Microscopy Exam 1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
4 ways we describe light
monochromatic vs polychromatic
linerarly polarized vs nonpolarized
coherent vs noncoherent
collimited vs divergent
monochromatic light
light having a single wavelength or frequency
polychromatic light
Light of many colors (wavelengths) usually referred to as white light.
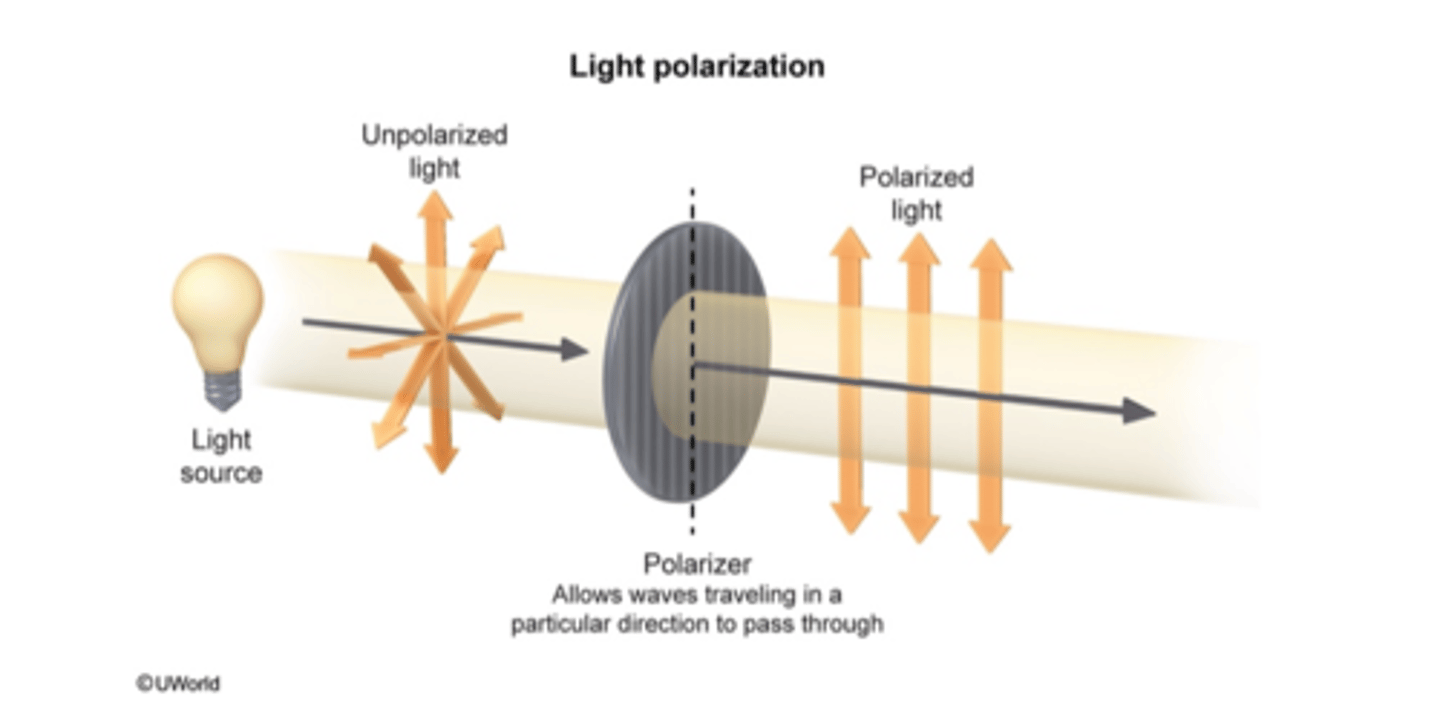
polarized light
light that vibrates in only one direction
