Lab Practical
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Informative characters are shared by…
two taxa
uninformative characters are shared by…
more than two taxa
invariant characters are shared by…
all taxa
Homologous traits vs homoplasious traits
homology:
common ancestry
Homoplasy:
convergent evolution
morphology and behavior is homoplasy
Linnaean ranking system
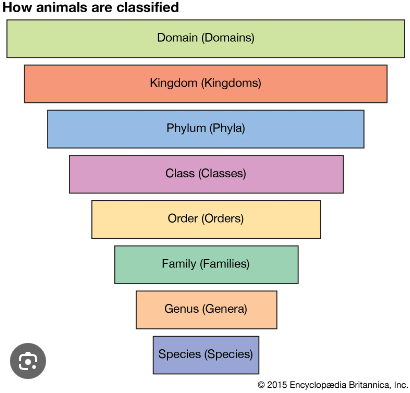
What are microbe morphology, habitat, and pathogenicity all examples of?
homoplasy
Archaea/Bacteria/Eukaryotic/LUCA traits
Archaea:
ether linked membranes, methanogenesis
lack cell wall
Bacteria
peptidoglycan cell wall
Eukaryotes
linear chromosomes, larger ribosomes, mitosis, nucleus
LUCA
circular DNA, DNA bases, amino acid codons, 70S ribosome, lipoprotein membrane, ester linkages
LGT happens through
conjugation
bacteria sex
transformation
absorb DNA outside
transduction
virus involvement
How to tell where a gene came from in a new strain of bacteria? (Different species of bacteria)
LGT = you found different, random mutation = you did not find different
Rhizobium
bacteria that provide plants with nitrogen
Anabaena
in water ferns and fixed nitrogen
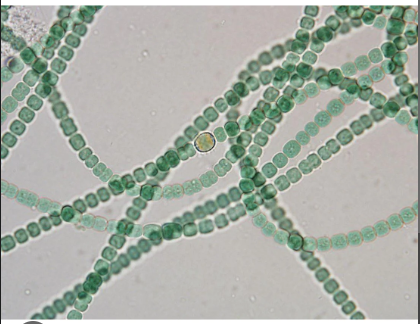
termite hindgut
ciliated microbial eukaryotes found in normal light
archaea seen under UV light
these produce the cellulases needed to break down cellulose
Aerobic, obligate, aerotolerant anaerobes, facultative
aerobic
need oxygen
obligate
can’t tolerate oxygen
aerotolerant
don’t need it but can tolerate
facultative
can use oxygen but doesn’t need to
syntrophy
the secondary metabolites of microbes in one layer are used by microbes in the layer below
Many microbe species are found using metagenomics. What does this mean?
eliminates need to culture microbes, allowing research to be done despite “Great plate count anomaly”
phase contrast microscopy and how to find it on microscope
allows you to view transparent parts of a living specimen under a microscope without using stains as stains would normally kill specimens
move filter wheel to pH1 and replace right eyepiece with phase contrast telescope
Naegleria experiment
can be amoeboid or non-amoeboid
amoeboid = food
non-amoeboid = no food so moving to new environment
cellular slime molds
slugs are aggregations of cells that travel to a new location
slugs eventually form a fruiting body that sexually reproduces
in response to low nutrients
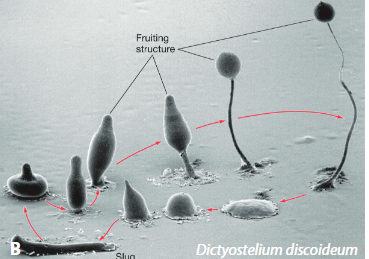
plasmodial slime molds
single cell with many nuclei
move by amoeboid motion
when conditions harsh, either form fruiting body or goes dormant

endosymbiotic origins of organelles (nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast)
nucleus
unknown
mitochondria
alpha proteobacterium
chloroplast
cyanobacteria
evidence of endosymbiosis of organelles
organelles reproduce via binary fission
ribosomes in organelles resemble bacterial ribosomes
cells cannot reproduce organelles if they are removed/destroyed
what is the gametangia in plants?
they house the archegonia and antheridia
archegonia vs antheridia
archegonia = eggs, antheridia = sperm
archegonia lost in angiosperms
antheridia lost in seed plants
How are megaphylls produced and which have them?
overtopping and webbing, all euphyllophytes
Rings on tree stump
older rings pushed outside
wider when more water
because more xylem produced when more water
Body of chara
chara is a glaucophyte
supported by water
water distributed by osmosis
body of liverwort
supported by turgor pressure, water distributed by osmosis
Liverwort
in bryophytes (first one)
gametophyte dominant
swimming sperm

