Vertebral Column: Osteology, Ligaments & Neurovasculature
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover the essential vocabulary and definitions related to the vertebral column, including osteology, ligaments, neurovasculature, and anatomical structures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
lumbosacral angle
130-160 degrees.
how many vertebrae
33, 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbral. 5 sacral and 4 coccygeal
Neurovasculature
The network of nerves and blood vessels.
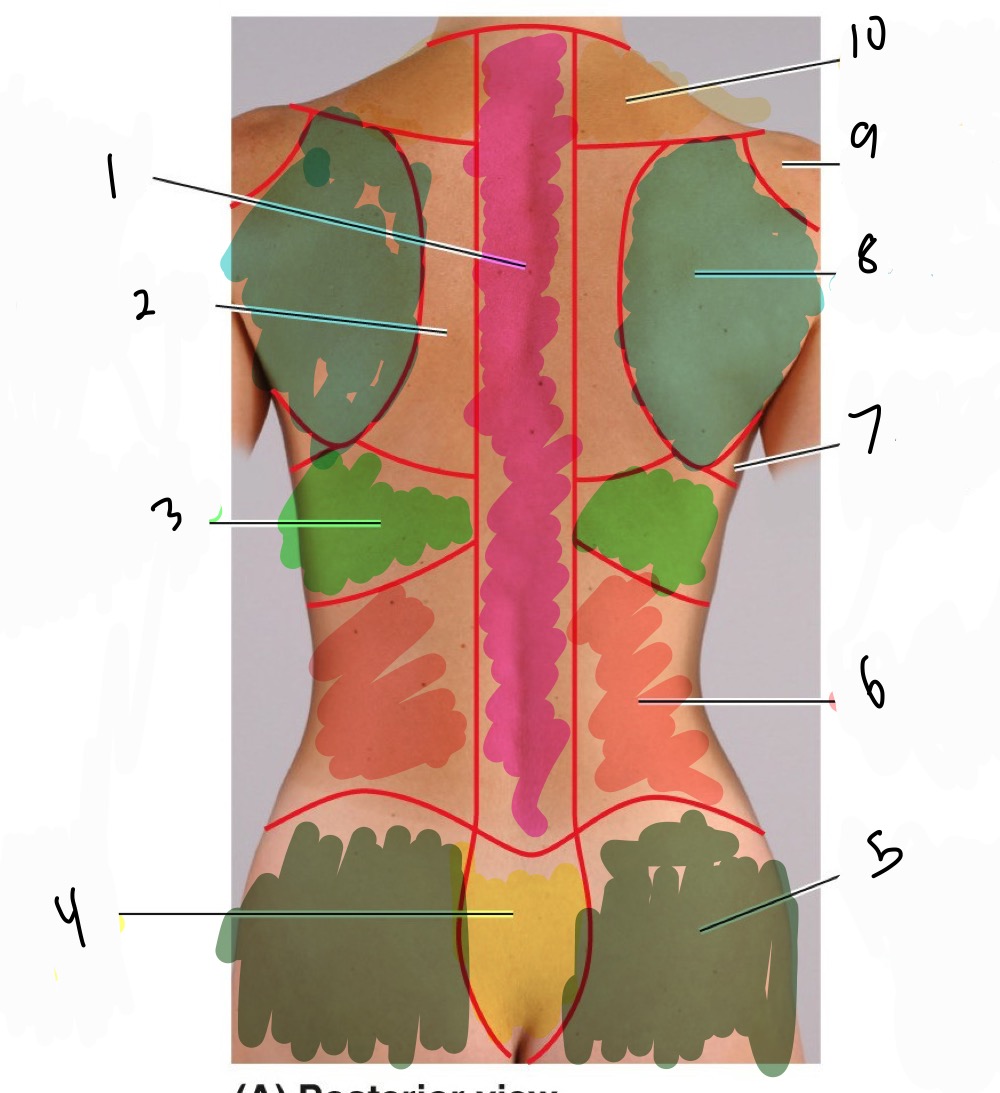
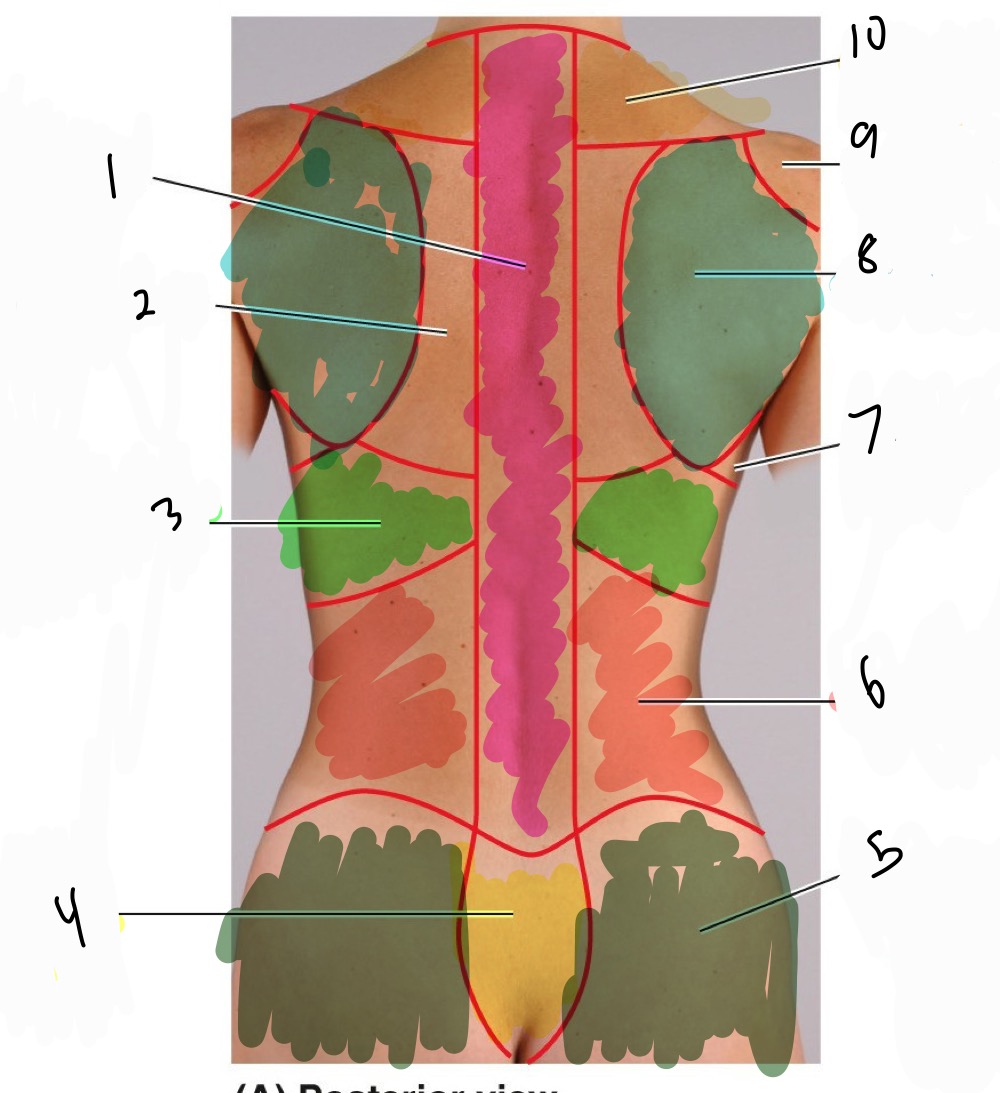
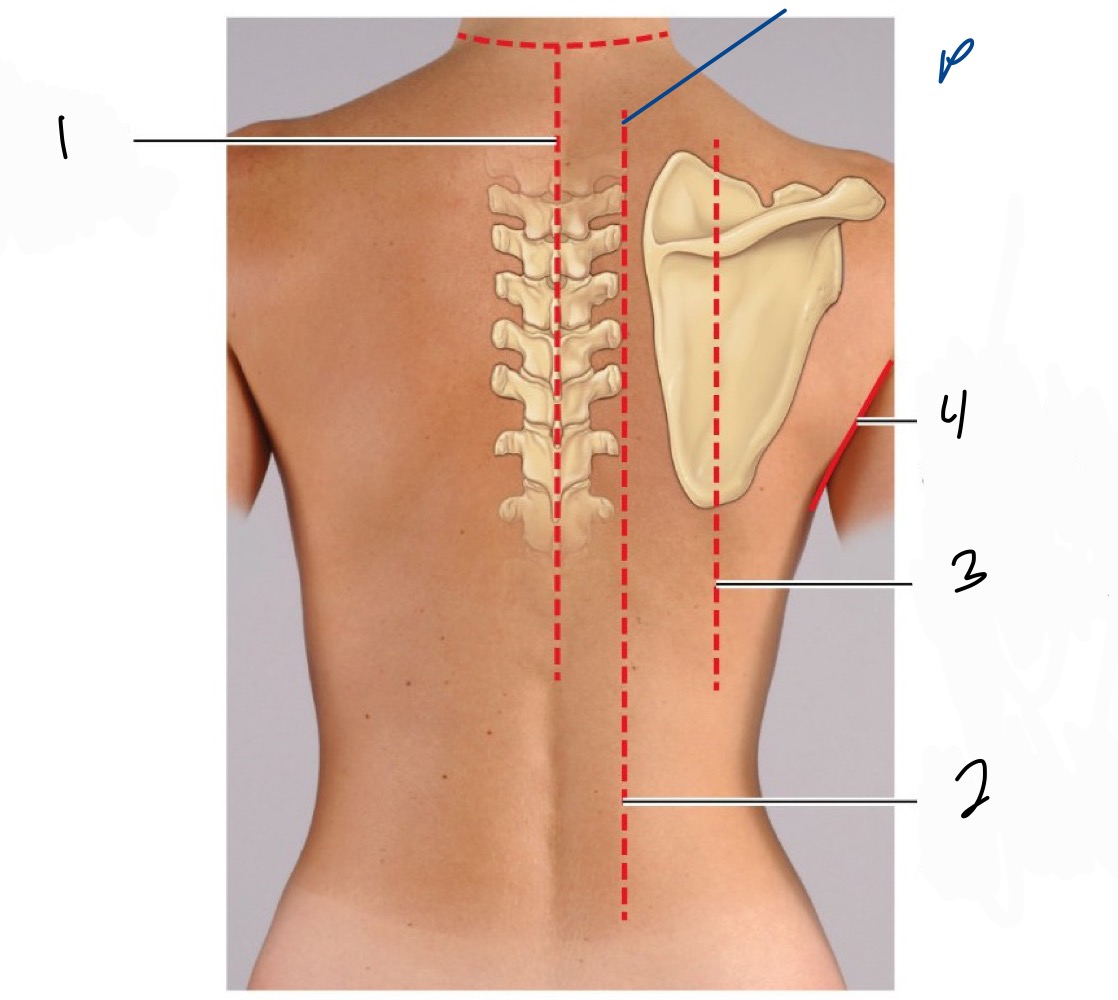
Name 1-10 the regions of the back
1 Vertebral region
2 interscapular egion
3 infrascapular region
4 sacral region
5 gluteal region
6 Lumbar region
7 lateral pectoral region
8 scapular region
9 deltoid region
10 suprascapular region
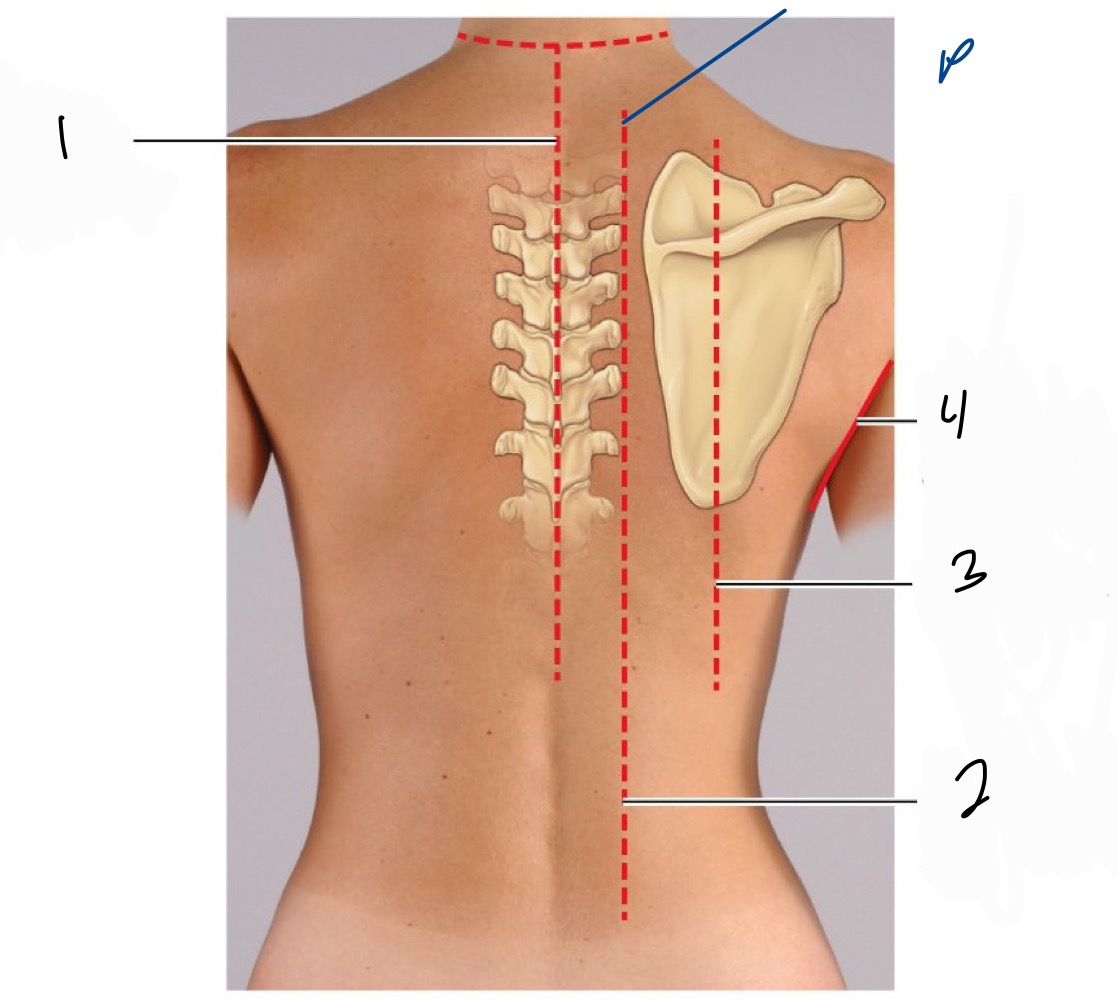
Name the back lines 1-4
