AP Bio Chapter 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The chemical context of life
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass.

2
New cards
Element
Any substance that cannot be broken down to any other substance by chemical reactions.
3
New cards
Compound
A substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio.
4
New cards
Essential Elements
A chemical element required for an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce.
5
New cards
Trace Elements
An element indispensable for life but required in extremely minute amounts.

6
New cards
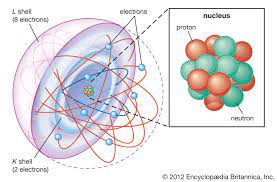
Atom
The smallest unit of matter than retains the properties of an element.
7
New cards
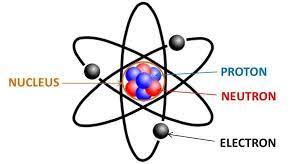
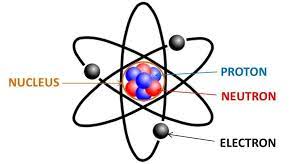
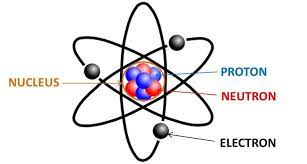
Neutrons
A subatomic particle having no electrical charge (electrically neutral), with a mass of about 1.7 times ten to the negative 24 g, found in the nucleus.
8
New cards
Proton
A subatomic particle with a single positive electrical charge, with a mass of about 1.7 times ten to the negative 24 g, found in the nucleus of an atom.
9
New cards
Electrons
A subatomic particle with a single negative electrical charge and a mass about 1 two-thousandths that of a neutron or proton. One or more electrons move around the nucleus of an atom.
10
New cards
Atomic Nucleus
An atom’s dense core, containing protons and neutrons.
11
New cards
Dalton
A measure for mass and subatomic particles; the same as the atomic mass unit, or amu.

12
New cards
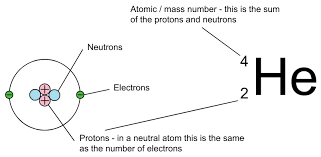
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, unique for each element and designated by a subscript.
13
New cards
Mass Number
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
14
New cards
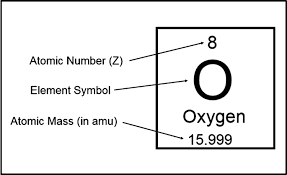
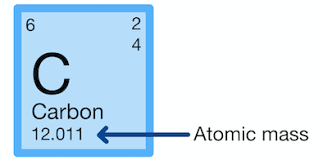
Atomic Mass
The total mass of an atom, equivalent to the mass in grams of 1 mole of the atom. (For an element with more than one isotope, the atomic mass is the average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes, weighted by their abundance.)
15
New cards
Isotopes
One of several atomic forms of an element, each with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons, thus differing in atomic mass.
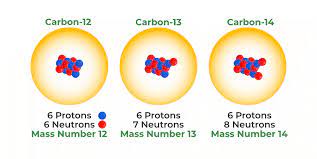
16
New cards
Radioactive Isotope
An isotope (an atomic form of a chemical element) that is unstable; the nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off detectable particles and energy.
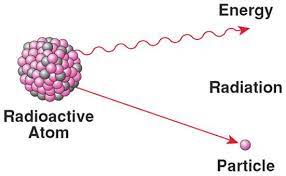
17
New cards
Half-Life
The amount of time it takes for 50 percent of a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay.
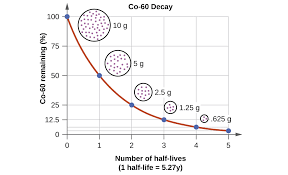
18
New cards
Radiometric Dating
A method for determining the absolute age of rocks and fossils, based on the half-life of radioactive isotopes.
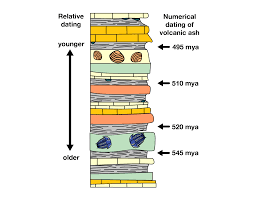
19
New cards
Energy
The capacity to cause change, especially to do work (to move matter against an opposing force).

20
New cards
Potential Energy
The energy that matter possesses as a result of its location or spatial arrangement (structure).

