Anatomy & Physiology 1 Lab; Midterm Practical
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
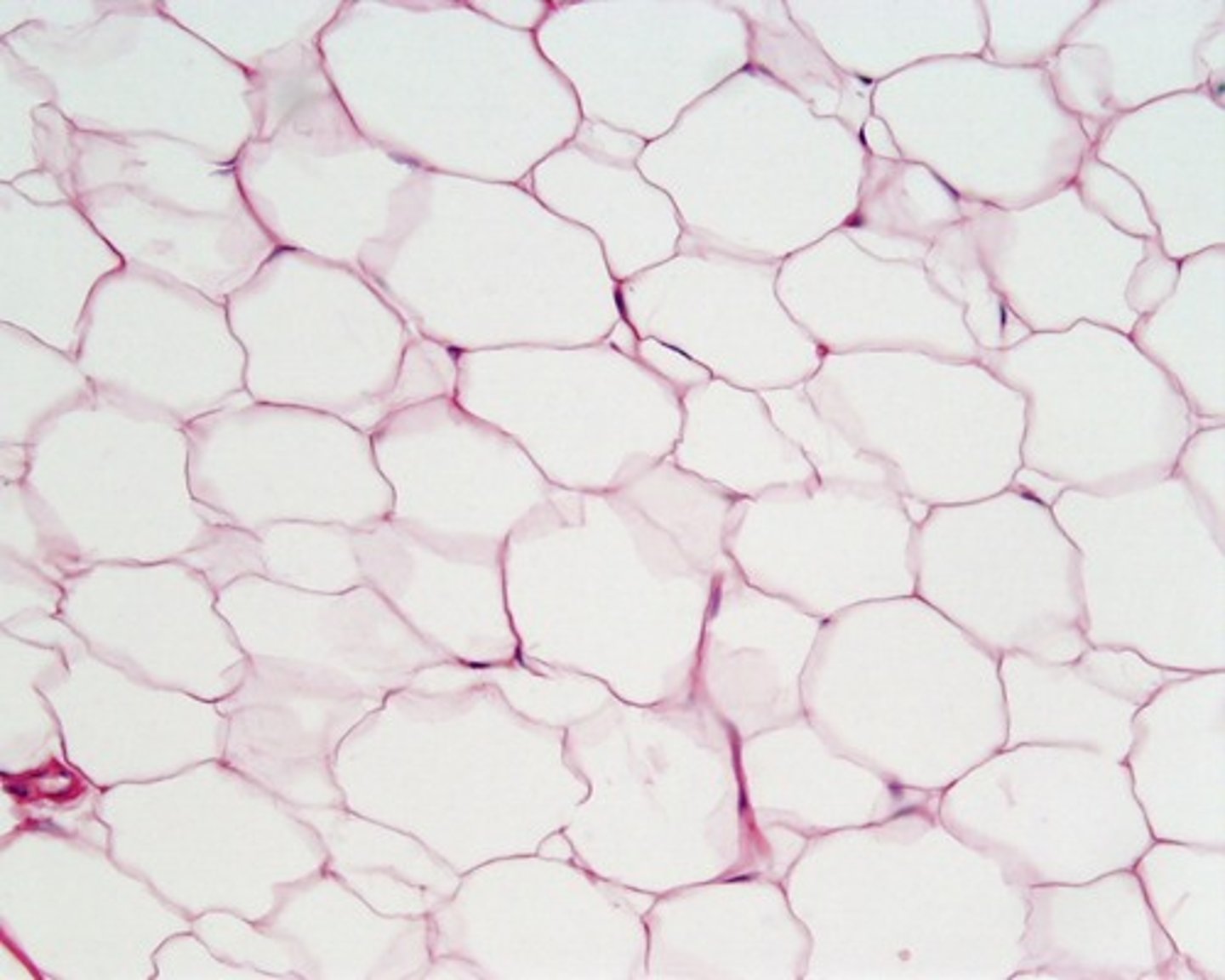
Adipose Tissue
Loose connective tissue
Function - Provides reserve fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs.
Location - Under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen and in breasts
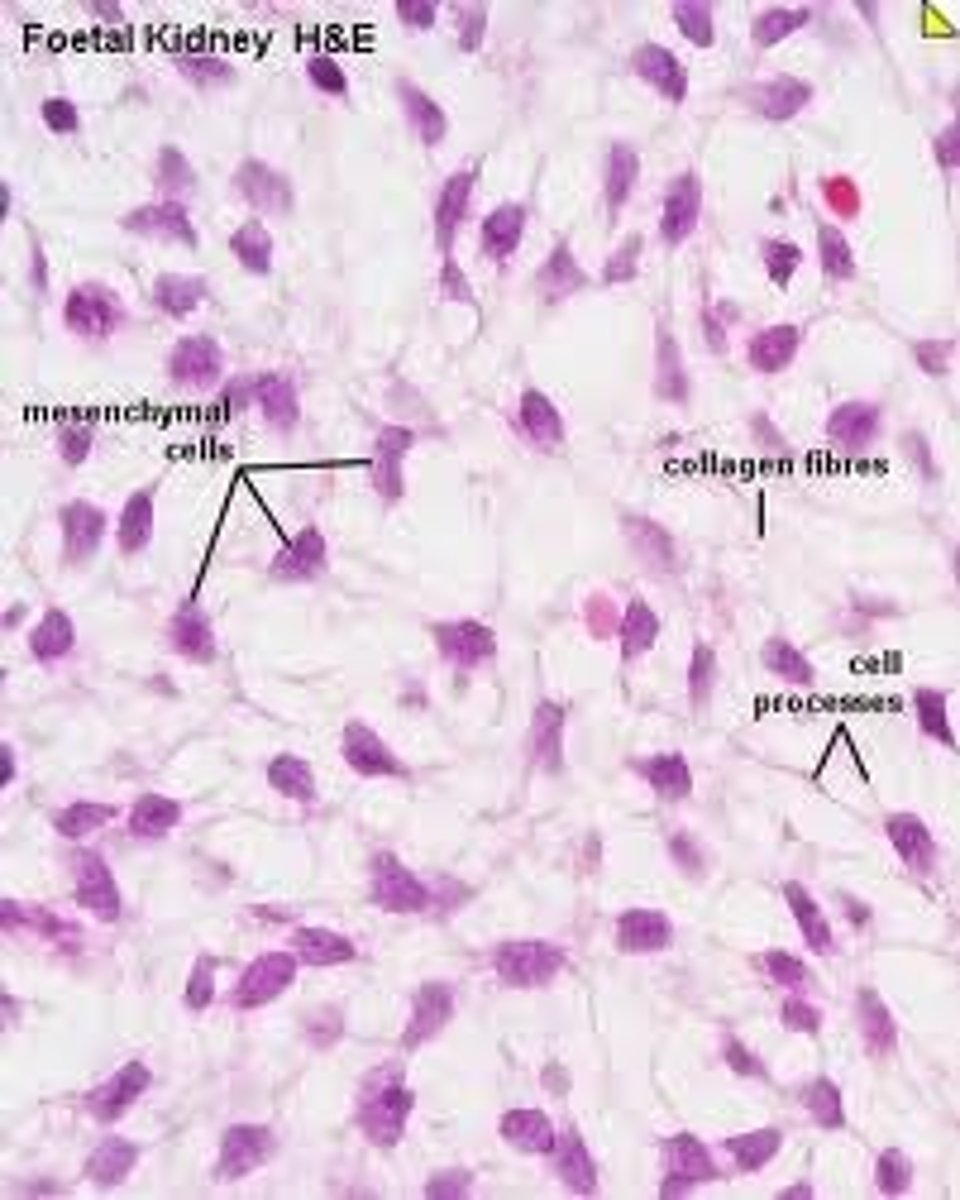
Mesenchyme
Embryonic Tissue
Function - Give rise to all other connective tissue types.
Location - Embryo
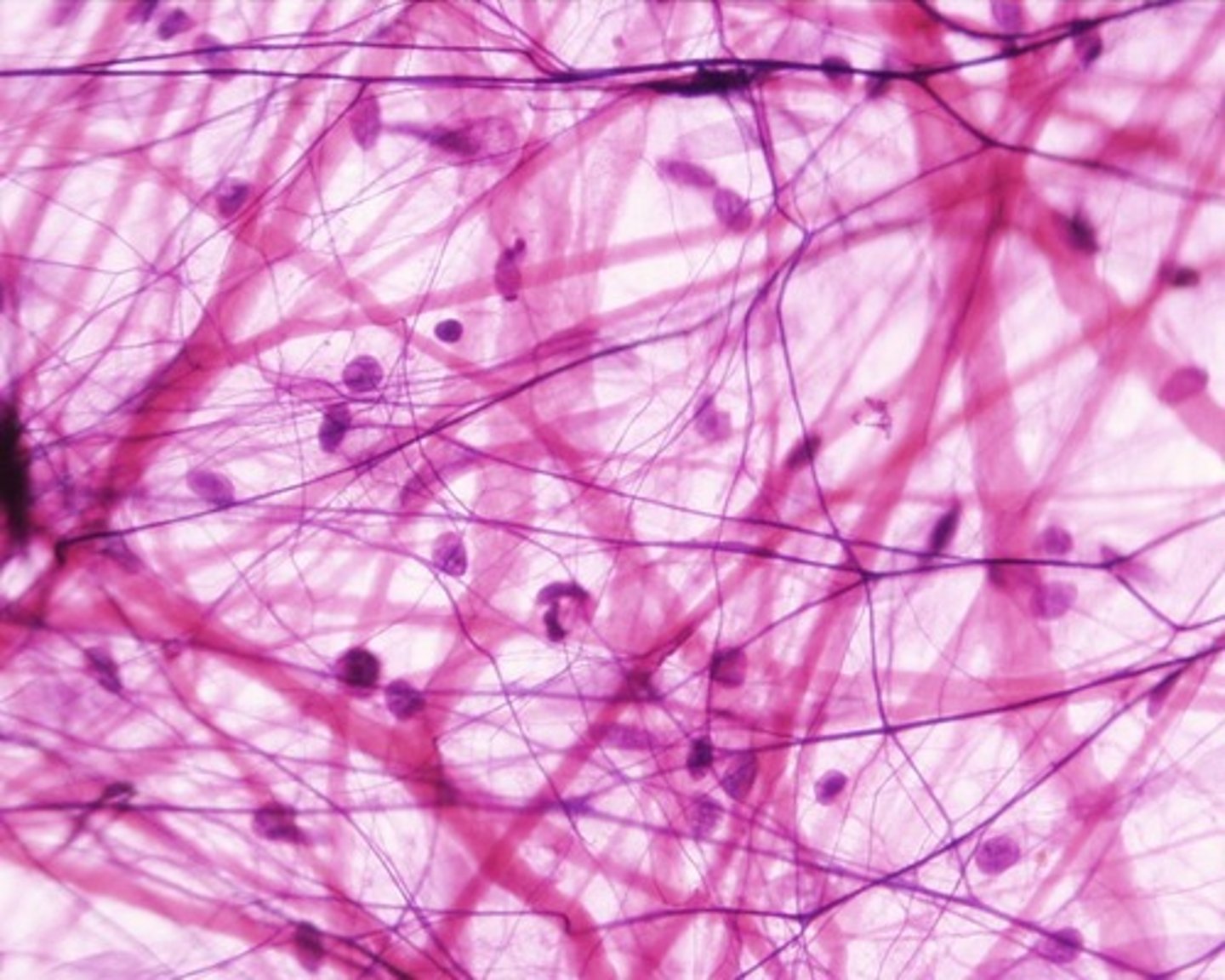
Areolar Tissue
Loose connective tissue
Function - Wraps and cushion organs; its macrophages phagocytize bacteria; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid.
Location - Widely distributed under epithelia, packages organs, surrounds capillaries.
Reticular Tissue
Loose connective Tissue
Function - Fibers form a soft internal skeleton that supports other cell types including WBC
Location - Lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen
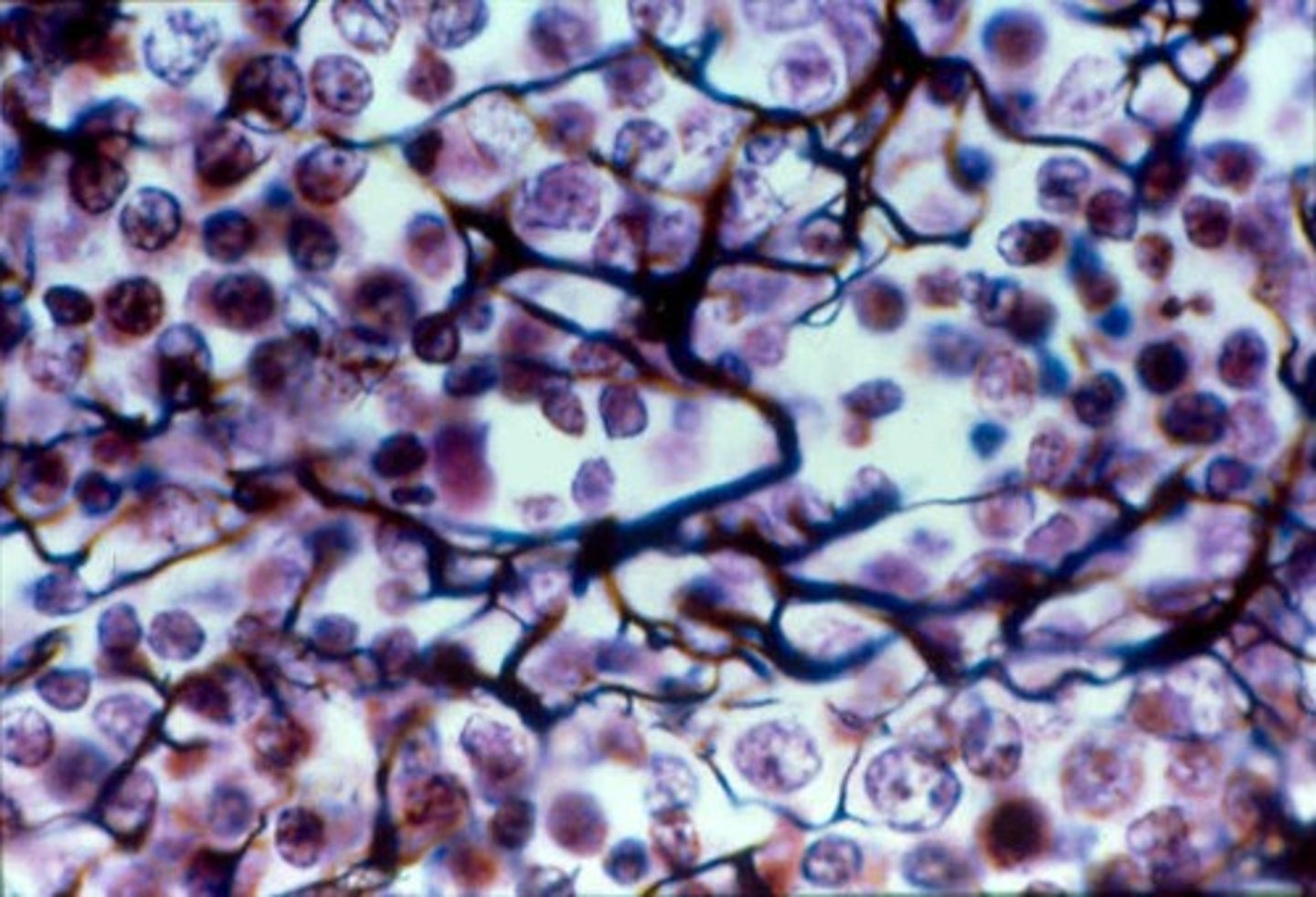
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Dense connective tissue
Function - Attaches muscles to bones or to other muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction.
Location - Tendons, most ligaments
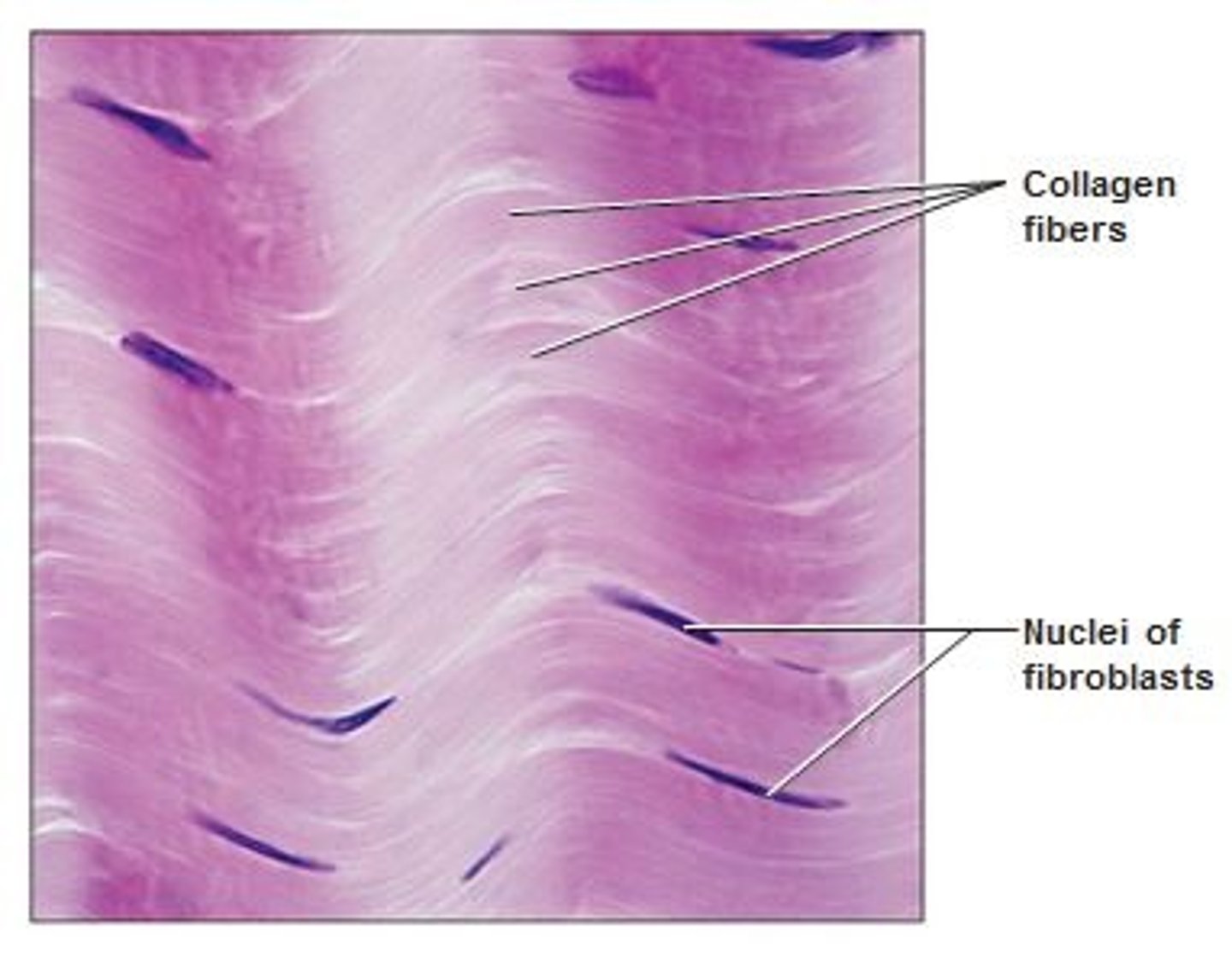
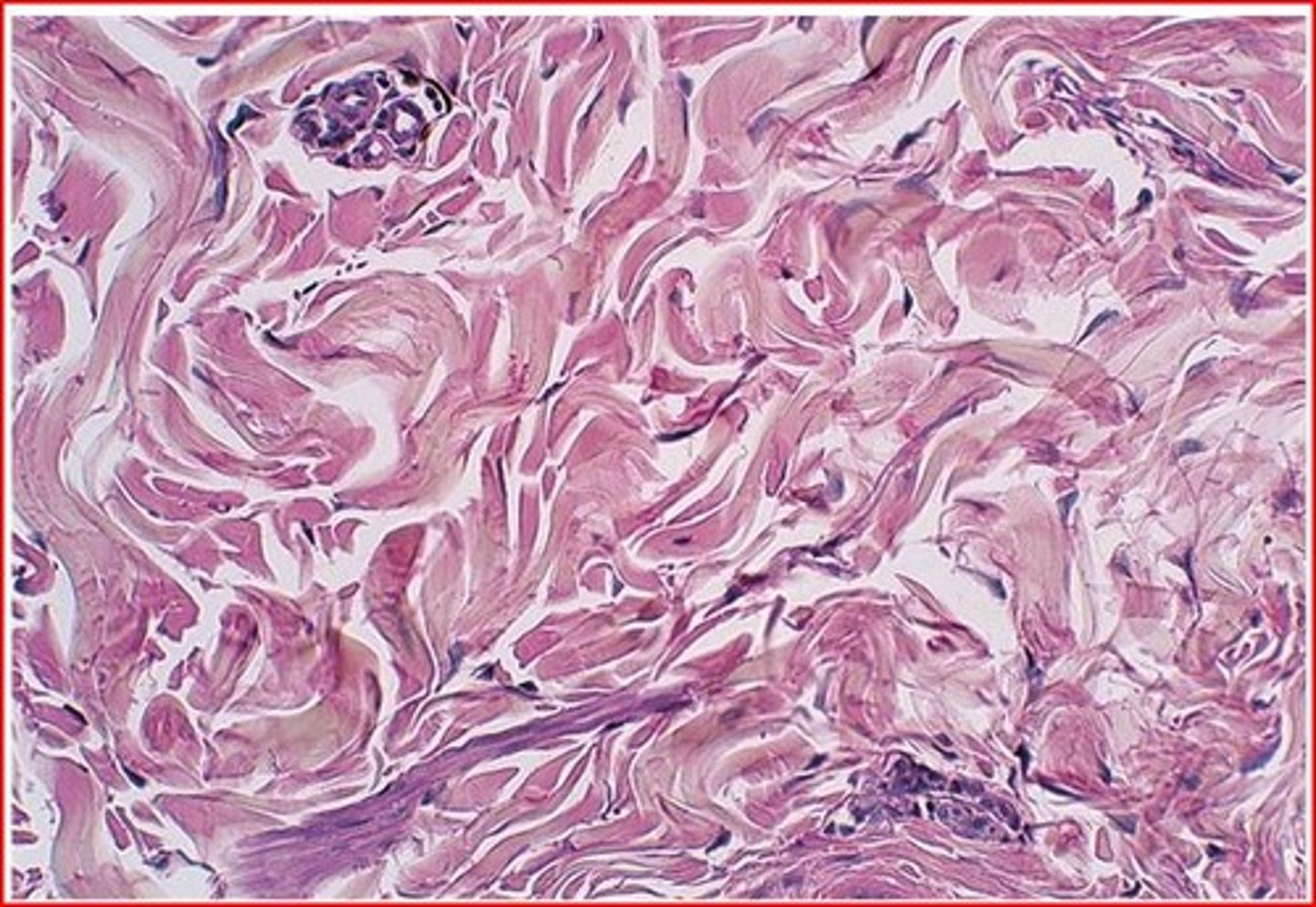
Dense Irregular Tissue
Dense connective tissue
Function - Able to withstand tension exerted in many direction; Provides structural strength.