1 Post. median line
paravertebral line
scapular line
post. axillary
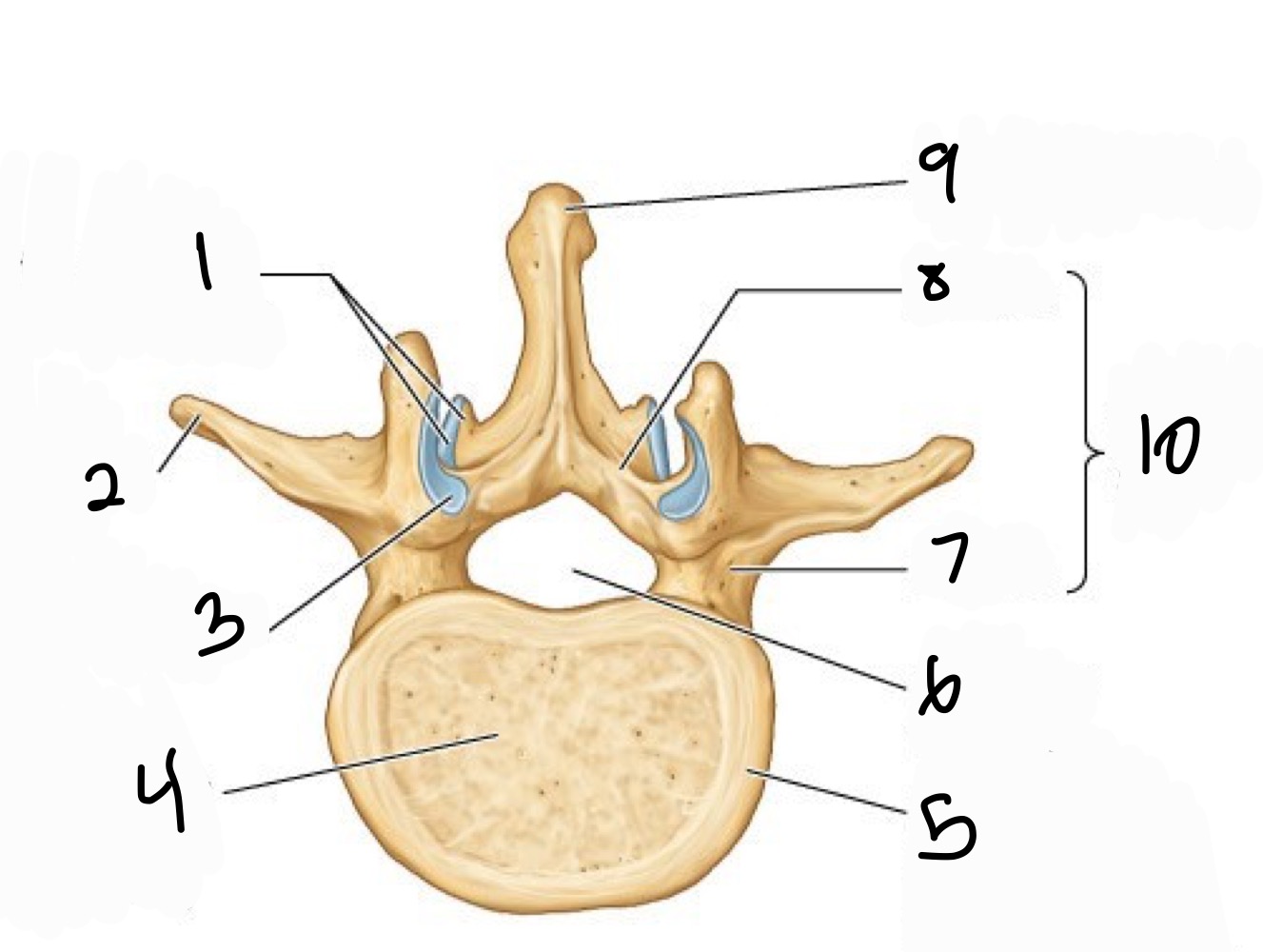
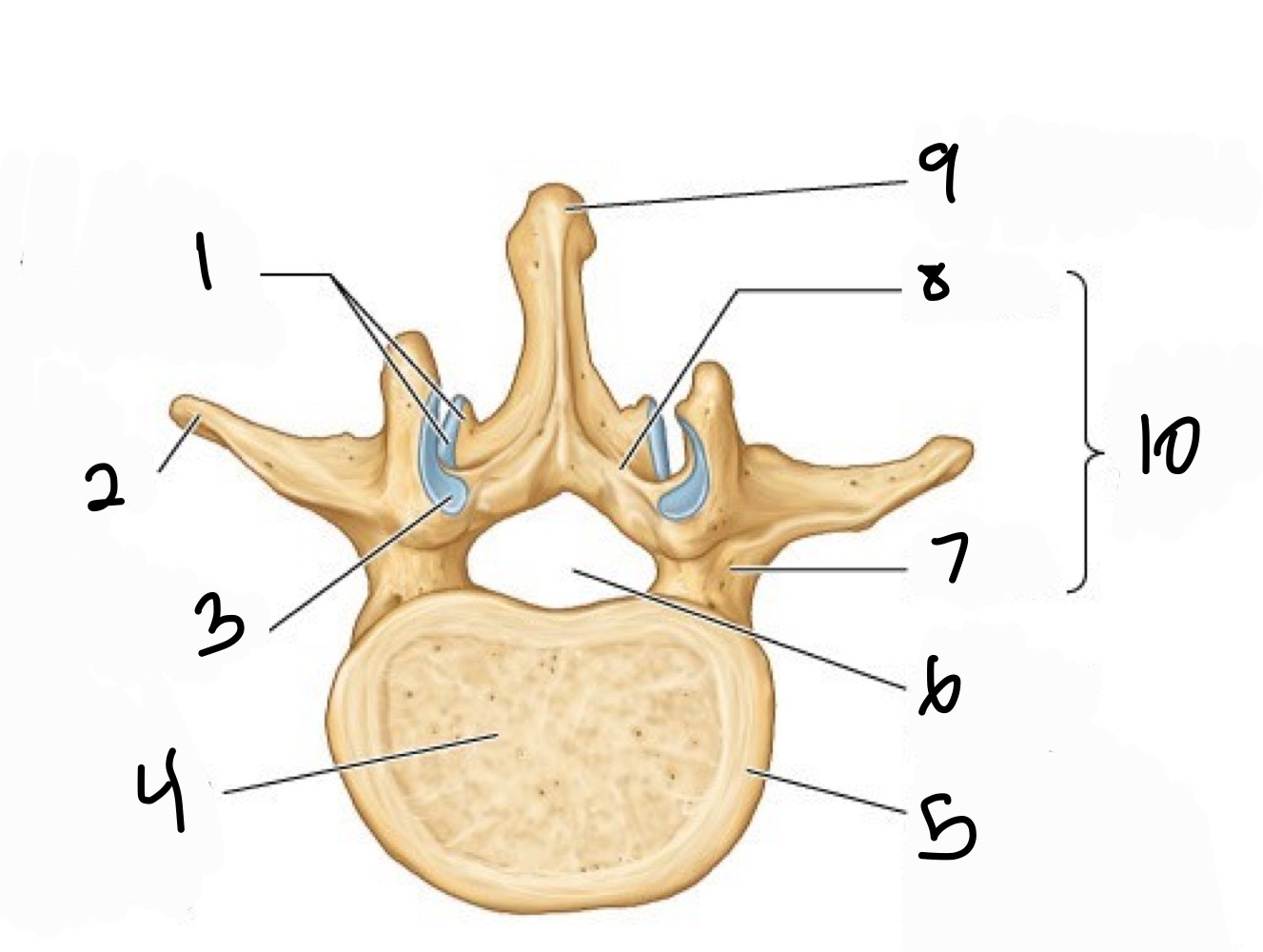
Name 1-10
1 inferior articular provess +facet
2 transverse process
3 sup articular facet
4 vertebral body (from centrum)
5 epipysial rim ( from arular epiphysis)
6 vertebral formanen
7 pedicle
8 Lamina
9 spinous process
10 vertebral arch
Intervertebral discs
Cartilage pads located between vertebrae that provide cushioning.
