MAN ch.10
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
engineering approach
It designs work for efficient operations that result from clearly specifying the tasks to be performed, the methods to be used, and the workflow among individuals.
traditional jobs and traditional work groups
engineering approach produces what two kinds of work design?
traditional jobs
When the work can be completed by one person, such as with bank tellers and standalone machine operators, and they involve highly routinized and repetitive tasks with clear time and motion specifications.
traditional work groups
When the work requires coordination among people, such as on manufacturing assembly lines, and they are composed of members who perform relatively routine yet related tasks.
true
true or false: The engineering approach remains an important work design intervention because its efficiency and cost savings can be measured readily and it is well understood, easily implemented, and directly managed.
true
true or false: the engineering approach can result in low motivation and low job satisfaction for employees with high growth-need strength.
reengineering approach
the fundamental redesign of business processes to achieve substantial improvements in performance. Typically applied under the rubric business process reengineering (BPR), it transforms how organizations traditionally produce and deliver goods and services.
true
true or false: BPR interventions identify which business processes to reengineer, assess their workflows, and redesign them for greater streamlined performance.
prepare the organization
identify and analyze core business processes
define performative objectives
design the new processes
restructure the organization to support the new business processes
BPR (business process reengineering) application steps
dramatic business outcomes
significant performance improvements
positive results of BPR
high failure rate
inconsistent application and outcomes
over reliance on IT
negative results of BPR
the motivational approach
this approach to work design views the effectiveness of jobs primarily as a function of employee psychological needs and seeks to improve performance and satisfaction by enriching jobs to fulfill those needs.
Frederick Herzberg and his colleagues
who started the motivational approach to work design?
Herzberg’s two factor model
proposed that certain attributes of work, such as meaningfulness, responsibility, and recognition, serve as “motivators” to increase job performance and satisfaction. Other attributes called “hygiene factors,” such as company policies, working conditions, pay, and supervision, do not motivate people but rather prevent them from being dissatisfied with their work.
job characteristics model
proposes that core job dimensions affect employees’ critical psychological states, which, in turn, produce personal and job outcomes. Individual differences affect how well job enrichment achieves those outcomes.
skill variety
task identity
task significance
what are the three job dimensions that create meaningful work?
skill variety - one of three job dimensions that create meaningful work
Using different types of skills to do a job.
Example: A nurse does many tasks like caring for patients and doing paperwork.
task identity - one of three job dimensions that create meaningful work
Doing a whole job from start to finish.
Example: Building a full wheel assembly instead of just one part.
task significance - one of three job dimensions that create meaningful work
Knowing your work has an important effect on other people.
Example: Teachers or police officers make a big difference in people's lives.
It increases the feeling of responsibility for work outcomes.
what does autonomy in work increase?
It affects the knowledge of results of the work.
What critical state does feedback affect?
Yes, a strong score in one area (like task significance) can help balance out weaker areas.
Can one strong job dimension make up for lower ones?
High internal work motivation
Better job performance
Greater job satisfaction
Lower absenteeism and turnover
What does the JCM say critical psychological states lead to?
making a thorough diagnosis
designing enriched jobs
assessing results
application stages for job characteristics model (JCM)
They affect employee attitudes (like job satisfaction) more than behaviors (like performance or absenteeism).
What do studies show the core job dimensions affect most?
Yes — newer research includes social, decision-making, and information-processing job aspects.
Has the JCM been updated or expanded?
Creativity, employee health, and organizational citizenship behavior.
What new outcomes are linked to work design?
sociotechnical systems approach
explains how work systems are made of both social and technical parts that must work together to succeed.
sociotechnical system
a joint system of people (social) and tools/processes (technical) working together to perform tasks and produce outcomes.
Social part – the people, their relationships, and communication
Technical part – tools, methods, and information used to complete tasks
What are the two parts of a sociotechnical system?
