Biology II chapter 1 - MOLECULAR GENETICS
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fill in the blank
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
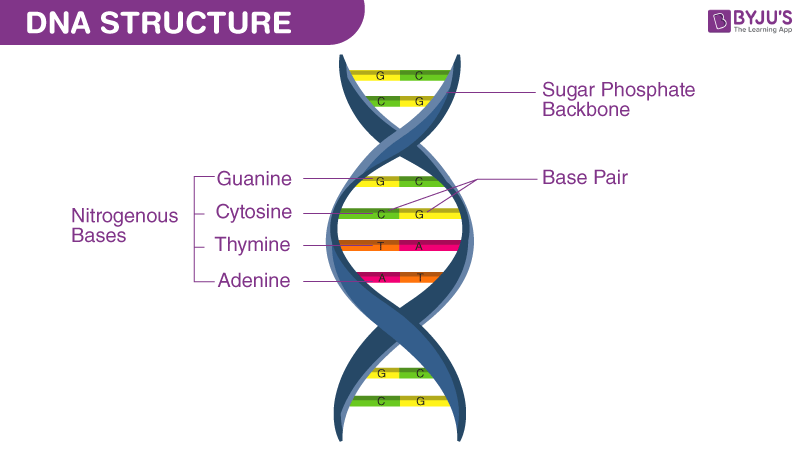
Three main components of nucleotides:
a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
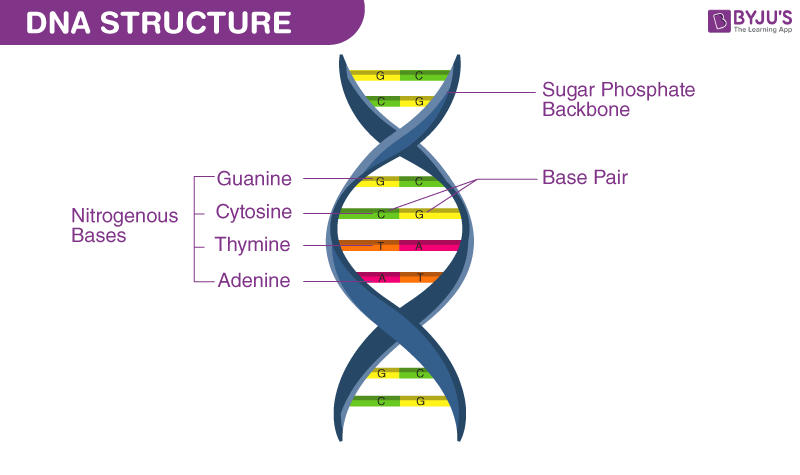
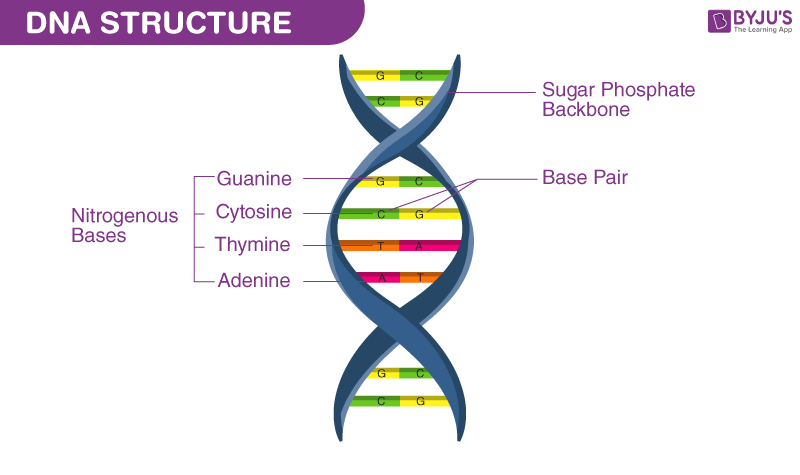
The ____ and _____ groups form the backbone of each strand, alternating with each other.
sugar
The specific pairing of the ______ bases _____ with thymine (in RNA, uracil - U) and _____ with guanine holds the strands together by _____ bonds.
