IB Biology HL - likely long answer question responses
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
DNA replication
-DNA helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two stands of DNA
-DNA gyrase relieves the strain during uncoiling
-Semi-conservative process
-DNA polymerase III can only add nucleotides to the end of an existing chain or a primer
-DNA primase adds RNA primer
-DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides in a 5' to 3' direction
with complementary base pairing to thymine and cytosine to guanine)
-DNA polymerase III moves towards the replication fork on one strand and away from it on the other
-Continuous adding of nucleotides on the leading strand and discontinuous on the lagging strand
-DNA polymerase I replaces the RNA primers with DNA
-DNA ligase joins the Okazaki fragments together
Explain the processes by which light energy is converted into chemical energy
-Plants convert light into chemical energy (e.g. glucose) by photosynthesis
-Photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophyll absorb light
-These pigments are arranged in photosystems
-This excites the electrons
-The excited electrons then pass along the chain of electron carriers from photosystem II to photosystem I
-Energy from electrons is used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane into the thylakoid space, creating a proton gradient
-This proton gradient causes the protons to pass through ATP synthase, causing it to spin and generate ATP
-The electrons from photosystem I are then used to reduce NADP
-ATP and reduced NADP are used in the light independent reaction
Oxygen is needed to complete aerobic cell respiration.
Explain how chemical energy for use in the cell is generated by electron transport and chemiosmosis.
-NAD and FAD is reduced in the KREBS cycle by gaining two hydrogen atoms
-Reduced NAD/FAD delivers electrons to the electron transfer chain, which is in the mitochondrial inner membrane
-The electrons release energy as they flow along the electron transfer chain, until they are accepted by oxygen, which is the terminal electron acceptor
-This energy is used to pump protons into the intermembrane space, creating a concentration gradient.
-As the protons pass through ATP synthase, energy is released, causing the ATP synthase to spin and convert ADP to ATP.
-This process is called oxidative phosphorylation
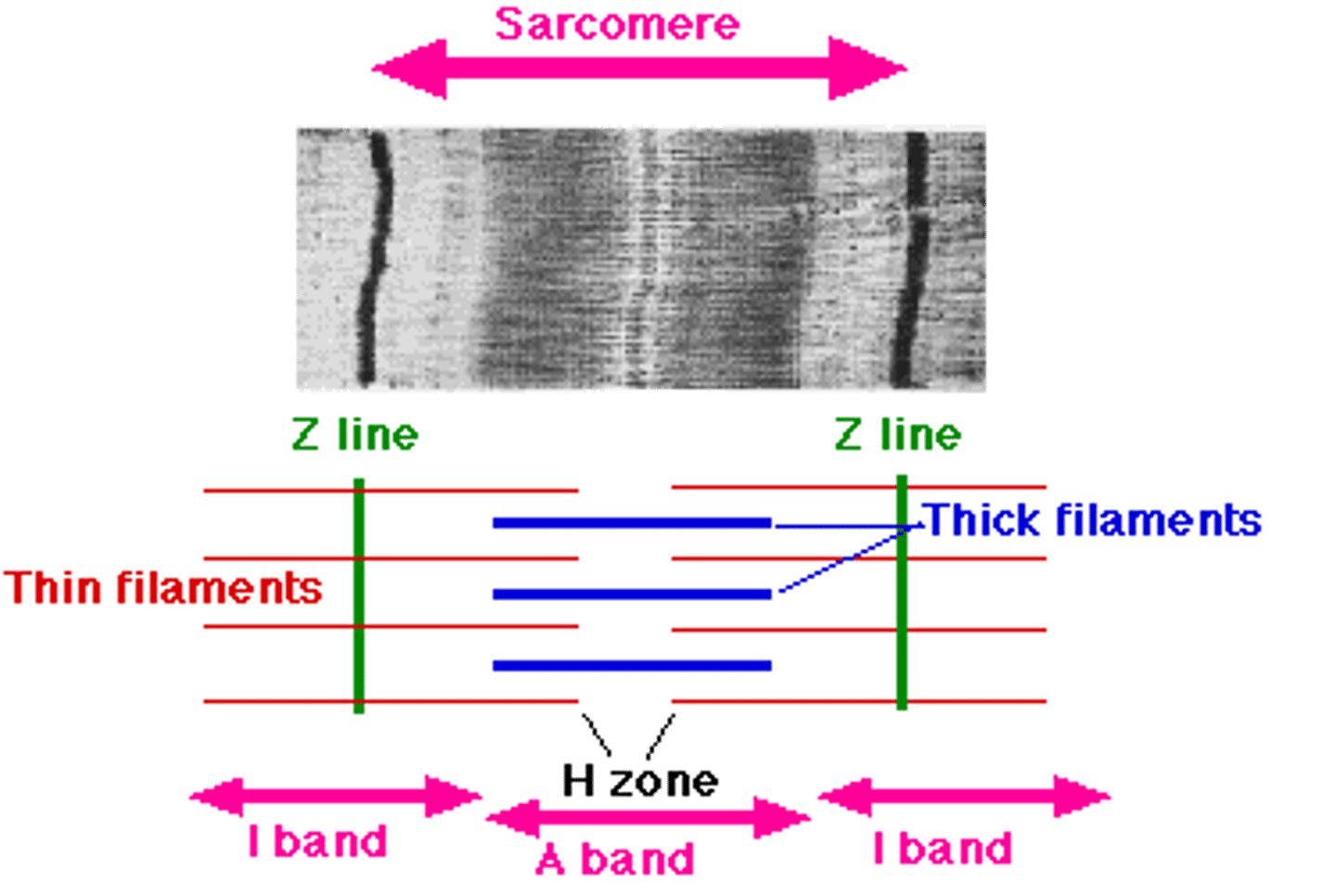
Explain muscle contraction
-There are myofibrils in muscles fibres
-Sarcomeres are the repeating units in myofibrils and they are arranged end to end, shortening during muscle contraction.
-Nerve impulses stimulate muscle contraction by triggering a release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
-These calcium ions then bind to troponin
-Troponin then causes tropomyosin to move, exposing the actin binding sites
-The myosin heads form cross-bridges with the actin filaments
-The myosin heads then change shape, pulling the actin towards the centre of the sarcomere
-ATP is used to break the cross bridges, allowing them to move back to their original positions.
-If calcium ions are still present, this cycle will continue, further contracting the muscles
-Labelled diagram of actin/myosin (+myosin heads, actin are the thin filaments, myosin are thick filaments)
Explain how the structure of the nephron and its associated blood vessels enable the kidney go carry out its functions
