COM1009 Algorithms and Data Structures
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Insertion Sort Algorithm
Runtime:
Best case: Sorted ascending => n-1
Worst case: Sorted descending =>
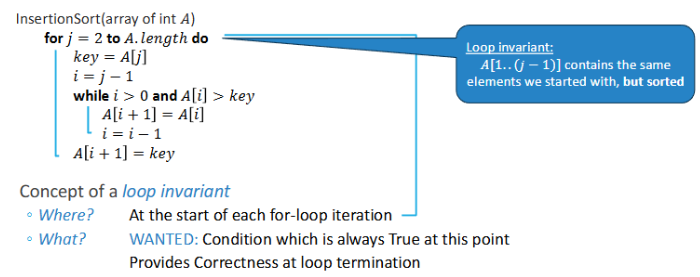
Merge Sort
A divide and conquer algorithm that sorts an array by recursively dividing it into halves, sorting each half, and then merging the sorted halves back together.
Priority Queue Naïve Implementation
Each element x of a set M, has priority x.key. Array position containing the highest priority is at A[iM] which is checked each time an element is inserted into an array with a priority (Insert(priority p)), FindMax() returns A[iM]. ExtractMax() removes the element with highest priority and sets the new maximum as needed.
![<p>Each element x of a set M, has priority x.key. Array position containing the highest priority is at A[iM] which is checked each time an element is inserted into an array with a priority (Insert(priority p)), FindMax() returns A[iM]. ExtractMax() removes the element with highest priority and sets the new maximum as needed.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b28b6141-a52e-4bcb-b679-a22b2295730d.png)
Heap
A heap is an array corresponding to a binary tree, for which all levels are full except the last and is filled left to right.
A heap ‘A’
Has the max-heap property,, if…
For every node i > 1
A[parent(i)] >= A[i]
Called a max-heap
Has the min-heap property if…
For every node i > 1
A[parent(i)] <= A[i]
Called a min-heap
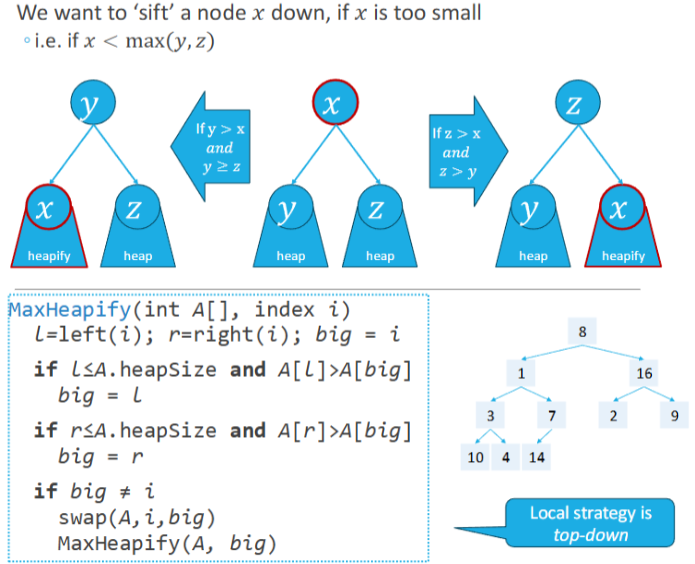
MaxHeapify
Is a procedure to maintain the max-heap property in a binary heap. It ensures that the subtree rooted at a given node follows the property by comparing the node with its children and swapping if necessary.
Trees are stored in arrays where the child nodes of an element are at index x2 and index x2 +1
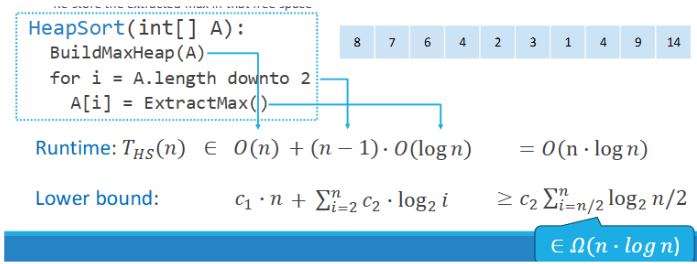
Heap Sort Algorithm
A comparison-based sorting algorithm that utilizes a binary heap data structure to sort elements. It first builds a max-heap from the input data and then repeatedly extracts the maximum element from the heap, placing it at the end of the sorted array.
