OCR Chemistry A - Organic reactions & mechanisms
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Alkane to Haloalkane
Halogen and UV light
Haloalkane to Alcohol
nucleophilic sub NaOH, h2so4 catalyst, reflux
Alkene to Alkane
H2, Ni catalyst
Alcohol to Haloalkane
Sodium halide/H2SO4
Alkene to Alcohol
H2O (steam)/H3PO4
Alcohol to Alkene
H3PO4, heat
secondary alcohol to ketone
K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, reflux
Primary alcohol to aldehyde
K2Cr2O7/H2SO4, distil
primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, reflux
Haloalkane to Nitrile
NaCN or KCN, ethanol, reflux
Haloalkane to Amine
NH3/ethanol
EXCESS ETHANOLIC AMMONIA
ketone to secondary alcohol
NaBH4
aldehyde to primary alcohol
NaBH4
Alcohol to Ester
Carboxylic acid/conc. H2SO4
OR
Acid anhydride
Carboxylic acid to ester
Alcohol/conc H2SO4/heat
Aldehyde/Ketone to Hydroxynitrile
NaCN(aq)/H+(aq)
Hydroxynitrile to Amine
H2/Ni
Hydroxynitrile/Nitrile to Carboxylic acid
H2O, HCl, Heat
ester to carboxylic acid
dilute acid, heat
Ester to Carboxylate
OH-, heat
Acyl chloride to ester
alcohol
Acyl chloride to carboxylic acid
H2O
Carboxylic acid to acyl chloride
SOCl2
Acyl chloride to primary amide
NH3
Acyl chloride to secondary amide
primary amine
nucleophilic addition
Carbonyl compounds with NaBH4
Ketones/aldehydes to hydroxynitriles
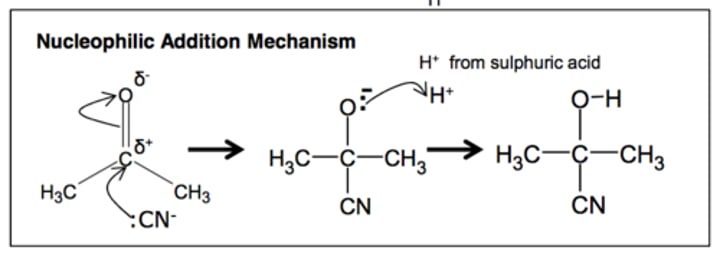
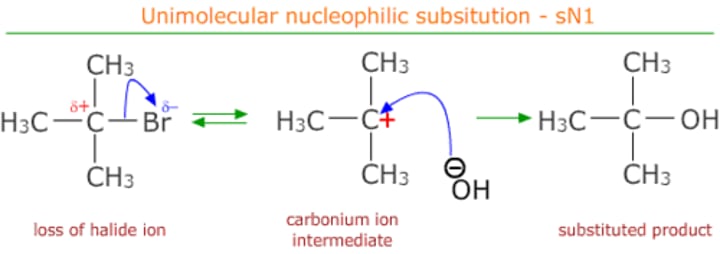
Nucleophilic substitution
Haloalkane to alcohol
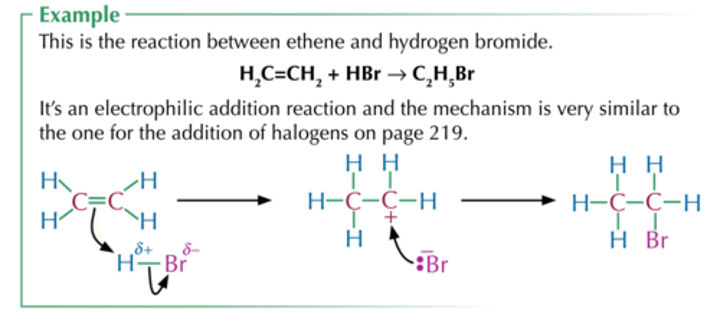
Electrophilic addition
Alkene to haloalkane
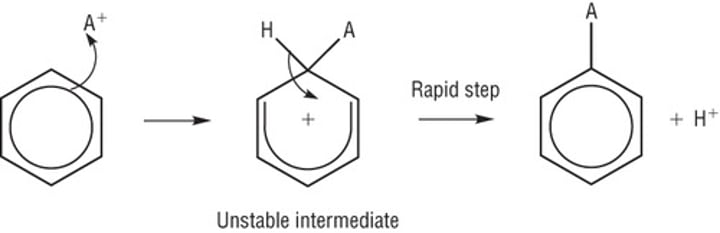
Electrophilic substitution
Benzene
Kekule's model
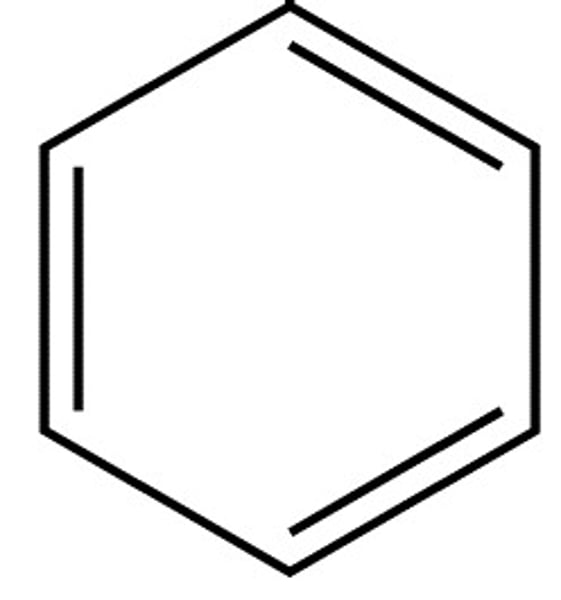
Evidence to disprove Kekule's model