It means designing the social and technical parts to work well together so both performance and employee well-being are high.
goal of sociotechnical system: joint optimization
Work outcomes – like products, services, or decisions
Social outcomes – like job satisfaction and good relationships
What are the two types of outcomes from STS?
manage external interactions and internal autonomy to respond to changing conditions
goal of sociotechnical system: adaptation
environmental interaction
systems are open to their environments, requiring effective boundary management for optimal functioning
self-managed work teams
use the sociotechnical systems approach where team members manage interrelated tasks with control over assignments and methods
responsibilities of self-managed work teams (SMWTs)
complete outcome (products, services, information) and manage support functions (maintenance, quality control)
compensation of SMWTs
based on skills and knowledge, with team performance as the pay standard
applications of self-managed work teams (SMWTs)
used across sectors and organizational structures, including mechanized and digitalized STS
technical interdependence
technical uncertainty
two technical dimensions
technical interdependence
the level of cooperation required among workers to produce a product or service.
technical uncertainty
the level of information processing and decision-making required by employees to complete a task
low interdependence
Tasks can be performed individually (e.g., field sales, call centers).
high interdependence
Tasks require coordination among team members (e.g., software development, oil refining, major surgery)
low uncertainty
Tasks are repetitive and can be externally controlled (e.g., assembly lines).
high uncertainty
Tasks require ongoing information processing and decision-making by employees (e.g., emergency services, professional work).
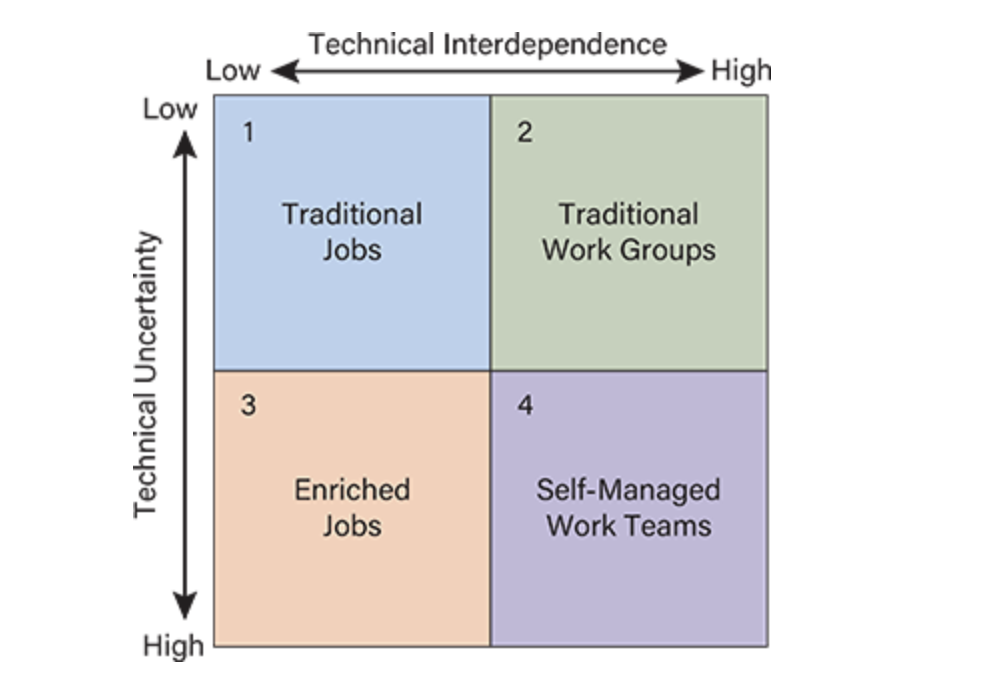
Quadrant 1 (Low Interdependence & Low Uncertainty):