Photons can oscillate on any axis (in 2 dimensions) as it travels
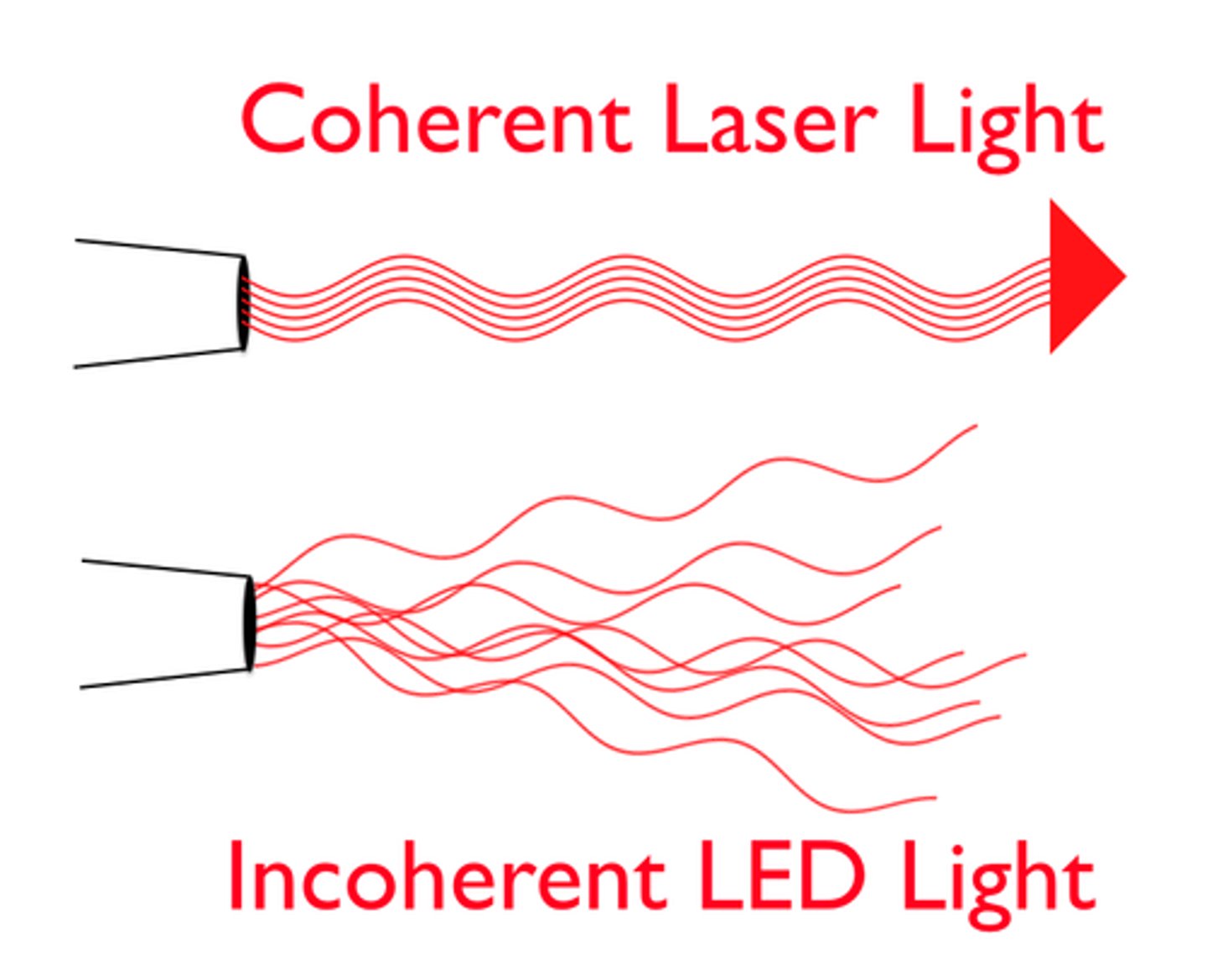
coherent light
Light of only one wavelength that travels with its crests and troughs aligned
Our cones detect
red, blue, green
when photons interact with an object, they can ____
Reflection
Refraction
Diffraction
Absorption/energy transfer/Fluorescence
Birefringence
If n2 > n1:
Light rays 'bend' towards the normal