Does not react readily with bromine (does not undergo electrophilic addition)
Hydrogenation enthalpy less exothermic than expected
Length of C-C bonds
Delocalised model of benzene
Each carbon uses 3 out of 4 electrons to bond to 2 other carbons
Each electron has electron in p-orbital
P-orbitals overlap sideways above and below the plane to form ring of electron density
Creates system of pi-bonds
Phenol to Nitrophenol
dilute HNO3
What can phenol not react with?
Na2CO3
Why is phenol more reactive than benzene?
Lone pair of electrons in p-orbital of oxygen atom delocalise into the benzene ring
Electron density increased
Less stable
More susceptible to electrophilic attack
Bromination of phenol
Forms white ppt
Bromine decolourises
Room temp.
Nitration of phenol
Mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol
Room temp.
Test for carbonyl group
Add 2,4-DNPH
If present, orange ppt forms
Recrystallise
Measure melting point
Compare to known values
Test for aldehydes
Tollens reagent: silver mirror if aldehyde present
Silver ions act as oxidising agent
Aldehyde oxidised to carboxylic acid
Why are carboxylic acids soluble in water?
Polar C=O and O-H bonds allowing them to hydrogen bond.
Carboxylic acids and metals
Hydrogen gas formed (effervescence)
Metal disappears
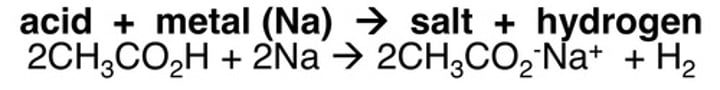
Carboxylic acid and metal oxide
salt, water
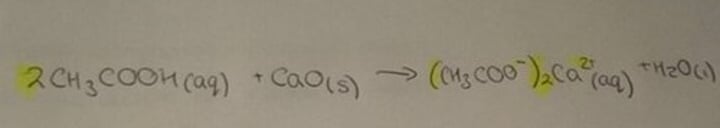
Carboxylic acid and alkali
salt, water
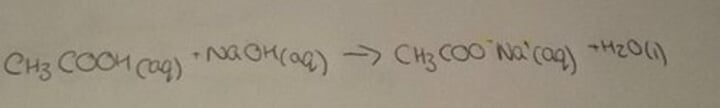
Carboxylic acid and carbonate
Salt, water and carbon dioxide
2 carboxylic acids can condense into a(n) ____________
Acid anydride
Why should preparation of acyl chloride be carried out in a fume cupboard?
