Introduction to economics (copy)
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Microeconomics:
A branch of economics which studies the behaviour of individuals and firms in particular markets
Macroeconomics:
A branch of economics which studies the behaviour of the government and the economy as a whole
What type of science is economics?
Social science - studies the behaviour of individuals and societies when allocating scarce resources to meet unlimited needs and wants
The basis of the study of economics:
microeconomics and macroeconomics
The nine central concepts of the economics course:
Well-being
Interdependence
Scarcity
Efficiency
Choices
Intervention
Change
Equity
Sustainability
Define Factors of Production
refers to the resources required to produce goods and services
Factors of Production:
Capital
Entrepreneur
Land
Labour
Define the factors of Production
Capital - man-made resources
Entrepreneur - the skill of organising the three other factors of production
Land - natural resources
Labour - human resources (workers)
What are factors of income?
Factor income is income received from the factors of production
What is the factor of income for capital?
interest
What is the factor of income for Entrepreneur/enterprise?
Profit
What is the factor of income for land?
Rent
What are the 3 basic economic questions?
What how much to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
What is the process of the circular flow of income?
households provide resources to businesses
firms provide income to households
firms use the resources to produce goods and services for households
households provide expenditure (spend money) to businesses
the cycle repeats
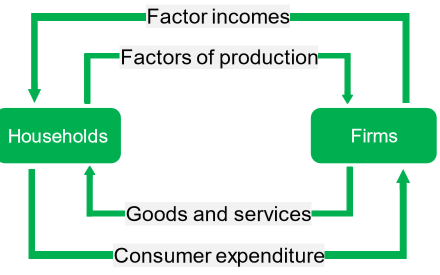
What does the circular flow of income show?
the interaction between households and firms
Why is this model over-simplified? What are the assumptions made?
There are no injections or leakages:
only 2 economic agents
no gov intervention (tax/gov spending)
no financial sector (savings/investments)
no foreign economics involved (trade= imports
/exports)
what does sustainability mean?
the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs
What is a leakage in the circular flow of income?
What is an injection into the circular flow of income?
refers to the withdrawal of money from the circular flow of income
refers to the additional money added into the circular flow of income
hhhh
hhhhhhhhhh
ksdfhskfsdkfskfh
lasjdfhaslfhsaa
asdfjsakfjsfkfjakfa
kasdfsakfjskfj
iyiyiyuiuyiy
oiuouououoiouio
1
2
3
4
5
6