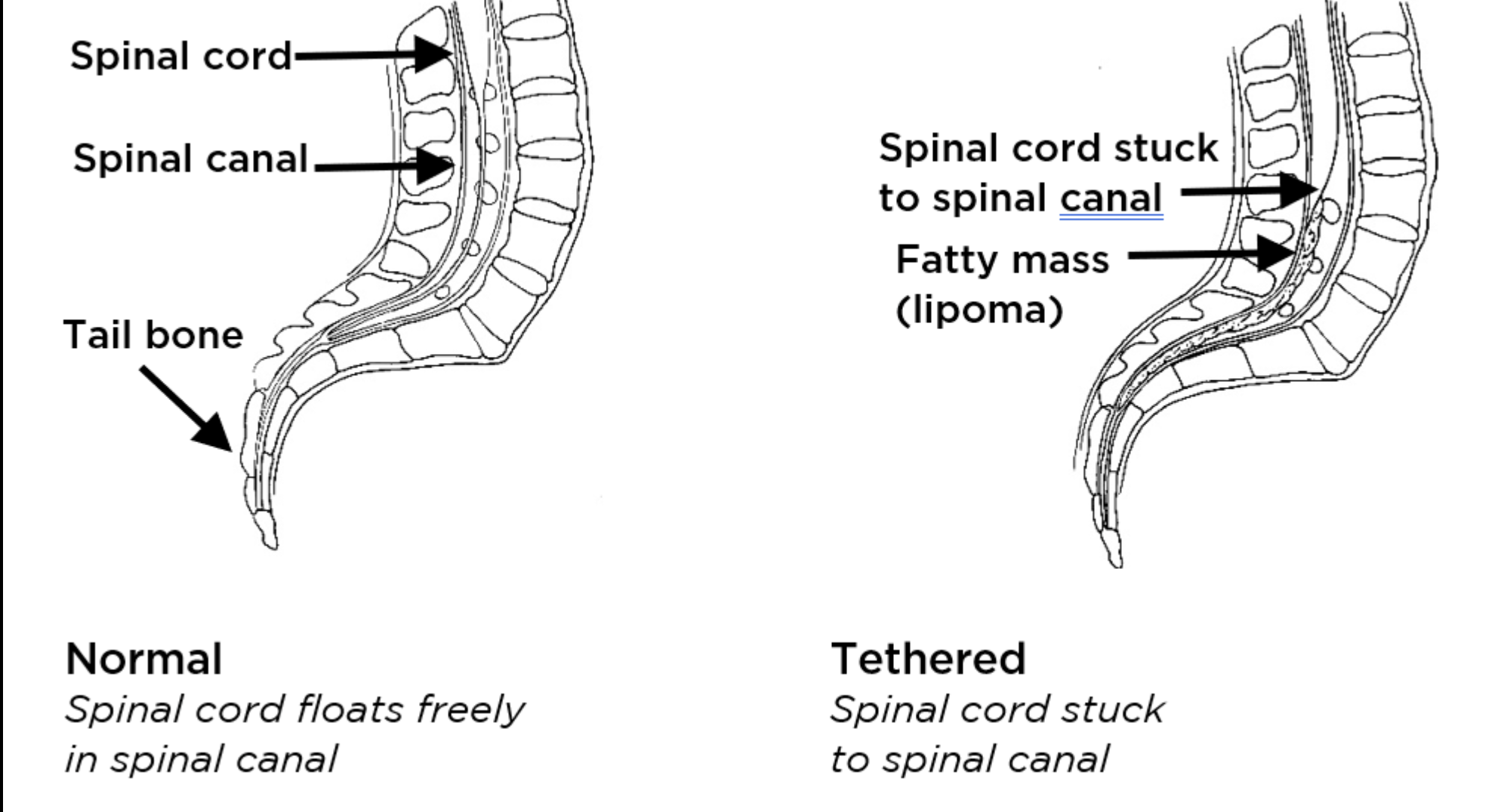
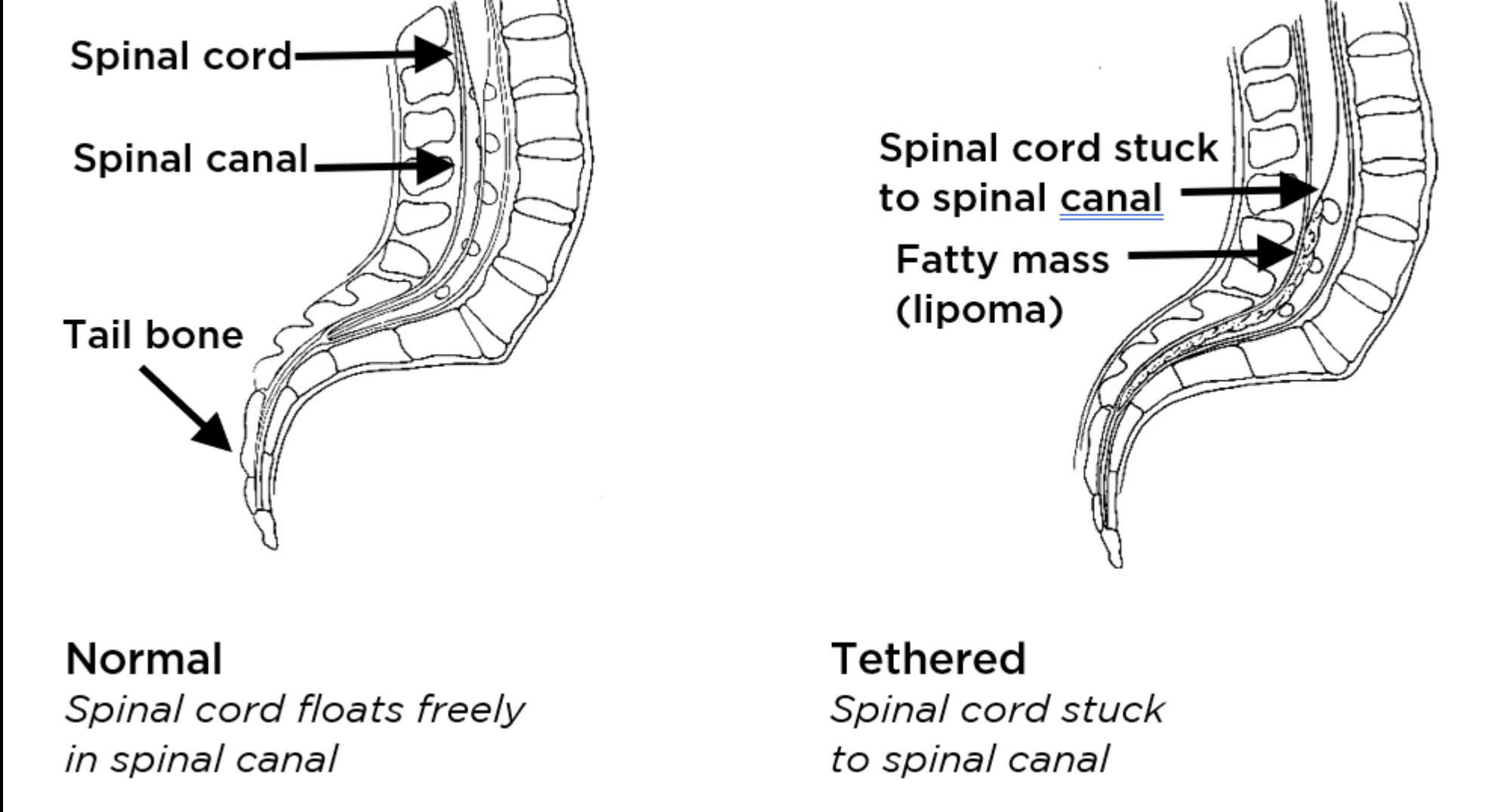
Tethered Dura:
Define:
Can Cause:
Define:
Abnormal fixation of the SC/Dura
Causes:
Traction and Neurological Symptoms ESPECIALLY c Movement or Growth
Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (IPAH):
Prevalence:
Describe:
IPAH can lead to:
RARE
Define:
Progressive disease where there is abnormally high BP in Pulmonary Artery c no identifiable cause
Lead to:
R Heart Failure
Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (IPAH):
Physiology: (4)
Pulmonary Artery becomes narrowed, thickened, or stiff
Increase Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (Afterload)
R Ventricle has to work harder to push blood to lungs
Overtime » R Ventricle Hypertrophy » R HF
Define:
Nociplastic Pain:
