Lab 6-Bones of the lower limb and Joints
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Articular Surface with Sacrum
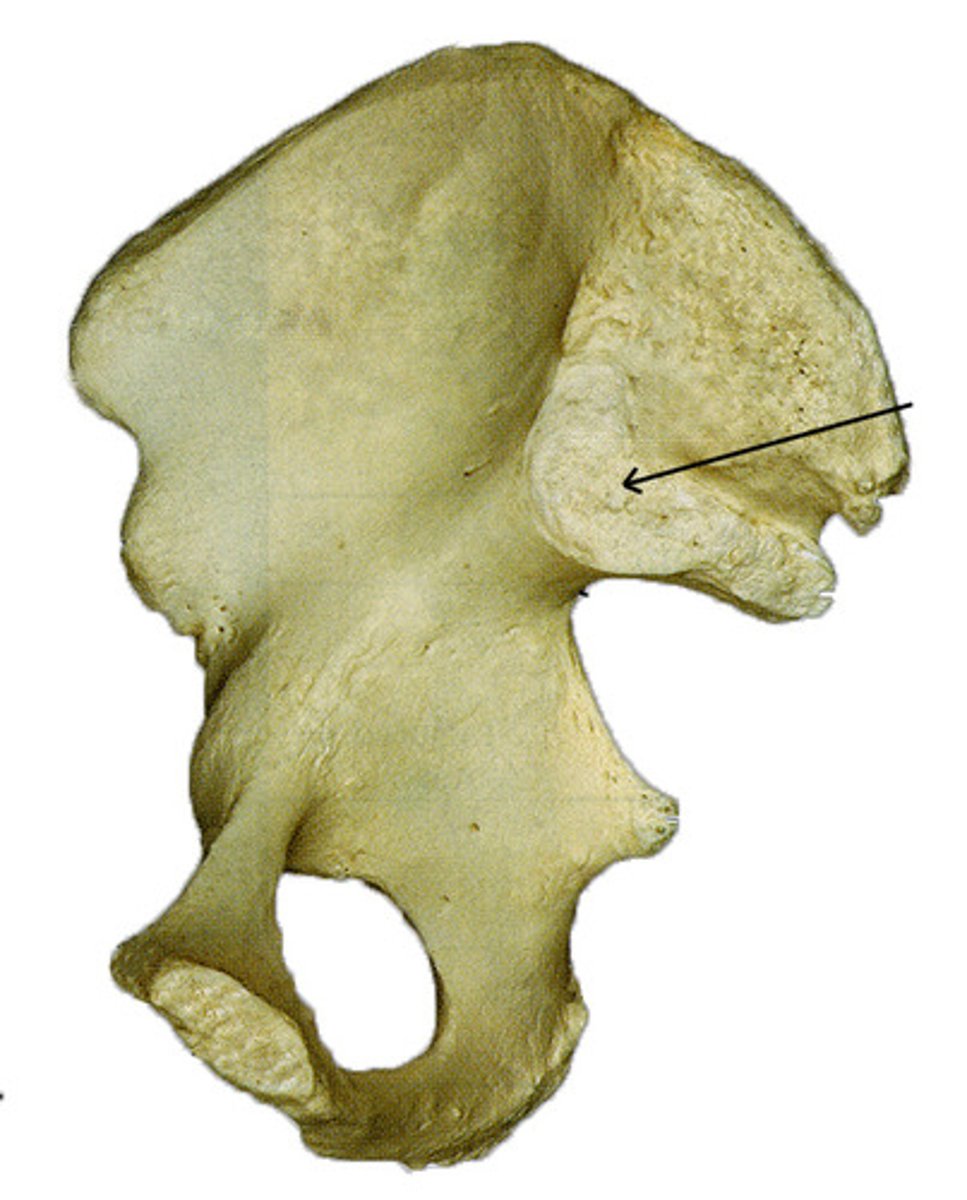
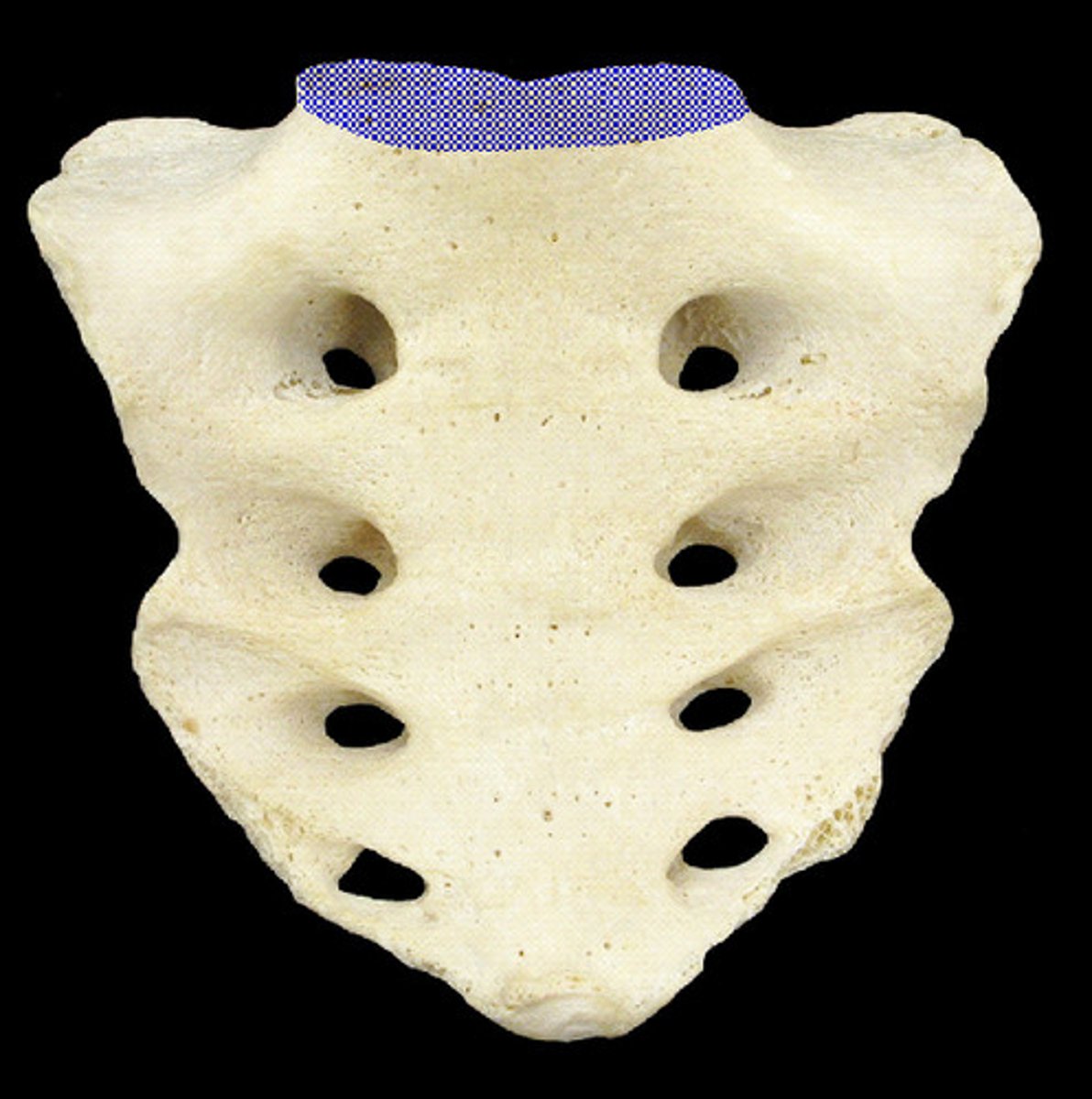
Base of sacrum
ilium
Pubis
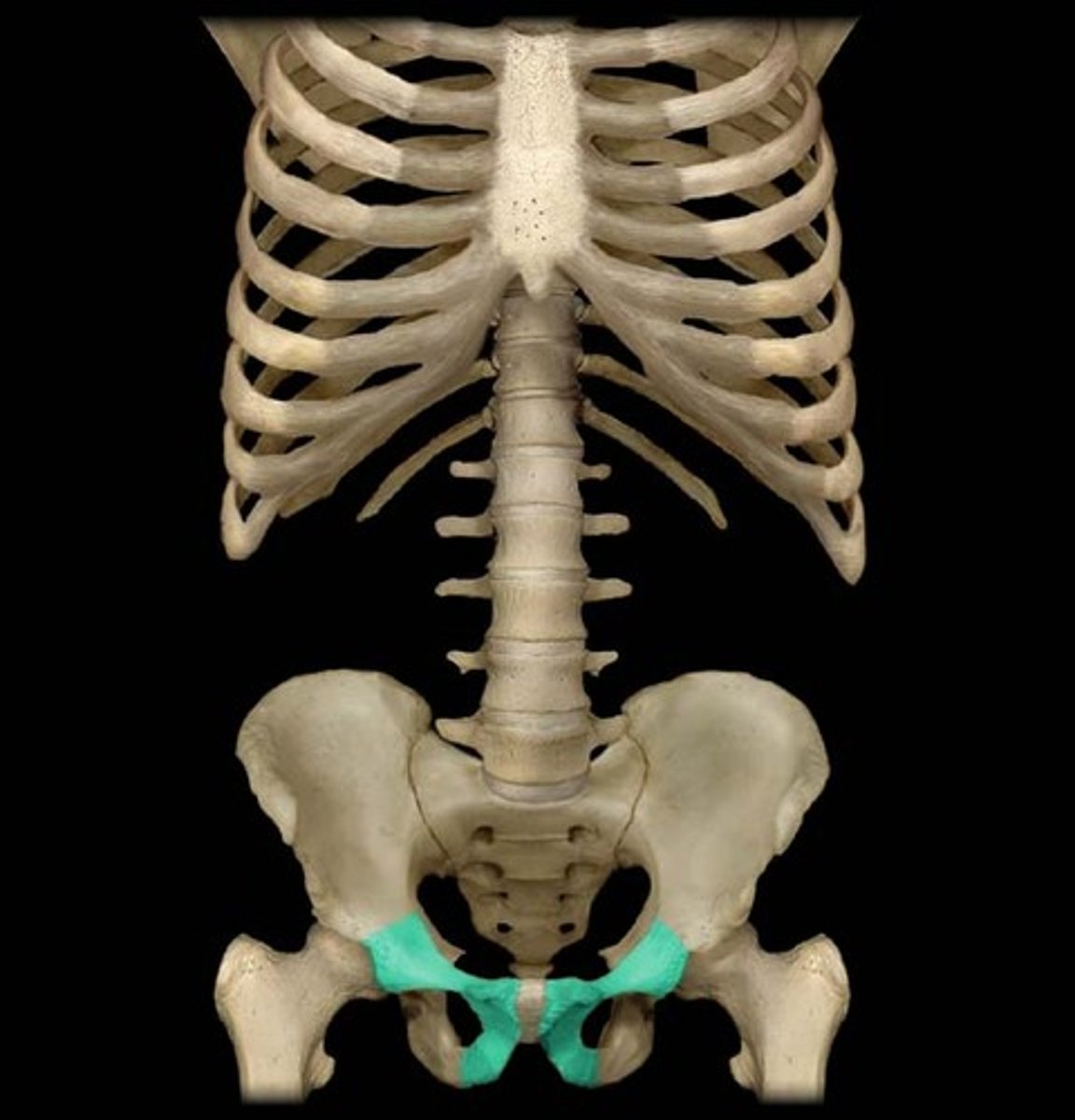
Ischium
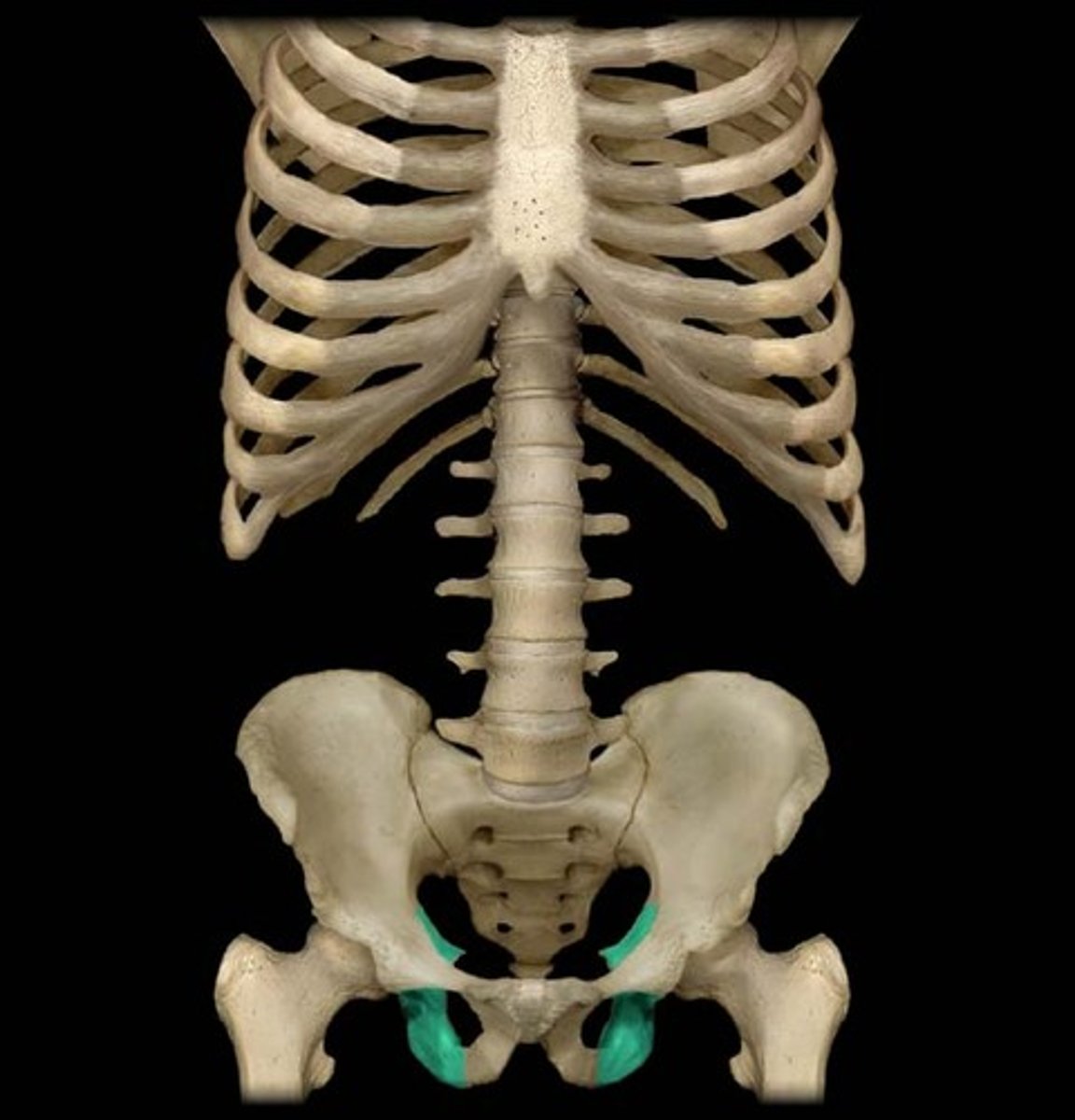
Pevic Inlet
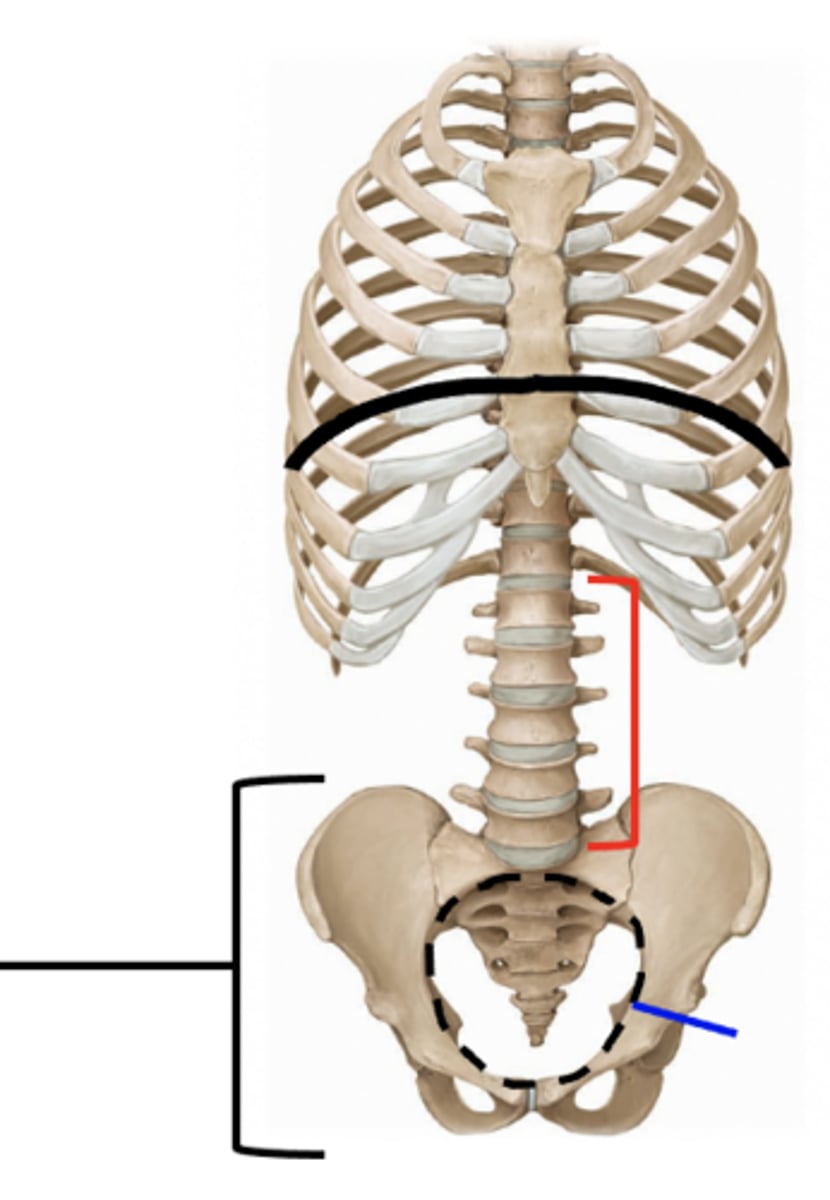
pubic symphysis
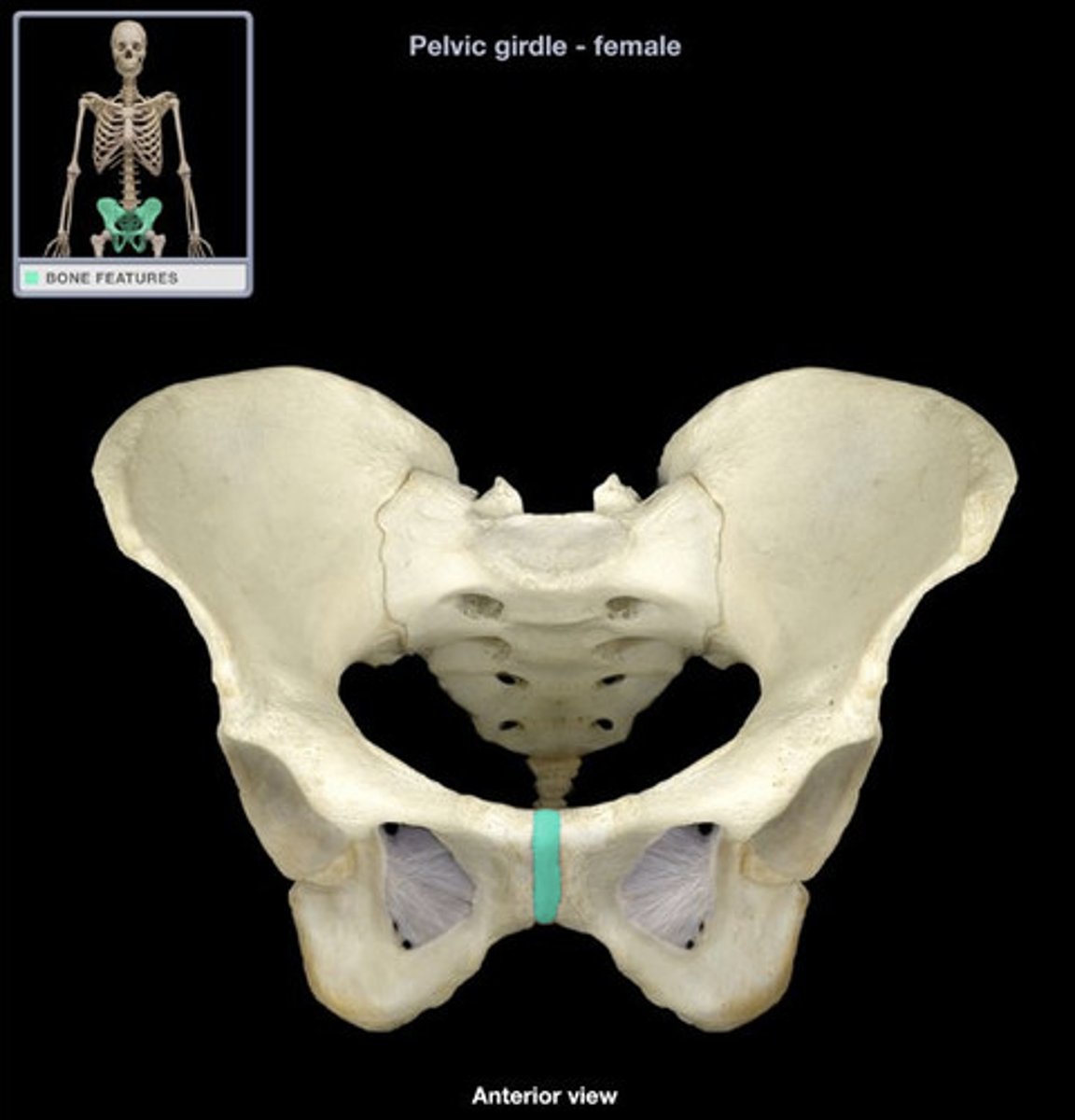
posterior superior iliac spine
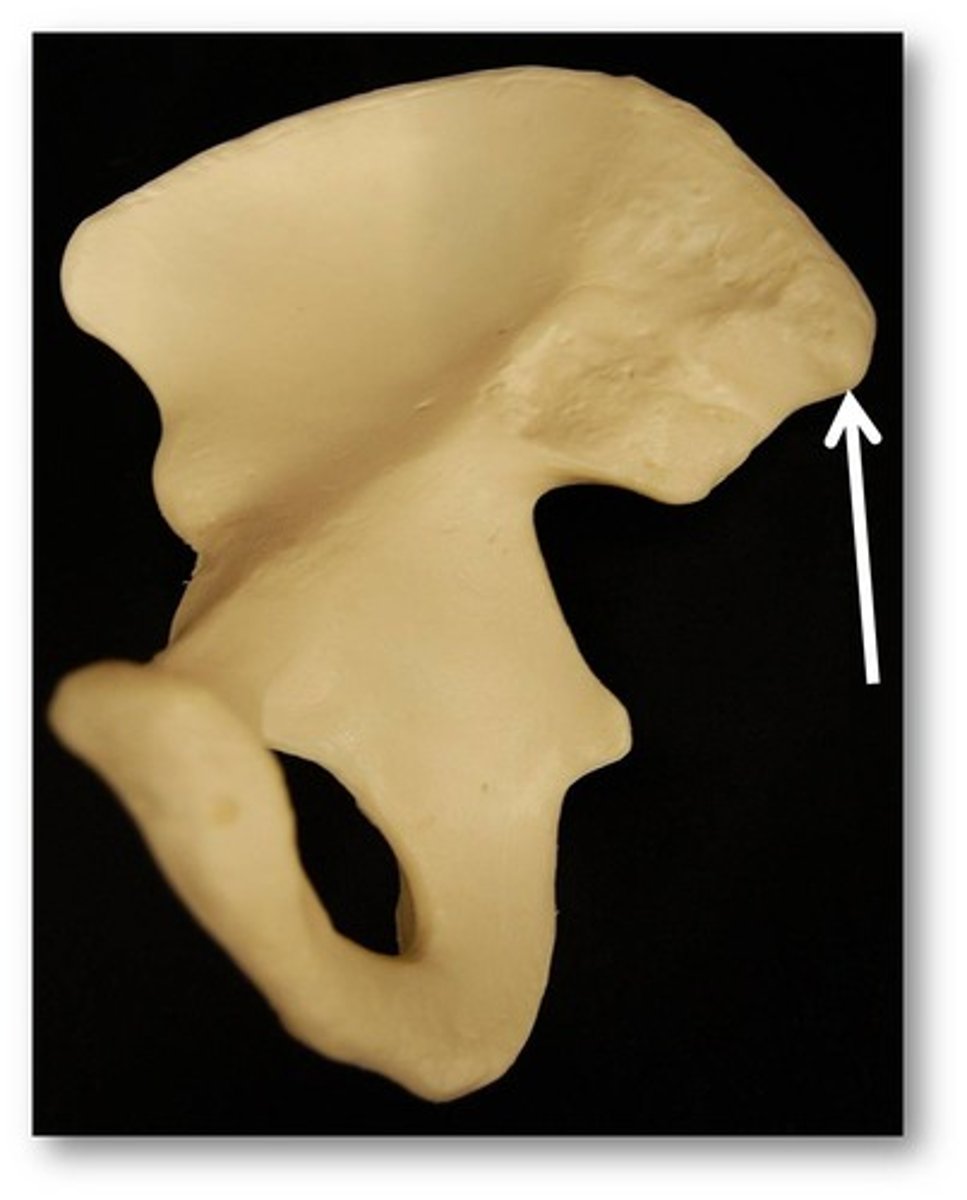
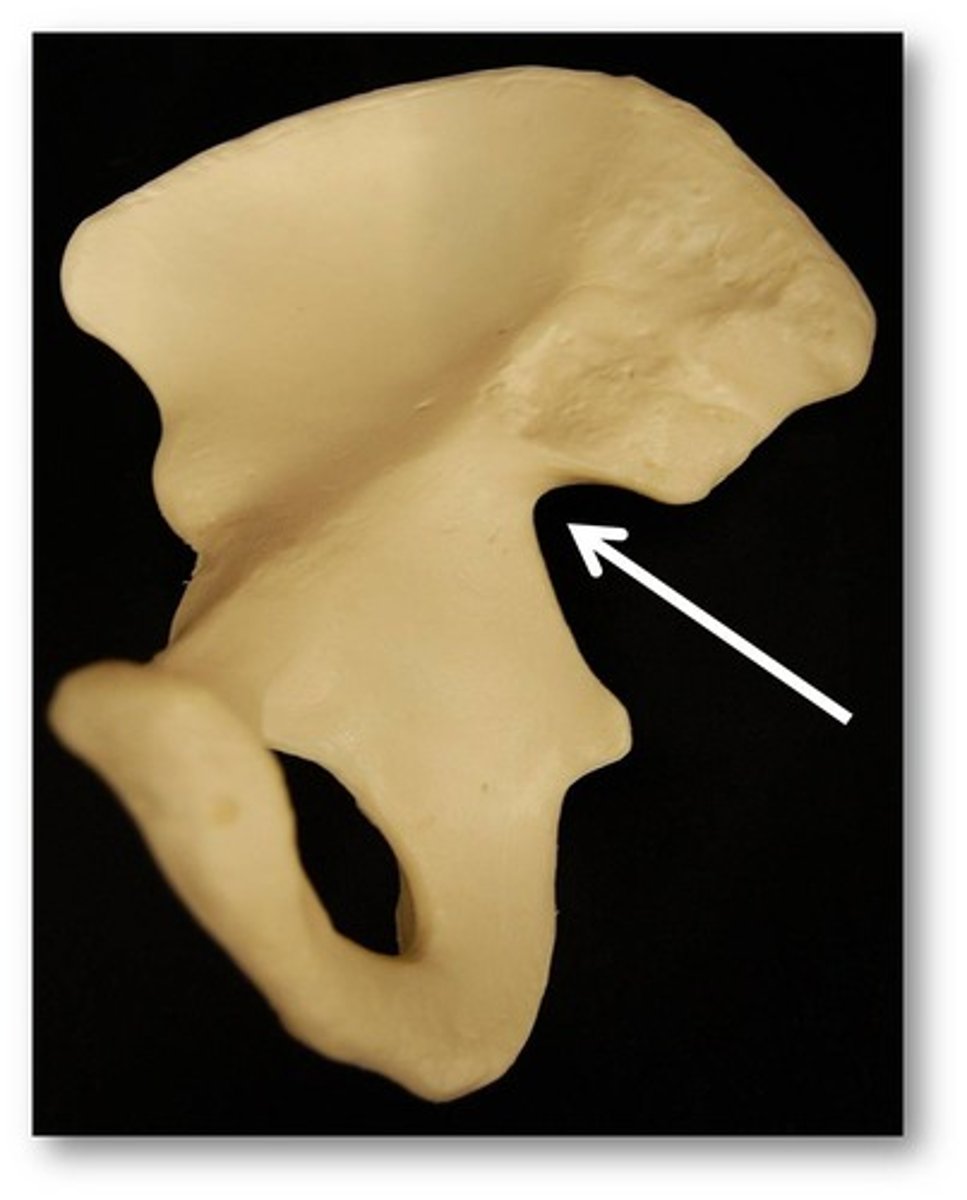
greater sciatic notch
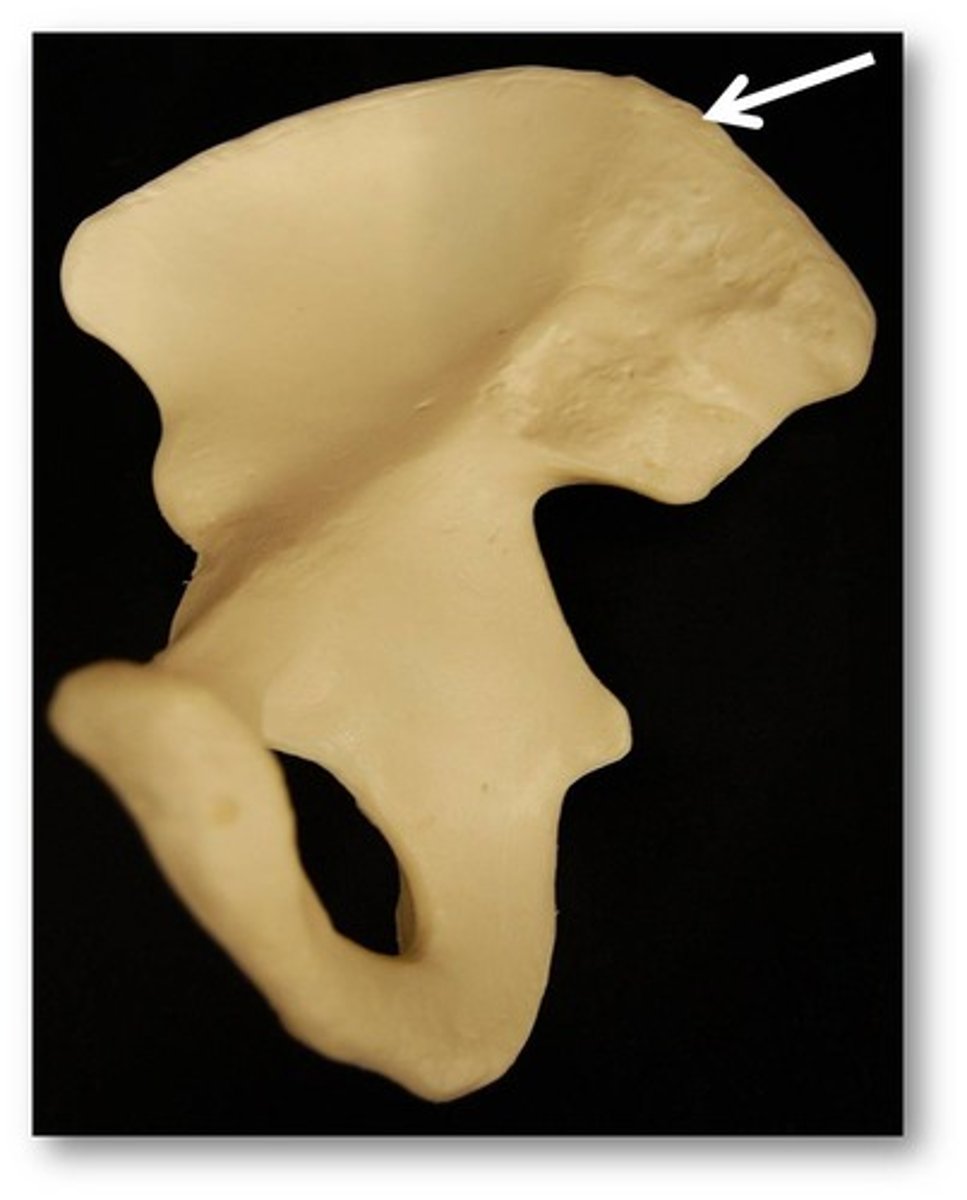
iliac crest
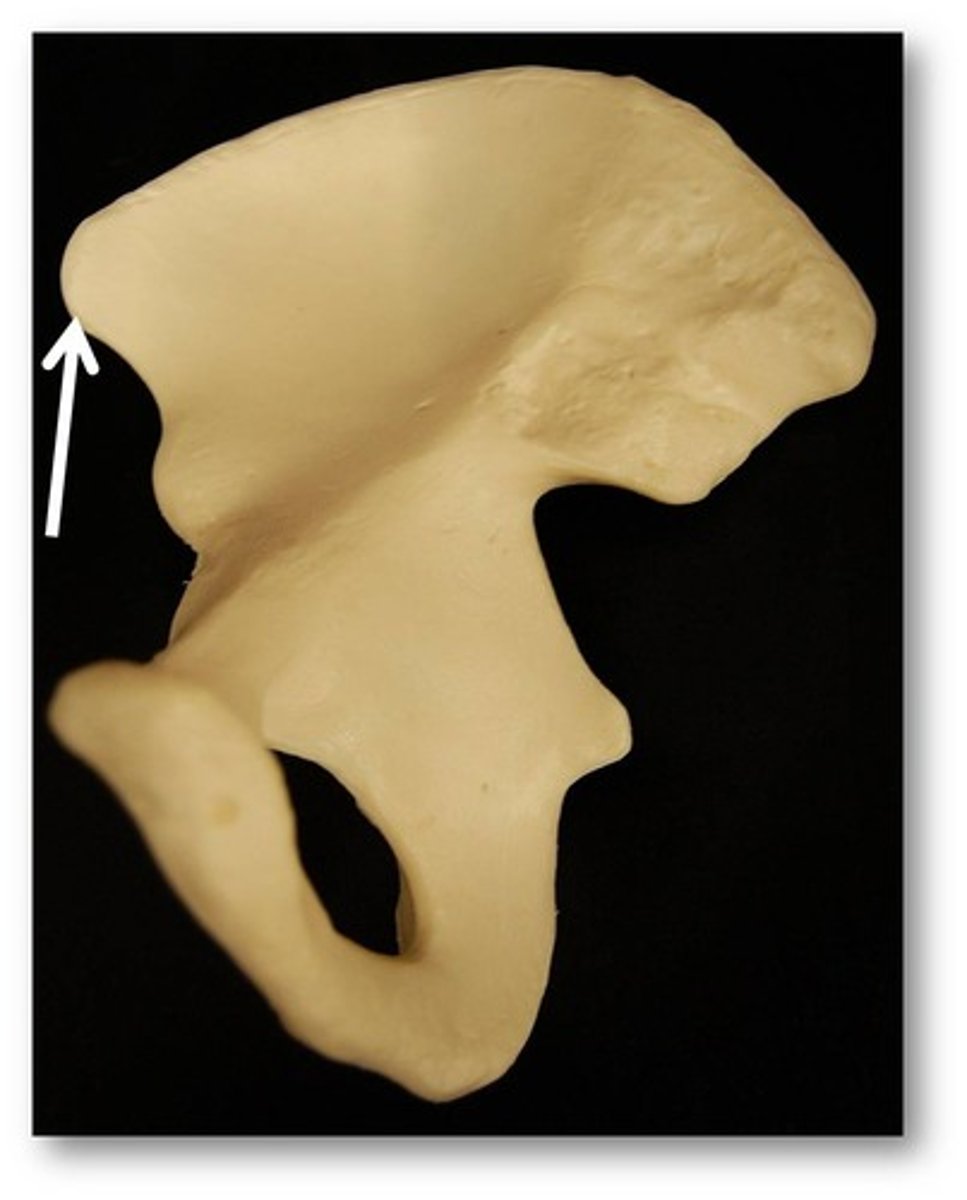
anterior superior iliac spine
ischium
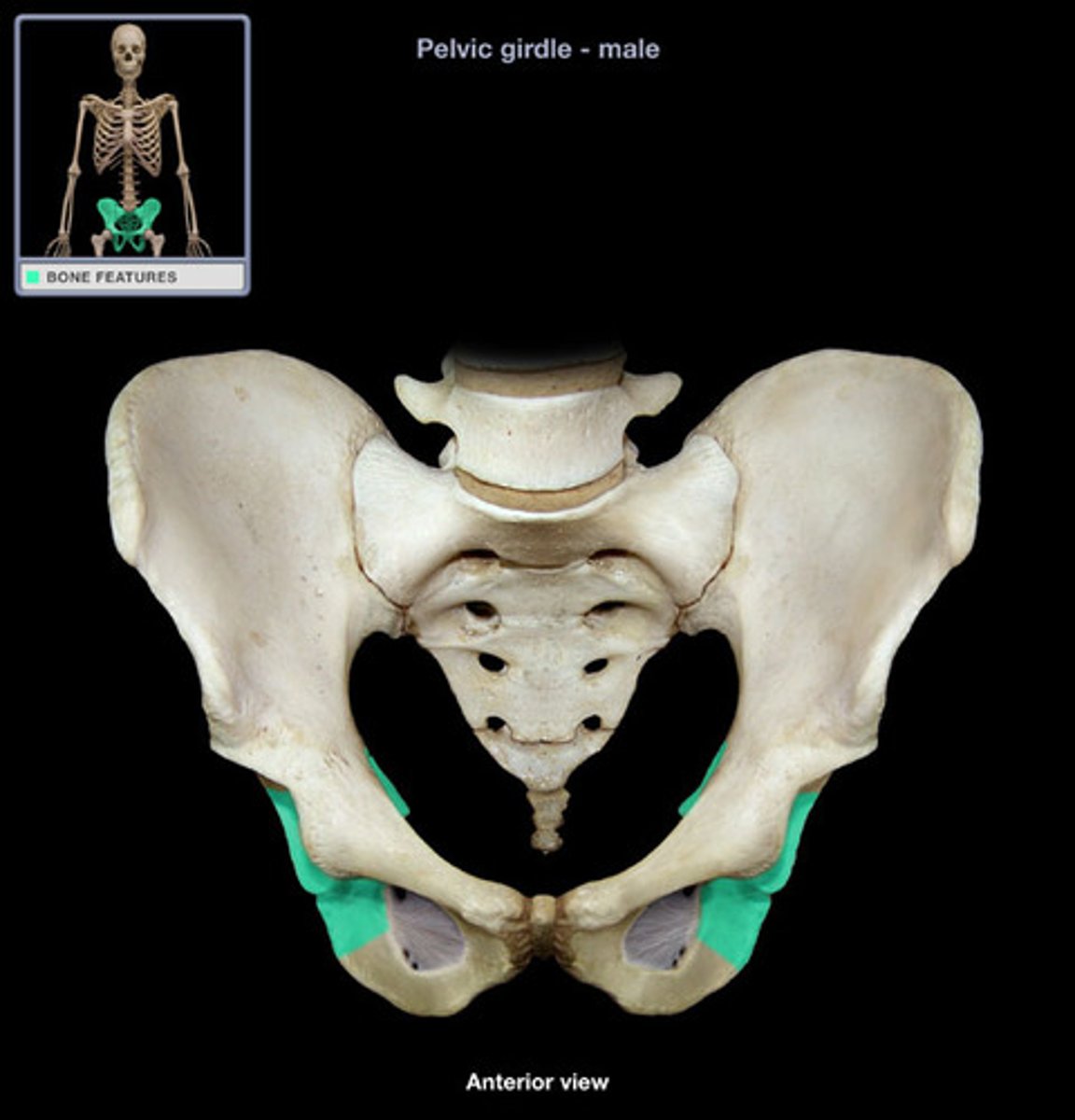
ischial tuberosity
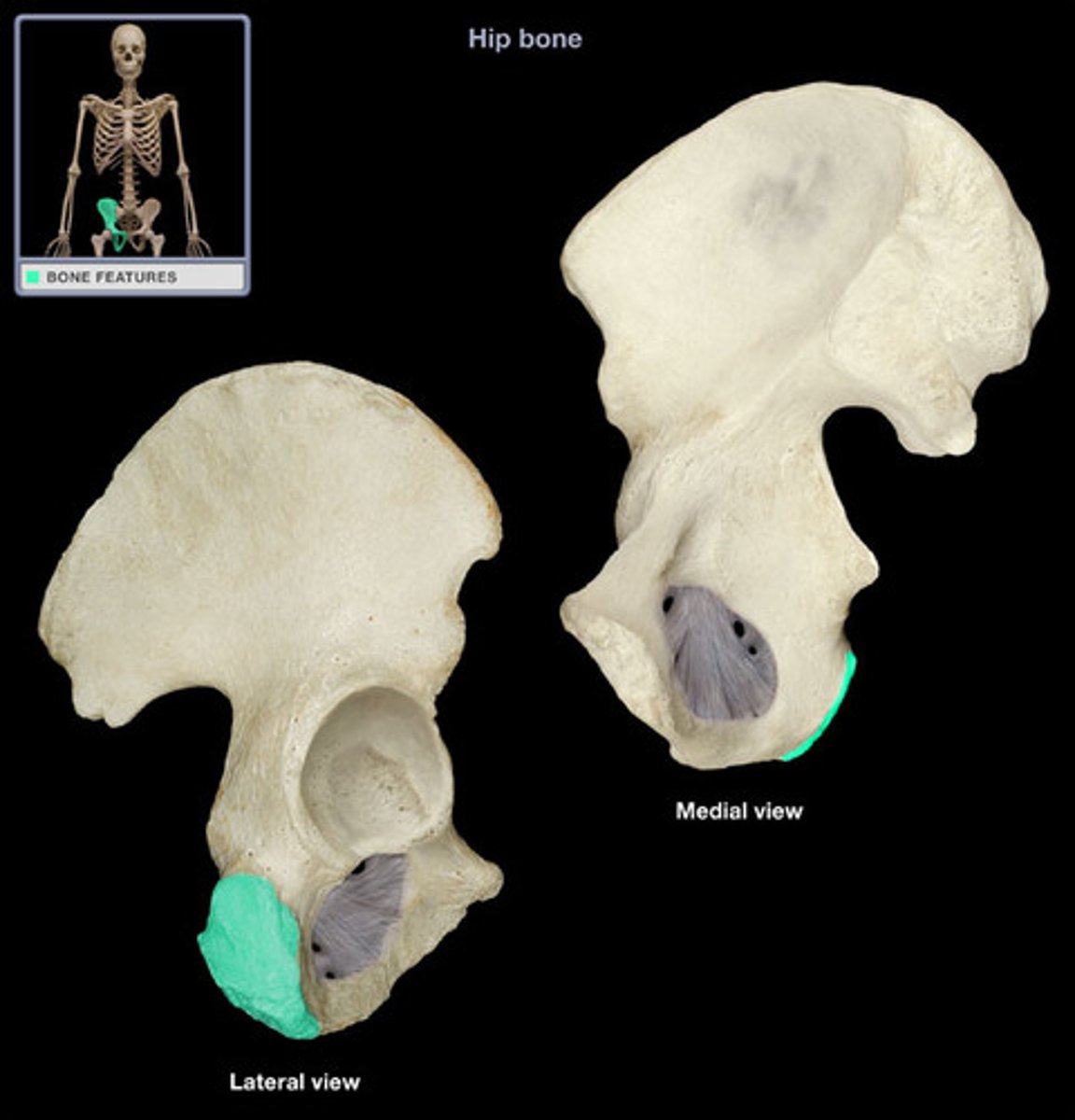
Ischoipubic ramus