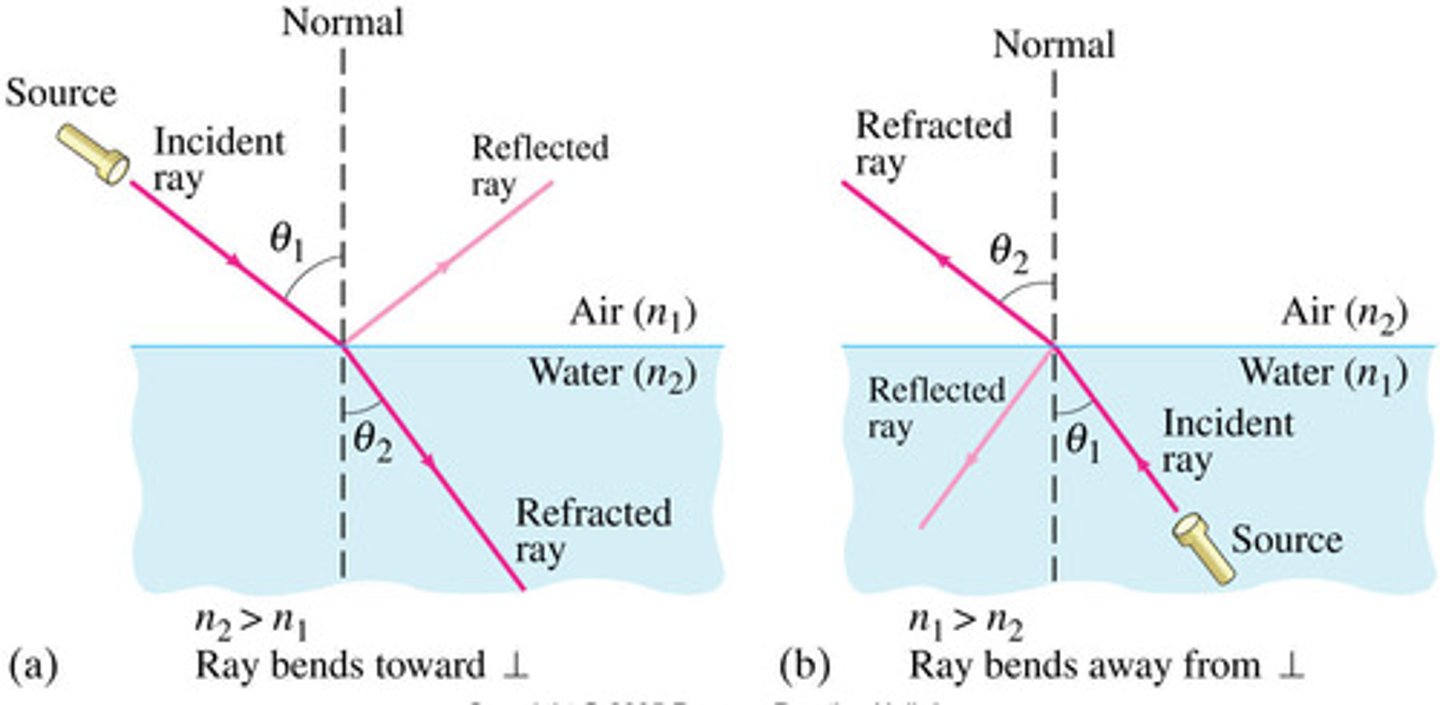
If n2 < n1:
Light rays 'bend' away the normal
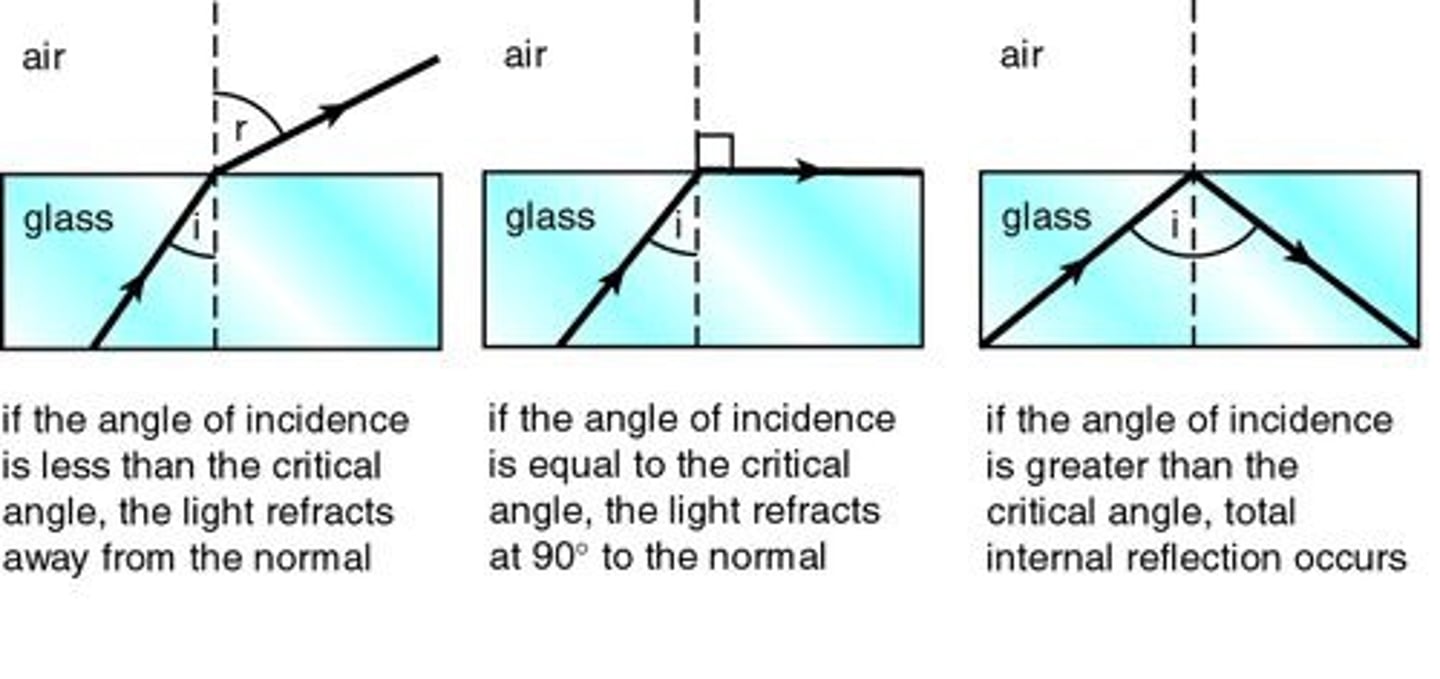
critical angle
the angle of incidence that produces an angle of refraction of 90 degrees
refractive index is _____ dependent
wavelength
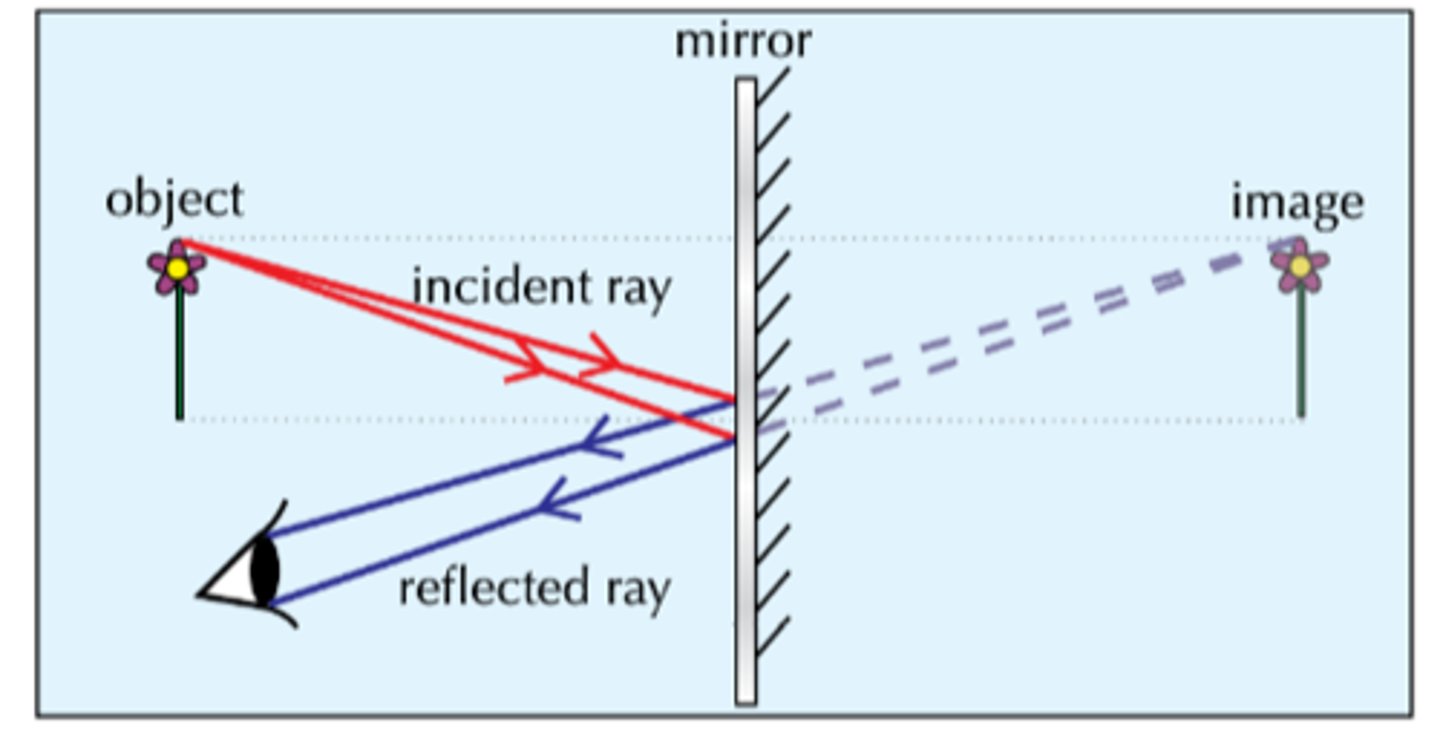
real image
An upside-down image formed where rays of light meet.
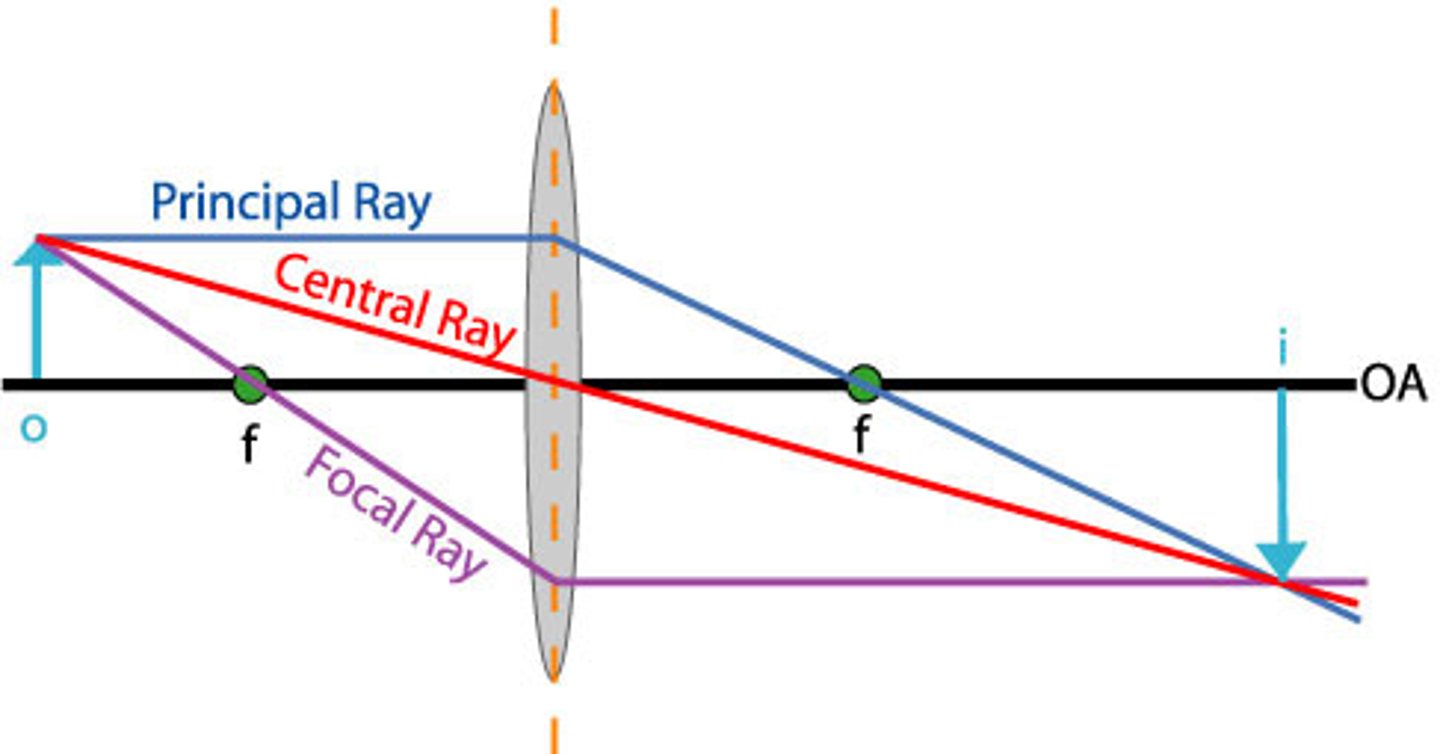
virtual image