Lumbosacral angle
The angle formed between the lumbar and sacral regions.
Haematopoiesis
The formation of blood cells in the body.
Zygapophyseal joints
Joints between the articular processes of adjacent vertebrae.
Anterior longitudinal ligament
A ligament that runs down the anterior length of the vertebral column.
Posterior longitudinal ligament
A ligament that runs down the posterior length of the vertebral column.
Interspinous ligaments
Ligaments that connect adjacent spinous processes.
Ligamentum flavum
A ligament made of elastic tissue that connects vertebrae.
Lordosis
Exaggerated inward curve of the spine.
Kyphosis
Exaggerated outward curve of the spine.
Scoliosis
Abnormal lateral curvature of the spine.
Facet joints
Joints formed between the superior and inferior articular processes of vertebrae.
Cervical vertebrae
The seven vertebrae in the neck region.
Thoracic vertebrae
The twelve vertebrae in the upper back.
Lumbar vertebrae
The five vertebrae in the lower back.
Sacral vertebrae
Five fused vertebrae forming the sacrum.
Coccygeal vertebrae
Four fused vertebrae forming the coccyx or tailbone.
Annulus fibrosus
The tough outer layer of intervertebral discs, concentric lamellae of fibrocartilage
Nucleus pulposus
The inner gel-like core of intervertebral discs.
Uncovertebral joints
Joints of luschka found between uncinate processes in the cervical spine. (c3-c6)
Craniovertebral joints
Joints between the skull and the first cervical vertebra.
Atlanto-occipital joint
The joint between the skull (occipital bone) and the first cervical vertebra.
Atlanto-axial joint
The joint between the first and second cervical vertebrae.
Transverse ligament
A ligament that holds the dens of the axis against the atlas.
Functional curves
Curvatures of the spine that improve strength and flexibility.
Craniovertebral joint ligaments
Ligaments stabilizing the craniovertebral region.
Facet syndrome
Discomfort resulting from dysfunction of the facet joints.
Proprioception
The body's ability to sense its position and movement.
Nociception
The sensory perception of pain.
Innervation
The supply of nerves to a specific body part.
C2 vertebra
Also known as the axis, which allows head rotation.
C1 vertebra
Also known as the atlas, which supports the skull.
C1 vertebra characteristics
no body, spinous process, sup. facets articulate with occipital condyle, inf. articulate with C2 (axis)
C7 vertebra
Also known as the vertebra prominens, the most prominent cervical vertebra.
Cervical curvature
The natural curve of the cervical spine.
Thoracic curvature
The natural curve of the thoracic spine.
Lumbar curvature
The natural curve of the lumbar spine.
Sacral curvature
The curvature of the sacral region of the spine.
Zygapophyseal joint alignment
The orientation of zygapophyseal joints affecting vertebral movement.
Intervertebral foramen
The openings between vertebrae that allow passage for spinal nerves.
Posterior median line
A midline reference on the posterior back.
Scapular line
A vertical line used as an anatomical reference point.
Paravertebral line
A line along the sides of the vertebral column.
Articular facets
Surfaces of the vertebrae that form joints.
Vertebral body
The thick, disc-shaped anterior portion of a vertebra.
Pedicle
The part of the vertebra that connects the body to the arch.
Lamina
The part of the vertebra that forms the posterior arch.
Vertebral canal
The space in the vertebral column that contains the spinal cord.
Spinal cord
The bundle of nervous tissue connecting the brain to the body.
Cervical rotation
Movement that occurs at the cervical spine.
Cervical flexion
Bending forward of the cervical spine.
Lumbar flexion
Bending of the lumbar spine forward.
Hyperextension
Excessive extension of a joint beyond its normal range.
Hyperflexion
Excessive flexion of a joint beyond its normal range.
Compression fracture
Fracture due to excessive pressure applied to vertebrae.
Burst fracture
Fracture caused by high-energy impact, typically axial loading.
Radiograph
An imaging technique that uses X-rays to view structures.
Epidural anesthesia
Anesthesia injected into the epidural space.
Transverse process
Lateral projections from each vertebra.
Spinous process
Posterior projection from each vertebra.
Cervical foramen
Openings in cervical vertebrae for spinal nerves.
Transverse foramina
Holes in cervical vertebrae through which arteries pass.
Costal facets
Articulating surfaces for rib attachment.
Craniovertebral region
The area at the junction of the skull and vertebral column.
Nuchal ligament
Ligament running along the back of the neck.
Supraspinous ligament
Ligament connecting the tips of spinous processes.
Anatomical landmarks
Identifiable structures used for reference in anatomy.
Ligamenta flava
Elastic ligaments connecting adjacent laminae.
Sacroiliac joint
Joint between the sacrum and the ilium.
Prevertebral space
The space in front of the vertebral column.
Lateral masses
Structures on the C1 vertebra supporting the superior articular facets.
Occipital condyles
Rounded surfaces on the base of the skull.
Apical ligament
A ligament connecting the dens to the foramen magnum.
Alar ligaments
Ligaments from dens to occipital condyle limiting rotation and fkexion at the atlanto-axial joint.
Tectorial membrane
A strong membrane continuation of the posterior longitudinal ligament to limit flexion and extension
Spinal nerve
Nerves that emerge from the spinal cord.
Vertebral foramina
The openings within vertebrae that create the vertebral canal.
Facet joint effusion
Fluid accumulation in facet joints often leading to pain.
Ligamentous stability
Stability provided to joints by ligaments.
Dynamic stabilizers
Structures that provide stability through movement.
Static stabilizers
Structures that hold joints in place at rest.
Fascia
Connective tissue surrounding muscles and organs.
Dural sac
Sack enclosing the spinal cord and cerebrospinal fluid.
Spinal ligaments
Ligaments associated with the spine providing support.
Innervation lf vertebral collumn
Medial articular branch of post. rami supplying zygapopyhseal joints
recurrent meningeal branch of spinal nerve supplying dura, periostium, ligaments, 1/3 of iv disc and bv
Orthopedic pathology
Study of diseases related to the musculoskeletal system.
Vertebral stability
The ability of the vertebrae to maintain alignment and support.
Spinal stenosis
Narrowing of spaces in the spine leading to nerve compression.
Telematoid mechanisms
Mechanisms responsible for abnormal spinal curvatures.