Probability Modelling Trick

Quicksort
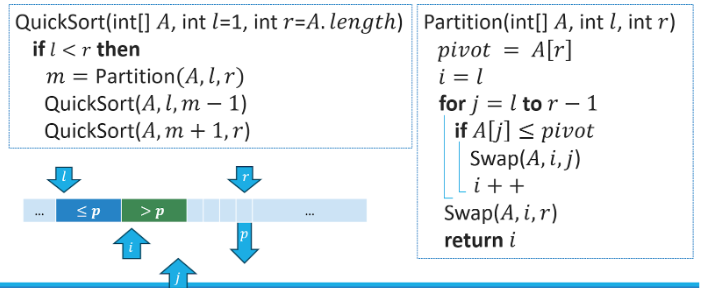
Growth Orders
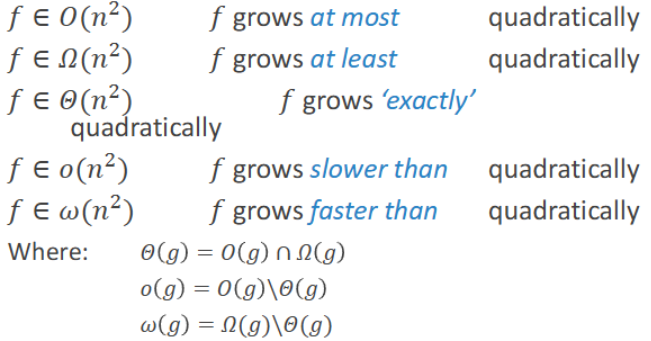
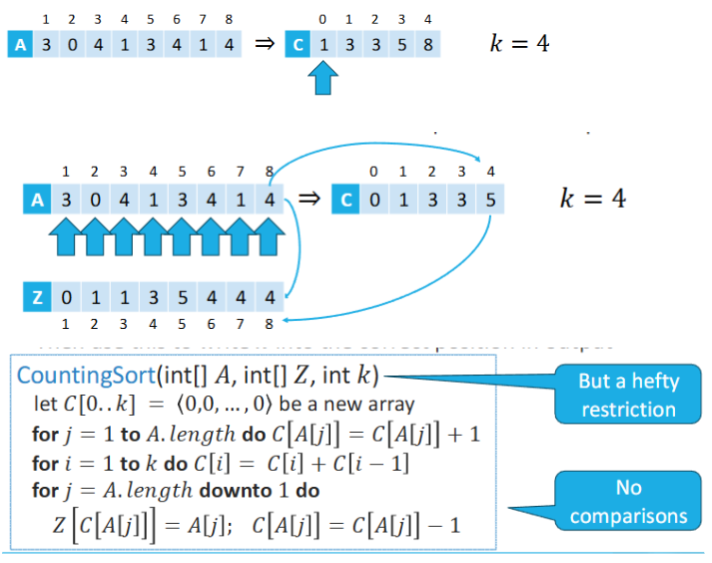
CountingSort
A linear time algorithm
For every x of the input, count numbers <= x
Use this to write x into correct position in output
A - input array
Z - output arrat
C - work array (where we count)
K - limit of the universe: {0,..,K}
Runtime for n numbers: O(n + k)
In-Order Traversal
Recursively travel left subtree of the root
Output value of the root
Recursively traverse the right subtree of the root

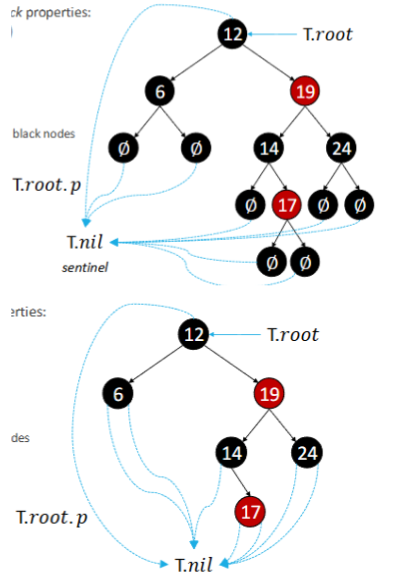
Red-Black trees
BST with the following properties:
Each node either red (bad) or black (good)
Root is black
All leaves are black and are nil
