fetal heart rate
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
fhr
- fetal heart rate
fhrb
- fetal hr baseline
efm
electronic fetal monitor
ua
uterine activity
uc
uterine contractions
us
ultrasound
toco
tocotransducer
fse
fetal scalp electrode
iupc
intrauterine pressure catheter
fetal monitoring purpose
to identify normal (reassuring) patterns from abnormal (non reassuring patterns)
fetal response/surveillance with EFM
• Monitor fetal oxygen supply and reserves
• Monitor fetal circulation
• Assess FHR response to contractions
basis for fetal monitoring- uterine activity
- contraction, frequency, duration, intensity
- resting tone
- relaxation time
- montevideo units (MVUs)
fetal compromise
• Reassuring vs nonreassuring patterns indicate fetal hypoxemia or asphyxia
types of fetal and uterine monitoring
- intermittent auscultation via doppler
- continuous external monitoring
- continuous internal monitoring
indications for electronic fetal monitoring
- hx of stillbirth
- comp of pregnancy
- pre-gestation or gestational condition
- induction of labor (oxytocin)
- preterm labor
- non-reassuring fetal status
- meconium-stained amniotic fluid
advantages for fetal monitoring
- assess adequate o2 during labor
- make decisions r/t type of birth in a timely manner to avoid comp
- can monitor trends
disadvantages of fetal monitoring
- ties mom to the bed in less than optimal position for labor and birth
- proof of potential problem for litigation
steps in interpreting fhr tracing
is there enough of a continuous strip for interpretation (20min)
identify fhr baseline
identify variability: absent, minimal, moderate, or marked
determine whether there are accelerations or decelerations (type)
evaluate uterine contractions: freq, duration, intensity
determine whether fhr is reassuring, nonreassuring, or ominous
document interpretation of fhr, notify physician or midwife as appropriate
define frequency
- calculated in minutes
- beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction
- look at smallest frequency and longest frequency an do an average
define duration
- calculated in seconds
- beginning to end of a contraction
- look at smallest and longest and do an average
intensity
- mild, moderate, strong
- palpate uterine fundus for external monitoring
- in beginning of labor, the contractions/uterus will be more squishy/moderate like nose; then moderate as it progresses; then strong like forehead
normal fhr**
110-160
tachycardia
> 160 that lasts for at least 10 min
bradycardia
< 110 that lasts for at least 10 min
causes of tachycardia
- fetal hypoxia
- maternal fever
- hyperthyroidism
- maternal or fetal anemia
- parasympathetic drugs: atropine, hydroxyzine
- sympathomimetic drugs: ritodrine, terbutaline
- chorioamnionitis
- fetal tachyarrythmia
- prematurity
causes of severe fatal bradycardia
- prolonged cord compression
- cord prolapse
- tetanic uterine contractions
- paracervical block
- epidural and spinal anesthesia
- maternal seizures
- rapid descent
- vigourous vaginal exam
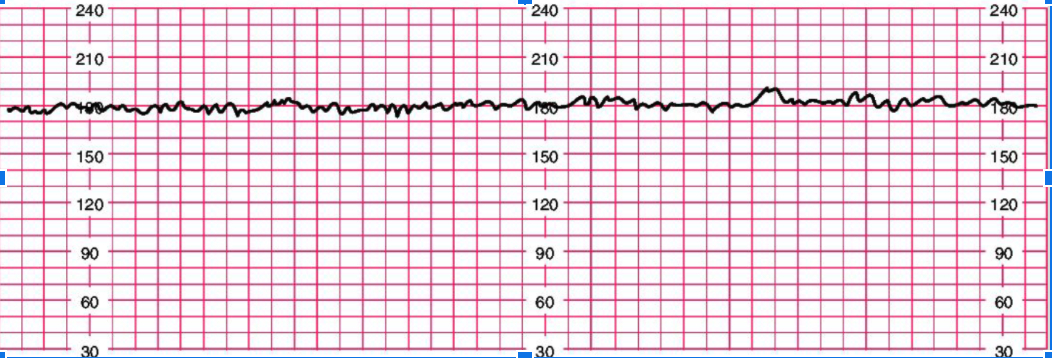
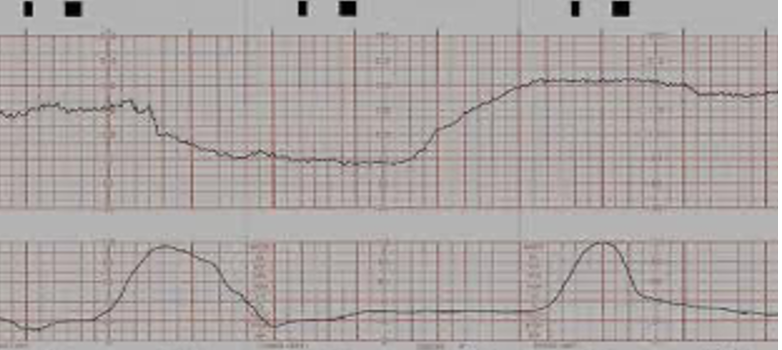
explanation of FHR strip
each box is 10 seconds
the bold lines equal to 1 minute
in this example: the FHR baseline is 180
variability
irregular waves of fluctuation in baseline FHR of two cycles per minute
does not include accelerations or decelerations in baseline
quantified as beats per minute and is measured from peak to trough
absent variability
- undetectable from baseline
- no accelerations or decelerations
- same BPM over and over again
- not good
minimal variability
- < 5bpm
- only go up or down half a block
moderate variability
- 6-25 bpm = normal
- means good o2 and brain activity
- accelerations are okay
- fluctuating 1-2 blocks
marked variability