Obturator foramen
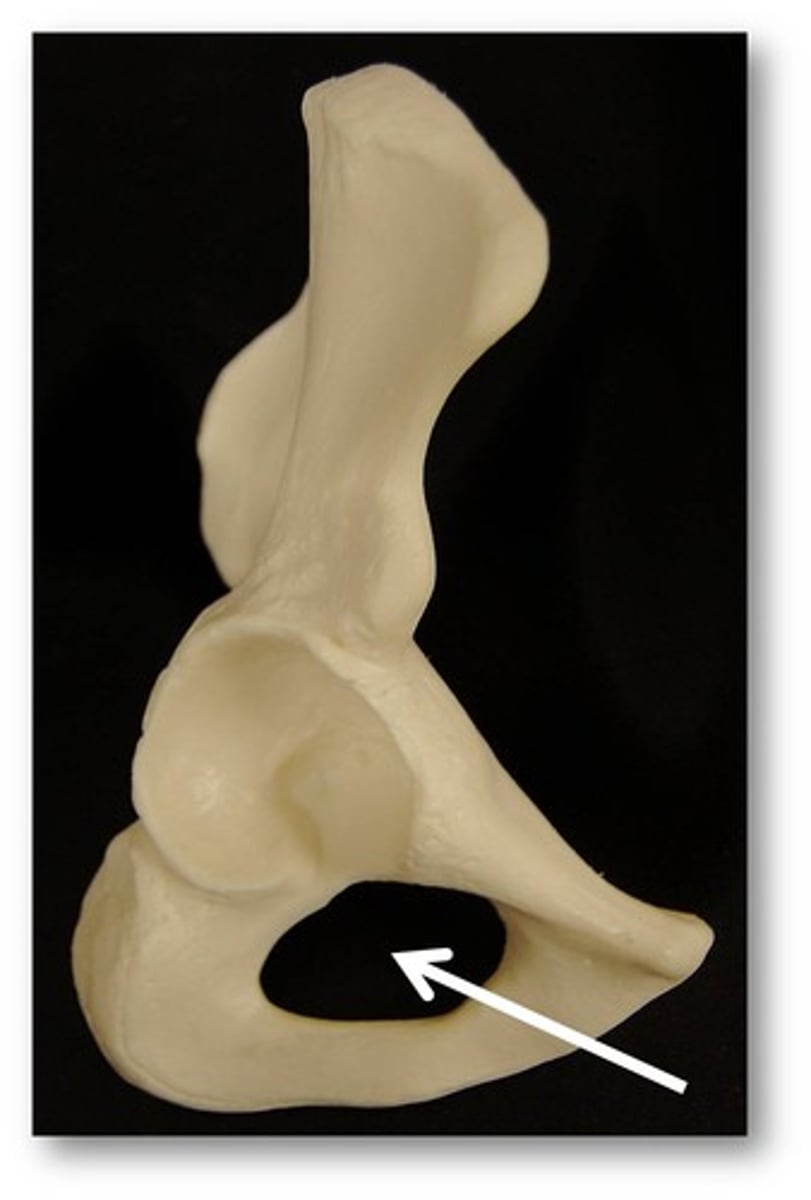
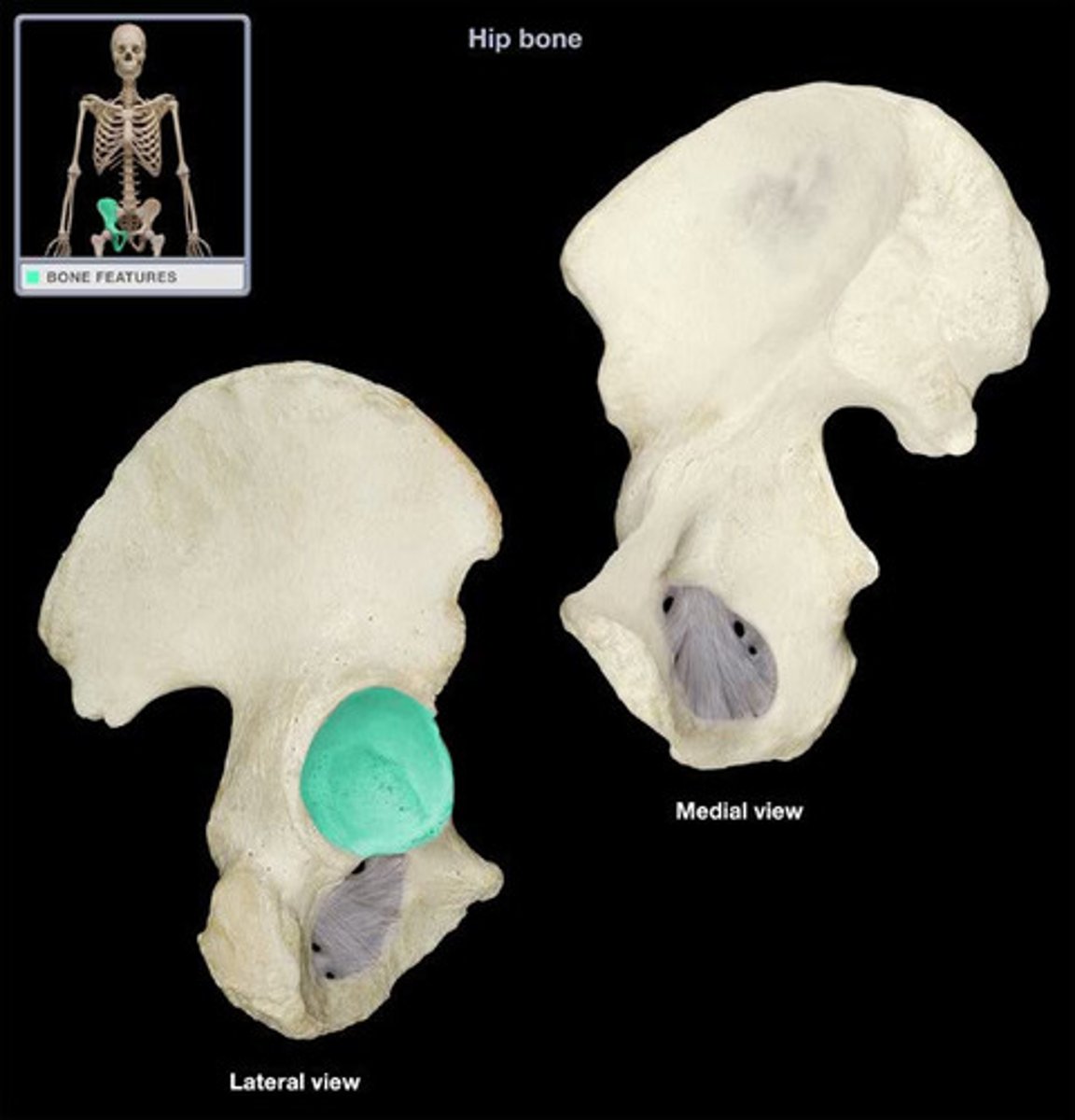
acetabulum
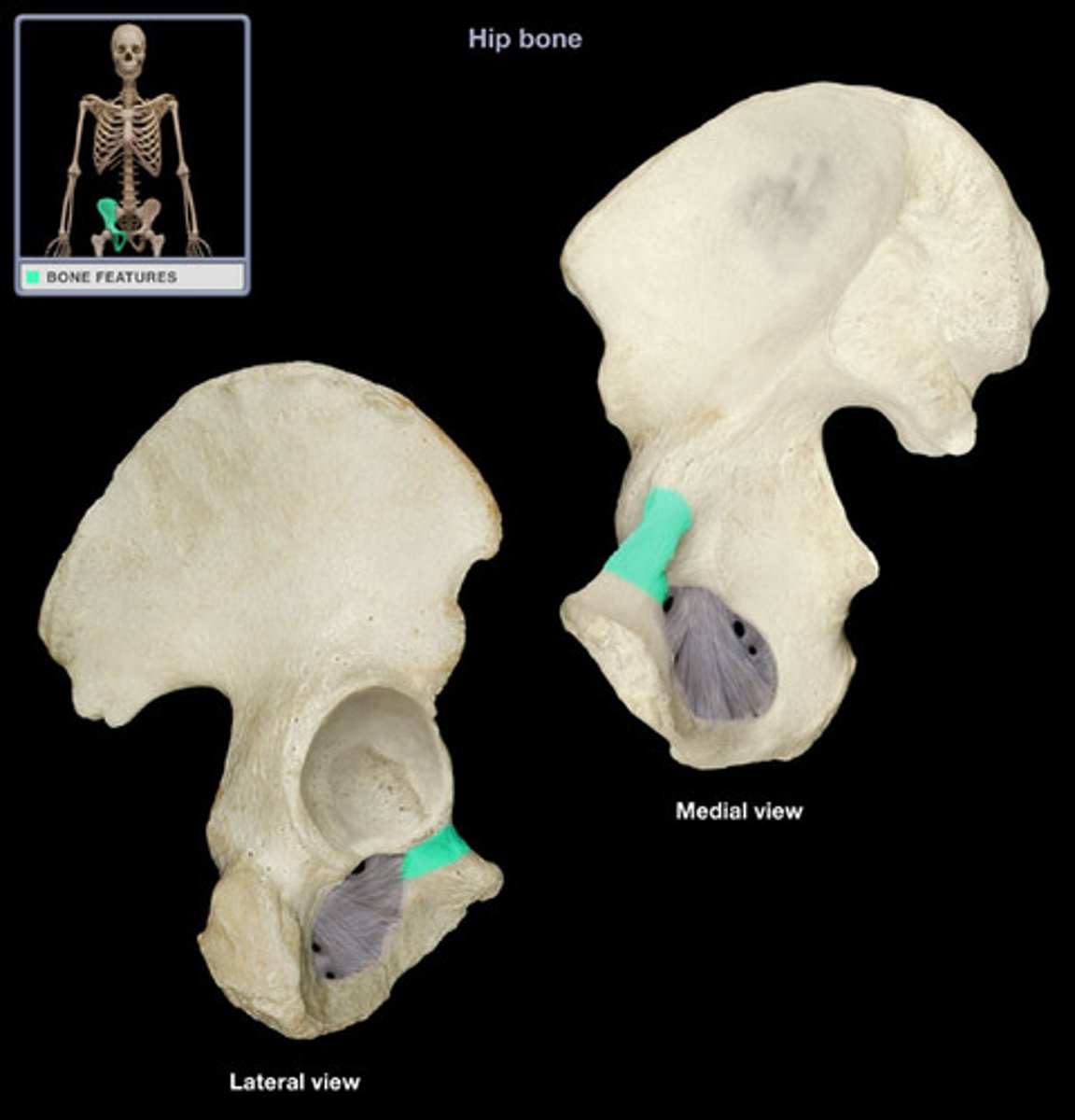
Iliopubic ramus
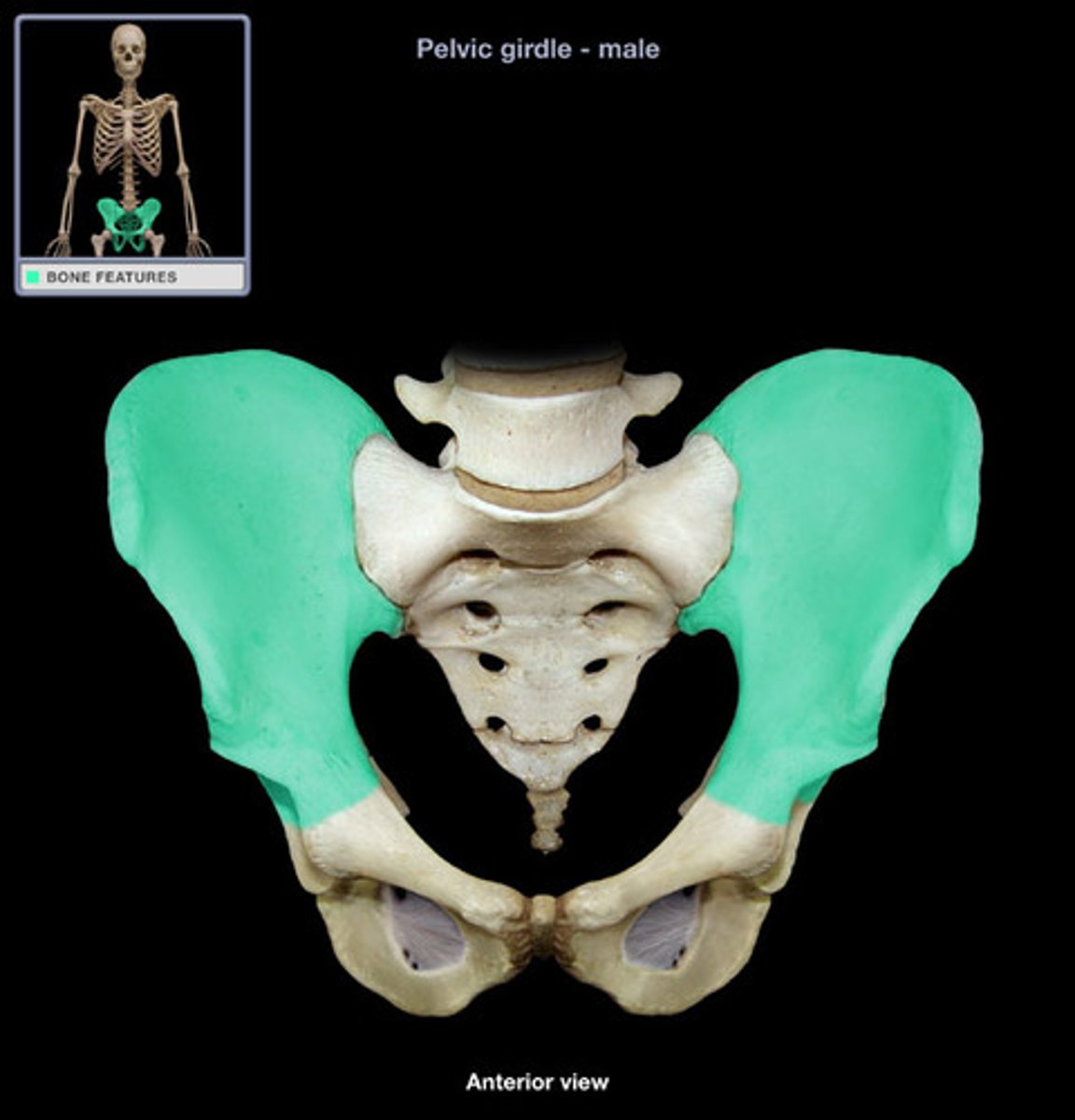
Determining sex based on pelvis (male)
Heart shaped, 60 degrees, V shaped
determining sex based on pelvis (female)
Oval shaped, 90 degrees, U shaped
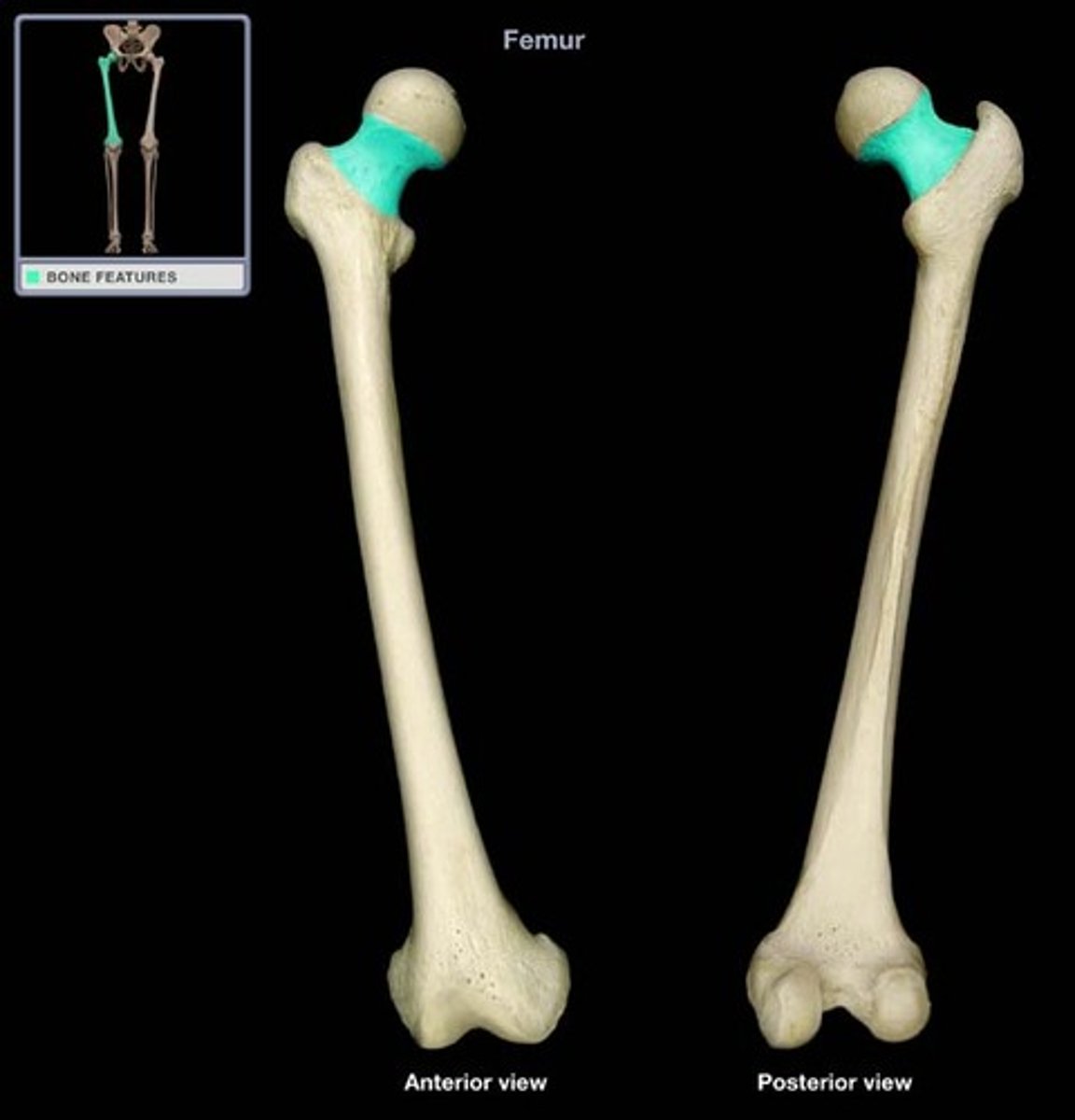
Neck of the femur
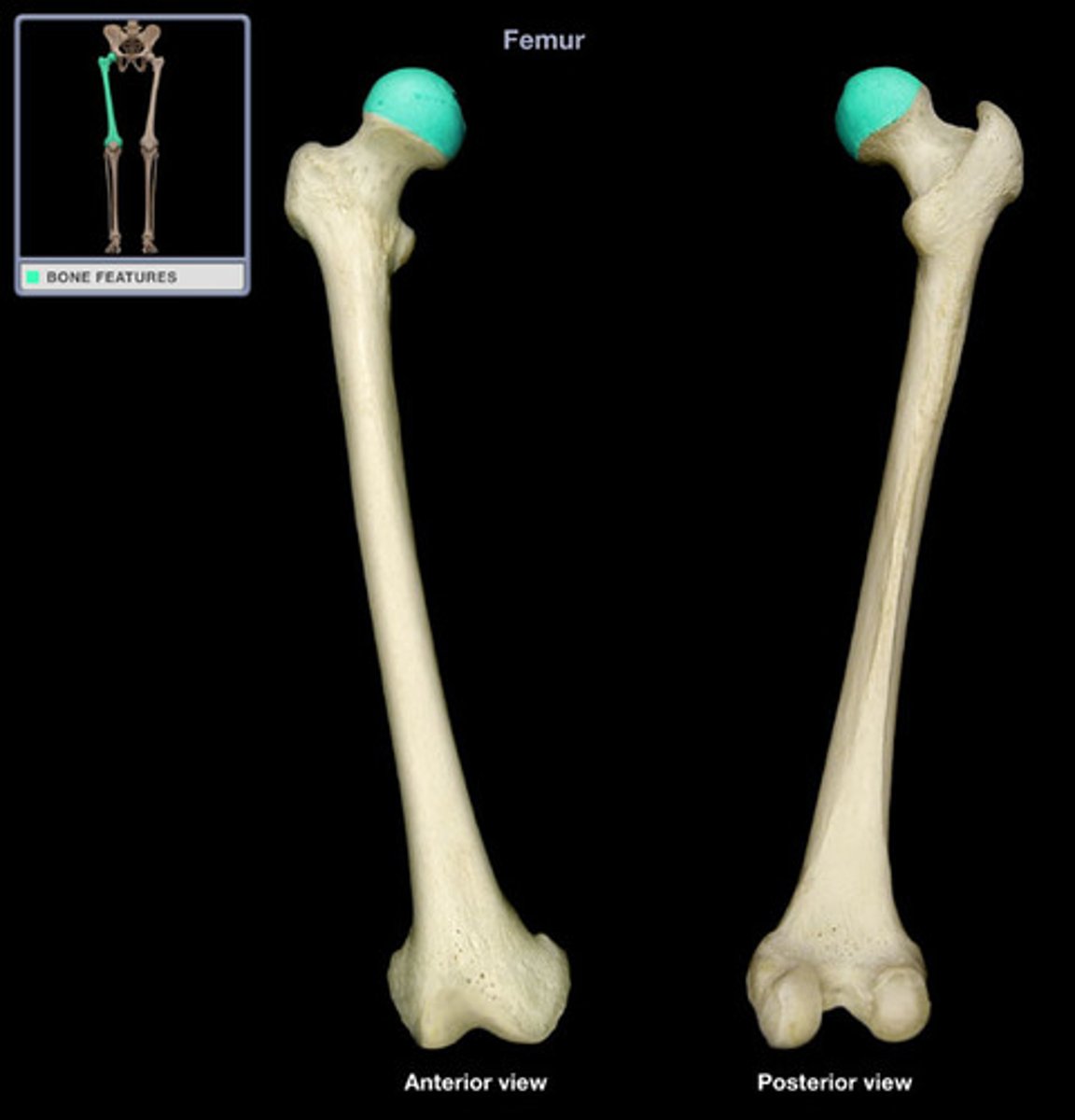
Head of the Femur
greater trochanter
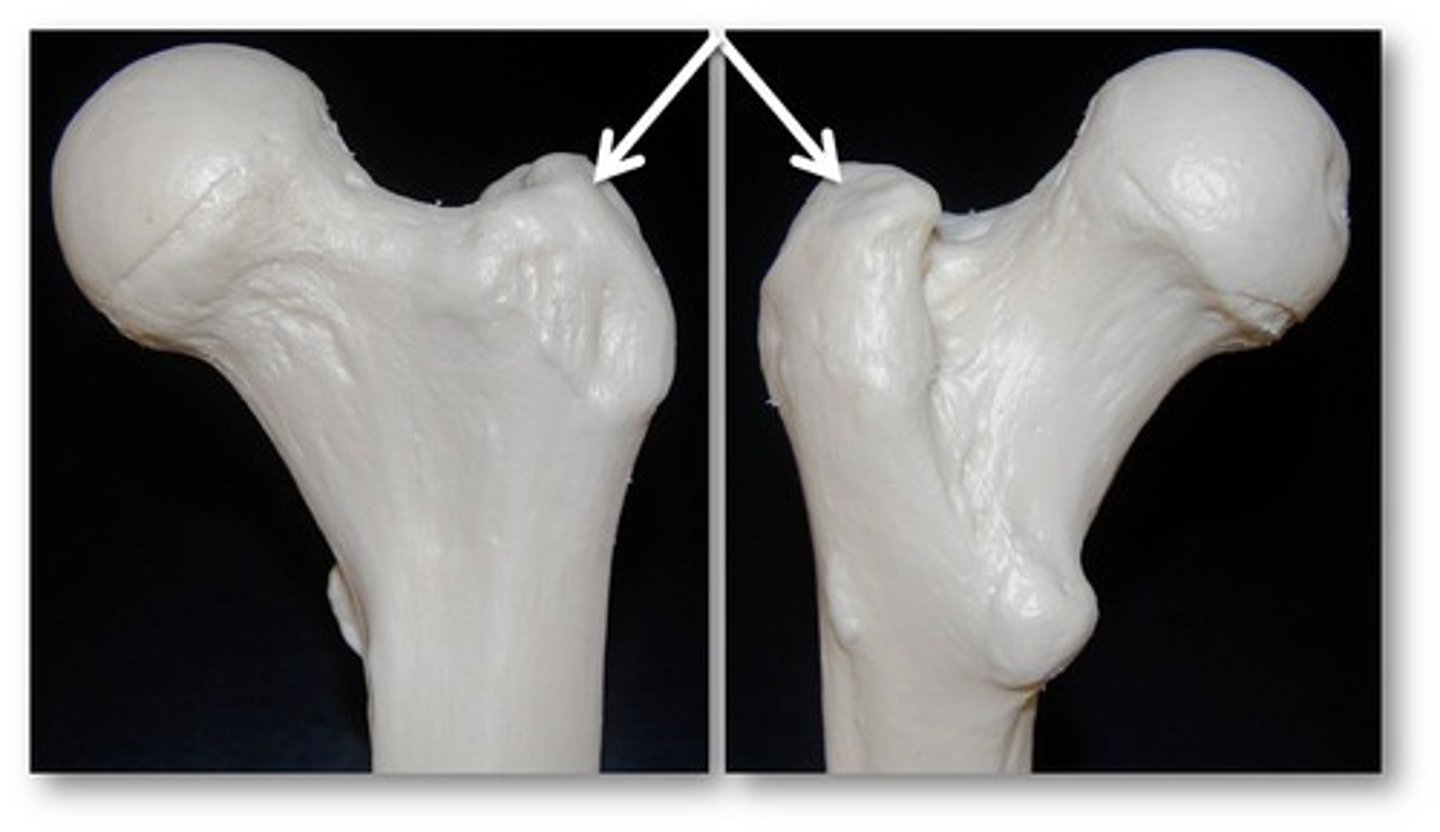
Lesser trochanter
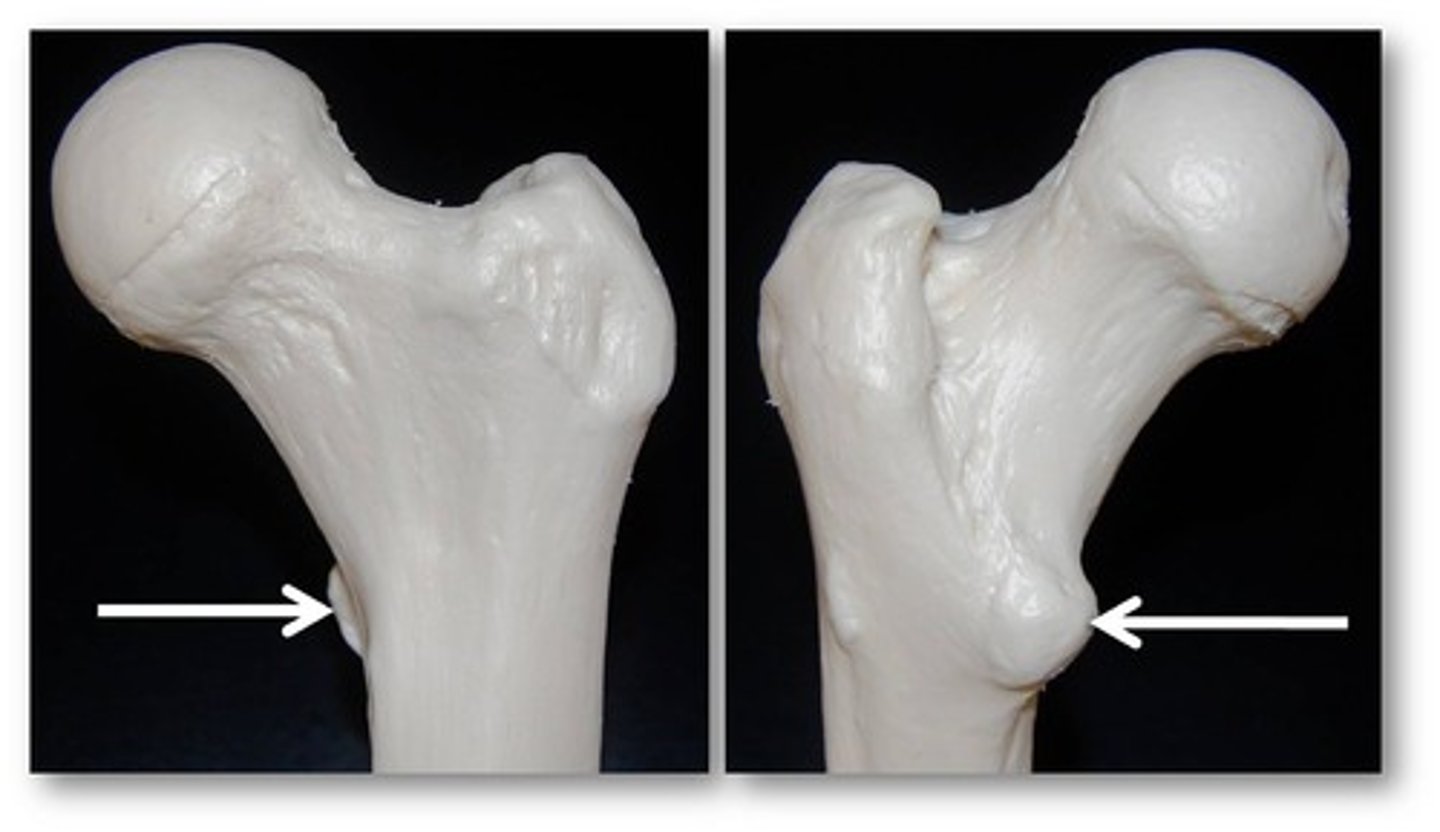
gluteal tuberosity
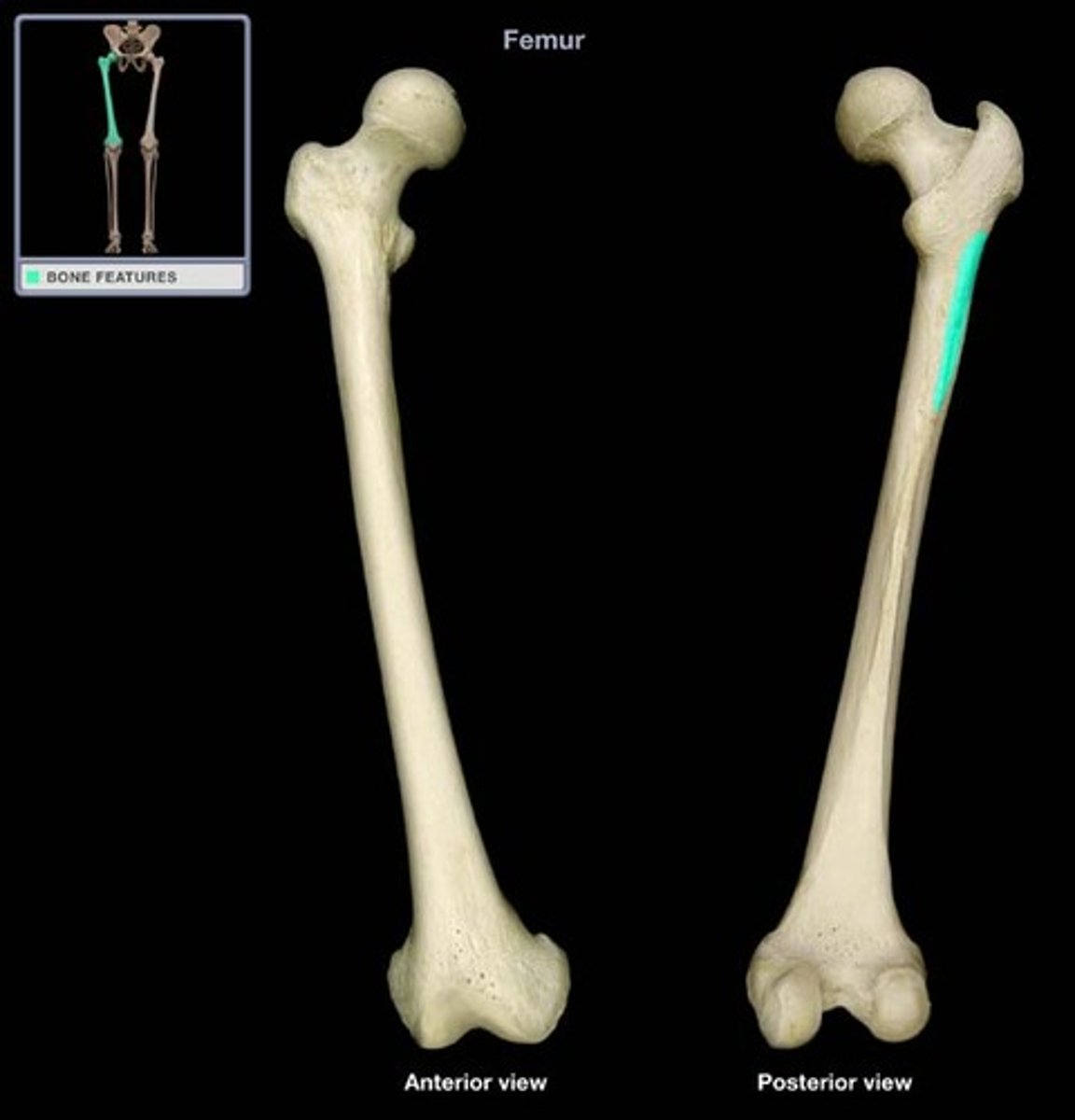
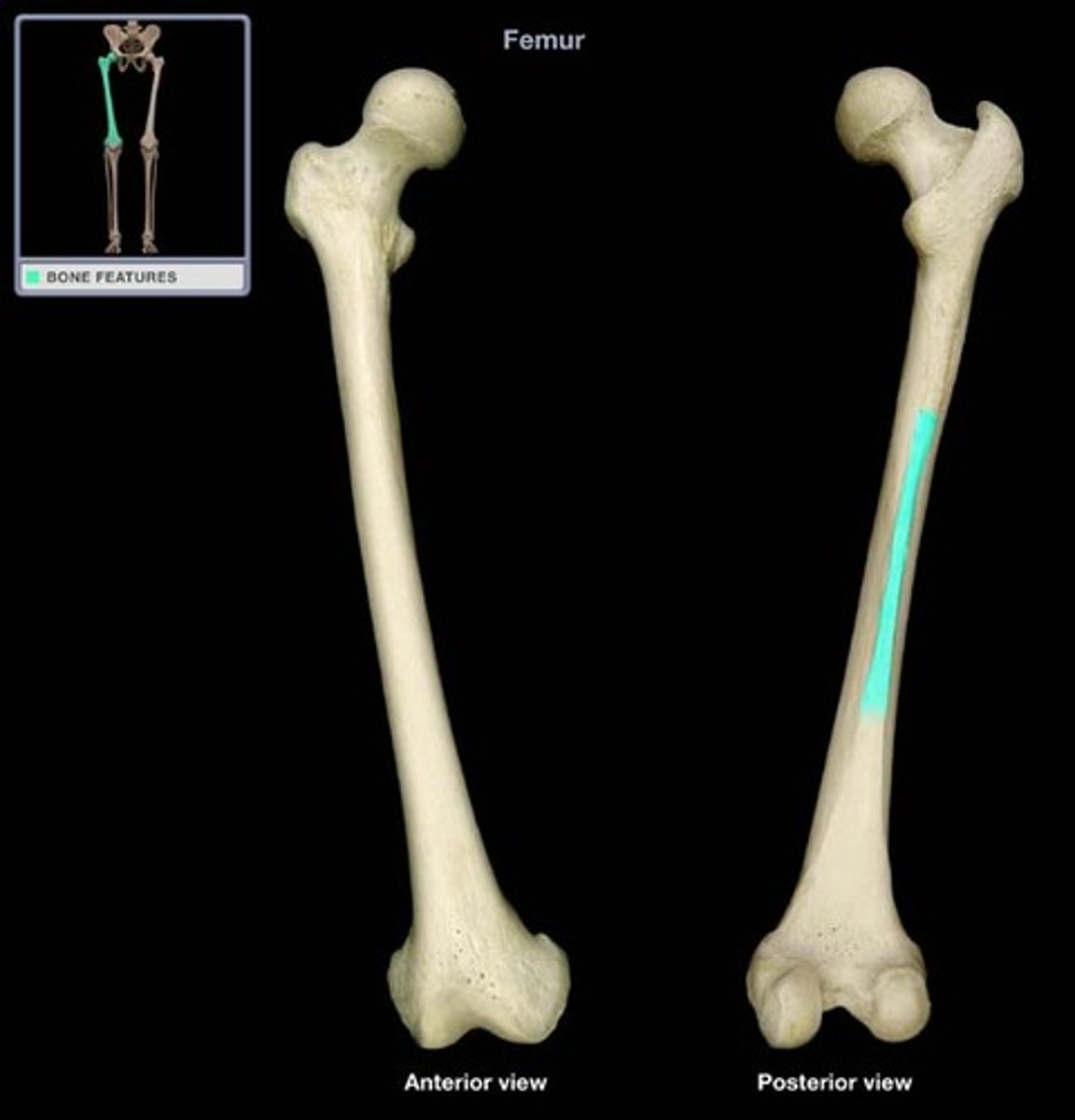
Line aspera
Later condyle
inferior to the epicondyle
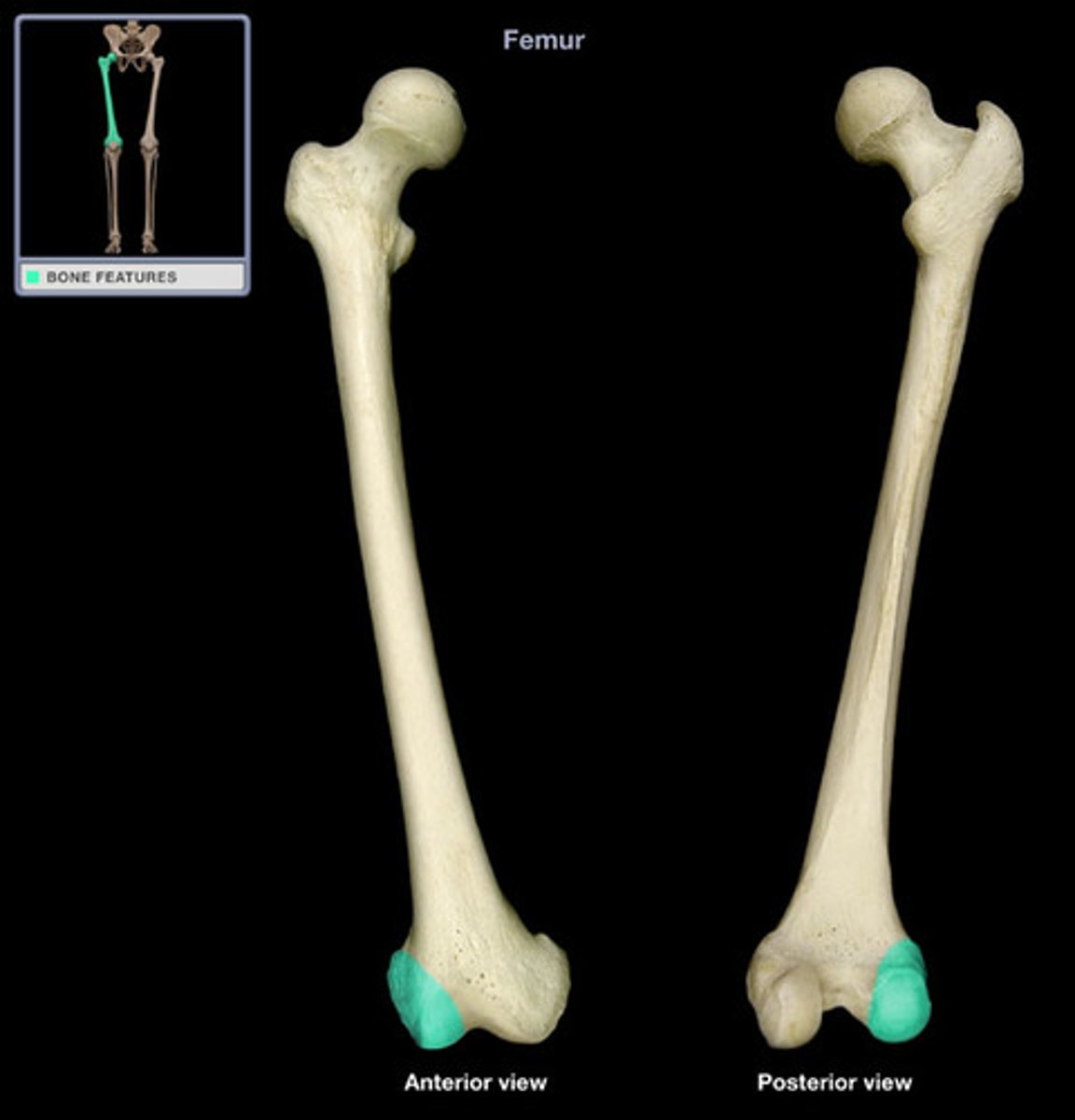
Lateral epicondyle
superior to lateral condyle