Toxic gases produced (HCl, SO2)
Acyl chloride and water
Violent reaction
HCl and carboxylic acid formed
acid anhydride + alcohol
ester + carboxylic acid
Ammonia + acyl chloride
Primary amine + NH4Cl
Primary amine + acyl chloride
Secondary amide + CH3NH3+Cl-
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
nitrile + hcl + 2h20 ---> carboxylic acid + nh4cl
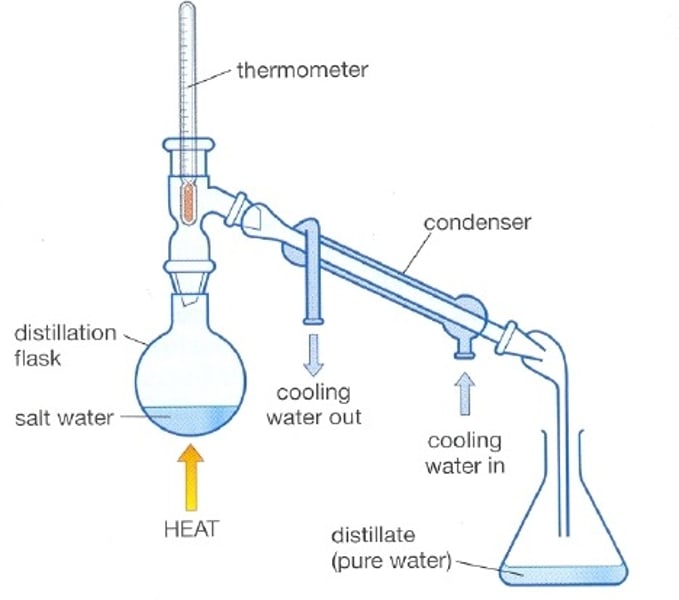
Distillation
A process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
Reflux
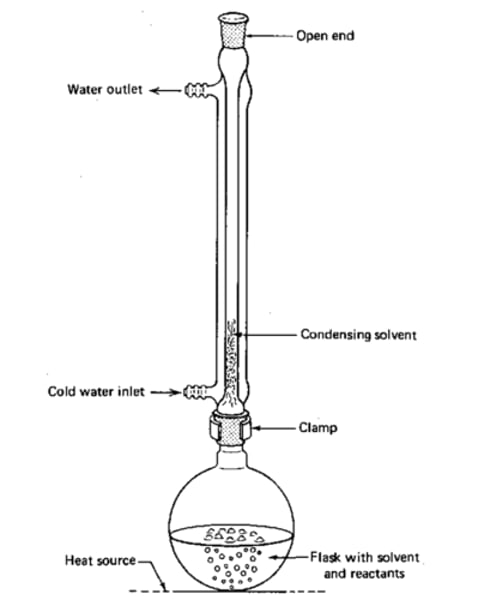
What do anti-bumping granules do?
Prevent large bubbles - even heating
How to purify an organic liquid
Use separating funnel
Add Na2CO3 - this will produce CO2
Invert funnel and open tap to release CO2 - invert until no more gas released
Add more water, the aqueous layer will grow
Separate the layers
Add a drying agent until it stops clumping and a clear solution is formed
Redistil to remove organic impurities
Large range = impure
How to purify an organic solid
Dissolve solid in minimum amount of hot solvent
Filter hot under reduced pressure to remove insoluble impurities (anti-bumping granules)
Leave to cool
Crystals reform
Wash crystals to remove soluble impurities
Dry crystals
Check purity using melting point or TLC
What does a yield over 100% mean?
Not dried properly
What is TMS used for?
Standard reference chemical against which shifts are measured
Gives shift of 0
Stereoisomers
molecules that have the same structural formulas and bonding patterns but different arrangements of atoms in space
Structural isomers
Molecules with the same molecular formula but with different structural arrangements of atoms.
What is a sigma bond?