Mosses
in bryophytes (second one)
gametophyte dominant
swimming sperm

hornworts
bryophytes (last one)
gametophyte dominant
swimming sperm

selaginella
lycophyte
heterospory
microphylls
dominant sporophyte
has strobili (cones)
but not separate male and female
micro and megasporangium are housed in same cone
= selginella more likely to self-fertilize
swimming sperm

lycopodium
lycophyte
microphylls
dominant sporophyte
swimming sperm

horsetails
monilophytes
chloroplast DNA inversion
megaphylls
swimming sperm

whisk fern
monilophytes
chloroplast DNA inversion
megaphylls
swimming sperm

ferns
monilophytes
chloroplast DNA inversion
sori on bottom
cluster of sporangia
megaphylls
swimming sperm

cycad
gymnosperms
integument (seed coat)
seeds/pollens
heterospory
BVC
ovule

ginkgo
gymnosperms
integument (seed coat)
seeds/pollens
heterospory
BVC
ovule

gnetophytes
gymnosperms
integument (seed coat)
seeds/pollens
heterospory
BVC
ovule
double fertilization (no endosperm)
vessel elements

conifers
gymnosperms
integument (seed coat)
seeds/pollens
heterospory
BVC
ovule

basal angiosperms
angiosperm
integument (seed coat)
seeds/pollen
heterospory
BVC
ovule
endosperm
double fertilization
carpel, fruit, vessel elements

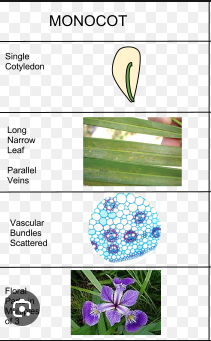
monocot
angiosperm
integument (seed coat)
seeds/pollen
heterospory
LOSS of BVC
ovule
endosperm
double fertilization
carpel, fruit, vessel elements
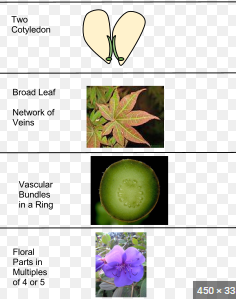
eudicot
angiosperm
integument (seed coat)
seeds/pollen
heterospory
BVC
ovule
endosperm
double fertilization
carpel, fruit, vessel elements
Gymnosperms Cones
has strobili (cones)
separate male and female cones
male = pollen
female = seed (typical looking cone)
central cell of a angiosperm ovule has a ploidy of what?
n + n
when it becomes FERTILIZED then it becomes 3n (endosperm)
Perfect flowers
both male and female parts
imperfect flowers
only have male parts or only has female partspo
humming bird (pollination)
flower is red
no landing pad
lots of nectar
flower has long tube
moth (pollination)
flower is white
sweet fragrance
flower has long tube
bee (pollination)
flower has landing pad
fly (pollination)
flower is purple / brown
mottled appearance
corpse-like odor
parts of a seed
radicle
embryonic root
hypocotyl
embryonic shoot
cotyledon
embryonic leaves derived from nutritive tissue
simple fruits
one flower
one carpel becomes fruit
there can be multiple seeds, as a carpel may contain multiple ovules

aggregate fruits
one flower with multiple carpels that fuse together to produce one fruit