-Osmoregulation of urea is a function of the kidney
-Ultrafiltration (filtering out smaller molecules) happens in the glomerulus
-Basement membranes act as a filter, preventing larger molecules (such as blood cells and proteins) being lost
-The pressure in the glomerulus is high because the afferent arteriole is larger than the efferent arteriole
-Selective reabsorption of glucose in the proximal convoluted tubule
-Microvilli increase the surface area for absorption
-Water is reabsorbed in the descending limb of the Loop of Henle
-Active transport of sodium ions out of the ascending limb from filtrate to medulla
-Ascending limb is impermeable to water
-Loop of Henle creates a solute gradient in the medulla
-Distal convoluted tubule adjusts concentrations of sodium ions, potassium ions and protons
-Water is reabsorbed in the collecting duct
-Collecting duct permeability to water varies due to the number of aquaporins (ADH)
-Osmoregulation by varying the amount of water reabsorbed in the collecting duct
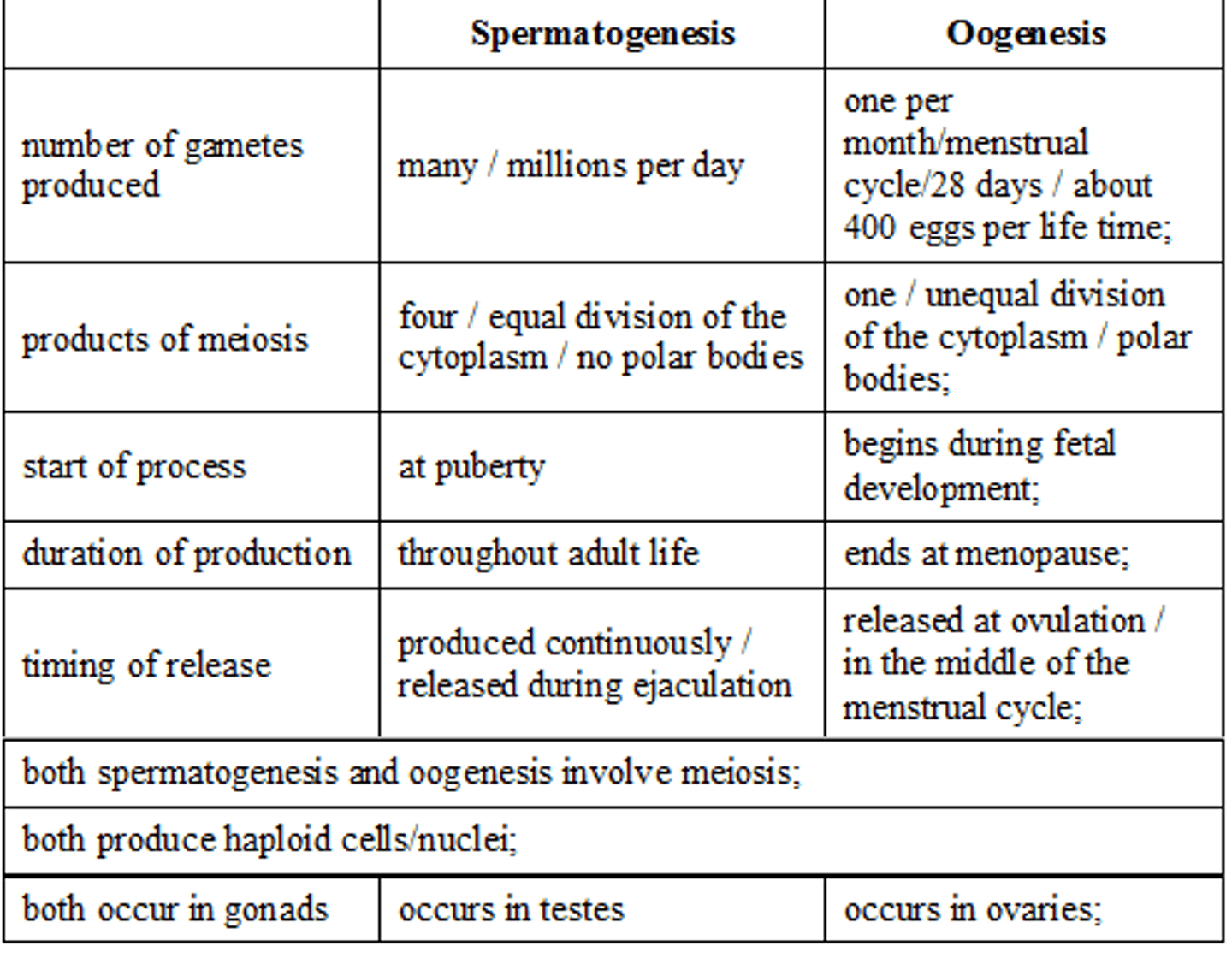
Compare and contrast Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
Similarities-
-Both result in haploid cells/gametes
-Both involve mitosis at the start
-Both have cell growth before meiosis
-Both involve meiosis
-Both involve differentiation to produce a gamete
Explain the process of water uptake and transport by plants
-Roots and root hairs absorb water by osmosis, which is a passive process
-Solute concentration inside the root is higher than in the soil due to active transport of ions and minerals into the root
-Water is transported in xylem vessels
-The flow of water is from roots to leaves
-Water movement in xylem is due to the transpiration pull, which is generated from the transpiration in leaves due to the evaporation of water from cell walls
-Cohesion and hydrogen bonds between water molecules allows water to be pulled up the xylem
-Adhesion of water to cell walls creates tension
-Lignin in xylem walls prevents collapse
In hot, dry conditions, plants lose water rapidly due to transpiration. Explain how the structures and processes of the plant allow this water to be replaced
-Water is absorbed in the roots by osmosis and travels from the roots to the leaves in xylem
-Active transport of ions into roots allows osmosis
-Evaporation of water in leaves creates a transpiration pull/tension
-Water is drawn through cell walls, out of the xylem by capillary action and adhesion to cellulose
-This creates tension in the xylem
-Hydrogen bonds make water cohesive, allowing it to be pulled up the xylem
-The xylem walls are lignified, allowing them to withstand the tension
ADAPTATIONS
-Deep, extensive root systems
-Waxy cuticle reduces transpiration
-Small/no leaves
-Few stomata/stomata in pits/rolled leaves reduce transpiration
-Hairs on leaf surface to reduce air flow near the leaf
-Stomata open at night to reduce water loss
Explain how an impulse passes along the axon of a neuron
-Resting potential is -70mV
-Sodium/.potassium pump maintains the resting potential
-When at resting potential, there are more sodium ions on the outside and more potassium ions on the inside
-Nerve impulse is an action potential that stimulates a wave of depolarization along the axon
-If the threshold potential (-50mV) is reached, sodium ion channels open
-Sodium ions diffuse in, causing depolarization
