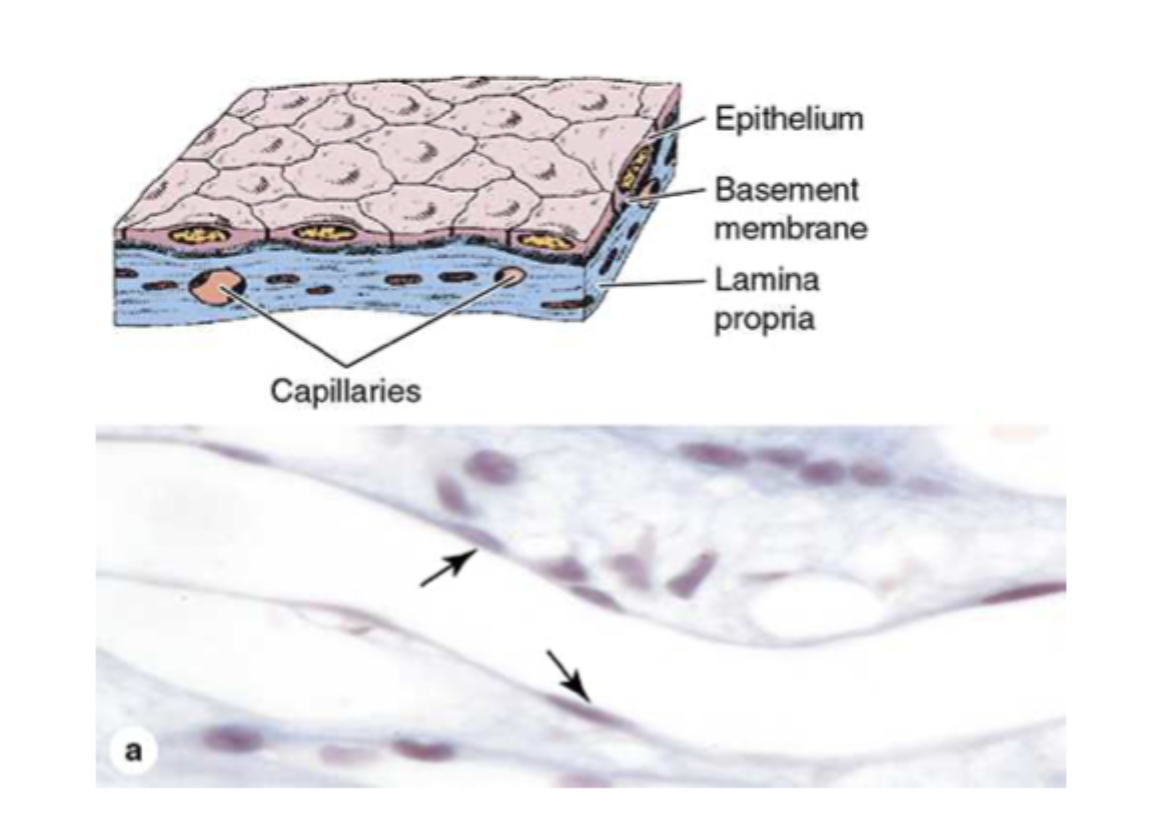
Epithelium
1/65
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
epithelial tissue
free surface which is exposed to external/internal space, basal surface which is attached to a basal lamina (basement membrane), anything that enters or leaves the body must pass through an epithelium
epithelial cells
closely packed cells with little extracellular material between cells, arranged in sheets or either simple or stratified cells, avascular, nerve supply, and high capacity for renewal
functions of epithelia
mechanical protection, absorption, secretion of materials, lubrication of surfaces, formation of a surface for diffusion, transportation, excretion, sensory reception, and reproduction
2 types of epithelia
covering and glandular
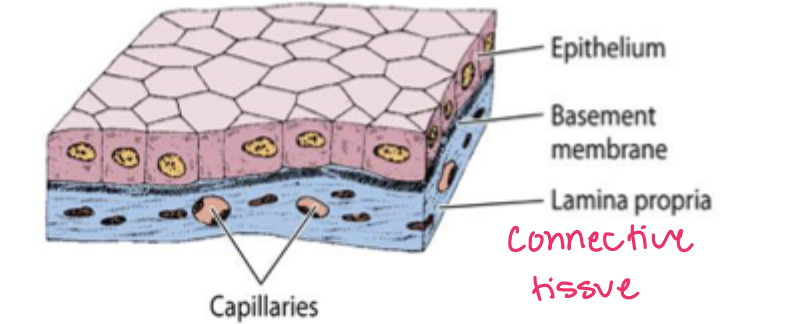
epithelial tissue sits on
connective tissue (lamina propria)
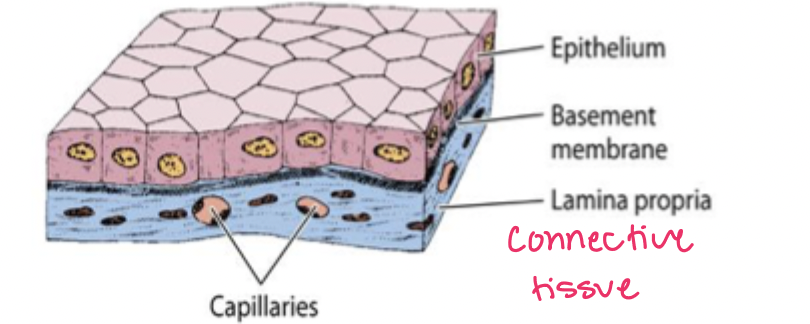
where is epithelial tissue?
rests on lamina propria, lines cavities of internal organs
papillae
evaginations into the connective tissue
why papillae?
increasing surface area for absorption and secretion and anchoring 2 tissues
what is the basement membrane made of?
basal lamina and reticular lamina
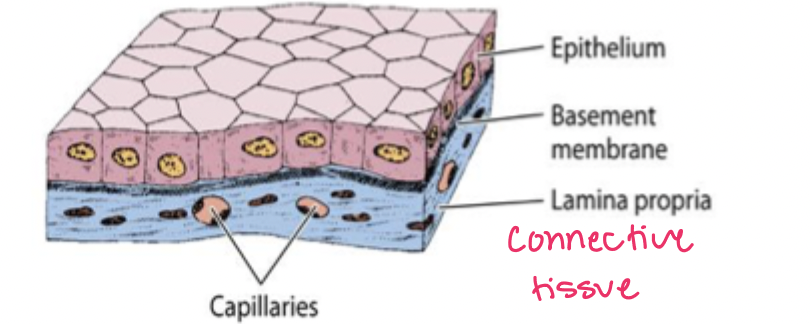
basal lamina
binds epithelial cells to underlying connective tissue
what is the basal lamina composed of?
type 4 collagen, glycoproteins, proteoglycans
reticular lamina
synthesized by lamina propria
what is the reticular lamina composed of?
type 3 collagen and connecting collagen
zonulae occludens
tight junctions
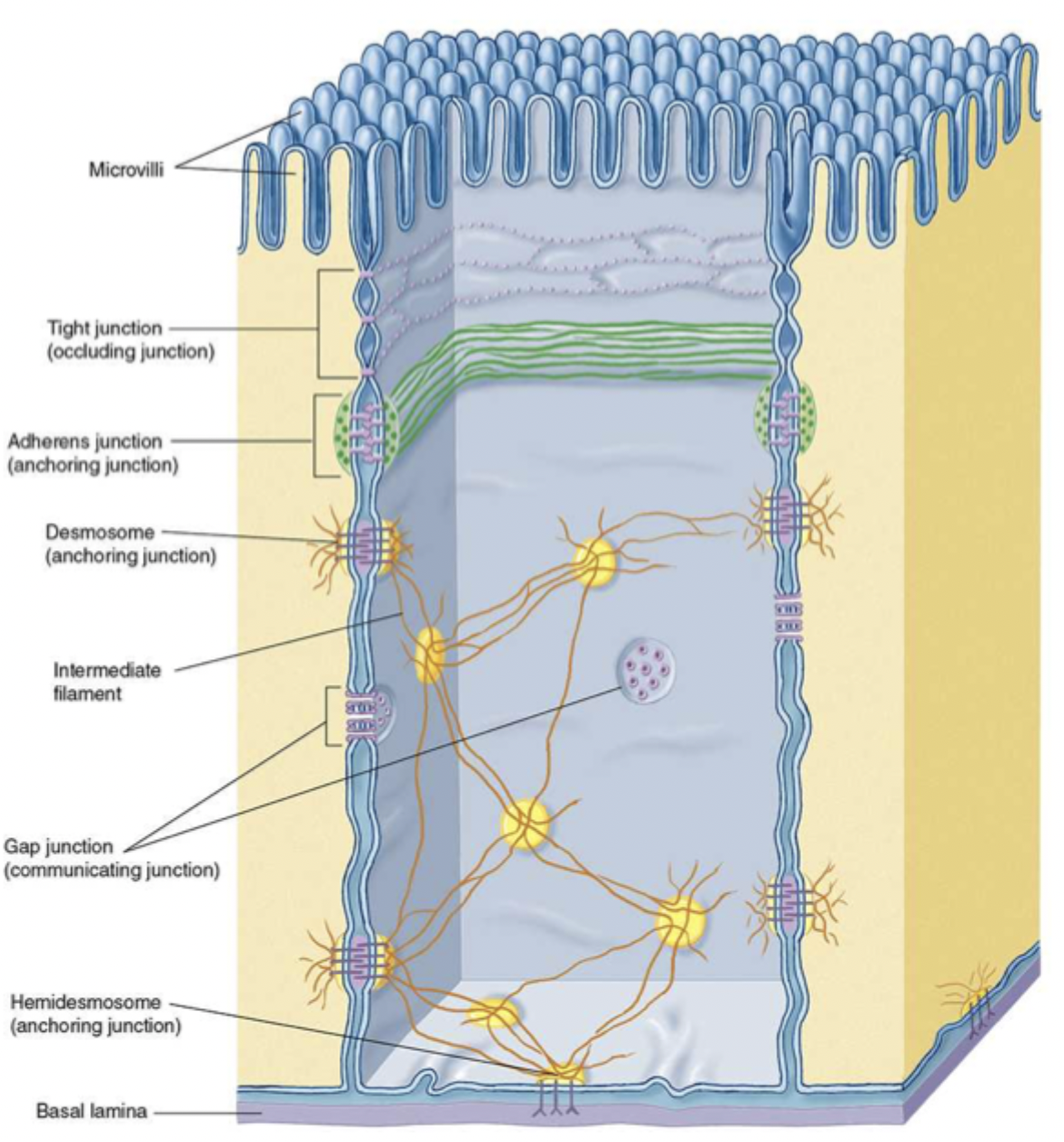
what do tight junctions do?
