VISUAL ARTS
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Element of Art
basic component or essential part of a work of art. Artist may use one or several elements at one time in a work of art.
Example.
line, shape, form, space, texture, value, or color
Principles of Art: Balance / Symmetry
Term definition.

Equalizing elements in a work of art to create visual equilibrium. Balance causes the viewer to feel that the elements have been arranged just right. Visual imbalance creates a feeling of uneasiness.
Principles of Art: Proportion
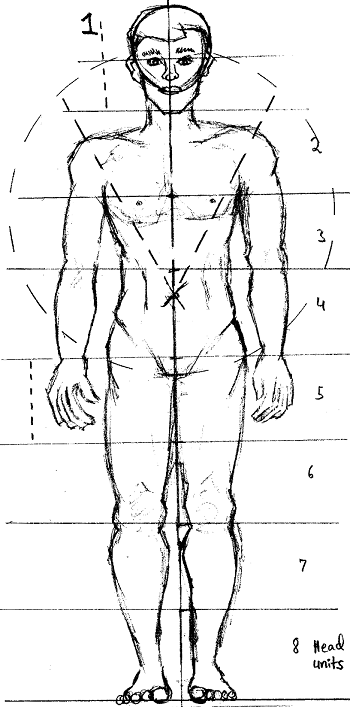
The relative size and scale of elements in a design. The relationship of one part to another and to the whole.
Hue
The name of a color
Example.
blue-green
Elements of Art: Value
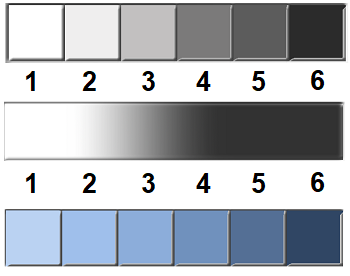
The amount of lightness or darkness a color possesses. White and Black are neutral colors. Adding one of them to a color will change the value.
Convergent Instruction
leads the student to a limited number of answers. This type of teaching may be used to teach a skill.
Principles of Art
How the various elements are composed in an artwork; may be used independently or in conjunction with other principles.
Example.
emphasis, contrast, pattern, rhythm, balance, proportion, or unity
Analogous Colors

Neighbors on the color wheel that have a common hue
Example.
violet, red-violet, red, red-orange and orange all have red in common
Principles of Art: Pattern

The visual repetition of elements such as line, shape, and color, and can be 2D decoration.
Elements of Art: Form

Forms are 3-dimensional shapes, having height, width and depth.
The Four Strands of Learning
How the TEKS for Visual Arts are organized. Perception Creative expression/performance Historical and cultural heritage Response/evaluationHow the TEKS for Visual Arts are organized. Perception Creative expression/performance Historical and cultural heritage Response/evaluation
Elements of Art: Space
Space is the area between or around shapes and forms.
Principles of Art: Unity

The arrangement of elements and principles within media to create a feeling of completeness or wholeness. Unity helps us to see the parts of a work of art as a whole.
Primary Colors
Term definition.
basic colors that cannot be created by mixing others
Example.
red, blue, and yellow are primary colors
Elements of Art: Shape

Shape is a 2-dimensional area defined by a boundary.
Principles of Art: Emphasis
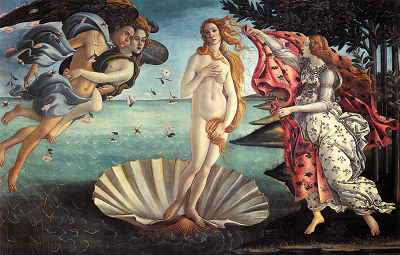
Stressing one element or area in a work of art to make it attract the viewer's attention first.
Principles of Art: Contrast

Differences in values, colors, textures and other elements to achieve emphasis and unity.
Elements of Art: Color

Derived from reflected light. The sensation of color is aroused in the brain by the response of the eyes to different wavelengths of light.
Divergent Instruction
leads the student to a wide array of answers, many of that the instructor does not know or see. This approach to instruction values the student’s natural abilities
Perception
The development and organization of ideas from the environment through increased visual awareness and sensitivity to surroundings, memory, and imagination
Opposite Color / Complementary Colors

Are positioned as opposites on the color wheel
Example.
Red/Green
Secondary Colors

orange, green, purple; occur when two primary colors are mixed.
Principles of Art: Rhythm

Repeating an element to make a work seem active or suggest movement or vibration.
Elements of Art: Line

A moving point on the surface of a canvas (or other media); it has width as well as length.

Texture is the way things feel or appear to feel.
Tertiary Colors

Occur when a primary color is mixed with a neighboring secondary color on the color wheel
Example.
blue + green = blue-green