-This causes the potassium ion channels to open, causing repolarization
-The gaps in the myelin sheath cause local currents and increase the speed of the impulse
Explain the structure and role of the placenta
-Disc-shaped structure
-Embedded in uterus wall
-Connected to the foetus by the umbilical cord
-Contains both foetal and maternal tissues
-Placental villi provide a large surface area for exchange of materials
-The blood of the foetus and mother flow close together, but do not mix
-Materials diffuse through membranes between the mother and foetus
-oxygen/nutrients/antibodies/hormones diffuse through membranes to foetus
-CO2 and other waste products diffuse from foetus to mother
-Takes over the role of the corpus luteum to produce hormones
-Produces oestrogen, progesterone and HCG
Explain how evolution may happen in response to environmental change with evidence from examples
-Evolution is the cumulative change in a population over time due to the change in allele frequency
-Variation in population
-Due to mutation and sexual reproduction
-Such as some bacteria will have a mutation for resistance towards a certain antibiotic
-More offspring are produced than can survive
-Therefore there is competition for resources and survival
-Survival of the fittest/ Those with the best adaptations survive
-When that antibiotic is used, those individuals will survive, but the others will die
-Favourable alleles passed on to next generation
-Alleles for adaptations to the changed environment increase in population
-Evolution by natural selection
Explain how nerve impulses pass from one neuron to another neuron
-Impulse reaches the pre-synaptic membrane
-This causes calcium channels to open
-Calcium ions diffuses into pre-synaptic neuron
-Vesicles containing neurotransmitter fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane and release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis
-The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft
-It then binds to a specific receptor in the post-synaptic membrane
-Sodium ion channels open in post-synaptic membrane and sodium ions enter
-This causes depolarization, leading to an action potential, in the post-synaptic neuron
-The neurotransmitter is then broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft
Explain how insects excrete nitrogenous wastes
-Nitrogenous wastes excreted as uric acid by Malpighian tubules
-Nitrogenous waste accumulates in hemolymph, where it is absorbed by Malpighian tubules
-Ammonia is converted to uric acid, a process requiring ATP
-The high solute concentration in Malpighian tubules causes water to be absorbed by osmosis, egich flushes the uric acid to the gut
-The water is reabsorbed from the faeces and returned to the hemolymph
-Uric acid precipitates so it can pass out with little water and is excreted with the faeces
-Uric acid is non-toxic
Discuss the role of genes and chromosomes in determining individual and shared features of the members of a species
-Mutation causes genetic differences
-Alleles are different versions of the same gene
-Different alleles of a gene give different characteristics
-Alleles may be dominant or recessive, the dominant always showing if present
-If two different alleles are both dominant, both influence the characteristic with codominance
-All members of a species have shared genes and these and inherited from parents
-Same sequence of genes on each chromosome in a species