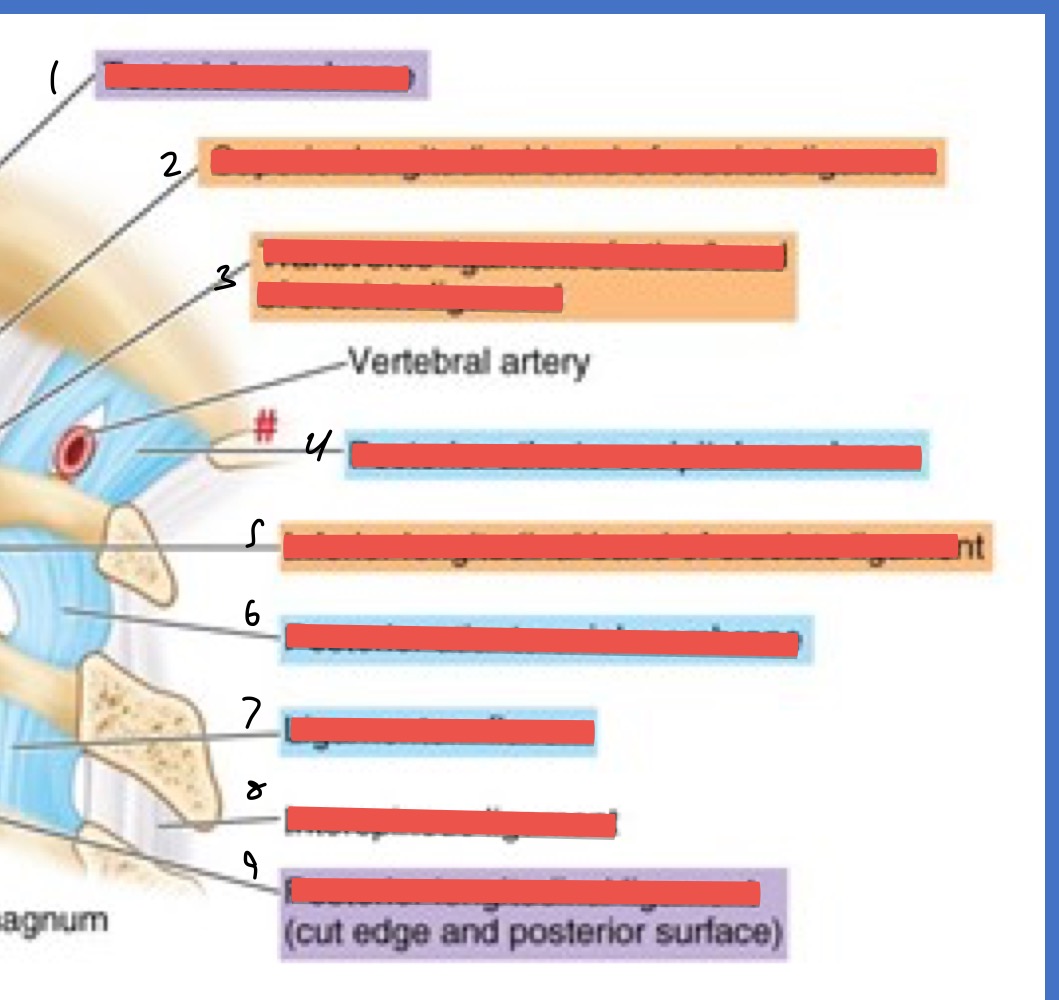
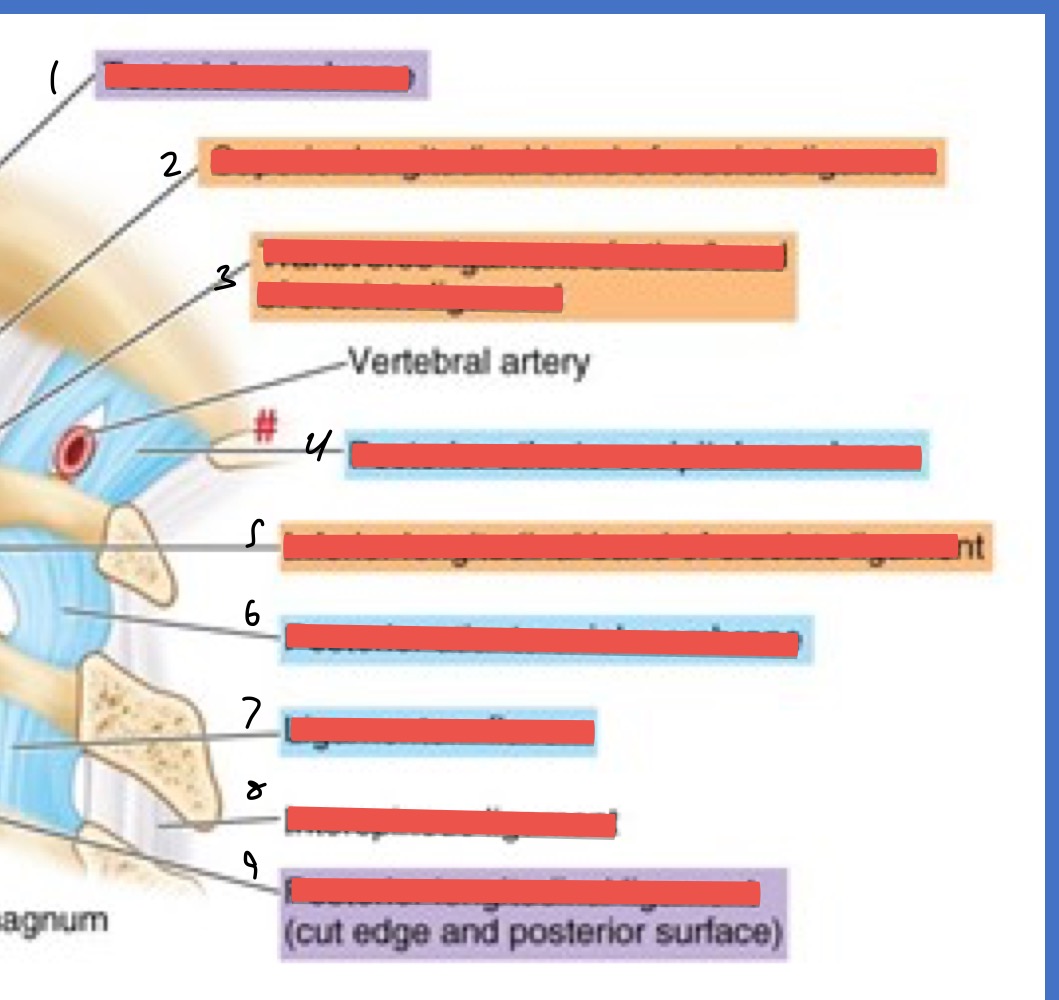
Name 1-9
Tectorial membrane
sup. longitudinal band of cruciate ligament
transverse ligament of atlas
post. atlanto-occipital membrane