Nociceptive Pain:
Neurogenic Pain:
Psychogenic Pain:
Correct: 3
Nociplastic Pain:
Associated c symptoms that do not have clear anatomical correlate, is widespread, and/or not consistent
Nociceptive Pain:
Pain resting from stimulation of nociceptors
Often with a clear stimulus-respose relationship between movement and symptoms
Neurogenic Pain:
Pain that arises from injury, dysfunction, or disease of the nervous system
Psychogenic Pain:
Pain where psychological factors are the primary cause
T4 Syndrome:
T4 actually means:
Describe:
Presentation: (4)
T4 = T2-T7
Describe:
Symptom complex especially Upper T/S
Unknown Cause
Presentation:
Hand or Hands always affected
Glove like distribution of parethesias
Dull aching or pressure in or around the head
No changes in reflex or myotomes

CRPS:
Common S/S: (4)
In final stage, affected limb is…
Correct: 4
CRPS:
Common S/S:
Burning or Aching Pain
ANS Dysfunction
Edema
Movement Disorder
Affected Limb = Cooler
CVA Terminology:
Anosognosia:
Ideational Apraxia:
Somatoagnosia:
Right and Left Discrimination Disorder:
A:
Denial or lack of awareness of the presence or severity of one’s paralysis
IA:
Inability to perform a task on motor or on command
S:
Lack of awareness of the body structure and relationship of body parts to oneself or to others
R and L:
Inability to identify R and L sides on one’s own body
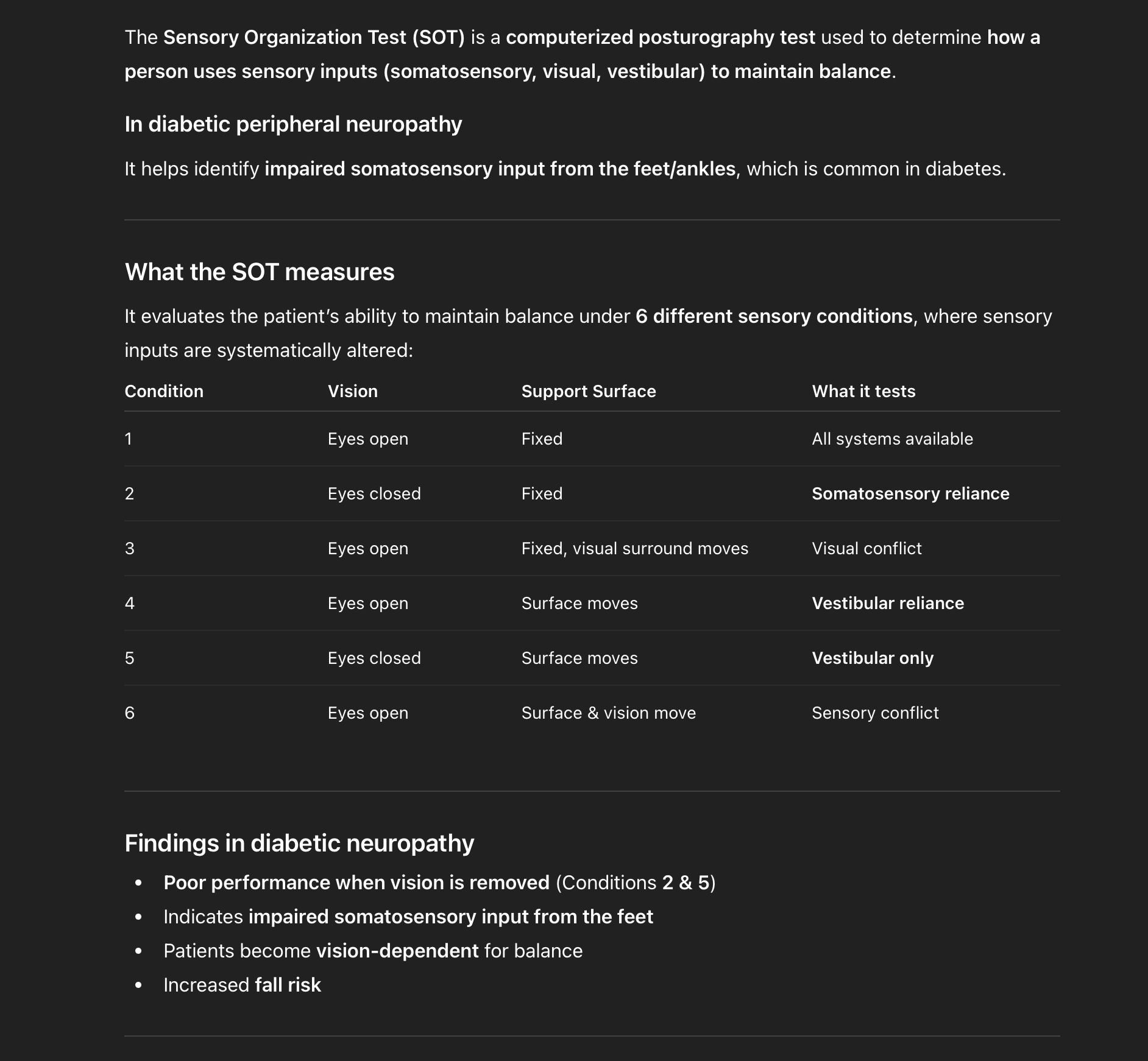
Sensory Organization Test (SOT)

On or after third postpartum day

Sit and Lean Forward
Meralgia Paresthetica:
Define:
This injury affects sensation where?
Define:
Entrapment or injury to the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve » Purely Sensory Nerve
Affects sensation:
Lateral Thigh
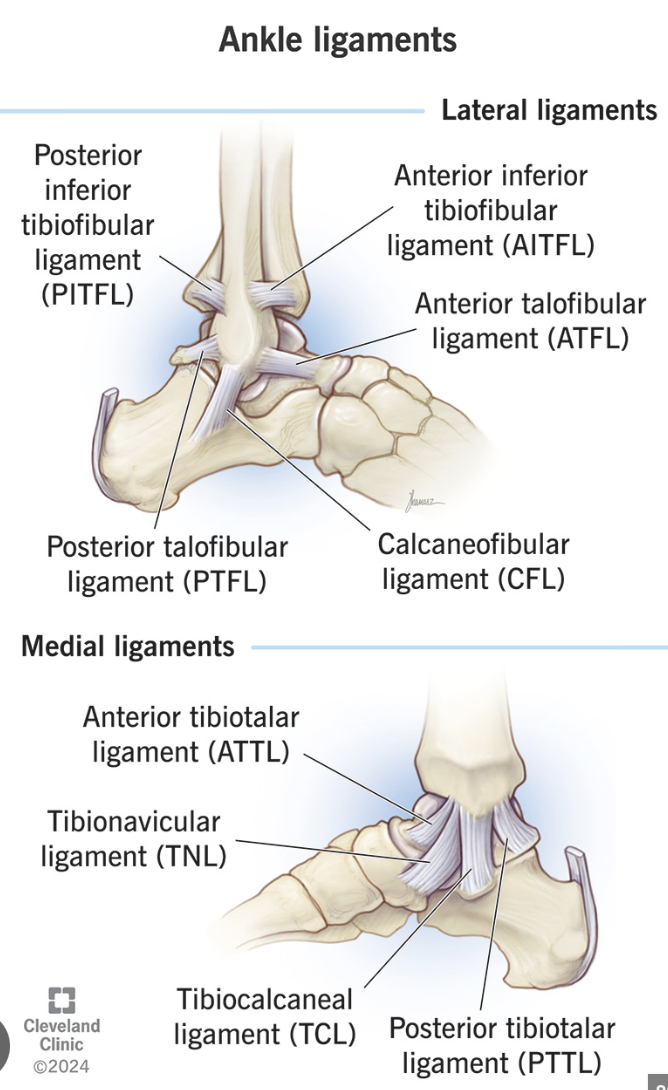
How to assess difference between:
Anterior TIBIO-FIBULAR Ligament Sprain:
Anterior TALO-FIBULAR Ligament Sprain (ATFL):
Anterior TIBIO-FIBULAR Ligament Sprain:
Compression of the Distal Shafts of the Tibia and Fibula (Syndesmosis Injury)
Anterior TALO-FIBULAR Ligament Sprain (ATFL):
Anterior Drawer
NOTE: READ THE FULL NAME OF THE LIGAMENT » DONT ASSUME ATFL
A patient in a persistent vegetative state in a nursing home has developed a Stage 2 ischial pressure injury. The pressure injury has not improved after 4 weeks of standard wound care treatment. The physical therapist should recommend a consultation with:
An orthotist to investigate lower extremity bracing.