an image that forms at a location from which light rays appear to come but do not actually come
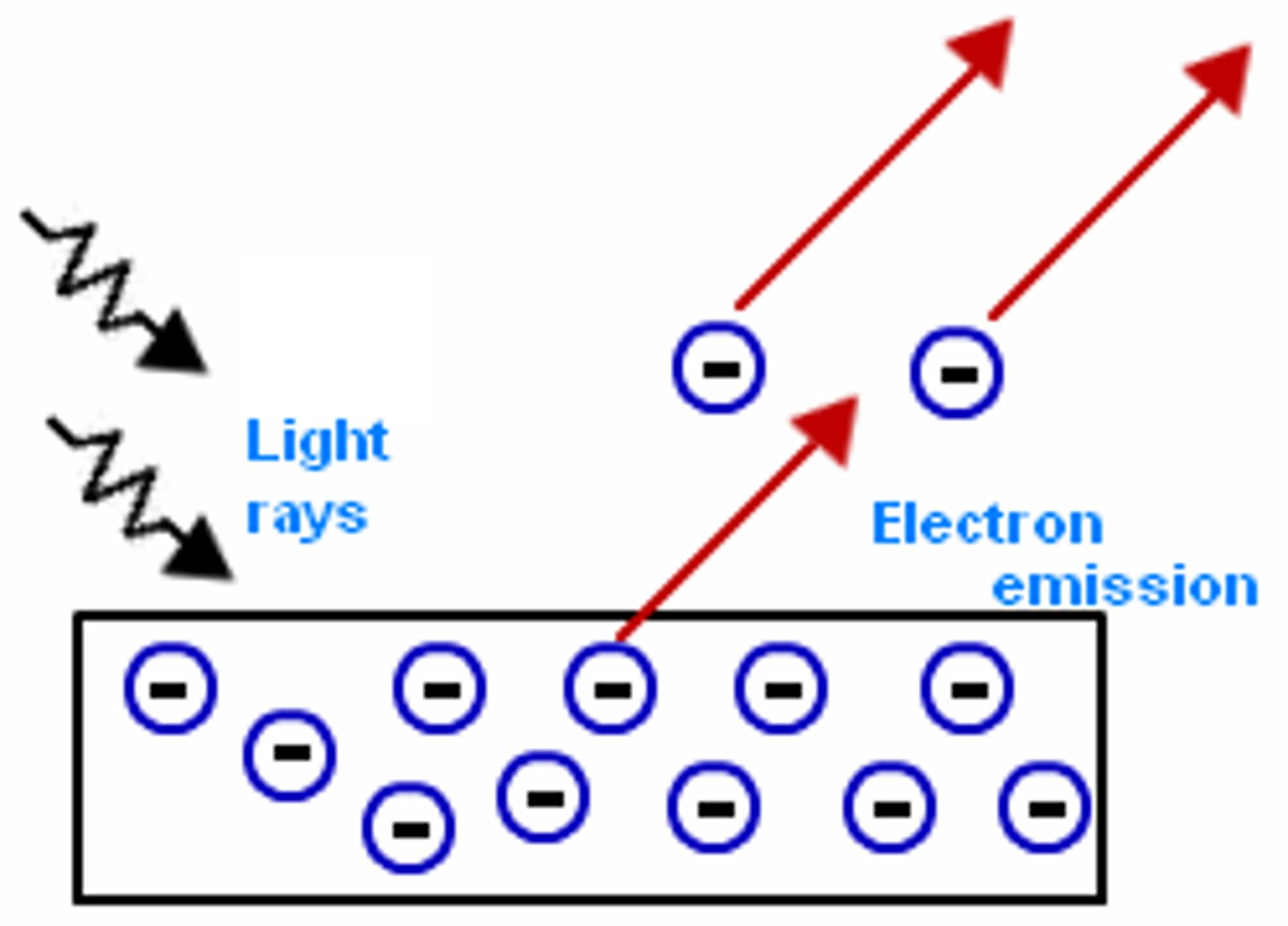
photoelectric effect
refers to the emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
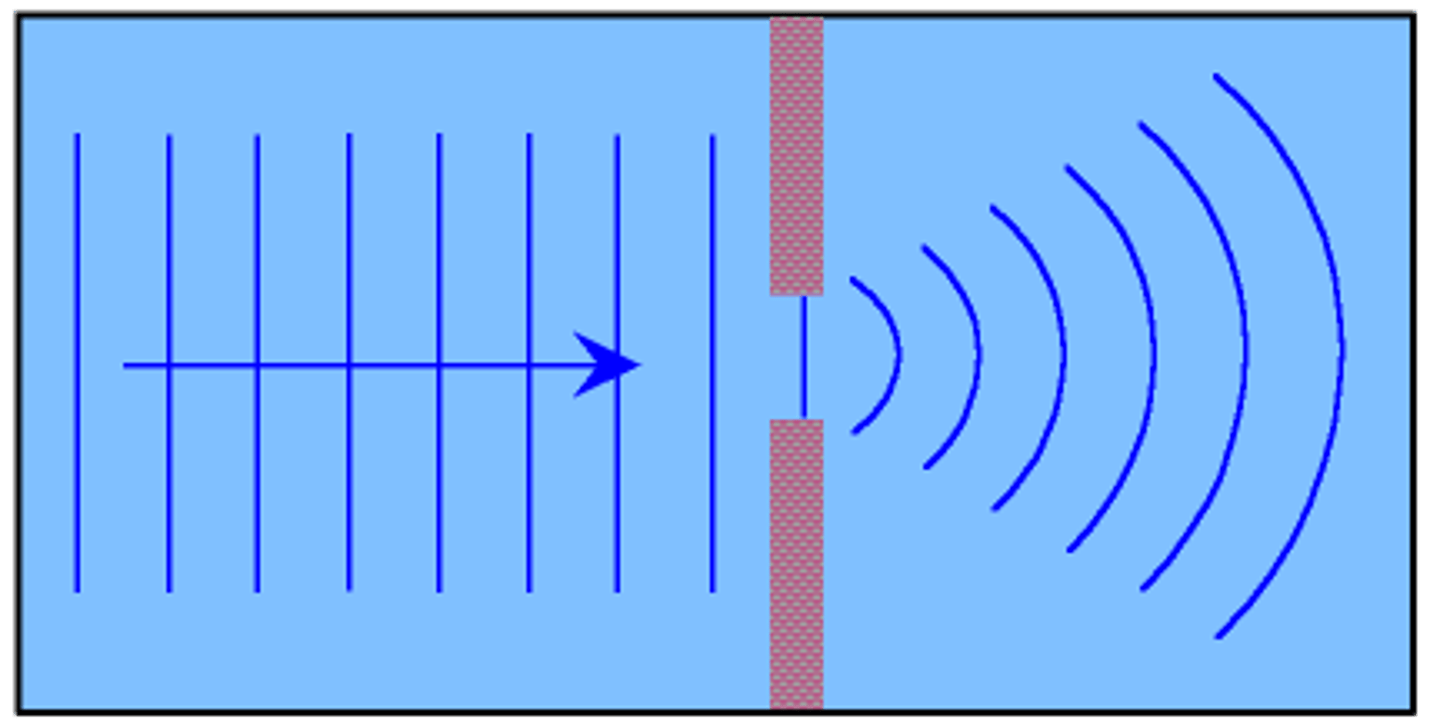
diffraction
Occurs when an object causes a wave to change direction and bend around it
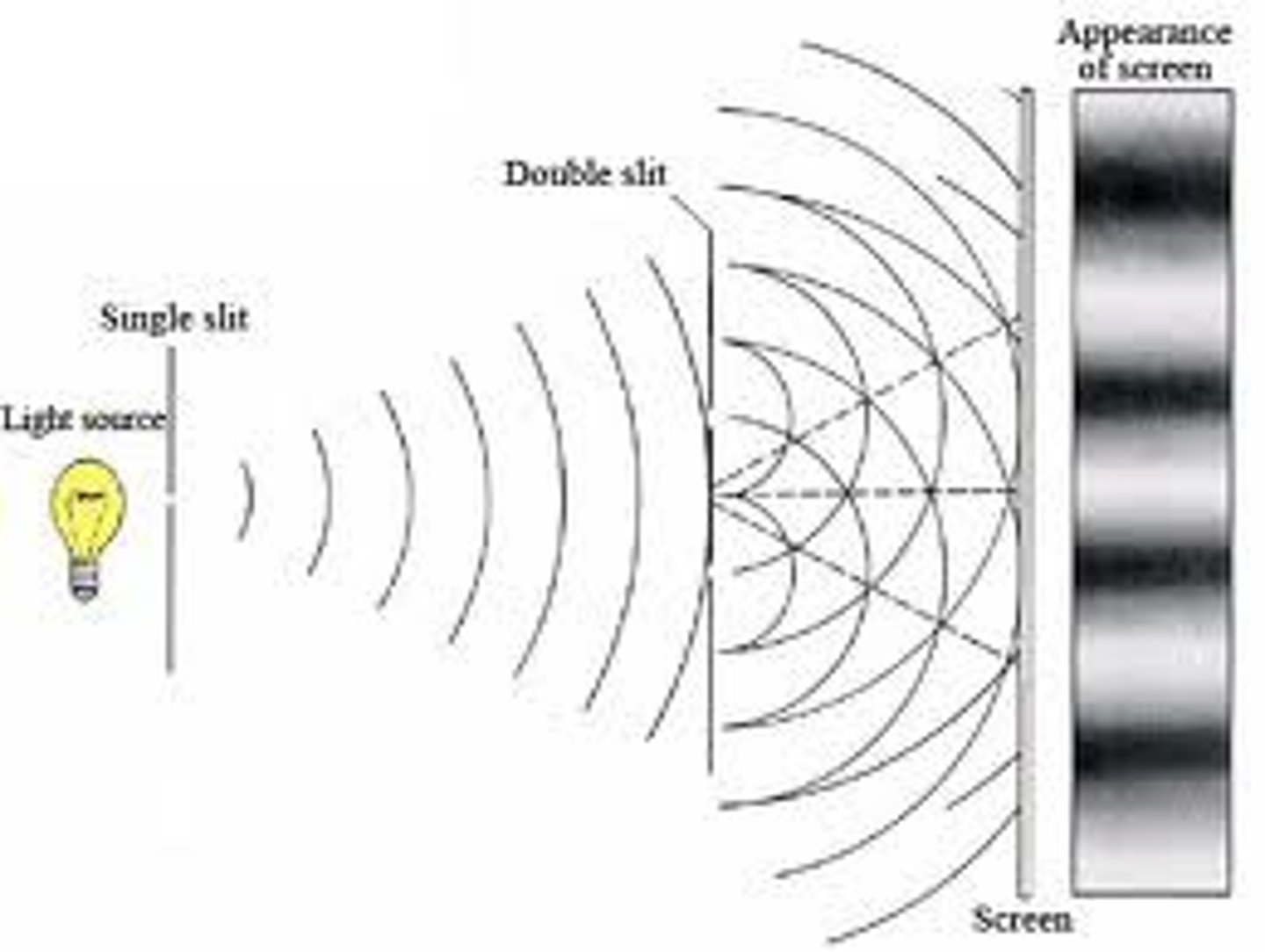
double slit experiment
proved that electrons have wave like properties (wave length)