inf. longitudinal band of cruciate ligament
post. atlanti-axial membrane
ligamentum flavum
interspinous ligament
post. longitudinal ligament
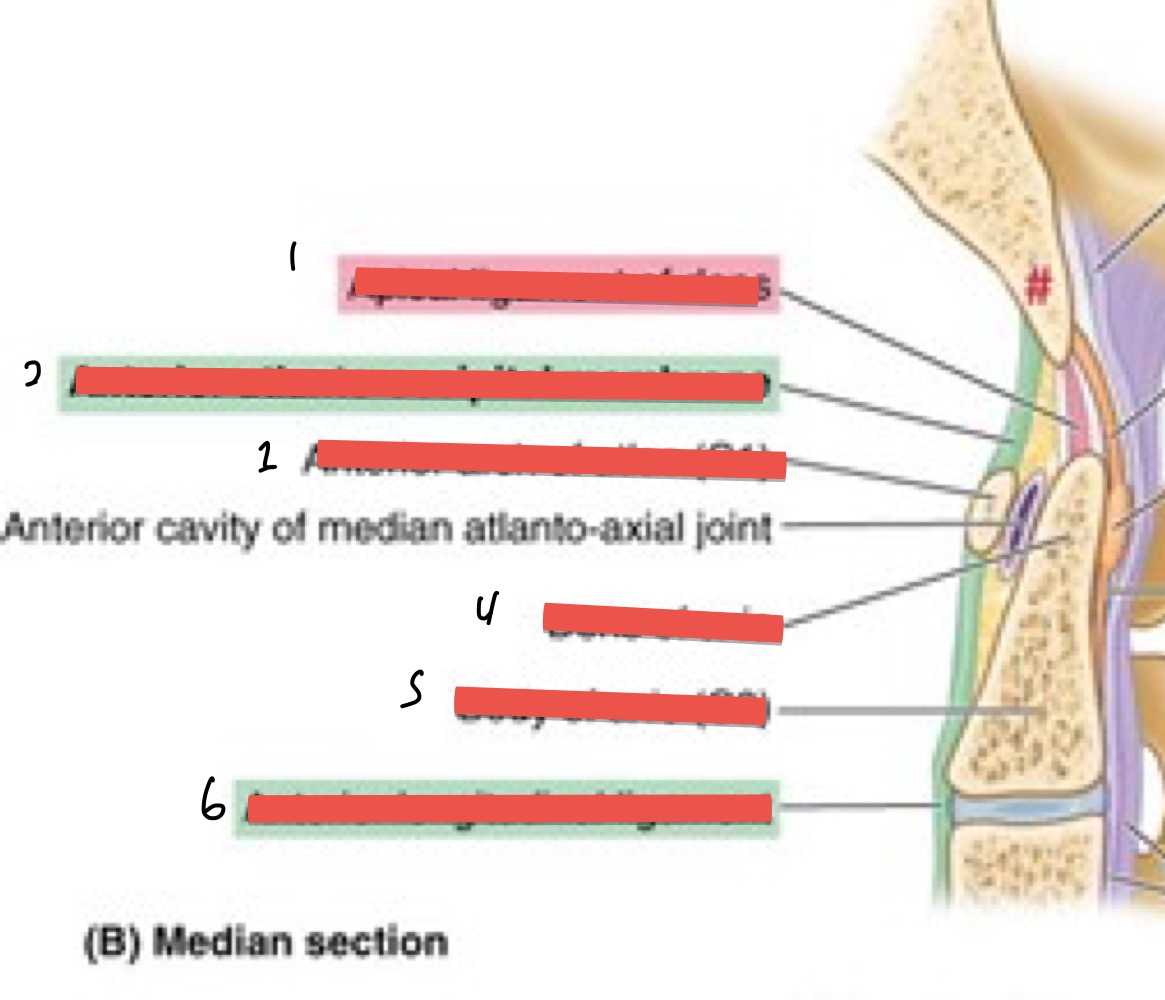
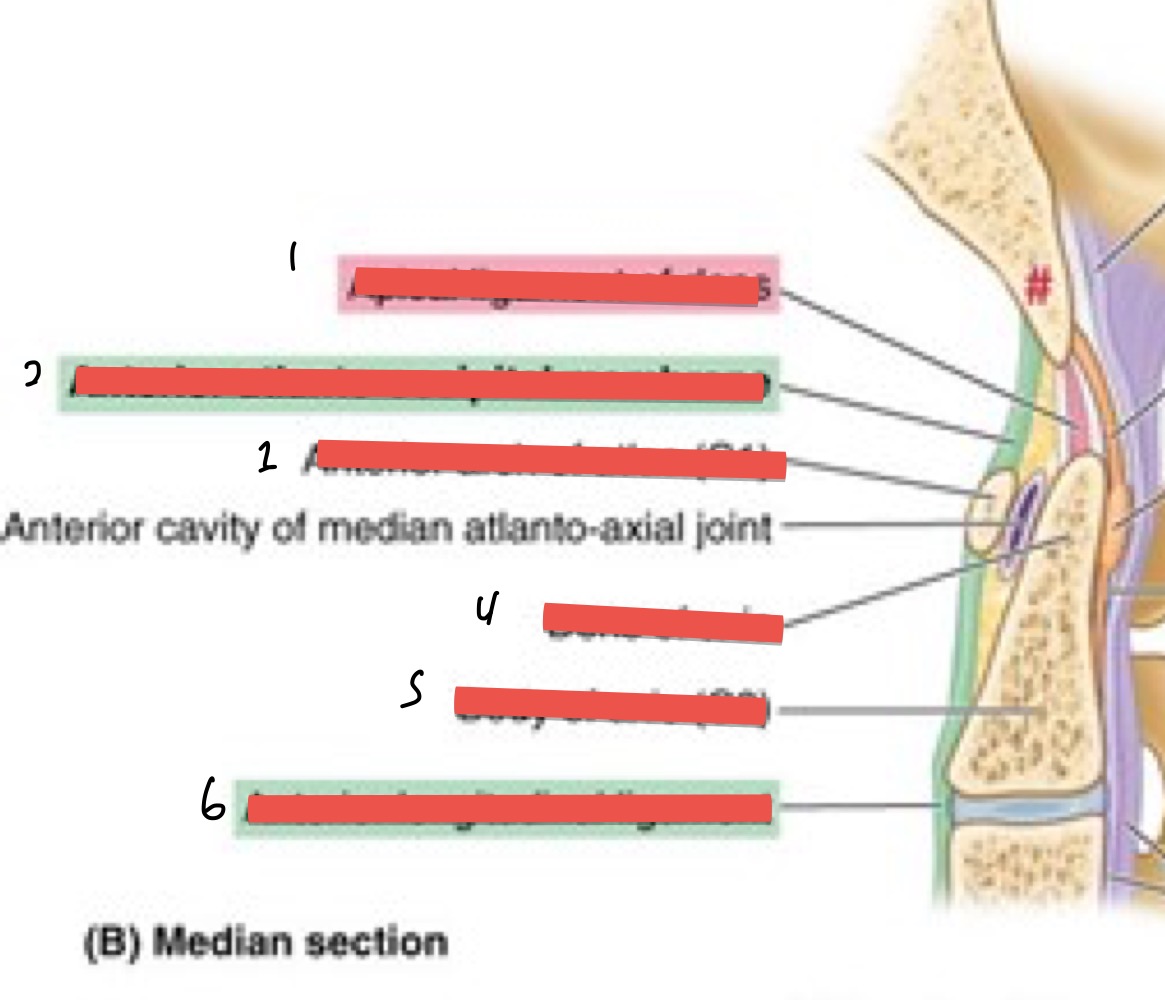
Name 1-6
apical ligament of dens