If a rode is red - its children are black
For each subtree - all root-to-leaf paths have the same number of black nodes
No red to leaf path has consecutive red nodes
The height h(v) of a node v is the number of nodes on the longest path from v to a leaf below v (excluding v)
The black-height bh(v) of node v is the number of black nodes on each path from v to a leaf below v (excluding v)
Inserting Nodes in BSTs
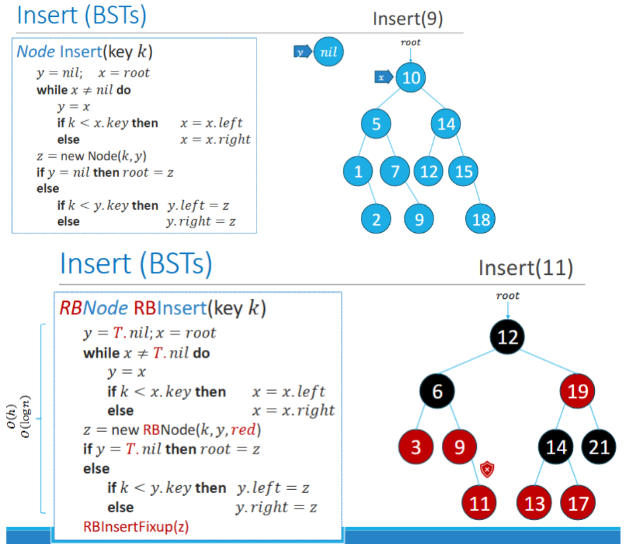
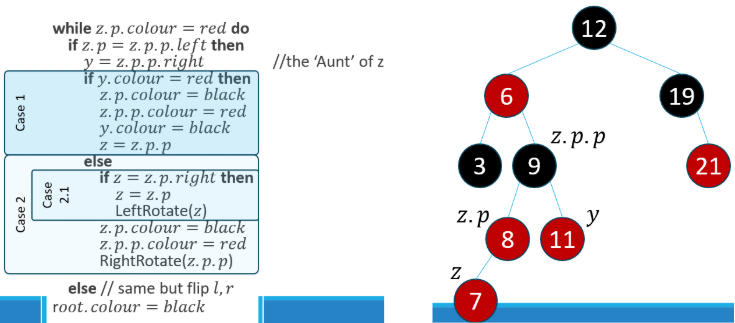
RBInsertFixup(Node z)
BSTs - Node Successor

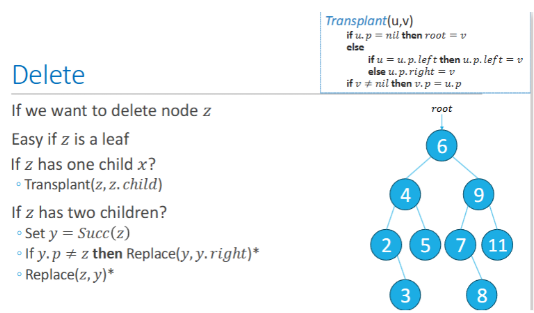
BSTs - Deleting nodes
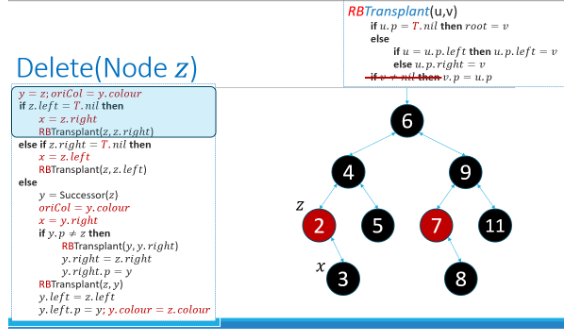
RBTs - Deleting nodes
Y - points to node that is deleted/removed
X - points to node that replaces y. Which is either the only child of y or nil