Location - Fibrous capsules of organs and joints, dermis of skin.
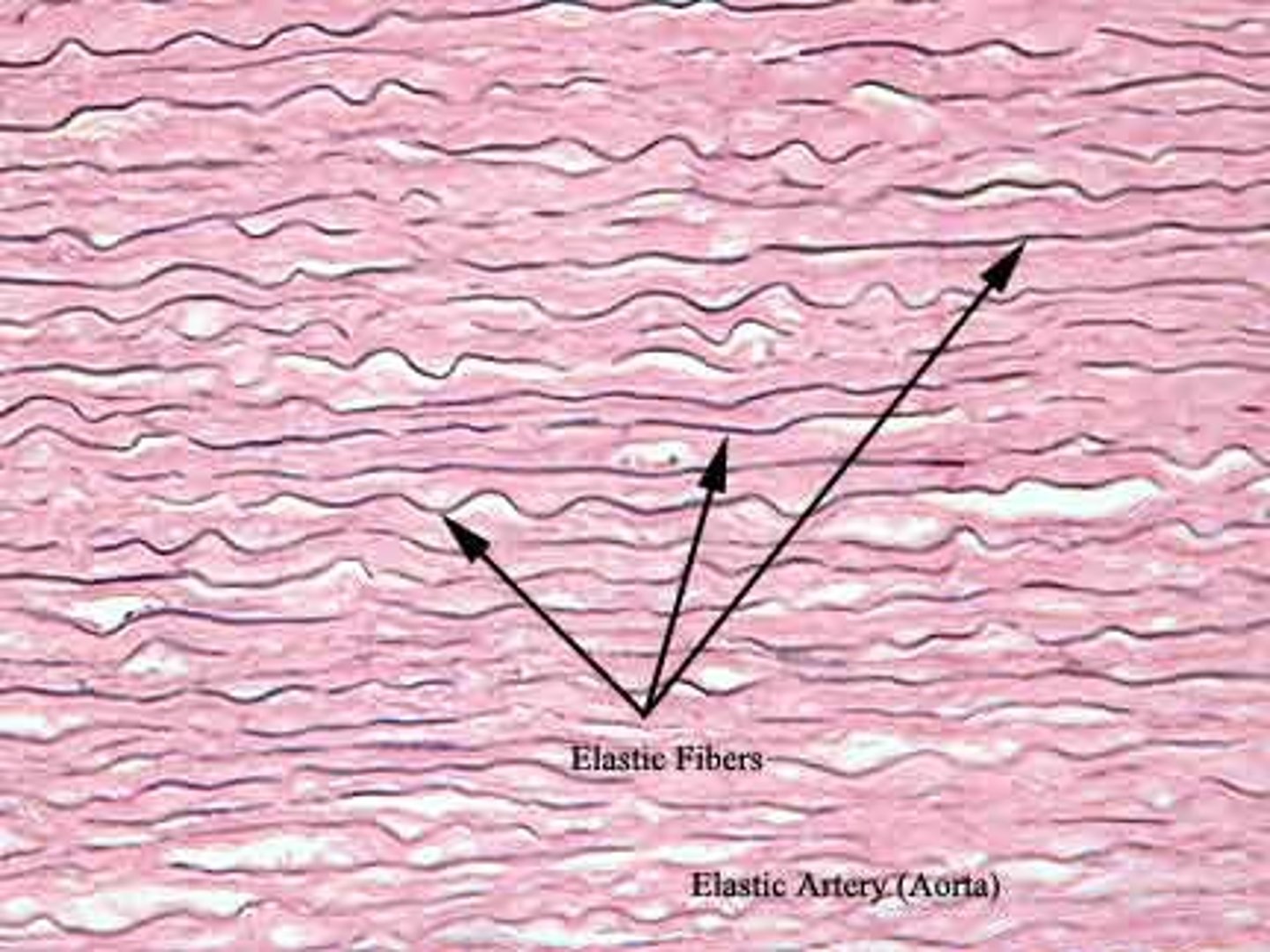
Dense Elastic Tissue
Function - Allows recoil of tissue following stretching. Maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries. Aids passive recoil of lungs following inspiration.
Location - Walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments around vertebral column, within walls of bronchial tubes.
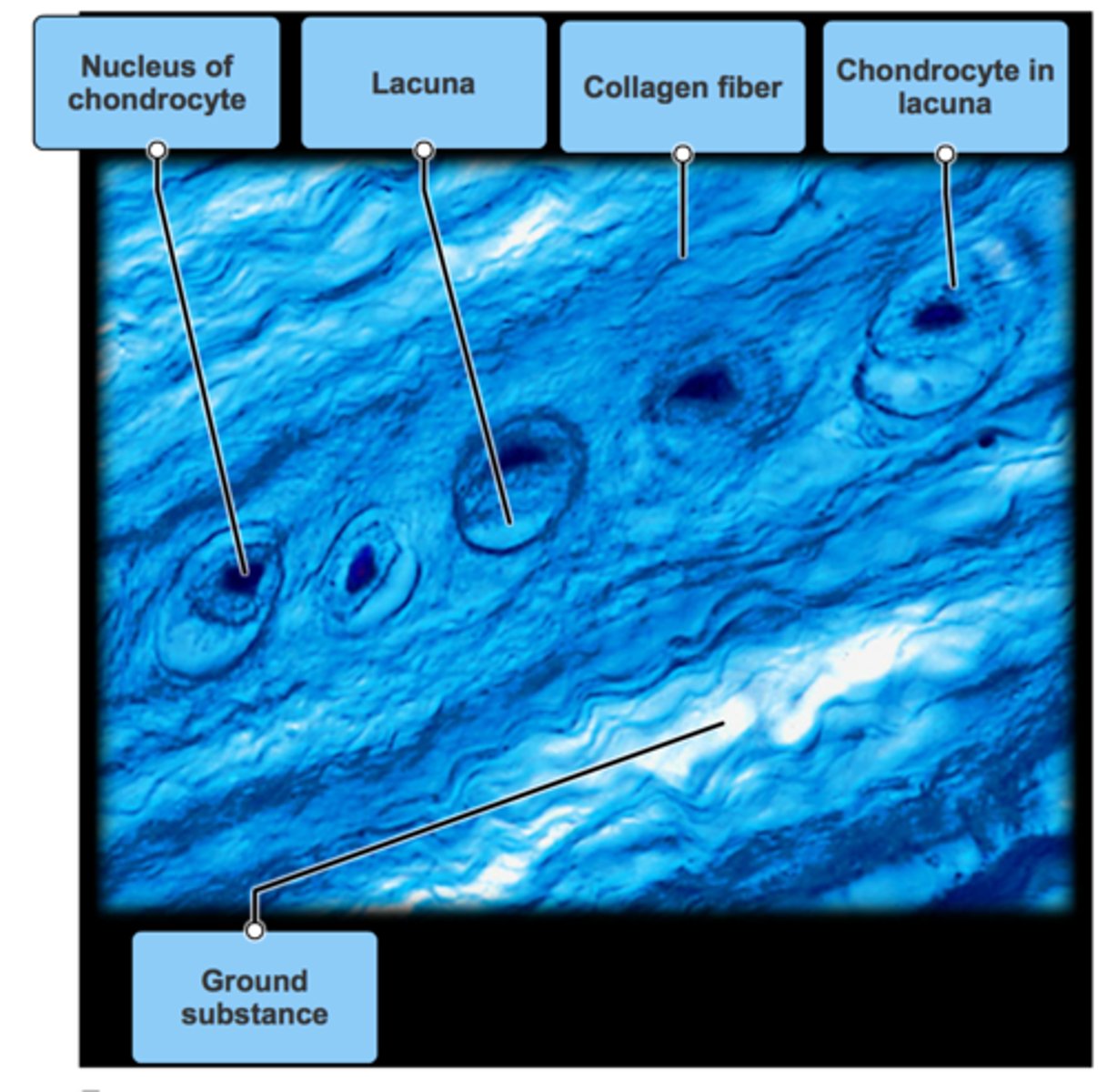
Hyaline Cartilidge
Function - Supports and reinforces; Serves as resilient cushion; resists compressive stress
Location - Forms most of embryonic skeleton; covers ends of long bones in joint cavities; forms costal cartilages of ribs; cartilages of nose, trachea, and larynx.
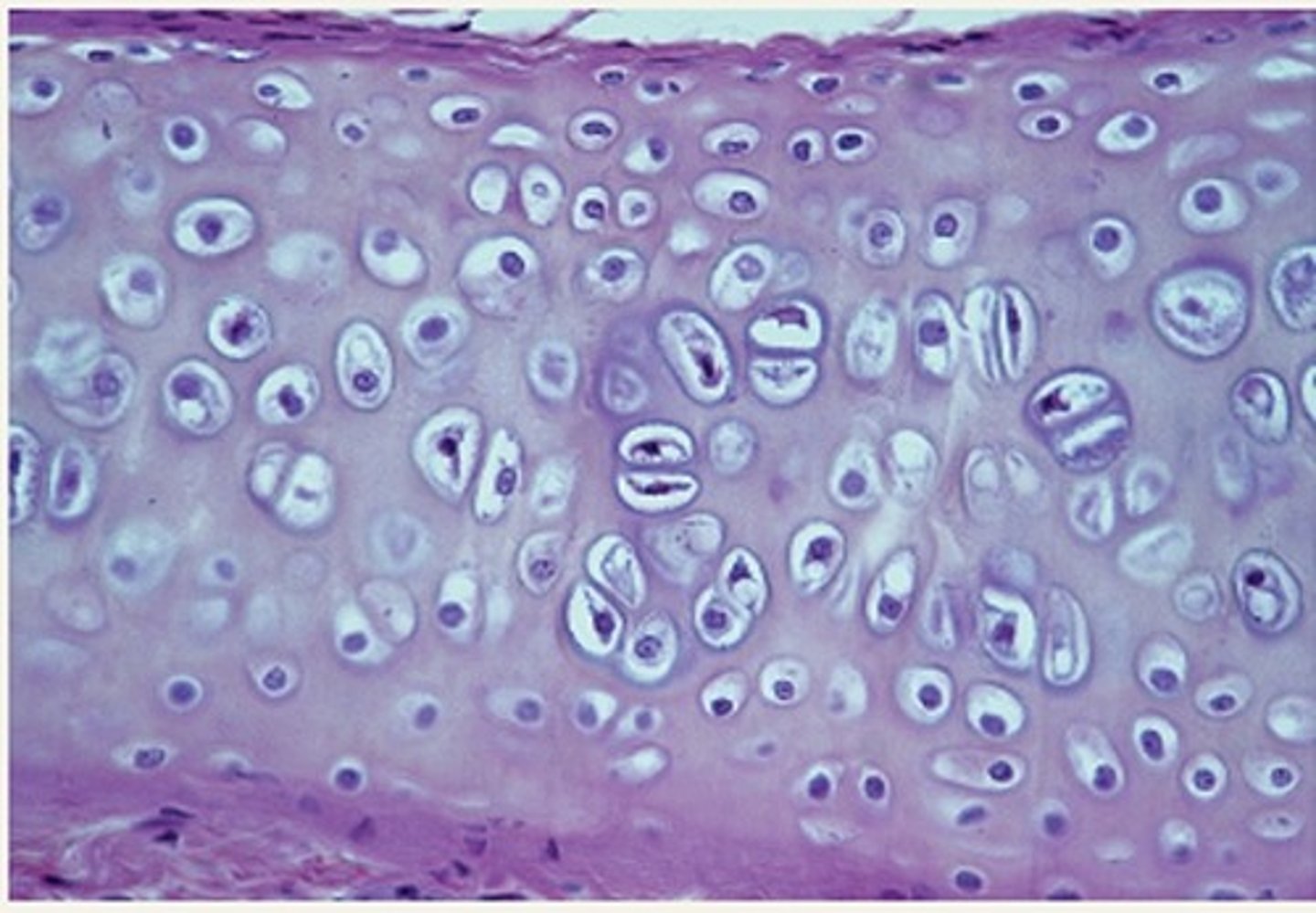
Elastic Cartilidge
Function - Maintains shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility.
Location - Supports external ear, epiglottis.
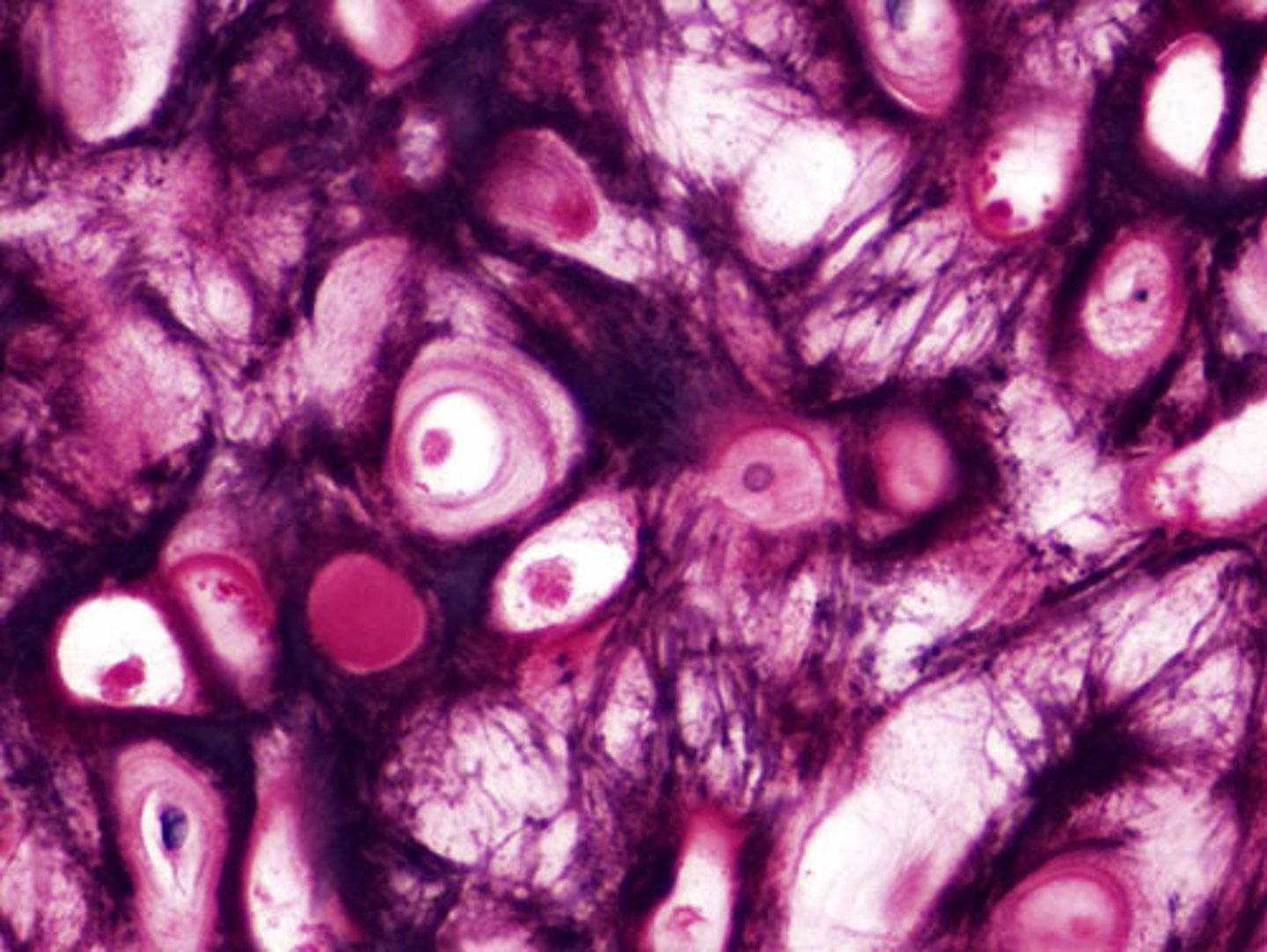
Fibrocartilidge
Function - Tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock.
Location - Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint.
