Muscle's Quiz #2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is the 3 types of Muscle tissue
skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth
Where is Skeletal Muscle Located
Attached to bones
What is the shape of Skeletal Muscle Cells
Elongated
How many Nuclei do Skeletal Muscle Cells have
Multinucleated
does skeletal muscle have striations and is it involuntary or voluntary control?
Yes, striated and voluntary control
Where is Cardiac Muscle Located
Heart wall (myocardium)
What is the Cell shaped of Cardiac Muscle
Elongated, arms/branches, with intercalated Discs
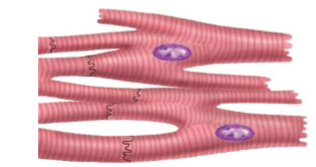
How many Nuclei Does Cardiac muscle have
2
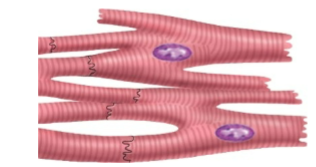
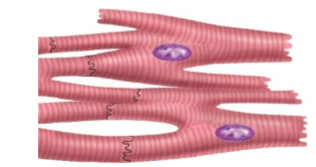
does Cardiac Muscle have striations and is it involuntary or voluntary control?
Yes, striations, involuntary control
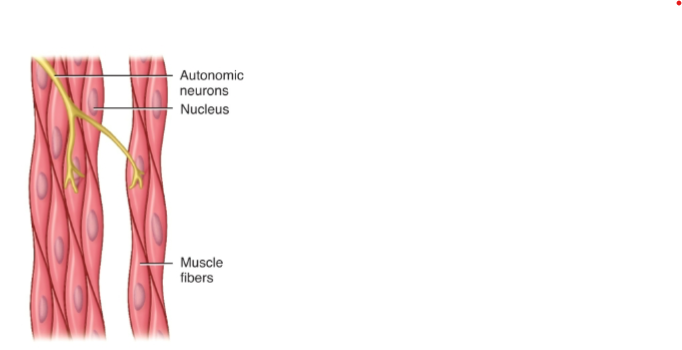
where is Smooth Muscle Located?
walls of hollow organs (stomach, intestines, blood vessels)
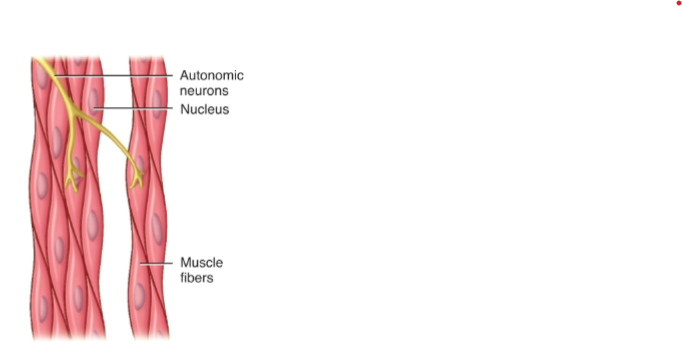
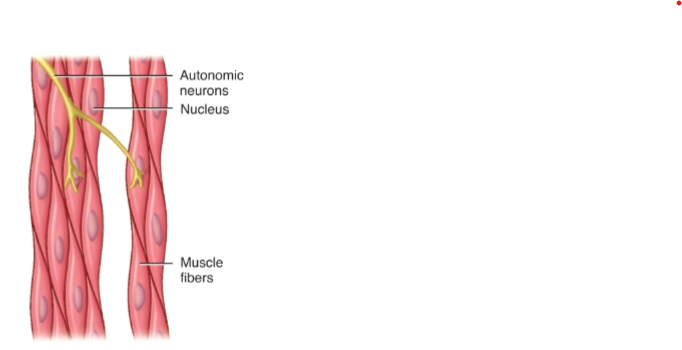
What is the Cell Shape of Smooth Muscle
Cell oblong and tapered ends
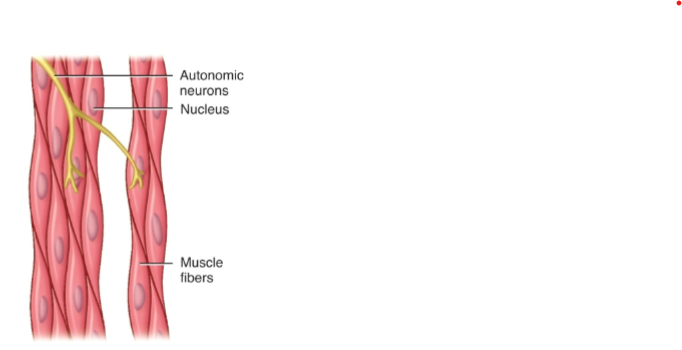
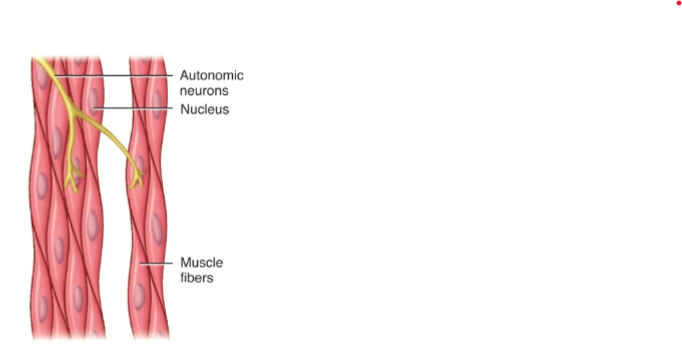
does Smooth muscle have striations and is it involuntary or voluntary control?
