final exam
1/94
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
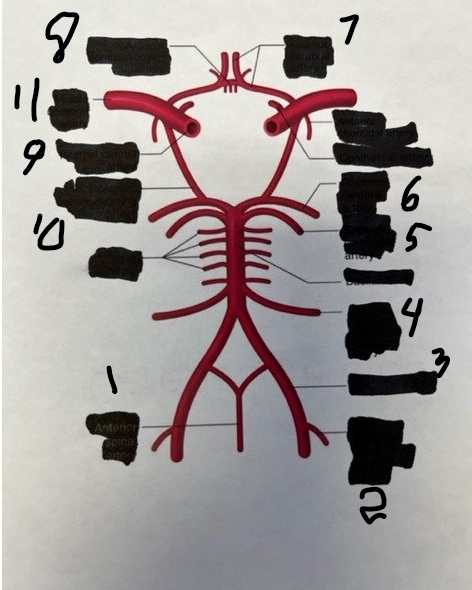
1
spinal
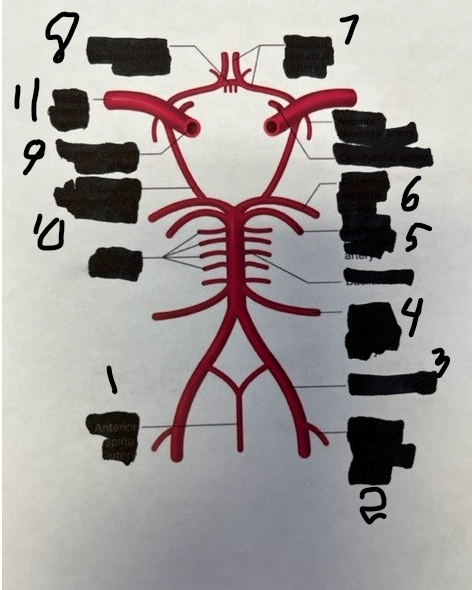
2
posterior inferior cerebellar
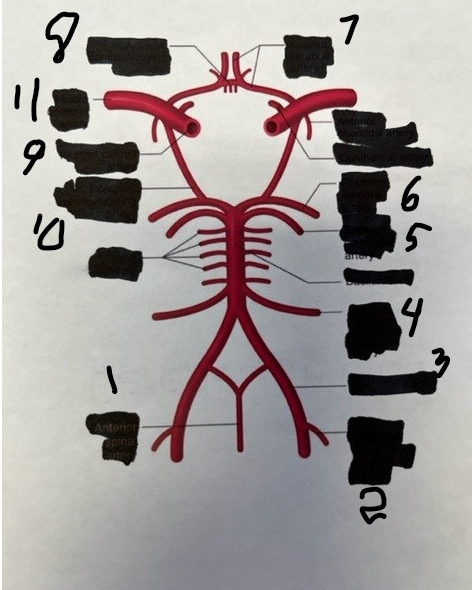
3
vertebral
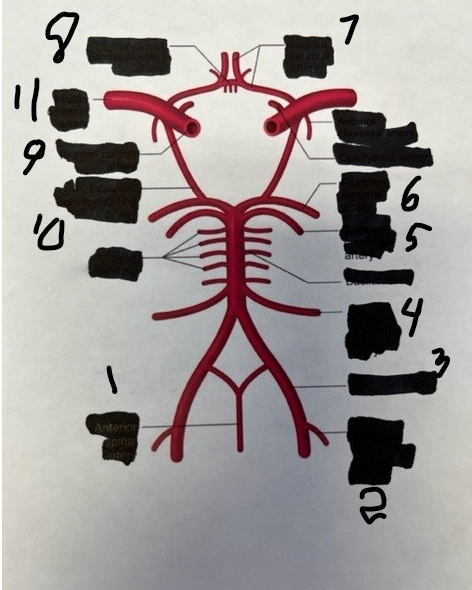
4
anterior inferior cerebellar
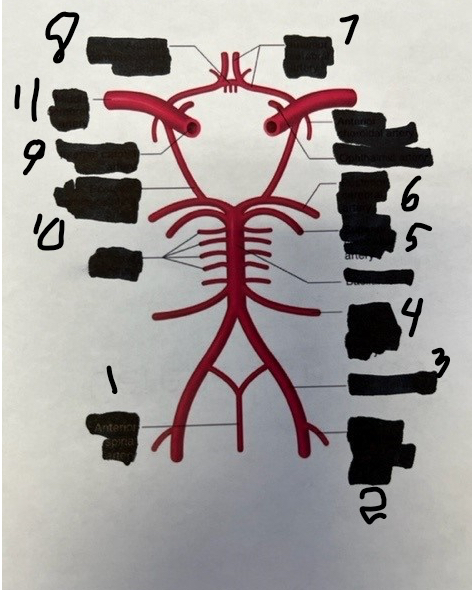
5
superior cerebellar
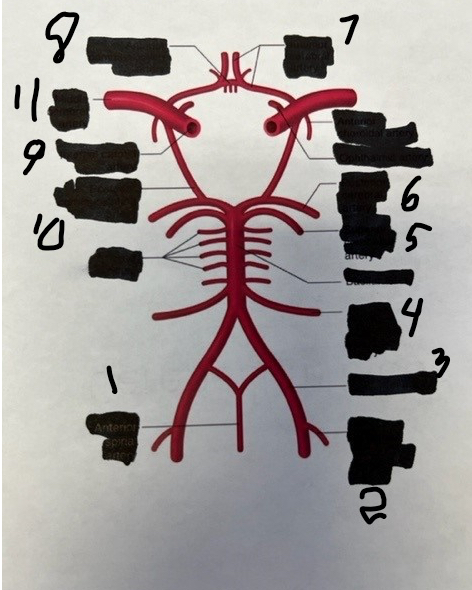
6
posterior cerebral
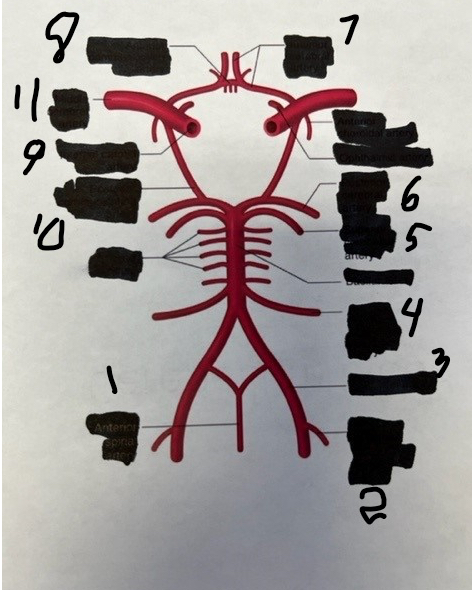
7
anterior cerebral
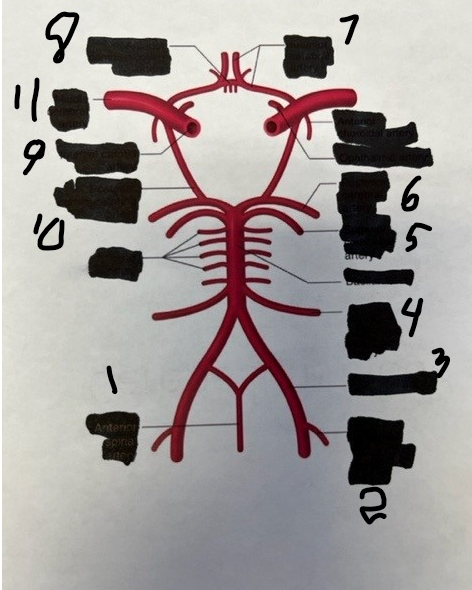
8
anterior communicating
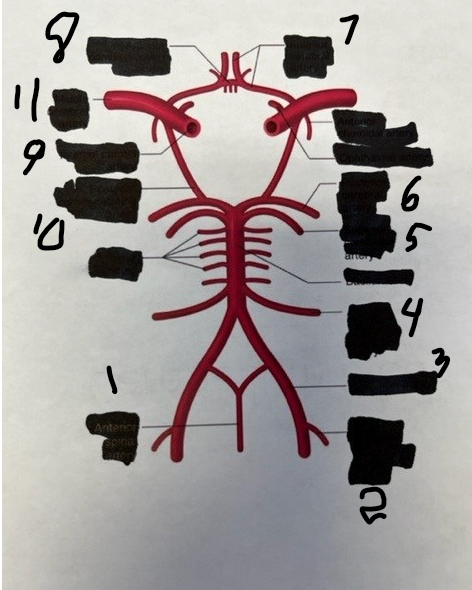
9
internal carotid
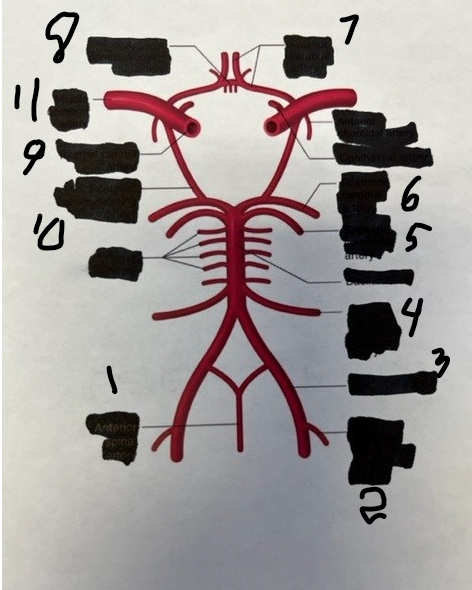
10
posterior communicating
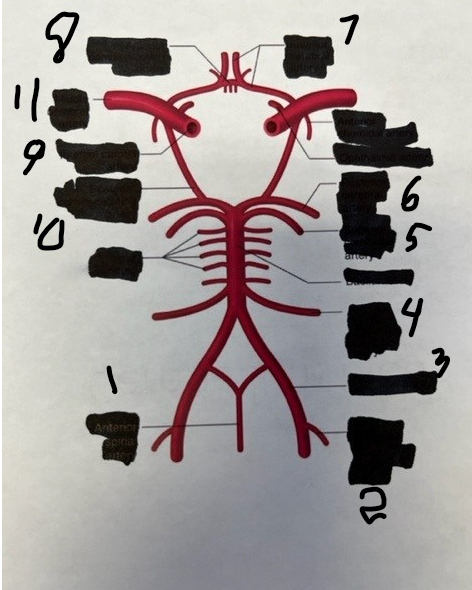
11
middle cerebral
Which cortical potentials are likely to be affected by poor perfusion first?
median nerve
pressure at which a vessel’s wall collapses
critical closing pressure
pressure at which a closed vessel will open
critical opening pressure
To reperfuse a closed vessel, the COP must be much (greater/lesser) than the CCP
greater
Latency (increases/ decreases) when the patient's body temp increases
Decreases
Amplitude (increases/decreases)as body temp increases
Increases
Latency(increases/ decreases) as temp decreases