A nutritionist to investigate level of protein.
A respiratory therapist to administer oxygen therapy.
A surgeon to perform a skin flap.
» WHY?
Increased __ __ are linked to improved __ __ healing in pts c pressure injuries.
A nutritionist to investigate level of protein.
INCREASED PROTEIN LEVELS » WOUND HEALING
Hemipalegic Posture:
What position is an IDEAL early standing posture in which to develop UE and LE control?
This posture helps affected extremities weight bear out of what?
This position is easily tolerated by what pop?
Modified Plantigrade
Synergy patterns
Elderly pts
HR:
If a patient has an irregular HR > 100 bpm, what is the most accurate method of measuring HR?
HR faster than 100 bpm OR slower than 60 bpm should me measured at…
Auscultate the apical heart for at least 60 sec
> 100 OR < 60
Measured at the FULL MINUTE
Could miss the irregular heart beat if done at 15 or 30 second intervals
What is the MAXIMUM current density that should be used to initiate iontophoresis when the current amplitude is 10 milliamperes and the conductive surface area is 20 cm2?
0.2 milliamperes/cm2
0.5 milliamperes/cm2
5 milliamperes/cm2
20 milliamperes/cm2
To calculate current density, the current amplitude is divided by conductive surface area; therefore, 10/20 = 0.5.
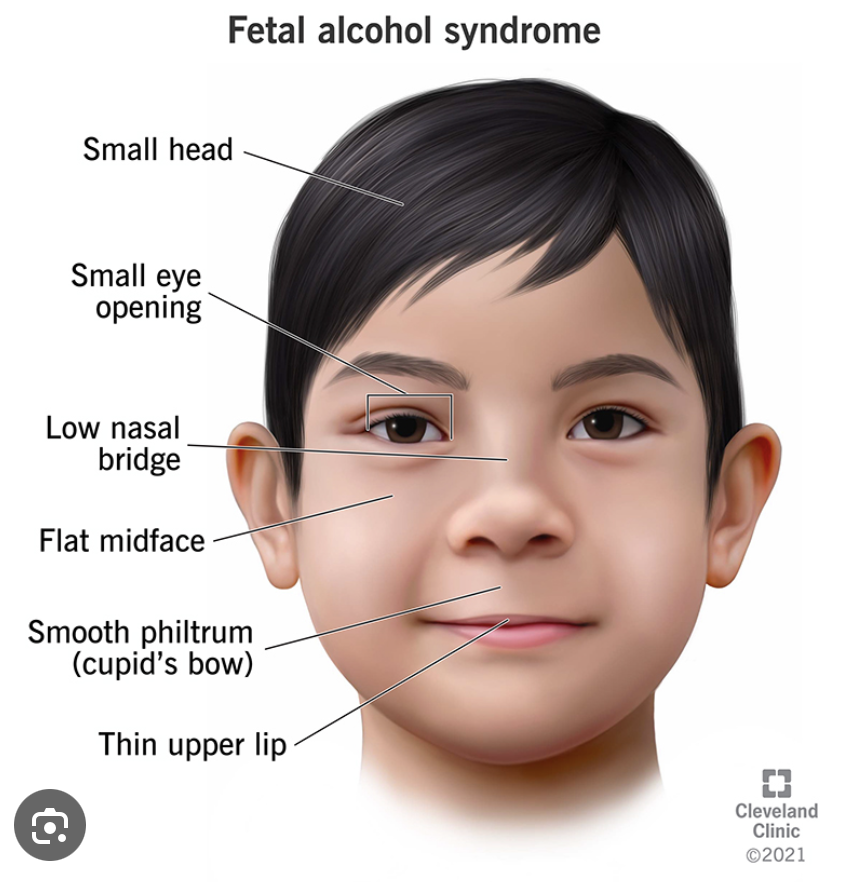
A 4-year-old child has maxillary hypoplasia, an elongated mid face, and a short, upturned nose. The child has a short attention span and poor growth. Which of the following interventions would be MOST appropriate for the child?