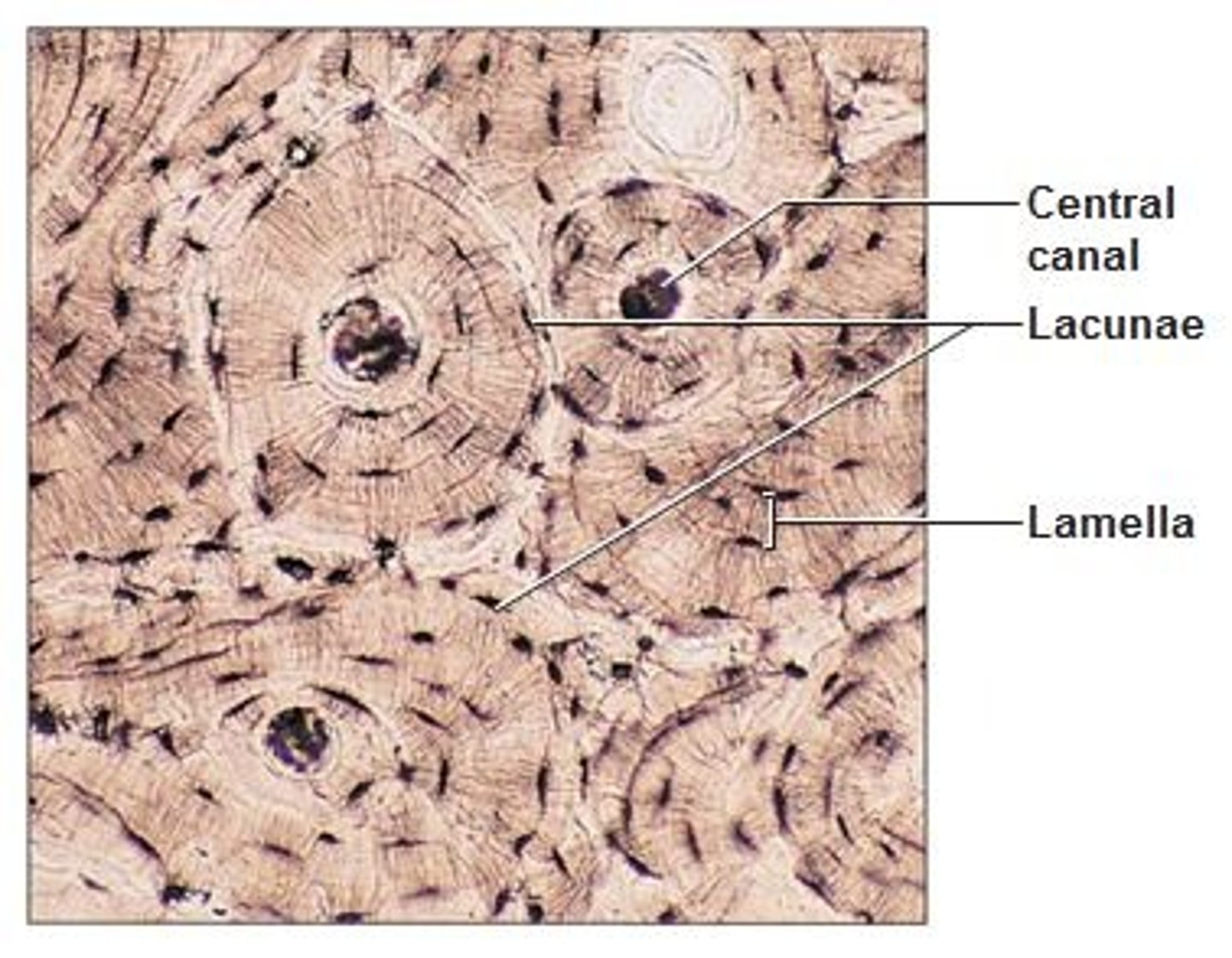
Osseous Tissue
Function - Bones provide supports and protect; provides levers for muscle to act on; stores calcium and other minerals; bones marrow is site for blood cell formation.
Location - Bones
Blood Tissue
Function - Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, waste.
Location - contained w/i blood vessels.
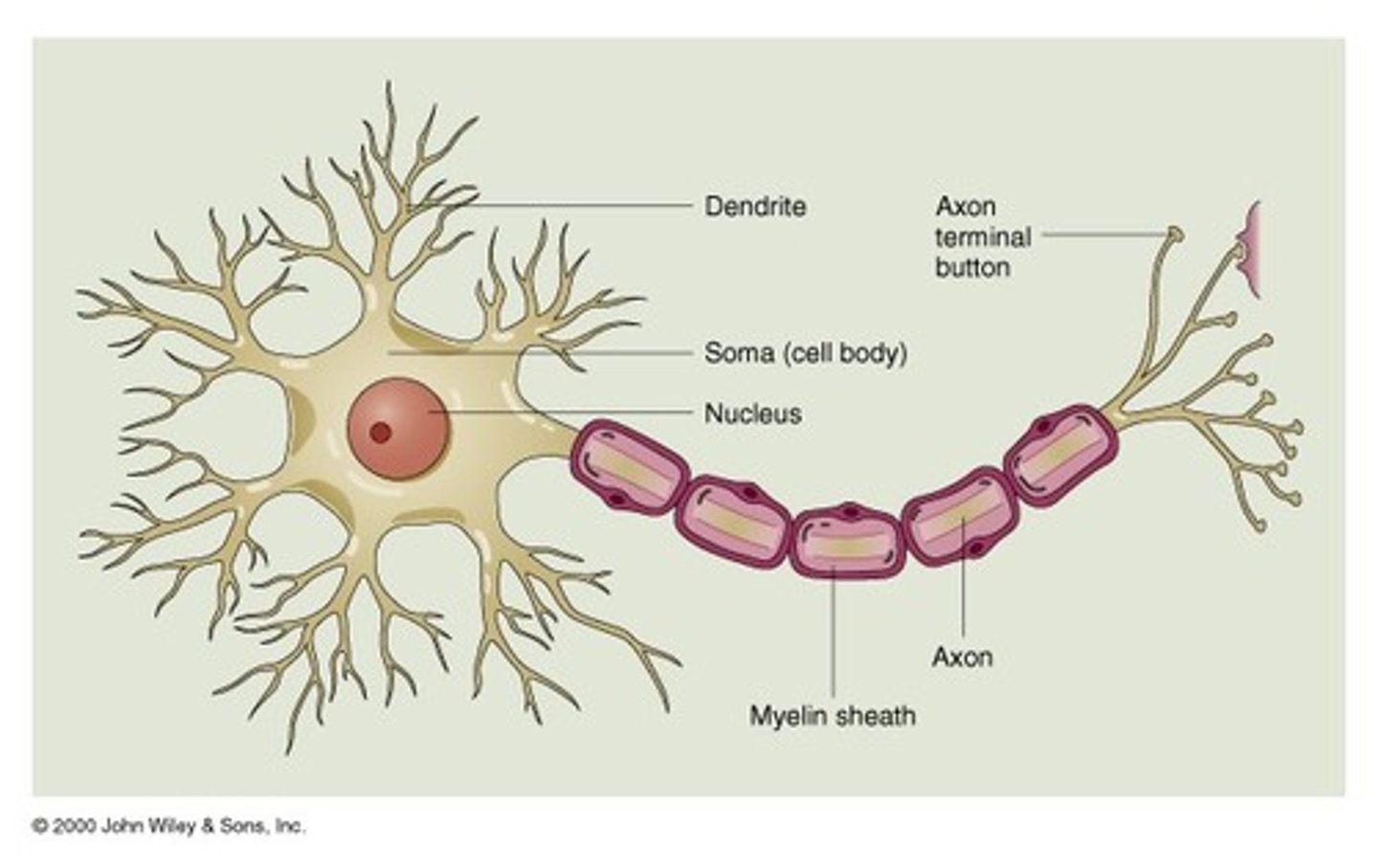
Nervous Tissue
Neurons: specialized to receive stimuli and conduct wave excitation/impulses to all parts of the body.
cell body: contains the nuclei and most of the organelles
cytoplasmic projections: dendrites & axon
Neuroglia/Glial cells: support, protect and bind neurons.
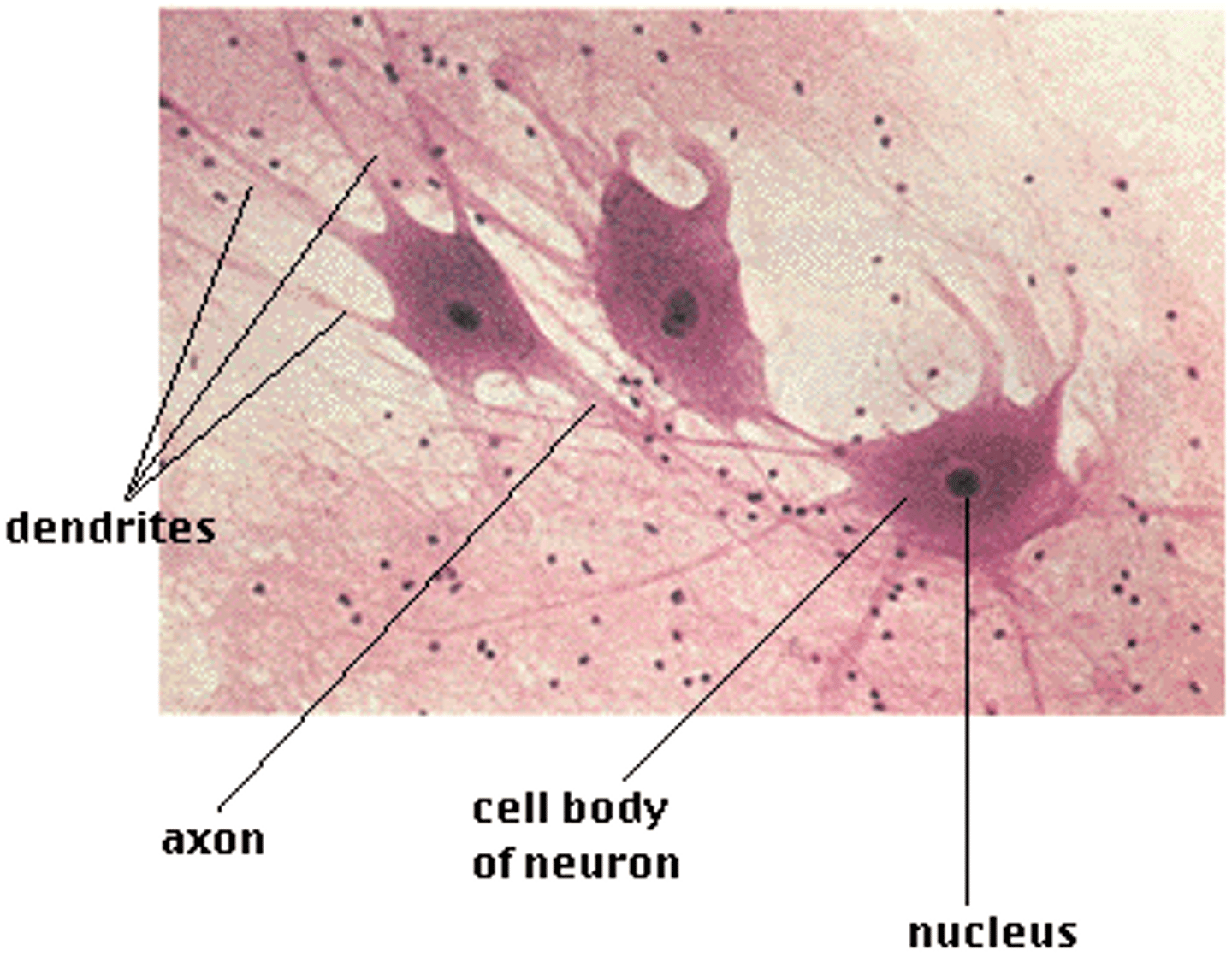
Parts of Neurons
Cell body
Dendrites
Receptive regions
Axons
Nerve impulse generators and transmitters
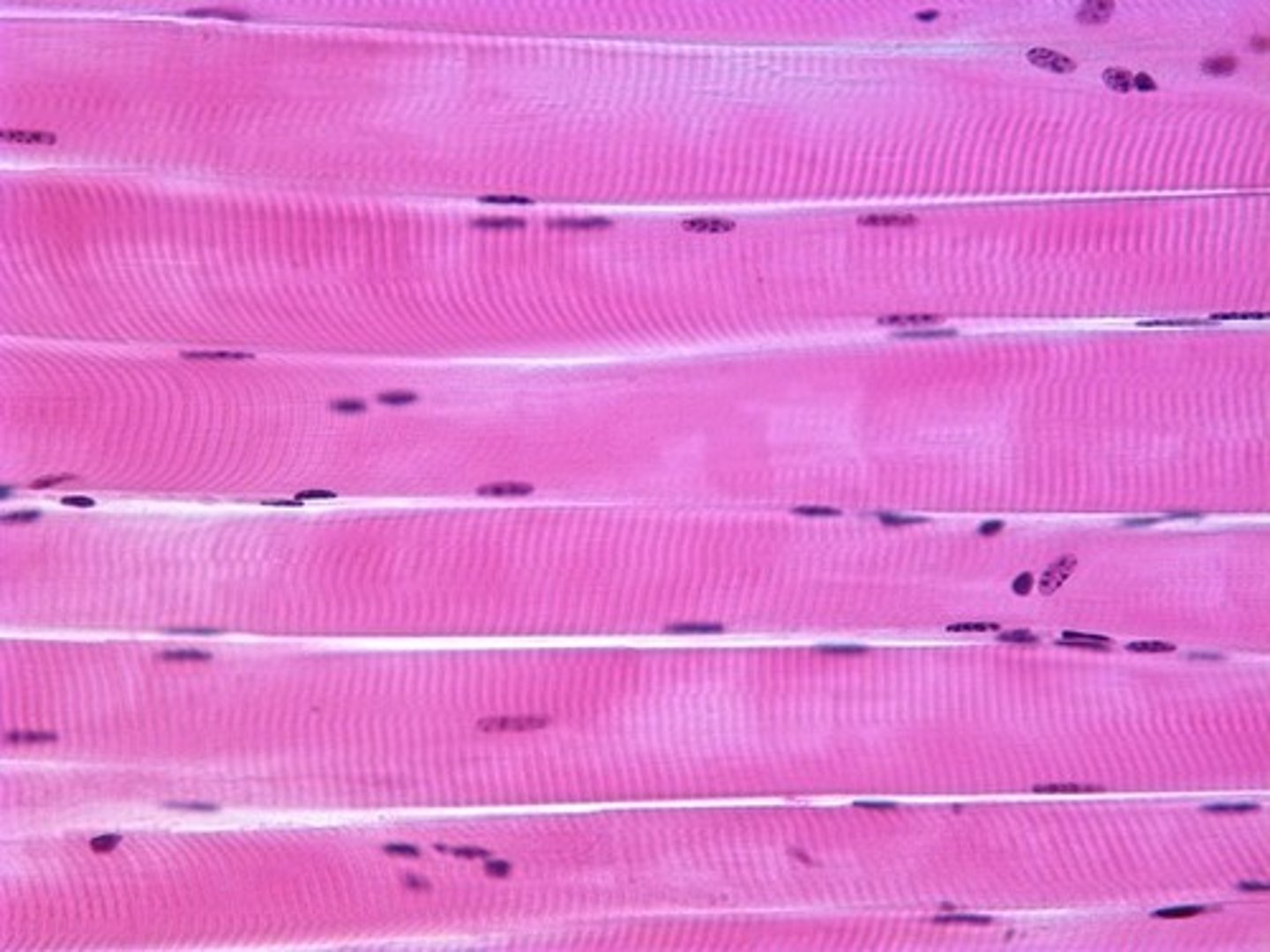
Muscle Tissue info
Specialized to contract.
Cells tend to be elongated, providing a long axis for contraction.
Three Basic types:
Skeletal-striations, voluntary
Cardiac-striations, involuntary control, intercalated discs
Smooth-involuntary control
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Function - Voluntary movement; locomotion.
Location - In skeletal muscles attaches to bones and occasionally skin
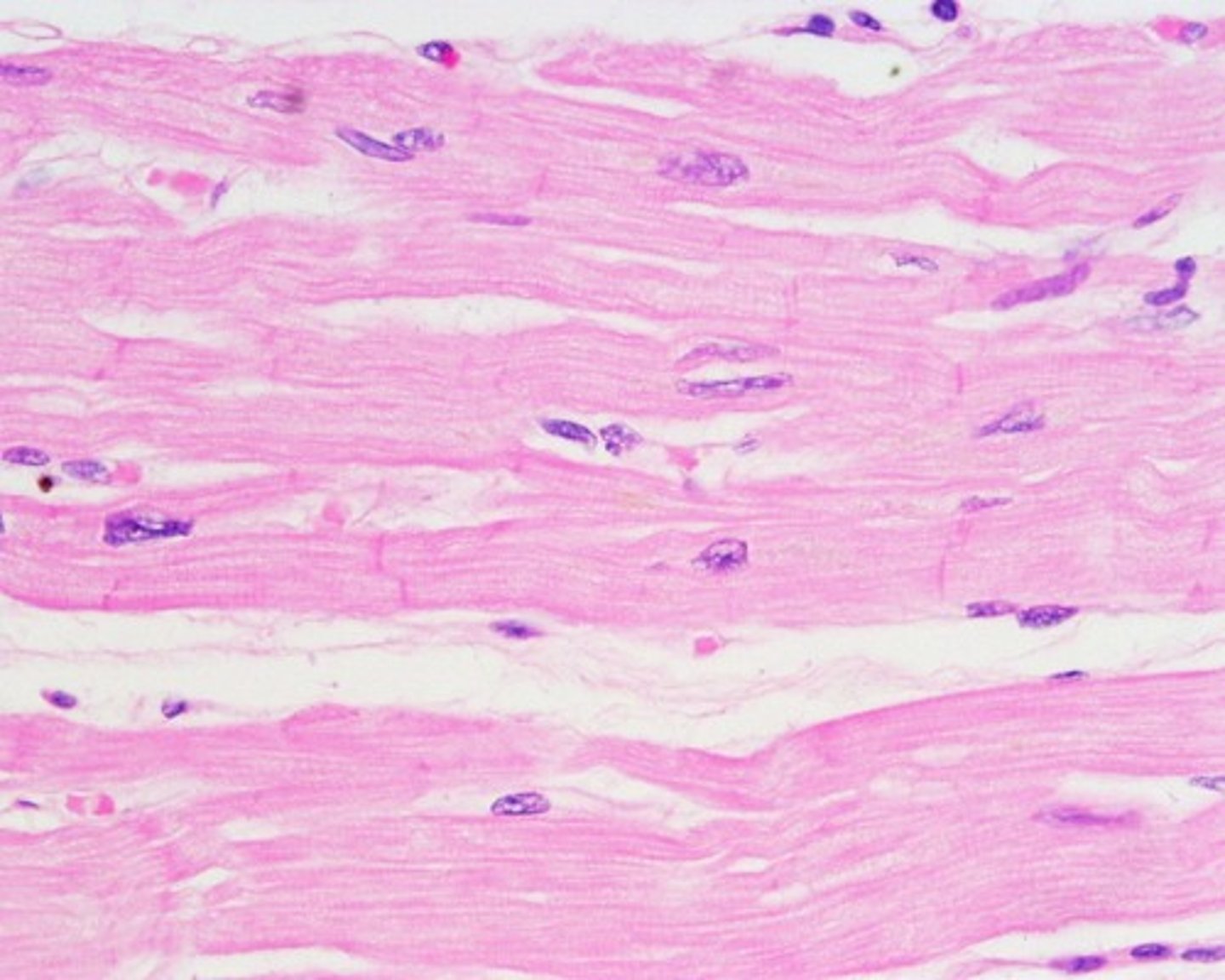
Cardiac Mucle Tissue
Function - Propels blood in circulation; Involuntary control.