Example: Call centers
Design: Traditional jobs with little interaction or self-control
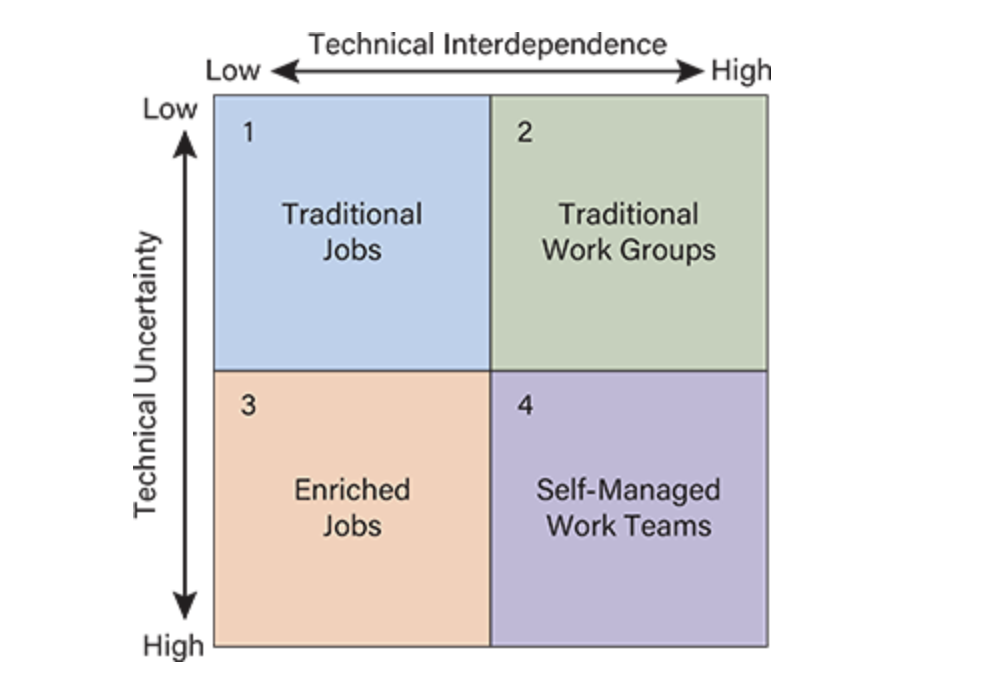
Quadrant 2 (High Interdependence & Low Uncertainty):
Example: Data centers
Design: Traditional work groups with scheduled interaction and external control
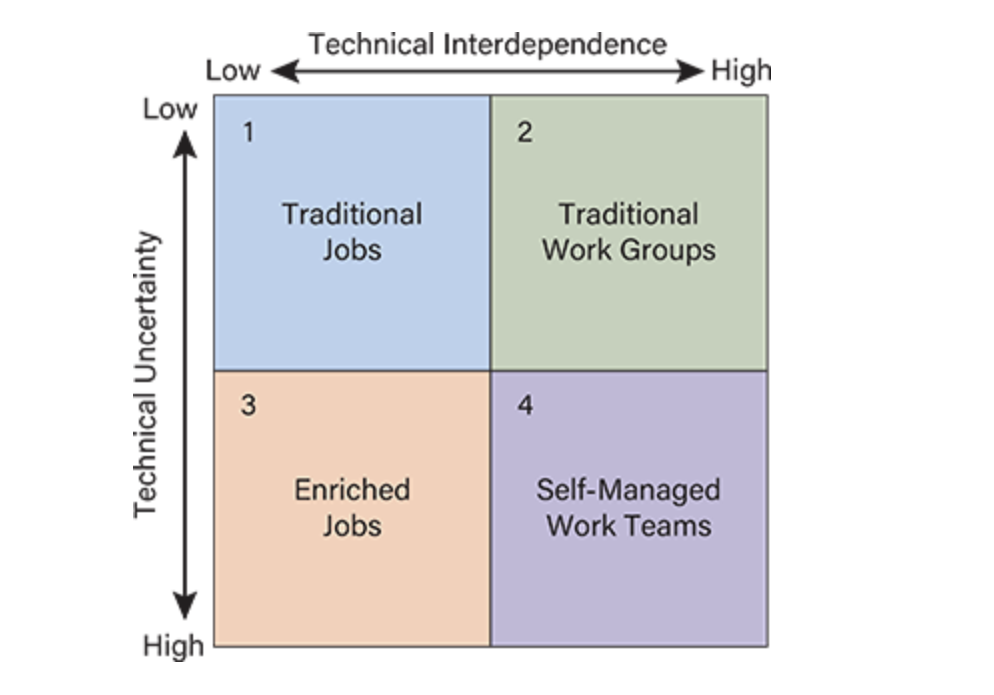
Quadrant 3 (Low Interdependence & High Uncertainty)
Example: Field sales
Design: Individual jobs with enriched internal control
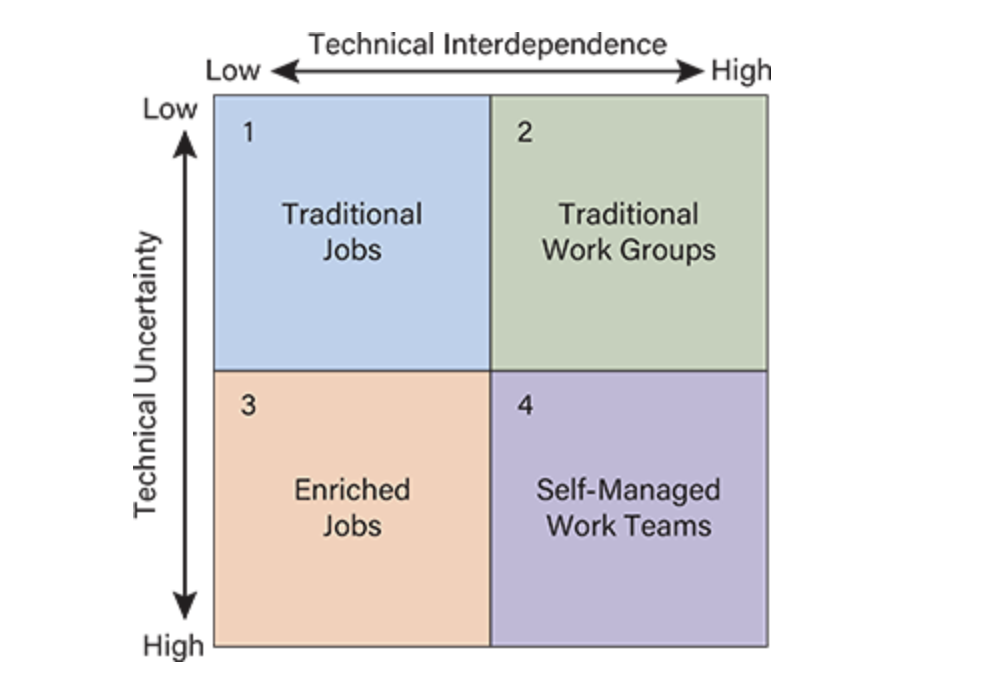
Quadrant 4 (High Interdependence & High Uncertainty)
Example: Firefighting teams
Design: Self-managed teams with autonomy and shared task control
social needs – Desire for meaningful social relationships at work
growth needs – Desire for personal accomplishment, learning, and development
These needs influence what types of work designs employees find satisfying.
what are the two personal needs in work design?
low social needs
prefer individualized jobs with minimal interaction
high social needs