Gait training with a rolling walker
Sensory desensitization activities
Activities to inhibit spasticity
Dynamic balance activities
»
What condition does this child have?
What are 4 main characteristics/impairments associated with this condition?
Dynamic balance activities
»
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
4:
Fine Motor Dysfunction
Visuomotor Deficits
Balance Problems
Weak Grasp
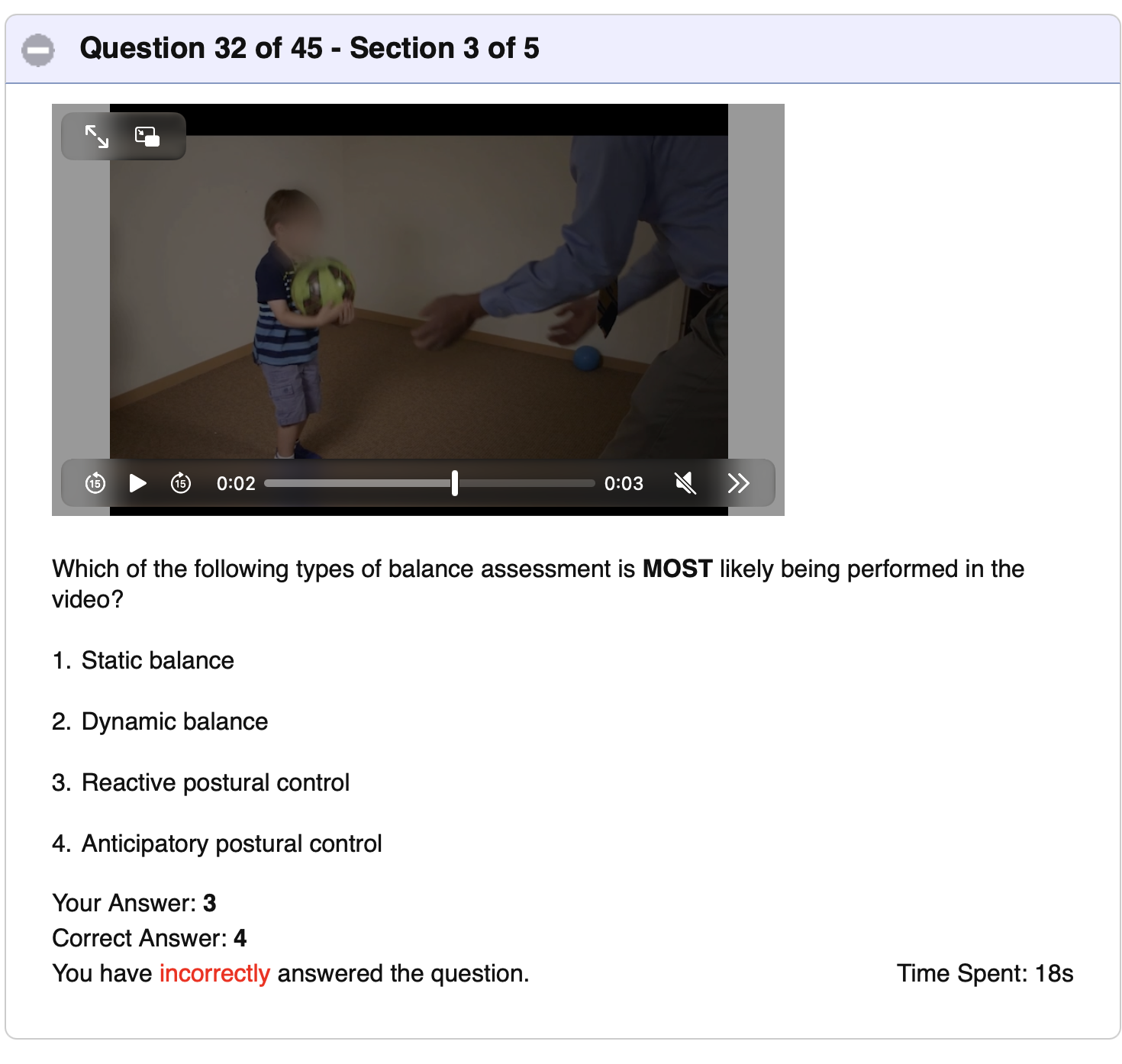
Postural Control:
What is the difference between… tested?