ant. atlanto-occipital membrane
ant. arch of atlas
dens of axis
body of axis (c2)
ant. longitudinal ligament
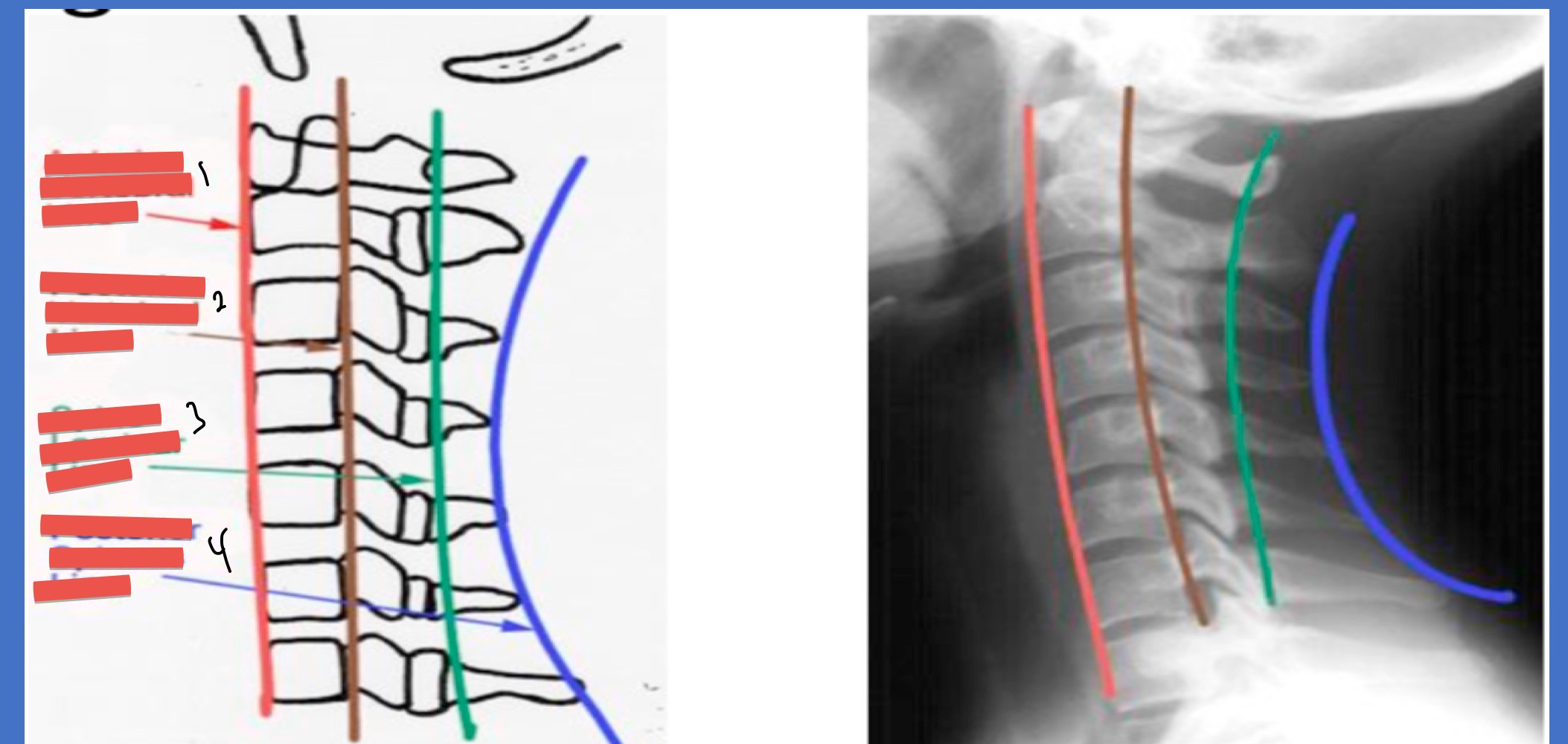
Name the lines 1-4
Ant vertebral line
post. vertebral line
spino-laminar line
