cestoda II (tapeworms)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
cyclophyllidean cestode general features
very common; most important tapeworms in vet med
adults → infect intestine of definitive host
metacestodes → major source of pathology
eggs vary in shape and size; larvated with hooks
taeniasis
infection of adult taenia spp. in intestines of definitive host
infective stage is a cysticercus
cysticercosis
infection of metacestodes in various tissues in intermediate host
infective stage is an egg with oncosphere
taenia pisiformis definitive host
dog
taenia pisiformis intermediate host
rabbit, hare (peritoneum, other)
taenia transmission
ingestion of intermediate host infected with cysticerci
taenia taeniaeformis definitive host
cat
taenia taeniaeformis intermediate host
rodents (liver)
taeniasis pathology
very common
causes little disease (asymptomatic) unless in large numbers
taeniasis diagnostic stage
eggs/proglottids in feces
taeniasis treatment
praziquantel or other anthelmintics
avoid ingestion of cysticerci in intermediate hosts
humans: cooking/freezing meat; meat inspection & surveillance
cattle/swine: avoid egg contamination
cysticercosis pathology
can be pathogenic depending on larval species and intensity (e.g. T. multiceps in CNS)
economic importance
cysticercosis diagnostics
clinical signs (depends on location); necropsy/slaughter
difficult to diagnose
cysticercosis treatment
no effective treatment → need to prevent
drugs not effective against larvae
treatment could lead to anaphylactic shock
strong immune response after killing off larvae
taenia saginata definitive host
humans ONLY
taenia saginata intermediate host
cattle (muscle; cysticercus)
taenia saginata pathology
little pathology in human infections; heavier infection can cause GI disturbance
little pathology in cattle
economic importance → condemnation/down-grading of meat
taenia solium definitive host
humans ONLY (adult worms)
taenia solium intermediate host
swine, human (embedded larval stage in muscle; other tissues; cysticercus)
taenia solium pathology
adult worm infection
little pathology in human infections; heavier infection can cause GI disturbance
metacestode infections
swine: economic impact
human cysticercosis: serious → can end up in brain (acquired epilepsy)
taenia solium diagnostics
cysticercosis: serology, imaging
proglottids or eggs in feces
taenia solium treatment (cysticercosis)
difficult, inflammation & allergic reactions
avoid ingestion of eggs
hydatid disease
disease caused by asexual reproduction of metacestodes (hydatid cyst) in intermediate hosts (mammals, including humans)
unilocular cyst
one big cyst with smaller cysts inside → daughter cyst bud off within original cyst
multilocular cyst
numerous daughter cysts bud off original cyst → can spread around body
echinococcus granulosus definitive host