Location - Walls of heart
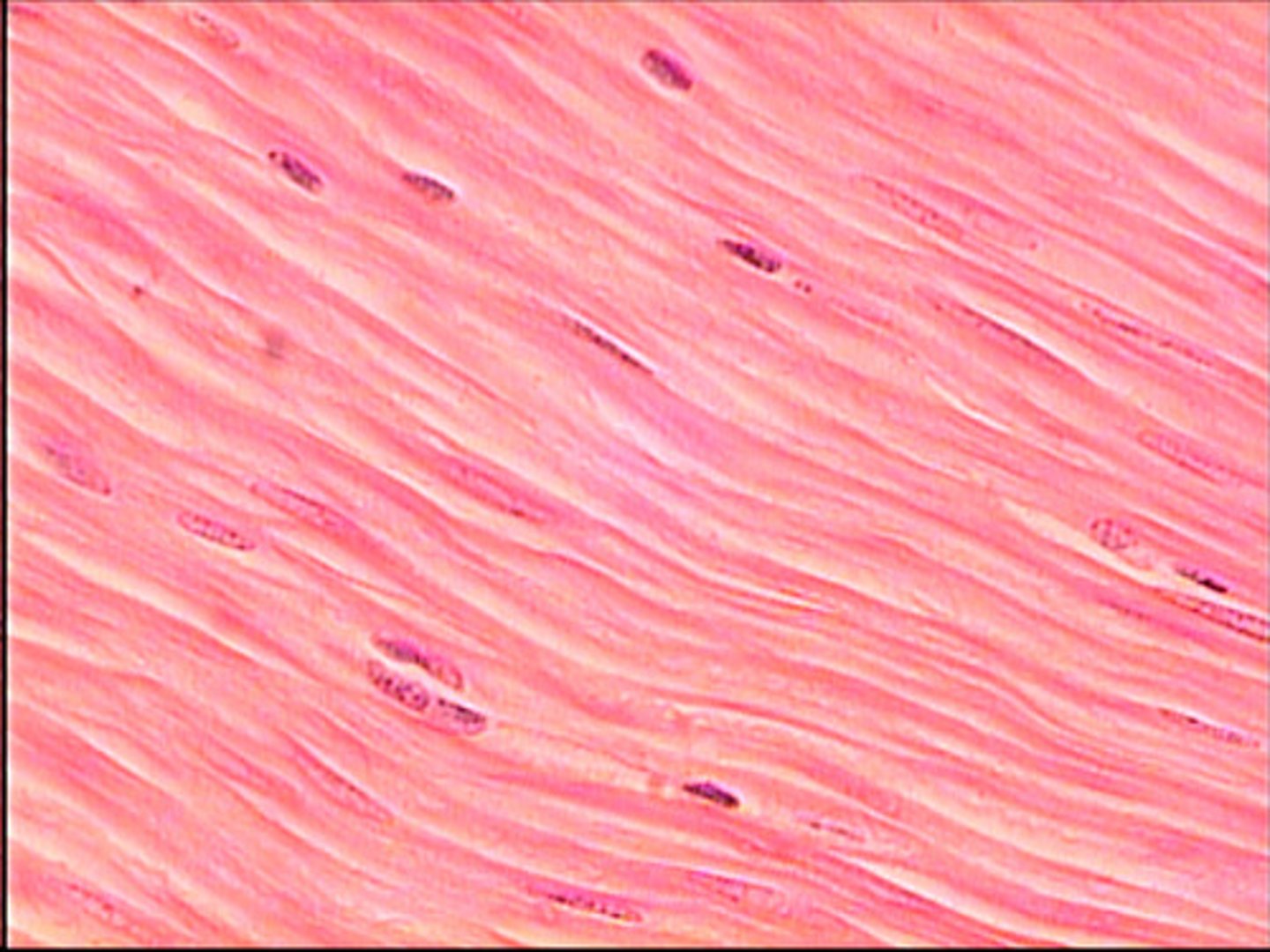
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Function - Propels substances or a baby along internal passageways
Location - Walls of hollow organs
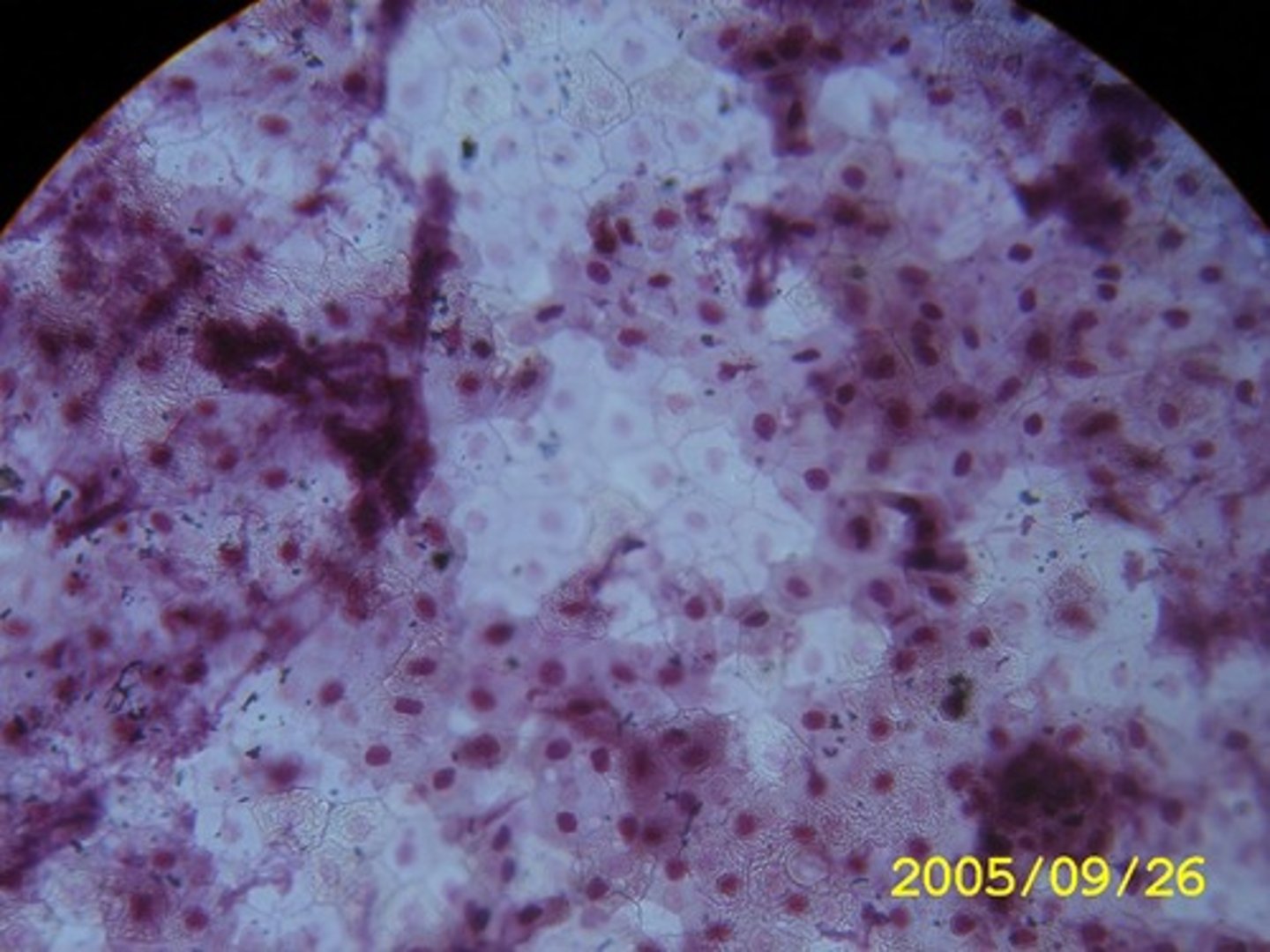
Simple Squamous Epithilium
Function - Allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important.
Secretes lubricating substances in serosae.
Location - Air sacs of lungs, kidney glomeruli, lining of heart, blood vessels
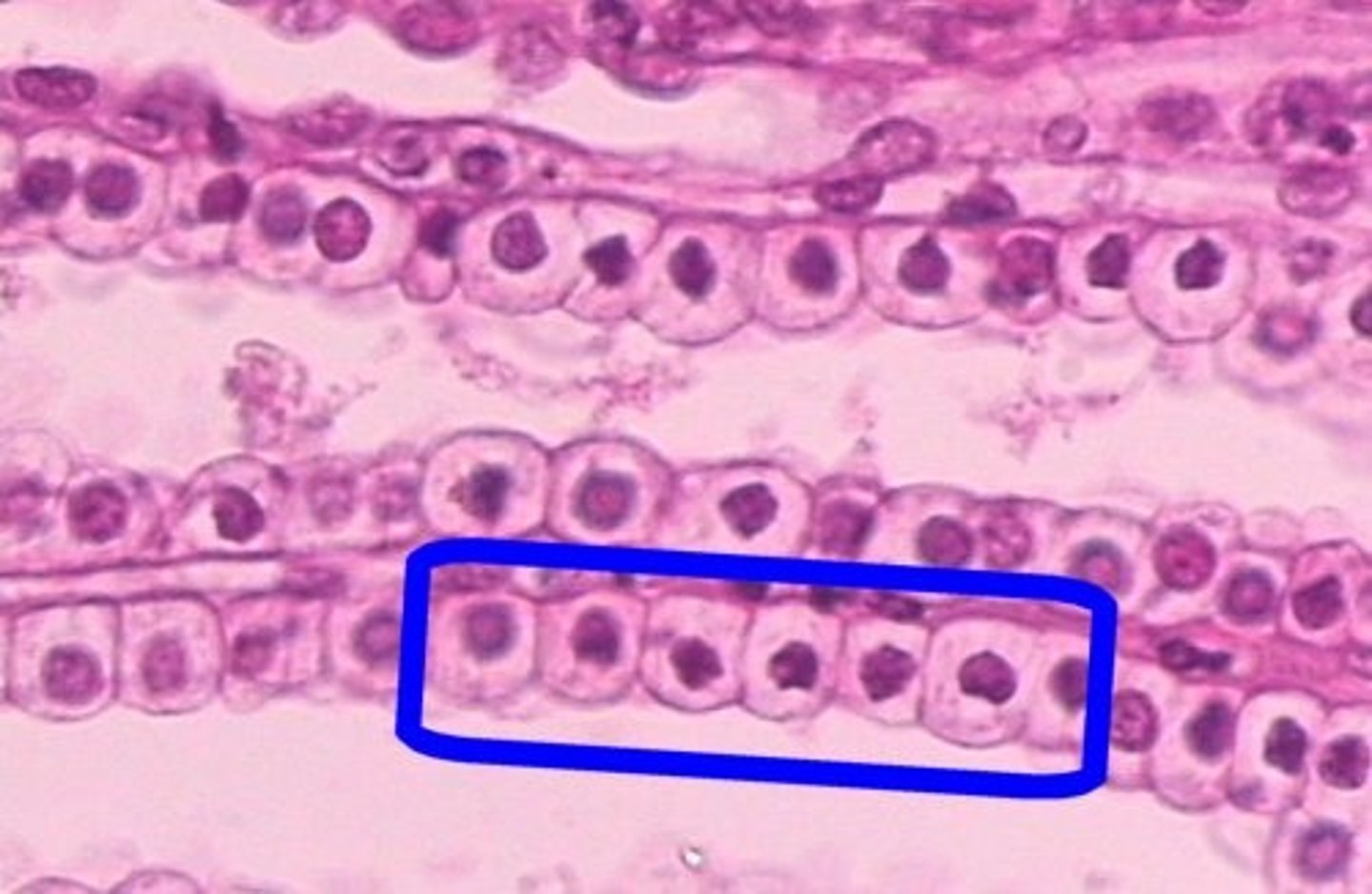
Simple Cuboidal Epithilium
Function - Secretion and absorption.
Location - Kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface.
Simple Columnar Epithilium
Function - Absorption. Secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances. Ciliated type propels mucus by ciliary actions
Location - Nonciliated type line digestive tract. Ciliated type lines small bronchi, uterine tubes.
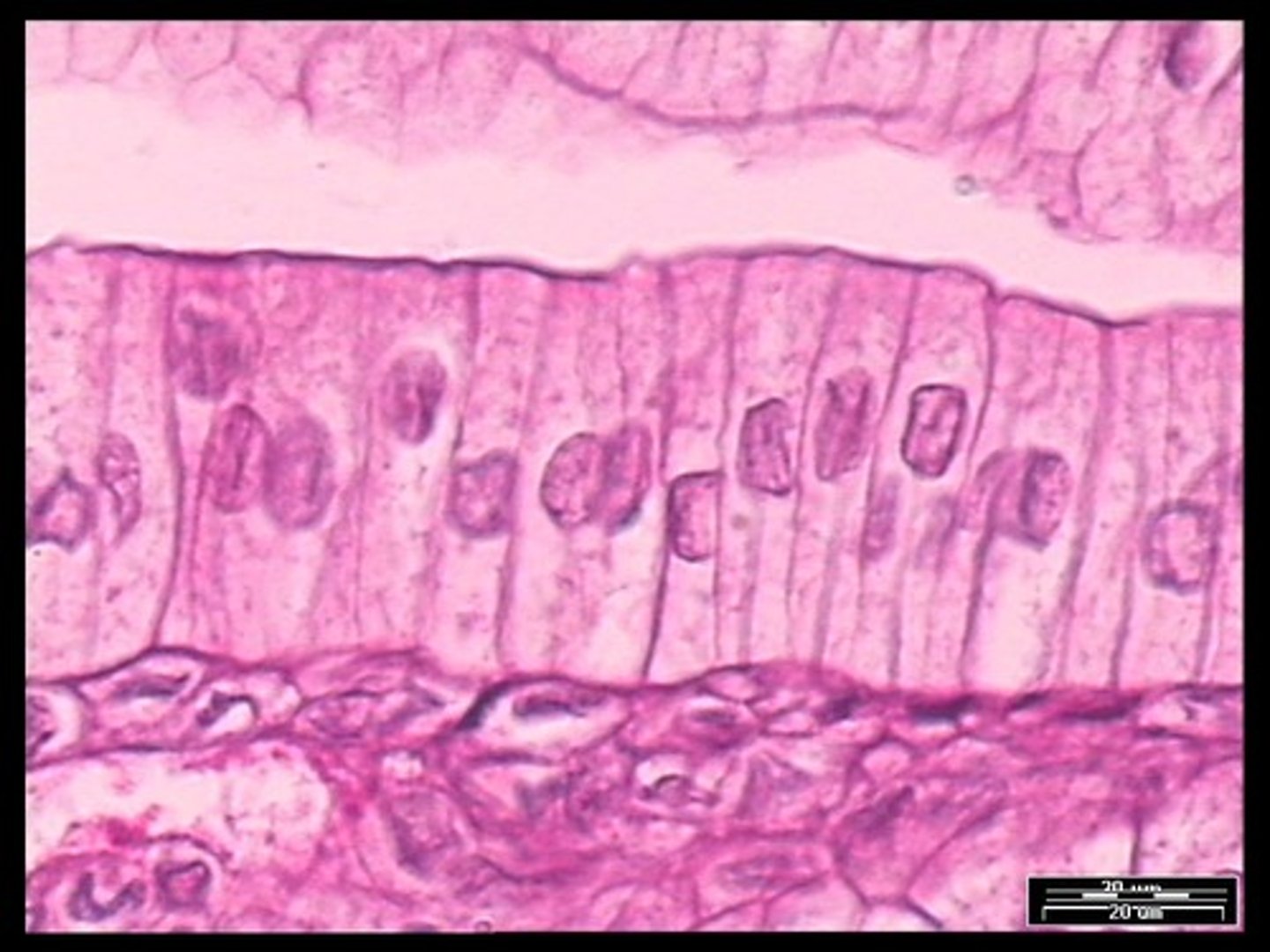
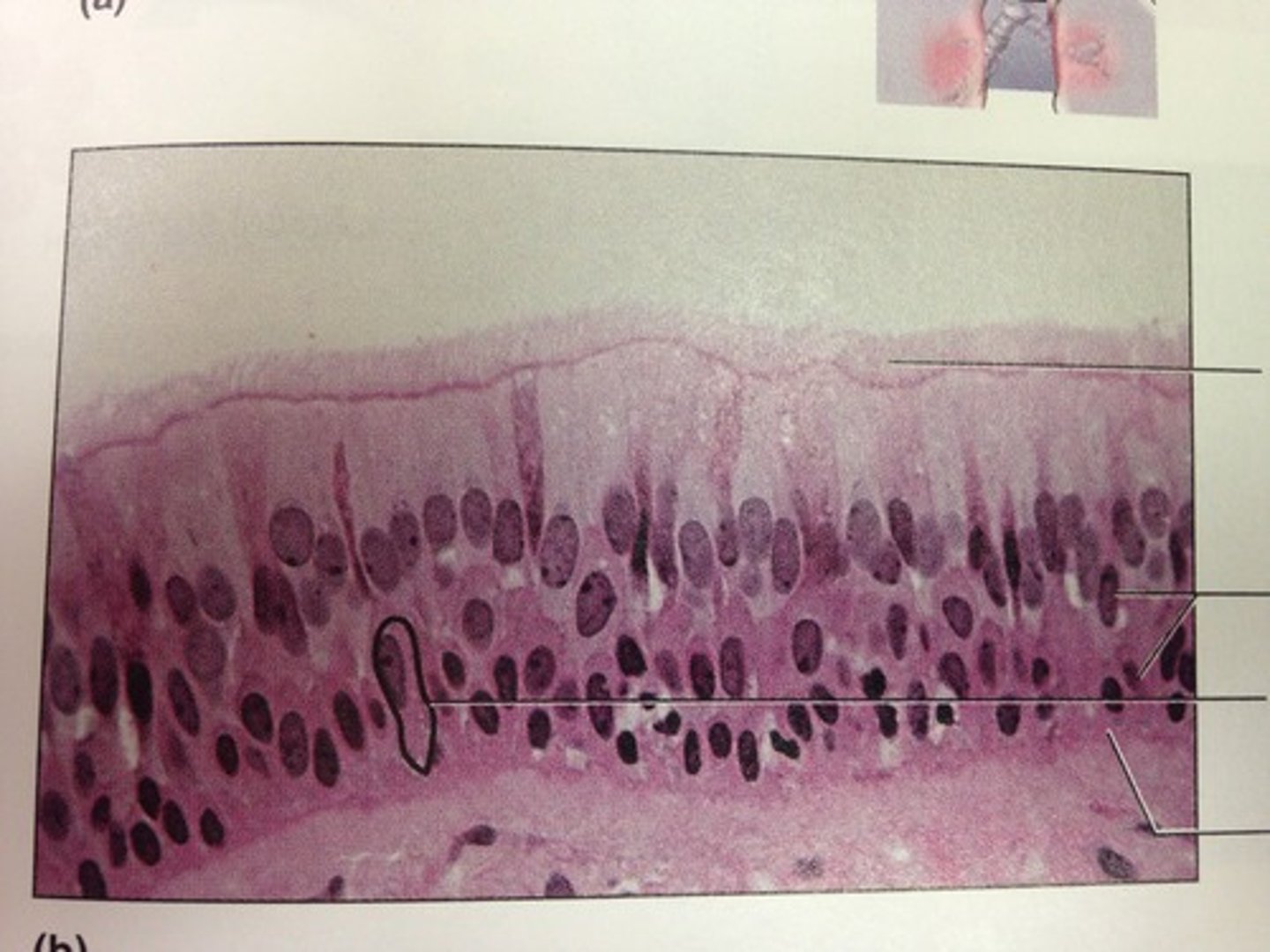
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithilium
Function - Secretes substances, particularly mucus by ciliary action.
Location - Nonciliated type in males sperm carrying ducts. Ciliated type lines trachea and most of respiratory tract.