Increases
Amplitude (increases/ decreases) as temp decreases
Increases
Cortical SSEPs start to decrease at what temp?
32°
Peripheral steps start to increase at what temp?
32°
At what temp are cortical responses absent?
22°
At what temp are peripheral responses absent?
<18°
Hypoxia is indicated by a pulse oximetry below
95%
What responses are the first to be affected by any type of SSEP change?
Cortical
The condition of excessive cow above 45mmhg that decreases blood PH, causing blood to become more acidic
Hypercapnia
The normal pH of blood is between
7.36 -7.44
The percentage of blood solids is defined by
Hematocrit
A hematocrit below what percent y may cause steps to become decreased in amplitude and decreased in latency
10
An infarct of the middle cerebral artery would result in sensory and motor deficits where?
contralateral upper extremity/face
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
motor
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
sensory perception
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
hearing
What is the function of the occipital lobe?
vision
We monitor the posterior 1/3 of the spinal cord via
somatosensory evoked potentials
When recording compound muscle action potentials from the hands, the spinal cord tract that is activated is the
lateral corticospinal tract
The DCML pathway is composed of how many neurons?
3
The lateral corticospinal tract consists of how many neurons?
2
Cranial nerve 7 is the
facial nerve
Patients with a lesion in the lower motor neuron will experience what type of paralysis?
flaccid
The corticospinal tracts in the spinal cord are perfused by which artery?
anterior spinal
The vertex electrode position in the International 10/20 System that is located 50% along the midline anterior-posterior measurement is called
Cz
SSEP change criteria includes what percent amplitude and what latency?
50% amplitude decrease and/or 10% latency increase
During what phase of general anesthesia does intubation occur?
induction
The return of protective reflexes accompanies which phase of general anesthesia?
emergence
Which two anesthetic agents are most detrimental to MEPs and CMAPs?
halogenated agents and nitrous oxide
Which of the following is most potent?
2% isoflurane
Increasing concentrations of isoflurane will have what effect on subcortical potentials?
no effect
Which may be a part of a TIVA regimen?
all of these
What is the preferred level of muscle relaxing (TOF) for EMG monitoring?