nitrogenous
adenine
cytosine
hydrogen
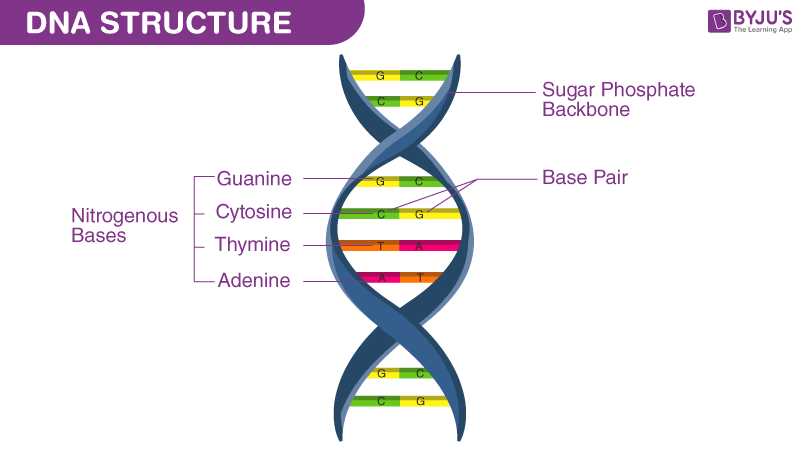
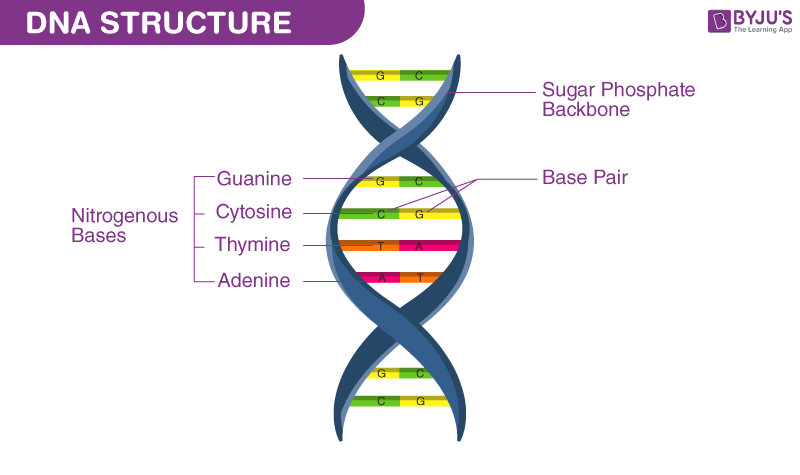
genetic information
The specific sequence of these base pairs along the DNA strand carries the _____.
nucleotides form
dna
__?__ (the long molecule that stores all genetic information) → ____ (a specific segment of DNA that carries instructions, often to make a protein) → _____ (An alternative version of a gene)
DNA
____ (the long molecule that stores all genetic information) → __?__ (a specific segment of DNA that carries instructions, often to make a protein) → _____ (An alternative version of a gene)
gene
____ (the long molecule that stores all genetic information) → _____ (a specific segment of DNA that carries instructions, often to make a protein) → __?__ (An alternative version of a gene)
allele
3 steps with keywords:
helicase enzyme
5′ - 3′ direction
Okazaki fragments
Replication forks
🧬 DNA Replication Mechanism
Initiation: begin at origins → ___?___ unwinds the DNA by breaking H2 bonds → ______ proteins stabilize the unwound strands & prevent them from rejoining → Topoisomerase acts ahead of helicase, relieve ______ preventing knots/tangles.
helicase enzyme
Initiation: begin at origins → _____ unwinds the DNA by breaking H2 bonds → ___?___ stabilize the unwound strands & prevent them from rejoining → Topoisomerase acts ahead of helicase, relieve ______ preventing knots/tangles.
Single-strand binding proteins
Initiation: begin at origins → _____ unwinds the DNA by breaking H2 bonds → ______ stabilize the unwound strands & prevent them from rejoining → Topoisomerase acts ahead of helicase, relieve ___?___ preventing knots/tangles.
supercoiling
___?___: Primase lays down RNA primers → DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in 5′ - 3′ direction → Leading strand synthesized continuously → Lagging strand synthesized discontinuously as Okazaki fragments → DNA polymerase replaces RNA primers with DNA → DNA ligase seals gaps.
elongation
Elongation: Primase lays down RNA primers → ________ adds nucleotides in 5′ - 3′ direction → Leading strand synthesized continuously → Lagging strand synthesized discontinuously as Okazaki fragments → _________ replaces RNA primers with DNA → DNA ligase seals gaps.