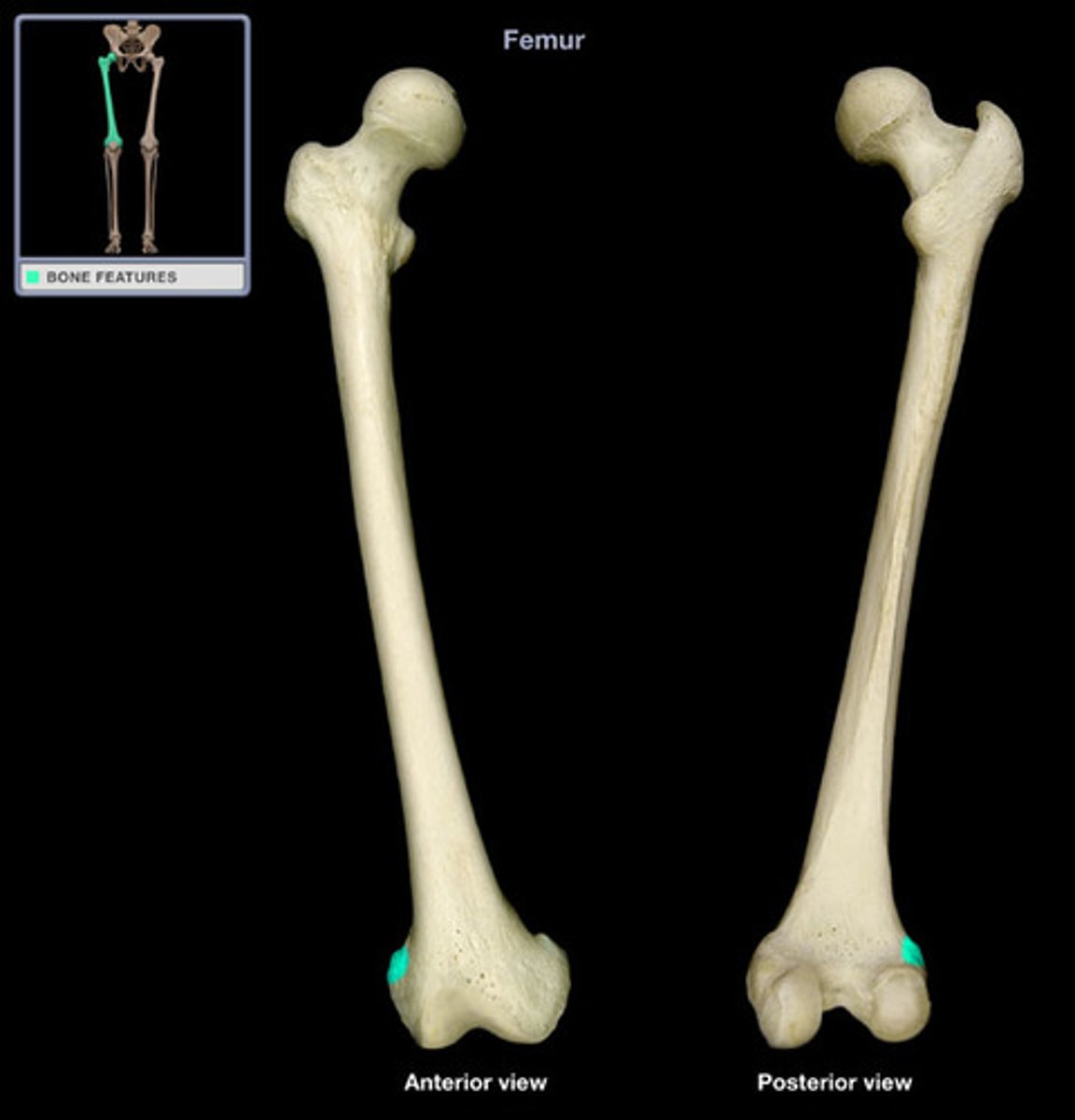
Medial condyle
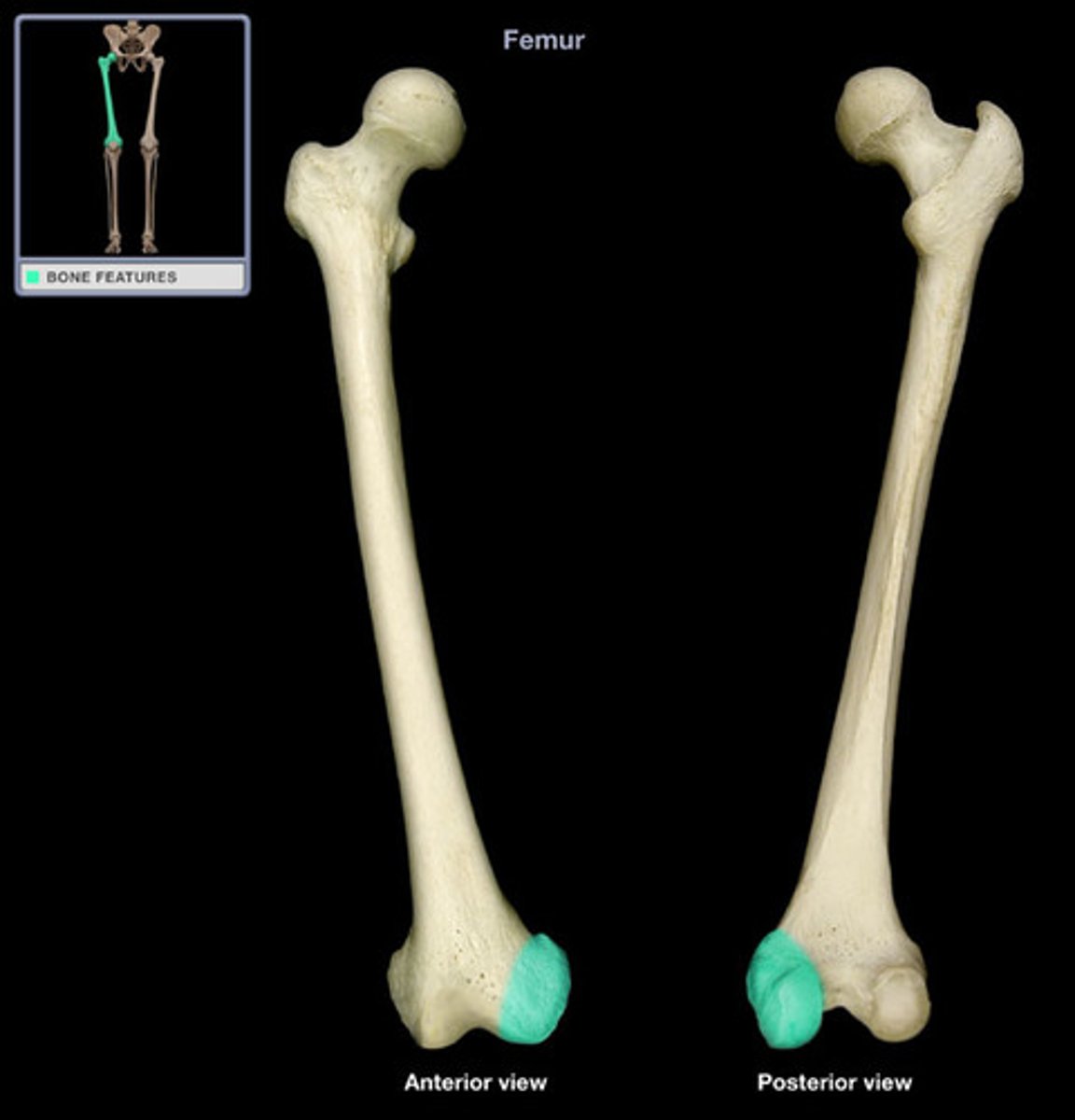
Medial epicondyle
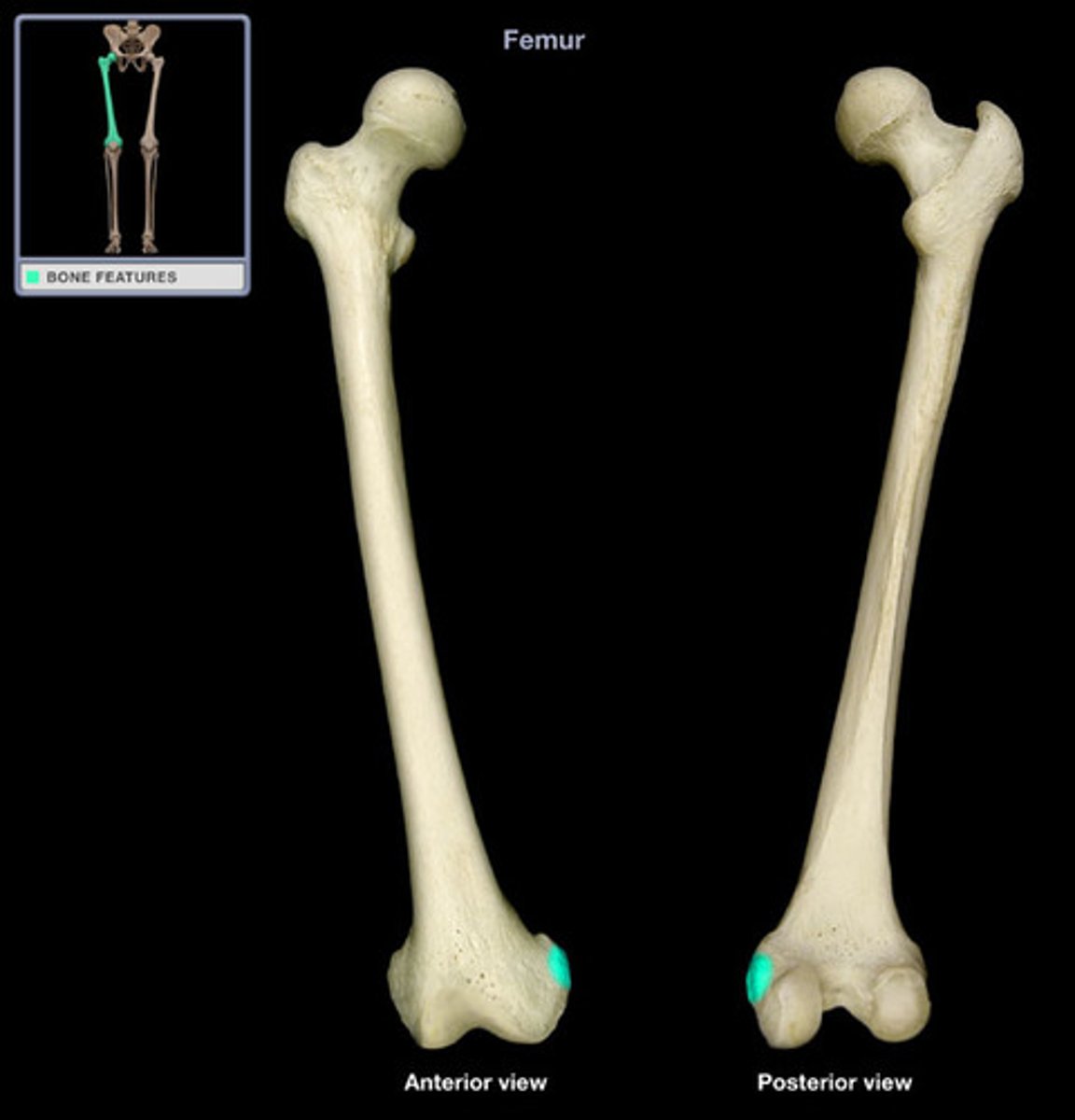
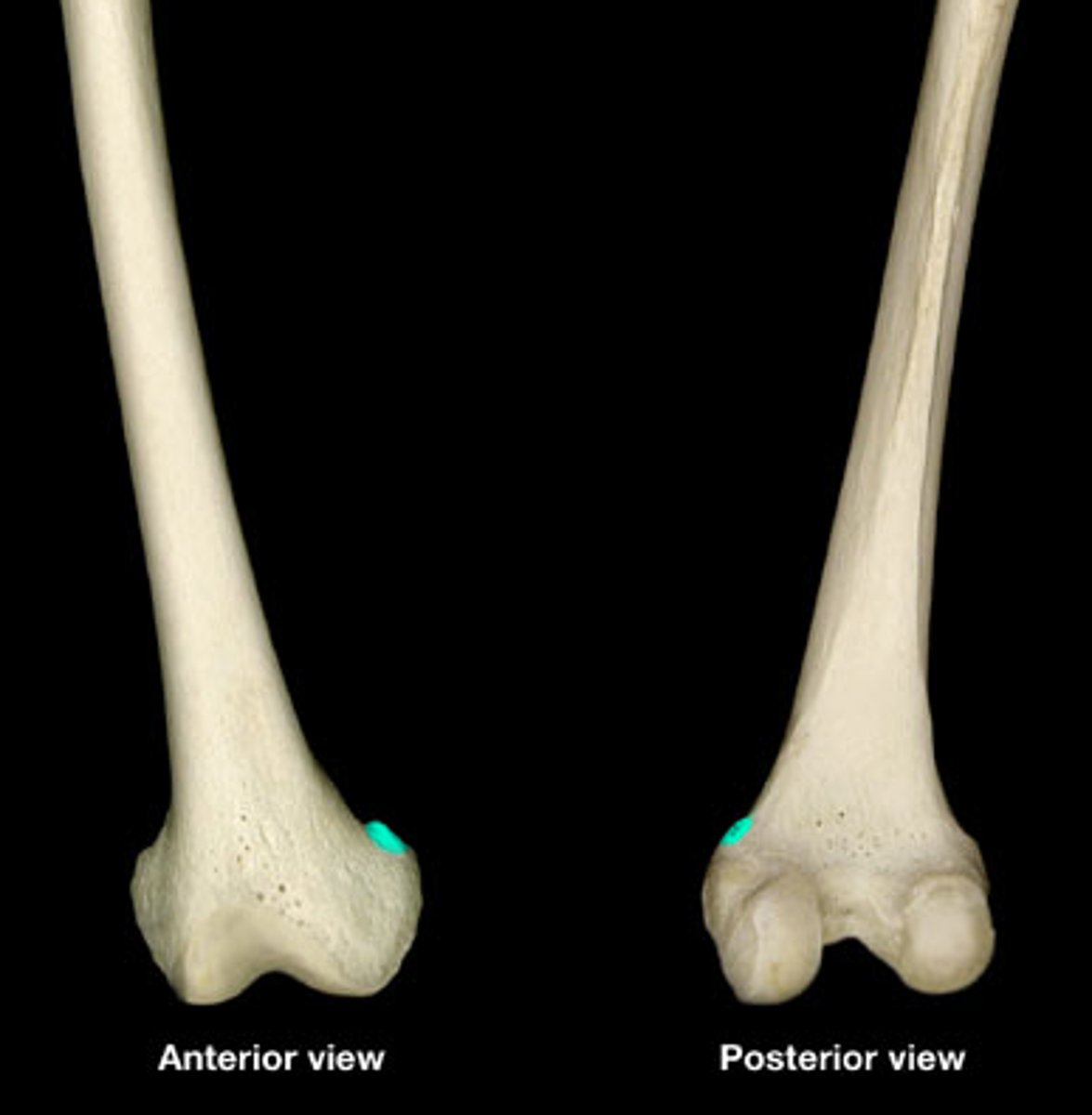
adductor tubercle
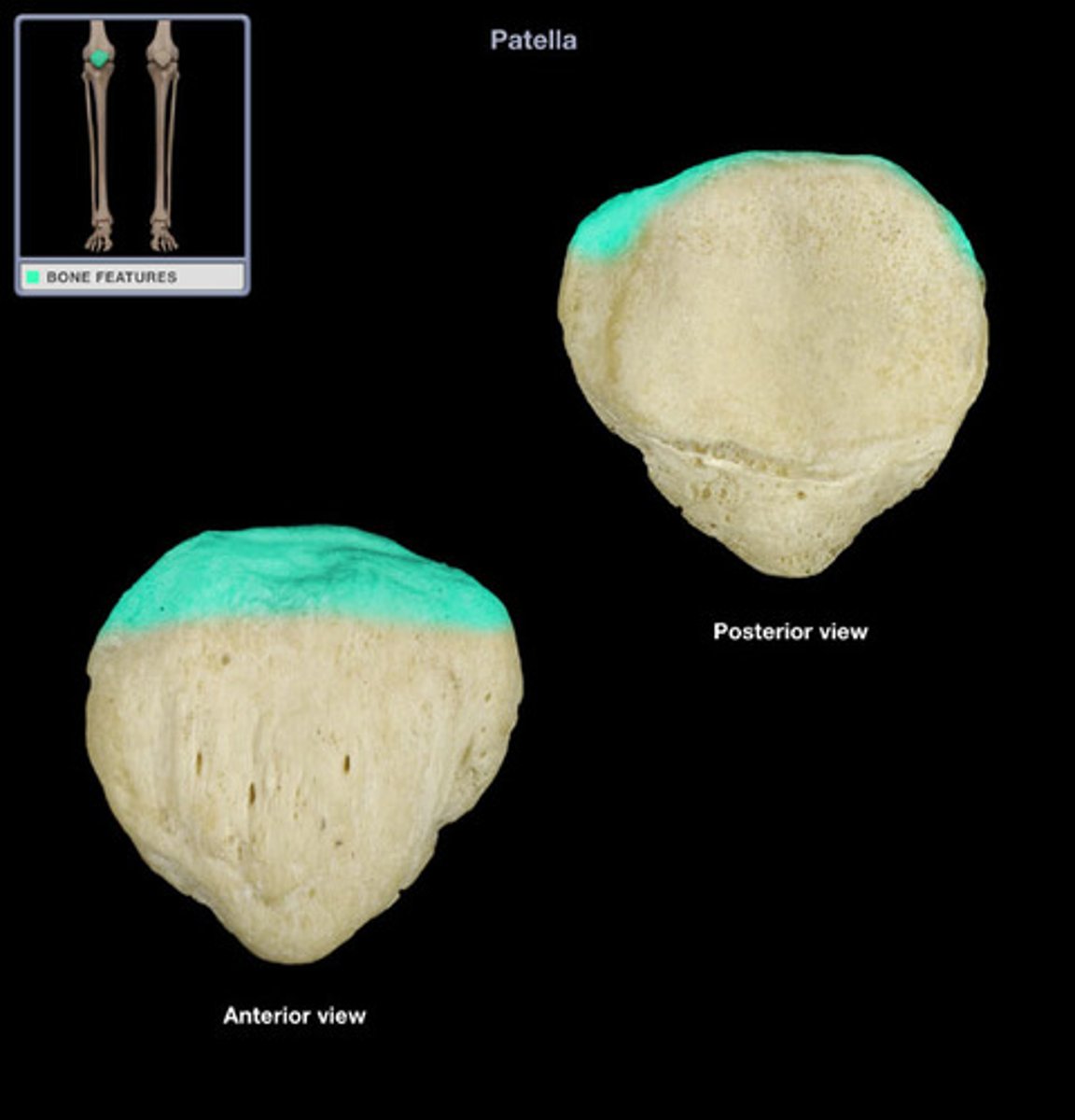
base of patella
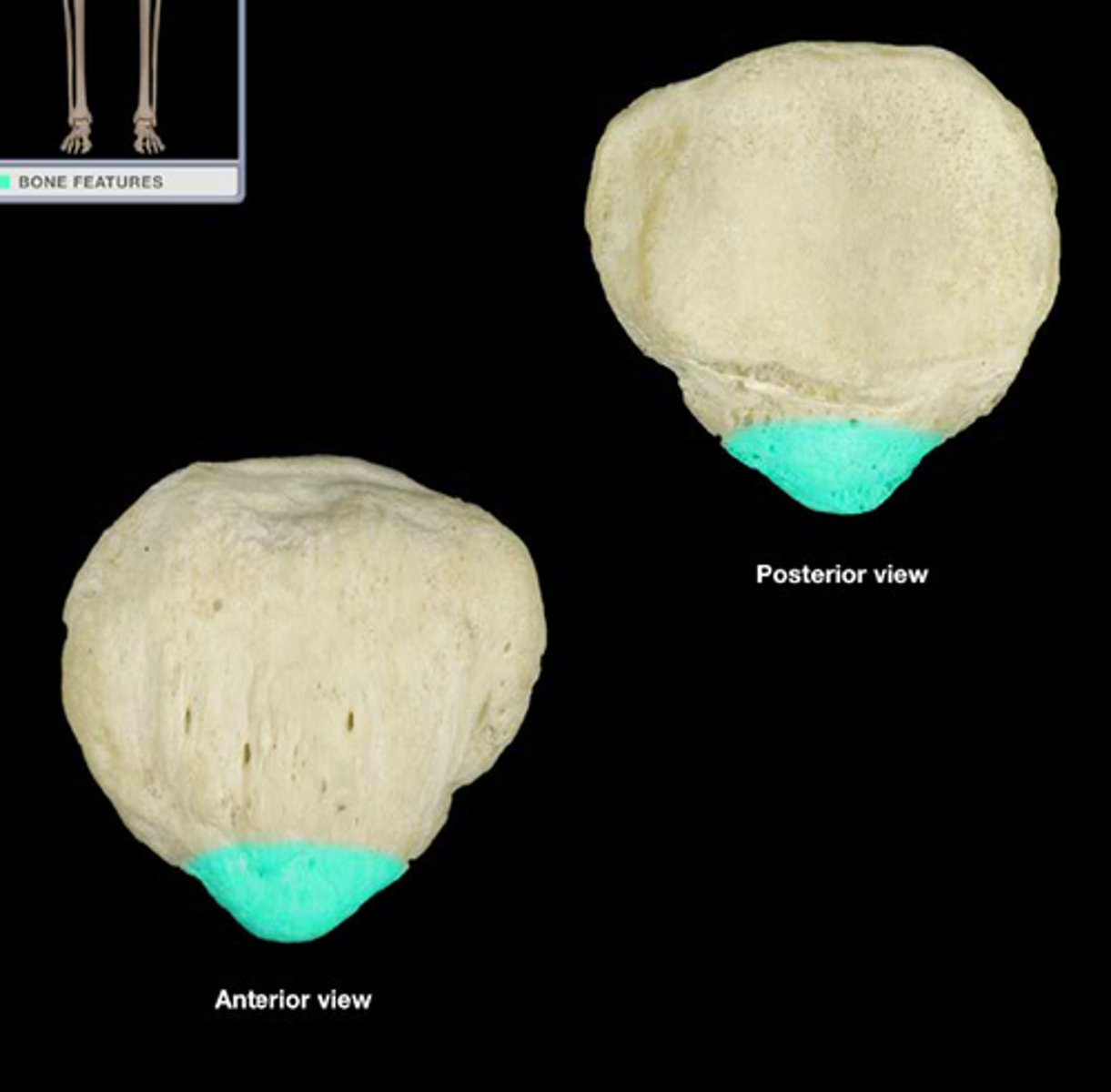
apex of patella
facet for condyle of femur
intercondylar eminence
tibia
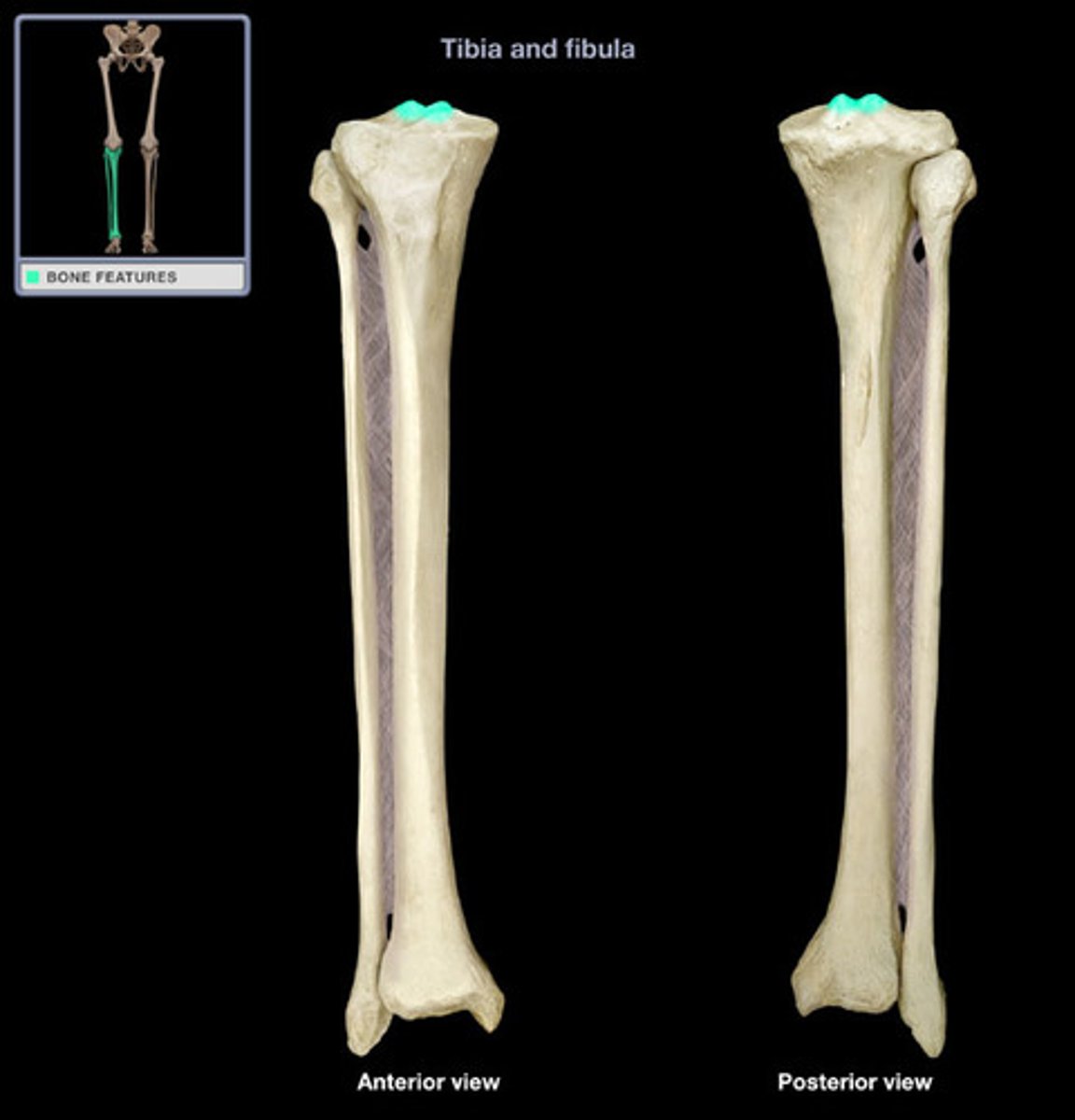
Lateral condyle
tibia
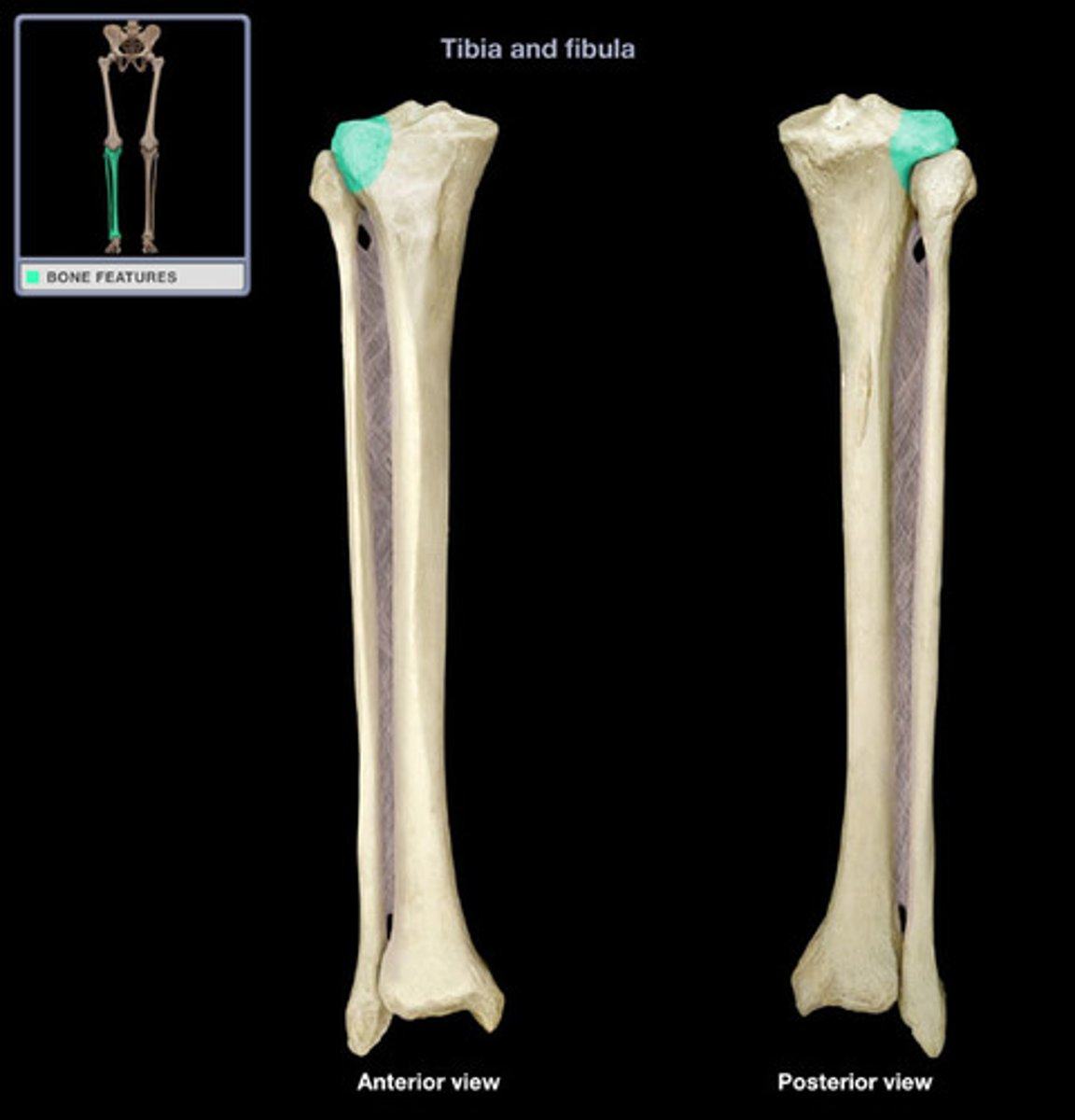
medial condyle
tibia
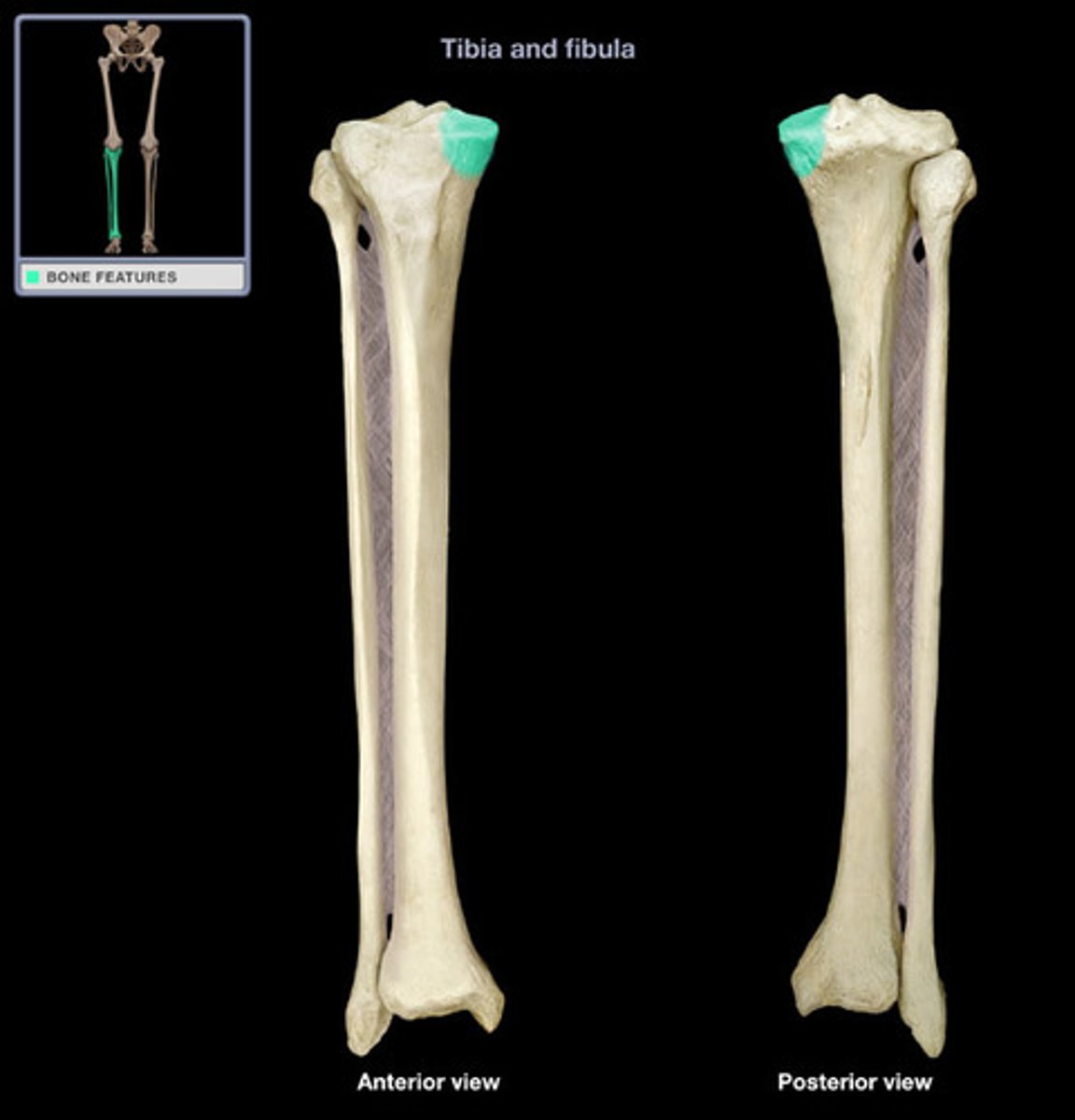
tibial tuberosity
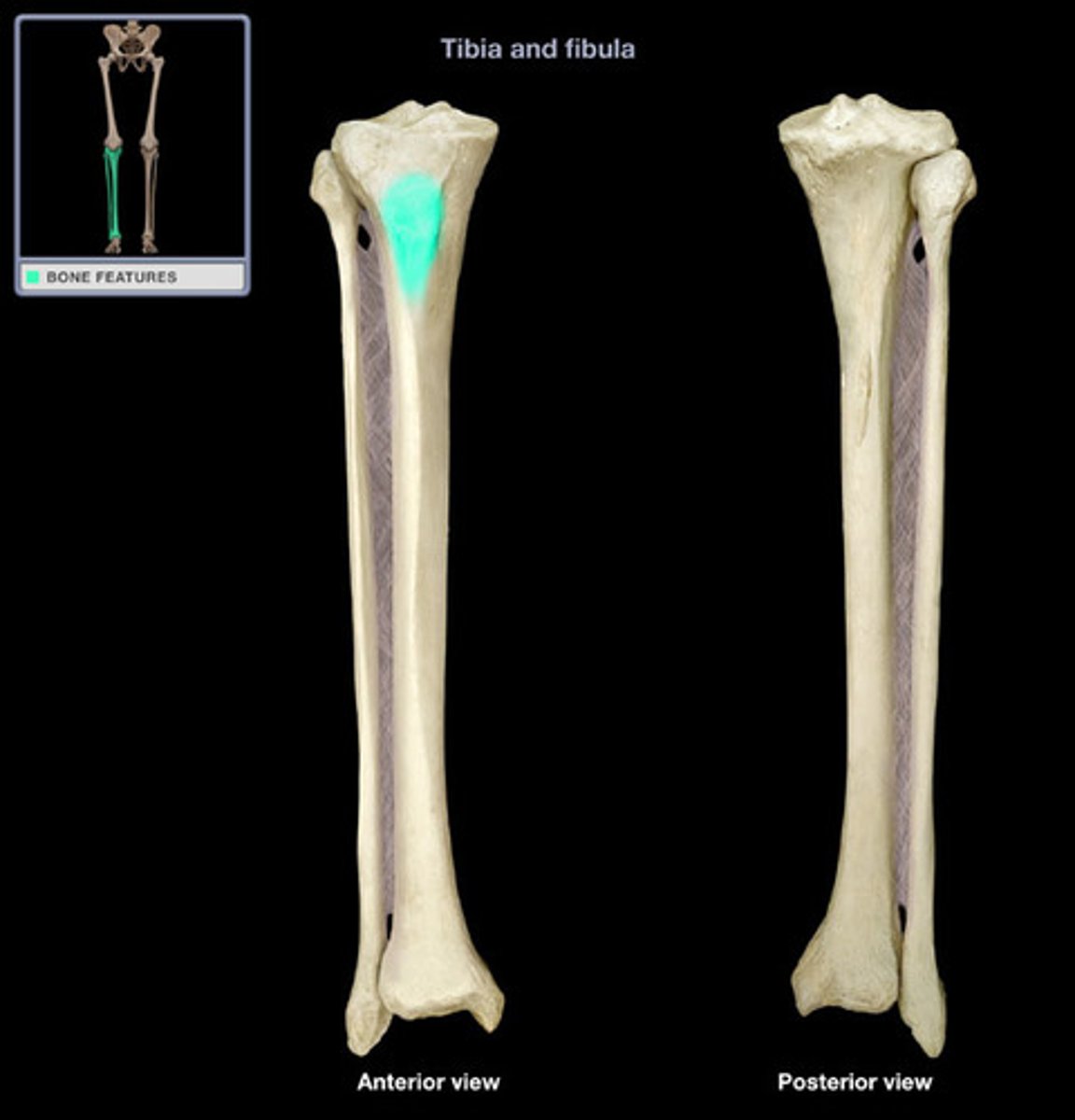
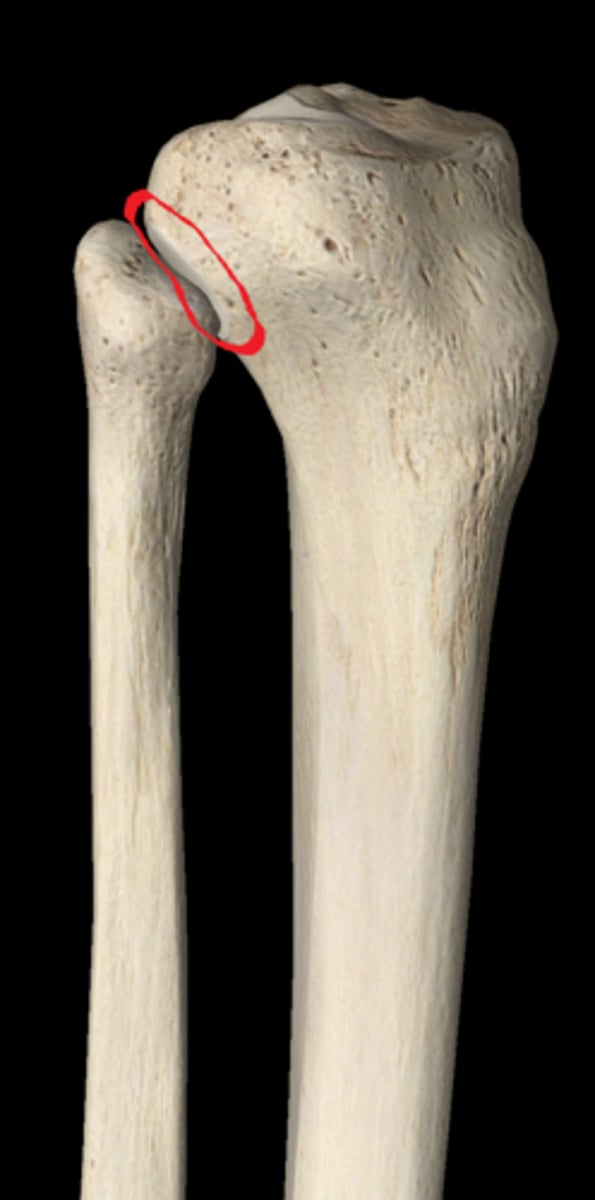
superior tibiofibular joint with fibular articular surface
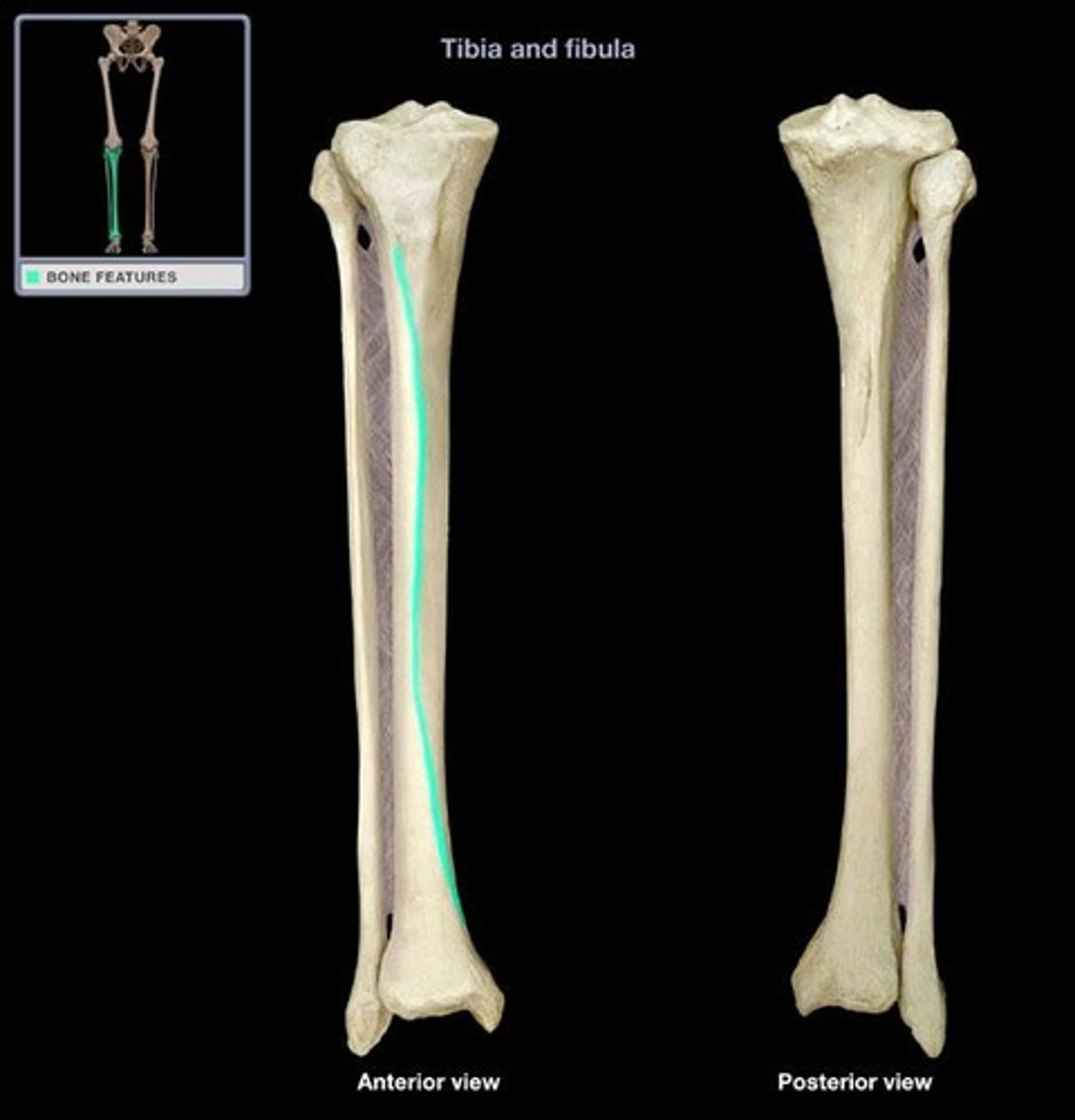
anterior tibial crest
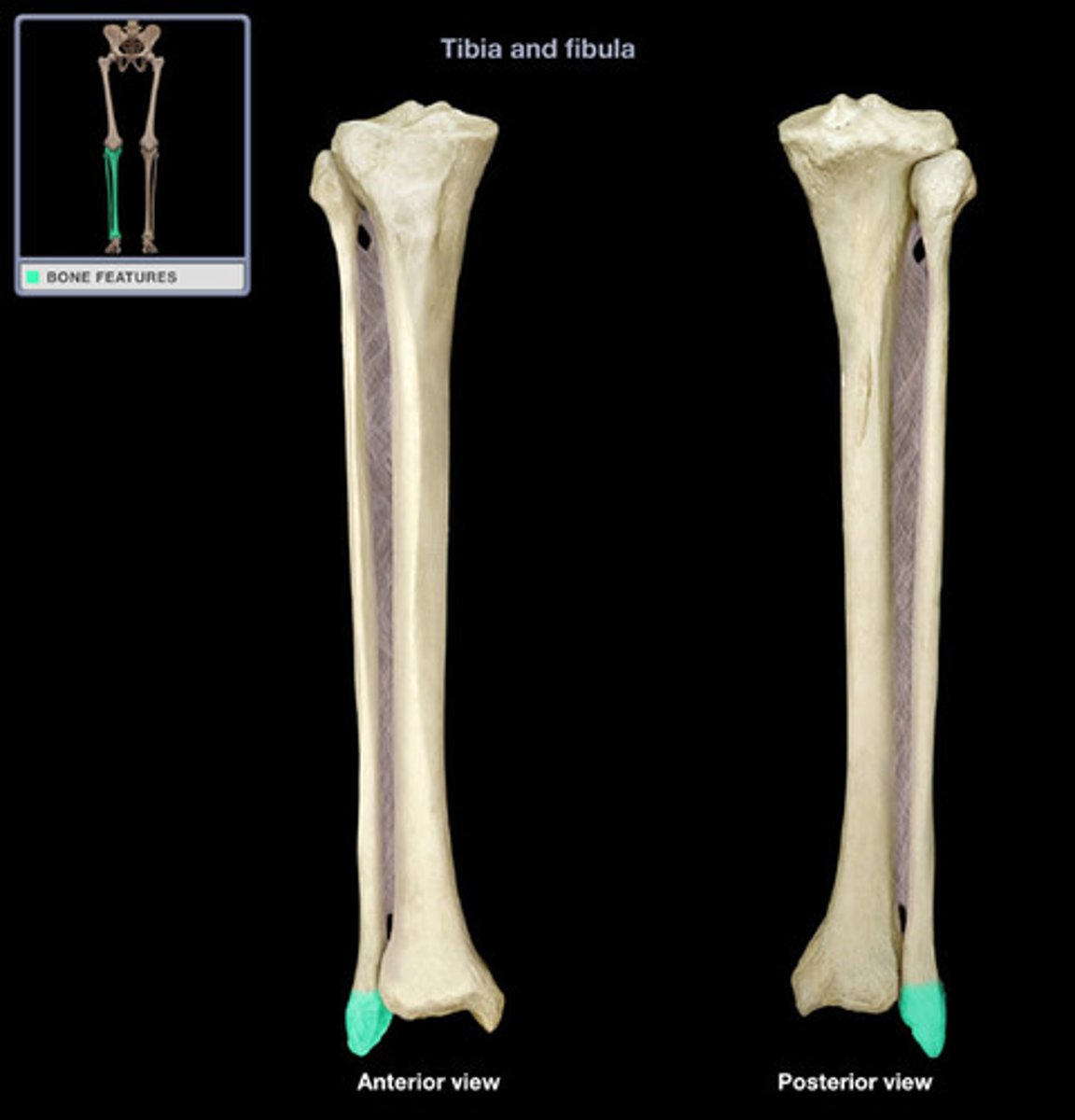