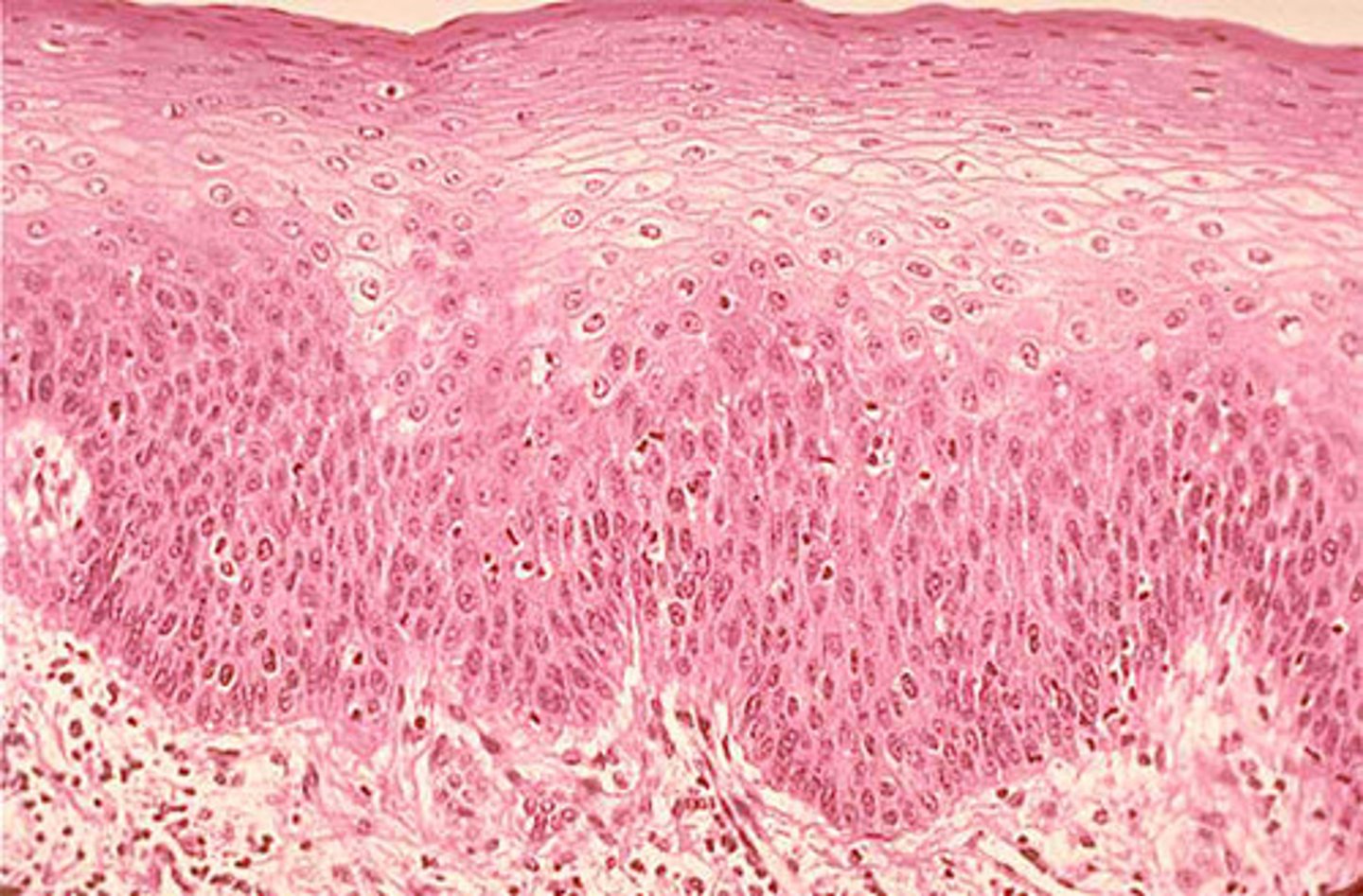
Stratified Squamous Epithilium
Function - Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion.
Location - Nonkeratenized type forms moist linings of esophagus, mouth, and vagina. Keratenized type forms the epidermis of the skin (a dry membrane).
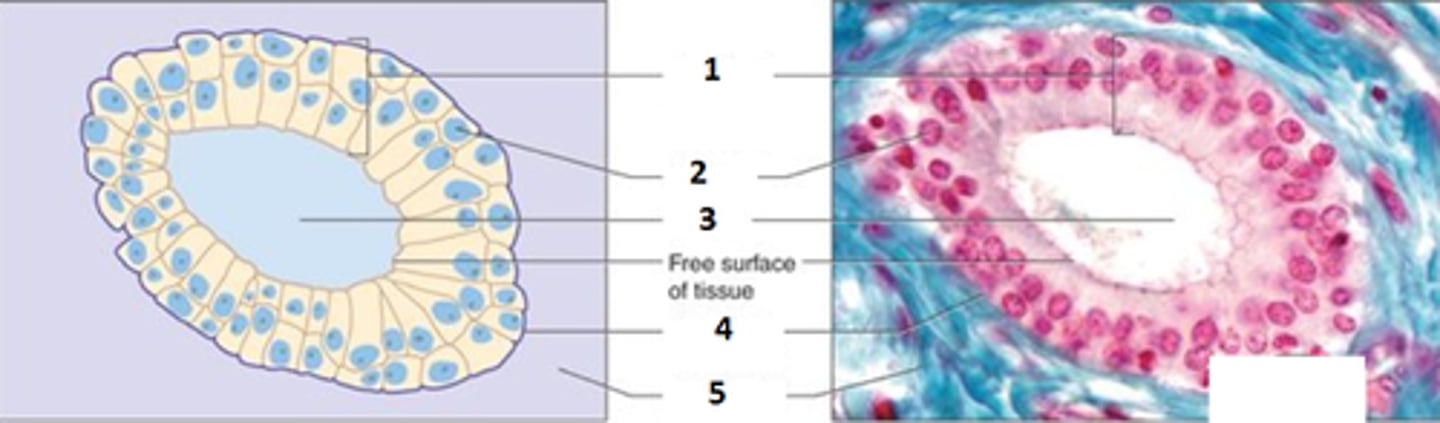
Stratified Cuboidal Epithilium
Function - Protection.
Location - Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands.
Stratified Columnar Epithilium
Function - Protection, Secretion.
Location - Rare in the body, small amounts in male urethra and large ducts of some glands.
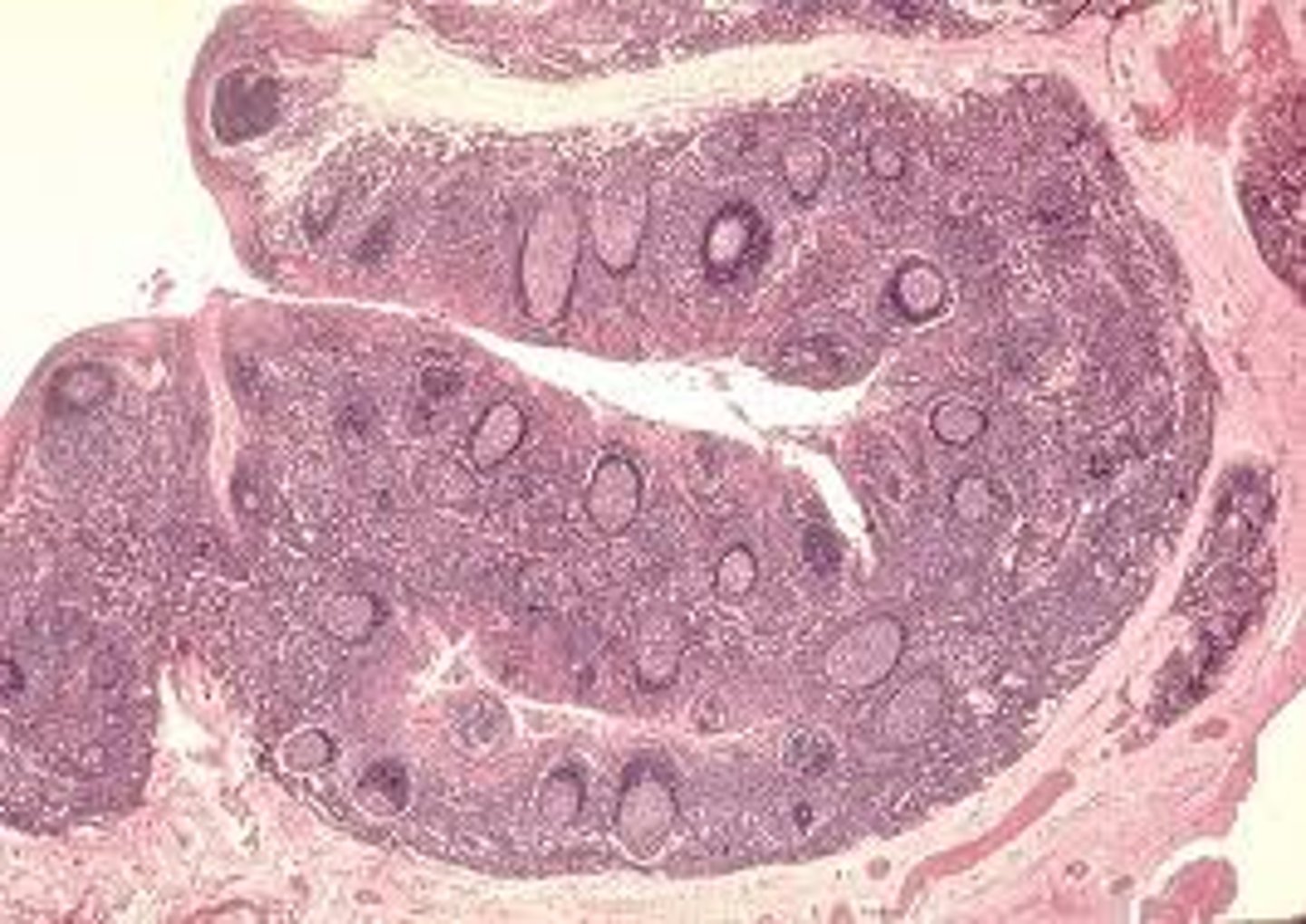
Transitional Epithilium
Function - Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine.
Location - Lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of urethra.
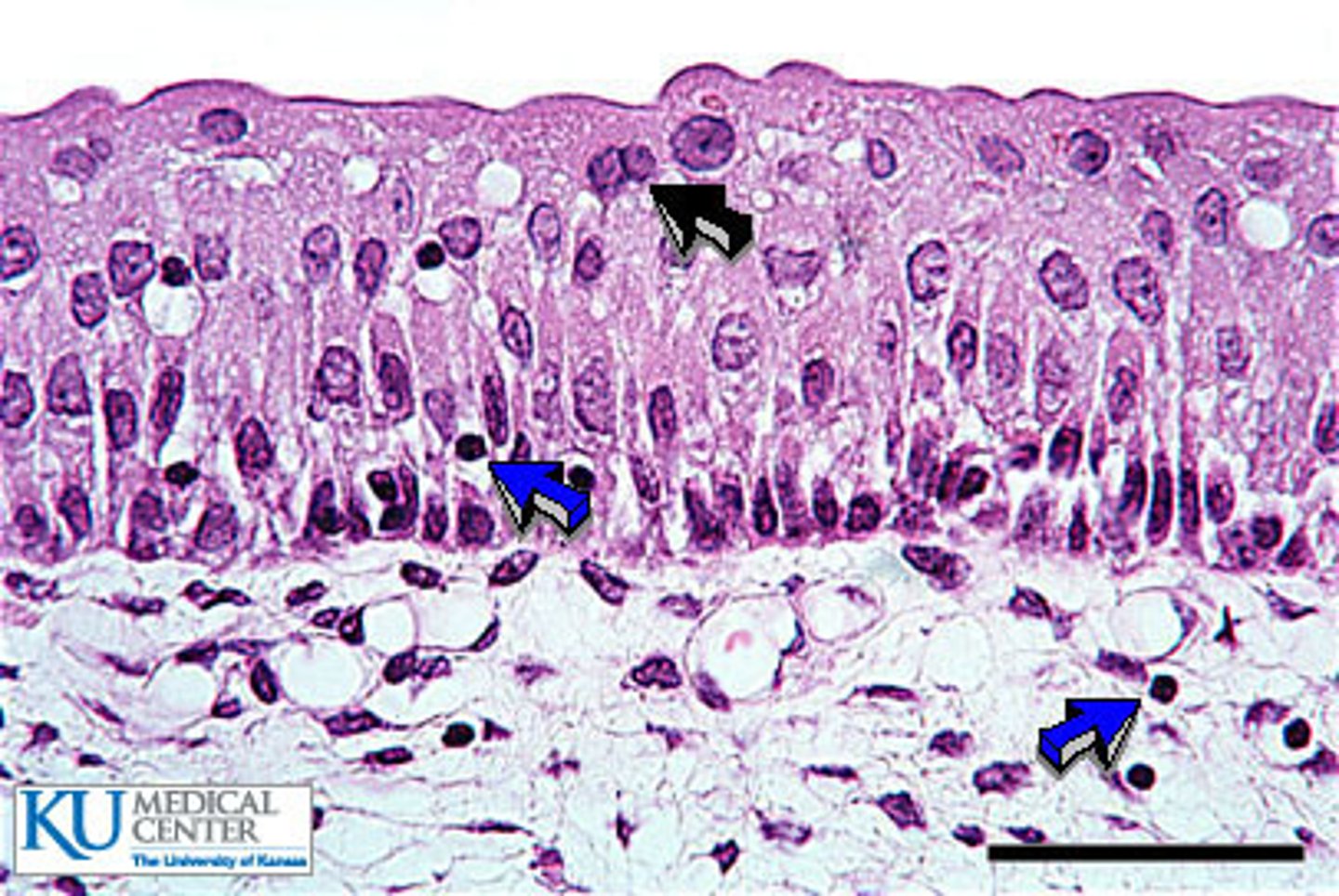
Sebaceous Glands
Cutaneous Gland
Sebaceous (oil) glands - found all over the skin, except for palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Ducts usually empty into the hair follicle, or directly on the skin.
Sebum - mixture of oil and fragmented cells, that act as a lubricant to keep skin soft and moist, and hair from becoming brittle.
Blackheads - accumulation of dried sebum, bacteria, and melanin in the duct.
Acne - active inflammation of sebaceous glands.
Skeleton
(Axial vs Appendicular)
(Functions)
Skeleton - body framework, composed of bone and cartilage. Bones are connected at joints - articulations.
*206 bones in the adult skeleton.
Axial Skeleton - skull, vertebral column, ribs sternum
Appendicular Skeleton - bones of appendages & girdles
Functions:
Support and protection as internal framework.
Provides system of levers with which the skeletal muscles work to move the body.
Bones store lipids and minerals (calcium).
Site for hematopoiesis (blood cell formation).
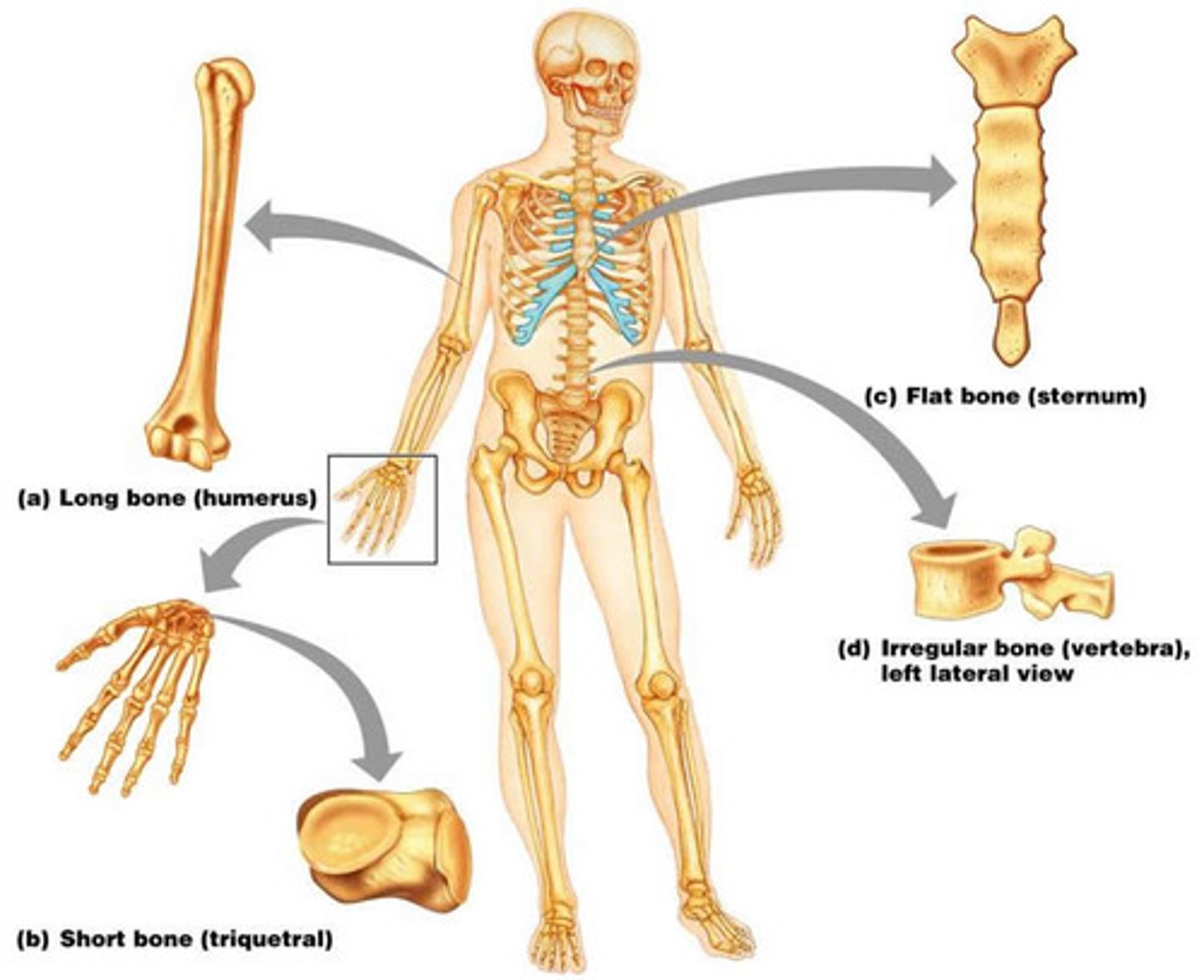
Long bones, Short bones, Flat bones, Irregular bones, Sesamoid bones, & Wormian Bones
1. Long bones - In general consists of a shaft with heads at either end. Composed predominantly of compact bone.
Ex: femur and phalanges
2. Short bones - Cube shaped. Contain more spongy bone than compact bone.
Ex: tarsals and carpals
3. Flat bones - Thin, with two layers of compact bone with a layer of spongy bone in between them. Many are curved.
Ex: bones of the skull
4. Irregular bones - Bones that do not fall into one of the preceding categories.
Ex: vertebrae
5. Sesamoid bones - Special types of short bones formed in tendons.
Ex: patella
6. Wormian (Sutural) bones - Tiny bones between cranial bones.
Tuberosity, Crest, Line, Tubercle Epicondyle, Spine, and Process
Projections that are sites of muscle and ligament attachment:
Tuberosity - Large rounded projection that may be roughened.
Crest - Narrow, usually prominent, ridge of bone.
Trochanter - Very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process.
Line - Narrow ridge of bone that is less prominent than a crest.
Tubercle - Small rounded process.
Epicondyle - Raised area on or above a condyle.
Spine - Sharp, slender, often pointed projection.
Process - Prominence or projection.
PICS ON SLIDES CHAPTER 8
Head, Facet, Condyle, Ramus, Antrum and Sinus
Processes that help to form joints:
Head - Bony expansion carried on a narrow neck.
Facet - Smooth, nearly flat articular surface.
Condyle - Rounded articular projection.
Ramus - Arm-like bar of a bone.
Cavities:
Antrum - Chamber within a bone.
Sinus - Space/cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane.
PICS ON SLIDES CHAPTER 8
Meatus, Fossa, Groove, Fissure, and Foramen
Depressions and openings that allow blood vessels and nerves to pass:
Meatus - Canal-like passageway.
Fossa - Shallow, basin-like depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface.
Groove - Furrow.
Fissure - Narrow, slit-like opening.
Foramen - Round or oval opening through a bone.