DNA polymerase
Termination: ______ (Y-shaped region) meet or reach end → RNA primers removed & replaced with DNA → DNA ligase seals backbone → Two identical DNA molecules (semi-conservative).
Replication forks
regulatory sequences (promoter, enhancers/silencers) + coding sequences (exons, introns) + UTRs + terminator = gene of what???
eukaryotes
Promoter: DNA sequence where RNA polymerase and transcription factors bind to start transcription.
Coding region: sequence that is transcribed into RNA and often translated into protein.
Terminator: sequence signaling the end of transcription.
general structure of gene
________: sequence that is transcribed into RNA and often translated into protein.
Coding region
_____: sequence signaling the end of transcription.
Terminator
_____: DNA sequence where RNA polymerase and transcription factors bind to start transcription.
Promoter
The process of copying a gene’s DNA sequence into RNA called _____
Transcription
The process of synthesizing a protein from the mRNA sequence.
Translation
to convert genetic information in mRNA into a functional protein.
Occurs in the cytoplasm, on ribosomes.
mRNA is read in codons (three-nucleotide sequences).
tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acids according to the codon sequence.
Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, forming a polypeptide chain → folds into a functional protein.
to create an RNA copy of the gene that can leave the nucleus for protein synthesis.
Occurs in the nucleus (in eukaryotes).
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, unwinds DNA, and synthesizes pre-mRNA (complementary to the DNA template strand).
In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA is processed: introns are removed, exons are spliced together, a 5′ cap and 3′ poly-A tail are added → mature mRNA.
gene muation
all is correct
🧪 Causes of Gene Mutations
Spontaneous Mutations: Occur naturally during DNA replication or repair processes.
Induced Mutations: Result from exposure to environmental factors such as radiation, chemicals, or viruses.
Example: In sickle cell anemia, a single nucleotide change causes a glutamic acid to be replaced by valine in hemoglobin, altering its function
Substitution
Example: A frameshift mutation occurs when nucleotides are inserted or deleted in numbers not divisible by three, shifting the reading frame and potentially altering the entire protein
Insertion/Deletion:
it happens because DNA is very long, but it needs to be compact enough to fit inside a cel
when a DNA double helix twists on itself, like a phone cord that gets over-twisted
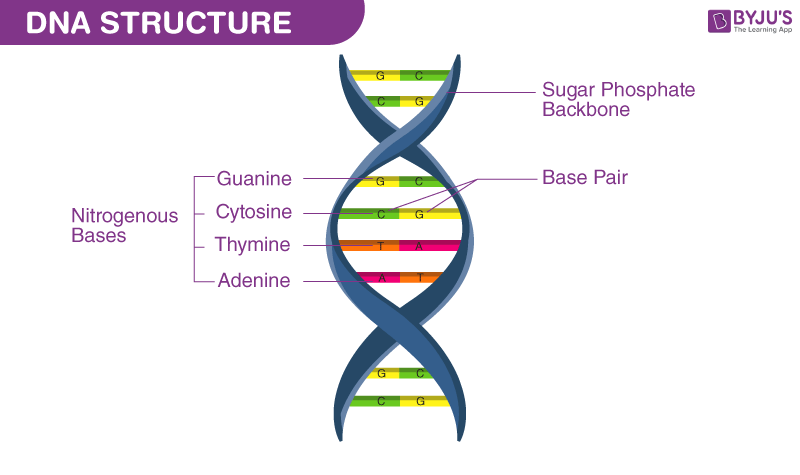
The ____ and _____ groups form the backbone of each strand, alternating with each other.
phosphate
Example: A mutation in the gene for hemoglobin can cause sickle cell disease, where the altered protein leads to misshapen red blood cells .
Missense Mutation:
Mutation
│
├── Spontaneous (natural errors)
│ ├── In germ cells (egg/sperm) → Hereditary (passed to offspring)
│ └── In somatic cells (body) → Non-hereditary (not passed on)
│
└── Induced (caused by mutagens: radiation, chemicals, viruses)
├── In germ cells → Hereditary
└── In somatic cells → Non-hereditary
diagram flow (Spontaneous → Germline vs Somatic → Hereditary vs Non-hereditary)
Which part of DNA actually carries genetic information?
The sequence of nitrogenous bases
Why can one gene make multiple proteins in eukaryotes?
Alternative splicing of RNA exons