Test for anions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
The eight anions
Thiosulfate, sulfate, sulfite, carbonate, hydrogen carbonate, nitrate, chloride, phosphate
Reagent of test for thiosulfate
Dilute HCl (Hydrochloric acid)
Precipitate of test for thiosulfate
Sulfur - a yellow precipitate
Products of test for thiosulfate
4 products:
NaCl
H2O
S (yellow precipitate)
SO2 (Has a distinct smell and is quite pungent)
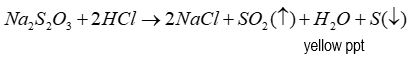
How to identify sulfur dioxide
By putting a spot of potassium permanganate on filter paper and putting it reaction. The purple colour disappears as sulfur dioxide acts as a reducing agent reducing Mn (+7) which is purple to Mn (+2) which is colourless
Reagent of test for sulphates
Barium chloride
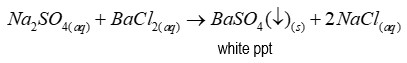
Precipitate of test for sulphates
Barium sulfate (a white precipitate)
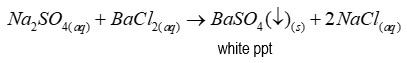
Reagent of test for sulfites
Barium chloride
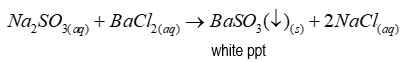
Precipitate of test for sulfites
Barium sulfite (a white precipitate)
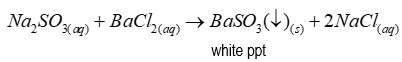
If sulphate is present when distinguishing between sulphate and sulphite
After adding dilute HCl to distinguish, no reaction occurred. Precipitate remains as barium sulphate is insoluble in dilute acid.
If sulphite is present when distinguishing between sulphate and sulphite
After adding dilute HCl to distinguish, a reaction occurs. Precipitate disappears as barium sulphite is soluble in dilute acid and sulfur dioxide is given off.
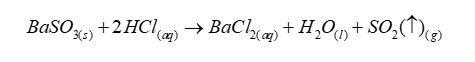
Reagent to test of presence of carbonate or hydrogen carbonate ions in aqueous solution
Dilute acid
When carbonate or hydrogen carbonate is present
Then carbon dioxide will be given off on the addition of dilute acid. Note effervescence due to release of carbon dioxide
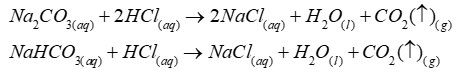
To test for carbon dioxide gas
Bubble the carbon dioxide gas through a colourless solution of limewater. The limewater turns milky white. Note - limewater is an aqueous solution of calcium hydroxide.
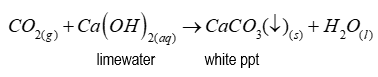
Reagent to distinguish between a carbonate and hydrogen carbonate ion
Magnesium sulfate
When carbonate is present
After adding magnesium sulfate, a white precipitate forms - (magnesium carbonate)
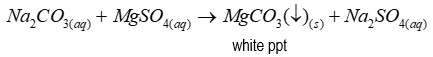
When hydrogen carbonate is present
After adding magnesium sulfate, no precipitate forms as magnesium hydrogen carbonate is soluble in solution
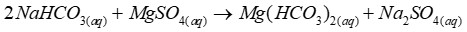
If clear hydrogen carbonate solution is boiled
White precipitate is formed as hydrogen carbonates decompose in heating
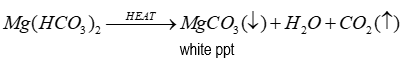
Reagent(s) of test for nitrates
1- Freshly made iron (II) sulfate
2- Concentrated sulfuric acid
Test for nitrates is also known as the
Brown ring test
Method to test for nitrates
-Add sodium nitrate to test tube
-Add fresh iron (II) sulfate solution
-Add concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) solution carefully down inside the test tube
-Concentrated sulfuric acid falls down the bottom, as it is more dense
-If a brown ring forms at the junction, then this shows the presence of a nitrate ion in aqueous solution
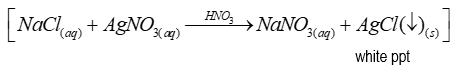
Reagent(s) of test for chlorides
-Silver nitrate solution
- (and conc. nitric acid)
Positive test for chlorides
After adding reagent(s), immediate white precipitate is formed (ionic reaction)
Reagent(s) of test for phosphates
Ammonium molybdate (and conc. nitric acid)
Condition - Heat gently
Positive test for phosphates
Yellow precipitate formed - Ammonium phosphomolybdate