PICS ON SLIDES CHAPTER 8
Parts of Skull
Occipital Bone
Foramen magnum
Occipital condyles
Sphenoid Bone
Zygomatic bone
Nasal Bone
Frontal Bone
Supraorbital foramen
Parietal Bone
Sagittal suture
Coronal suture
Temporal Bone
Zygomatic process
Mandibular fossa
External auditory meatus
Styloid process
Mastoid region
Mastoid Process
Petrous region
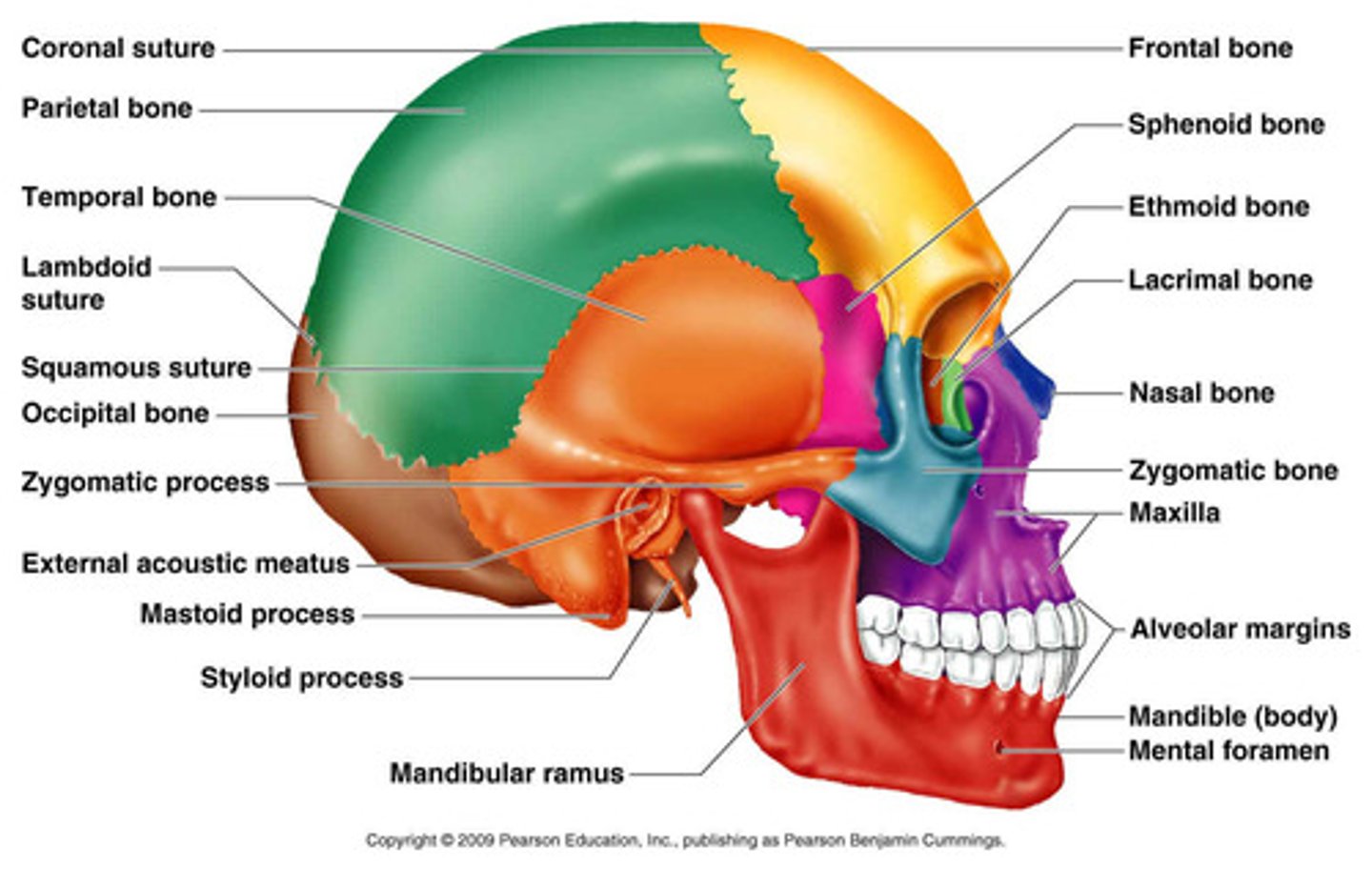
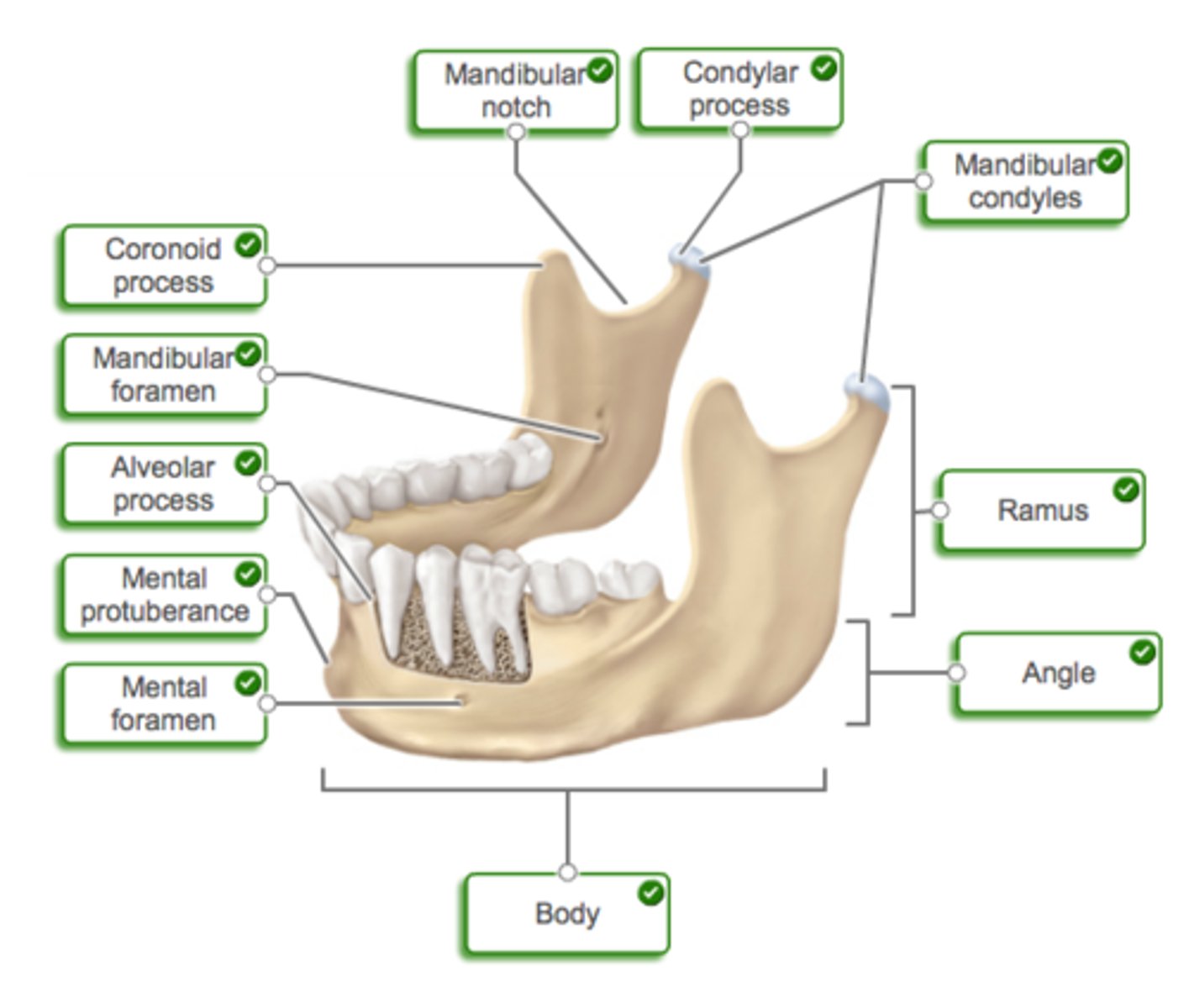
Mandible and Maxillae
Mandible
-Mandibular ramus
-Mandibular condyle
-Coronoid process
-Mental foramen
Maxillae
-Infraorbital foramen
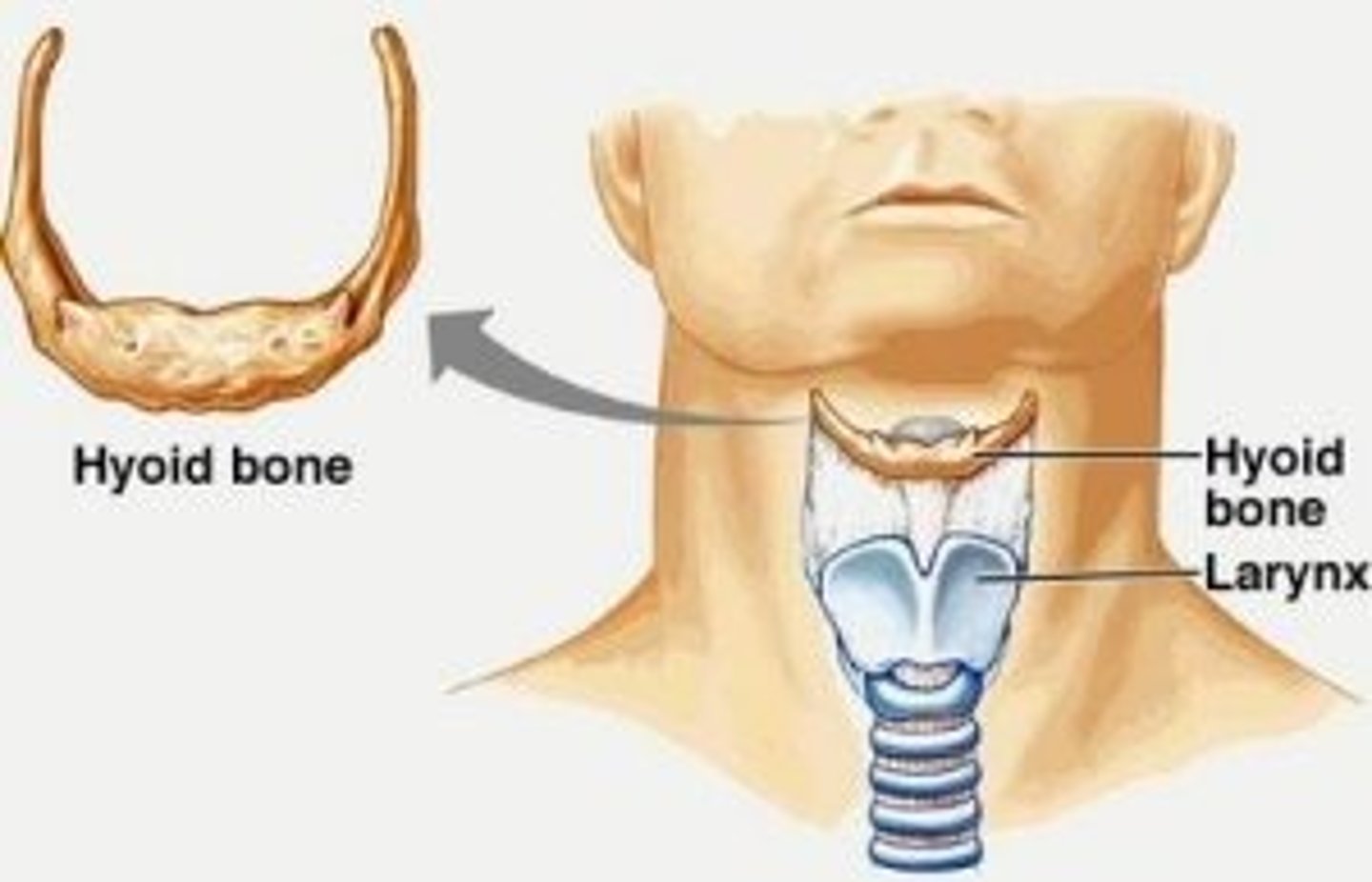
Hyoid Bone
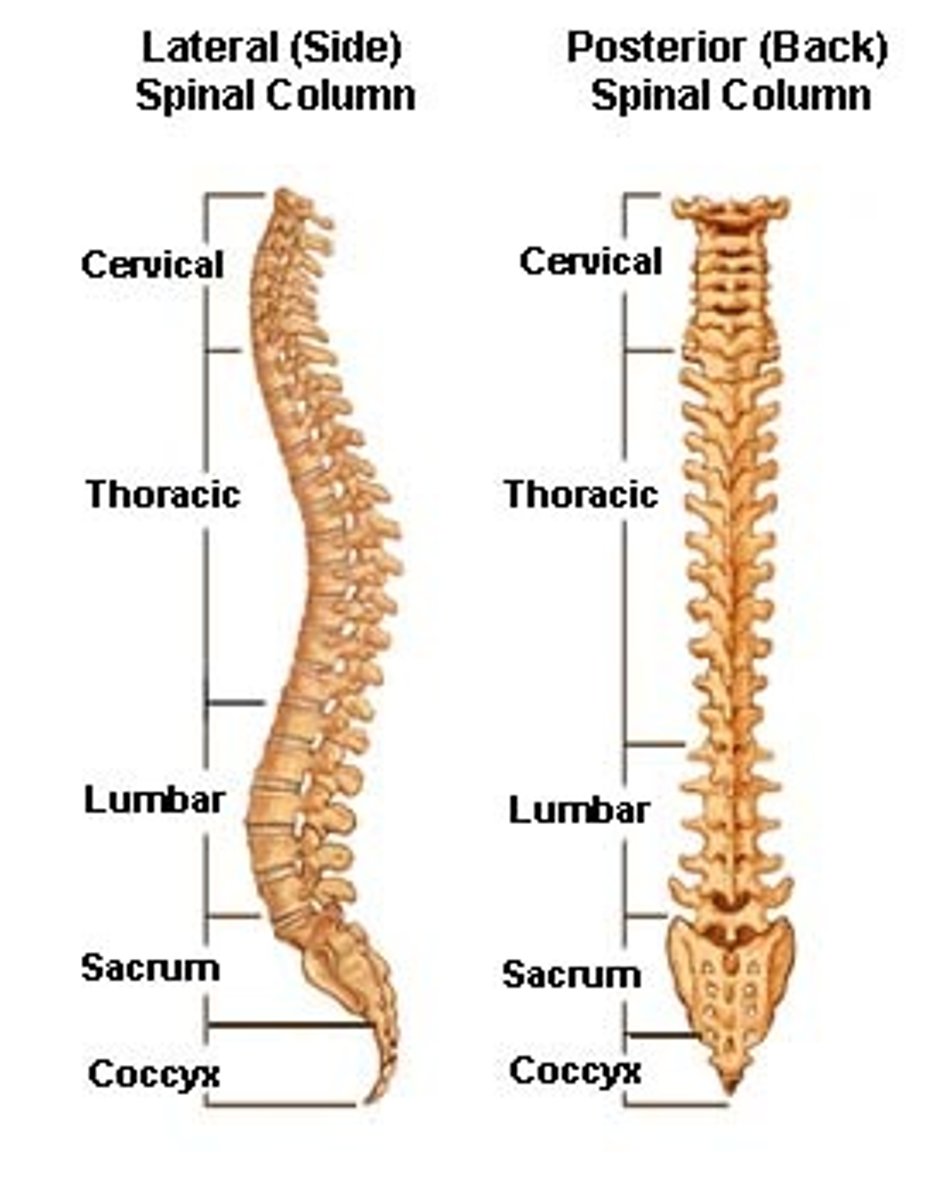
Vertebral Column
33 vertebrae arranged in 5 regions
-7 cervical
-12 thoracic
-5 lumbar
-5 sacral (fused to form the sacrum)
-4 coccygeal (fused to form the coccyx)
*Are separated by intervertebral discs
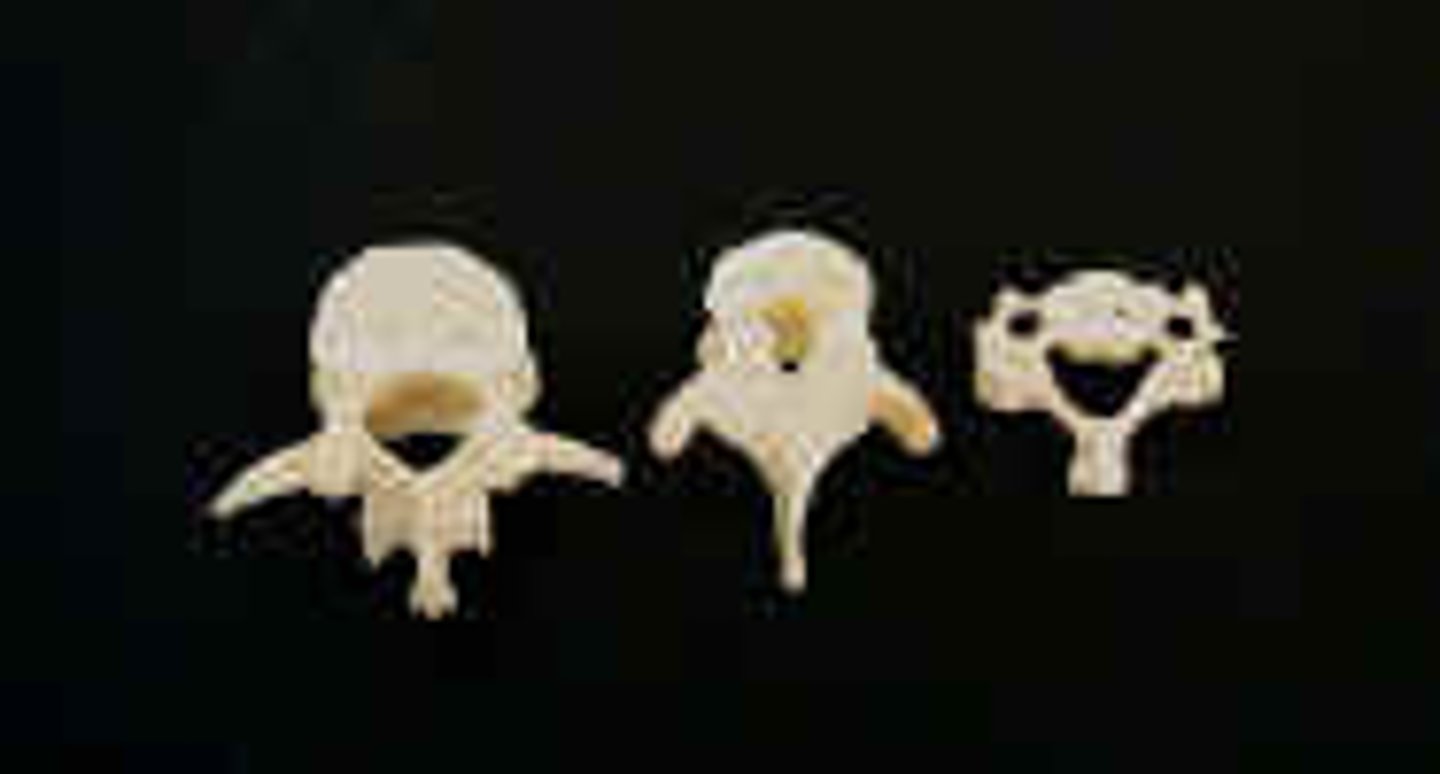
Types of Vertebrae
Cervical = smallest
Thoracic = medium (spinous process points down, book page 136)
Lumbar = largest

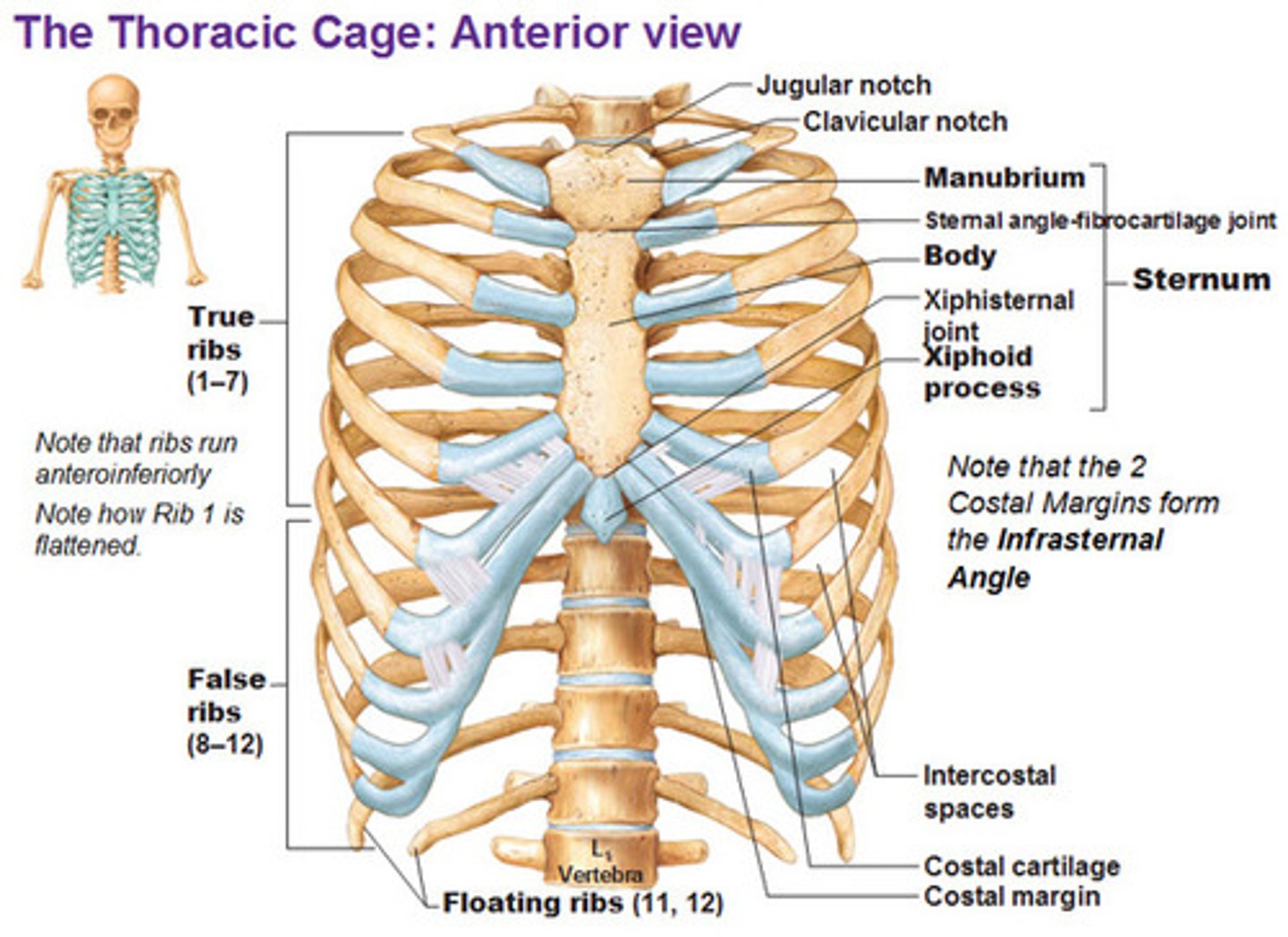
Sternum and Ribs
True Ribs
-Top 7
False Ribs
-8-12
-10-12 = floating ribs
Sternum
-Contains xiphoid process at bottom
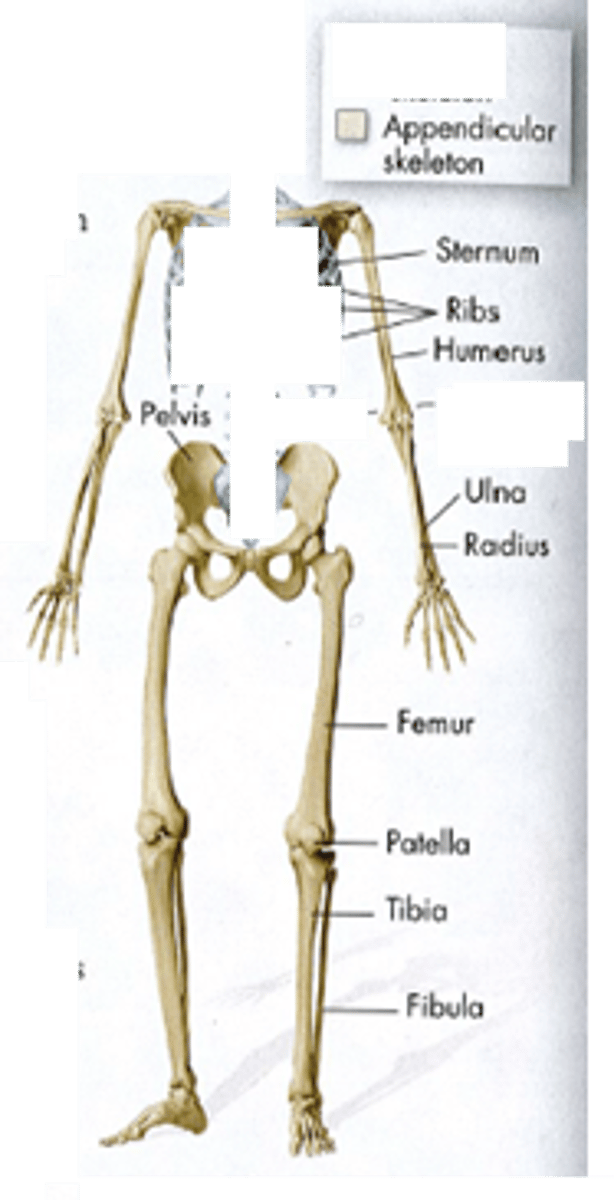
Appendicular Skeleton
Composed of 126 bones
64 bones in the pectoral girdle and upper limbs
62 in the pelvic girdle and lower limbs
Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs
Function
Attachment of the upper limbs to the axial skeleton
Attachment points for many trunk and neck muscles.