closes off ICS, prevents diffusion between cells, separates lumen, connecs actin filaments of one cell to another
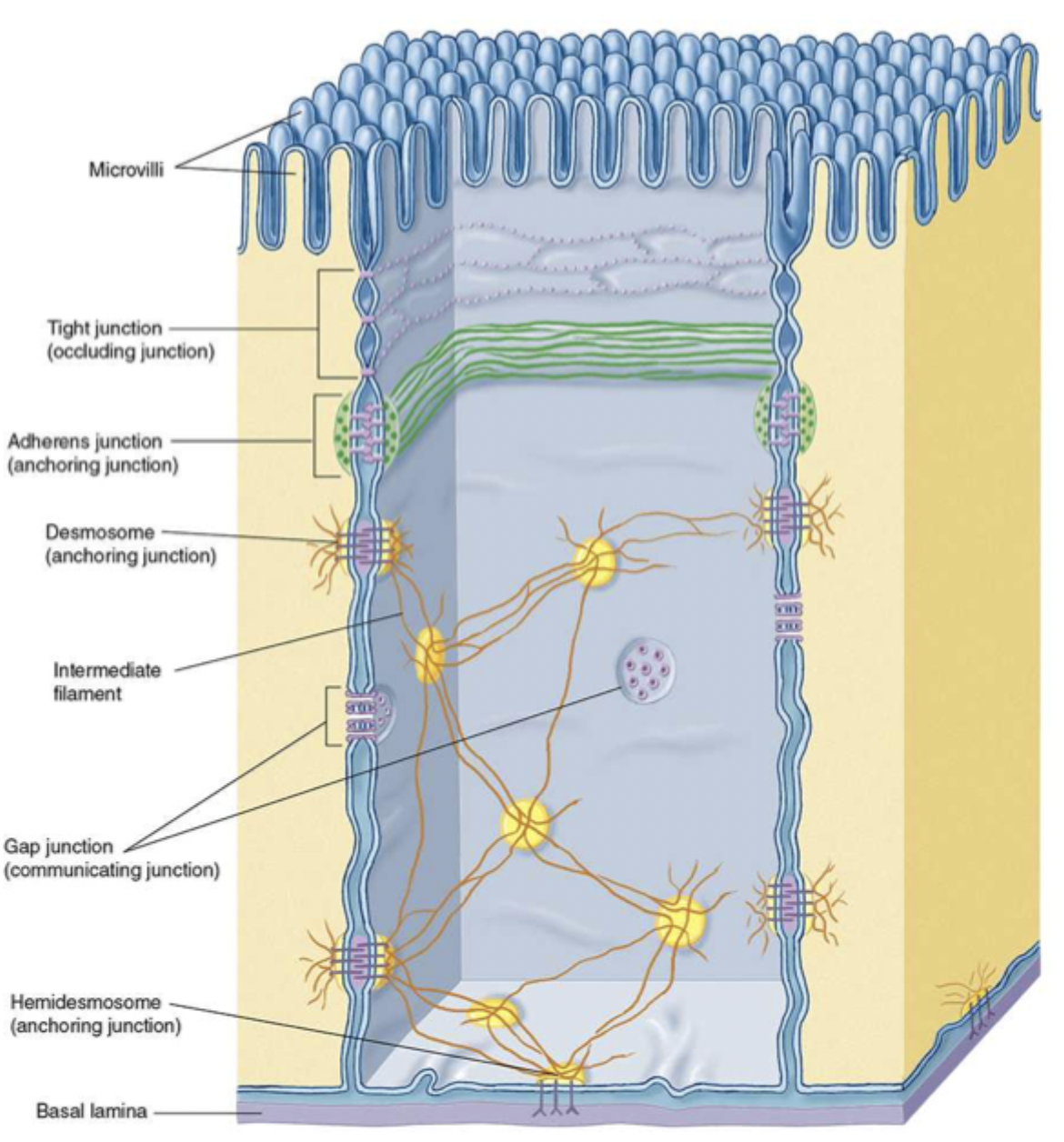
what proteins are in tight junctions?
occludin and claudin
macula adherens
desmosome
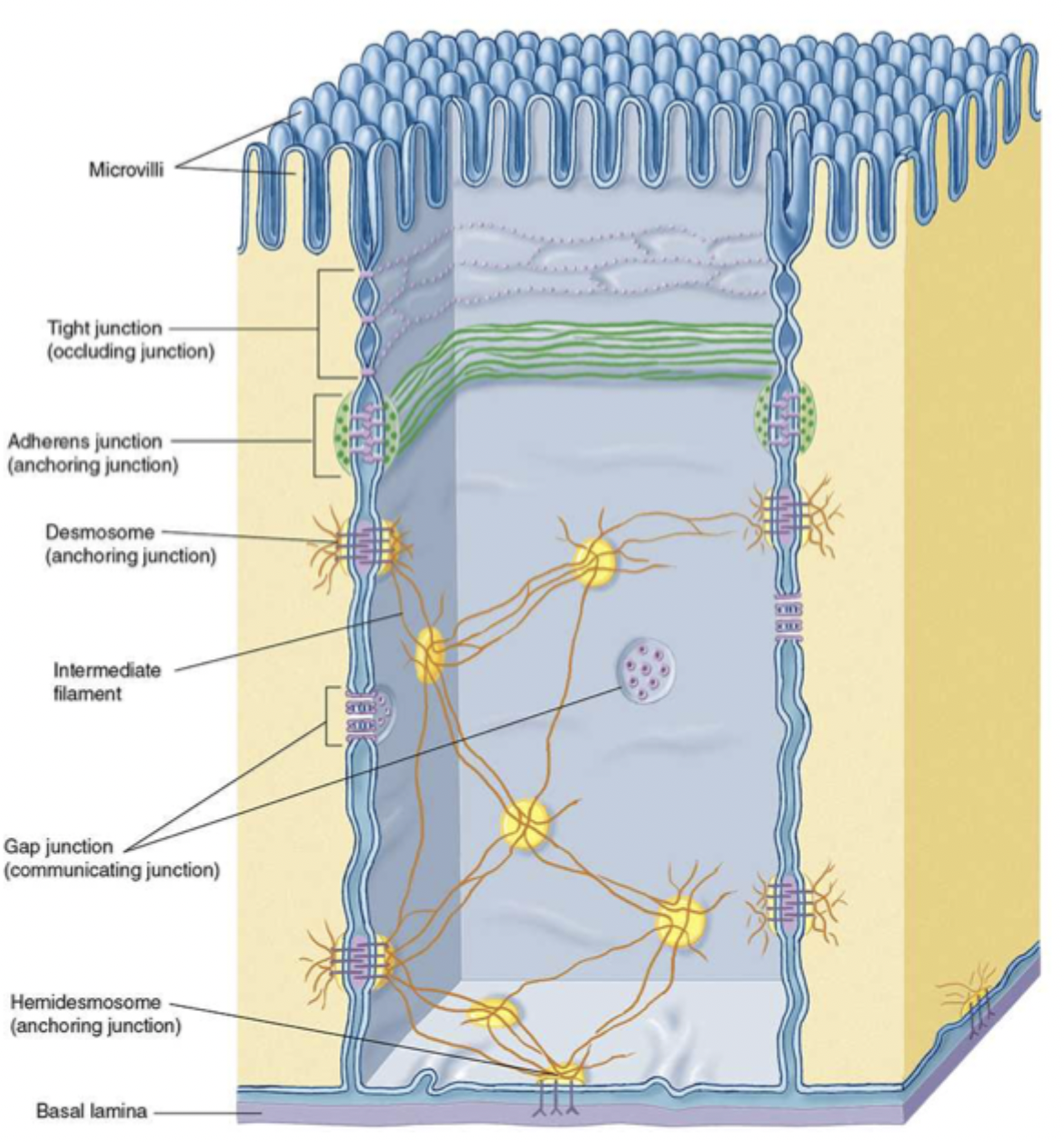
what is a desmosome?
strong spot links between cells ex. keratin
what do hemidesmosomes do?
join epithelial cells to basal lamina involving integrins
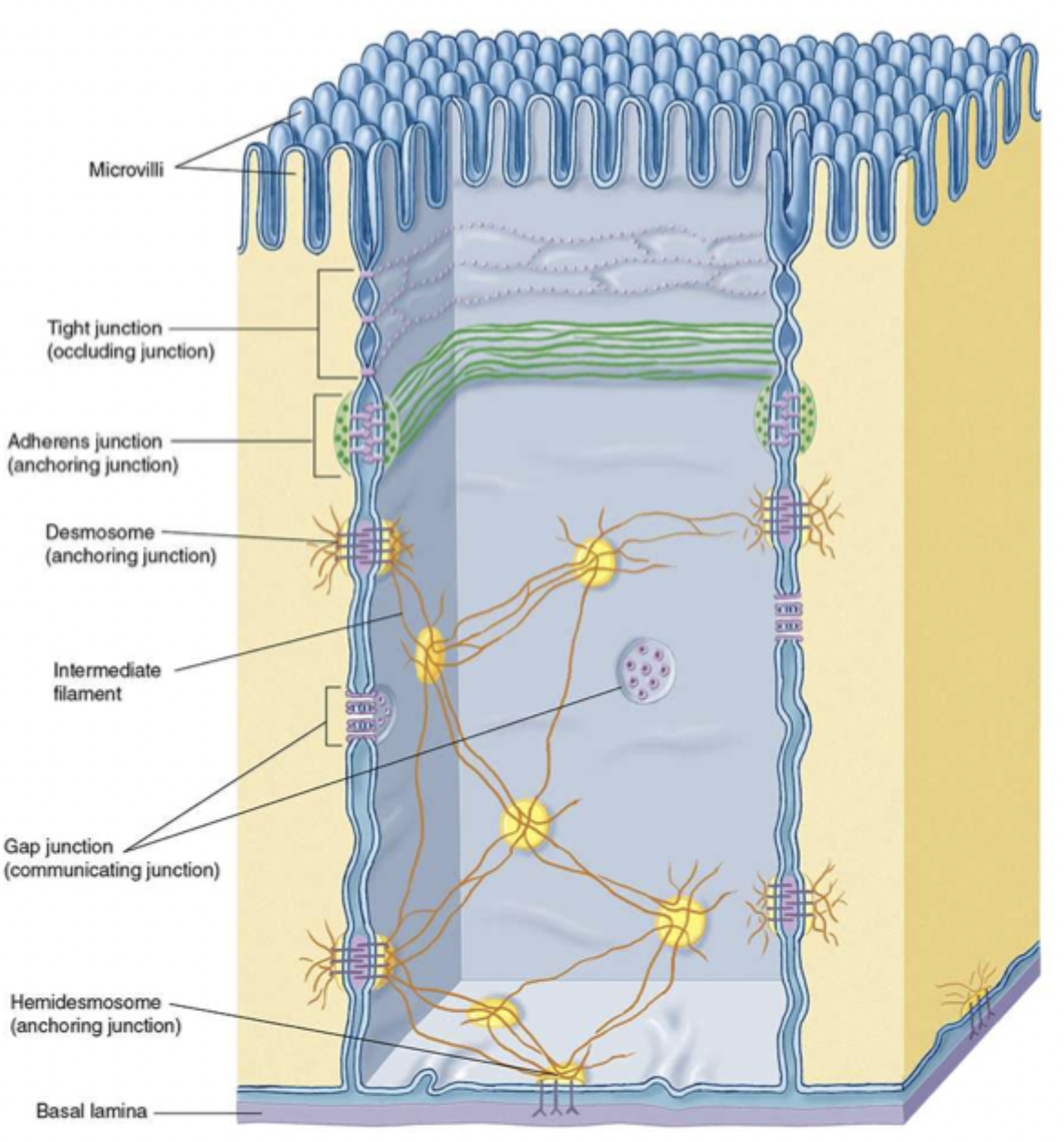
integrins
interact with basal lamina and extracellular matrix, affect cell movement and shape
gap junctions do what?