-Each species has the same number of chromosomes
-Some individuals have an extra chromosome, e.g. Down's syndrome (humans who have an extra copy of chromosome 21)
-X and Y chromosomes determine gender of an individual
-Sexual reproduction and meiosis give new combinations of genes
Explain the production of antibodies
-Each antibody corresponds to a specific antigen
-Antibodies are necessary for immunity
-Phagocyte engulfs pathogen and then displays the antigen from the pathogen on the outside
-Antigens from the pathogen correspond to specific T lymphocytes
-T lymphocytes activate B lymphocytes
-B cells divide by mitosis to form clones
-Plasma cells secrete specific antibody
-Some b lymphocytes will act as memory cells
Explain the roles of specific hormones in the menstrual cycle, including positive nd negative feedback
-Anterior pituitary secretes FSH which stimulates the ovary for follicle to develop
-Follicles secrete estrogen
-Estrogen stimulates more FSH receptors on follicle cells
-Increased estrogen results in positive feedback on the anterior pituitary
-Estrogen promotes development of uterine lining
-Estrogen stimulates LH secretion
-LH levels increase and cause ovulation
-LH results in negative feedback on follicle cells and estrogen production
-LH causes follicle to develop into corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone
-Progesterone thickens the uterus lning
-High progesterone results in negative feedback on pituitary, preventing FSH and LH secretion
-Falling progesterone leads to menstruation
Explain the control of gene expression in eukaryotes
-mRNA conveys genetic information from DNA to ribosomes where it guides polypeptide production
-Gene expression requires the production of specific mRNA through transcription
-Most genes are not being transcribed at any one time
-Some genes are only expressed in certain cells/tissues
-Proteins can increase/decrease transcription by preventing or enhancing the binding of RNA polymerase
-Hormones/chemical environment can affect gene expression
-Nucleosomes limit access of transcription factor to DNA
-DNA methylation appears to control gene expression
-Some DNA methylation patterns are inherited
-Gene expression can be regulated by post-transcriptional splicing
Explain how circulation of the blood to the lungs and to other systems is separated in humans and what the advantages of this separation are
-Called double circulation
-The heart has separate pumps to send deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood to other systems
-Each side of the heart has an atrium and ventricle
-The left ventricle pumps blood to the tissues via the aorta and the right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery
-The left atrium receives blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein and the right atrium receives blood from the tissues via the vena cava
-Important because high blood pressure is required to pump blood around the body, but this high blood pressure would damage lungs
-Therefore, the pressure of blood returning from the lungs is not high enough to continue to the tissues, so has to be pumped again
-This double pump system also keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separate, so that all tissues receive blood with a high oxygen content
Describe the process of endocytosis
-The fluidity of the membrane allows endocytosis
-Plasma membrane engulfs molecules