lateral malleolus
distal end of fibula
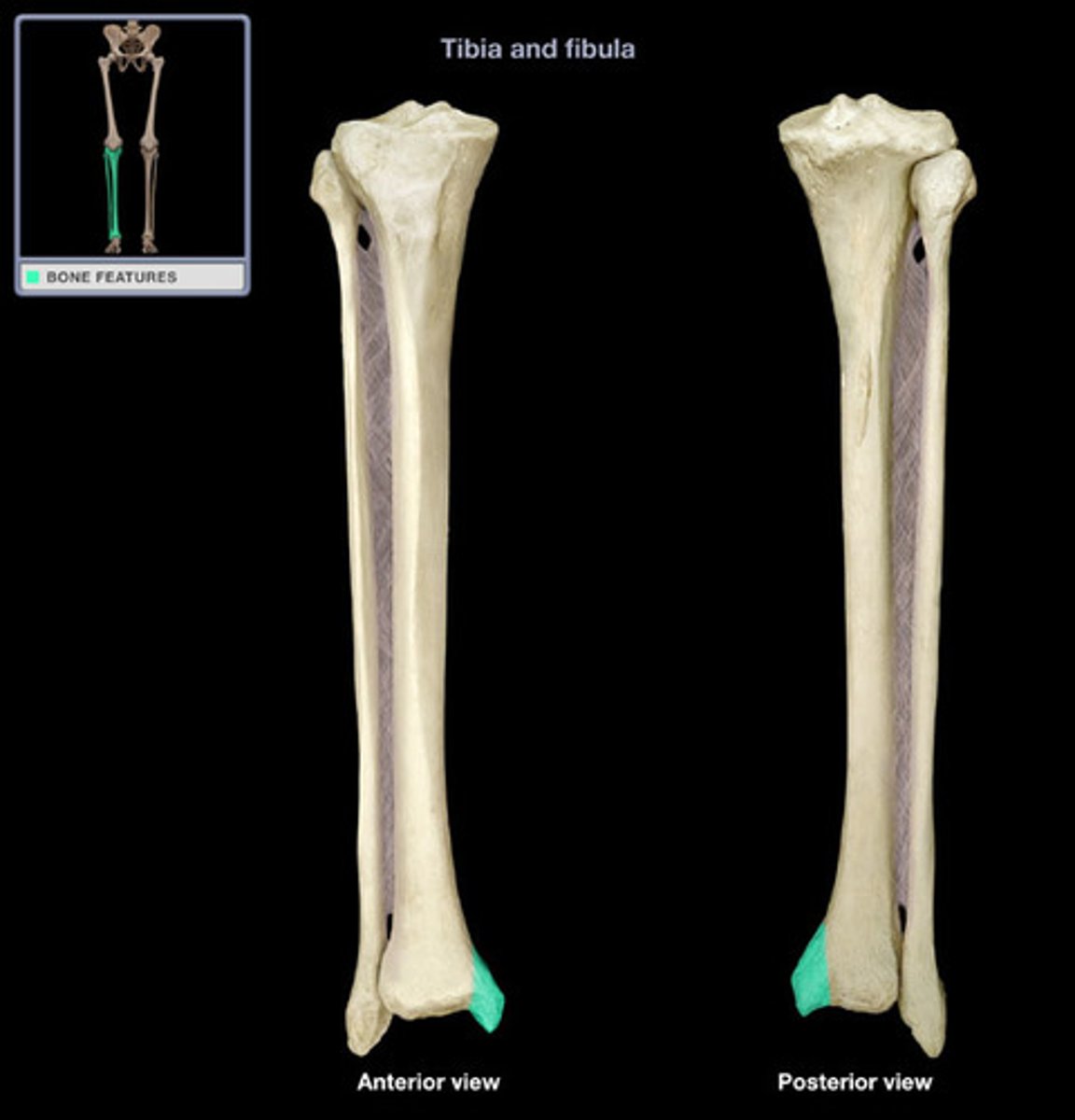
medial malleolus
distal process on medial tibial surface
articular surface of medial condyle
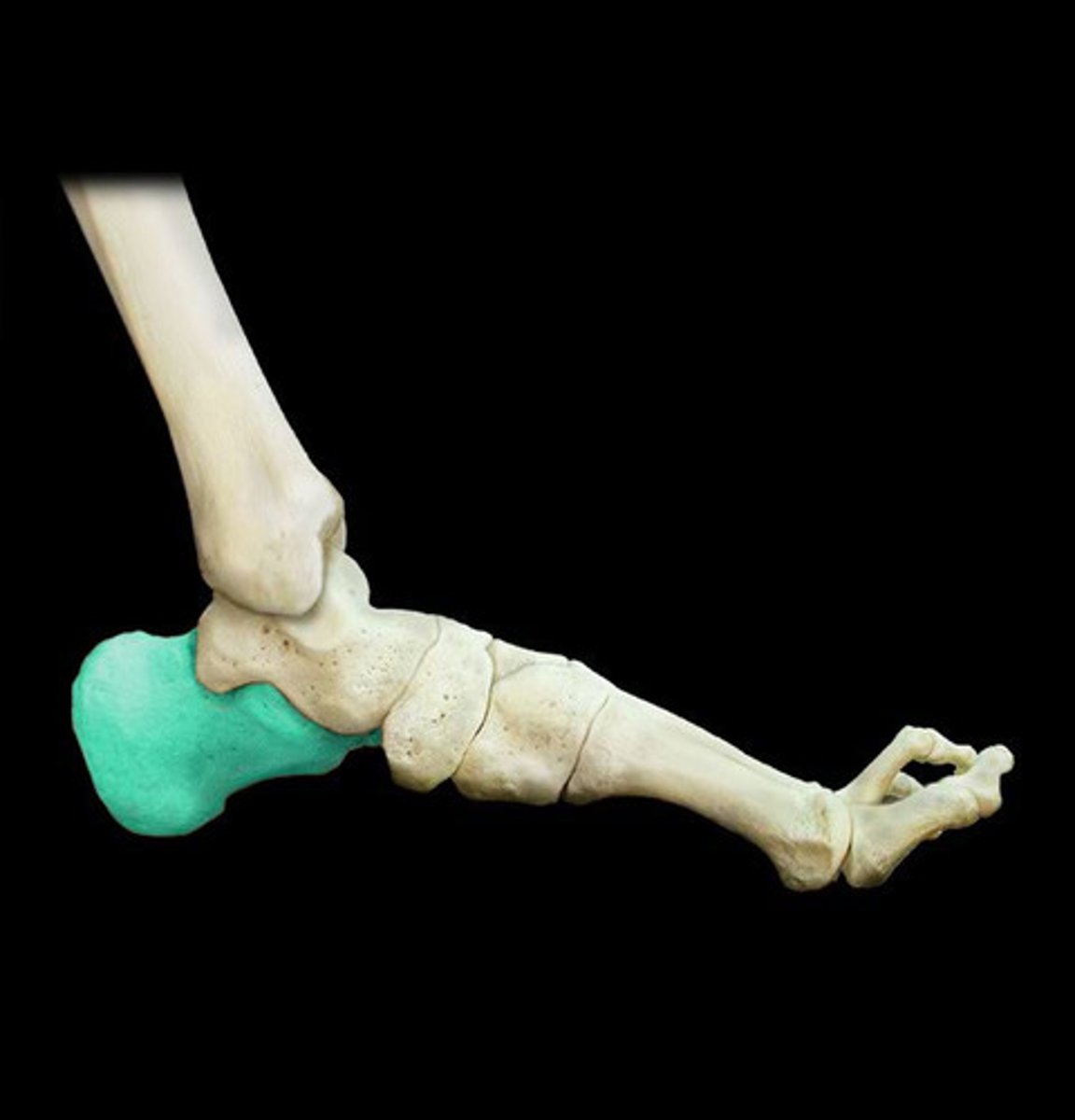
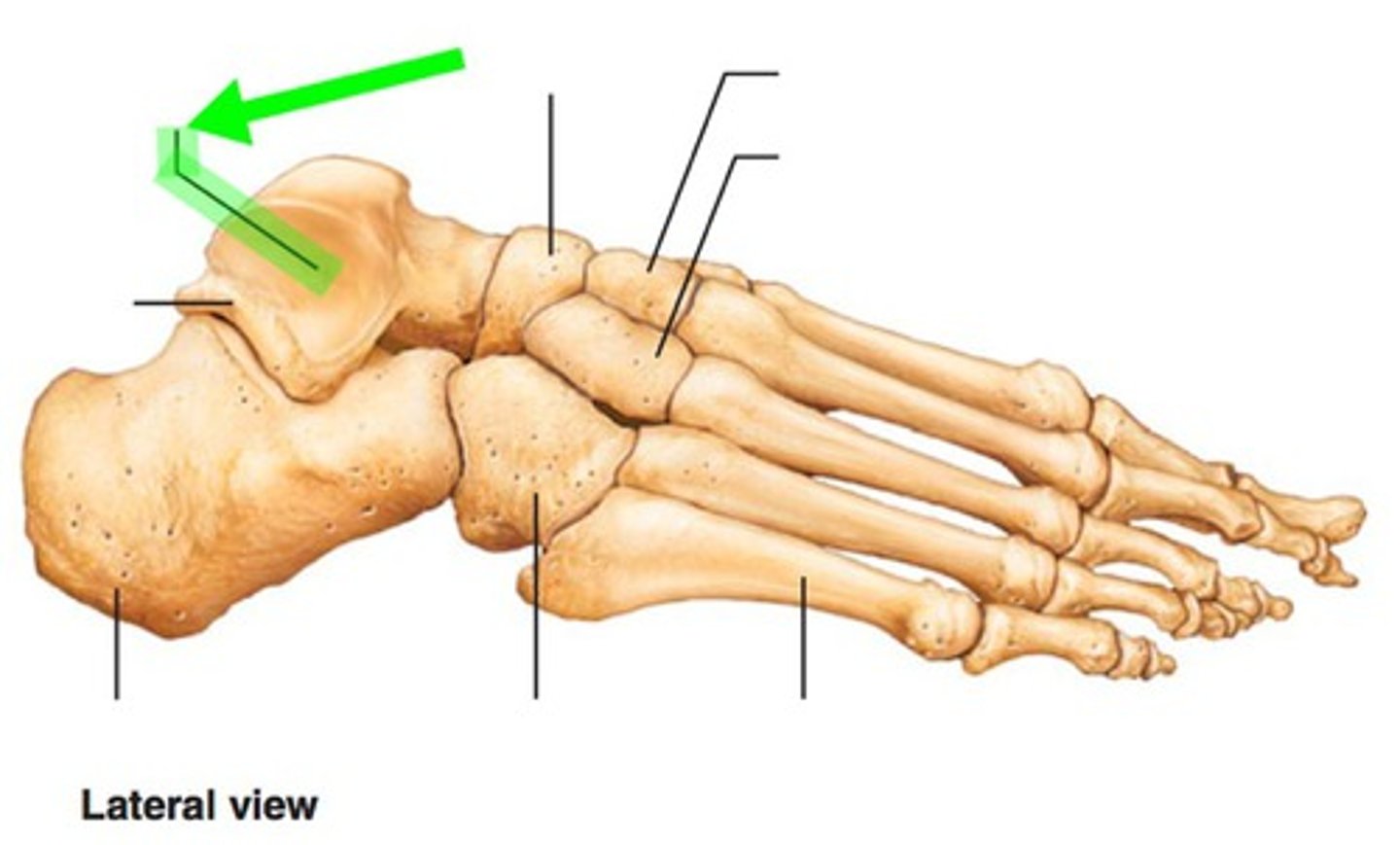
calcaneus
trochlea of talus
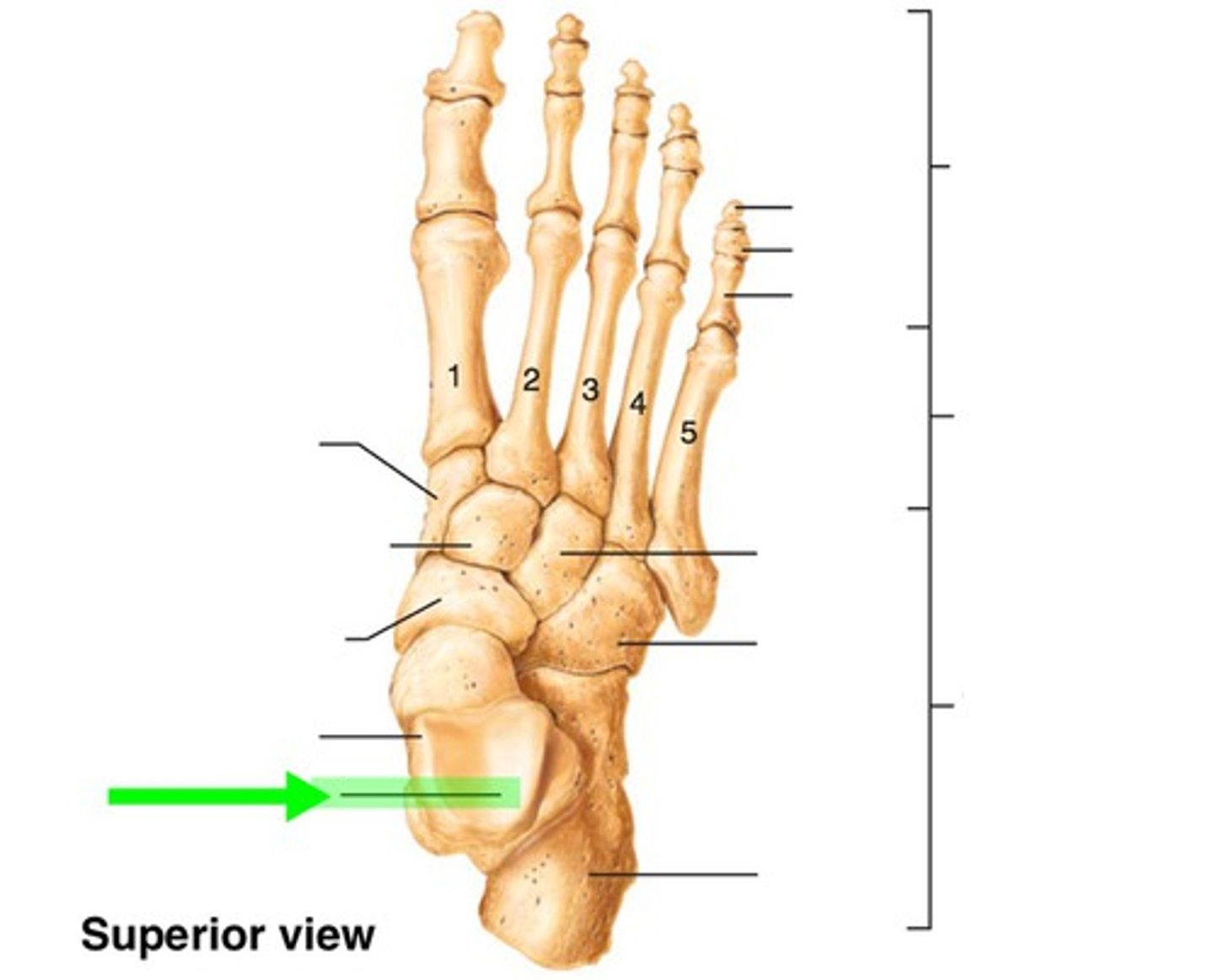
navicular
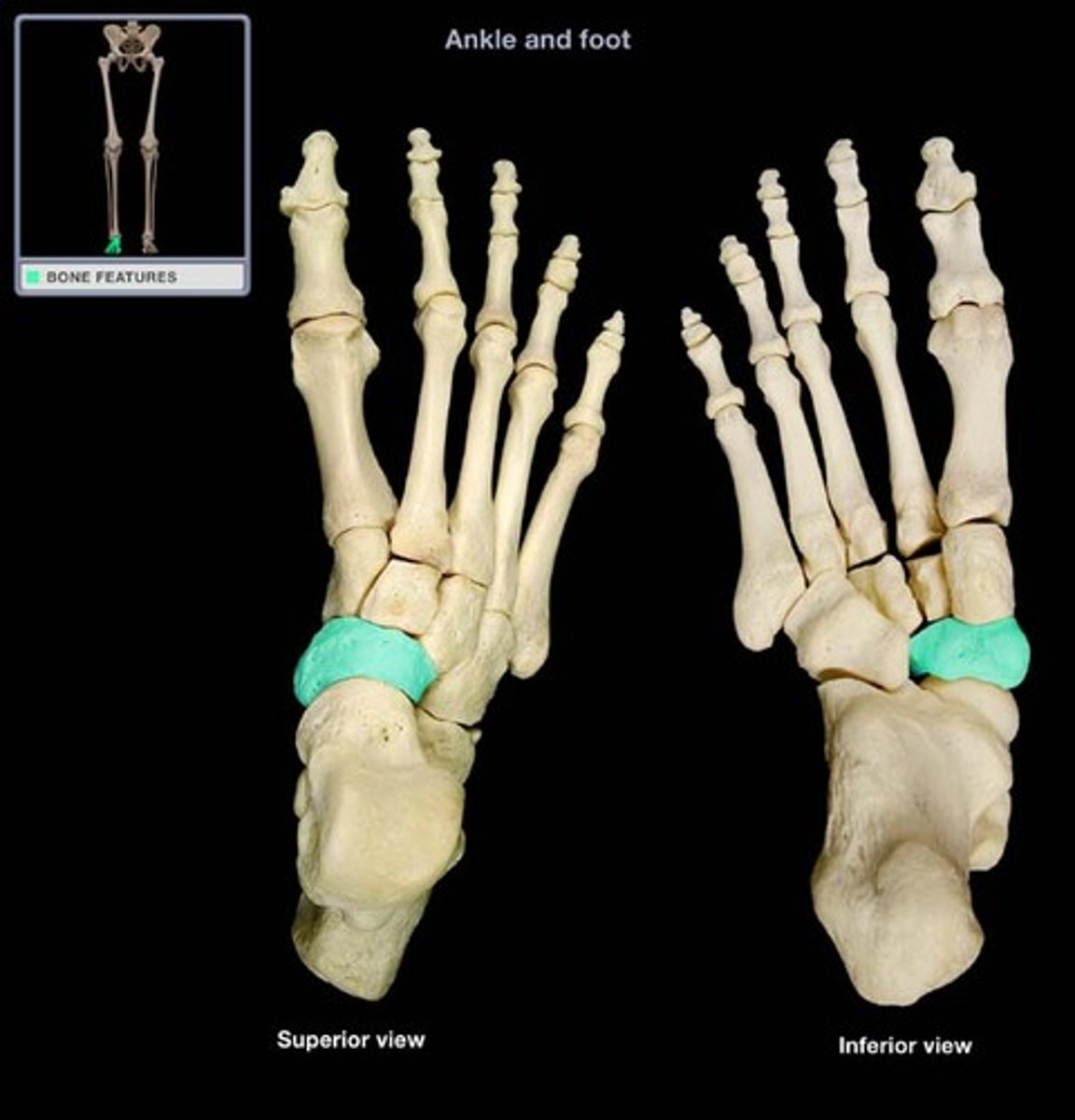
intermediate cuneiform
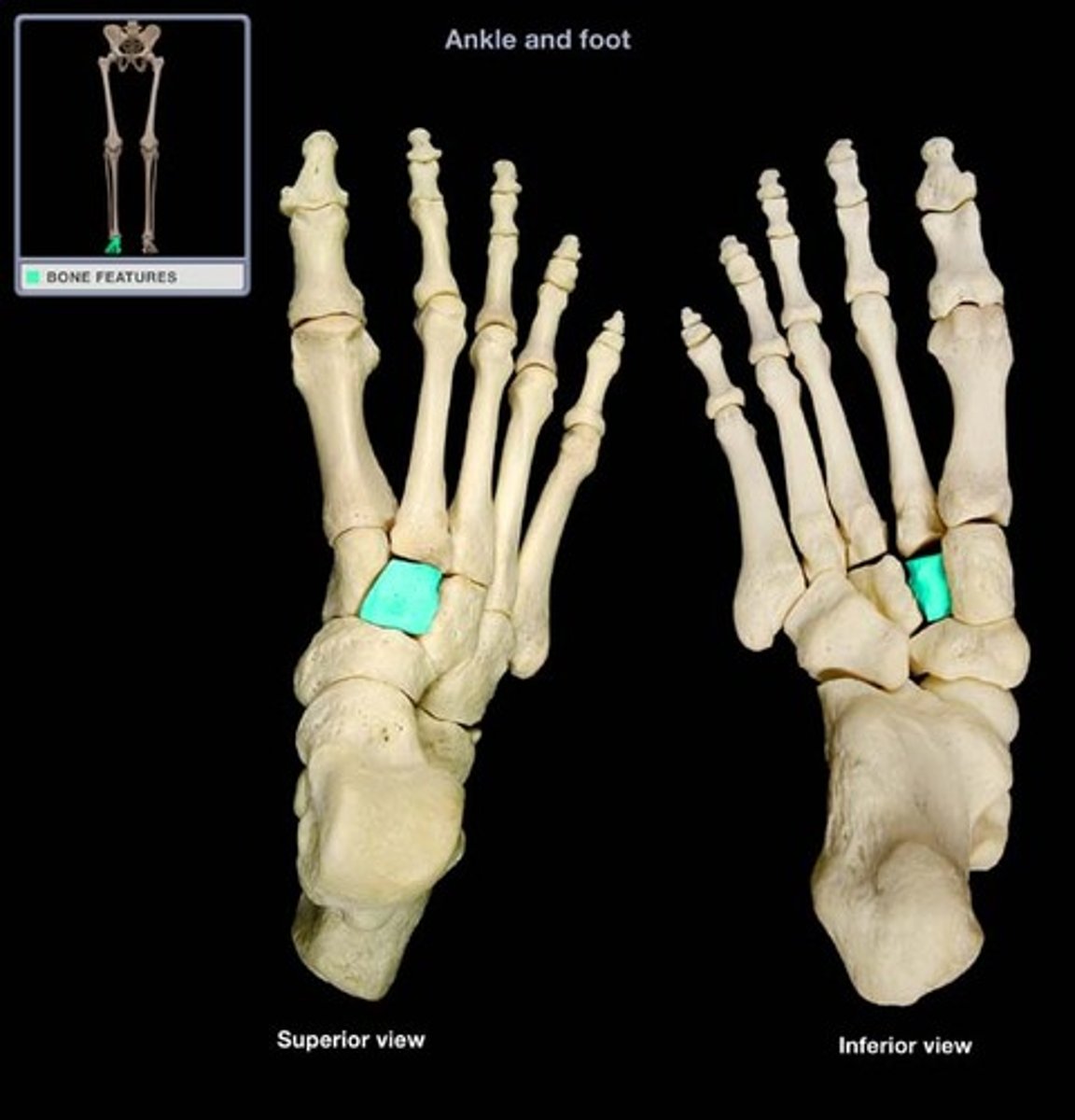
medial cuneiform
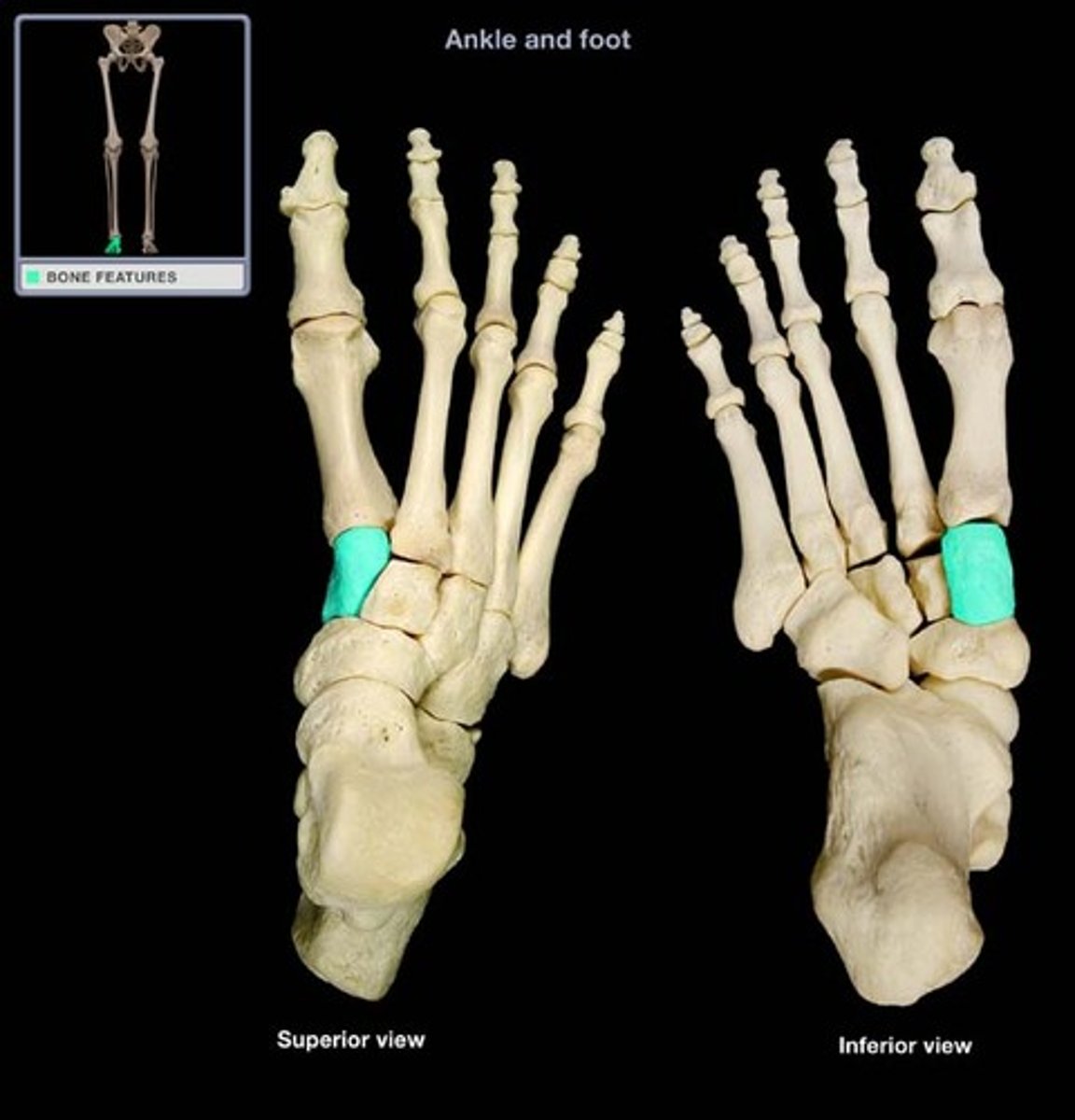
lateral cuneiform
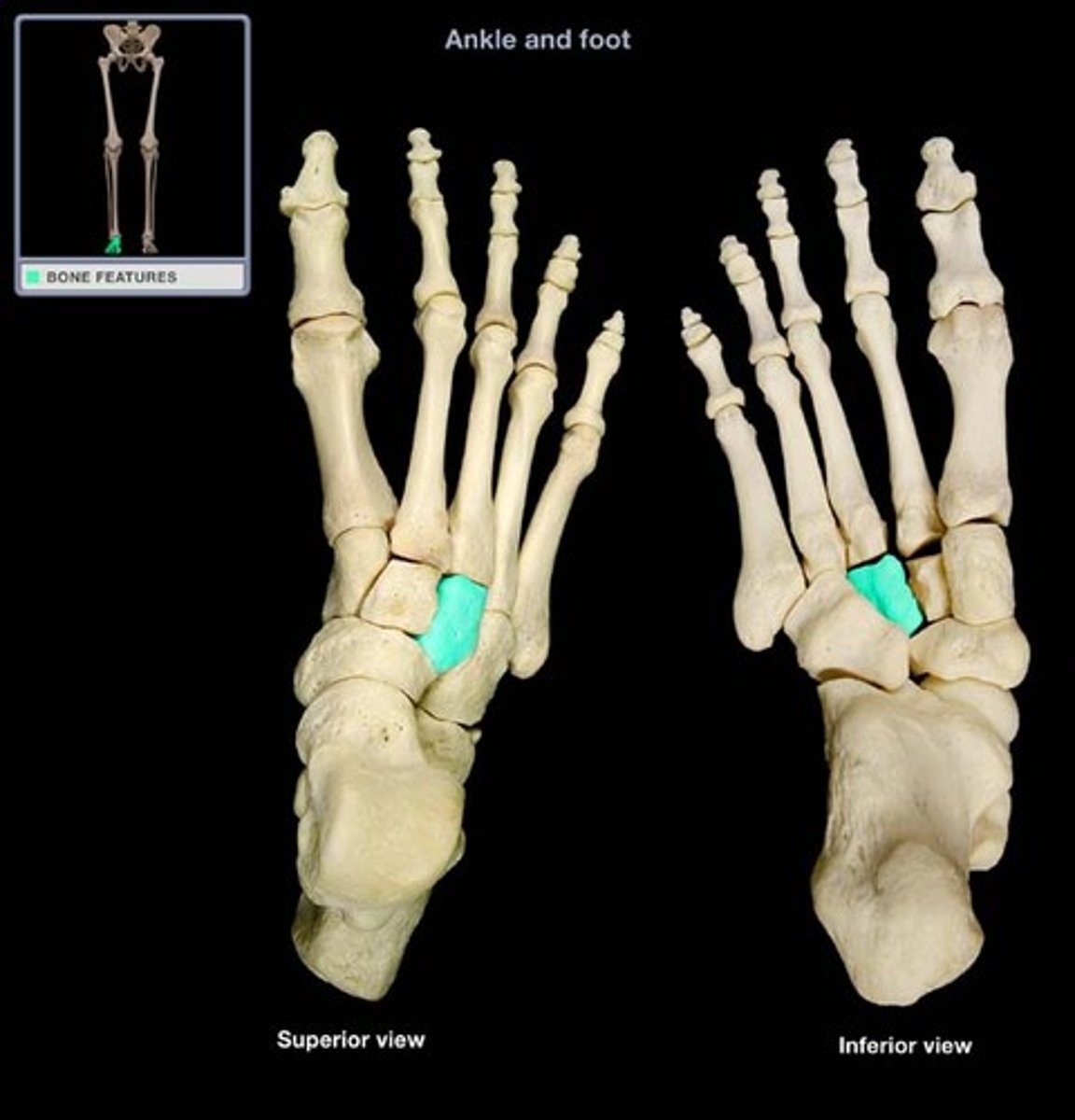
cuboid
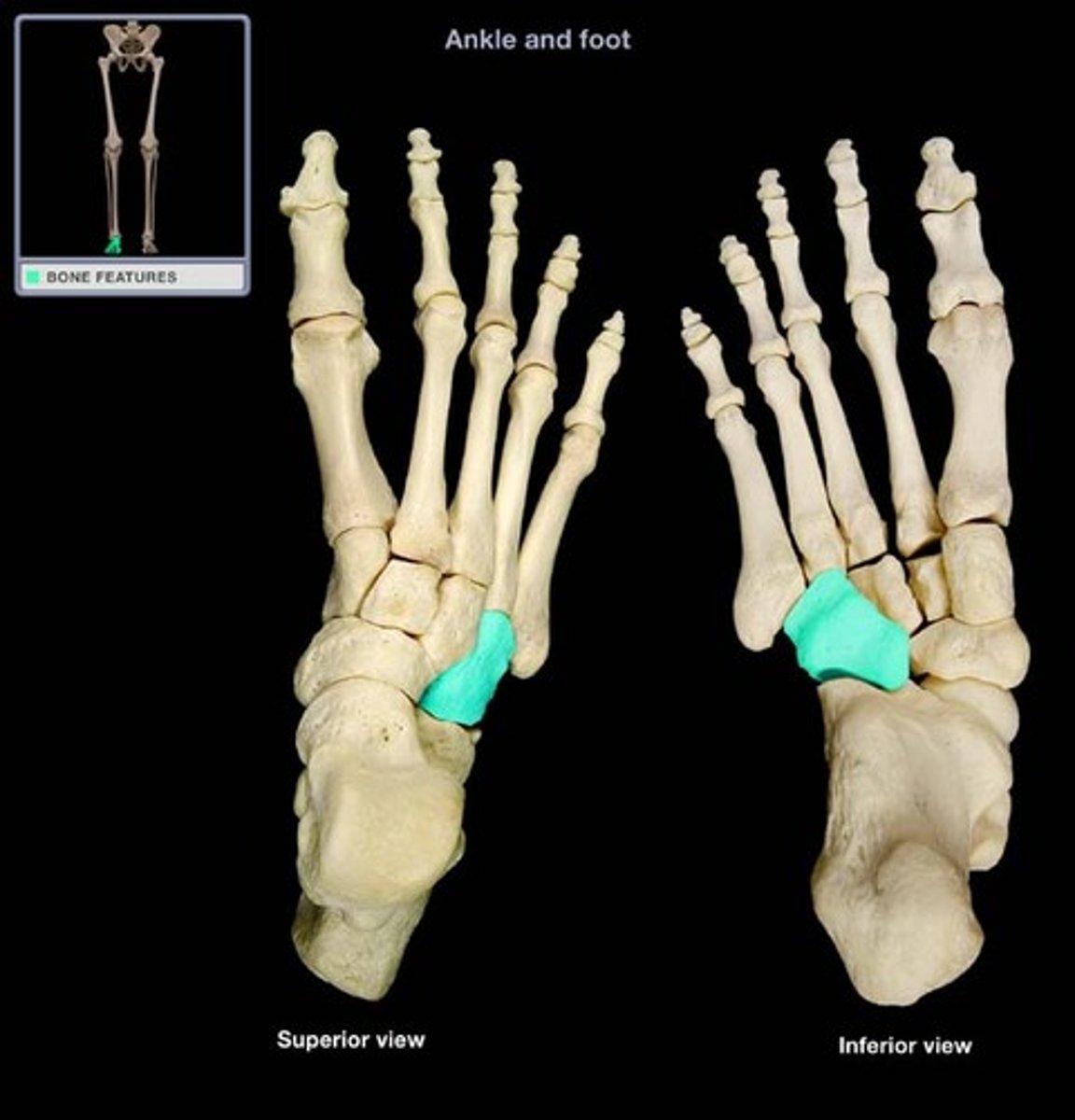
lateral malleolar facet
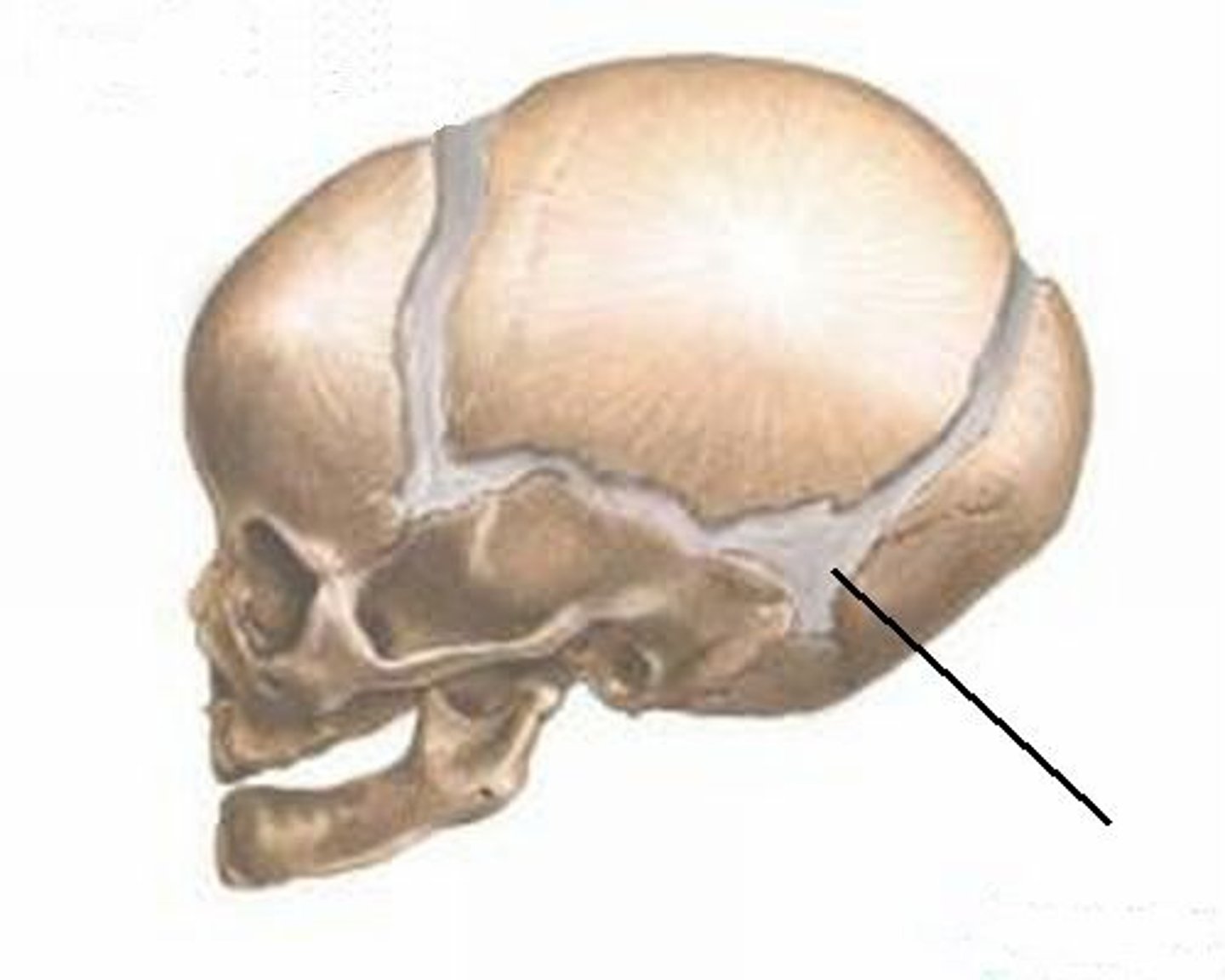
posterior fontanel (joint)
Joint
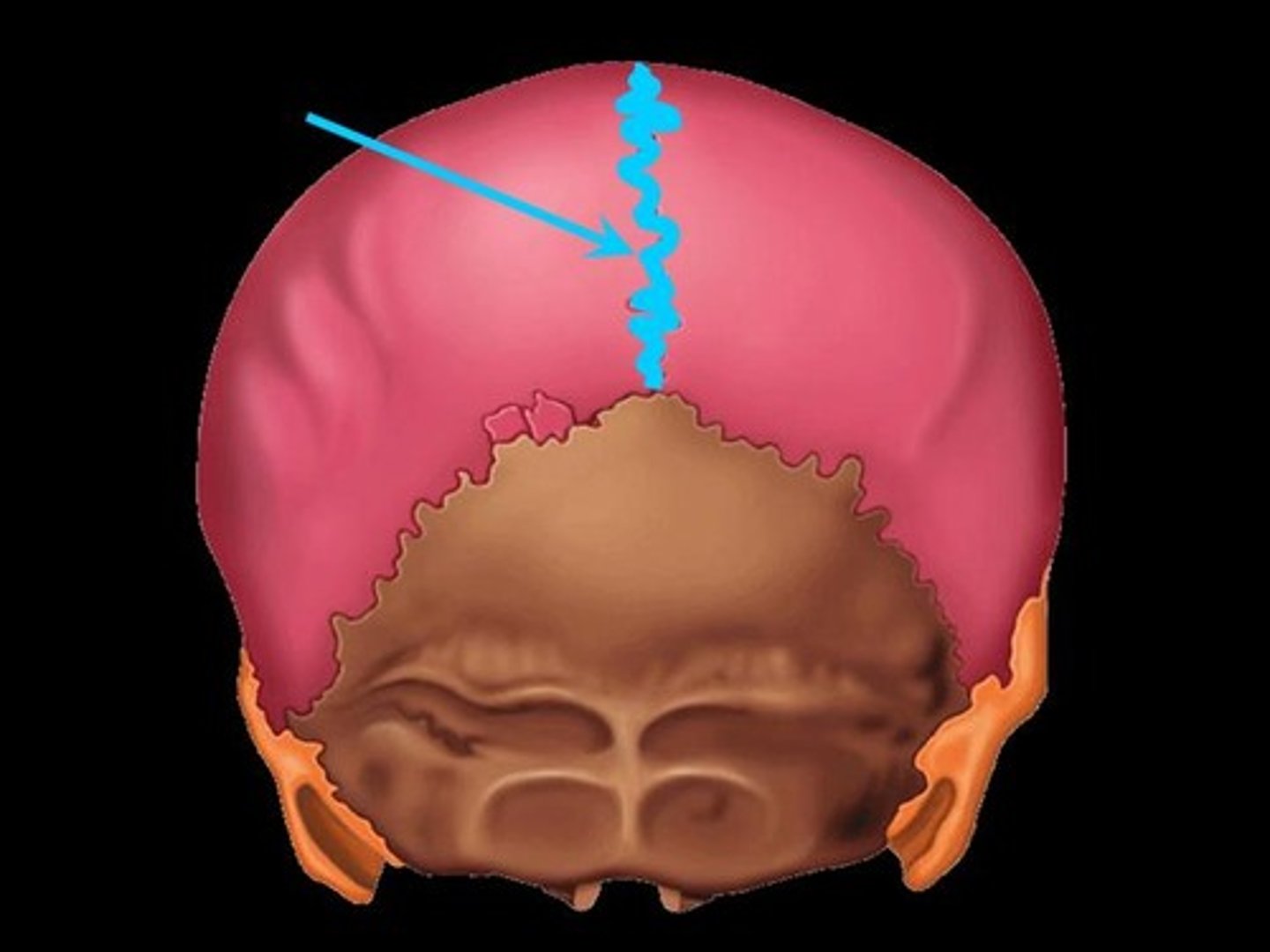
sagittal suture
joint
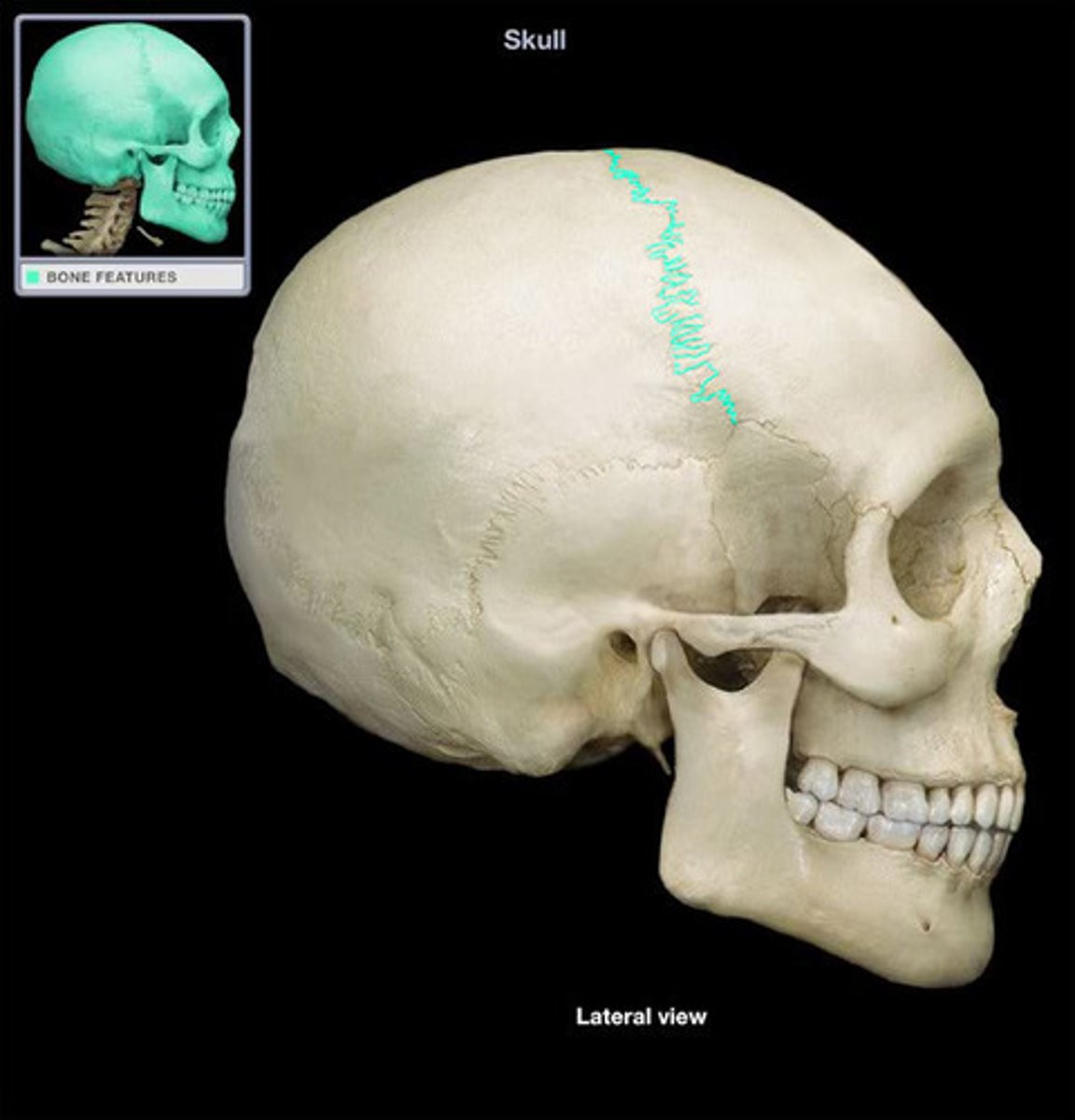
coronal suture