communication
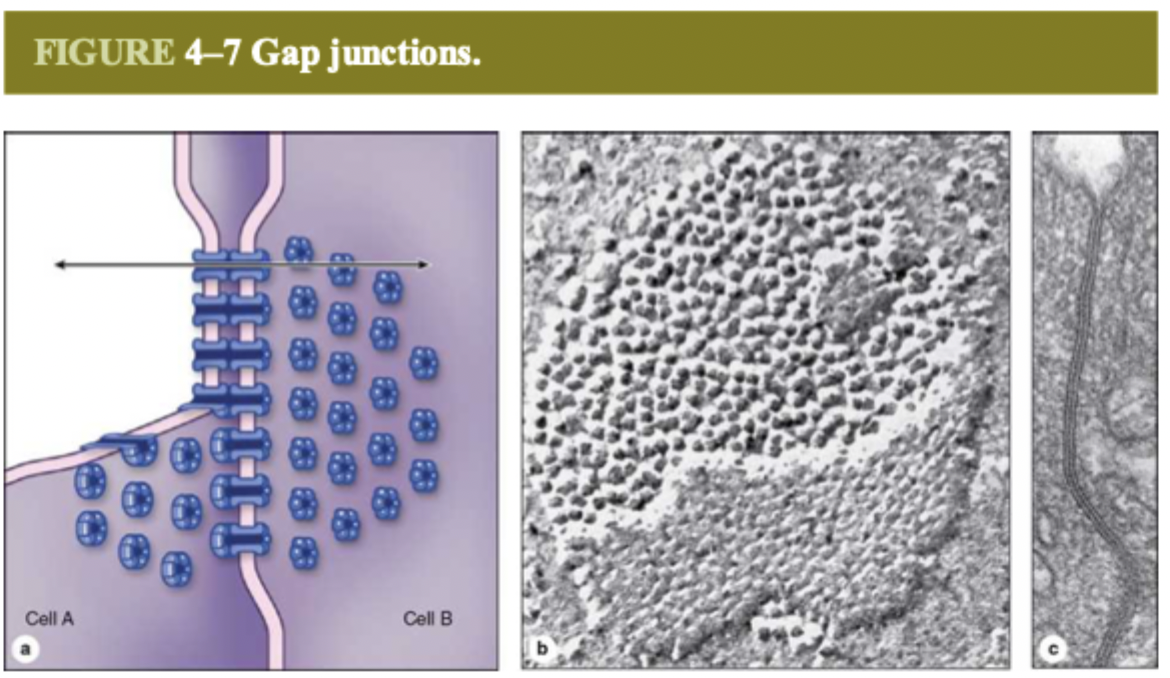
how do gap junctions do their job?
form connexons between adjacent cells like nerve or cardiac cells and allow signalling molecules to pass through
connexons
small diffusion channel between adjacent cells
what are connexons made of?
6 integral proteins called connexins
what are the three specializations of free surfaces?
cilia, microvilli, and stereocilia (long microvilli)
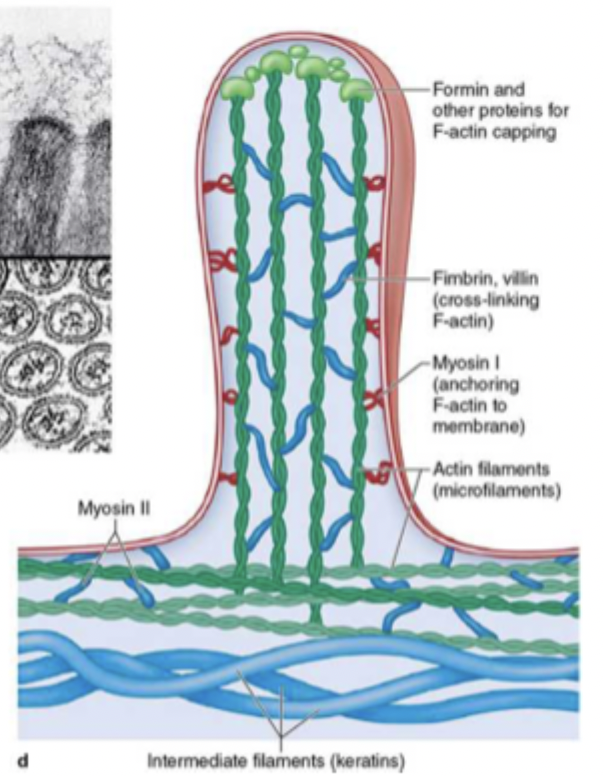
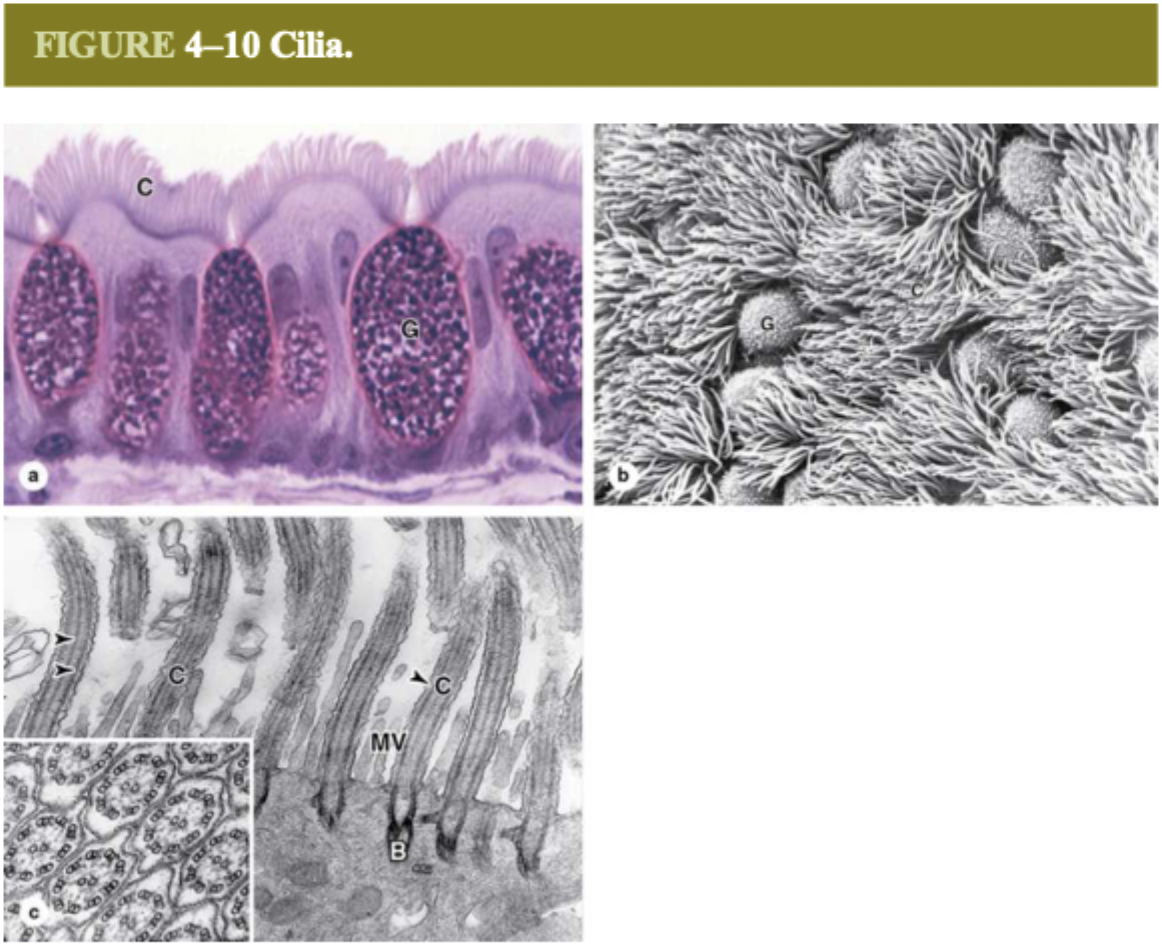
cilia
move mucus and other substances
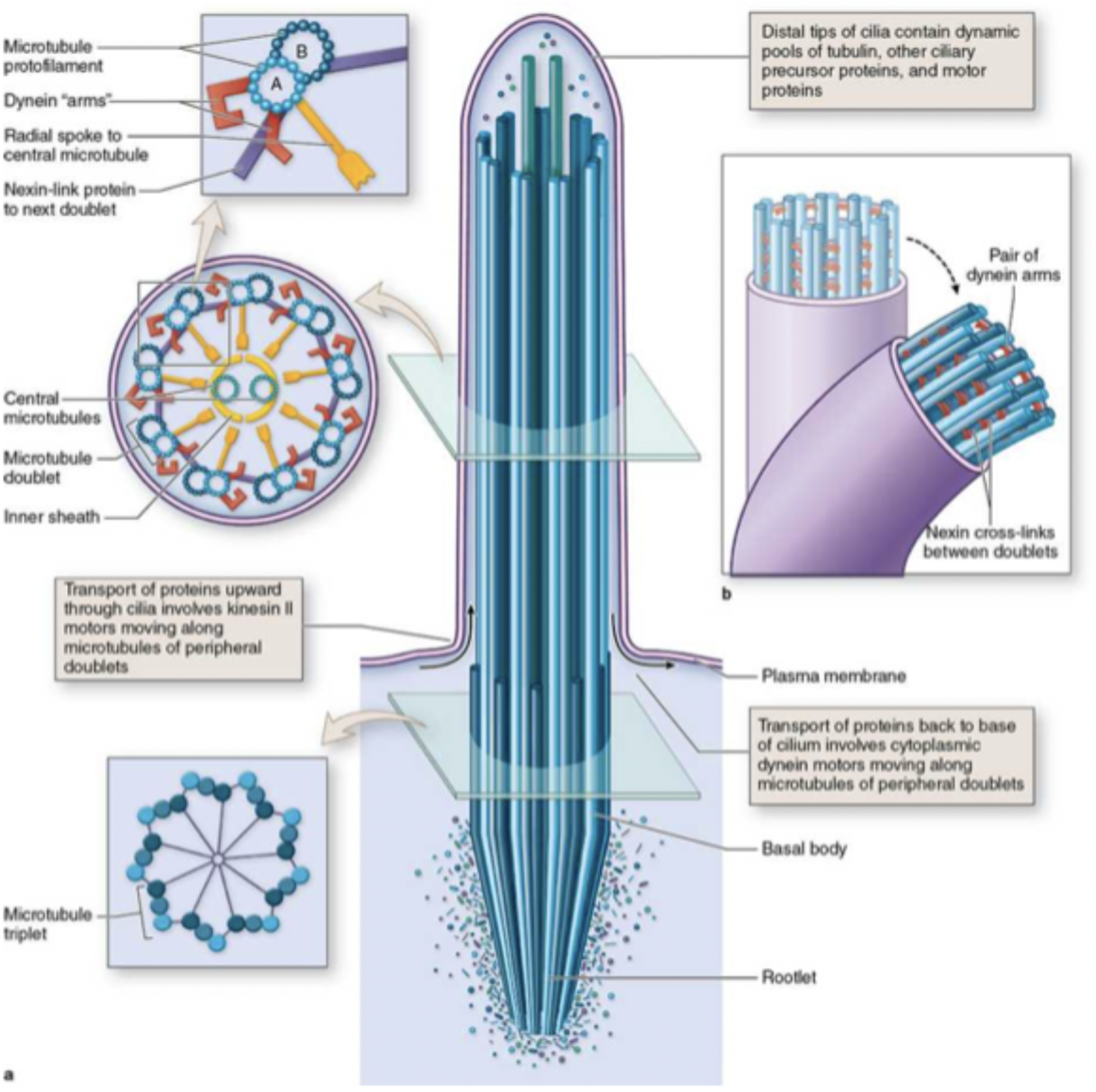
where are cilia found?