Orbitals completely overlap
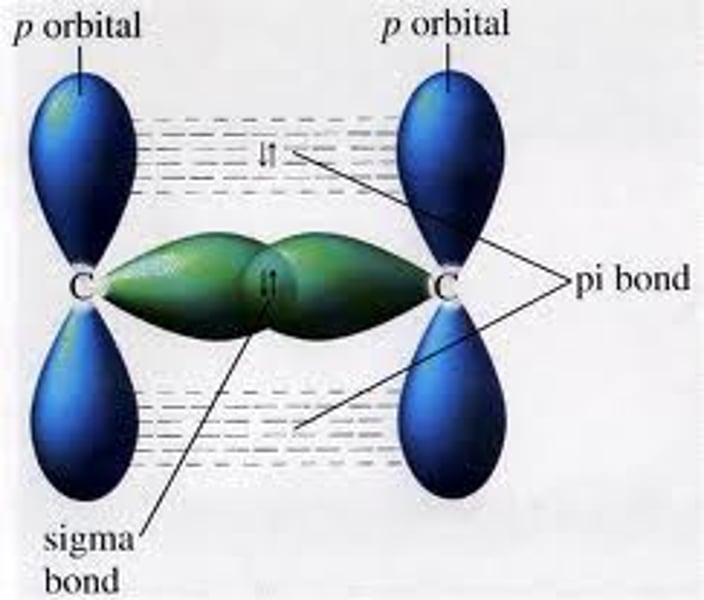
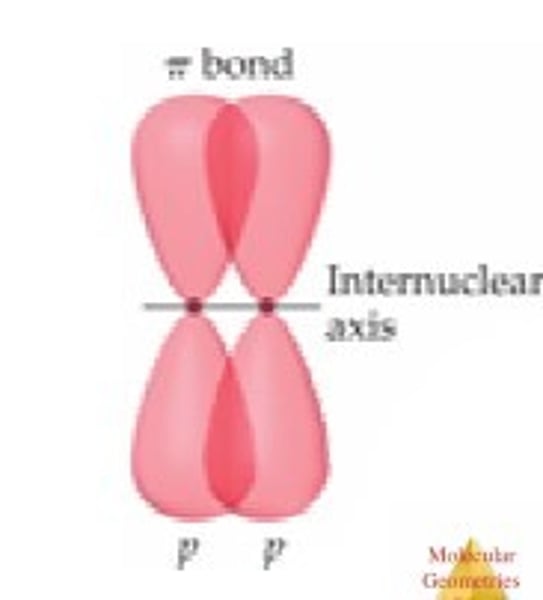
What is a pi bond?
Partials sideways overlap of adjacent p orbitals above and below the plane of the bonding carbon atoms.
Cis/trans isomerism
A special type of E/Z isomerism in which there is a non-hydrogen group and a hydrogen atom on each C of a C=C double bond: the cis isomer (Z isomer) has the H atoms on each carbon on the same side; the trans isomer (E isomer) has the H atoms on each carbon on different sides of the bond.
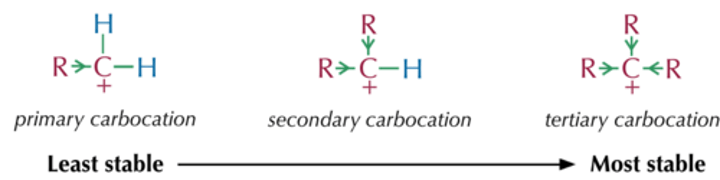
What is the most stable carbocation?
tertiary carbocation
Recycling polymers
Conserve finite fossil fuels
Decrease waste going to landfill
Polymers must be sorted by type
PVC recycling
Disposal and recycling of PVC hazardous due to high chlorine content
Dumping PVC in landfill not sustainable
Grind PVC and use to manufacture new products
waste polymers as fuel
Some have high stored energy value
Can be incinerated to produce steam to power turbine producing electricity
Feedstock recycling
Chemical and thermal processes that can reclaim monomers, gases or oil from waste polymers
Bioplastics
produced from plant starch, cellulose, plant oils and proteins
Biodegradable polymers
polymers that can be broken down by microorganisms into water, carbon dioxide and biological compounds
Photodegradable polymers
Contain bonds that are weakened by absorbing light to start the degradation
How do CFCs destroy ozone?
Have long residence time in trophosphere
UV breaks down CF2Cl2 into CF2Cl and Cl
Chlorine radicals and ozone depletion
Cl + O3 -> ClO + O2
ClO + O -> Cl + O2
Overall
O3 + O -> 2O2
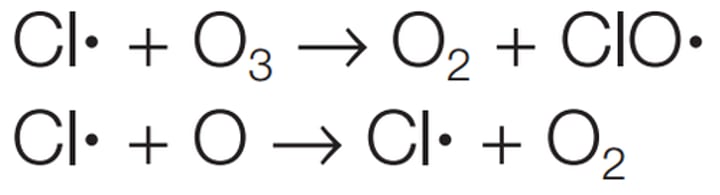
Nitrogen oxide radicals and ozone depletion
