T3 mendelian & non-mendelian inheritance
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
mendel’s laws of inheritance
law of dominance & uniformity
law of segregation
law of independent assortment
law of dominance & uniformity
if atleast 1 dominant allele is present → dominant trait will appear
law of segregation
during gamete formation, 2 alleles for each gene separate randomly → each gamete receive only 1 allele from each gene
law of independent assortment
genes for different traits are passed on independently of one another
human karyotype
46 chromosomes → 23 pairs
SRY gene
sex-determining region on Y → controls male sex development
pseudoautosomal regions (PAR) - location
tips of both X and Y chromosomes
pseudoautosomal regions (PAR) - function
allows pairing & exchange of genetic material (crossing over) during meiosis
sex-limited traits
expressed in only 1 gender BUT genes are presented in both gender
sex-limited traits - controlled by…
autosomal genes
sex-limited traits - expression depends on…
sex hormones
sex-influenced traits
appear in both genders BUT expression differs → dominant in one sex, recessive in another
typical mendelian inheritance
autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, x-linked dominant, x-linked recessive, Y-linked
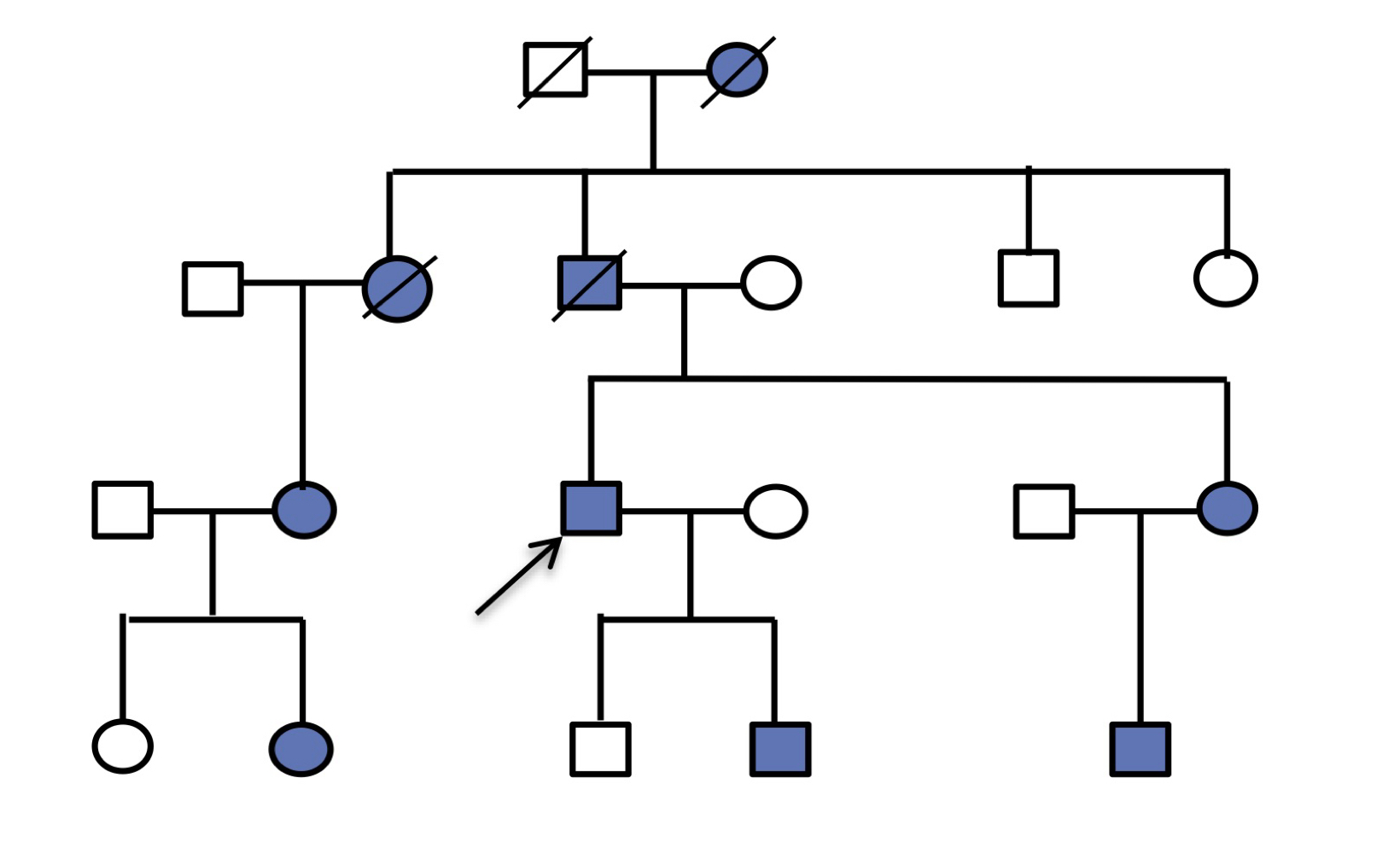
autosomal dominant - pattern
appears in every generation, both sexes affected equally, male-to-male transmission can occur
autosomal dominant - diseases
polydactyly & familial hypercholesterolemia
polydactyly
extra fingers / toes
familial hypercholesterolemia - heterozygotes