airy disk
A bright central point surrounded by rings of light and dark caused by the pattern of interference of spherical wavefronts converging at the focal point.
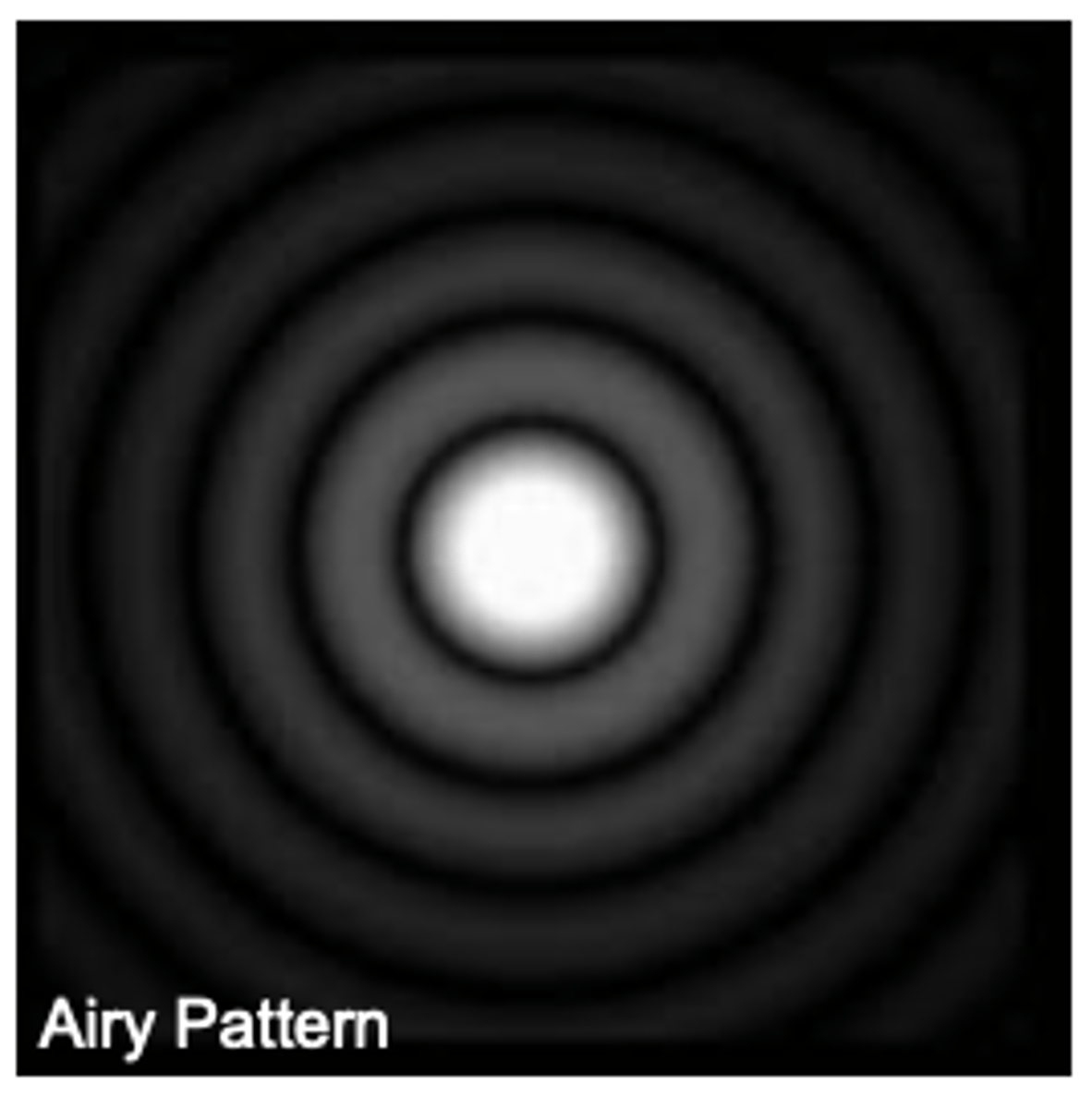
What we use to probe objects influences the image we generate, smaller probes improve ______
Resolution of Space
spherical aberation
a loss of definition in the image arising from the surface geometry of a spherical mirror or lens.