multiple fruits
multiple flowers with a single carpel each fuse to form a multiple fruit
primary vs secondary metabolites
primary is necessary
secondary is not needed but increases survivability
epiphytes
modifications to roots, stems, and leaves that allow them to grow on top of other plants
trichomes
extensions of plant
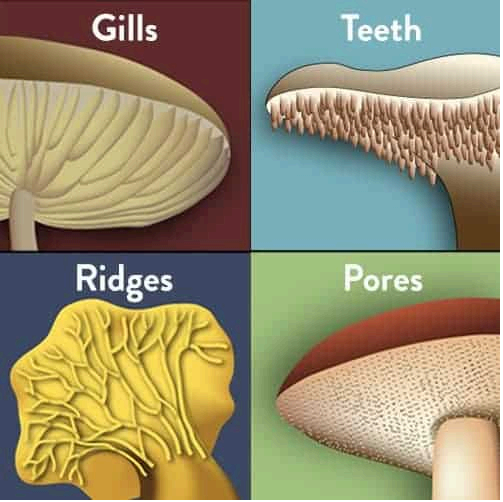
Fungi identification
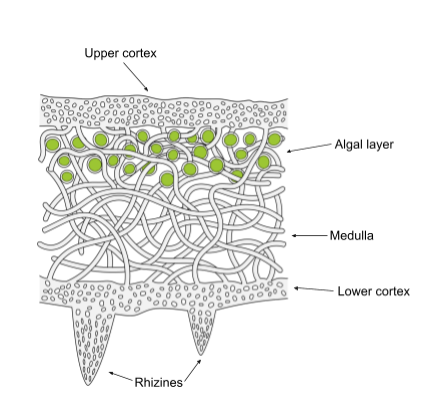
Lichens
symbiosis between fungus and algae or cyanobacteria
most fungi need it
lichens have independently evolved multiple times
Septate vs Aseptate (Fungi)
Septate
cytoplasm of each hyphal cell is separate
Aseptate
cytoplasm is connected
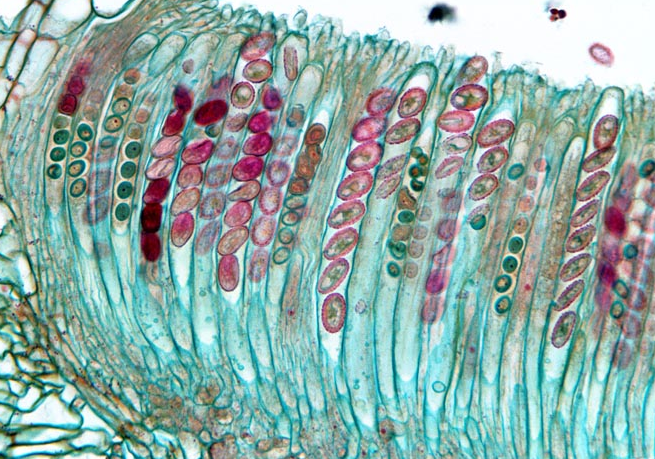
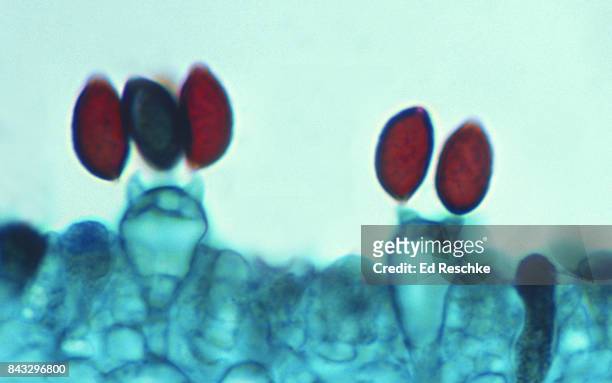
Ascomycetes Identification
Look for ascus where it’s a straight line (8 red dots inside)
Basidiomycota Identification
Look for basidium where there are 4 red spores
Porifera
Sponges
blastula doesn’t develop into a gastrula
meaning no gut
asymmetric
spicules
structures / defense
calcium or glass
not cephalized
aquiferous system
branched water canals
filter feeders
Ctenophores
radial symmetry
diploblastic development
complete gut
nervous system (nerve net)
no connection of nerves into a brain
simple musculature
Cnidarians
sea anemones, corals, sea jellies, cube jellies, hydrozoans
radial symmetry
incomplete gut
diploblastic
ectoderm / endoderm
two body forms: polyp and medusa
polyp is sessile with oral end up
medusa is motile with oral end down
alternate between two forms (not all)
cnidocyte
harpoon thingy
most common type is the nematocyst
nerve net
not cephalized