very high LDL, tendon xanthomas, premature coronary artery disease
familial hypercholesterolemia - homozygotes
no normal LDL receptors, severe hypercholesterolemia, early coronary disease
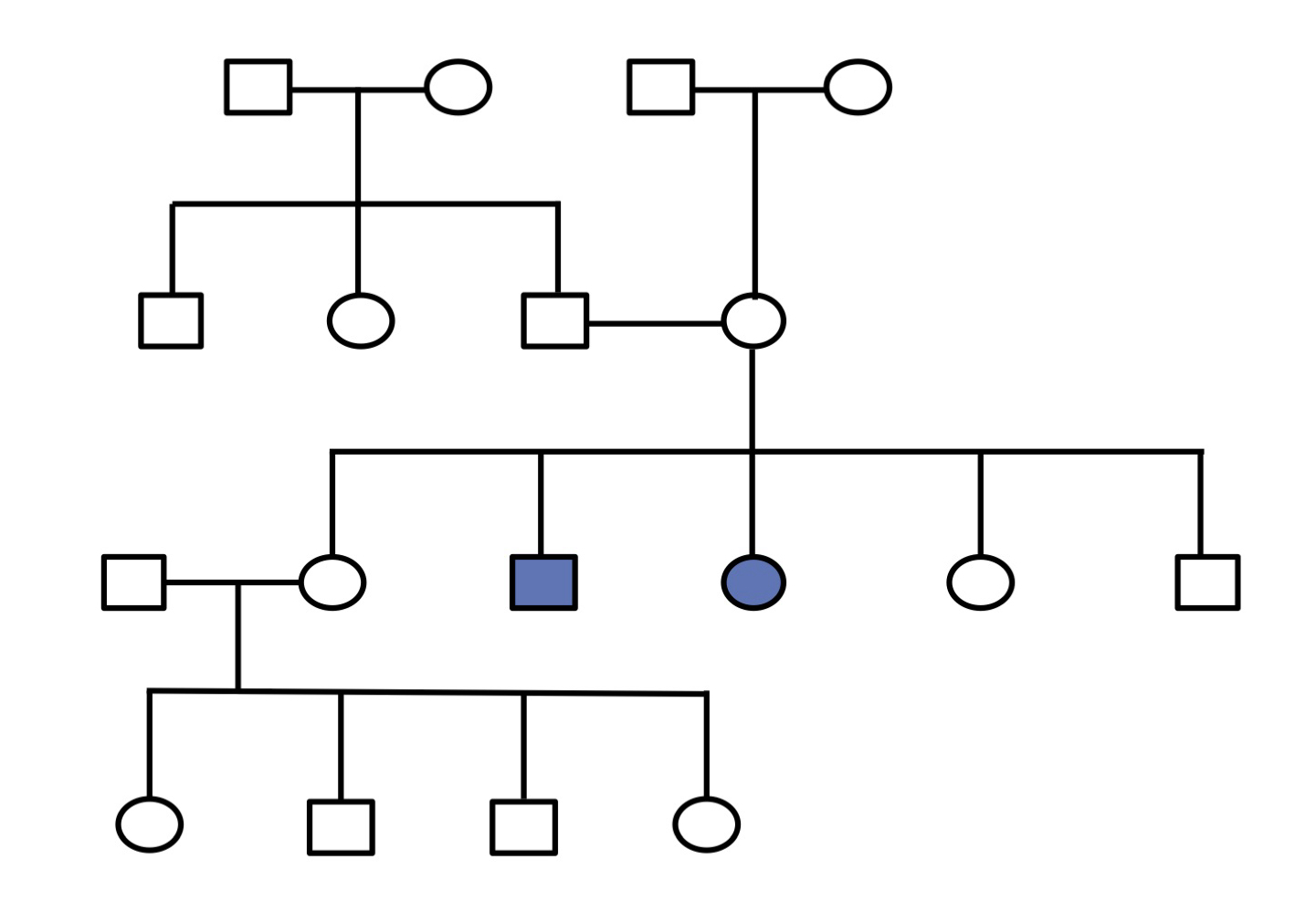
autosomal recessive - pattern
often skip generations, both sexes affected equally
autosomal recessive - diseases
hypotrichosis & sickle cell
hypotrichosis
lack of hair growth
sickle cell disease
point mutation in beta-globin gene → glutamine becomes valine at position 6
HbS/HbS
sickle cell anemia disease
HbA/HbS
sickle cell trait → heterozygous condition
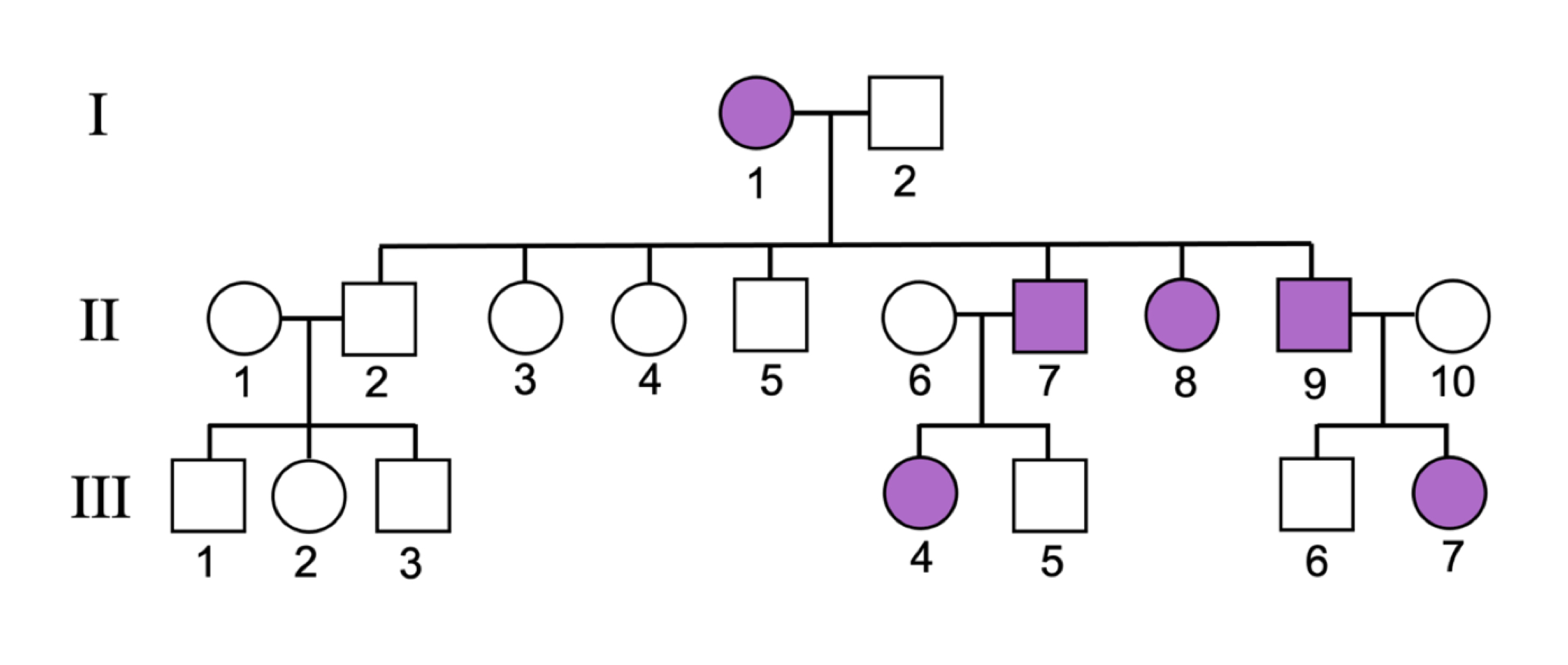
x-linked dominant - pattern
does not skip generations, affected males must have affected mother, affected father must have all daughters affected
x-linked dominant - diseases
vitamin D-resistant rickets
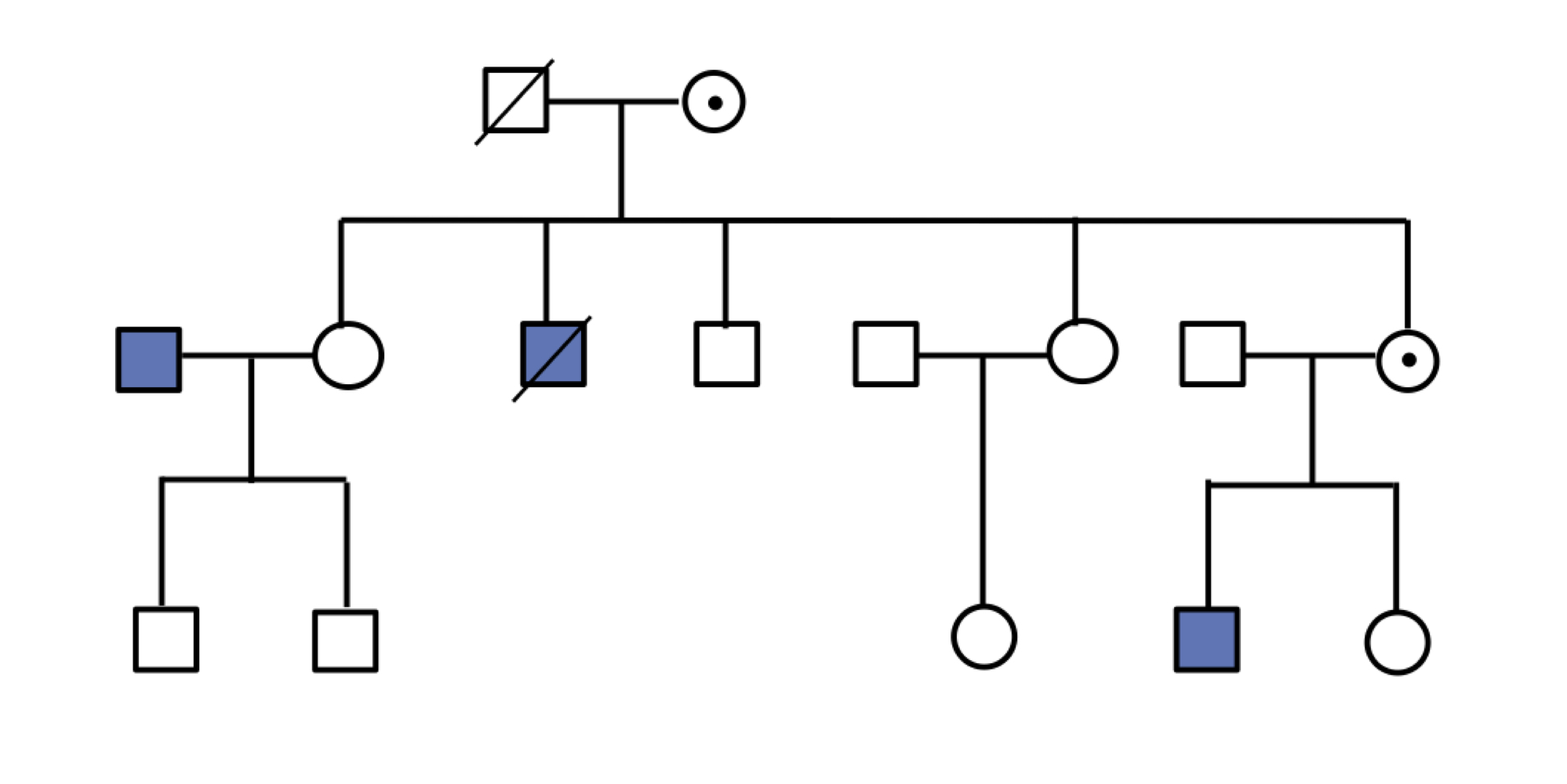
x-linked recessive - pattern
mostly males affected (requires only 1 X), skip generations via female carriers, no male-to-male transmission
x-linked recessive - diseases
hemophilia in queen victoria family & duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
severe muscle weakness in early childhood
Y-linked (holandric) - pattern
trait appears only in males, affected father have all sons affected, father-to-son
Y-linked (holandric) - diseases
hairy ear rims & retinitis pigmentosa
retinitis pigmentosa
night blindness → progress to complete blindness
XY females with gonadal dysgenesis
SRY mutation → Y chromosomes fail to initiate testis development → remain as streak gonads (non functional connective tissues)
atypical mendelian inheritance