4/4 twitches
A depolarizing muscle blocker
binds to acetylcholine receptors and causes prolonged depolarization of the end plate
When testing train of four to assess the level of muscle relaxation, the peripheral nerve should be stimulated how frequently?
2 times/second
Which of the following causes an increase in amplitude of cortical SSEP responses?
ketamine
Which medication is avoided during cranial surgery because it can cause an increase in intracranial pressure?
ketamine
All of the following can cause burst suppression of the EEG except
sufentanyl
What monitoring modality is most highly impacted by anesthetic medications?
visual evoked potentials
Loss of memory of an event
amnesia
All of the following will help create conditions favorable for IONM except
administering a bolus of propofol
A neuron fires an action potential because of a high frequency excitatory input. This is an example of what type of summation?
temporal
Myelinated actions conduct action potentials (rapidly/slowly) and exhibit _____ _____
rapidly; saltatory conduction
The sodium potassium pump pumps how many ions in and out of the cell?
3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in
These structures open and close as the membrane potential changes
voltage-gated ion channels
What is the process by which a neuron is brought to firing threshold by convergent excitatory inputs?
spatial summation
What is the process by which a neuronal membrane potential moves in the positive direction toward threshold of activation?
depolarization
Which neurotransmitter is active at the neuromuscular junction?
acetylcholine
This structure is the initiation point of the action potential
axon hillock
What is the function of the sodium potassium pump?
to establish and maintain the resting potential
What causes the decay of the action potential?
Action potentials do not decay
What effect does neurotransmitter binding to the post-synaptic membrane receptors have on the neuron
not enough information to determine
A monosynaptic reflex occurs
to prevent injury to the body before the central nervous system is even aware it has occurred
If regional blood flow drops below a critical threshold due to a period of significant hypotension, which of the following areas would demonstrate functional changes first?
cerebral cortical grey matter
When spinal cord cerebrospinal fluid pressure increases, _______ must be increased in order to maintain spinal cord blood flow?
spinal cord perfusion pressure
In a patient with chronic hypertension, the systemic blood pressure required to support autoregulation of spinal cord and cerebral perfusion pressure is _____ compared to normal.
increased
Which of the following occurring around the time of an observed attenuation or abolishment of evoked potentials may be the result of significant neurological trauma?
blood pressure spike
Mild to moderate hypothermia usually results in changes in ________ but leaves_______ unchanged.
latency, amplitude
Which of the following are the potential causes of an increase in amplitude of evoked potentials resulting from supramaximal stimulation?
reduction of inhalational agent
Which of the following structures has the greatest ischemic tolerance?
peripheral nerve
A progressive loss of the popliteal fossa, subcortical, and cortical recordings in the left tibial nerve SSEP over the course of 10 minutes during an anterior lumbar interbody fusion is likely the result of
retraction of the left iliac artery
Changes in evoked potentials due to significant acute hypotension causing spinal cord ischemia are generally observed
bilaterally
What is the term given to a region of tissue that is situated between the distributions of two major arterial distributions?
watershed zone
Where is the major spinal cord watershed zone located?
midthoracic
What would be the best first line intervention to significant evoked potential changes which are the result spinal cord ischemia caused by systemic hypotension?
increase the MAP
As a response to decreased blood pressure in the vascular bed of the spinal cord, autoregulation would (constrict/dilate) the arteries supplying the cord
constrict
Decrease in regional cerebral blood flow would cause a change in which modalities?
contralateral SSEP cortical responses and ipsilateral EEG
Which of the following best describes bipolar EMG recording in contrast to referential EMG recording?
bipolar indicates both electrodes are located within a single muscle for greater nerve root specificity
What is the threshold (mA) below which we consider the pedicure likely to be breached?
8
Which of the following could most likely cause a pedicure screw threshold of 3 mA?
medial breach of pedicure
What is the likely effect of testing pedicle screws with 1- twitches out of 4?
increased threshold value
Monitoring spontaneous EMG activity is based on the principle that
irritation or injury of motor nerve fibers in the surgical site results in the activation of muscle potentials
To monitor EMG for the C5 nerve root, you should place electrodes in the
deltoid
When stimulating pedicle screws, the stimulation probe should be plugged into the (anode/cathode)
cathode
A depolarizing muscle blocker
causes excessive release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction
Which of the following is not a characteristic of muscle?
pull ability