canids
echinococcus granulosus intermediate hosts
mammals: sheep (common), cattle, swine, humans
echinococcus multilocularis definitive host
canids/felids
echinococcus multilocularis intermediate hosts
rodents (mice), humans; multilocular cyst particularly affects liver
echinococcus diagnotics
serology, imaging of cysts
diagnostic stage: eggs → PCR or antigen ELISA
echinococcus treatment
praziquantel (adult worms)
hydatid disease: albendazole, surgical removal of unilocular cysts
feces disposal; avoid contacting/ingesting eggs
dipylidium caninum definitive hosts
dogs and cats
dipylidium caninum intermediate host
fleas/lice (cysticercoid)
dipylidium caninum life cycle
egg packets (larvated oncosphere)/proglottids passed in feces → ingested by flea larvae → cysticercoid in fleas/lice → intermediate host infected with cysticercoid ingested by definitive host
dipylidiasis pathology
little pathology with adult worm infections; incidental finding
dipylidiasis diagnostics
eggs/egg packets → fecal floatation
proglottids in fresh feces
dipylidiasis treatment
praziquantel, others effective
prevent flea infestation
zoonotic → important to treat dog or cat
mesocestoides intermediate hosts (2)
1st = mite (cystercercoid)
2nd = vertebrates, including dogs (many different 2nd vectors)
mesocestoides life cycle
egg passed in feces → hatches/ingested by mite (cysticercoid) → mite ingested by 2nd intermediate host (vertebrate) → 2nd intermediate host ingested by definitive host → adult worms in intestine
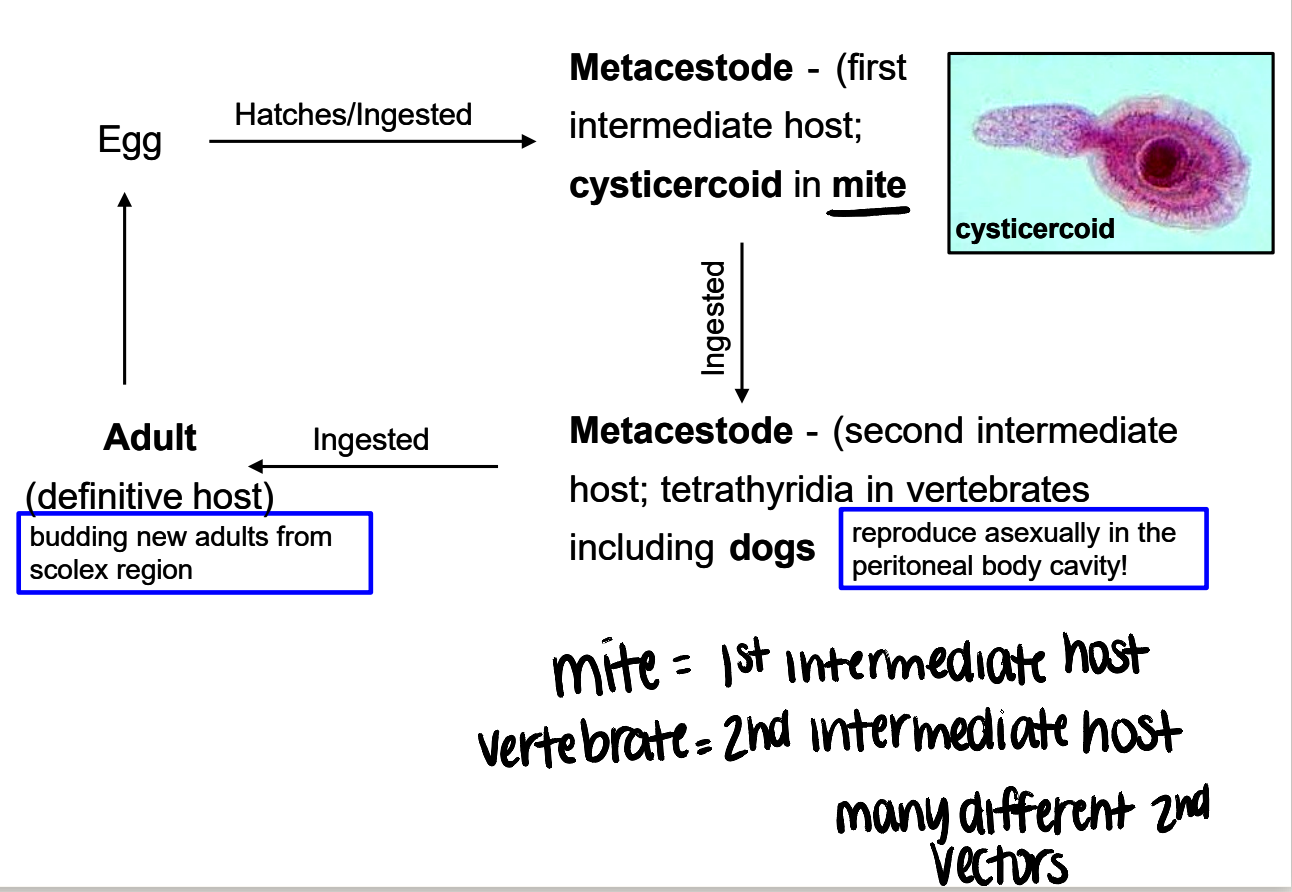
mesocestoides reproduction
asexual reproduction in peritoneal body cavity in second intermediate host
budding new adults from scolex region in definitive host
mesocestoides pathology
not common, but infections can lead to serious disease due to asexual reproduction of both larval and adult worm stages in dogs
mesocestoides diagnosis
thin shelled eggs with oncosphere
motile gravid proglottids with parauterine organ
mesocestoides treatment
praziquantel
note: must achieve 100% elimination of adults or infection can reoccur due to asexual development
moniezia definitive host
cattle, sheep, goats (large and small ruminants)
moniezia intermediate host
oribatid mites (cysticercoid)
moniezia diagnostic stage
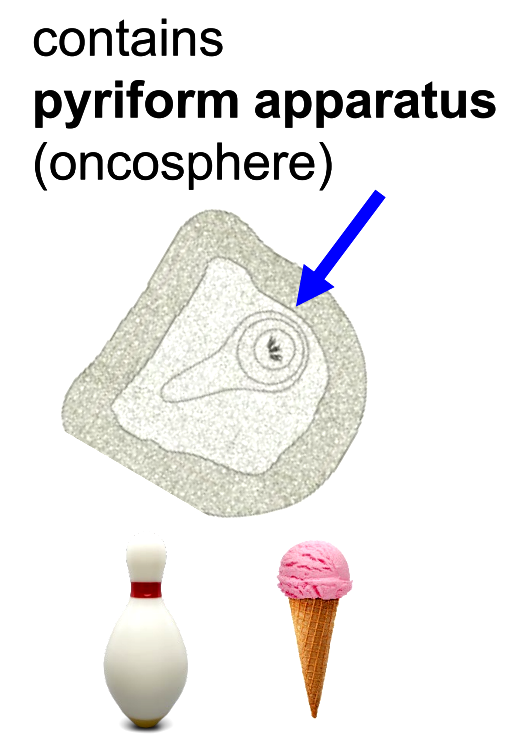
eggs in feces; contains pyriform apparatus (shaped like bowling pin/ice cream cone)
moniezia pathology
very common worldwide
responsible for subclinical parasitism = production loss
moniezia treatment
strategic deworming
anoplocephala perfoliata definitive host
horse → ileocecal orifice in intestines
anoplocephala perfoliata intermediate host
oribatid mites (cysticercoid)
anoplocephala perfoliata diagnostic stage
eggs in feces; contains pyriform apparatus
anoplocephala perfoliata treatment
praziquantel, pyrantel pamoate, strategic deworming