carnivorous (predatory)
combination of extracellular and intracellular digestion
planula larva
Mollusca
chitons, bivalves, snails, slugs, nudibranchs, clams, mussels, oysters, squids, octopuses, nautiluses
bilateria
protostomes
lophotrochozoa
complete gut
reduce coelom
open circulatory system
has mantle, visceral mass, and foot
mouth with radula
chainsaw tongue
well developed nervous system
trochophore larva
spiral, mosaic cleavage
bivalves
hinge separates shell
suspension-feeders
sessile
not cephalized
everyone else is predatory and cephalized
Annelida
polychaetes, earthworms, leeches
bilateria
protostomes
lophotrochozoa
segmentation
paired setae
chitinous
only polychaetes have paired appendages (parapodia)
closed circulatory system, cutaneous respiration
complete gut
spiral, mosaic cleavage
cephalized
Arthropoda
arachnids, horseshoe crab, centipedes, millipedes, crabs, shrimp, lobsters, barnacles, insects
bilateria
protostomes
ecdysozoa
ecdysis
exoskeleton
segmentation
paired jointed appendages
tagmosis
regional specialization of body
tagmata
paired compound eyes
reduced coelom and open circulatory system
complete gut
cephalized
Echinodermata
bilateria
deuterostomes
penta-radial symmetry
water vascular system
radial, regulative cleavage
triploblasty
complete gut
not cephalized
Chordata
tunicates
bilateria
deuterostomes
postanal tail
notochord
dorsal, hollow nerve cord
segmentation
cephalized
adult tunicates aren’t cephalized
What animal is this?
tunicate in chordata
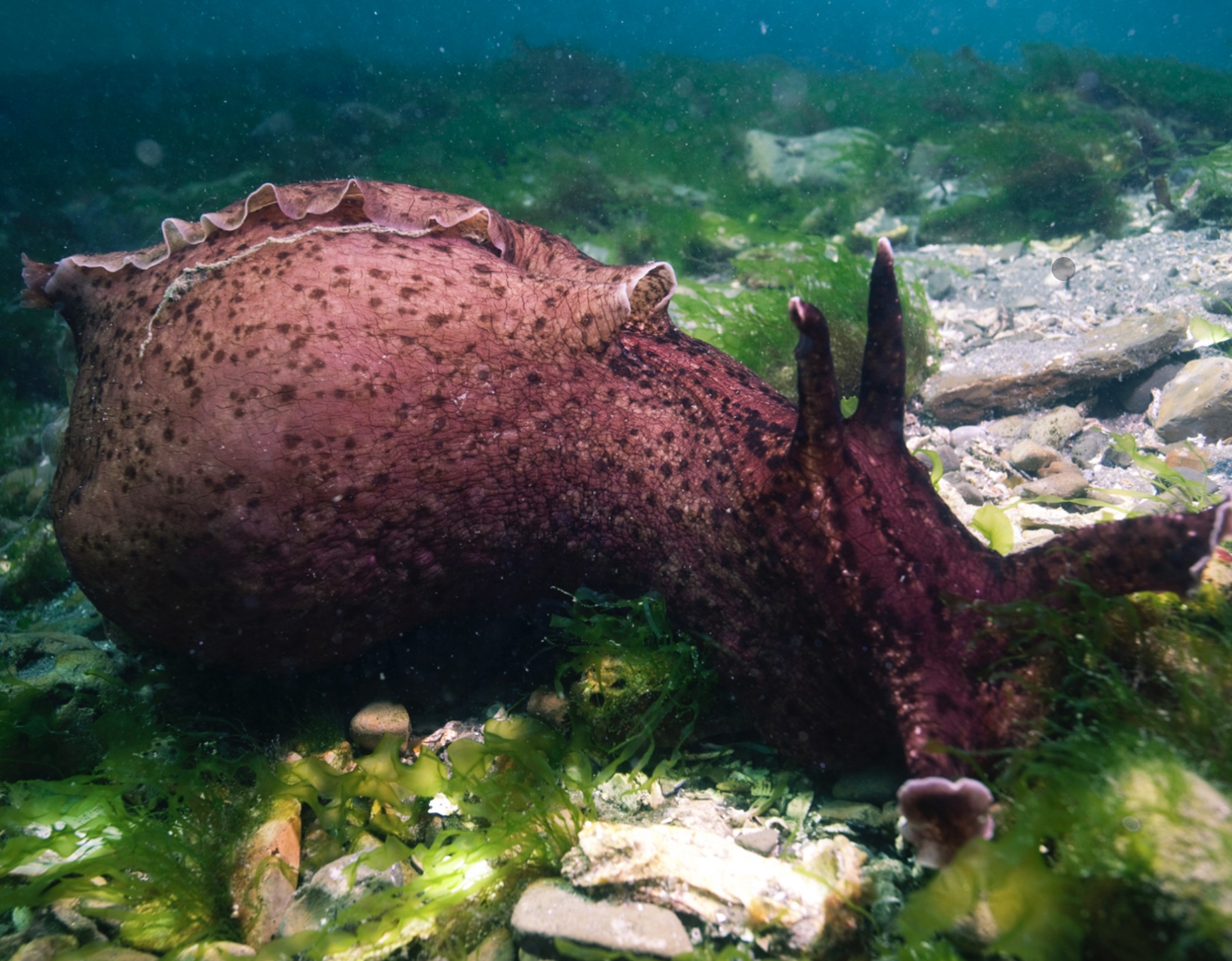

What animal is this?
sea hare in mollusca
What animal is this?
sea cucumber in echinodermata