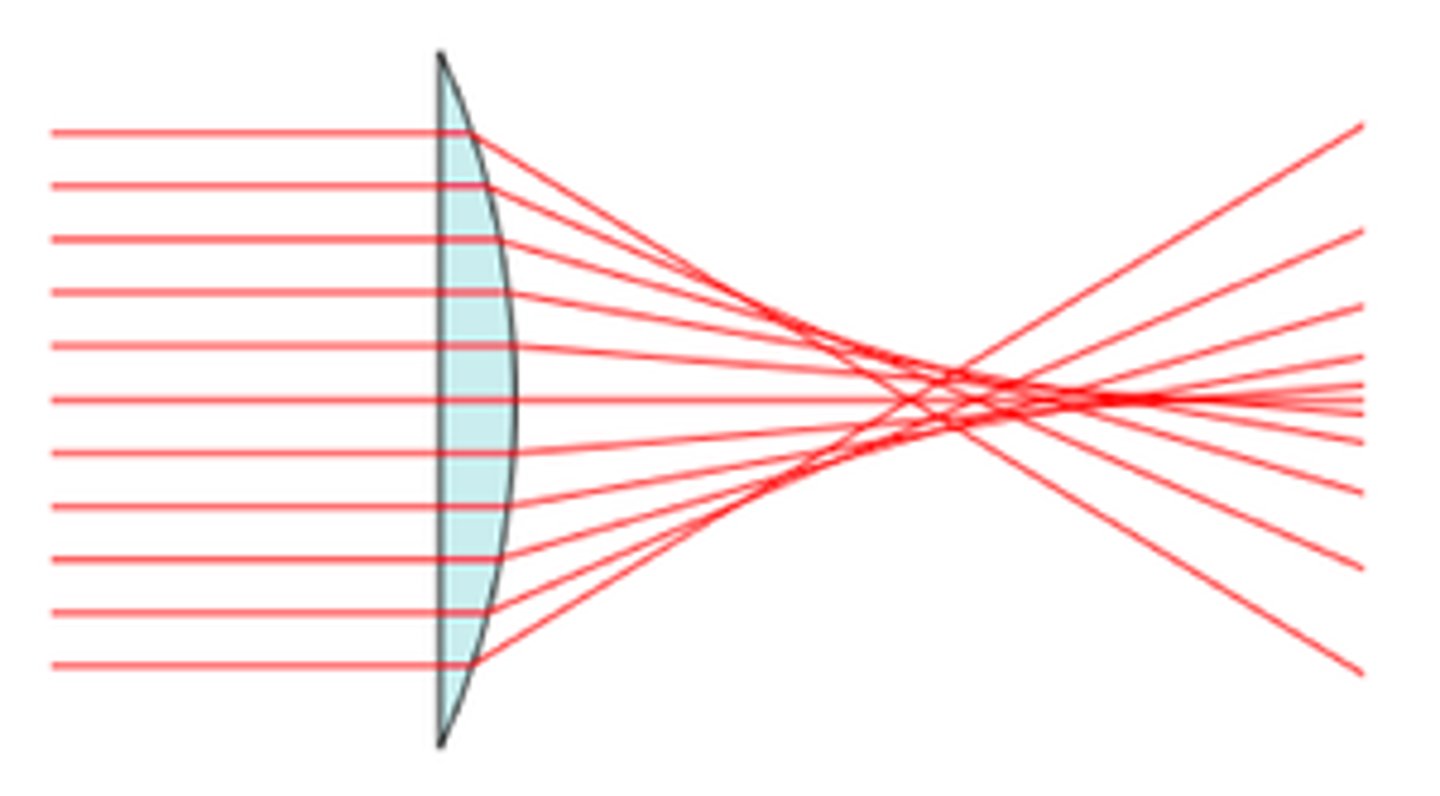
Numerical Aperture of an objective is ______
a measure of its ability to gather light
conjugate focal planes
A set of image or focal planes
Microscopes have ____ 'sets' of conjugate planes.
two
Koehler Illumination method
provide uniform light on the specimen plane while putting the light source on a separate conjugate plane
infinity light
parallel light between the objective and tube lens
How to define Imaging performance
Resolution of Time
Resolution of Space
Resolution of Light Sensitivity
Resolution of Signal (vs noise)
resolution of time
How well a phenomenon can be sampled across time
resolution of space
How accurately we can capture the dimensions of a phenomenon (target)
smallest distance between two points on a specimen that can be identified as two separate entities
Resolution of light sensitivity
The dynamic range (gray scale) of an image
resolution of signal
Clarity and visibility of objects in the image
We often 'stain' samples to increase contrast, thereby enhancing the Resolution of Signal
Rayleigh Criterion
2 points are resolved when they are 1 Airy disk radius apart (first maxima to first minima)
2 points are resolved when they their half maximum intensity touch (R = 0.51 λ/NA)
Airy disk is elongated along the _____ plane
z
Light intensity I
the rate of flow of energy per area per time
proportional to the amplitude of the wave squared I ∝ A^2
Contrast
the difference in intensity between the object (specimen) and background
Sampling
the act of creating discrete captures of continuous data (sound, light, etc). A camera samples light in both space and time