lack striations, and involuntary
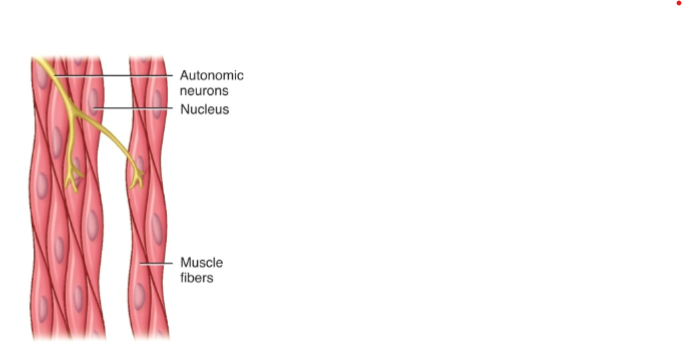
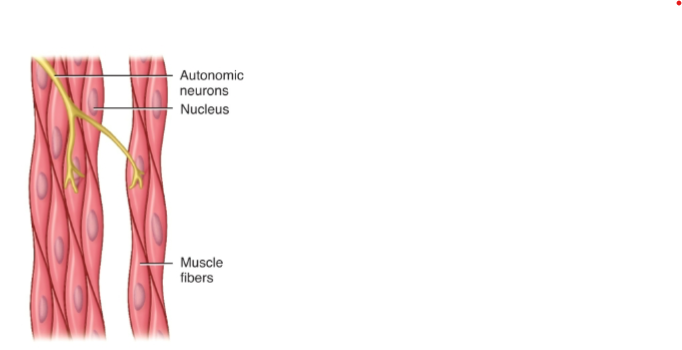
Does smooth muscle have nuclei?
Single nucleus
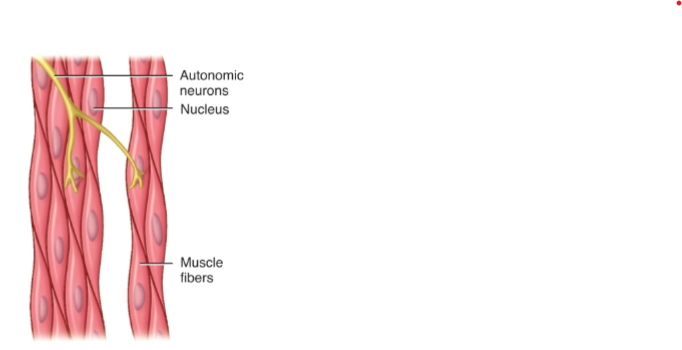
what is a muscle
Entire organ made of bundles of fascicles.
what is fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers (cells).
What is a muscle Fiber
muscle cell, multinucleated cell
where is Epimysium located
Outer layer covering the whole muscle.
Perimysium
Wraps around each fascicle.
Endomysium
Surrounds each individual muscle fiber.
Myofibrils
Long contractile organelles inside fibers.
Myofilaments
Thin (actin) and thick (myosin) filaments that slide for contraction
Sarcomere
Functional contractile unit, between Z-discs.
what are the proteins and function in Contractile
Actin (thin, pulls), Myosin (thick, motor protein with heads that attach to actin)
what are the 2 proteins in Regulatory
Troponin (binds Ca²⁺, moves tropomyosin) and Tropomyosin (blocks actin binding sites)
What are the 2 proteins in Structural
Titin (elasticity), Dystrophin (links myofibrils to sarcolemma).
What is the main element for contraction
Calcium (Ca²⁺)
Major neurotransmitter in skeletal muscle
Acetylcholine
What are the 4 rotator cuff Muscles
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor, Subscapularis SITS
What are the 3 intramuscular injection sites
Deltoid, Gluteus Medius, and Vastus lateralis
What is the Cardiovascular system composed of
Heart + blood vessels (pumps & transports blood).
What is the Circulatory system composed of
Includes cardiovascular + lymphatic systems (blood & lymph transport).
What is the 4 functions of the heart
Pumps blood
Maintains blood pressure
Delivers oxygen/nutrients, removes waste
Maintains systemic and pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary Circuit composed of
Right heart → lungs → left heart (oxygenates blood).
Systemic circuit composed of
Left heart → body tissues → right heart (delivers oxygen).
Pericardium Fibrous is the
outer, tough connective tissue
Pericardium Serous is the
parietal & visceral layers with pericardial fluid
Epicardium is the?
Outer
Myocardium is the?
Muscle layer, thickest
Endocardium lines?
inner, lines chambers
Striated is composed of
branched, single nucleus, involuntary.
Intercalated discs are composed of
Contains gap junctions and desmosomes → coordinate contraction.
Ventricles are
Larger/thicker than atria (pump blood out.)
Left Ventricles is
most muscular (pumps to whole body)
Right AV (Tricuspid) goes from
RA → RV
Left AV (Bicuspid/Mitral) goes from
LA → LV
Pulmonary semilunar
RV → Pulmonary artery
Aortic semilunar
LV → Aorta
Chordae tendineae & papillary muscles
Prevent AV valves from prolapsing.
Semilunar valves (pulmonary, aortic)
look like “half-moons.”
General function of all valves
Ensure one-way blood flow.