trachea, bronchi, oviducts
microvilli
increase surface area
where are microvilli found?
kidney tubule cell and intestinal absorptive cell
stereocilia (long microvilli)
for hearing
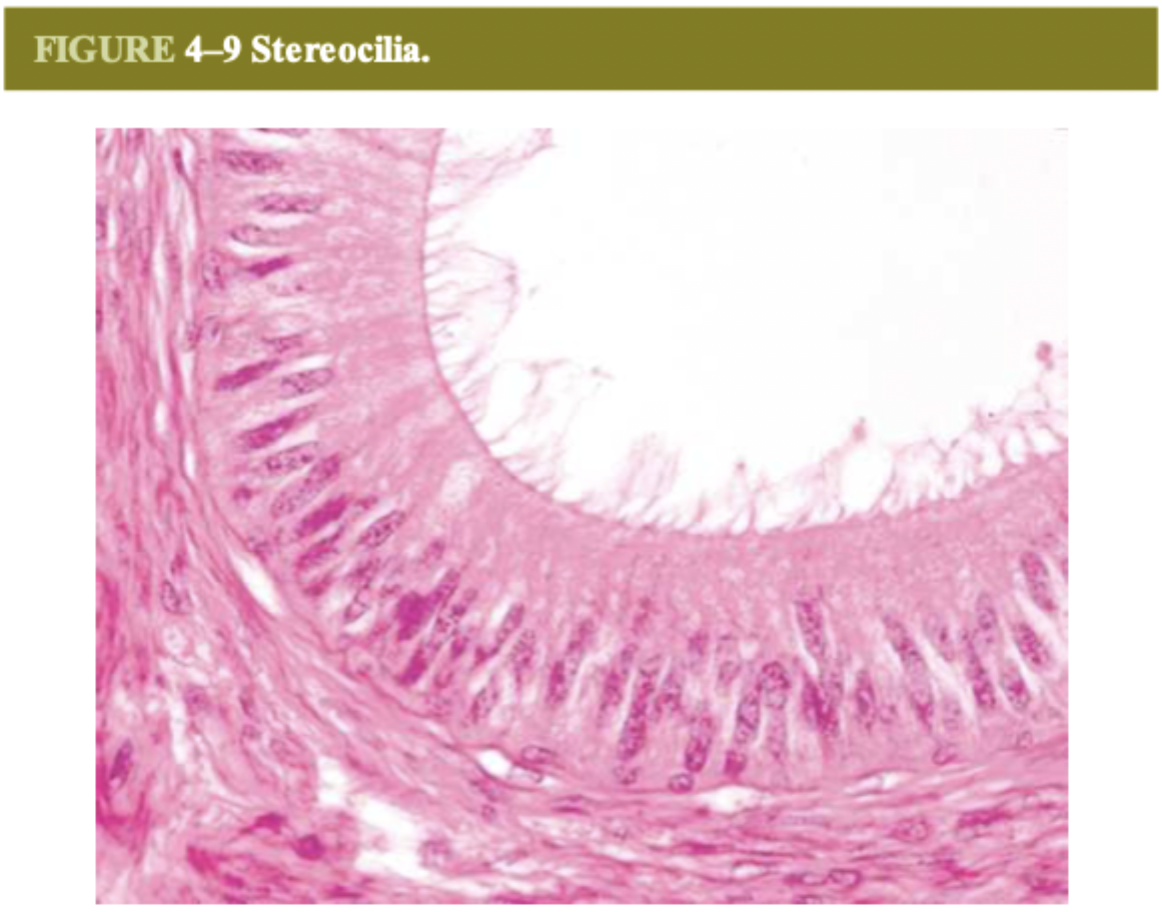
where are stereocilia found?
only in epididymis and sensory (hair) cells of inner ear
how is covering epithelia classified?
number of cell layers and shape of cell, named by most external layer
how do you classify simple epithelia?
single cell layer
how do you classify stratified epithelia?
multiple cell layers
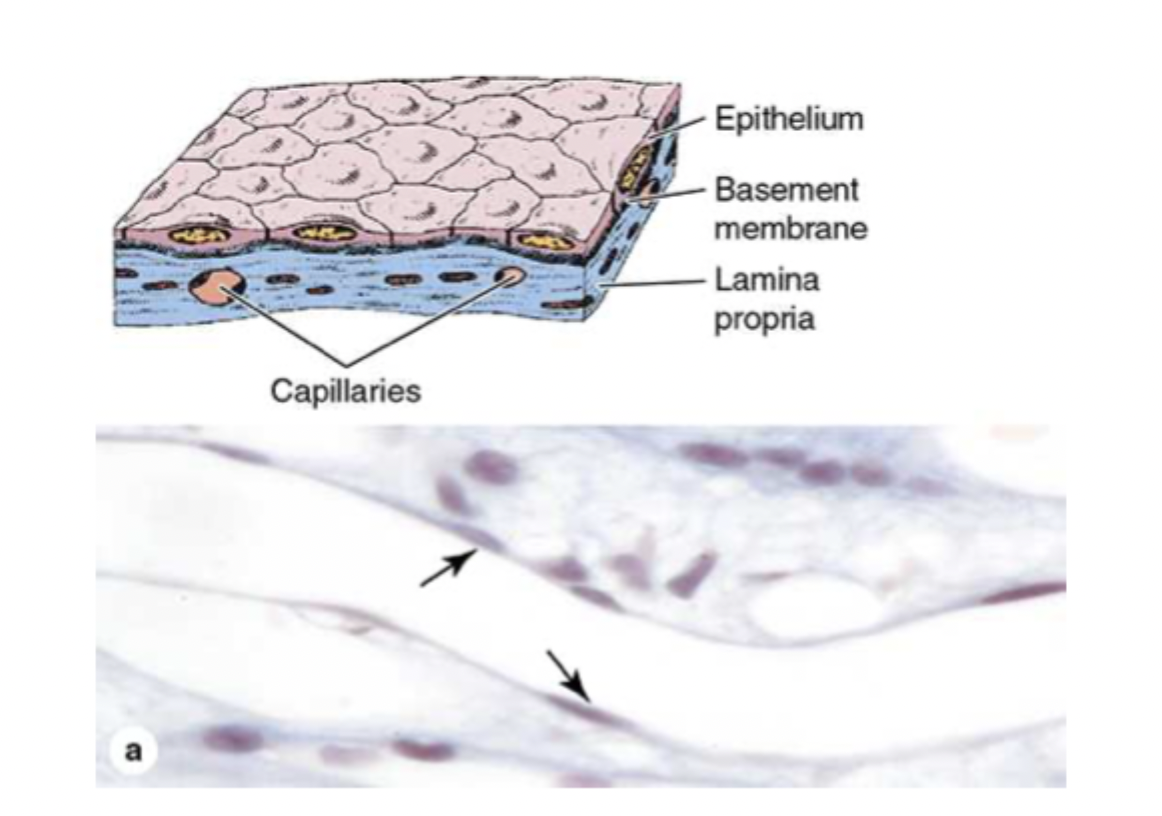
how do you classify squamous epithelia?
flat shape
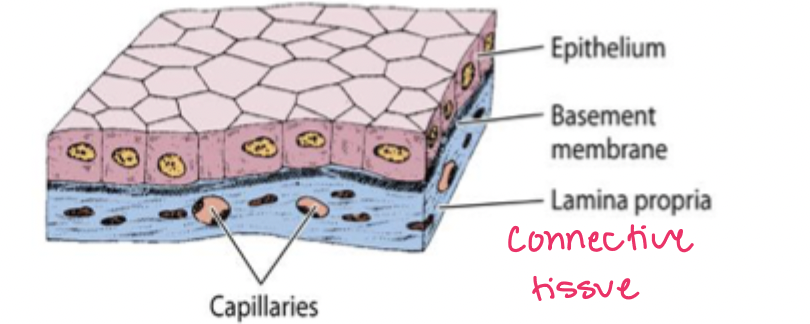
how do you classify cuboidal epithelia?
cube or hexagonal shape
how do you classify columnar epithelia?
tall or cylindrical shape
what is the purpose of simple squamous epithelium?