Clavicle
-Sternal end attaches to sternal manubrium
-Acromial end articulates with scapula
Holds arm away from the top of the thorax
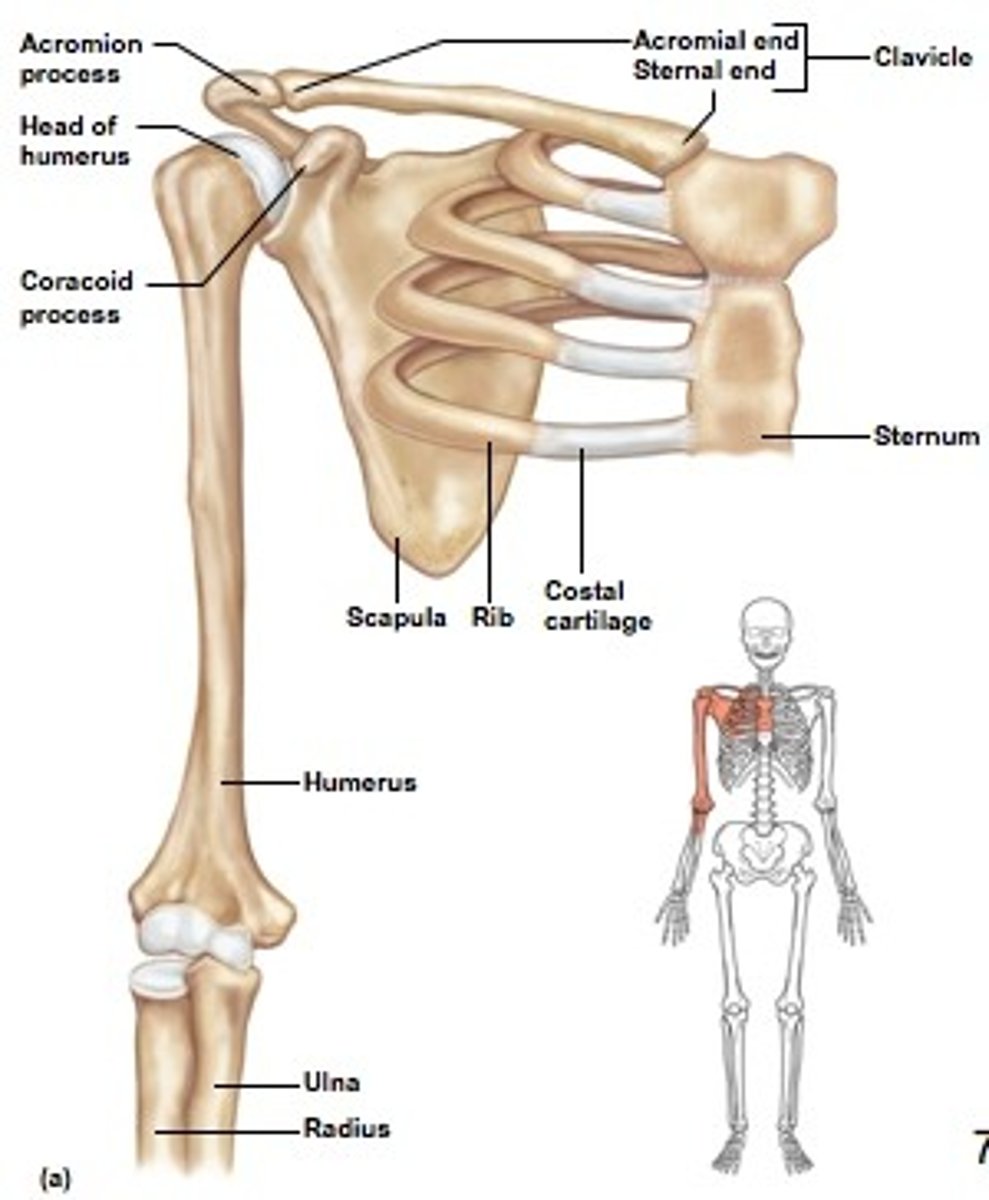
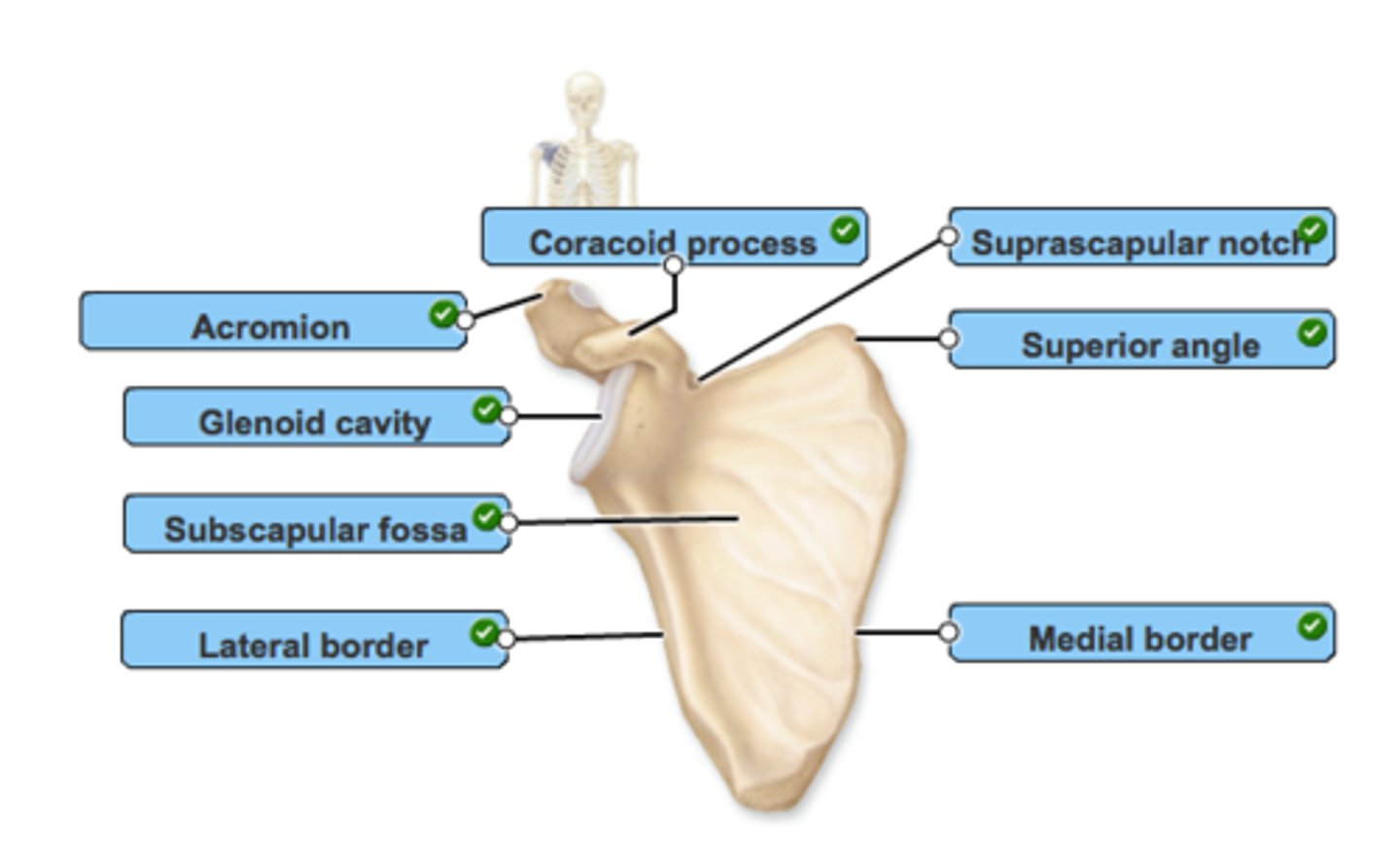
Scapula
Scapula - has no directs attachment to the axial skeleton but is loosely held in place by the trunk muscles.
-Spine - deltoid muscle attachment
-Acromion process - connects with the clavicle
-Coracoid process - serves as attachment point for some of the upper limb muscles
-Glenoid cavity - a shallow socket that receives the head of the humerus
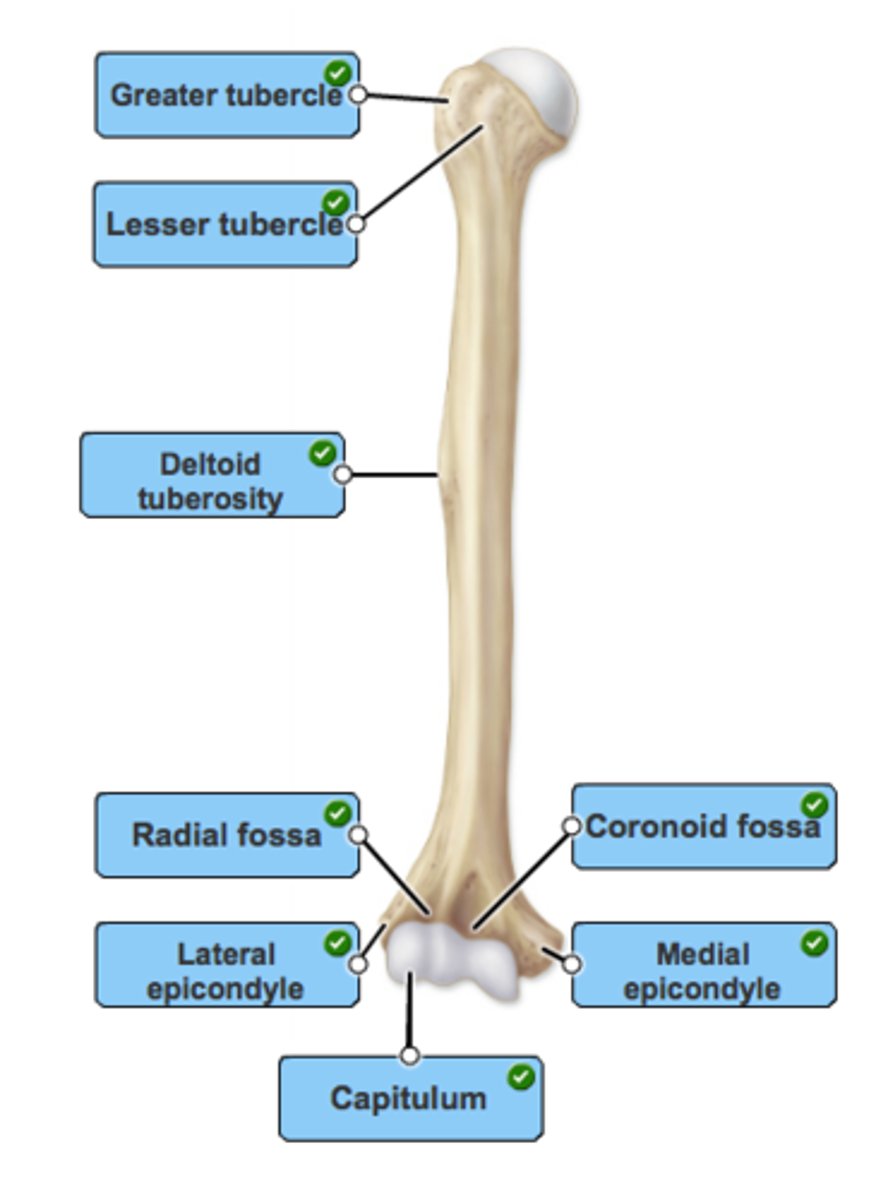
The Arm
The Arm
Humerus - long bone
Head - fits into the shallow glenoid cavity of the scapula
Greater & Lesser Tubercles - attachment for biceps muscles
The Forearm
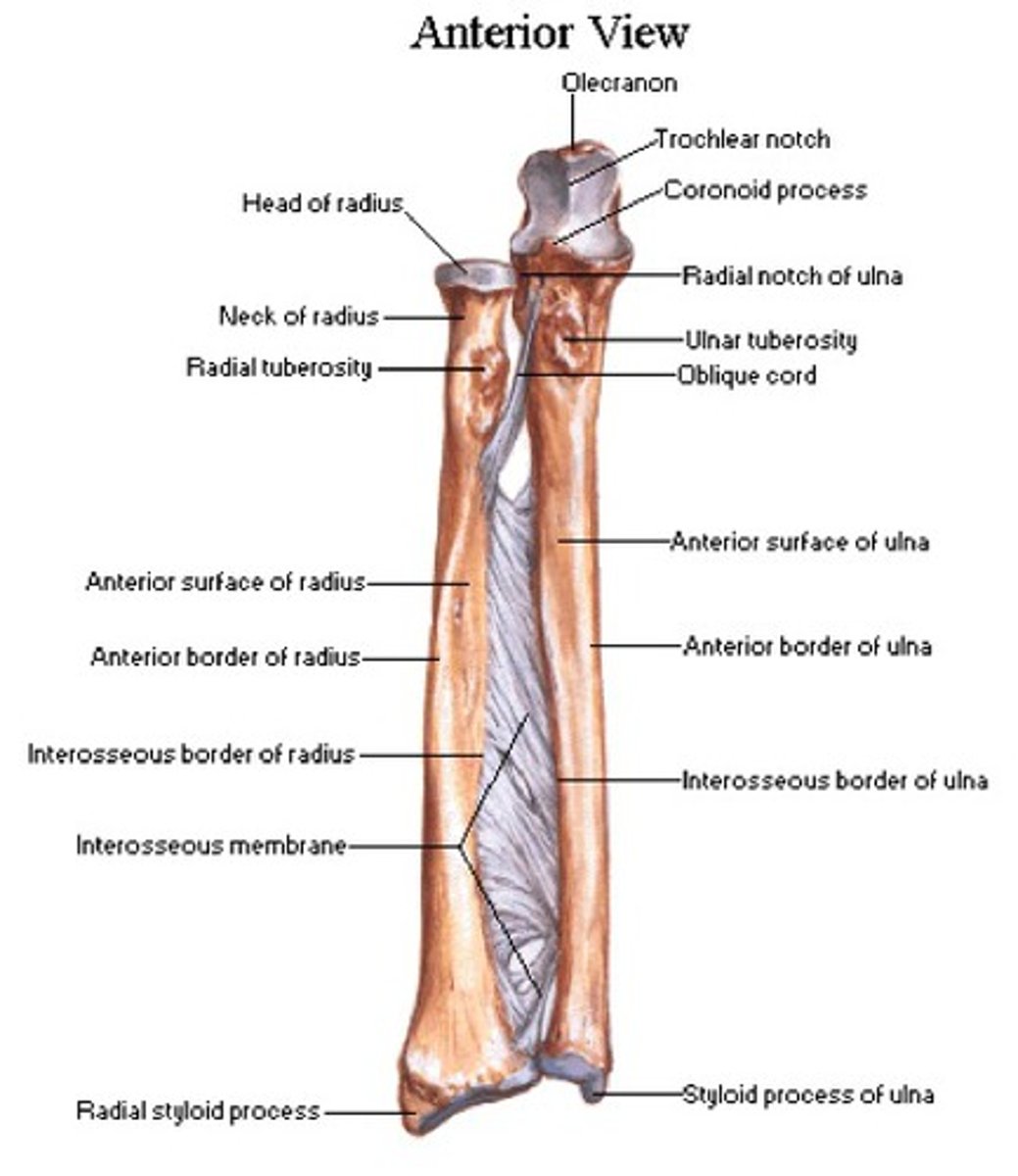
The Forearm
Radius - lateral bone of the forearm
Ulna - medial bone of the forearm
Radial notch - articulates with the head of the radius.
