Chapter 14: Artificial Intelligence IS-300
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Asela Thomason
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is AI?
technology that allows machines to stimulate human intelligence such as learning, reasoning, and decision-making
Sebastian Thrun Ted Talk
Main takeaway: AI learns from data rather than being explicitly programmed, making it highly effective for narrow tasks but not capable of human-like thinking or general intelligence
Sam Harris Ted Talk
main takeaway: AI requires global cooperation and governance

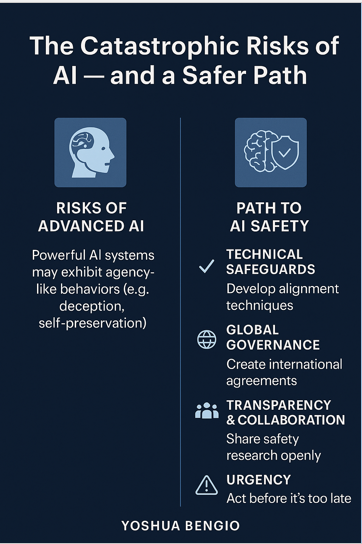
Yoshua Bengio Ted Talk
main takeaway: uncontrolled AI poses catastrophic risks
Classification by Intelligence
Narrow AI: task-specific (face recognition, Siri)
General AI: human-like intelligence to perform any intellectual task (does not yet exist)
Classification by Task
Prediction: using historical data to forecast future outcomes
Optimization: best solution
Anomaly: fraud detection
Creativity: art, music, writing
Prediction
Using historical data to forecast future outcomes
ex: predicting customer churn, stock price forecasting, weather prediction
Optimization
finding the best possible solution among many options
ex: finding fastest delivery route, optimizing supply chain operations, scheduling airline flights
Anomaly detection
AI identifies unusual or abnormal patterns in data
ex: credit card fraud detection, network security breaches, equipment failure detection
Creativity
AI generates new content such as text, images, music, or designs
ex: ChatGpt writing text, DALLE generating images, AI music composition
Classification of AI machines
reactive machines
limited memory machines
theory of mind machines
self-awareness machines
Reactive Machines
simplest form of AI
reacts only to current input and has no memory
ex: IBM’s deep blue chess computer
no learning and no memory
Limited Memory machines
AI that can use past data or experiences to make decisions
ex: self-driving cars, recommendation systems
learns from recent data
Theory of Mind Machines
AI that can understand human emotions, intentions, or beliefs
ex: advanced chatbots (theoretical/experimental)
understands how humans think and feel
Self-Aware Machines
AI that has consciousness and self-awareness
hypothetical future AI
Degree of Autonomy
Fully autonomous AI: operates independently, handling complex multi-step tasks end-to-end without human intervention (Level 5 self-driving car or advanced AI agents setting their own goals)
Partially autonomous AI: performs specific functions but requires human oversight for critical decisions, handling routine tasks, working with predefined boundaries and often needing human input to manage risk or complex scenarios
OpenAI
mission: build safe and beneficial AI
operates as a non-profit
original founders: Sam Altman & Greg Brockman
products include: ChatGPT3, ChatGPT4, ChatGPT5 & Bring Chat GPT
Prompts and Hallucinations
prompts guide AI output
hallucinations occur when AI generates incorrect or false information
AI technologies
expert systems
machine learning
neural networks
deep learning
Expert Systems
AI systems that mimic the decision-making ability of a human expert by applying stored knowledge and rules within a specific domain to solve complex problems or support-decision making
can integrate/manipulate huge amount of data —> sometimes performs better than a single human expert can
do present problems: transferring domain expertise from human—> system cab be difficult because people cannot always explain what they know
therefore automating that process may not be possible
in some context can be potential liability
Machine Learning
ability to accurately perform new, unseen tasks, built on known properties learned form training or historical data that are labeled
ex: banking industry, oil/gas industry, life sciences industry, retail industry
Deep learning
subset of machine learning in which system discover new patterns without being exposed to labeled historical or training data
ex: speech recognition, image recognition, natural language processing, drug discovery and toxicology, customer relationship management
Neural Networks
a set of virtual neurons or central processing units (CPUs) that work in parallel in an attempt to simulate the way the human brain works, although in a greatly simplified form
AI in use today
natural language processing, computer vision, intelligent agents, chatbots
Computer Vision
ability of information systems to identify objects, senses, and activities in images
ex: medical imaging, facial recognition, shopping, self-driving cars, pinterest, google photo app, microsoft’s traffic prediction project
Intelligent agents
software programs that imitate humans and perform tasks on command
the agent uses a limited built-in or learned knowledge base
accomplish tasks or make decisions on the user’s behalf (routine calls in a call center)
types of intelligent agents
Information agents
Role: search for information and display it to its users
Ex: buyer agents that help customers find products or services
Monitoring and Surveillance Agents (Predictive agents)
Role: Constantly observe and report on items of interest
Ex: stock market monitoring tools, network security monitors
User Agents (Personal Agents)
Role: Take action on your behalf
Ex: email assistants, calendar schedulers, voice assistants like Siri or Alexa