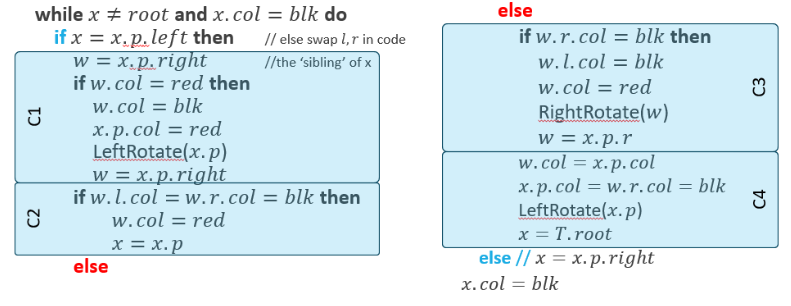
RBDeleteFixup
Improvement of delete method to avoid violations of colour rule
Greedy Algorithm - Iterative
General Greedy Strategy
Check if problem exhibits the optimal substructure property
Develop a recursive solution
Show that with a greedy choice, only one sub-instance remains
Show that the greedy choice is ‘safe’ (exchange argument)
Design a recursive greedy algorithm
Convert to an iterative algorithm

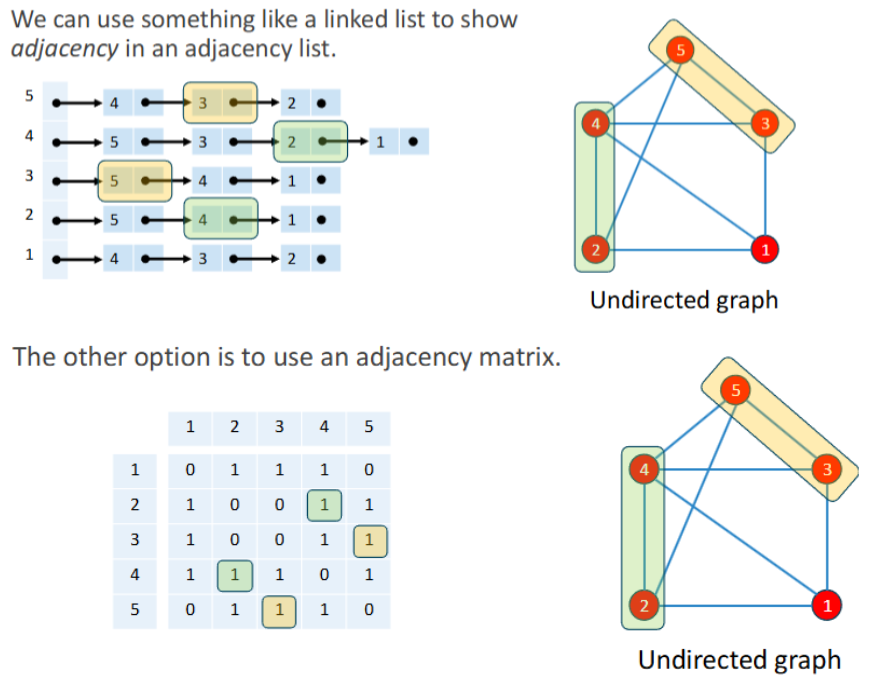
Ways of representing a graph (digitally)
Degree of a vertex
The number of connections that a vertex has
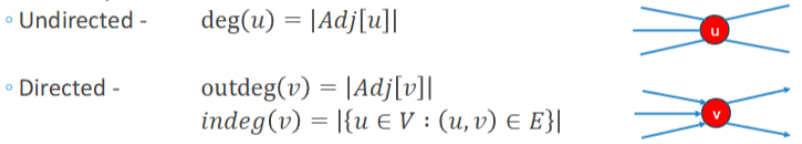
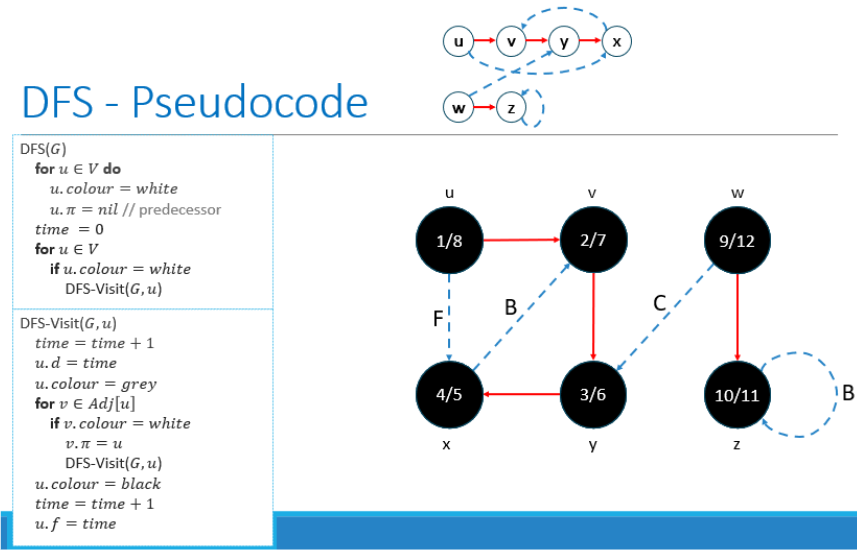
Depth First Search
Explore edges out of the most recently discovered vertex, backtracking when ‘stuck’