genetic anticipation, pseudoautosomal inheritance, pseudodominant inheritance, mosaicism, digenic inheritance, uniparental disomy, imprinting disorders
genetic anticipation
signs and symptoms appear at an earlier age → become mores severe in each successive generation
genetic anticipation - cause by…
mutation of trinucleotide repeat expansion (TNRE) → short DNA sequence repeat many times
genetic anticipation - as generation increase
number of repeats increases → earlier onset → more severe symptoms
genetic anticipation - examples
huntington disease & fragile X syndrome
huntington disease - repeat sequnce
CAG
hungtington disease - symptoms
progressive chorea and dementia due to HTT gene affected
fragile X syndrome - repeat sequence
CGG
fragile X syndrome - symptoms
learning disability, cognitive impairment due to mutation in FMR1 gene
pseudoautosomal inheritance
homologous regions on X and Y chromosomes undergoes recombination during meiosis → makes inheritance pattern looks autosomal (even though genes are on sex chromosomes)
pseudoautosomal inheritance - examples
leri-weill syndrome
leri-weill syndrome - cause
mutation or deletion of SHOX gene located on PAR1 region of X and Y chromosomes
leri-weill syndrome - symptoms
short forearms & short stature → recombination frequency higher in men than women
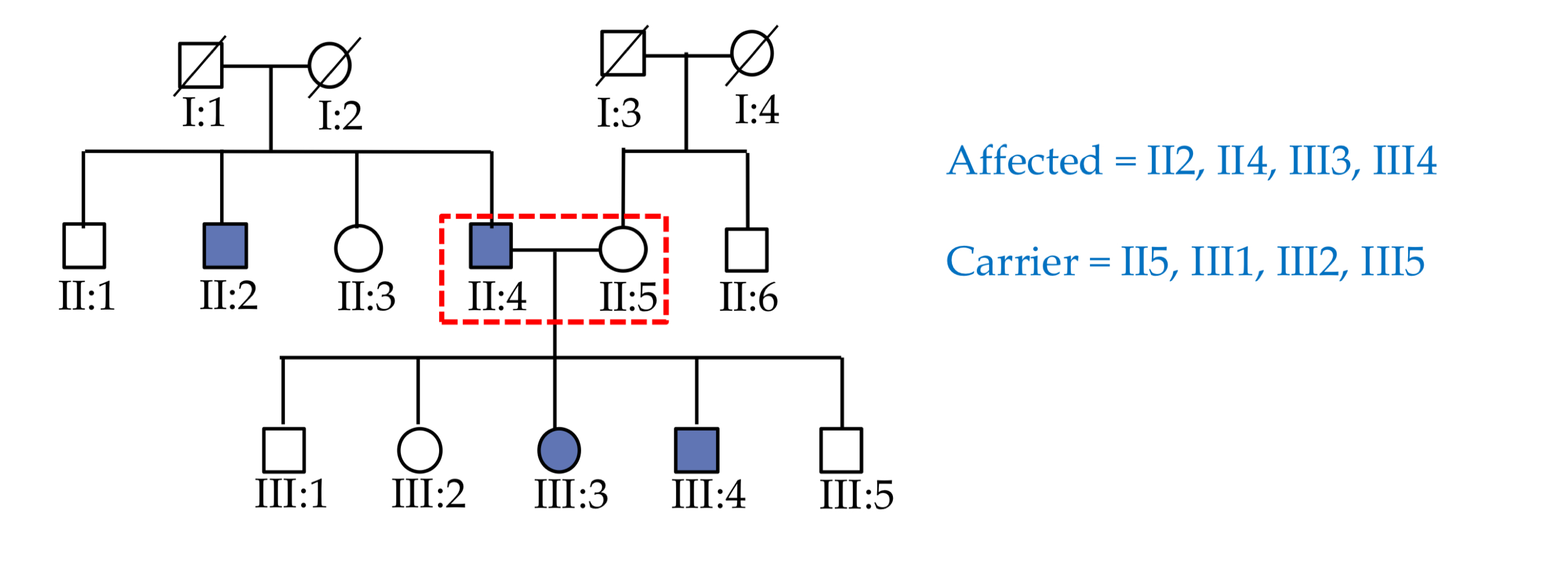
pseudodominant inheritance
recessive condition appears to follow a dominant pattern → homozygous recessive (affected) mates with heterozygous (carrier)
pseudodominant inheritance - example
gilbert syndrome
gilbert syndrome - cause