allow active and passive movement of substances like gasses or fluids through tissue
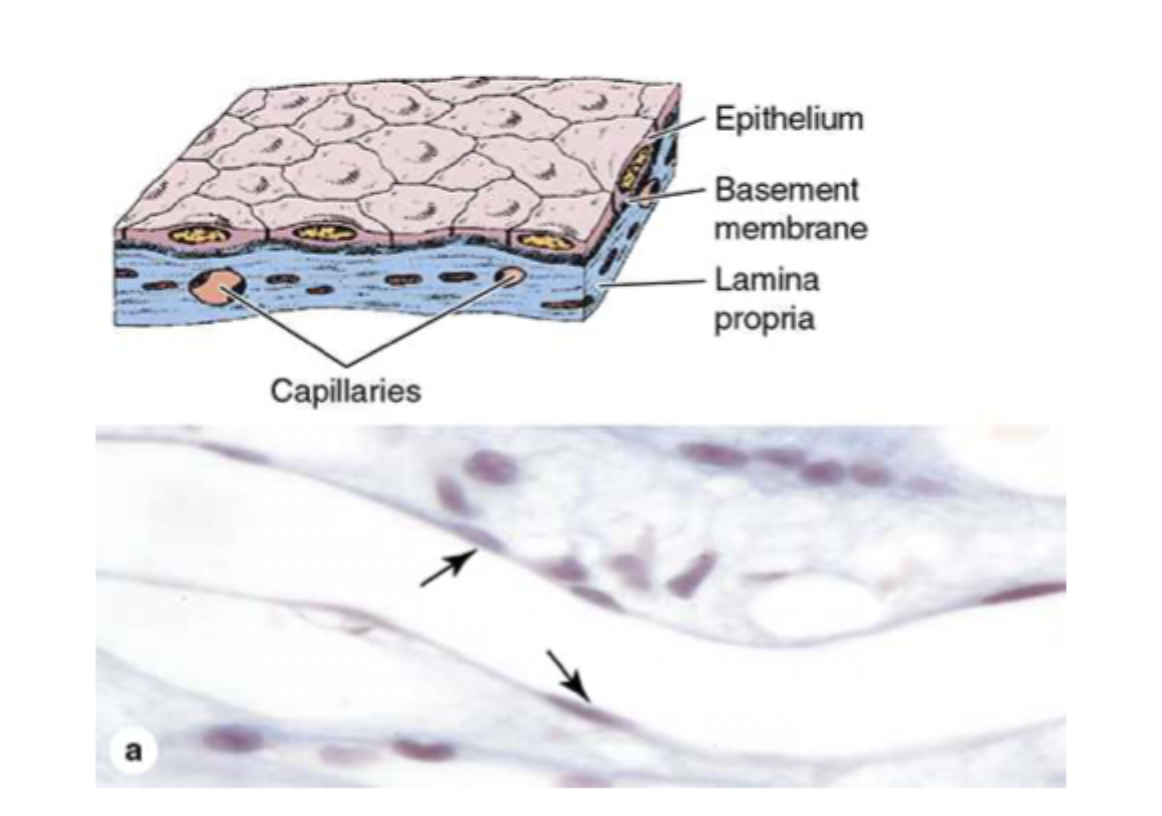
what are the special names for simple squamous epithelium?
endothelium and mesothelium
what is endothelium?
internal lining of the heart and blood vessels
what is mesothelium?
internal lining of the ventral body cavities
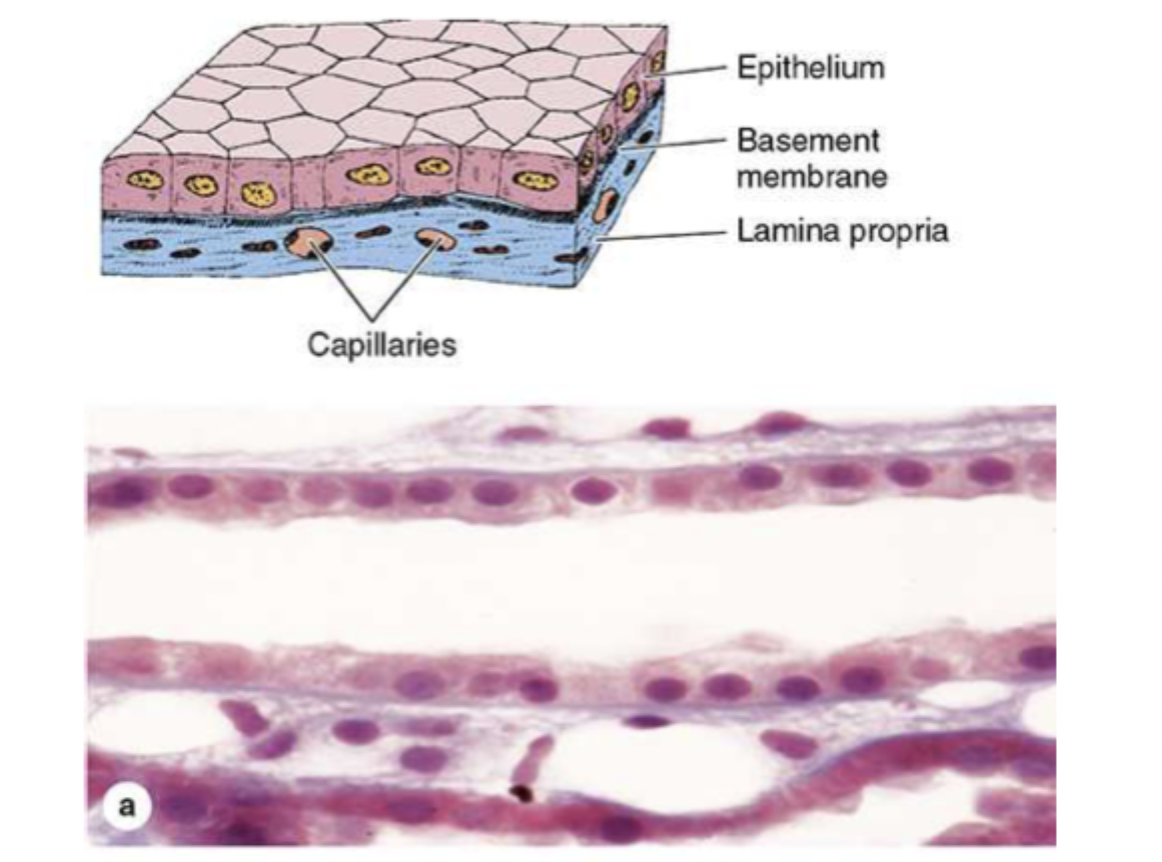
what is the purpose of simple cuboidal epithelium?
secretions (ex sweat or tears) or absorption (ex water)
what is the purpose of simple columnar epithelium?
protective, secretion, and absorption
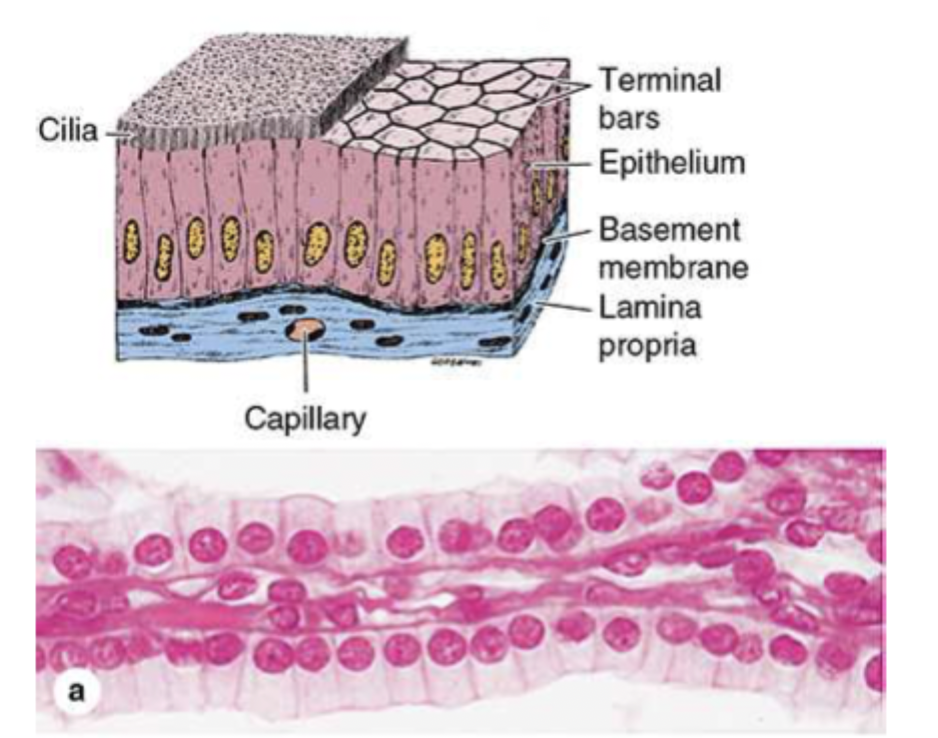
what are the 2 types of simple columnar epithelium?
ciliated which moves mucous or other substances and non ciliated
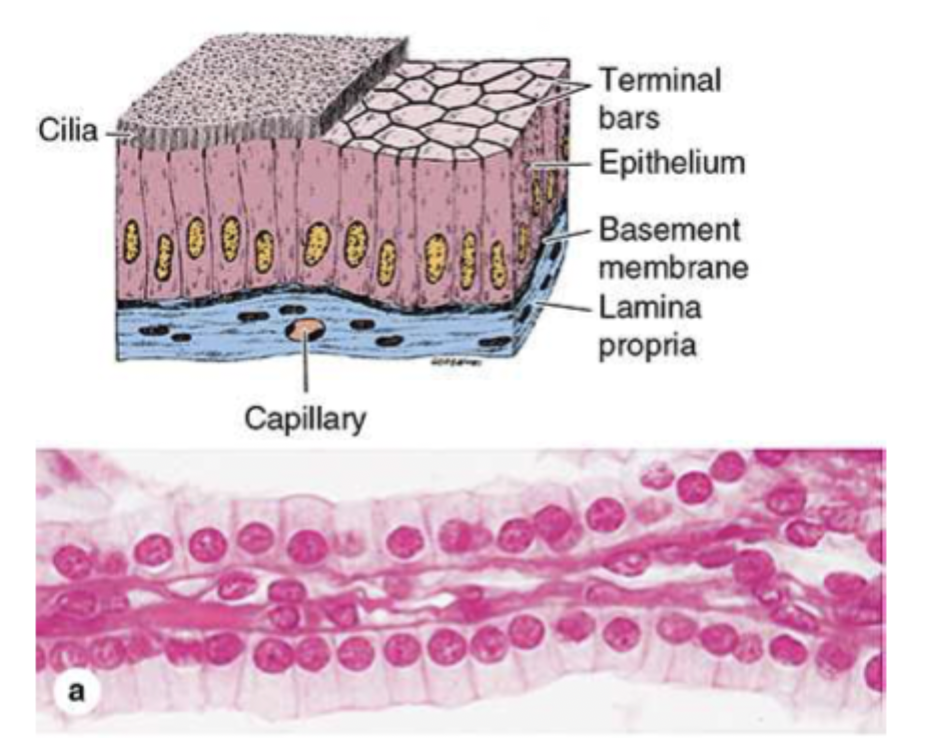
what are the 2 types of nonciliated simple columnar epithelium?