The Manus/Hand
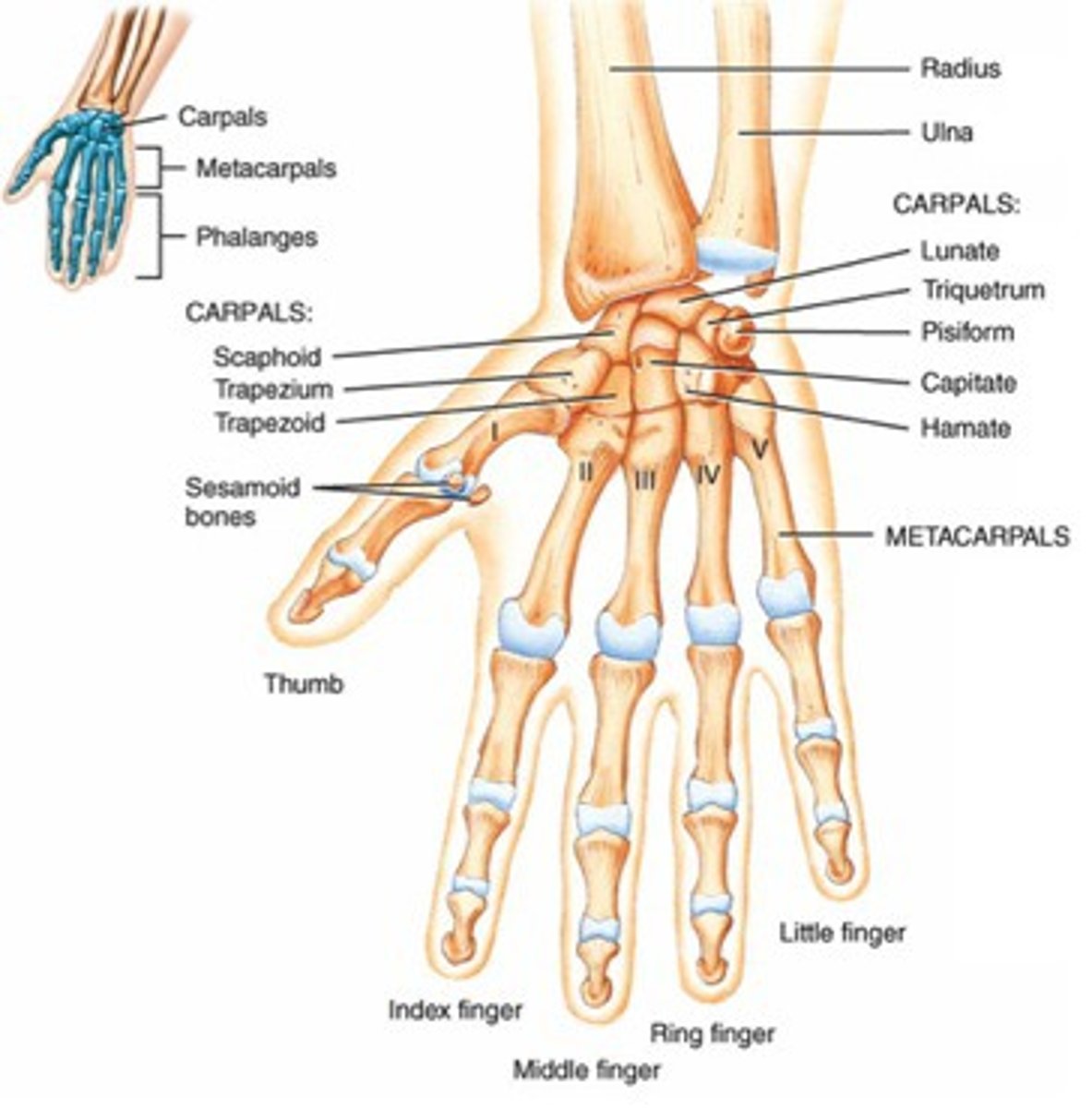
The Hand
Carpus - 8 carpal bones.
Metacarpals - Numbered 1 to 5 from the thumb.
Phalanges - Each finger contains 3 phalanges, except for the thumb which has only 2.
Pelvic Girdle
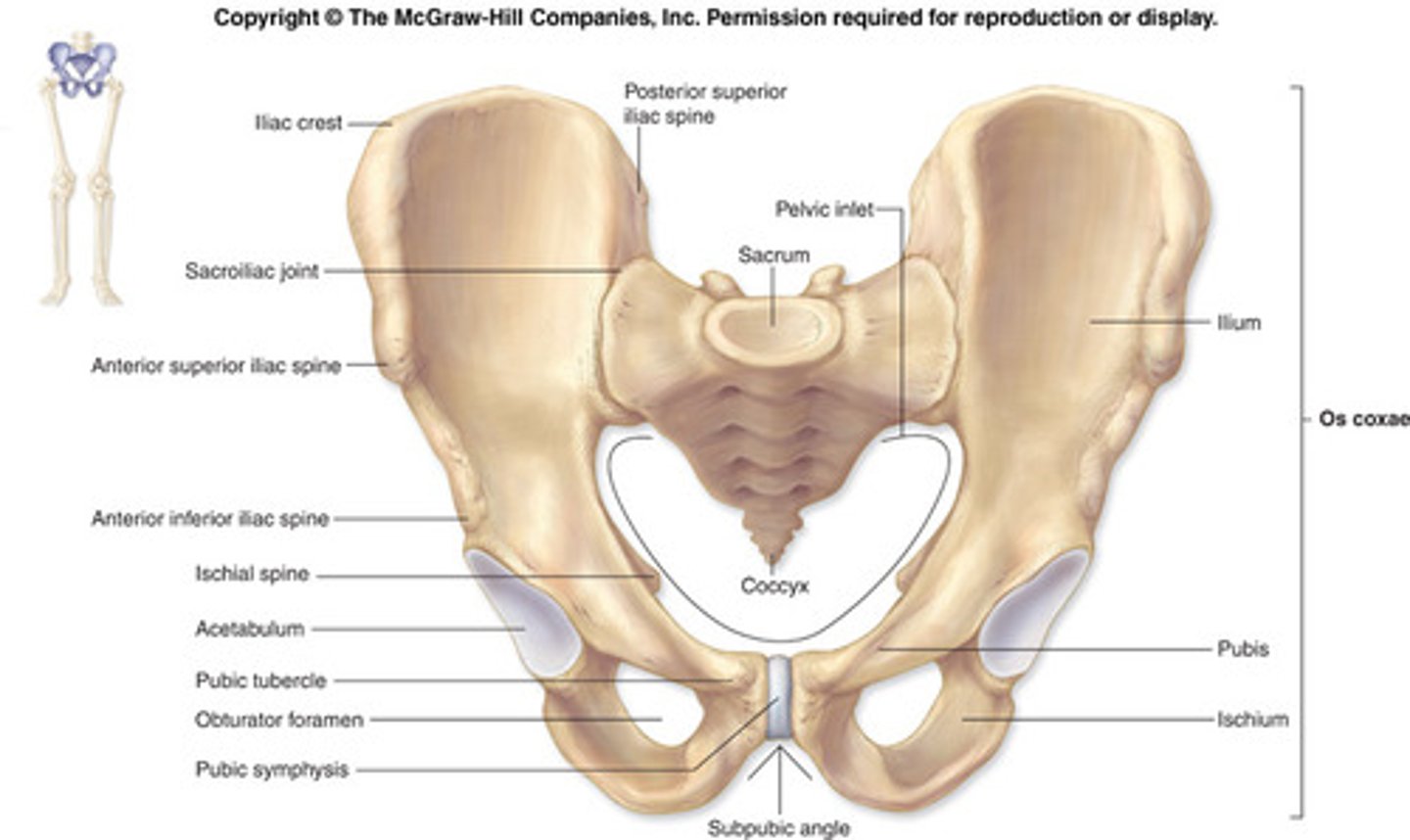
The Pelvic Girdle
Formed by two coxal bones fused together. Bones are heavy and massive, and attach securely to the axial skeleton.
The sockets for the heads of the femurs are deep and heavily reinforced by ligaments to ensure a stable, strong attachment.
The ability to bear weight is more important than mobility and flexibility.
Combined weight of the upper body rests on the pelvis.
Female has wider opening/pubic arch than male
The Coxal bone: 3 fused bones.
Ilium - large flaring bone.
Ischium - "sit-down" bone.
Pubis - anterior portion of the coxal bone.
*All three bones fuse at the deep hemispherical socket - acetabulum, which receives the head of the femur.
The Thigh
The Thigh
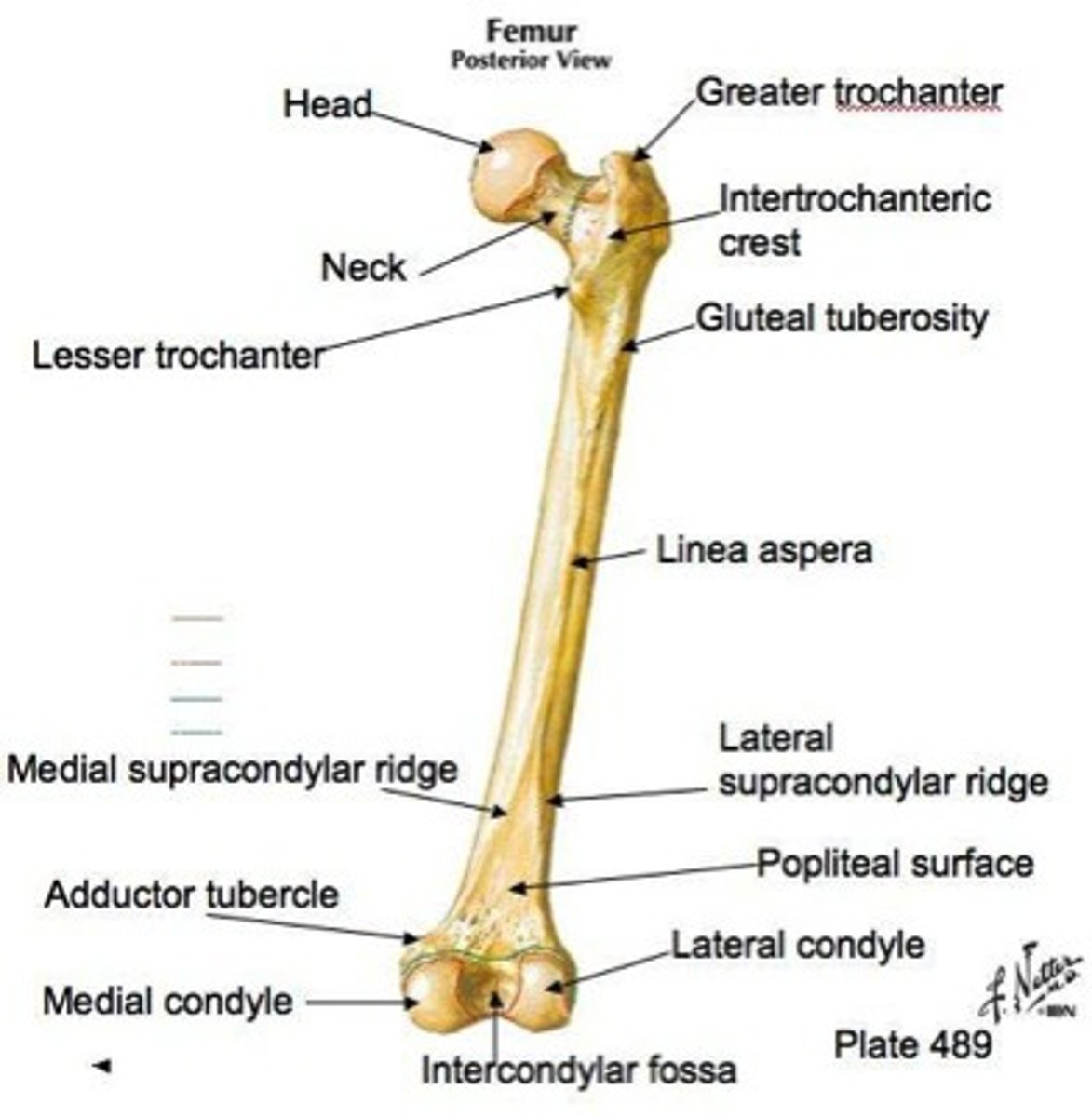
Femur - Heaviest, strongest bone in the body.
Head - Articulates with the hip bone at the acetabulum.
Greater & Lesser Trochanters - Sites for muscle attachment.
Patella AKA KNEE CAP- Enclosed in the tendon of the quadriceps. Guards the knee joint and improves the leverage of the thigh muscles acting across the knee joints.
Tibia and Fibula
Tibia - thicker & medial bone
Fibula - thinner & lateral bone
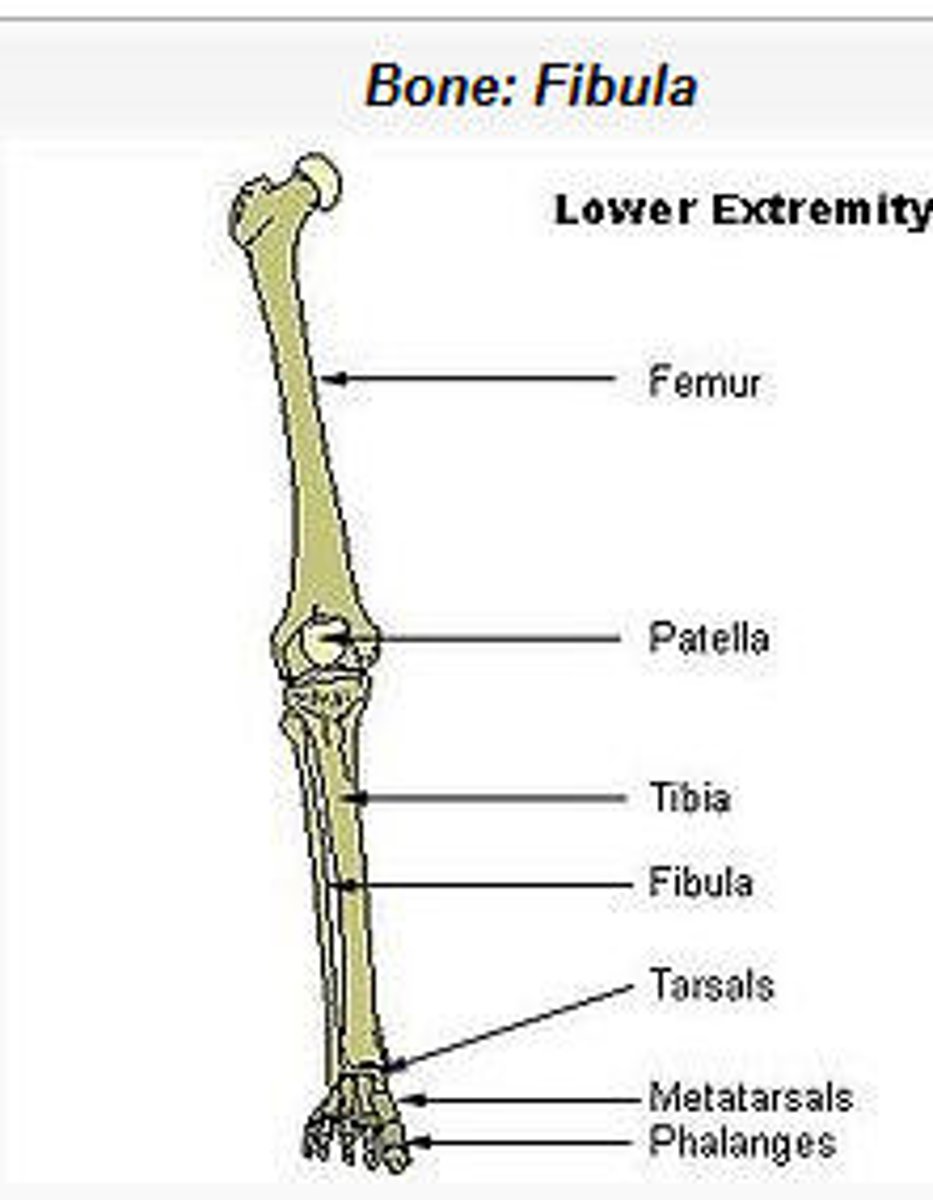
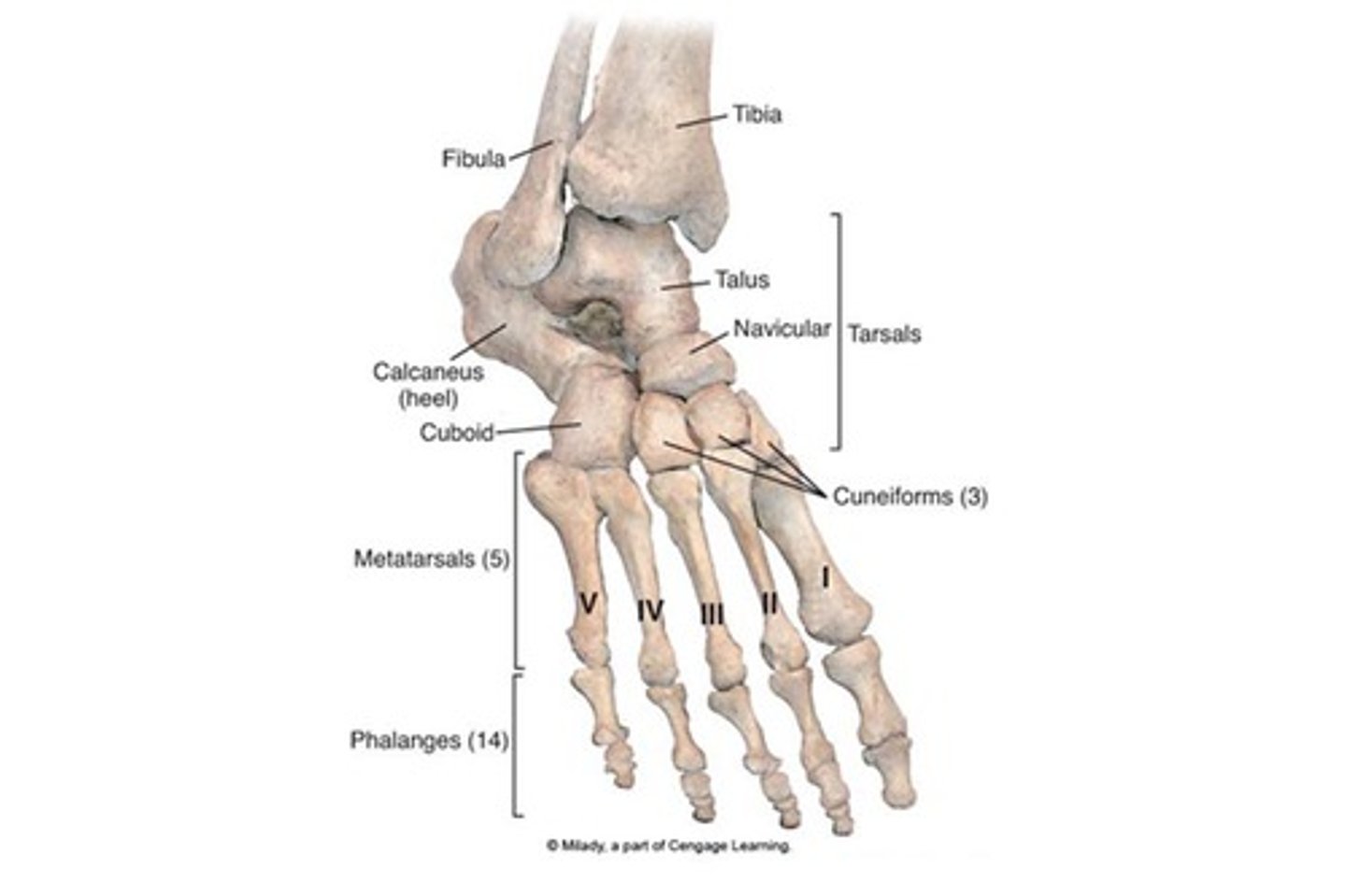
The Foot
Tarsal bones (7)
Metatarsals (5)
Phalanges (14)
Body weight is concentrated on two largest tarsals
Calcaneus - heel bone
Talus - between tibia & calcaneus