-Plasma membrane forms a pit, which is filled before the edges fuse together, forming a vesicle
-The inside of the plasma membrane becomes the outside of the vesicle membrane
-Vesicle breaks away from the plasma membrane and moves into the cytoplasm
-This is an active process
Explain the process of transcription in prokaryotes
-Transcription is the synthesis of RNA which is identical to one coding strand of DNA
-Antisense strand acts as a template
-RNA polymerase attaches to a sequence of DNA known as the promotor region
-RNA polymerase separates the two strands of DNA
-Which exposes DNA bases for pairing with RNA nucleotides
-RNA nucleotides matched with complementary bases: Adenine with uracil and cytosine with guanine
-Nucleotides are added in the 5' to 3' direction
-There are hydrogen bonds between RNA nucleotides and the complementary base of the DNA strand
-The hydrolysis of phosphate molecules provides energy for this reaction
-Terminator is a sequence of DNA signaling the end of transcription
-Which causes the RNA molecule to completely separate from the DNA
Explain how meiosis results in an effectively infinite genetic variety of gametes
-One homologous chromosome is from the mother and one from the father
-In prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair and crossing over occurs (in which alleles are swapped between the two chromosomes)
-There are many possible points of crossing over, and it occurs at random positions
-This means that the chromatids of metaphase I are not identical
-There is a random orientation of bivalents in metaphase I
-In anaphase, the chromosomes move to opposite poles, leading to an independent assortment of chromosomes
-This produces four genetically different gametes from each meiosis
-There are 2^23 combinations, without considering the variations created from crossing over
Explain the mechanism of ventilation of human lungs
-Ventilation is the movement of air into and out the lungs
During inhalation:
-External intercostal muscles contract as internal intercostal muscles relax, causing the ribcage to move up and out
-The diaphragm contracts, moving down and becoming flatter
-This causes the volume and pressure in the lung to increase
-Air flows into the lungs until the pressure are equal
During exhalation:
-Internal intercostal muscles and abdomen wall muscles contract
-External intercostal muscles relax, so ribcage is moved down/in
-Diaphragm relaxes
-Recoil of elastic fibres that stretched during inhalation
-This decreases the volume and pressure in the lungs, expelling the air
Explain the causes of sickle-cell anemia
-Sickle cell anemia is caused by a gene mutation (specifically a single base substitution)
-which changes the code of DNA (The DNA changes from CTC to CAC),
-leading to a change in the mRNA chain formed
-which in turn, leads to a change in transaltion
-and the tRNA adds the wrong amino acid to the polypeptide chain )valine instead of glutamin acid)
-which produces abnormal haemoglobin, causing the red blood cell to be sickle-shaped
-This lowers its ability to transport oxygen
Explain how males inherit haemophilia and how females can become carriers for the condition
-Haemophilia is due to a recessive allele on the X chromosome, meaning that it is a sex-linked condition
-Y chromosomes do not have the allele
-Females are XX and males are XY
-Males only have one copy of the allele, so the recessive allele will not be masked