joint
Anterior fontanel
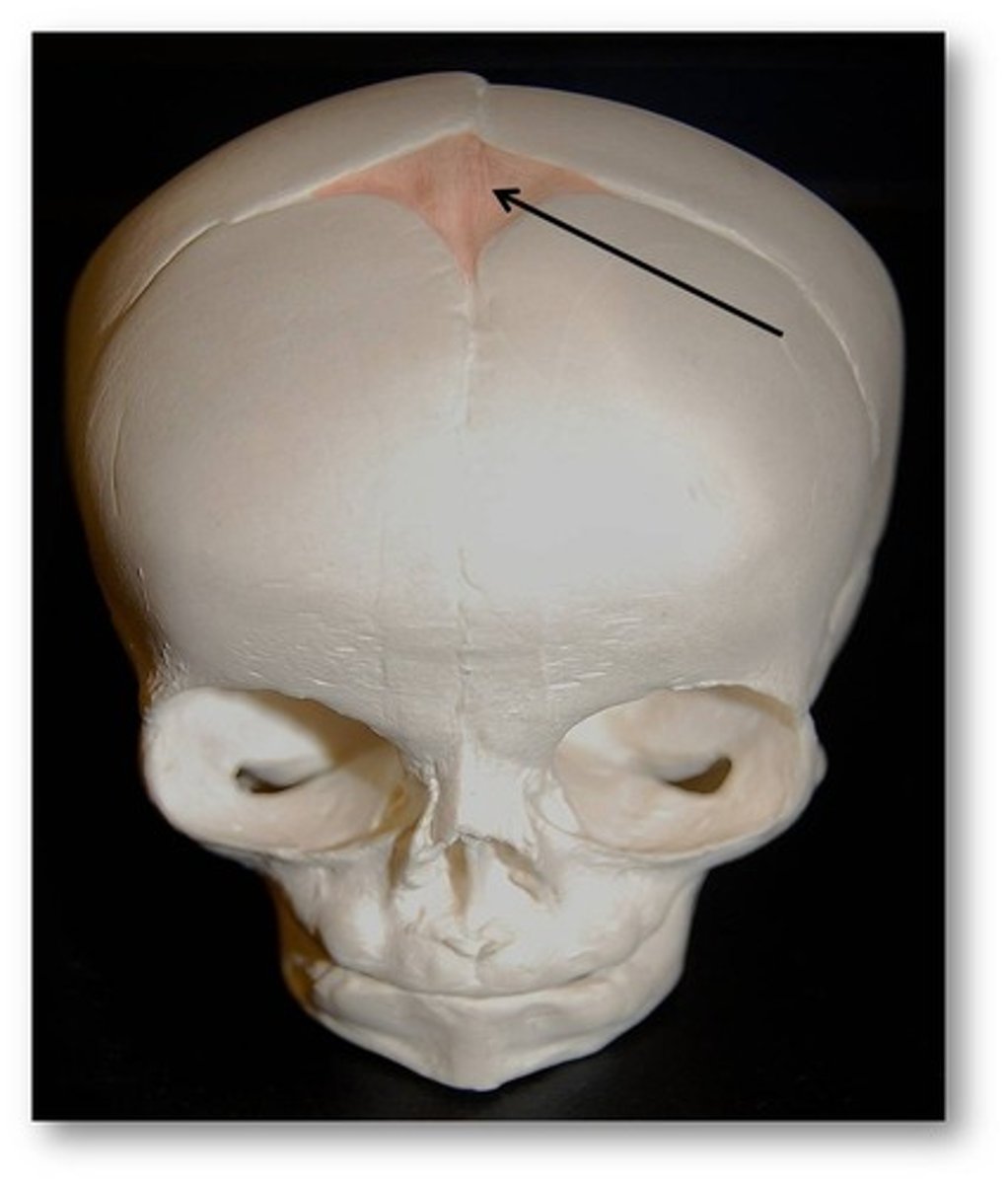
Synarthroses
joints held together by fibroue connective tissue
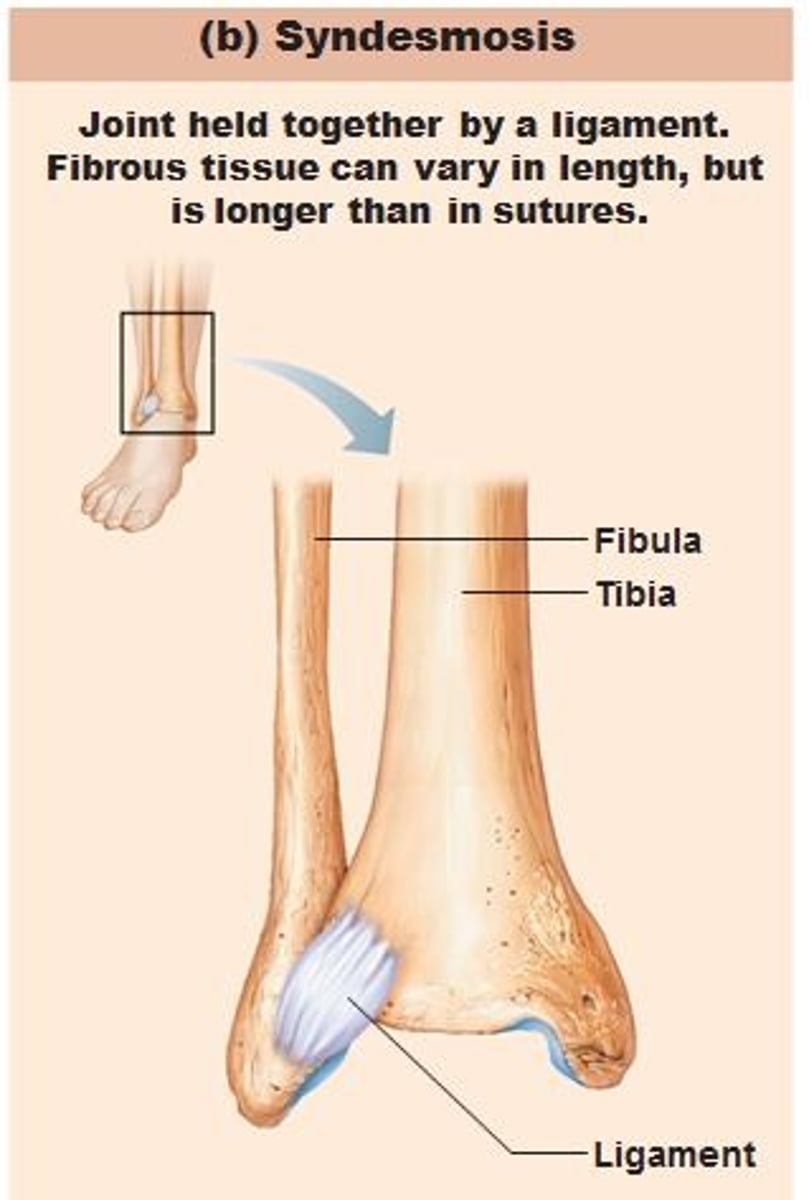
Syndesmoses
bones are united by connective tissue bands
*allow very slight movement
*ex: distal tibia and fibula, interosseous membrane between radius and ulna
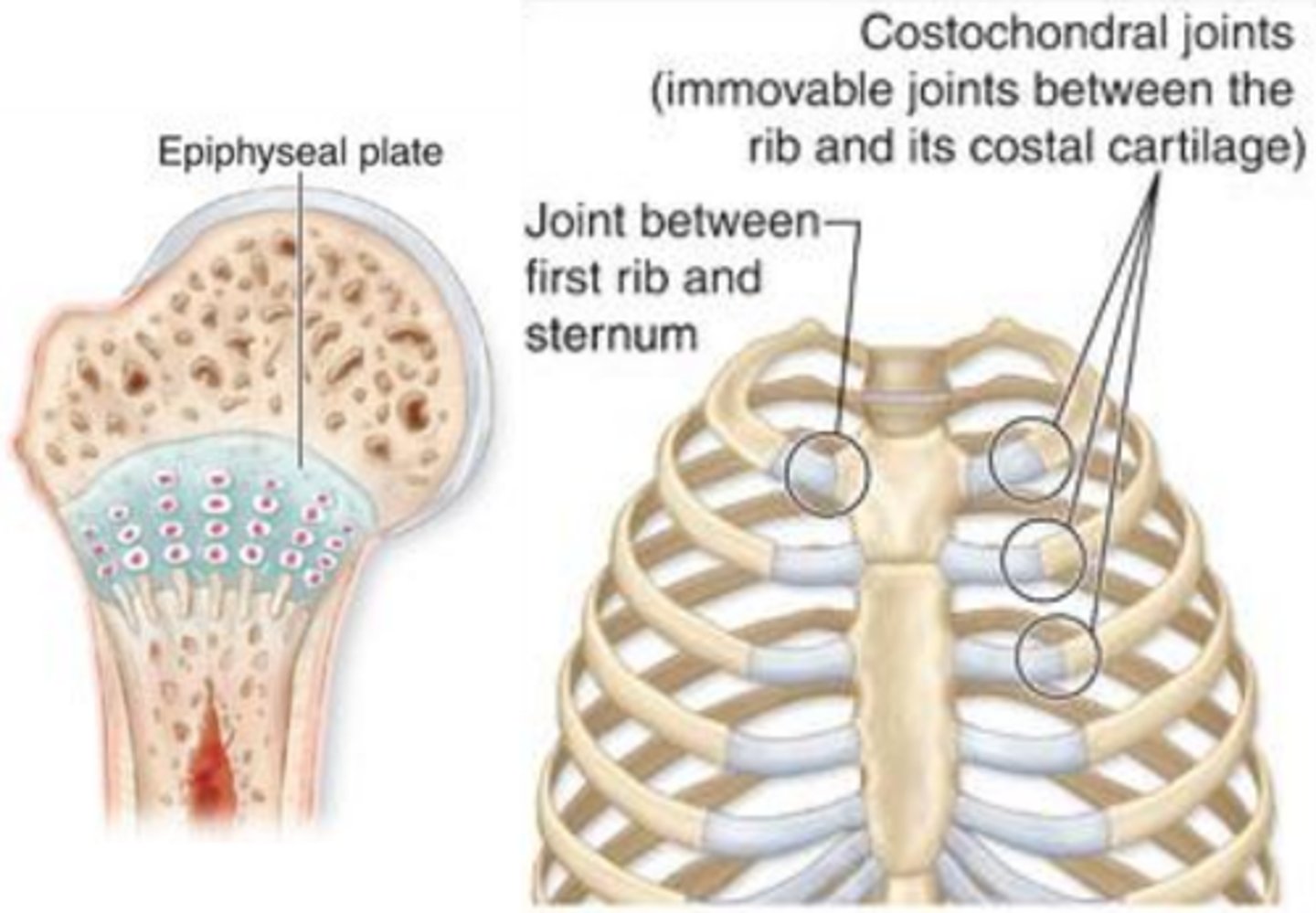
Synchondrosis
bones separated by hyaline cartilage
Permits slight bending in early life
ossify as time passes
Ex: epiphyseal plates and costal cartilages
what are bones separated by?
Cartilage in cartilaginous joints
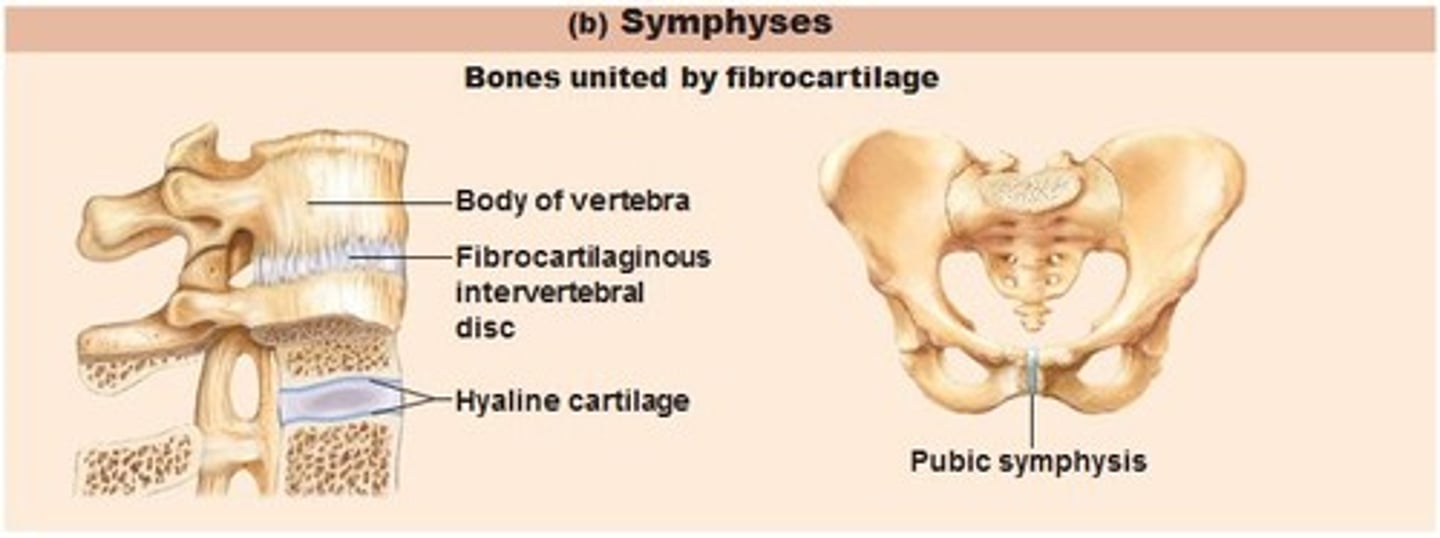
Symphyses (Cartilaginous Joint)
bones are articulates by a disk of fibrocartilage and allow slight movement
Ex: pubic symphysis, intervertebral disks
What are synovial joints surrounded by?