Reactive Postural Control:
Anticipatory Postural Control:
Reactive Postural Control:
Providing an unexpected EXTERNAL PERTURBATION OR CHANGE to test ability to maintain/recover balance
Anticipatory Postural Control:
Assesses ability to COUNTERACT a PREDICTED OR ANTICIPATED postural disturbance
Ex: Catching a Ball

Creep:
Creep is a permanent deformation of tissue through the application of…
Use of a dynamic splint will allow the application of such a load induce WHAT with minimal tissue damage and inflammation?
Low magnitude load over a long period of time
Rapid changes over an extended period of time
When selecting exercises for a patient who has diabetes mellitus, the patient's insulin injection site is important to consider because insulin has which of the following characteristics?
Longer duration of action if large muscle masses are involved in the exercise
Slower absorption if the injection site is in the exercised extremity
Faster delivery into the bloodstream if the injection site is in the exercised extremity
Faster degradation due to metabolic by-products in the exercised extremity
Faster delivery into the BLOODSTREAM if the injection site is in the exercised extremity

Cogwheel Resistance to Passive Manipulations =
Clasp Knife Phenomenon =
Cogwheel Resistance to Passive Manipulations =
Lesions of the Basal Ganglia
Clasp Knife Phenomenon =
Injury to Descending Motor Pathways from Cortex or Brainstem
Which of the following symptom indicates that the patient has a decompensated heart failure?
A. Presence of S2 heart sound
B. Gradual decrease in weight of the patient
C. Presence of indentations when pressure is applied to pretibial area
D. Increased appetite
»
What is this indicative of?
C. Presence of indentations when pressure is applied to pretibial area
Peripheral Edema

» Answer:
Uncompensated:
Forefoot VARUS =
Forefoot VALGUS =
Compensated:
Forefoot VARUS =
Forefoot VALGUS =
» A
Uncompensated:
Forefoot VARUS = Neutral Heel + BIG Toe Up
Forefoot VALGUS = Neutral Heel + LITTLE Toe Up
Compensated:
Forefoot VARUS = Neutral Forefoot + Calcaneal EVERSION
Forefoot VALGUS = Natural Forefoot + Calcaneal INVERSION
Define:
Spatial Relations Disorder:
Inability to…
AKA:
Figure Ground Discrimination:
Inability to…
Form Discrimination:
Inability to…
People is likely to confuse…
Anosognosia:
Spatial Relations
Inability to perceive the relationship of one object in space to another object, or to oneself.
AKA: Spatial Disorientation
Figure-Ground Discrimination:
Inability to visually distinguish a figure from the background in which it is embedded
Form Discrimination
Inability to perceive or attend to subtle differences in form and shape. The patient is likely to confuse objects of similar shape or not to recognize an object placed in an unusual position.
Anosognosia:
Lack of awareness, or denial, of a paretic extremity as belonging to the person, or a lack of insight concerning, or denial of, paralysis and disability.