Prefer group-oriented work environments with frequent interaction
Low Growth Needs
Prefer routine, repetitive work with limited complexity or decision-making
high growth needs
Prefer complex, challenging tasks with autonomy, variety, and feedback
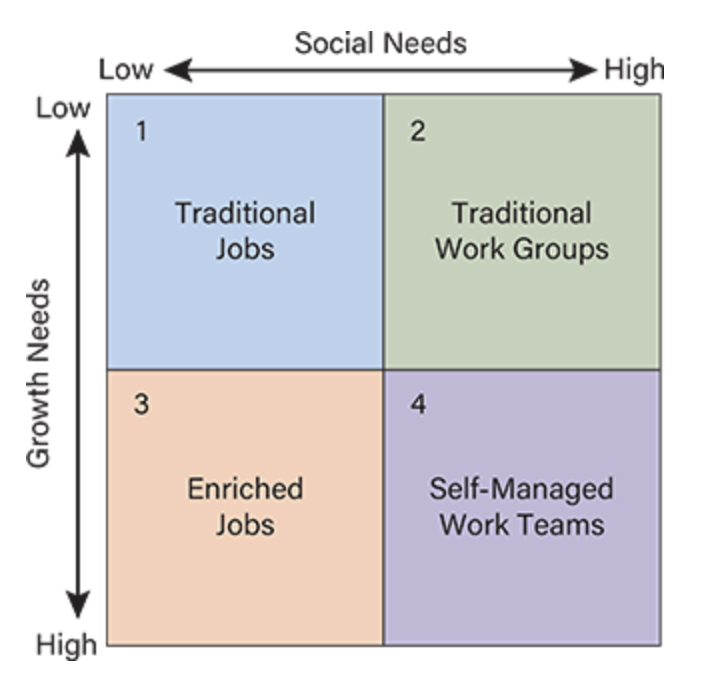
Quadrant 1 (Low Social, Low Growth):
Best Fit: Traditional jobs
Example: Basic clerical or production roles
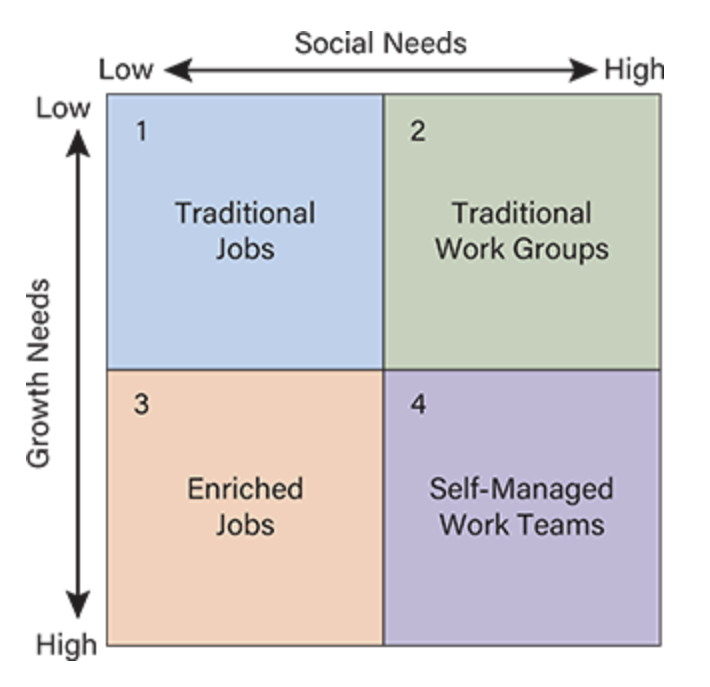
Quadrant 2 (High Social, Low Growth)
Best Fit: Traditional work groups
Example: Customer service teams with repetitive tasks
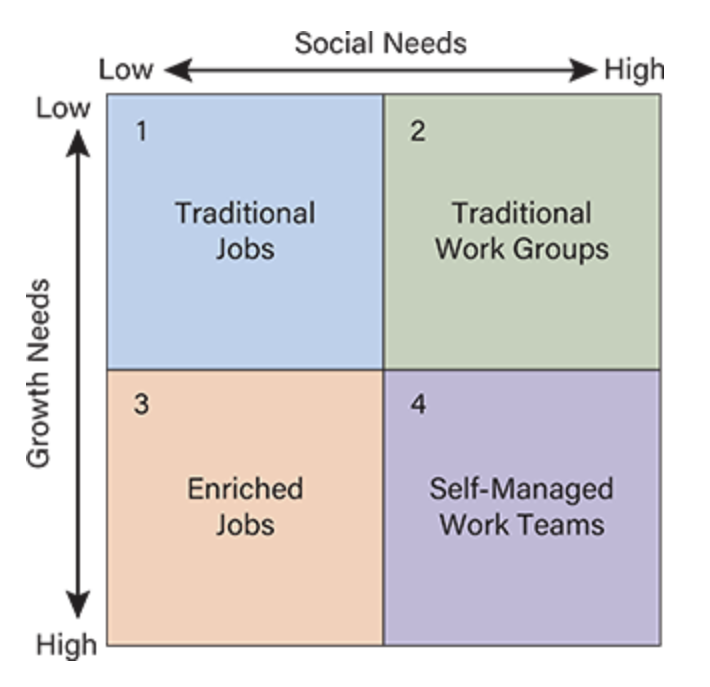
Quadrant 3 (Low Social, High Growth)
Best Fit: Enriched individual jobs
Example: Research scientists, skilled craftspersons
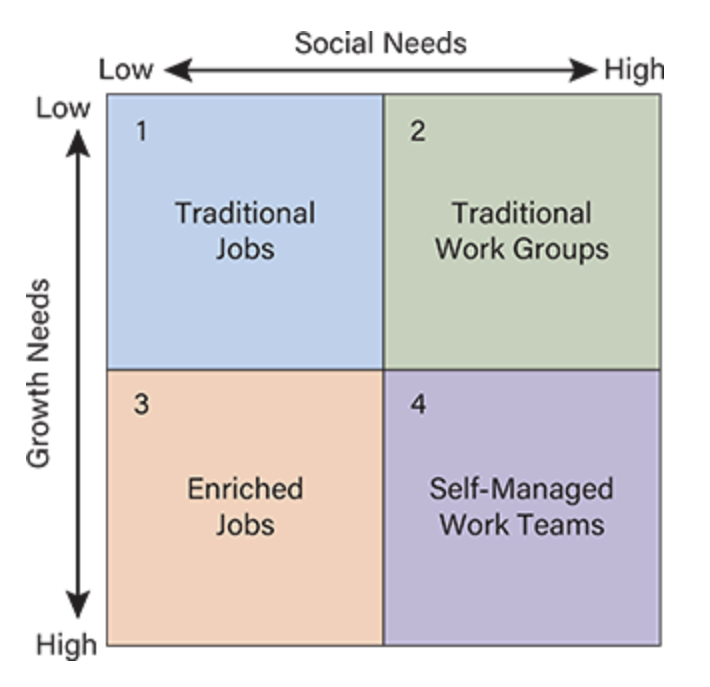
Quadrant 4 (High Social, High Growth)
Best Fit: Self-managed teams
Example: Astronaut teams, surgical teams, global supply chain teams
enriched jobs
jobs that offer high levels of discretion, skill variety, feedback about results