Synovial membranes
Synovial joints
contain synovial membranes which secrete hyaluronic acid (slippery)
Reduces direct bone to bone contact, many have disks of fibrocartilage that help reduce stress on joint
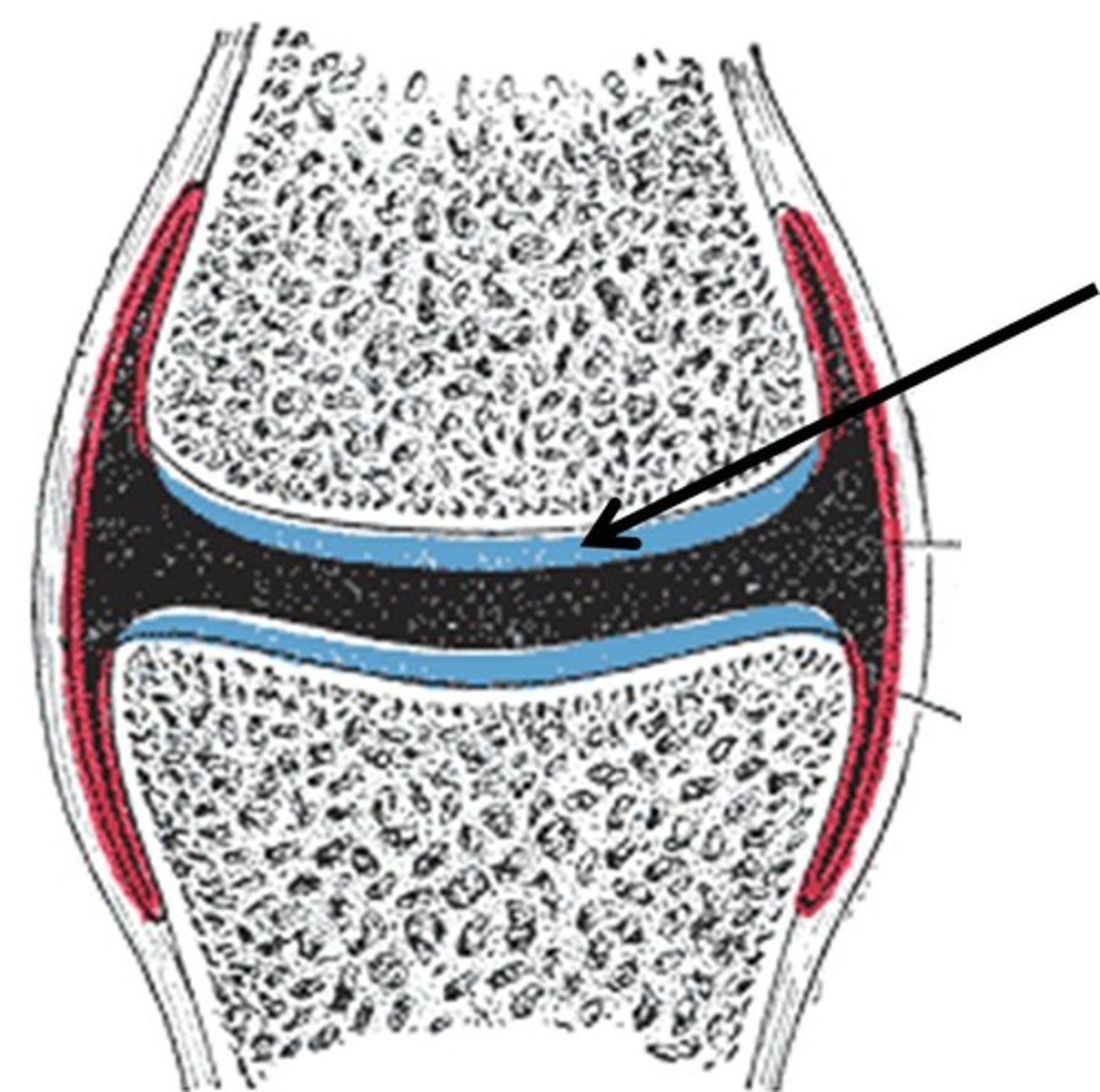
Articular cartilage
Fibrous joint capsule
3 functional classes of synovial joints
•Monaxial : movement of a joint in only one direction
•Biaxial : movement of a joint in two directions
•Multiaxial : movement of joint in more than two direction
Synovial cavity
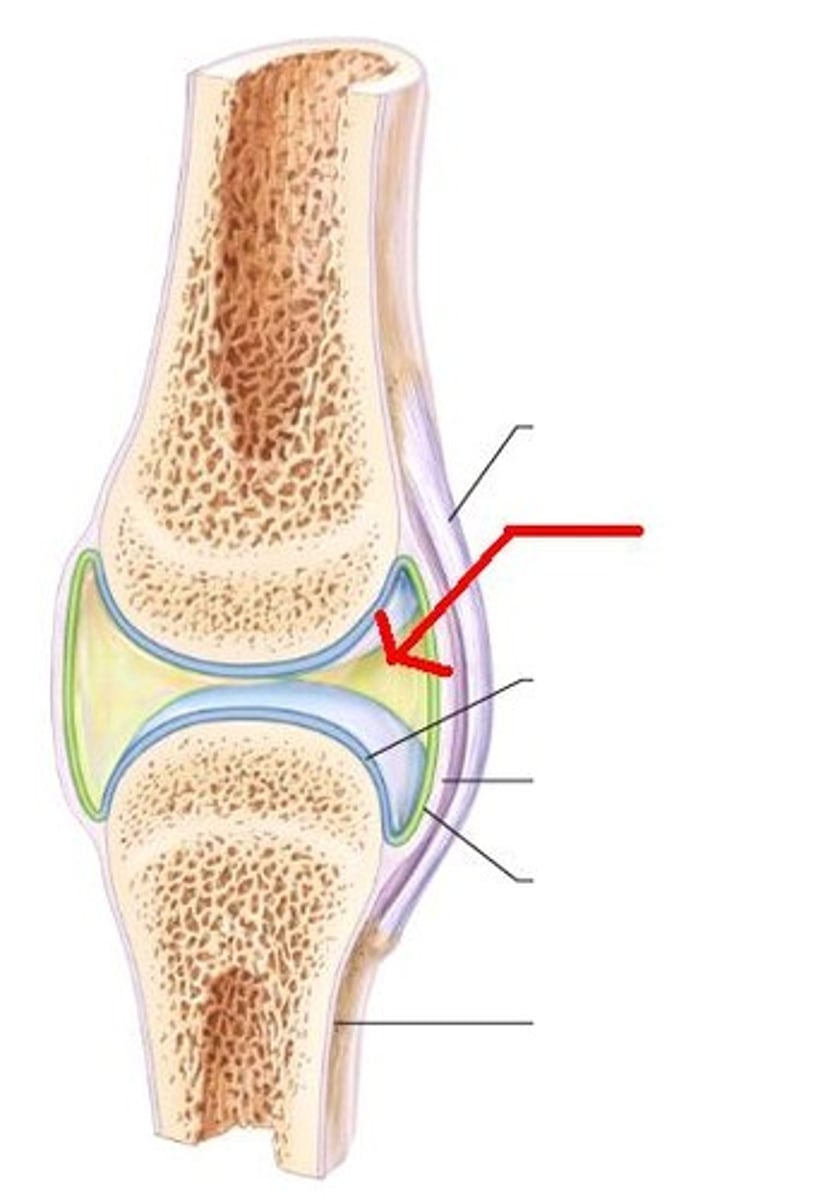
bursa
Joint capsule
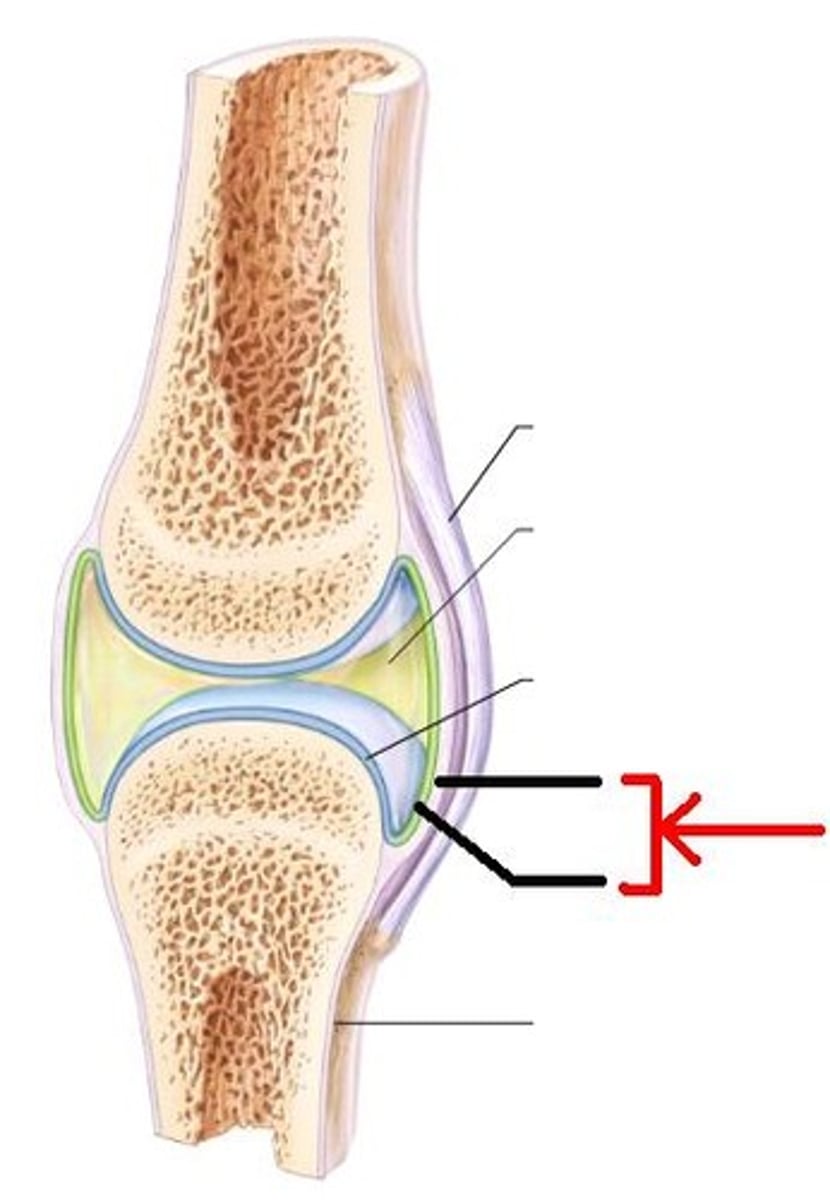
articular cartilage
ligament
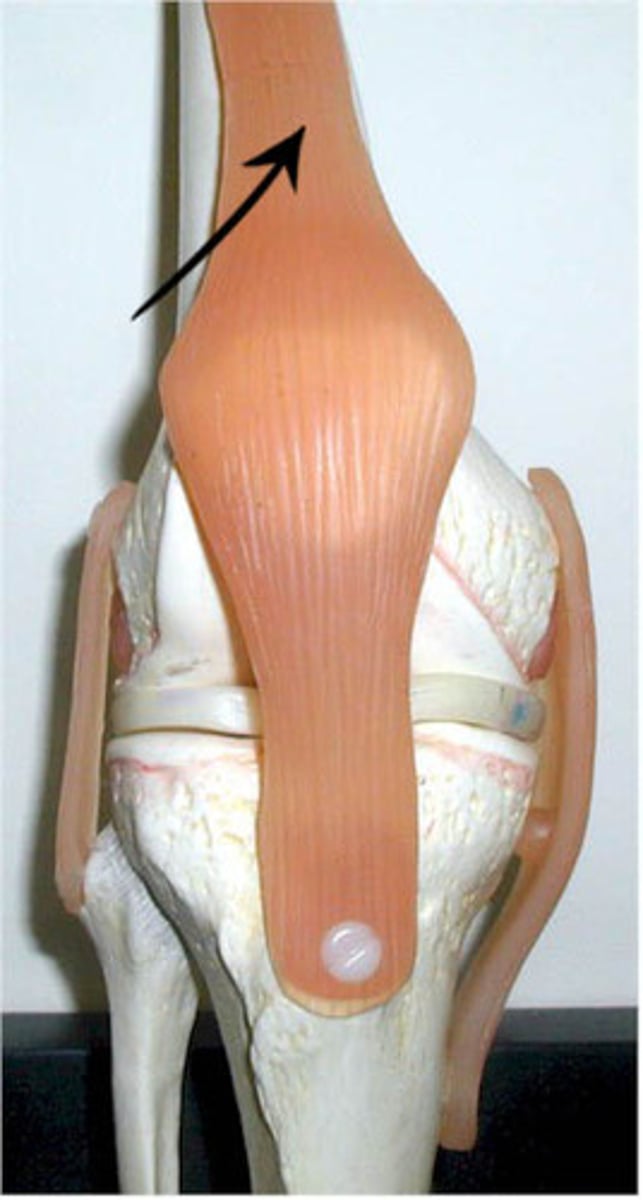
tendon
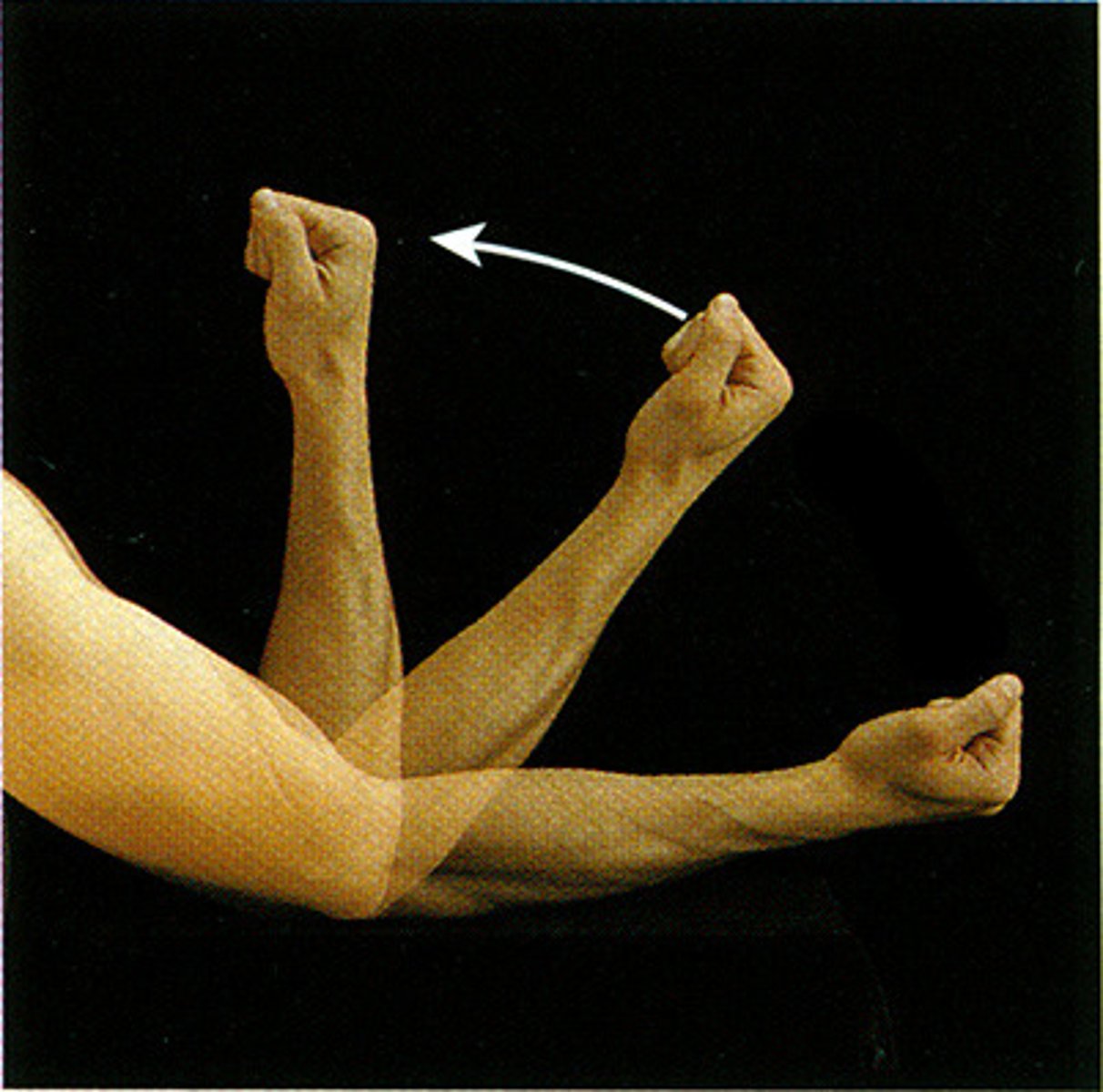
flexion
bringing two ventral surfaces closer together (except the knee)
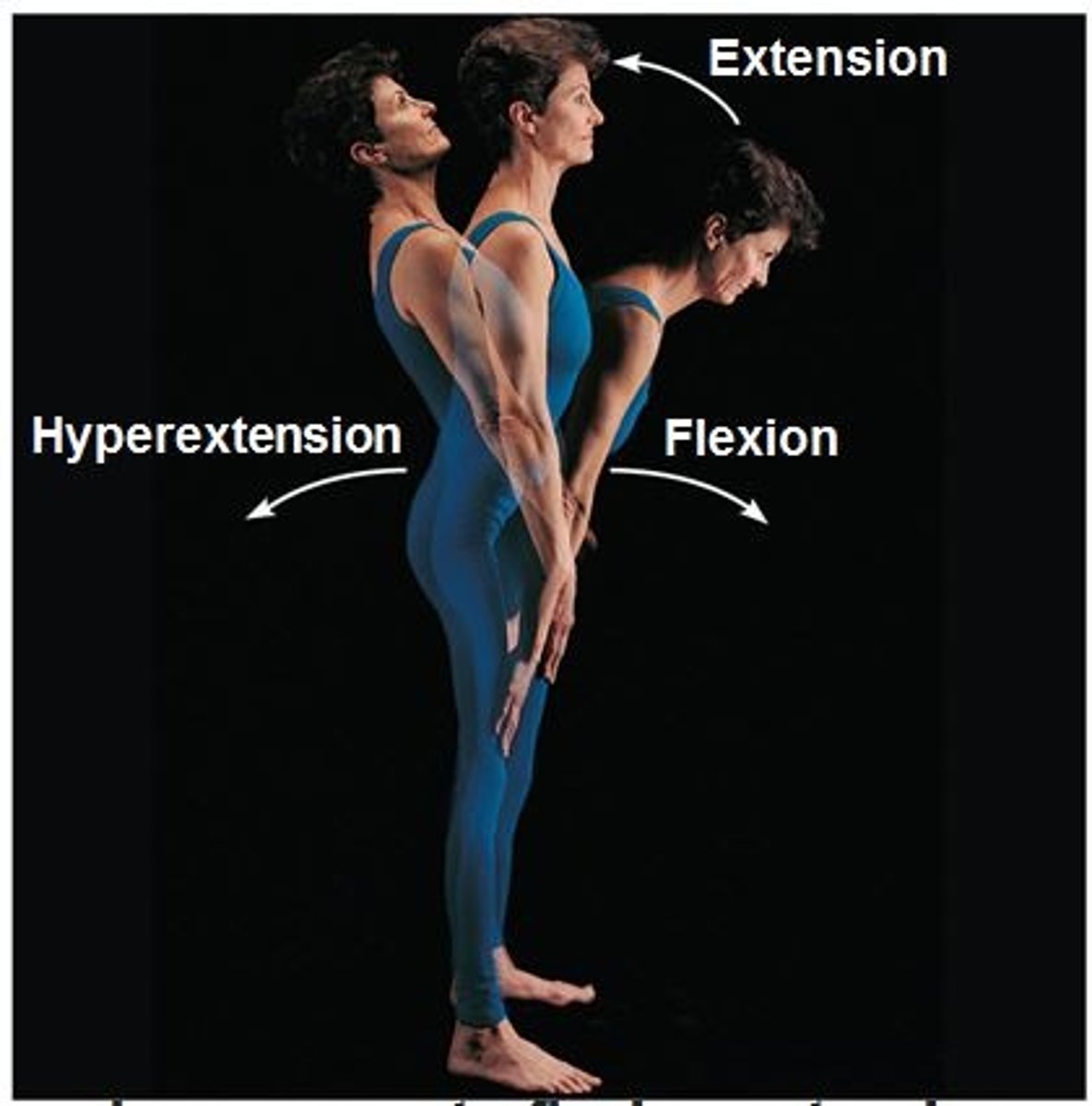
Extension
opposite of flexion
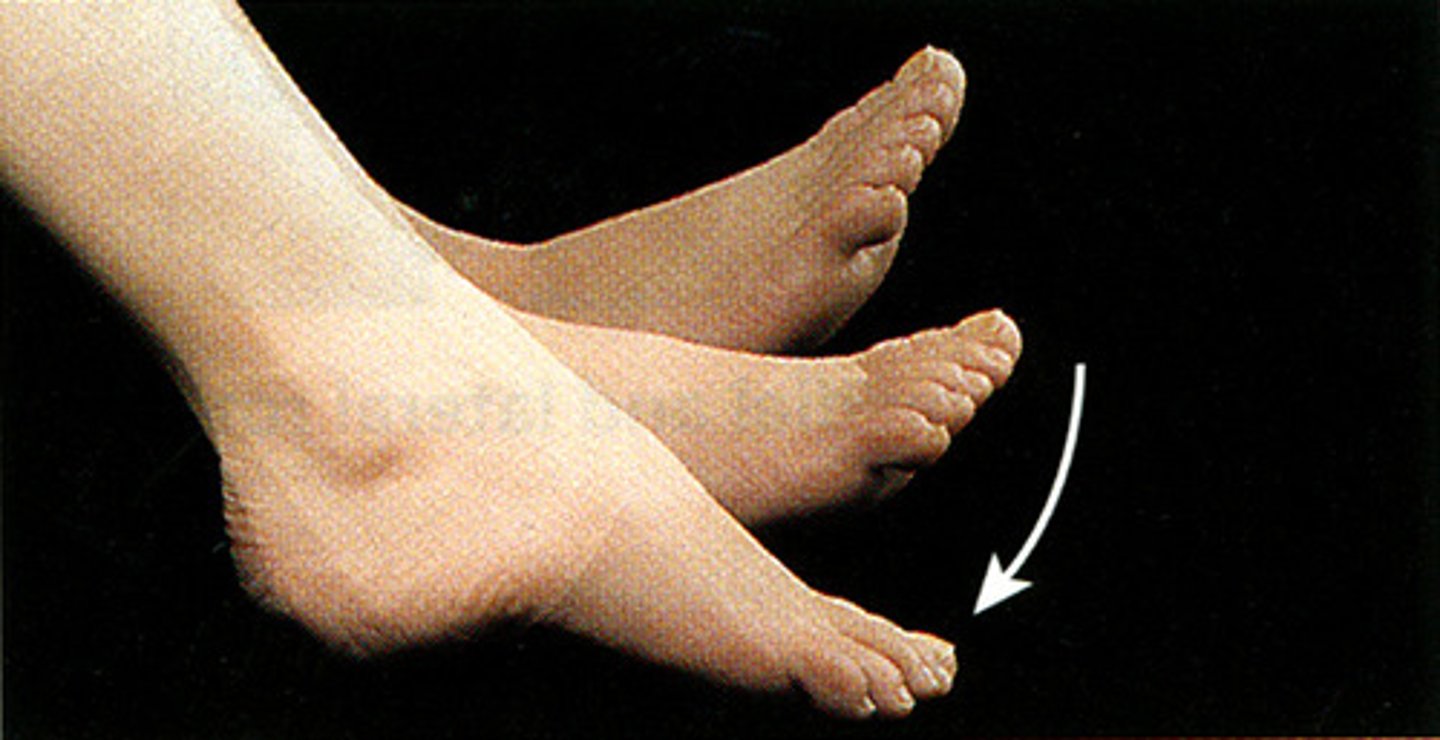
dorsiflexion
bringing the toes toward the shin
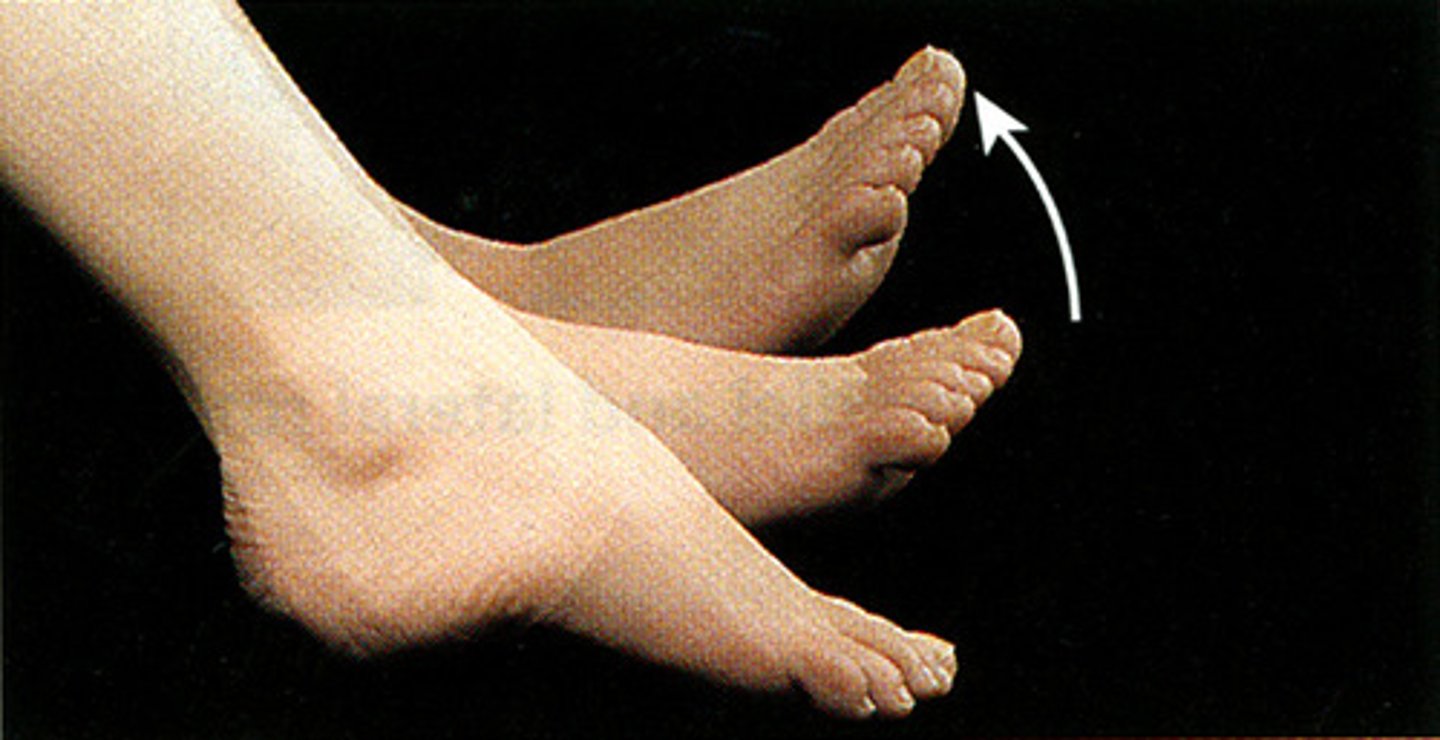
plantar flexion
flexion of the toes
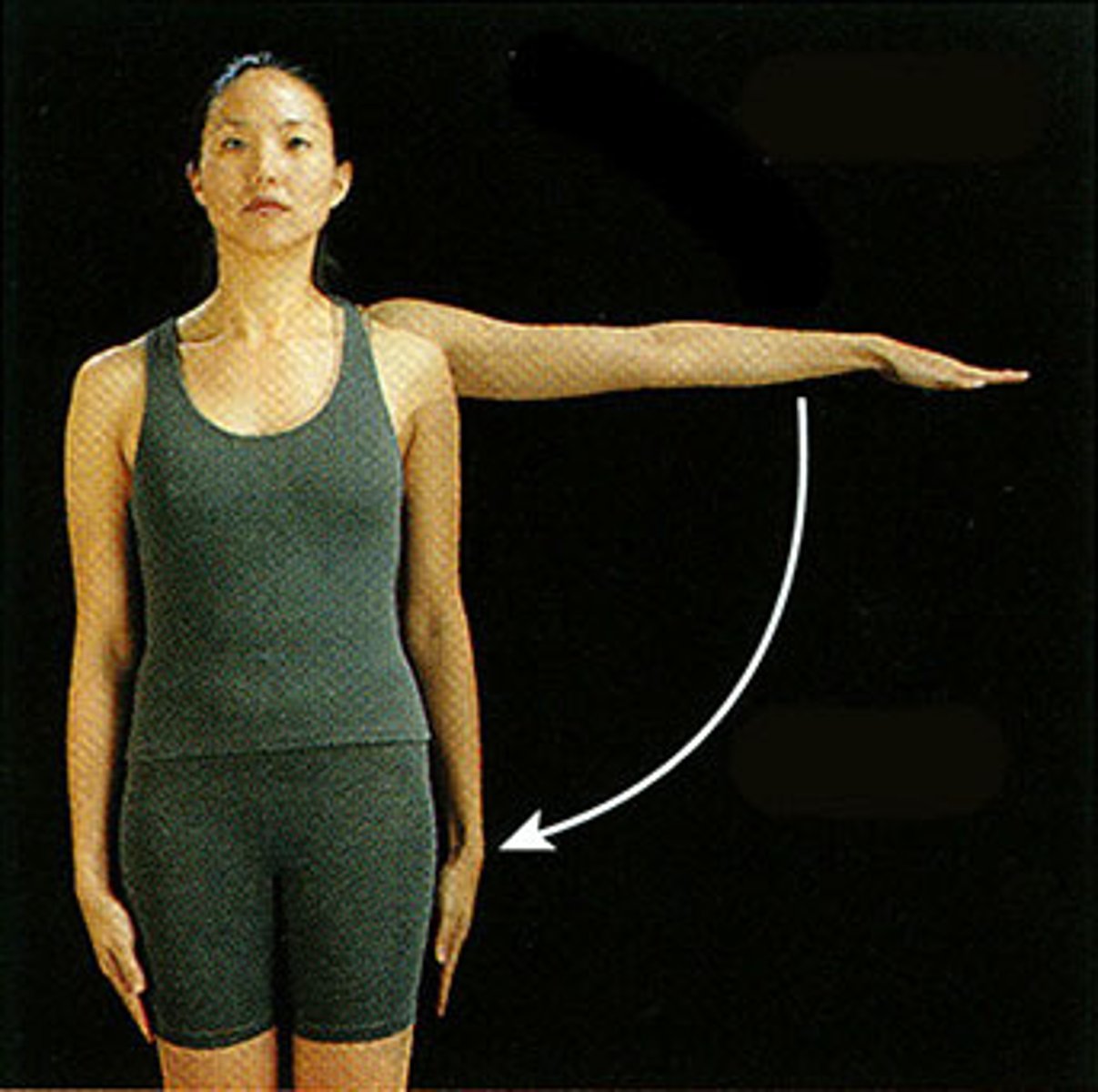
Abduction
movement of a limb away from the midline (note fingers)
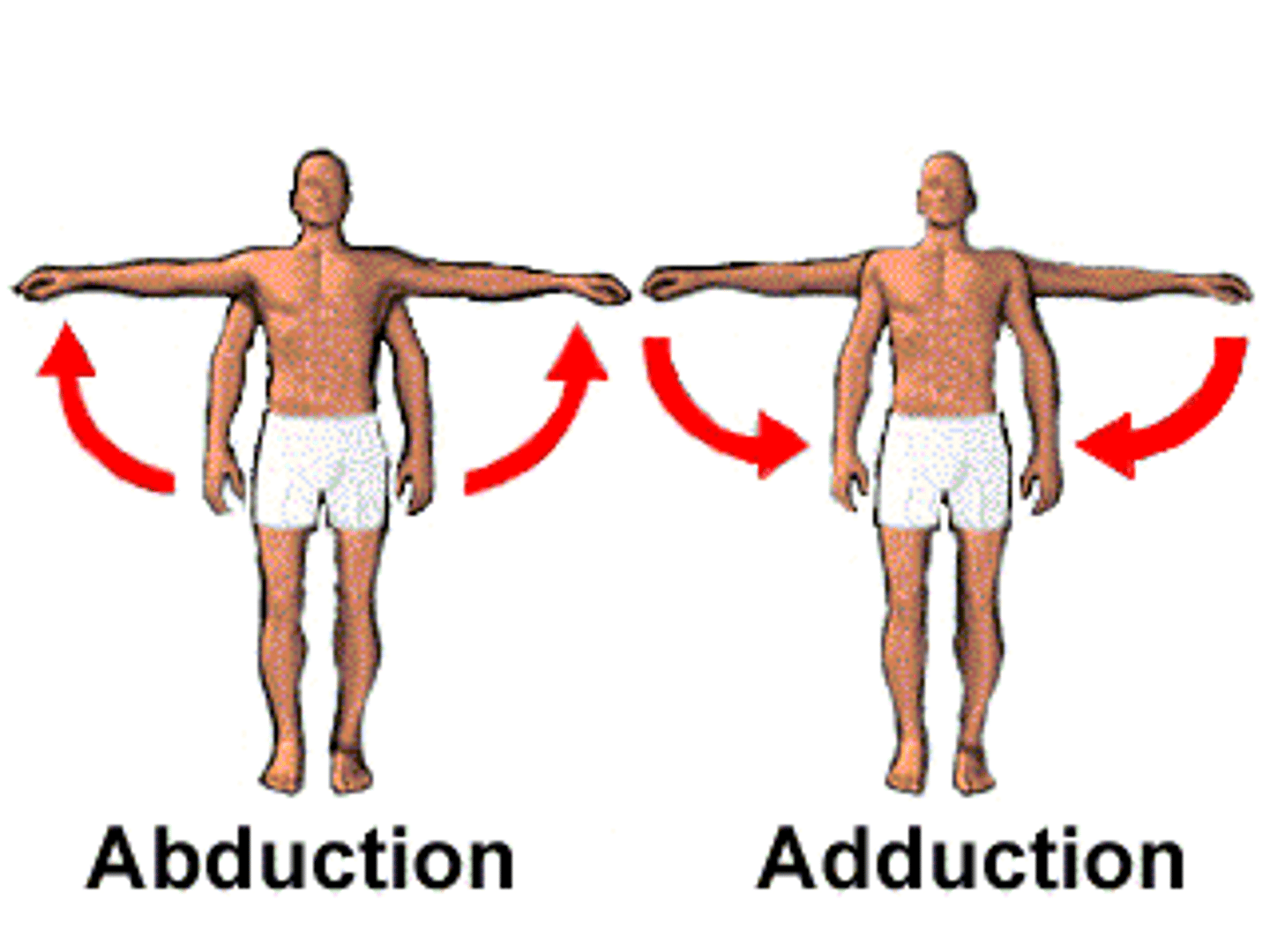
adduction
movement of limb toward the midline

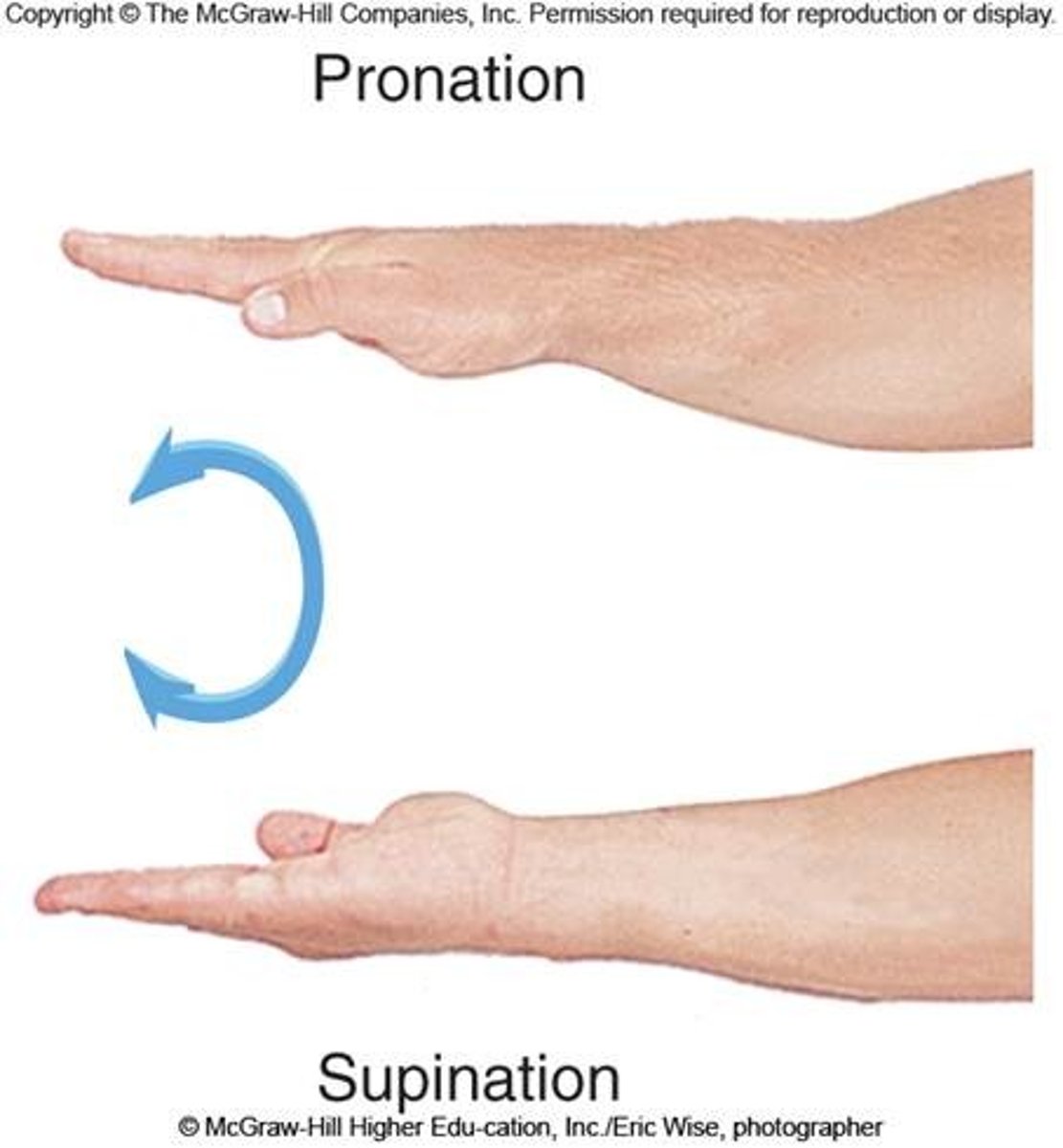
pronation
make the palm face posterior in AP