goblet cells which secret mucus or absorptive cells (have microvilli)
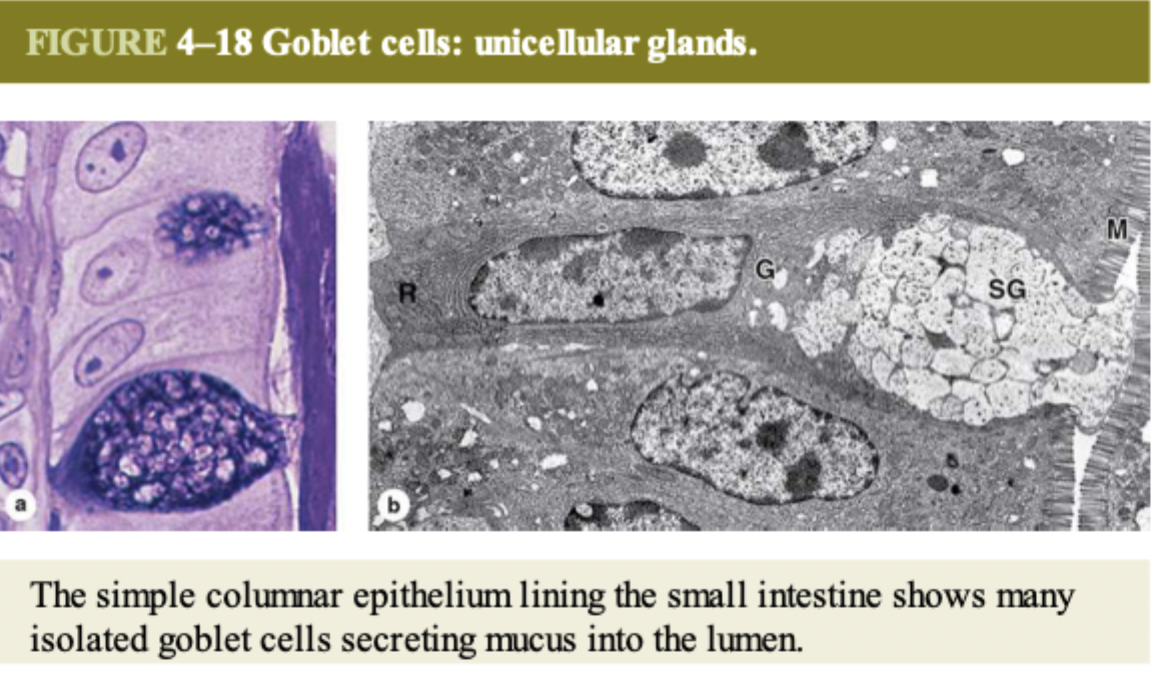
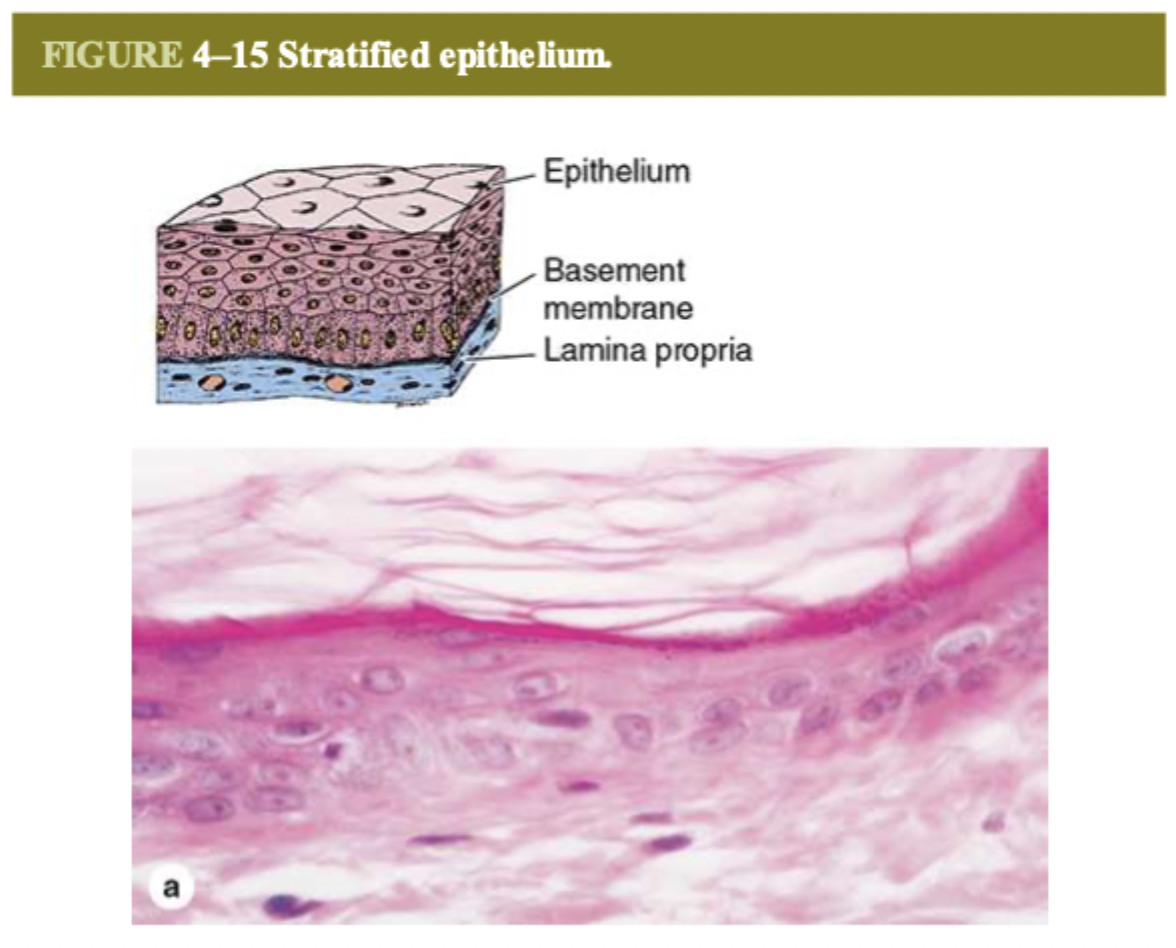
what do the layers of stratified squamous epithelium look like?
superficial layers are flat while the deeper layers are cuboidal, and the deepest (next to connective tissue) have continuous cell division
what are the 2 types of stratified squamous epithelium?
keratinized and non keratinized
where is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
skin, gums, pallet of mouth, top of tongue
where is non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
lining of the oral cavity, under the tongue
describe pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
columnar and appears to have multiple layers, but every cell attaches to the basement membrane, some cells do not reach the free surface, they may secrete or be ciliated
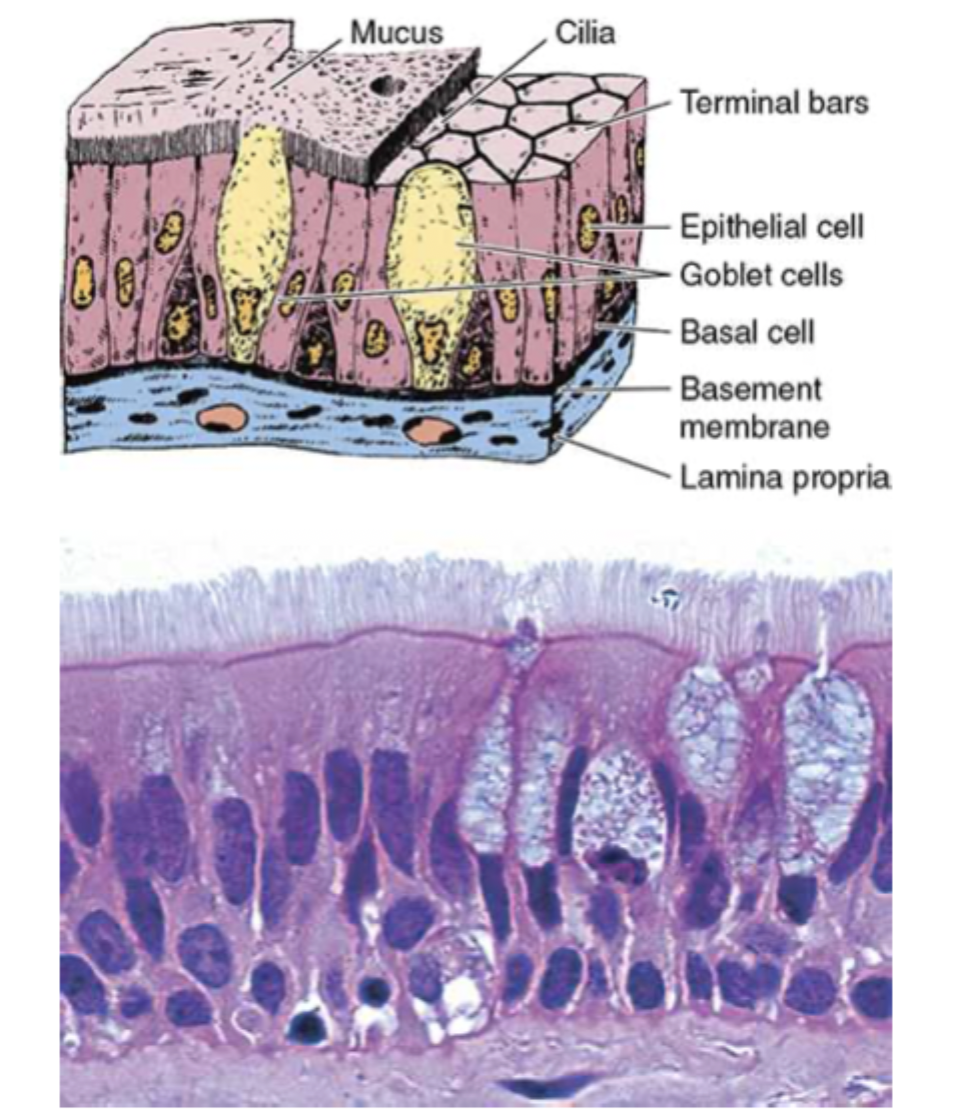
where is pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
seen mostly in the respiratory system
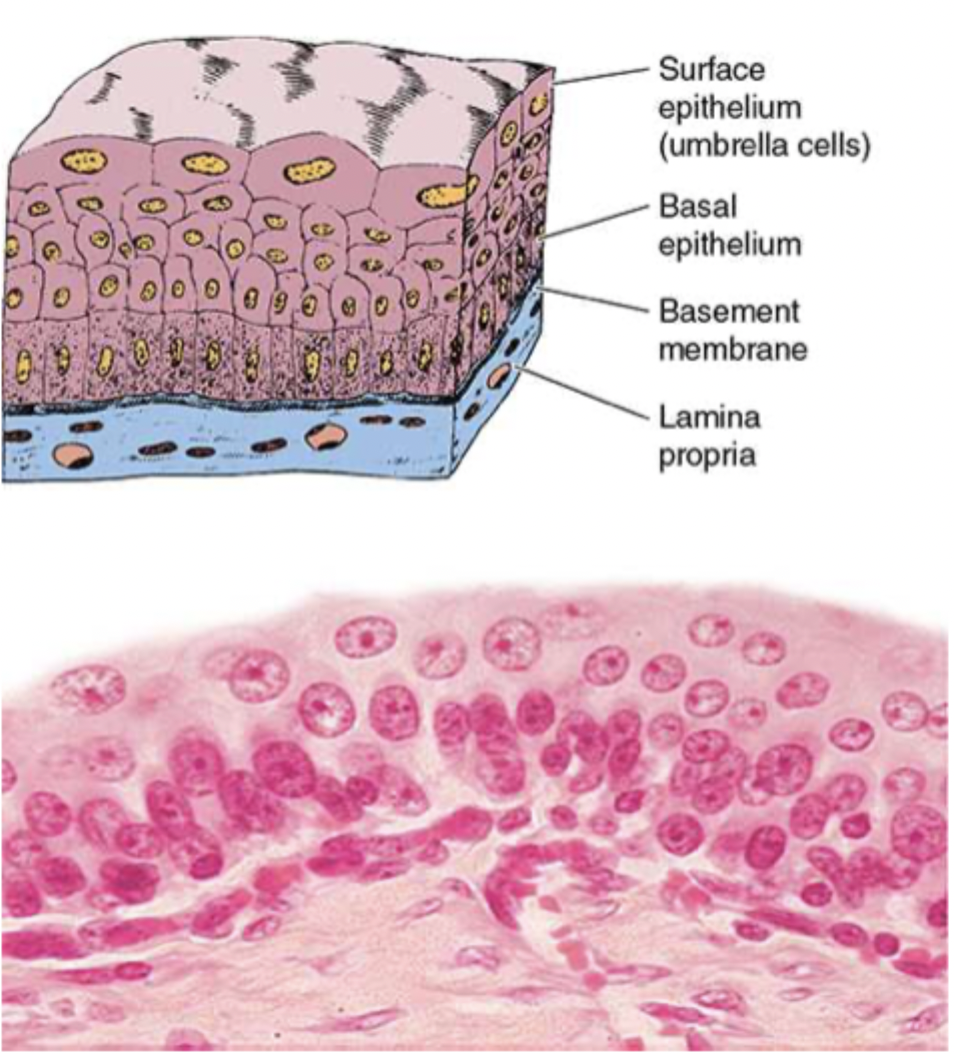
what is transitional epithelium?