- no patterns, rapid accels but dont last 15, no time inbetween
- above 2 blocks of fluctuation
accelerations
- 32 wks or greater: 15 beats above baseline lasting 15 seconds
- before 32 wks: 10 beats or greater above baseline, lasting 10 or more seconds
- predict adequate fetal oxygenation and absence of fetal acidemia
- it is a good thing! it is okay to see several times, and also okay if not any or very little
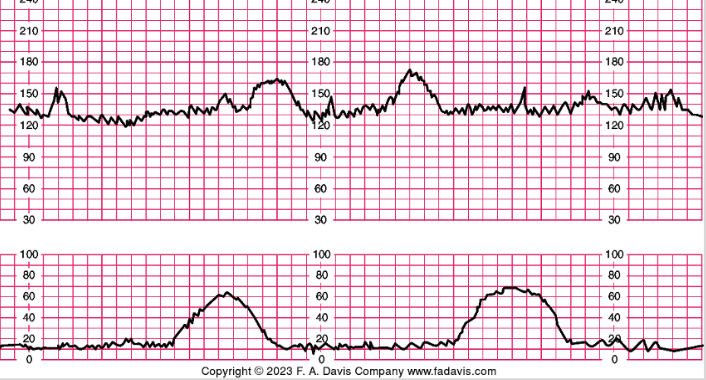
early decels
- caused by a vagal response produced when head is compressed by uterine contractions
- usually don’t see until later in labor at like 7/8; okay then, not really before
- little scoops of ice cream
- slowing of FHR starting at beginning of contraction and returning to baseline by end; mimics contractions
- do not indicate fetal distress, however, can indicate very strong uterine contractions and that head is descending
- gradual onset > 30 sec from onset to nadir (peak)
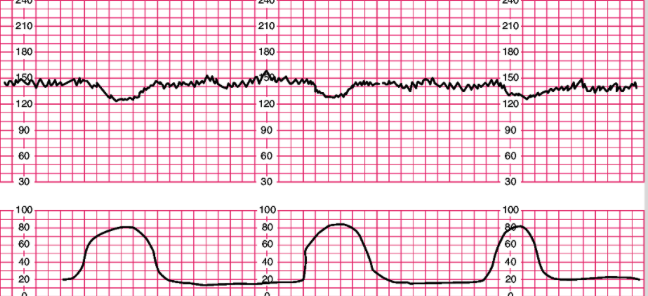
variable decels
- no relationship w contractions, can happen w or w out
- can occur at ANYTIME
- pattern of decelerations can change from one contraction to the next
- cause: compression of umbilical cord
- abrupt onest < 30 secs from onset to beginning of peak, lasting > 15 secs but < 2 min
- depth: > 15bpm
- shapes: u, w, v
- very abrupt drop in heart rate
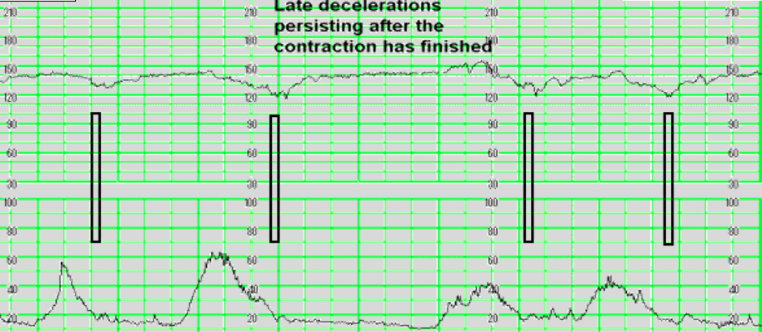
late decels
- slowing or fhr during contraction, with the rate only returning to baseline 30 secs of more after contraction ended - biggest drop/decrease is after contraction ends
- caused by utero-placental insufficiency
- sign of fetal distress or hypoxia
- gradual onset > 30sec from onset to peak
- always take seriously - most serious one
prolonged decels
- abrupt decreases in fhr below baseline that is decreased of > 15 bpm lasting > 2min but less than 10 min
- >10 min = baseline change to bradycardia
VEAL & CHOP
- variable caused by cord compression
- early caused by head compression
- accleration = okay (o2)
- late caused by placental insufficiency
tier classification cateory 1
- all normals - want to see this
- fhr: 110-160
- moderate variability
- absent late or variable decels
- present or absent accelerations; we want to see them, but okay if not
- present or absent early decels
tier classification cateory 2
- bradycardia not accompanied by absent variability
- tachycardia not accompanied by absent variability
- baseline variability: minimal, absent, marked
- no accelerations produced w fetal stimulation
- recurrent variables decels w overshoots or shoulders
- late decels, prolonged decels > 2 min but < 10min
tier classification cateory 3
- absent baseline variability and recurrent late decels, variable decels, or bradycardia
- sinusoidal pattern
- worst one
category 1 causes & interventions
- well oxygenated
- non acidotic
- intervention: cont efm, support labor
category 2 causes and interventions
- not predictive cause
- intervention: cont efm, intiate some intrauterine resuscitation
cateogory 3 causes & interventions
- acidosis, uteroplacental insuff, fetal hypoxia
- intervention: initiate intrauterine resuscitation
intrauterine resuscitation
- oxytocin off: less contractions and de-stress baby to try and get oxygen to it
- position change: esp for variable decelerations bc of cord compression
- ivfs (500 ml bolus): further pull circulation to fetus to help w/ oxygenation
- sterile vag exam
- notify hcp
- consider o2 of low o2 sat
- consider amnioinfusion: for variable, flush up fluids inside uterus to help float cord around
- consider tocolytics: stops contractions and relaxes uterus to stop stress
- prepare woman for c section or imminent svd: esp w/ late decels/recurrent or absent variability
- do all these things if late decel