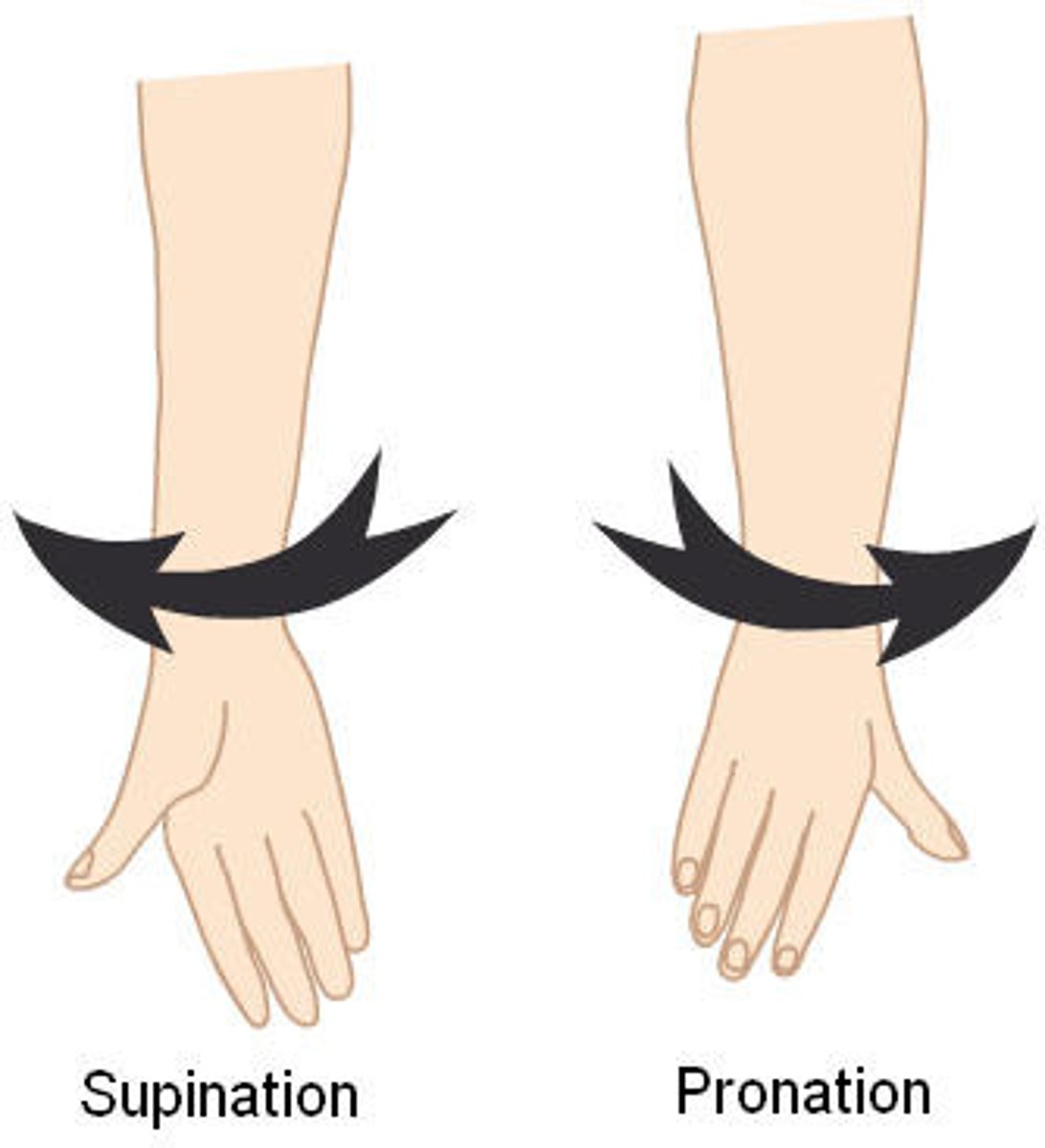
Supination
make the palm face anterior in ap
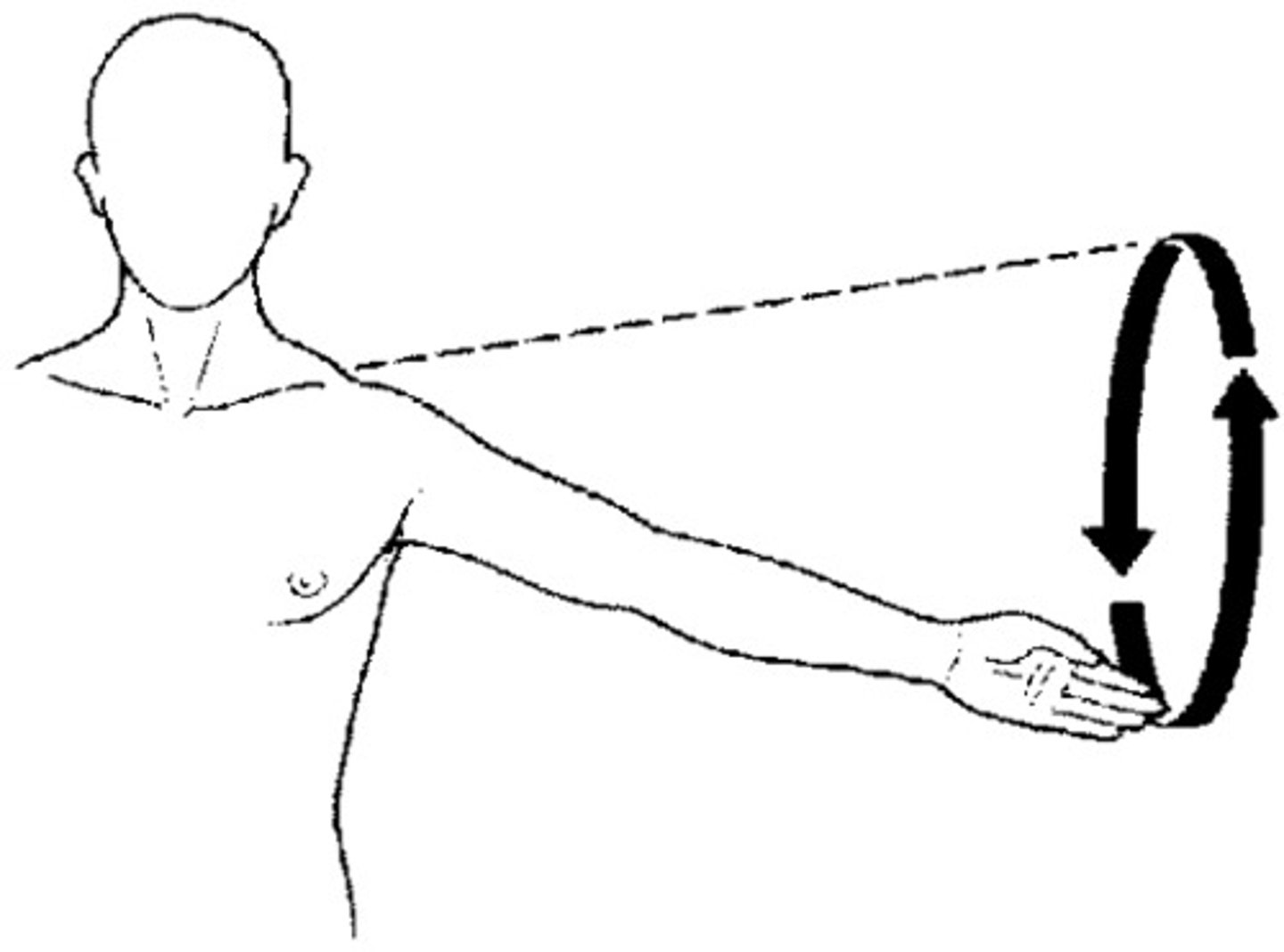
Circumduction
the distal end of a bone describes a circle while the proximal end stays staionary
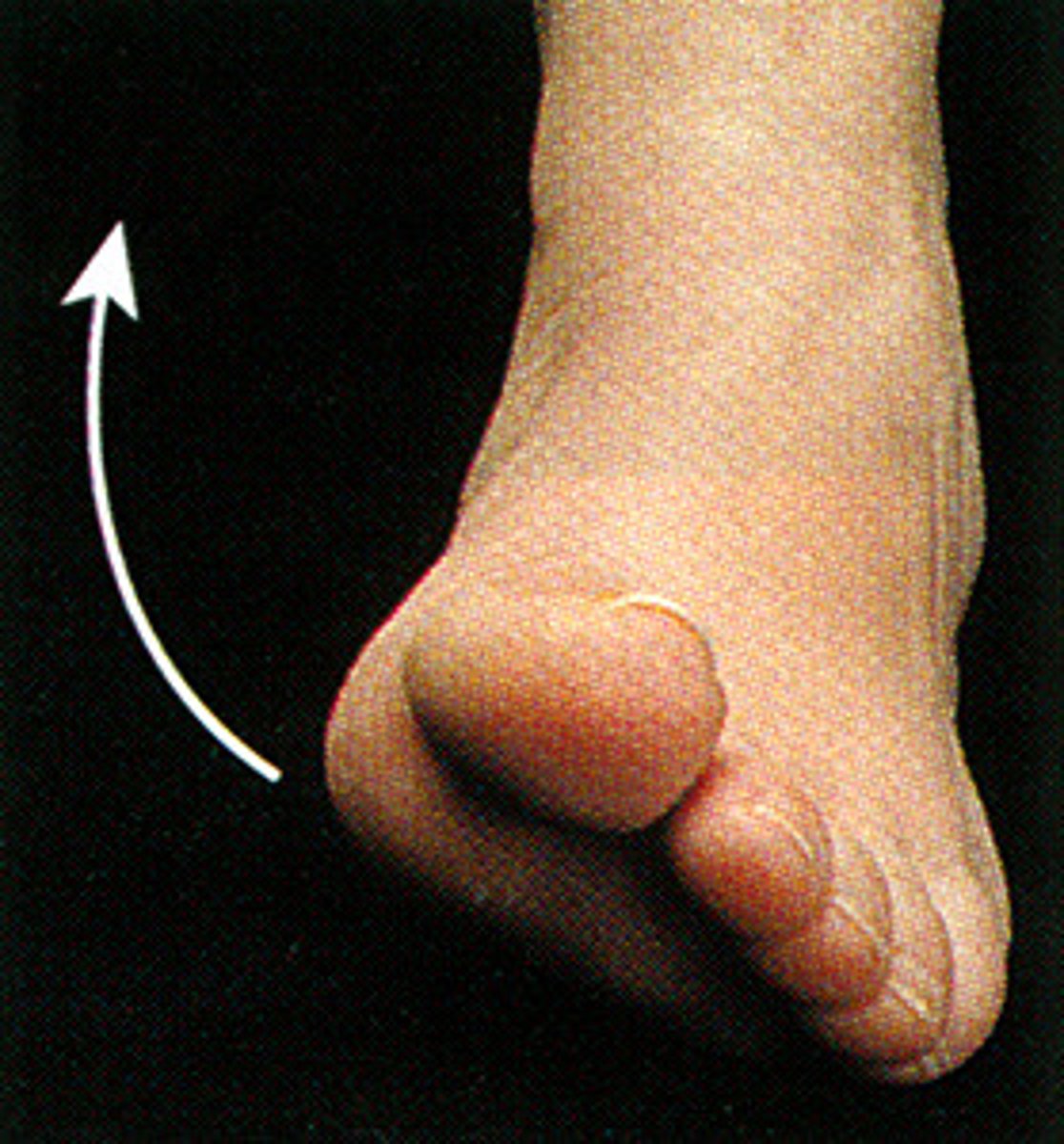
inversion
turning sole of foot medially at the ankle
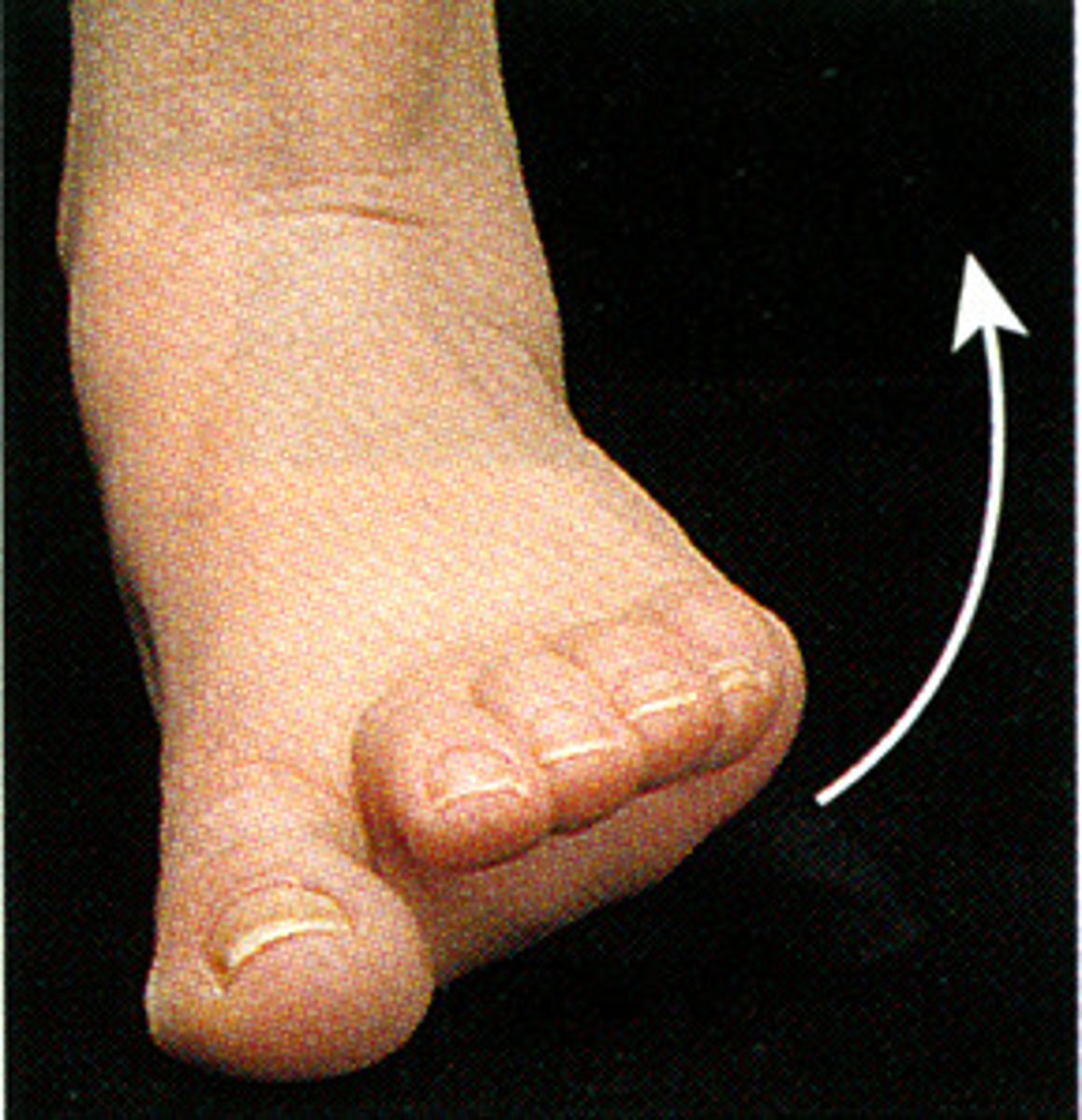
Eversion
turning sole of foot laterally at the ankle
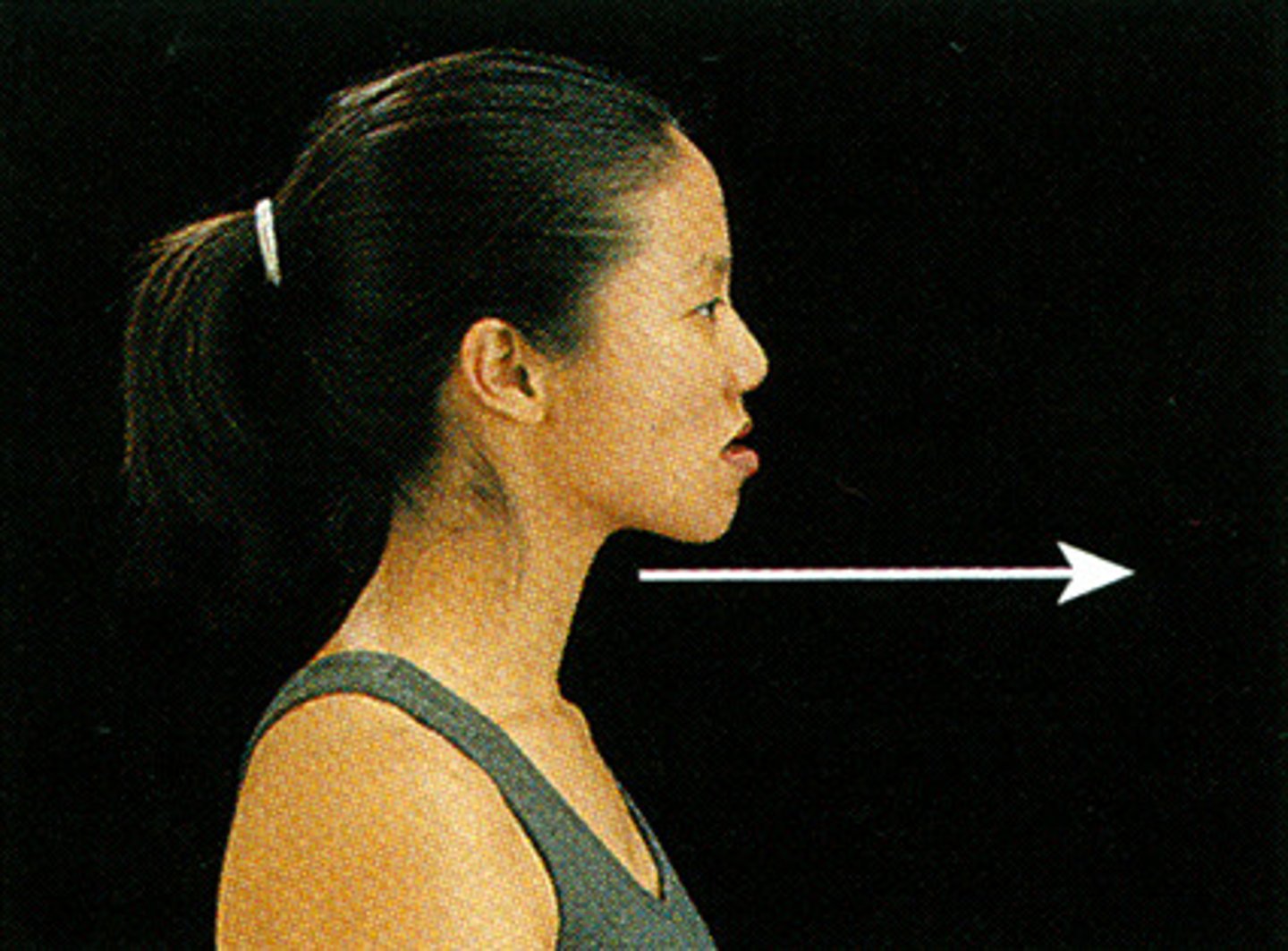
protraction
moving the mandible or clavicle anteriorly
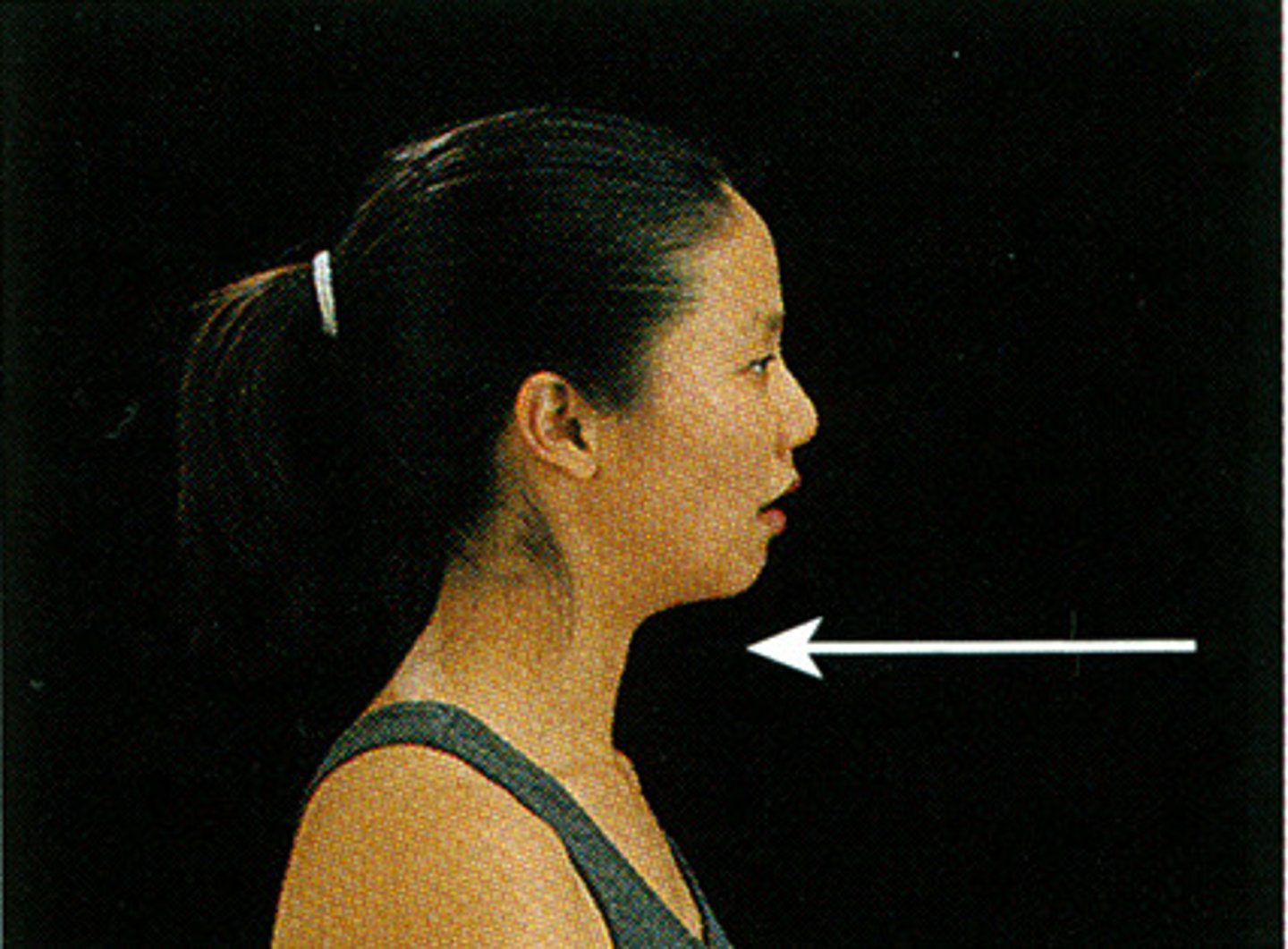
retraction
moving mandible or clavicle posteriorly
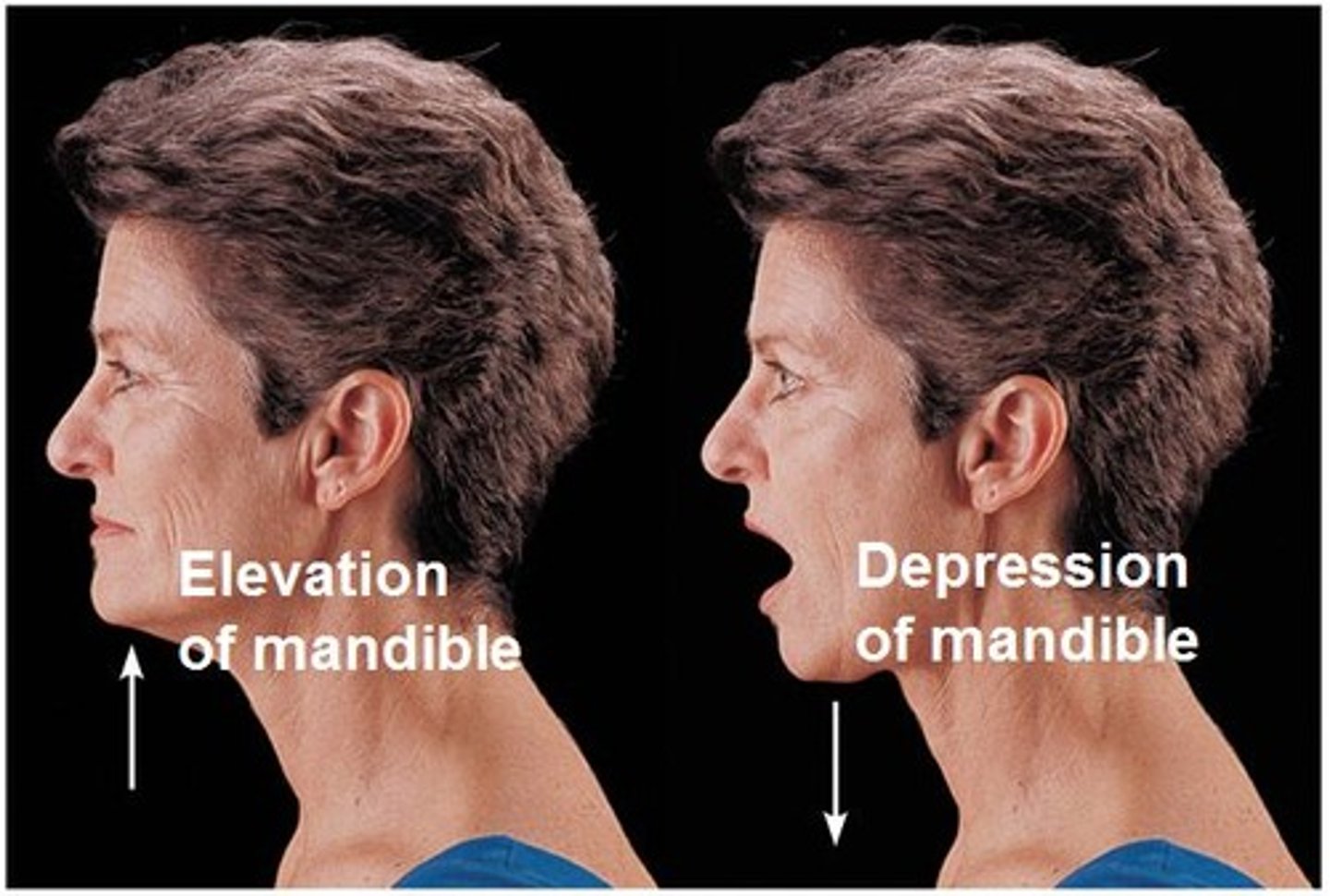
Elevation
movement in a superior direction
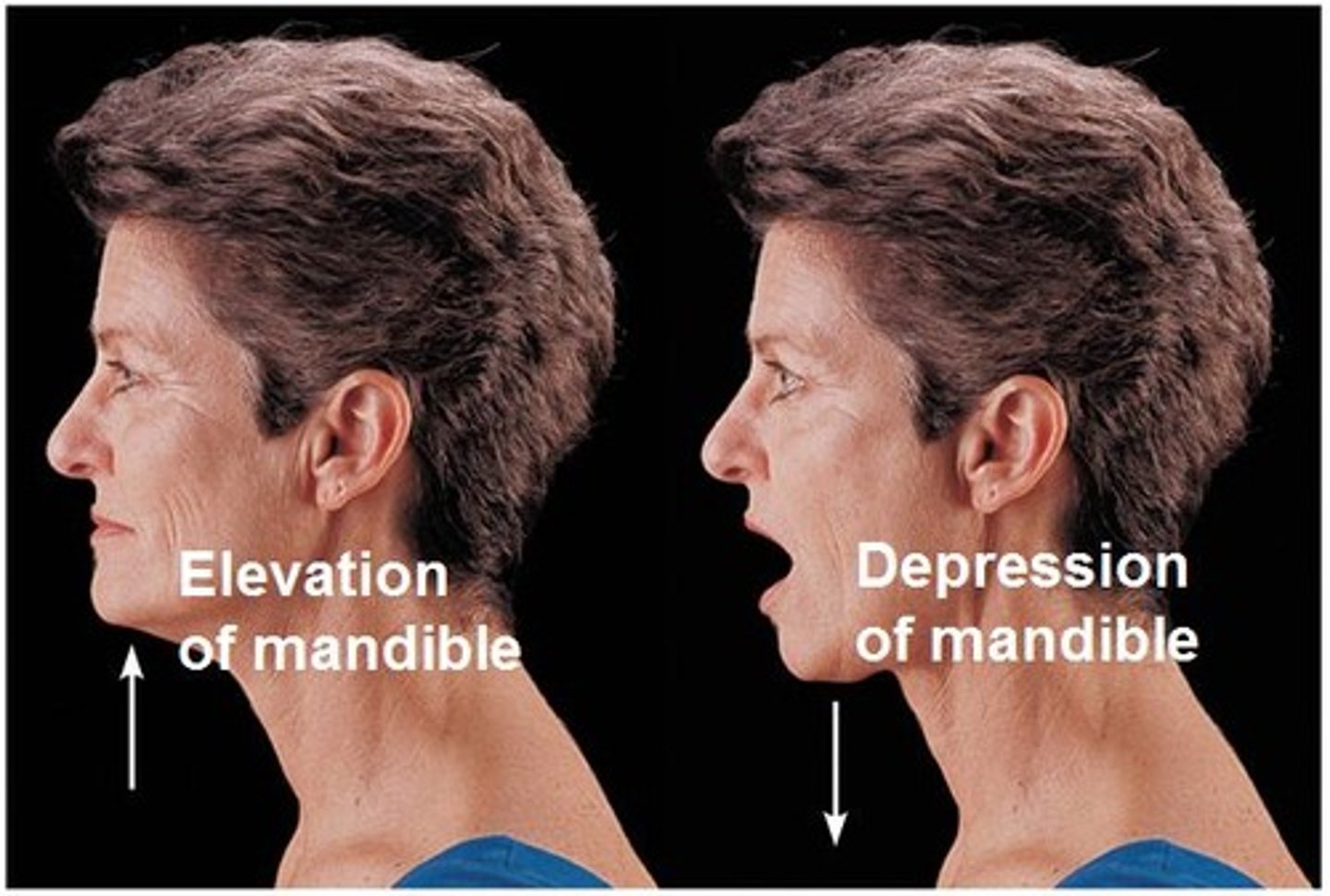
depression
movement in an inferior direction
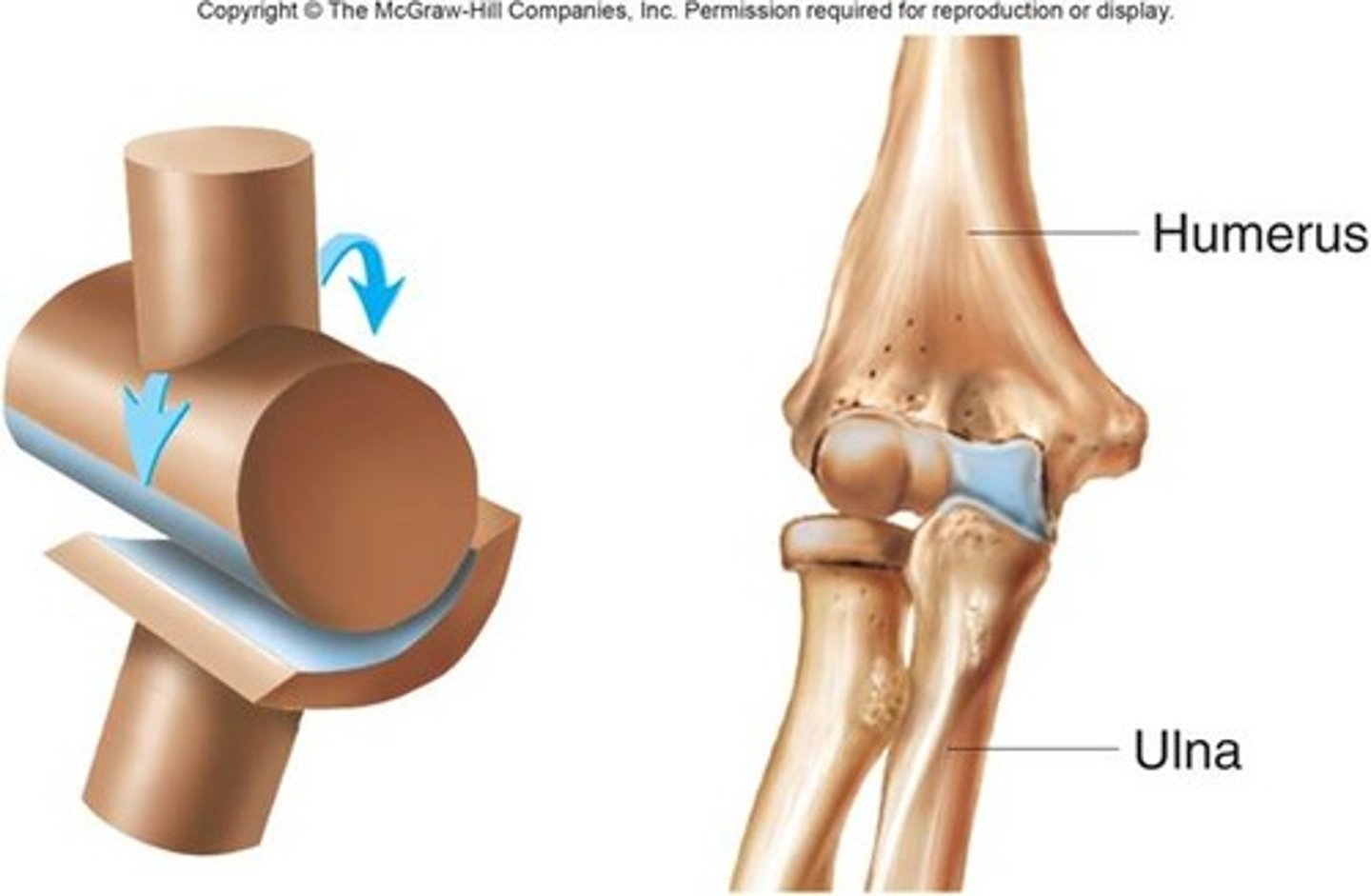
Hinge joints
concave surface of one joint acceots the convex surface of another joint
*monaxial
Movements-mainly flexion and extension
Ex:elbow knee, phalangeal joints
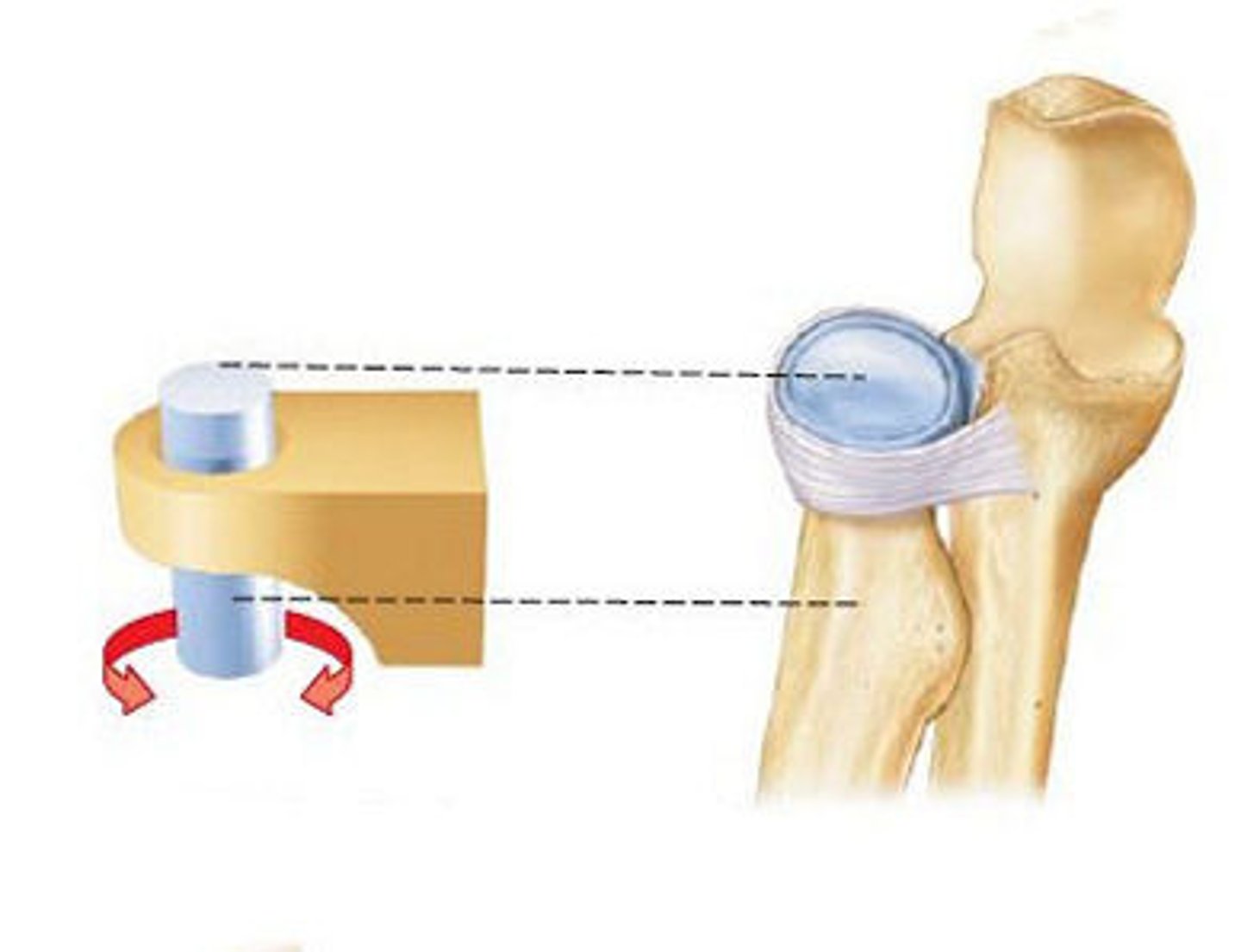
Pivot joints
also monoaxial, a rounded process of one bone fits into a shallow depression in another bone and then rotates
Movements- pronation and supination
Ex:proximal radioulnar joint, atlantoaxial joint
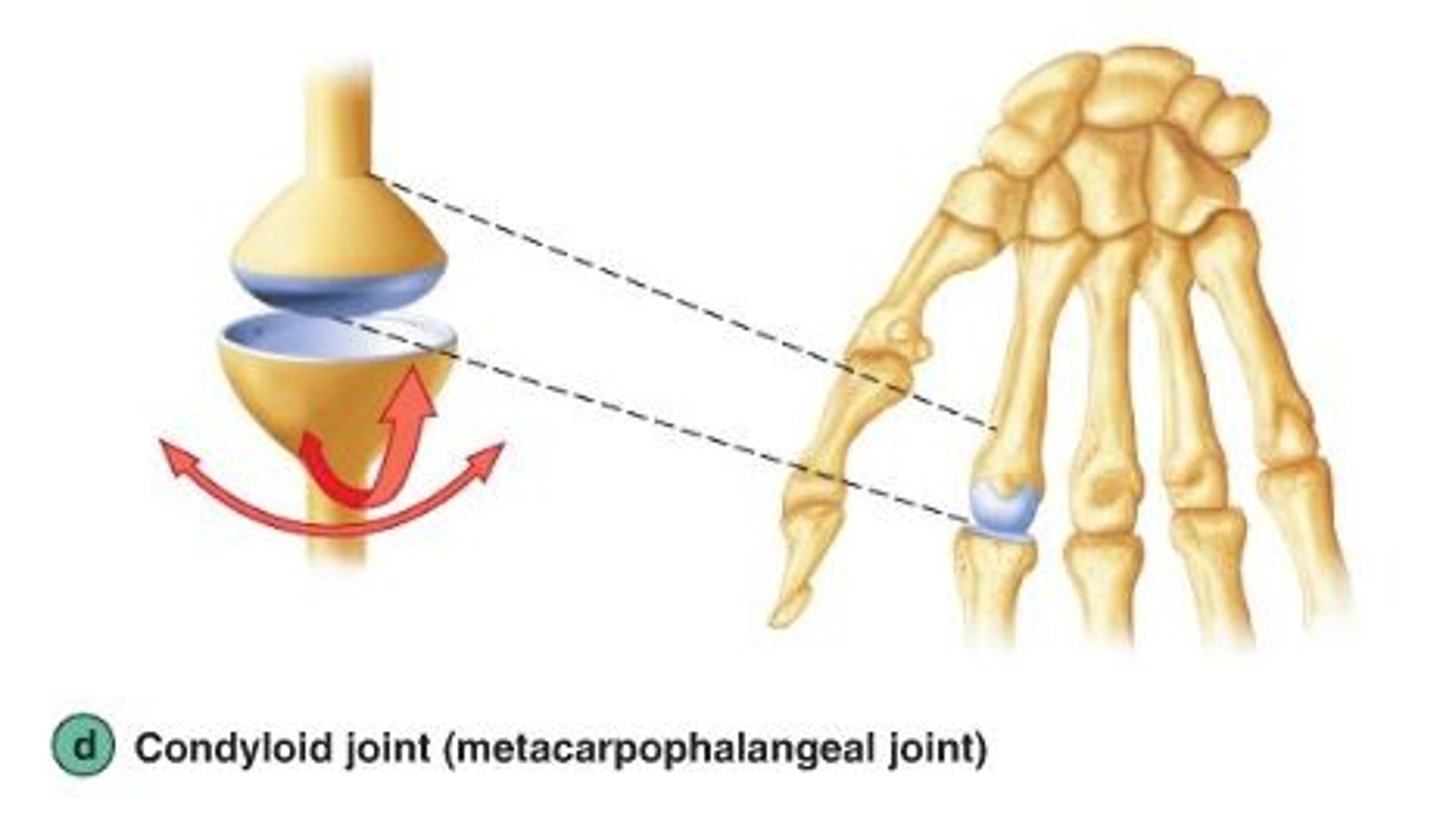
Ellipsoidal joints