missense mutation or promoter change in UGT1A1 gene (encodes bilirubin-UGT enzyme)
gilbert syndrome - symptoms
mild hyperbilirubinemia (elevated unconjugated bilirubin)
mosaicism
genetic abnormality arise during mitosis (after fertilization) → results in 2 or more genetically different cell lines within one person
mosaicism - types
somatic & germline
somatic mosaicism
mutation occurs in body (somatcic) cells → no transmission to offspring unless germ cells are affected
somatic mosaicism - examples
neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), patchy skin color, cafe-au-lait spots, eye color difference
germline mosaicism
mutation occurs in germ cells → parent appears normal but can pass mutations to offspring
mixed mosaicism
mutation affects both somatic and germline cells → parent can show mild symptoms and pass on condition to offspring
germline mosaicism - examples
tuberous sclerosis
uniparental disomy
both copies of a chromosome come from 1 parent instead of one from each
uniparental disomy - types
heterodisomy & isodisomy
heterodisomy
2 different homologous chromosomes from 1 parent → error in meiosis I
isodisomy
2 identical copies of the same chromosome from1 parent → error in meiosis II
uniparental disomy - mechanism
trisomy rescue: zygote has 3 copies of a chromosome → one chromosome is lost → both remaining copies are from 1 parent = UPD
uniparental disomy - consequences
usually no effect but can cause disorders when imprinted genes are involved
uniparental disomy - example
autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness
autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness - symptoms
