Microbiology Lab practical: microscopy and basic handling techniques and Isolation of Pure cultures
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
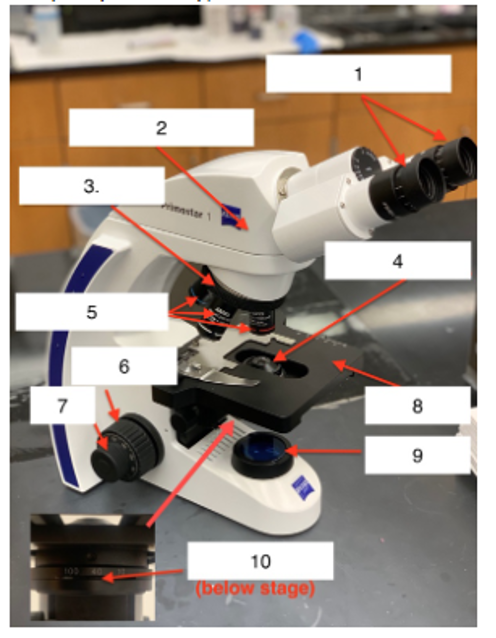
Identify the numbered parts on the microscope
Ocular lens
Body Tube
Nose piece
Condensor lens
Objective lens
Coarse knob
Fine knob
Stage
Illuminator
Iris Diaphragm
What is the function of the ocular lens?
The part you see through to view the specimen on the slide
What is the function of the Body Tube?
Connects the eye piece to the objective lenses
What is the function of the objective lenses?
They are the different magnifications you are able to use to view the specimen
What is the difference between the coarse knob and the fine knob?
The coarse knob is the one you use to start with and it helps bring the stage up towards the objective to see better, also helps bring into focus but still need the fine knob to view better
The fine knob is used to make the image clearer/ bring into focus better
What is the function of the Iris Diaphragm?
Controls the amount of light that passes through the condenser lens
contrasts
What does the condenser lens do?
Focus’ the amount of light from the Iris diaphragm onto the specimen
What is the total magnification for the 4X objective?
40X magnification
What is the total magnification for the 10X objective?
100x magnification
What is the total magnification for the 40X objective?
400x magnification
What is the total magnification for the 100X objective?
1000x magnification
which focus knobs should you use for the 4x, 40x, 10x, and 100x
Always start st the 4x objective and use the coarse knob to bring the image into focus, then use the fine knob to further bring the image into focus
You will then continue to use the fine knob the bring the image into focus with the 40x, 10x, and 100x
What do you need to add when transtioning from the 40x to the 100x objective?
Oil immersion
what does oil immersion do?
Helps improve the resolution to help sharp focus
prevents the light to get refracted
Describe how to use the par-focal nature of your microscope when observing a sample?
par focal, which means that if one objective lens has the object in focus, and you go to the next objective lens, only a minor adjustment
So start with the 4x objective and use the coarse knob and the fine knob to make the image clear
Then move onto the next objective and you now only have to use the fine focus knob to adjust the image a little ()
How do you properly carry a microscope?
Always handle with 2 hands one at the bottom on the microscope and the other at the body tube
Make sure the objective are at the lowest setting
What kind of paper do you use to clean oil off a microscope lens?
Lens paper
How do you properly store a microscope?
Store the objective lens facing the back of the case
objective lens at the lowest setting (4x)
With proper covering on
When looking at your wet mount under the microscope what did you notice about the difference in size between the bacterial cells and the cheek cells?
The cheek cells were significantly bigger than the bacterial cells
Are blood cells or bacterial cells bigger?
Blood cells
What tool should be used to inoculate a plate? What about an agar deep?
Plate= use an inoculated loop
Agar deep= use an inoculated needle
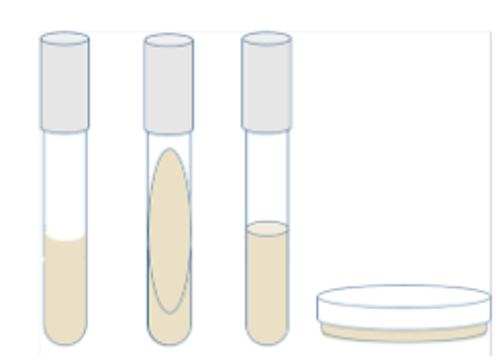
What are these types of medias?
Broth culture
Agar slant
Agar deep
Agar plate
what are the 4 things needed when labeling a sample?
Name
Date
Section
Culture
How should your plates be stored?
Upside down
What part of the microscope would need to be adjusted to increase or decrease the contrast during a wet mount? Where on the microscope is this part located?
The Iris Diaphragm is used for contrast
Below the stage
Why would a coverslip be used to observe bacteria?
To contain the bacteria onto the slide
stabilize it
Order the following organisms from largest to smallest: E. coli, S. cerevisiae, cheek cell
Cheek cell
S. cerevisiae/ yeast cell
E.coli
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a wet mount?
Advantages:
Able to see living cells
Types of movement (true motility vs. Brownian Motion)
Disadvantages
Not able to see structures of cell bc we can’t stain
Only able to view up to 40x
What is a pure culture?
A culture containing ONE species of bacteria
What is the method called used in lab for isolating organisms on the plate?
T-streak method