special stratified epithelium where the external layer (surface layer) is cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched
where is transitional epithelia?
lines pelvis of kidney, ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
what are the 2 major classifications of glands?
exocrine and endocrine
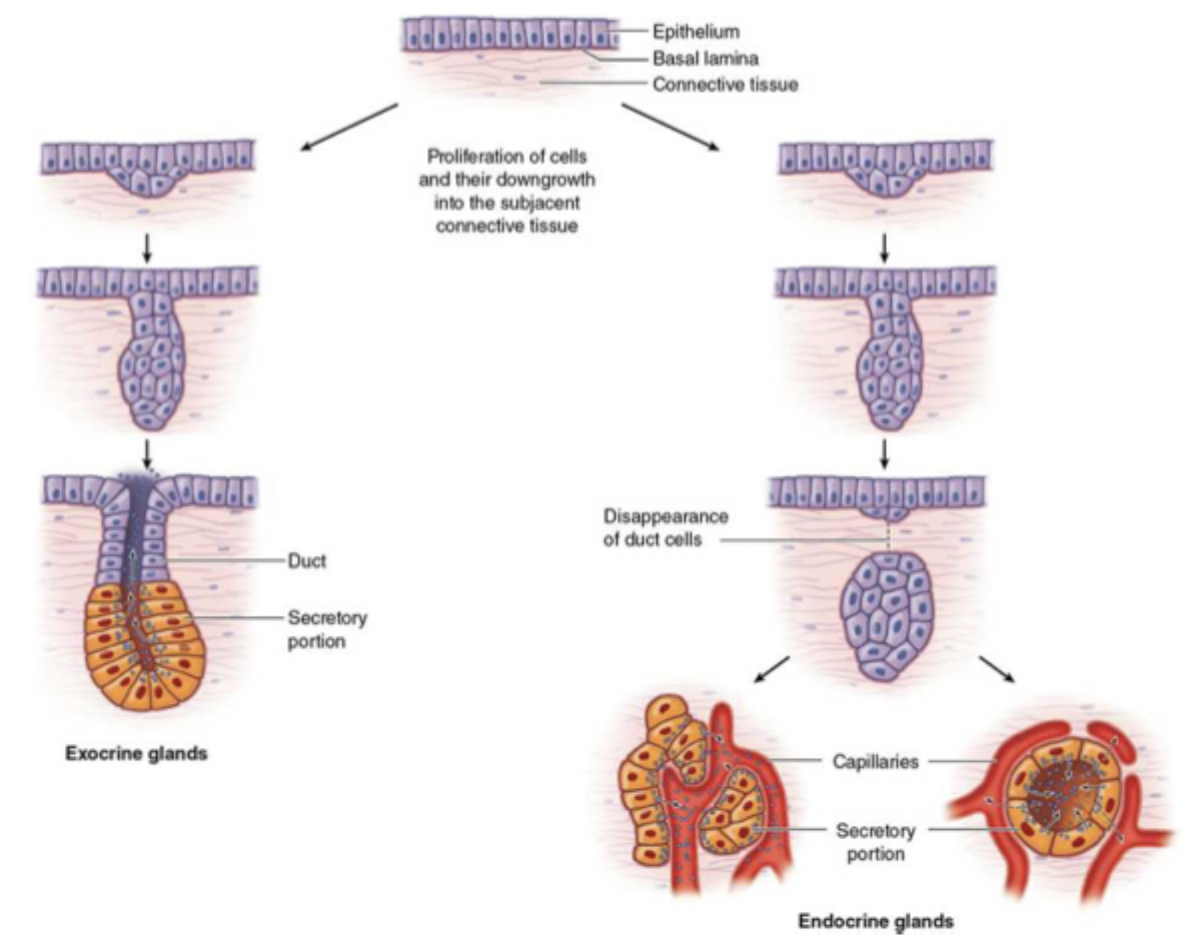
what is exocrine?
secretes into ducts that are usually divided into lobes and lobules
what is endocrine?
ductless, secrete into extracellular fluids and diffuse into blood
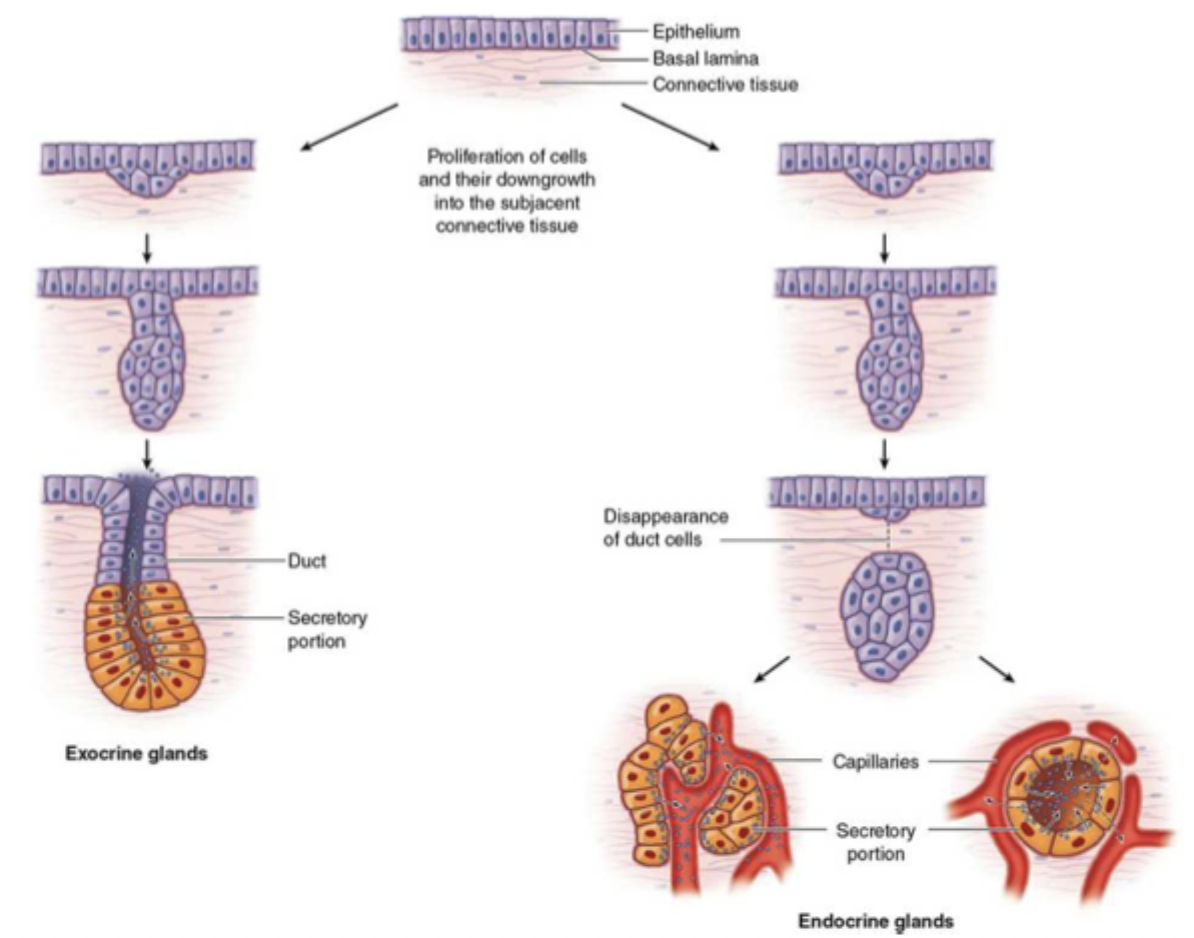
how are exocrine glands made?