alter connexin proteins → change structure of gap junction channel → affect function or survival of cells that are needed for hearing
autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness - causes
mutation in GJB2 gene → connexin 26 protein & GJB6 gene → connexin 30 protein, both on chromosome 13
imprinting disorders
only one allele (mom or dad) is expressed while the other is silenced (imprinted)
imprinting disorders - examples
prader-willi syndrome & angelman syndrome
prader-willi syndrome
loss of paternal contribution
angelman syndrome
loss of maternal contribution
non-mendelian inheritance
multifactorial traits & mitochondrial inheritance
multifactorial traits
many genes + environment act together to determine a trait or disease
multifactorial disorders - characteristics
occurs in isolation, risk in relatives, proband only affected member, environmental influence, gender difference, pedigree analysis cannot confirm, ethnic variation
purely genetic - concordance of MZ twins
100%
multifactorial - concordance of MZ twins
high but less than 100%
multifactorail traits - family correlation
closer relatives show stronger resemblance (genetic effect)
multifactorial disorders - example
coronary artery disease
coronary artery disease - pattern
runs in families (not mendelian), more common in men, high risk in african americans
continuous multifactorial traits - characteristics
continuosly graded distribution, no clear boundaries between normal & abnormal, controlled by many genes + environment
discontinuous multifactorial traits - characteristics