21
New cards
Electron Shells
An energy level of electrons at a characteristic average distance from the nucleus of an atom.
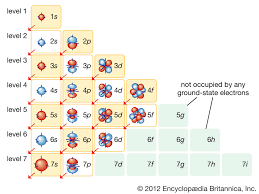
22
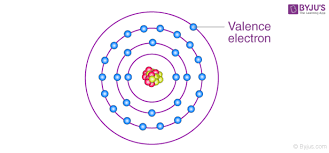
New cards
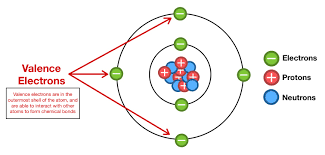
Valence Electrons
An electron in the outermost electron shell.
23
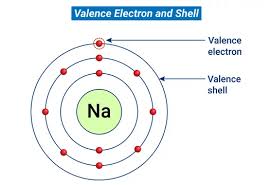
New cards
Valence Shell
The outermost energy shell of an atom, containing the valence electrons involved in the chemical reactions of that atom.
24
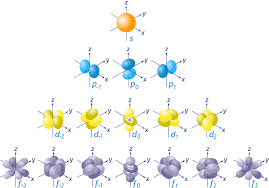
New cards
Orbital
The three-dimensional space when an electron is found 90% of the time.
25
New cards
Chemical Bonds
An attraction between two atoms, resulting from a sharing of outer-shell electrons or the presence of opposite charges on the atoms. The bonded atoms gain complete outer shell electrons.
26
New cards
Covalent Bond
A type of strong chemical bond in which two atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons.
27
New cards
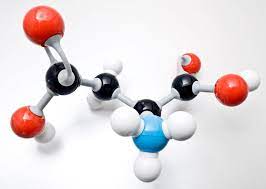
Molecule
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
28
New cards
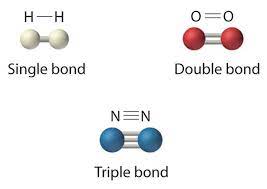
Single Bond
Single covalent bond; the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms.
29
New cards
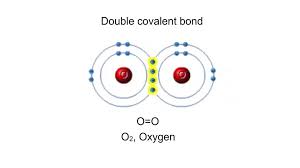
Double Bond
A double covalent bond; the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons by two atoms.
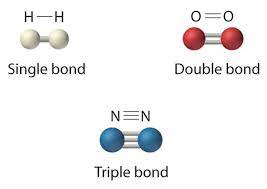
30
New cards
Valence
The bonding capacity of a given atom; the number of covalent bonds an atom can form, which usually equals the number of unpaired electrons in its outermost (valence) shell.
31
New cards
Electronegativity
The attraction of a given atom for the electrons of a covalent bond.

32
New cards
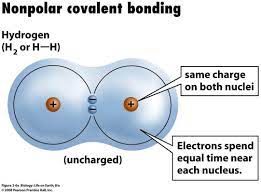
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
A type of covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally between two atoms of similar electronegativity.
33
New cards
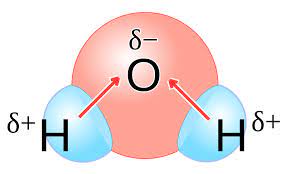
Polar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond between atoms that differ in electronegativity. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative and the other atom slightly positive.
34
New cards
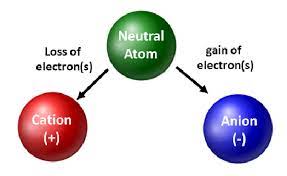
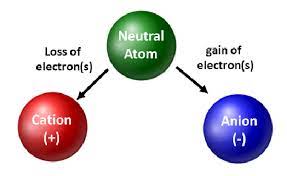
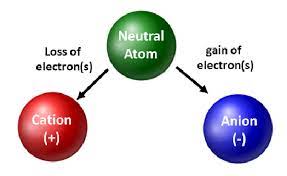
Ions
An atom or group of atoms that has gained or lost one or more electrons, thus acquiring a charge.
35
New cards
Cation
A positively charged ion.
36
New cards
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
37
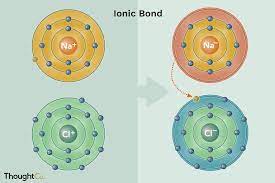
New cards
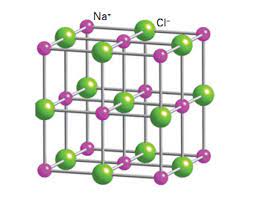
Ionic Bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
38
New cards
Ionic Compounds
A compound resulting from the formation of an ionic bond; also called a salt.
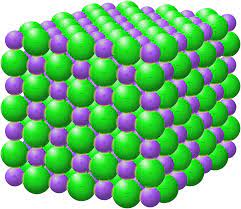
39
New cards
Salts
A compound resulting from the formation of an ionic bond; also called an ionic compound.
40
New cards
Hydrogen Bond
A type of weak chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of a polar covalent bond in one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule or in another region of the same molecule.
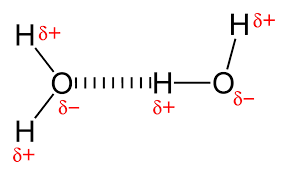
41
New cards
Van Der Waals Interactions
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial changes.
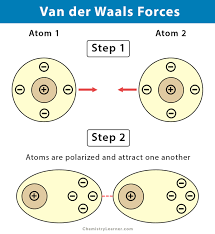
42
New cards
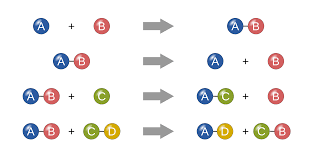
Chemical Reactions
The making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter.
43
New cards
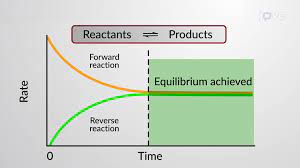
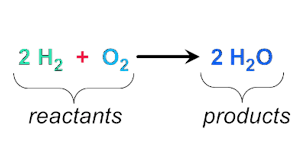
Reactants
The starting material in a chemical reaction.
44
New cards
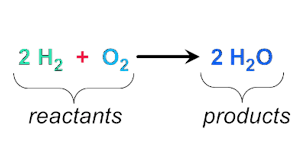
Products
A material resulting from a chemical reaction.
45
New cards
Chemical Equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, the state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, so that the relative concentrations of the reactants and products do not change with time.