undersampling can lead to
Aliasing: a distortion artifact that creates patterns in periodic structures
Nyquist Sampling Theorem
The radius of the Airy Disk has to be captured by at least 2 pixels for us to resolve them
steps of microscope use
Posture
Adjust Light
Adjust ocular/Eye piece distance
Put sample on stage and coarse focus with the lowest magnification setting
Adjust ocular focuses
Adjust Condenser height
Repeat focusing steps when changing magnification
Dark current
Thermally generated electrons that are indistinguishable from photo-generated electrons
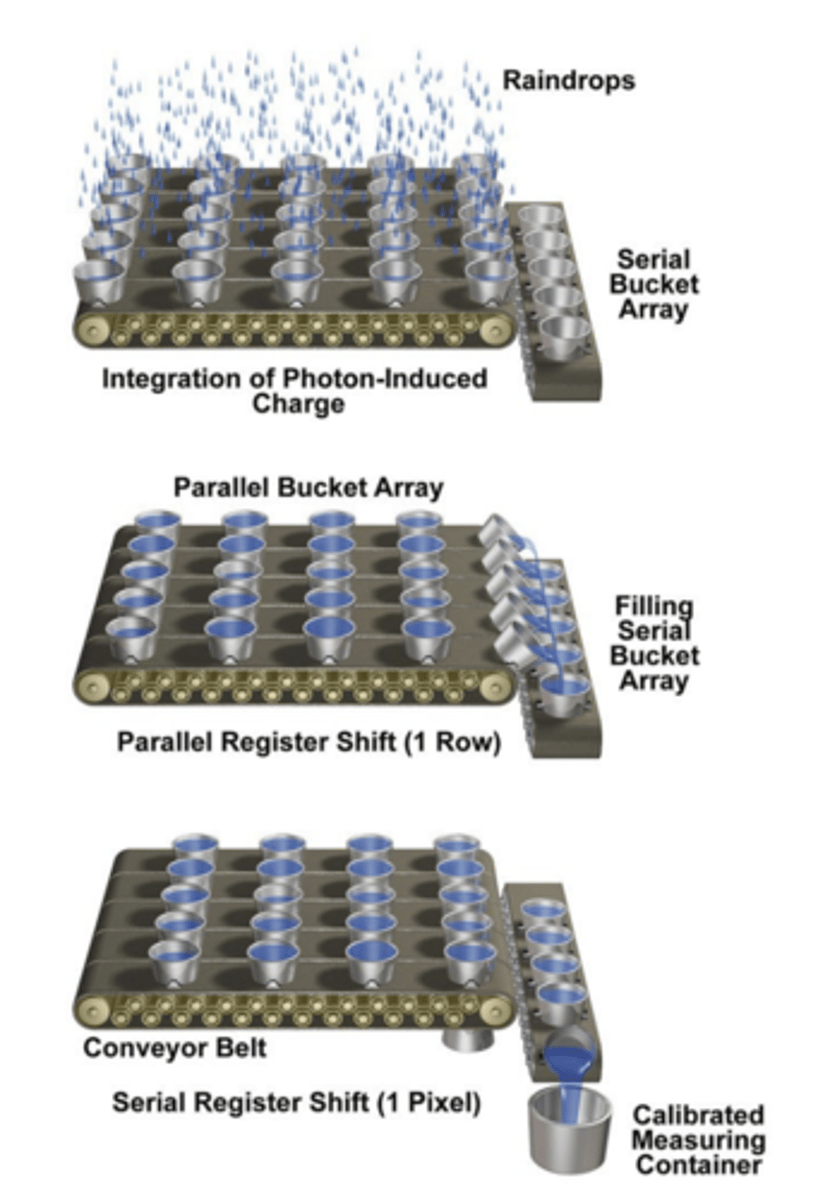
Charged Coupled Device (CCD) Cameras
pixels that are arranged in parallel registers and inputted serially
The sensor is exposed to light for a specific amount of time (exposure time, a camera setting)
Pixels are shifted off the parallel register onto the serial register
Pixels are 'read' one at a time (the output amplifier boosts the signal and assigns an analog voltage before assigning a digital value)
Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) Camera
pixels that each have their own electron to voltage converter, simultaneous processing of pixel information
CCD vs CMOS
CCD: Pixel transfer is slower so the capture rate is lower aka slower image acquisition rate and lower maximum frame rate
CMOS: Pixel to pixel variability is higher, aka higher noise
Analog, continuous signals are converted to
digital images that our computers can store
Digital values are
discrete, integer values with a finite range (gray levels or scale)
Signal to Noise Ratio
the amount of signal present compared to the amount of noise