either present or absent, depend on underlying continuous liability → disease appear only when liability crosses threshold
liability
total of genetic risk + environmental factors
discontinuous multifactorial trait - example
cleft lip & palate
cleft lip & palate - mechanism
parents can be unaffected (below threshold), each parent carries some underactive genes for lip/palate formation → together exceed threshold in child
discontinuous multifacotrial - further above threshold…
more severe the defect
general population - liability curve
further to the left (lower liability)
first degree relatives - liability curve
further to the right (higher liability)
mitochondrial inheritance
contain mtDNA separated from nuclear DNA → transmission of genetic material from mother
mitochondrial chromosomes - characteristics
self-replicating, codon usage is different, no introns, both DNA strands are transcribes & translated
mitochondrial inheritance - mother affected
all children affected
mitochondrial inheritance - father affected
no children affected
mitochondrial disorders - example
leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) - symptoms
bilateral central vision loss
leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) - cause
point mutations in mtDNA → mitochondrial dysfunction → death of optic nerve cells
progressive external ophthalmoplegia - cause
mtDNA deletions → mutations of nuclear gene that encodes polymerase gamma → mtDNA replication (autosomal dominant)
progressive external ophthalmoplegia - symptoms
weakness of external eye muscle
autosomal dominant
autosomal recessive
x linked dominant
x linked recessive
pseudodominant inheritance