-If their mother is a carrier, males have 50% chance of receiving the allele from their mother
-Haemophiliac males can have carrier daughters, but cannot pass it on to their sons
Explain the control of blood glucose concentrations in human
-Pancreatic cells monitor the blood glucose concentrations by negative feedback mechanisms
-Alpha and beta cells are in the islets of Langerhans and they send hormones through the bloodstream to target organs
-If the blood glucose conc is too high, Beta cell in the pancreas secret insulin in the bloodstream to the liver, where it causes the liver to convert glucose into glycogen
-which lowers the blood glucose level
-If the blood glucose conc is too low, alpha cells secret glucagon which stimulates liver cells to break down glycogen into glucose
-and release glucose into the bloodstream
-raising the blood glucose level
Describe the stages in the cell cycle that result in a rapid increase in the number of cells
-The cell cycle can be split into two sections: interphase and mitosis
-Interphase starts with a growth phase, in which proteins and organelles are replicated
-Then there is a synthesis phase, where DNA is replicated
-This is followed by another growth phase, which is the continuation of cytoplasm growth and duplication of organelles
-Then mitosis starts with prophase, where chromosomes supercoil, the nuclear envelope disappears and spindle fibres form
-Metaphase is the next section of mitosis, which is where the chromosomes line up at equatorial and spindle fibres attach to the centrosomes
-This is followed by anaphase, where the spindle fibres move the chromatids towards opposite poles of the cell
-In telophase, new nuclear membranes form around each cluster of chromosomes
-Finally, cytokinesis occurs, in which a new plasma membrane forms between the nuclei (and a cell wall in plant cells)
-resulting in two genetically identical cells
Giving one specific example, discuss genetic modification in organisms including the potential benefits and possible harmful effects
-Genetically modified organisms are organisms where characteristics are changed by the addition or removal of a gene
-This is possible due to universal genetic code, which allows genes to be transferred between species
-Gene transfer involves splicing genes into a host DNA
-After being placed into the host, the host cells are cloned
-E.g. rice modified with daffodil genes to have more beta-carotene, which the body converts to vitamin A
Potential benefits:
-Increases intake of vitamin A where meat is less readily available
--deficiency in vit A can cause blindness
Possible harmful effects:
-The long-term effects are unknown
-Farmers rely on rich countries to produce and sell seeds
Explain the use of karyotyping in human genetics
-Karyotyping gives an image of the number and type of chromosomes in a cell
-Data is collected by amniocentesis
-Requires cells in metaphase, where it bursts cells and spreads chromosomes
-Chromosomes are arranged in pairs, according to size
-Can be used to identify gender
-Male is XY, female is XX
-Used to identify chromosome mutations
-e.g. non-disjunction, leading to Down's syndrome, if extra chromosome 21
-used for pre-natal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities
-may lead to decision to abort the foetus
-Allows parents to prepare for consequences of abnormality in offsping