Continue until all vertices reachable from the start vertex have been discovered and explored
If any undiscovered vertices remain, continue using one of them as a new source
White - vertex not yet discovered
Grey - vertex discovered but not finished
Black - vertex finished (finished processing adjacent vertices
Runtime: O(|V| + |E|)
DFS Edge Classifications
Can classify edges in graph or tree
Tree edges (T) - edge of DFS forest
Back edges (B) - edge to an ancestor vertex
Forward edges - edge to a descendent vertex
Cross edges (c) - edge to a different tree (vertices not ancestor/descendent of each other
Topological sorting
A topological sorting of a directed acyclic graph is a linear ordering of vertices, such that for each edge (u,v), u appears before v
i.e. if vertices are arranged on a horizontal line all edges go left to right
Computing:
Call DFS(G) to compute start and finish times for each vertex
As a vertex is finished, insert into front of a list
When finished return list of vertices
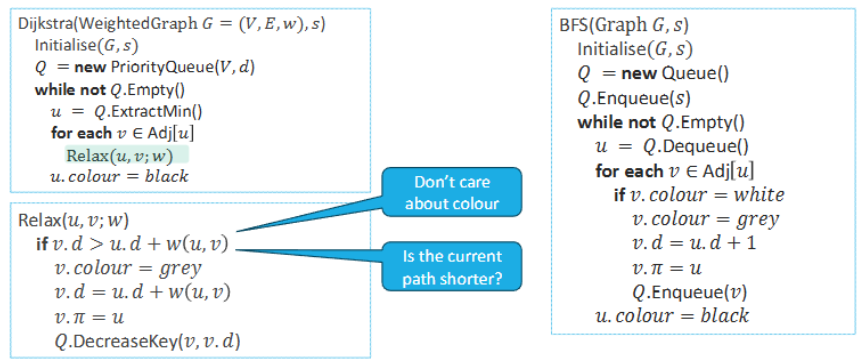
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
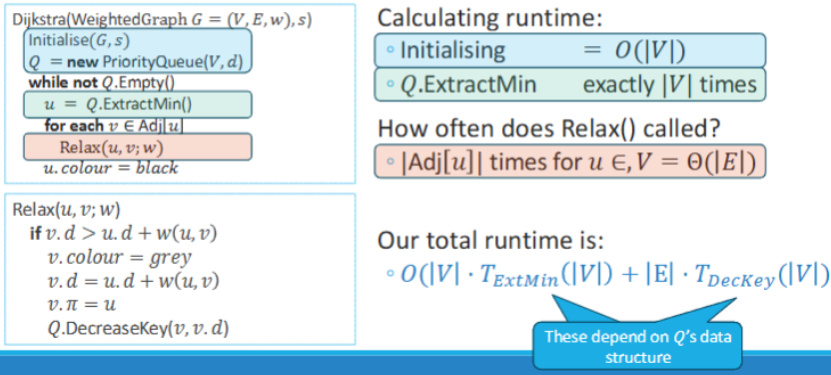
Dijkstra’s runtime
Jarník-Prim-Dijkstra (Prim’s algorithm)
Only cares about the weight of the last edge
In prim’s if a vertex is not in the queue then it is ‘black’

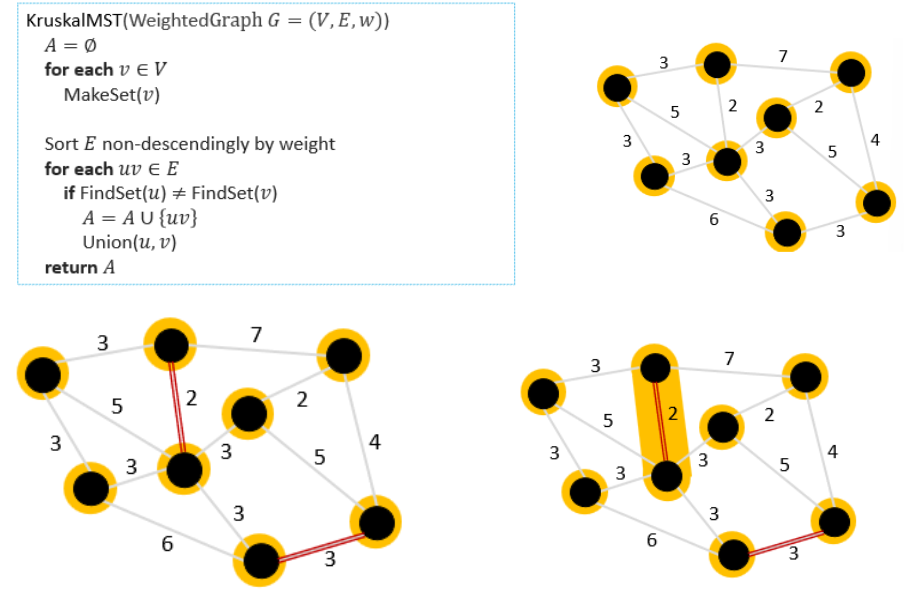
Kruskal’s MST Algorithm
Runtime: O(|E| x log|V|)
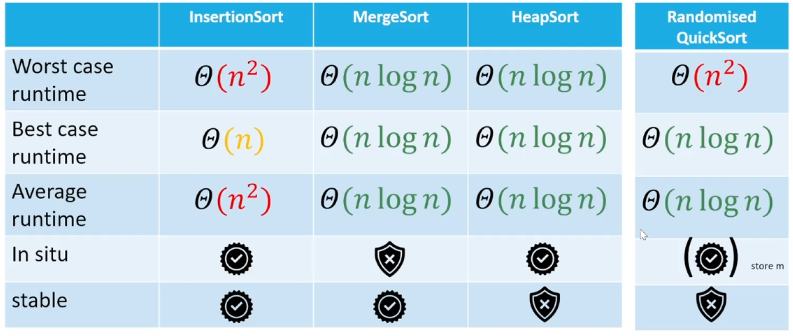
Sort Algorithms Summary
Loop Invariant
A condition or statement that remains true before and after each iteration of a loop