Pixel size and light sensitivity
Larger pixels can capture more light (from your target)
So you increase light sensitivity while decreasing resolution Large pixels can be 'made' via pixel binning (A camera setting)
Exposure time
The duration of time you let light hit the camera before you digitize it
Inversely related to maximum frame rate (number of images you can acquire per second)
Increasing the exposure time increases the total light (both signal and noise)
Gain
amplifies the brightness of all photons, but can increase signal more than background/noise)
Increasing the digital gain reduces the number of electrons assigned per gray level in a gray scale
i.e. if you normally have 10 electrons per gray level, doubling the gain will make it 5 electrons per level
Trade off between Dynamic range and SNR
Dynamic Range
The range from background level to the brightest signal
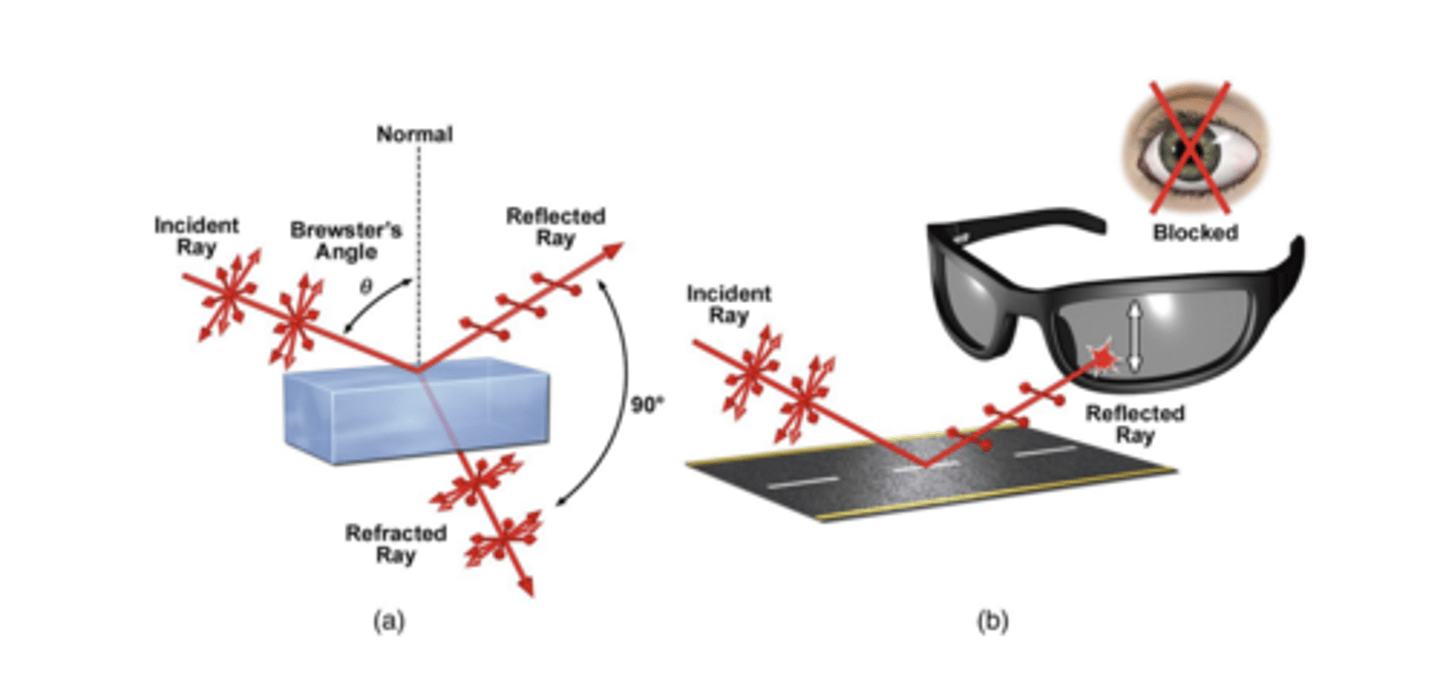
why polarized sunglasses are useful
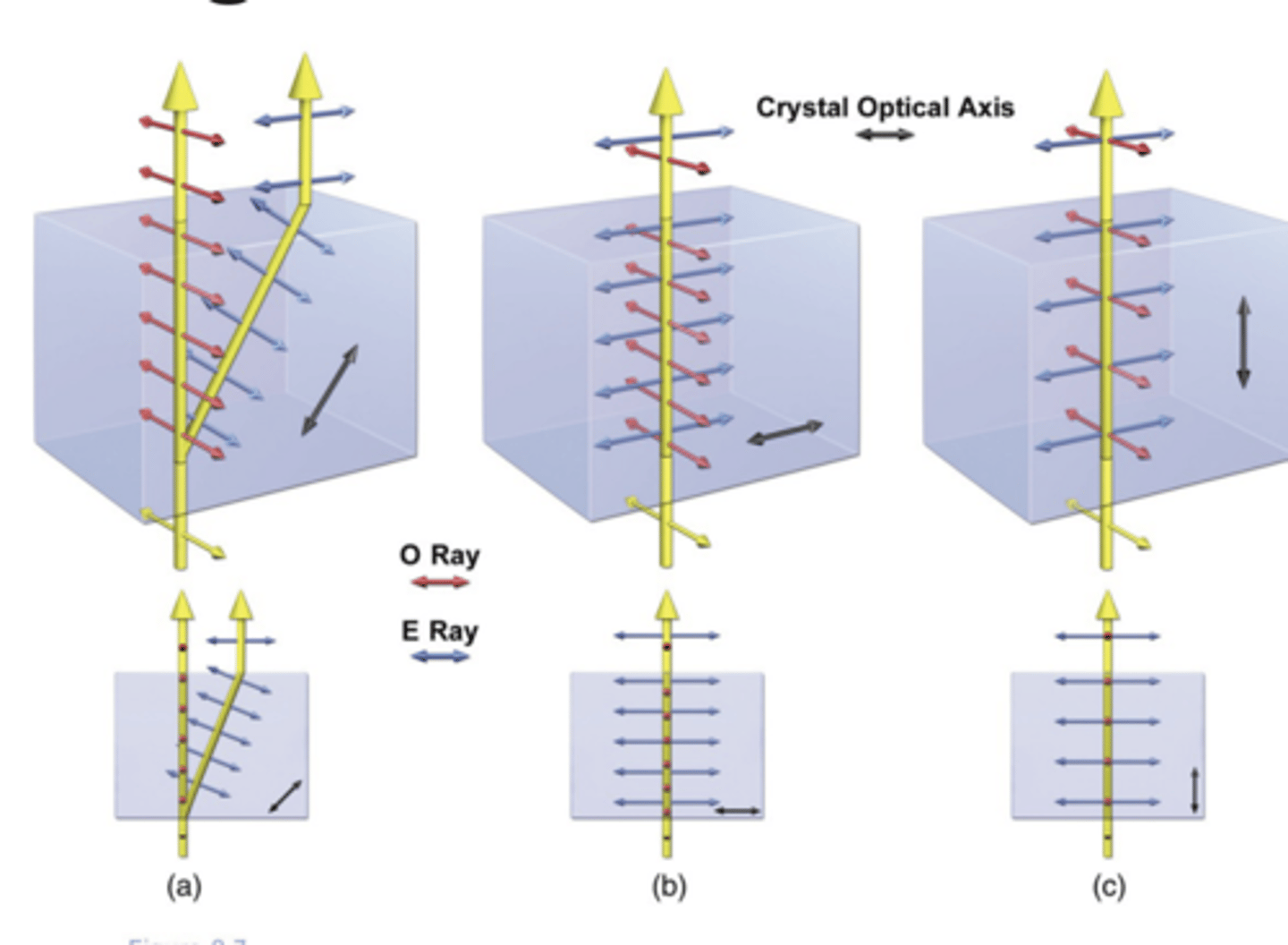
birefringence
where there are 2 (or more) refractive indexes usually based on polarization
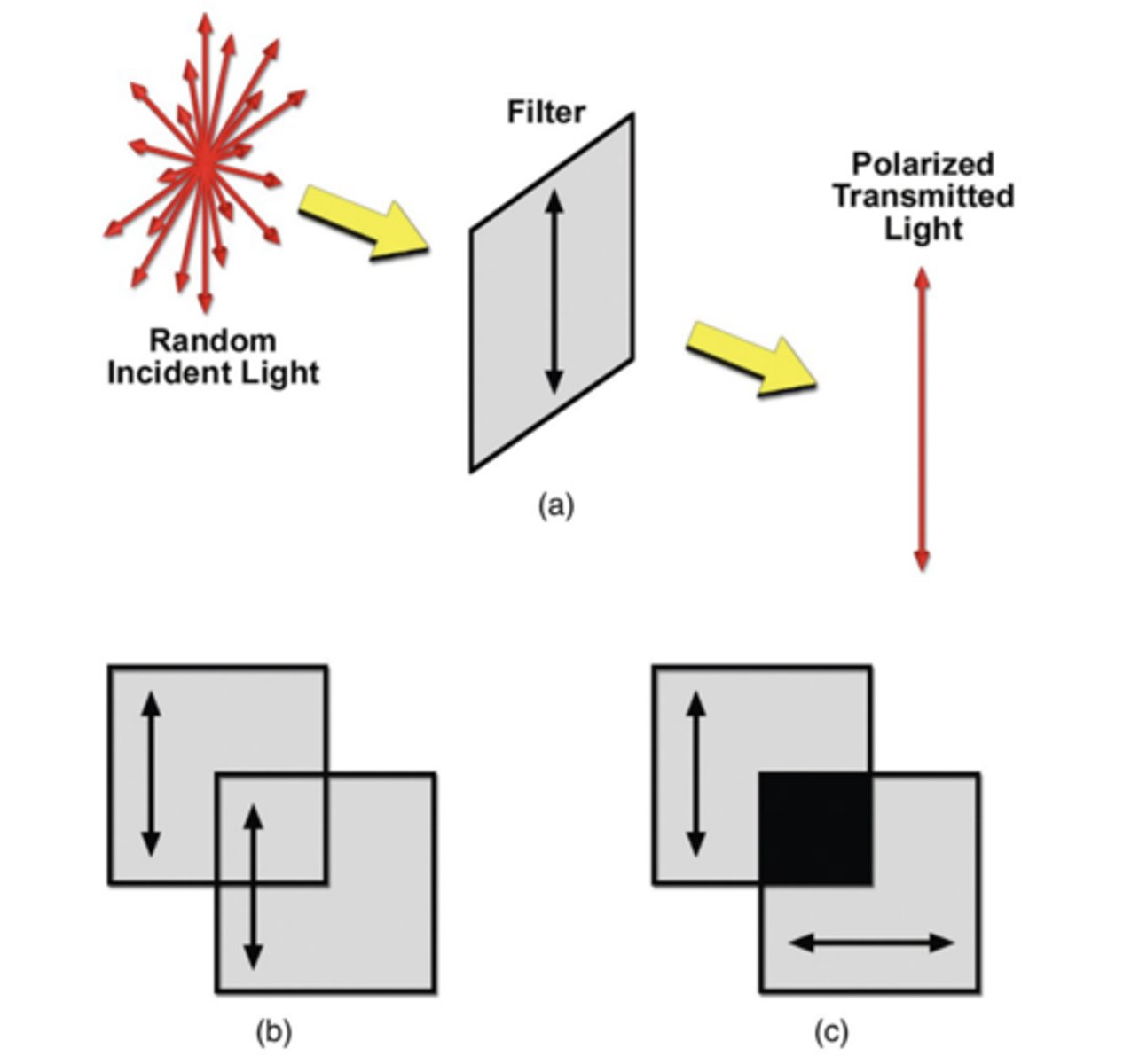
Fun pic of double polorization
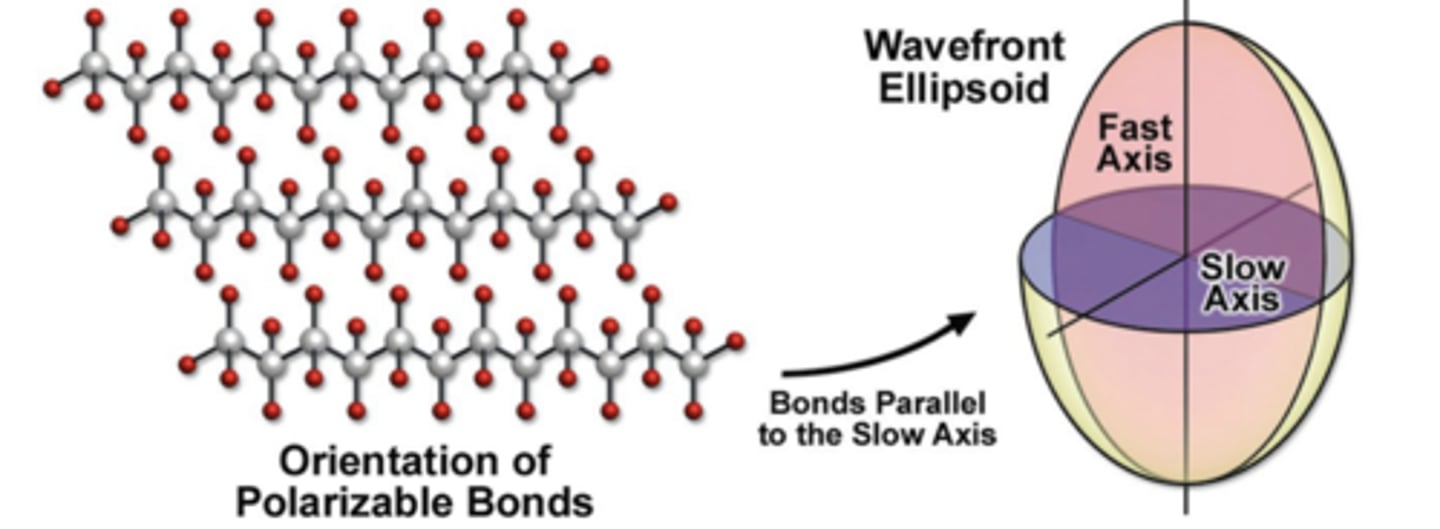
Birefringence causes
an elliptical wave front with a "slow" and "fast" axis
When linearly polarized light passes through a birefringent material
the fast and slow waves become out of phase.
The analyzer
combines the two waves and creates an interference color based on the difference between the fast and slow waves
The color is therefore dependent on the thickness of the material, and the refractive indexes of the fast and slow wave