the epithelial layer invaginates down into the connective tissue and the core cells break down, leaving a duct, the distal portion becomes secretory cells
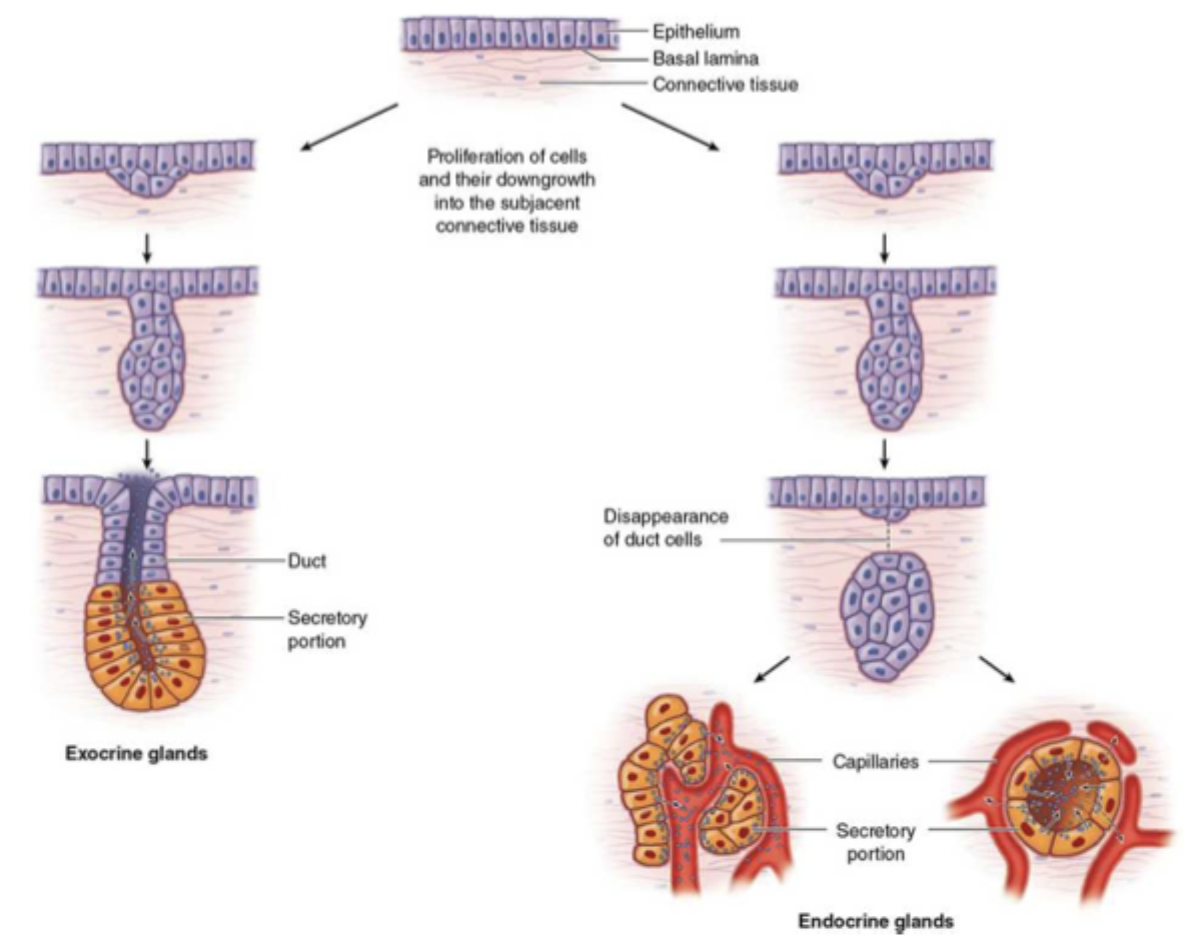
how are endocrine glands made?
the epithelial layer invaginates down into the connective tissue and disconnects from the surface layers, the distal portion becomes secretory cells and the gland is invaded by blood vessels (highly vascular)
how are exocrine glands classified?
structure, type of secretion and mode of secretion
what are the three types of secretion?
serous (watery), mucous (thick), and mixed
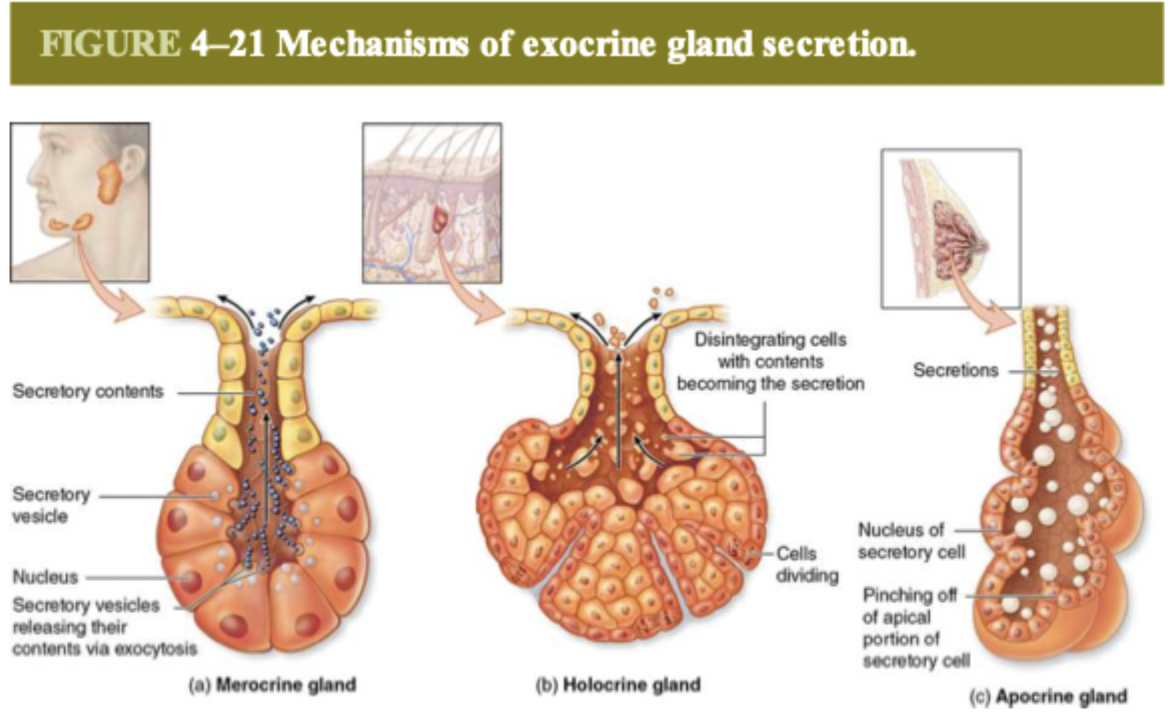
what are the three types of secretory patterns?
merocrine, holocrine, and apocrine
how do merocrine glands secrete?
the secretory vesicles in the cells release their contents through exocytosis
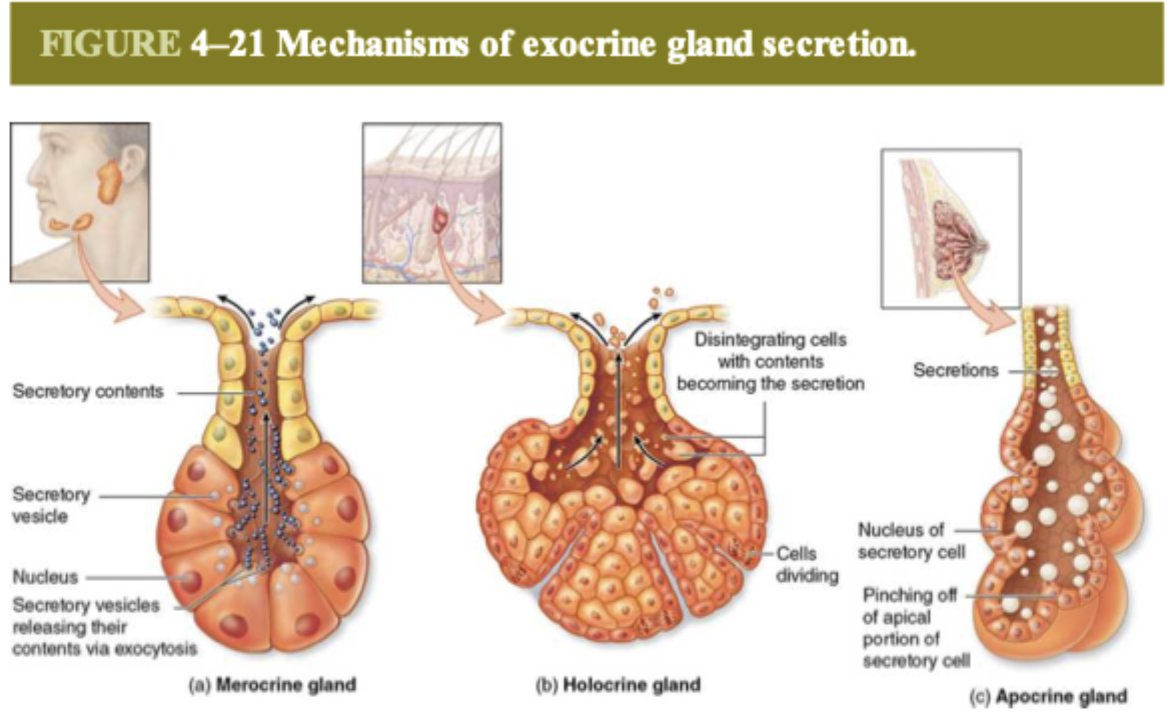
one example of merocrine gland
salivary glands
how do holocrine glands secrete?
the cells disintegrate with the contents becoming secretion
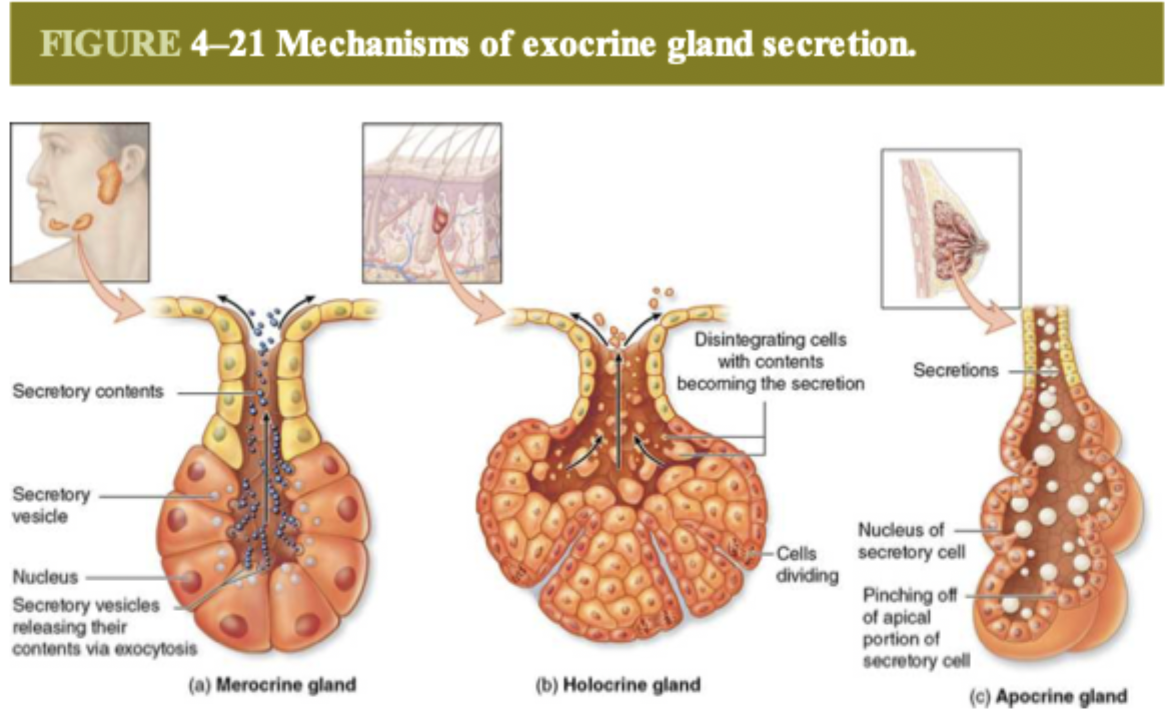
one example of holocrine gland
sebaceous glands
how do apocrine glands secrete?
the apical portion of the secretory cell is pinched off as the secretion