post. spinous line
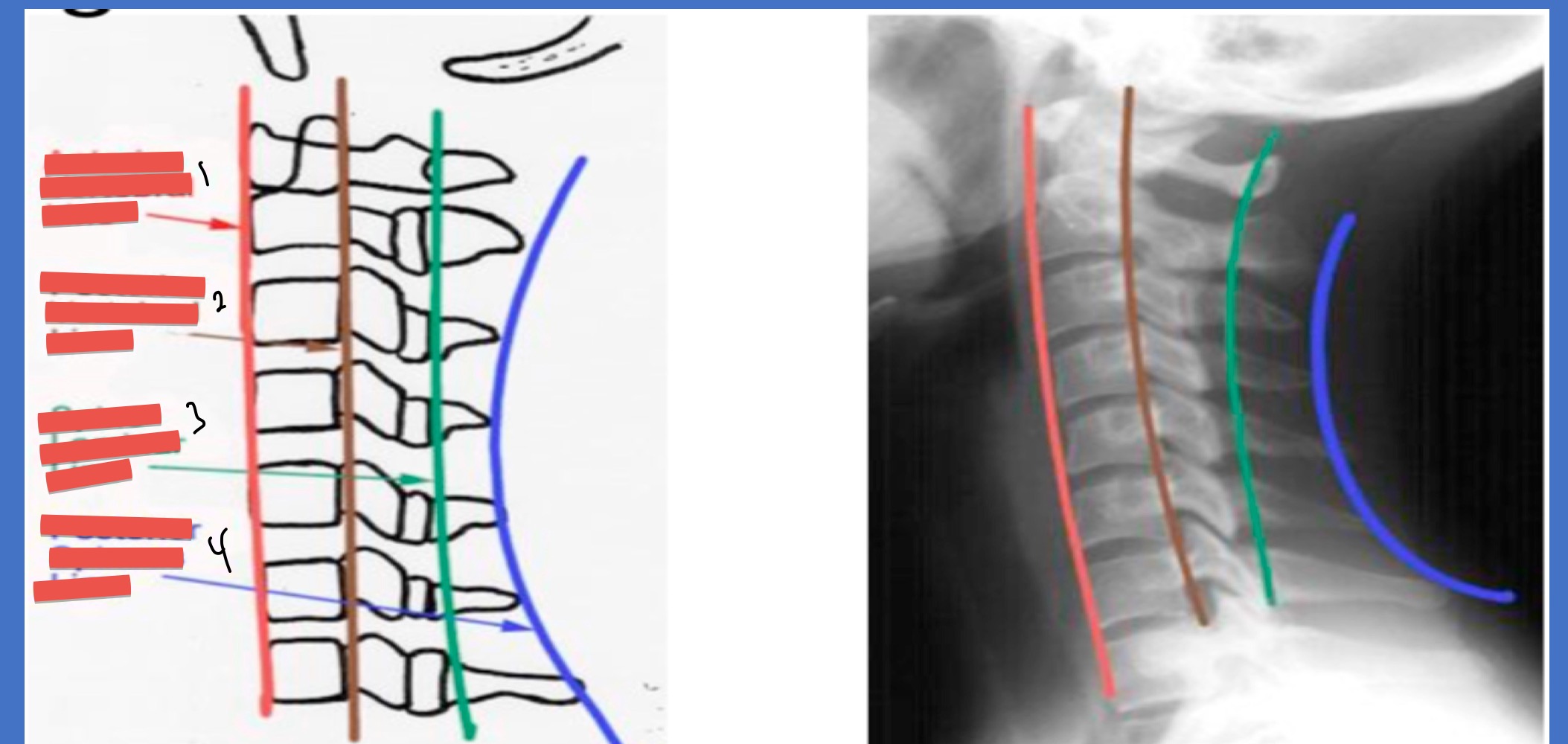
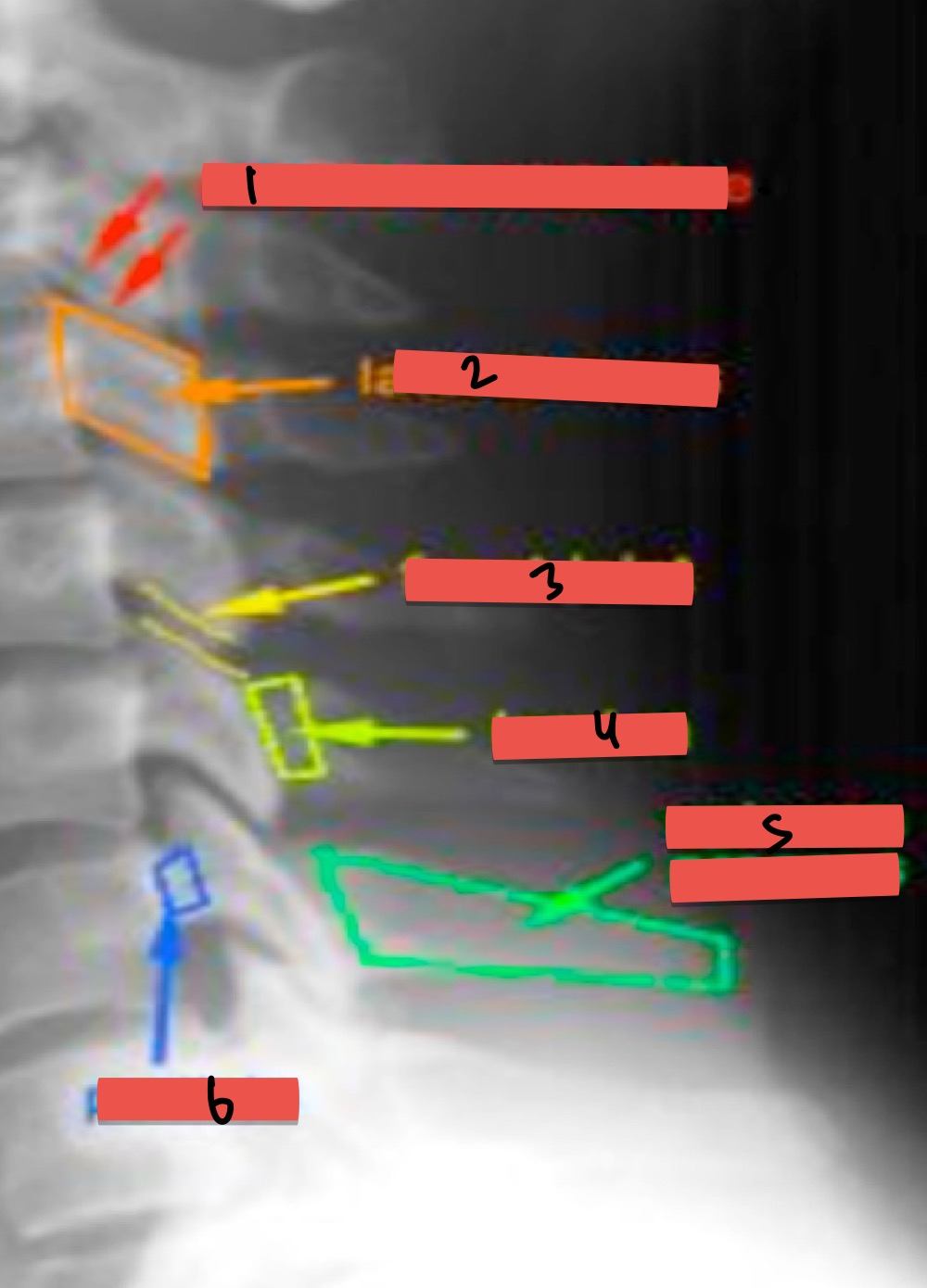
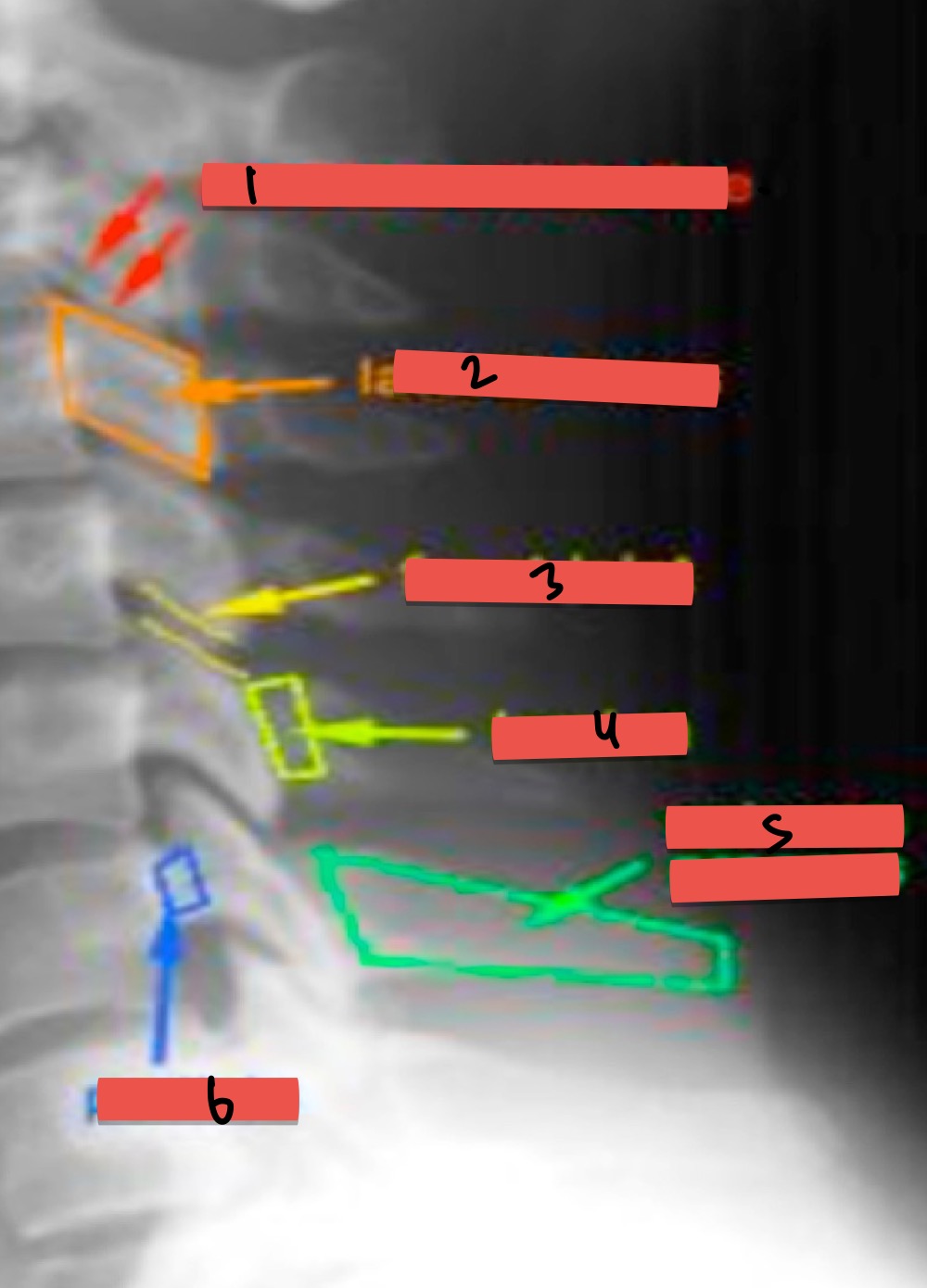
Name Xray presentations
double corticle line
lageral mass
facet joint
lamina
spinous process
pedicle