biaxial joints, an oval depression in one bone accepts an oval shaped condyle of another bone; movements-mainly flexion-extension, and a little adduction and abduction; Ex: metacarpals and phalanges
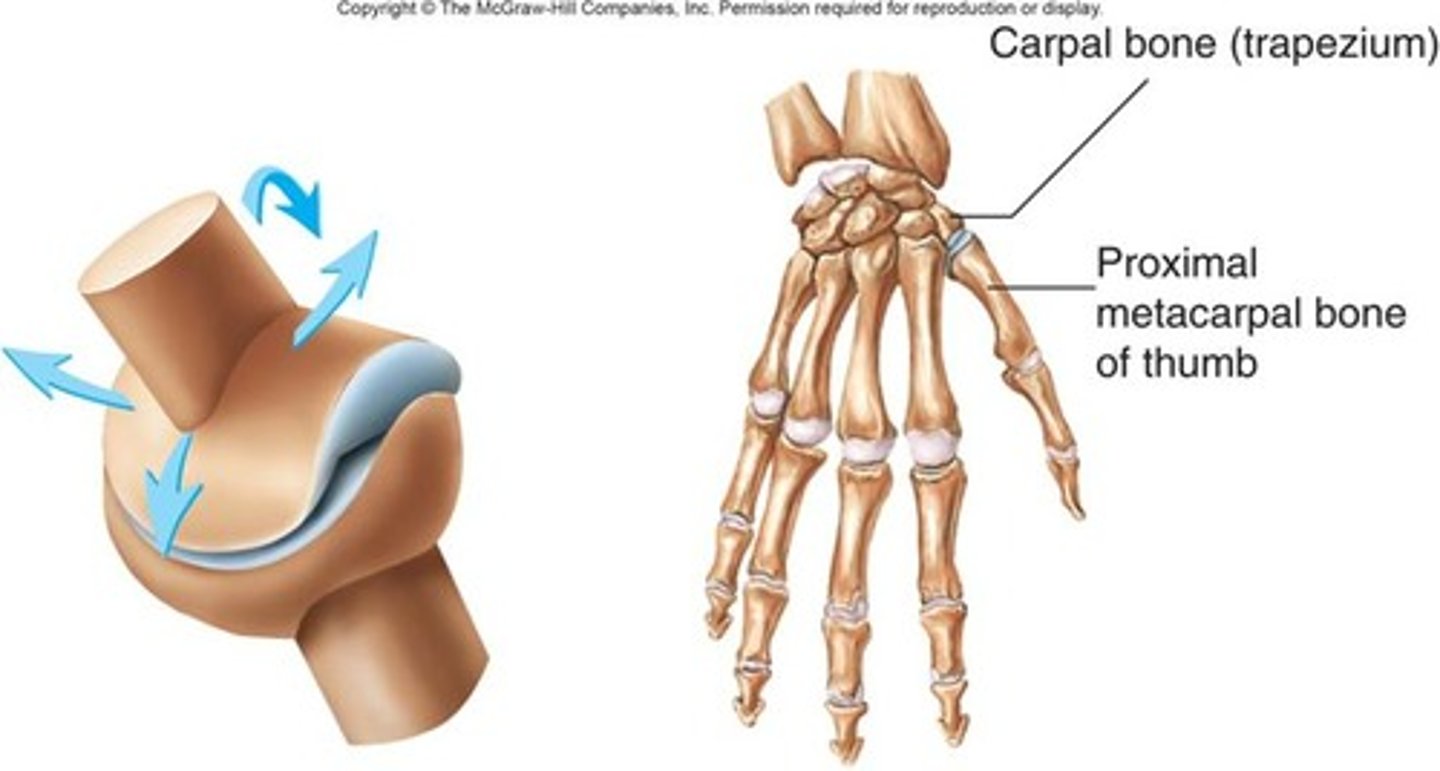
saddle joints
a convex surface which fits into a concavity, movements- medial/lateral, anterior/posterior, Ex: carpometacarpal joint of the first digit
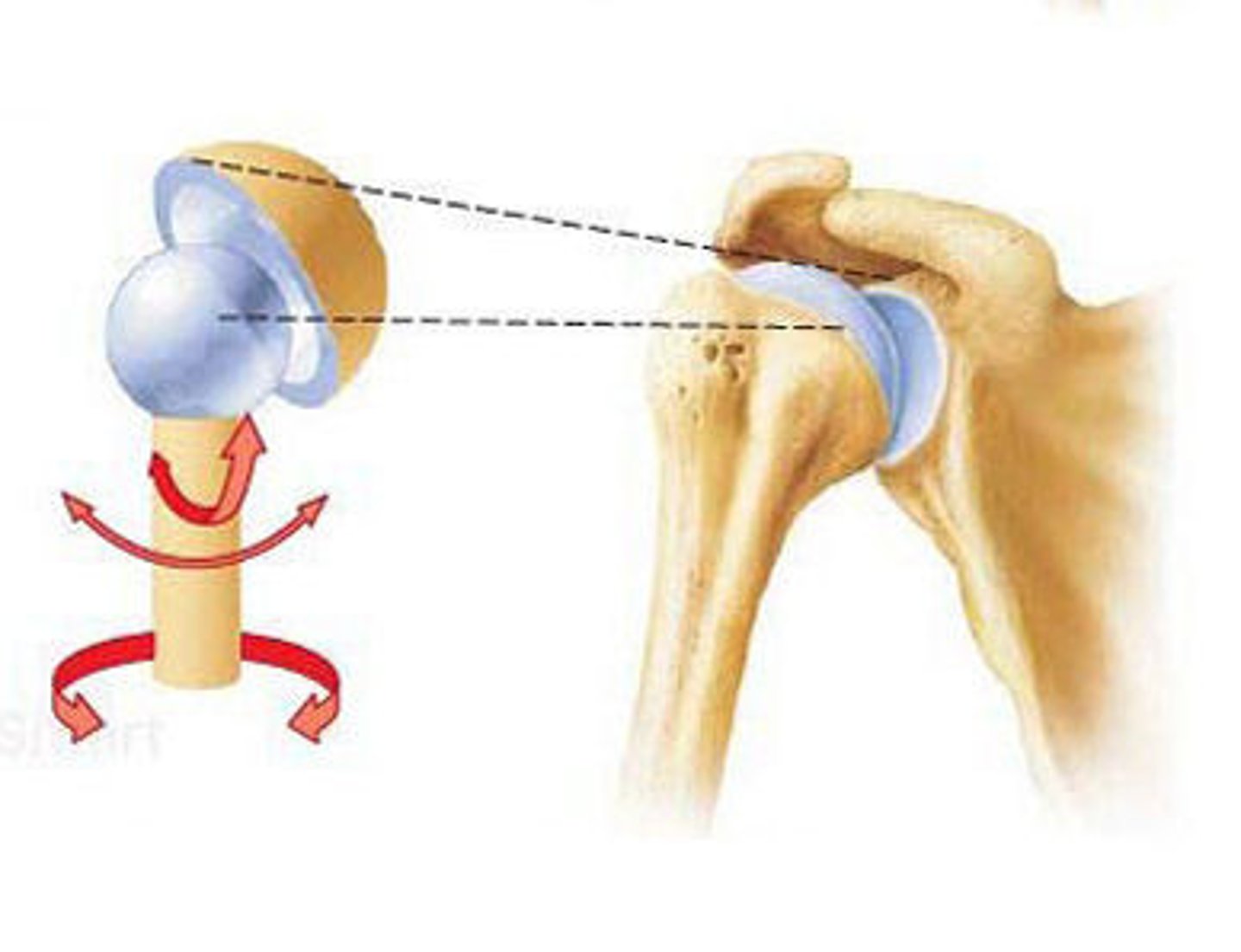
Ball and Socket Joints
Multiaxial
movements-circumduction, flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation
Ex: shoulder joint, hip joint
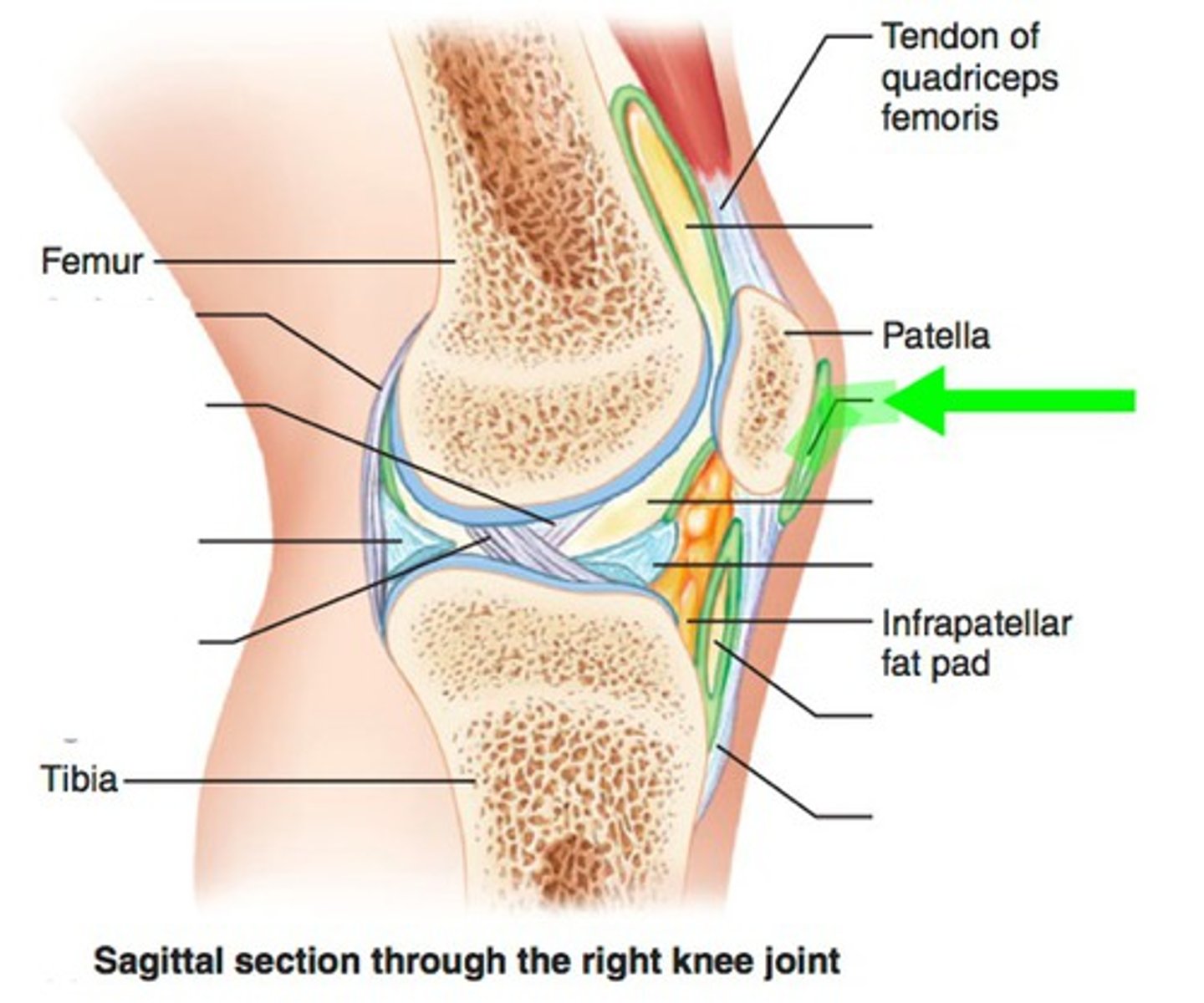
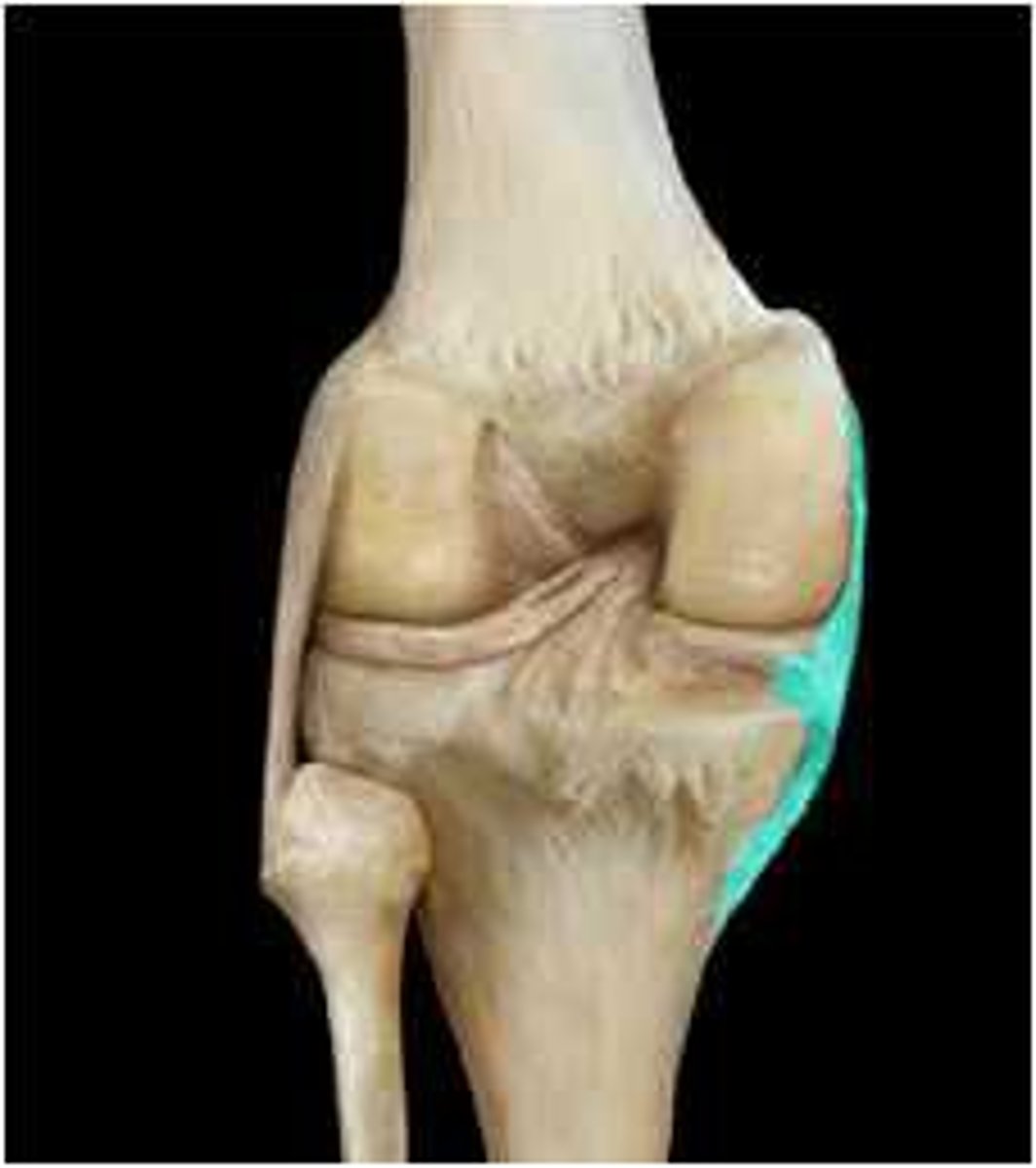
Tendon of Quadricepts
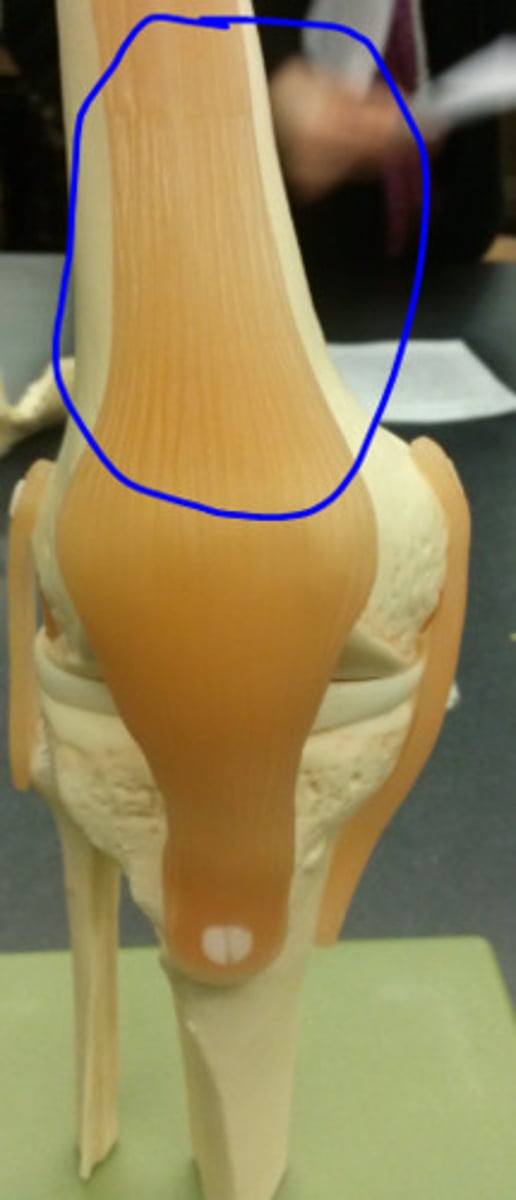
patella
Patellar Ligament
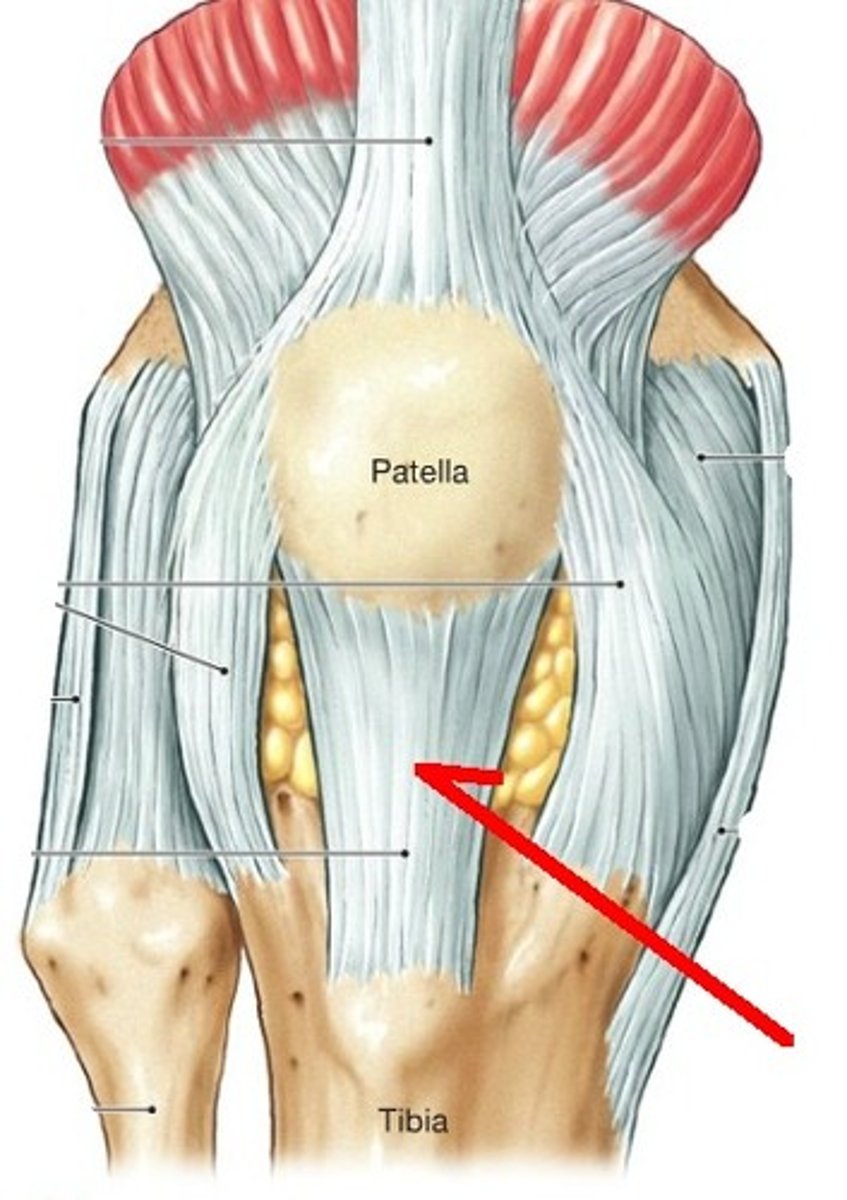
Fibular collateral ligament
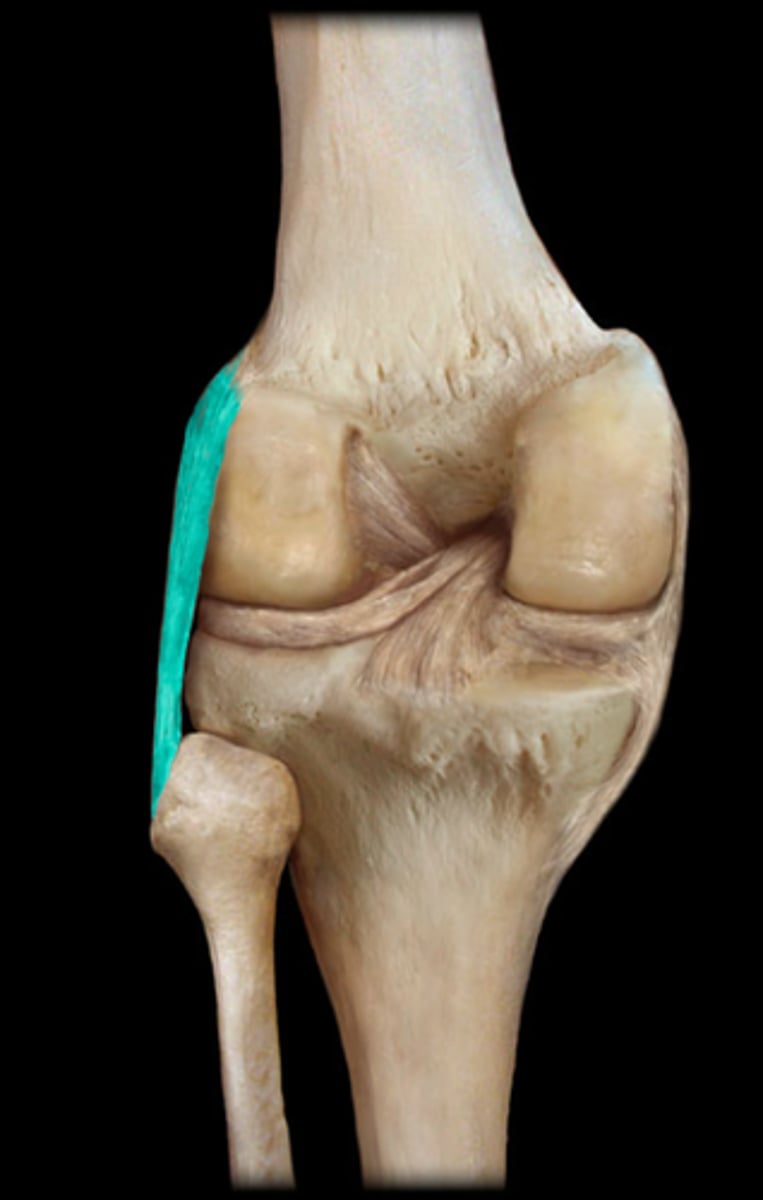
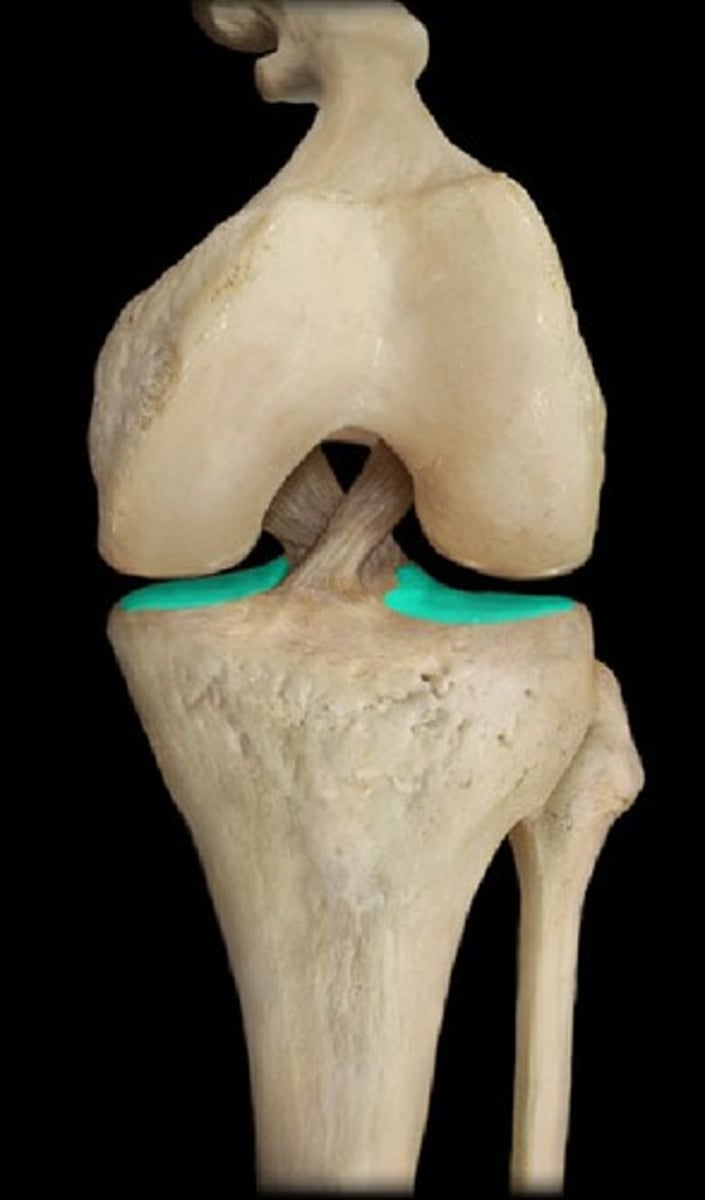
Lateral Meniscus
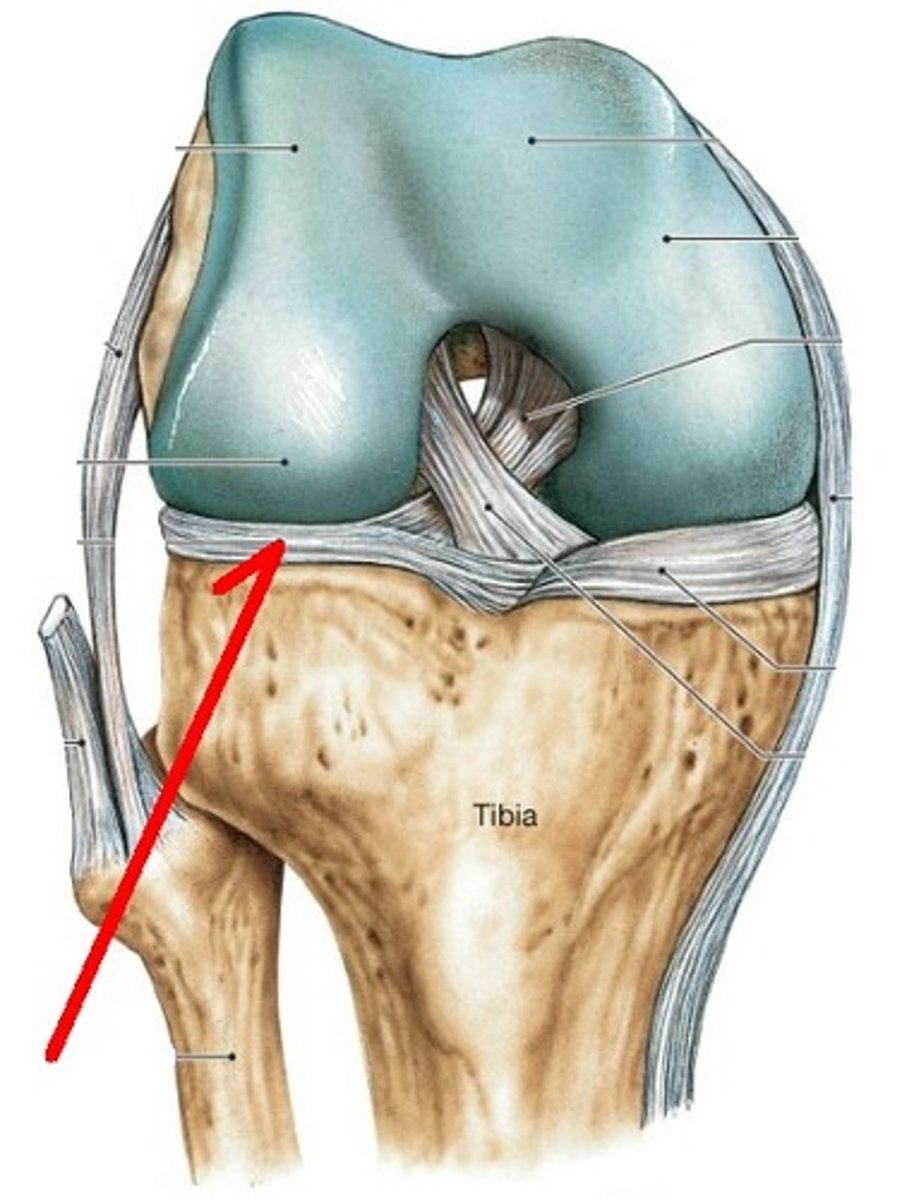
Posterior Cruciate ligament
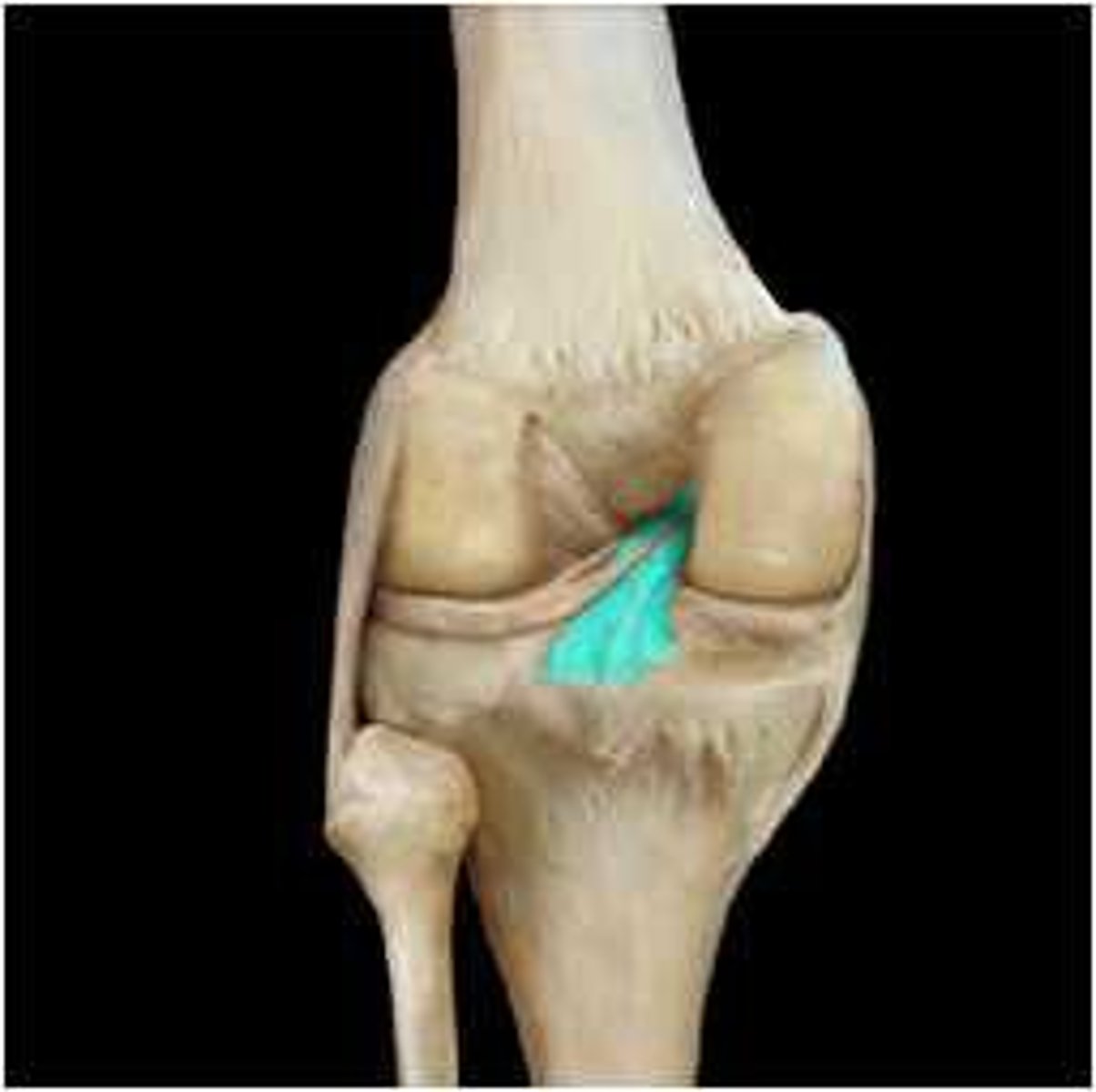
Tibial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
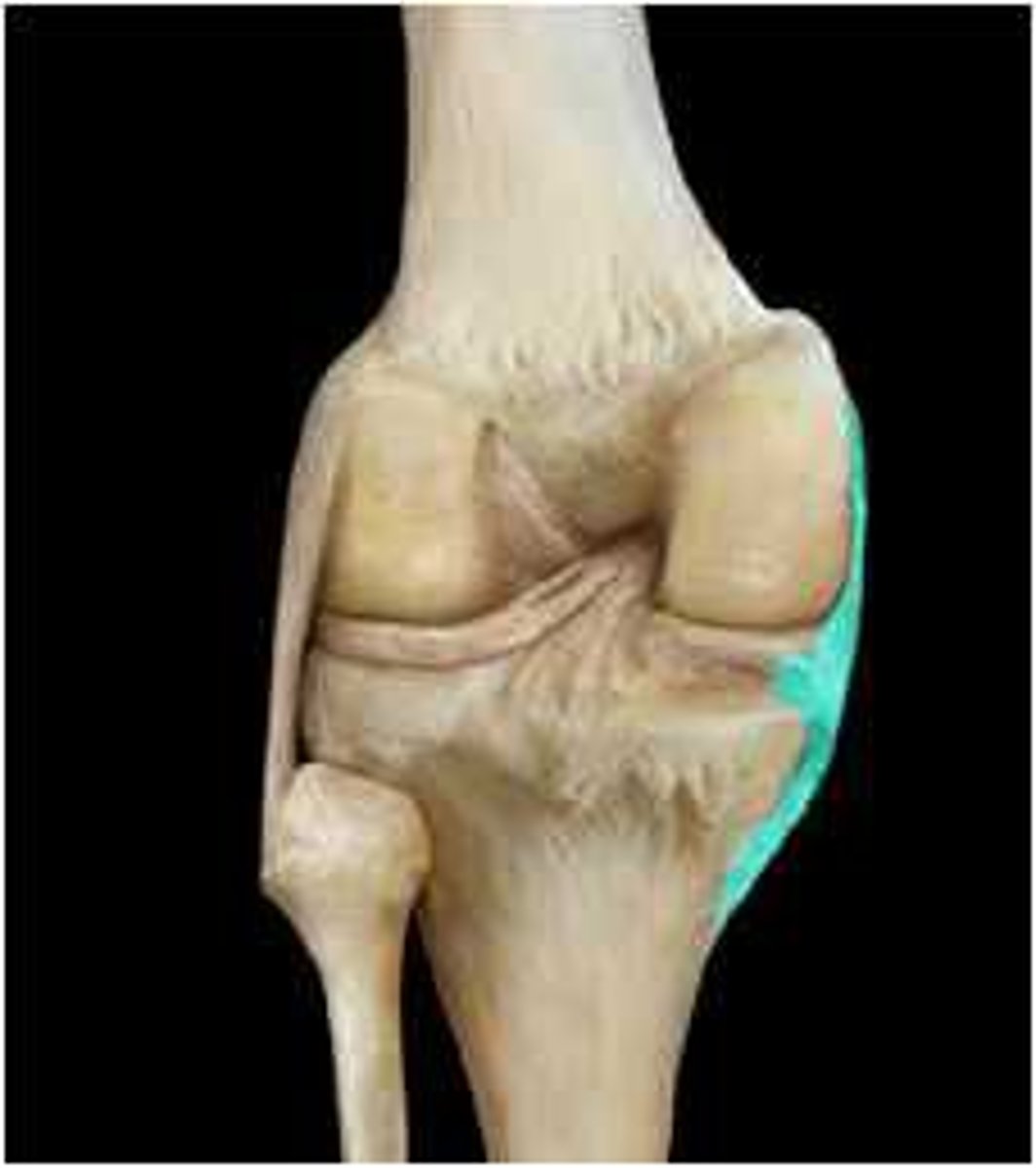
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
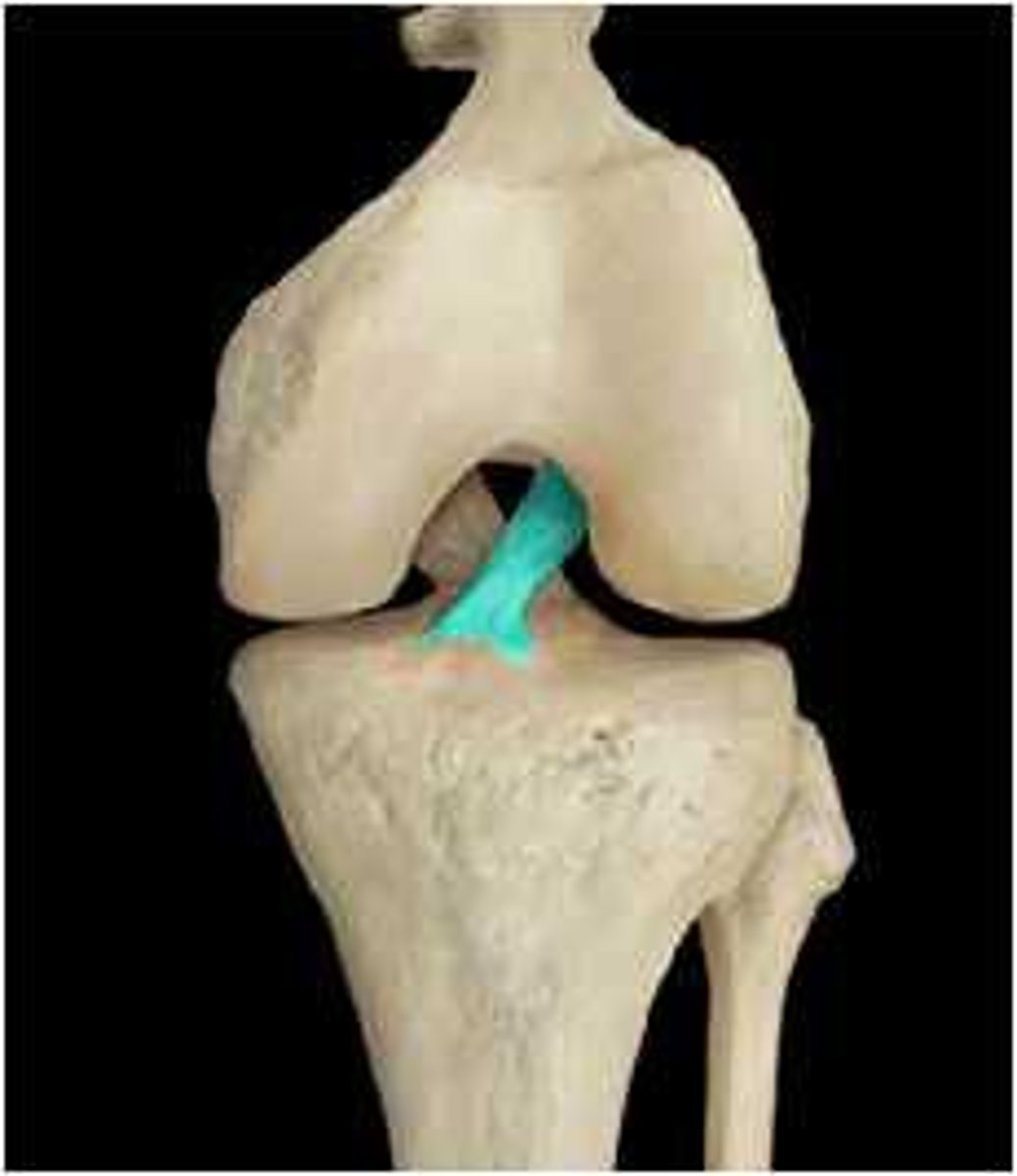
Medial Meniscus
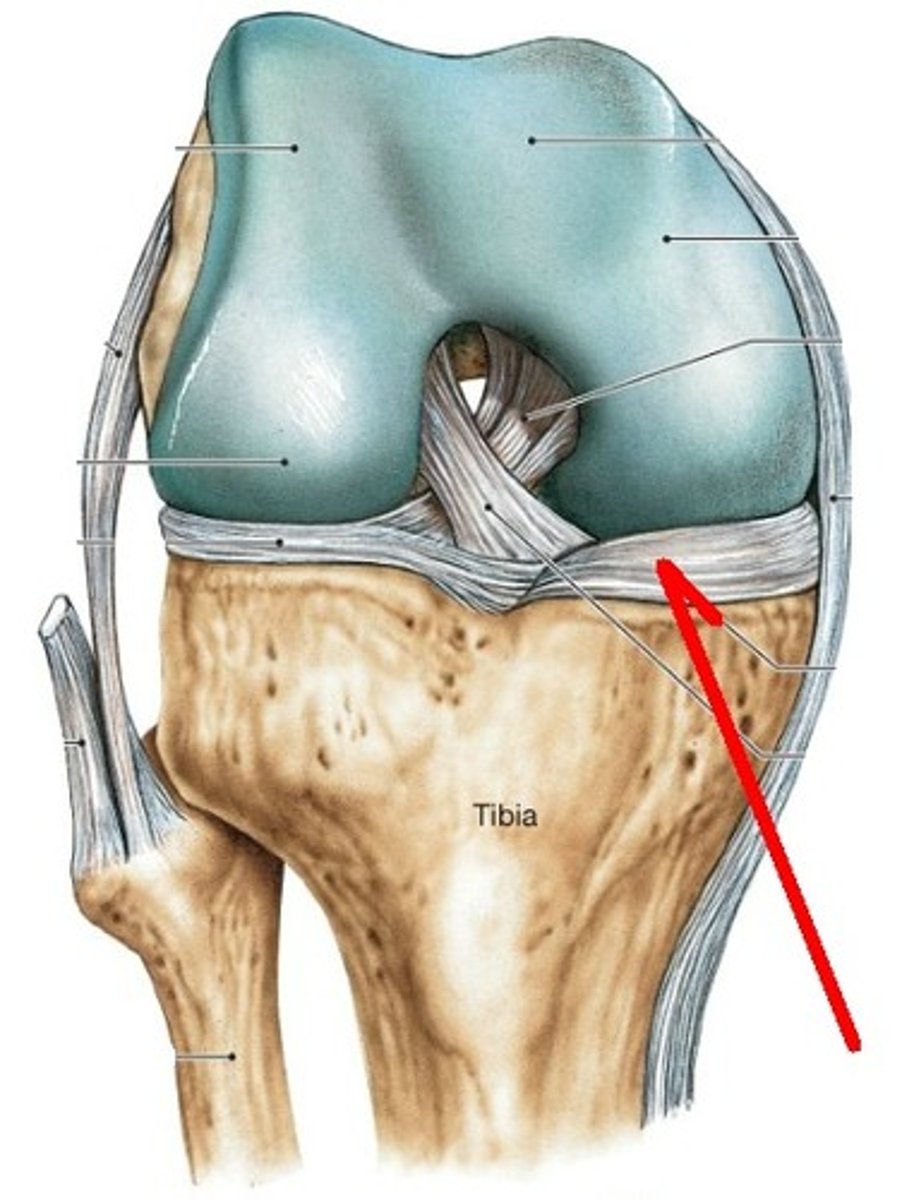
Unhappy trio
MCL, ACL, Medial meniscus
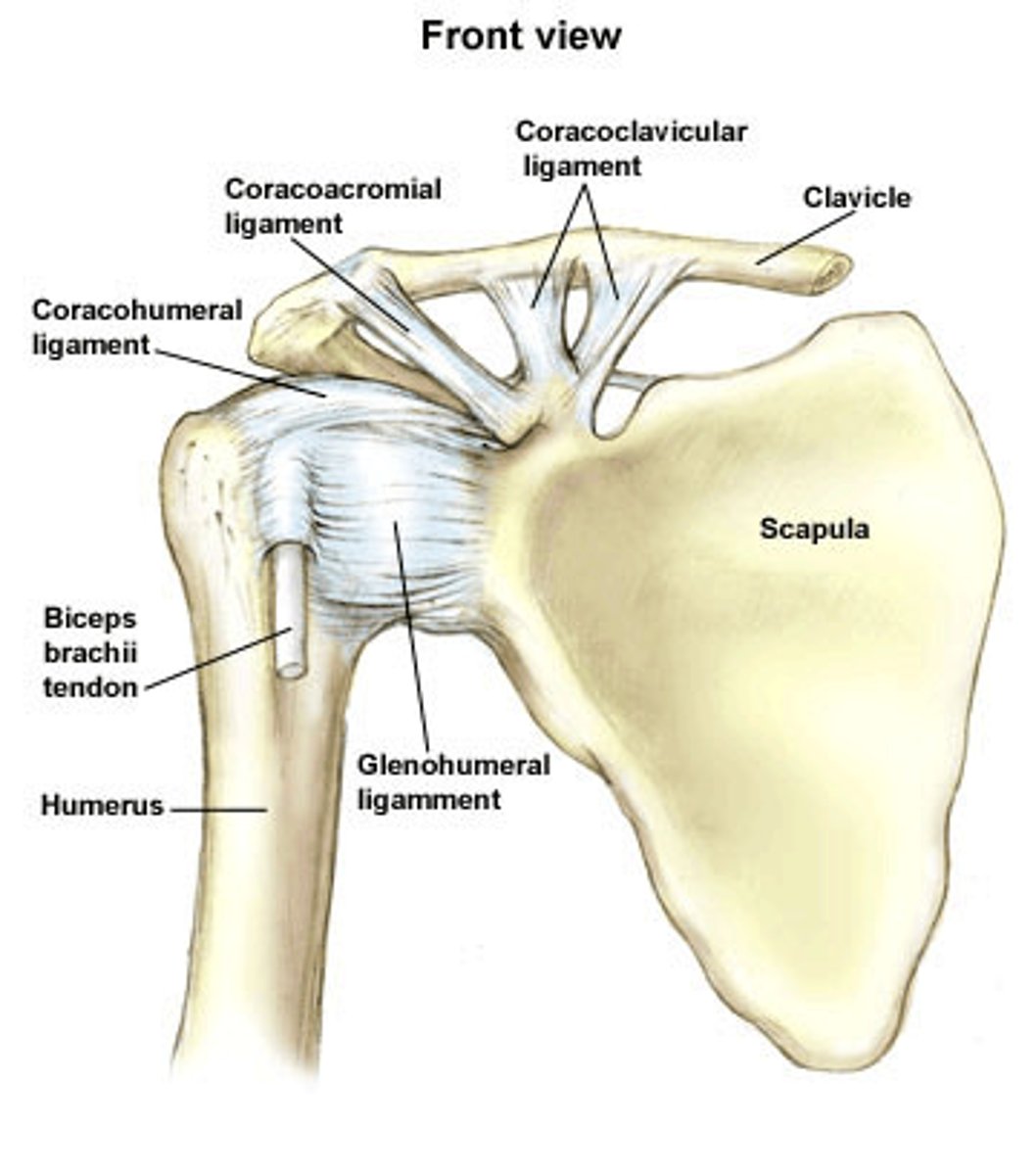
coracohumeral ligament
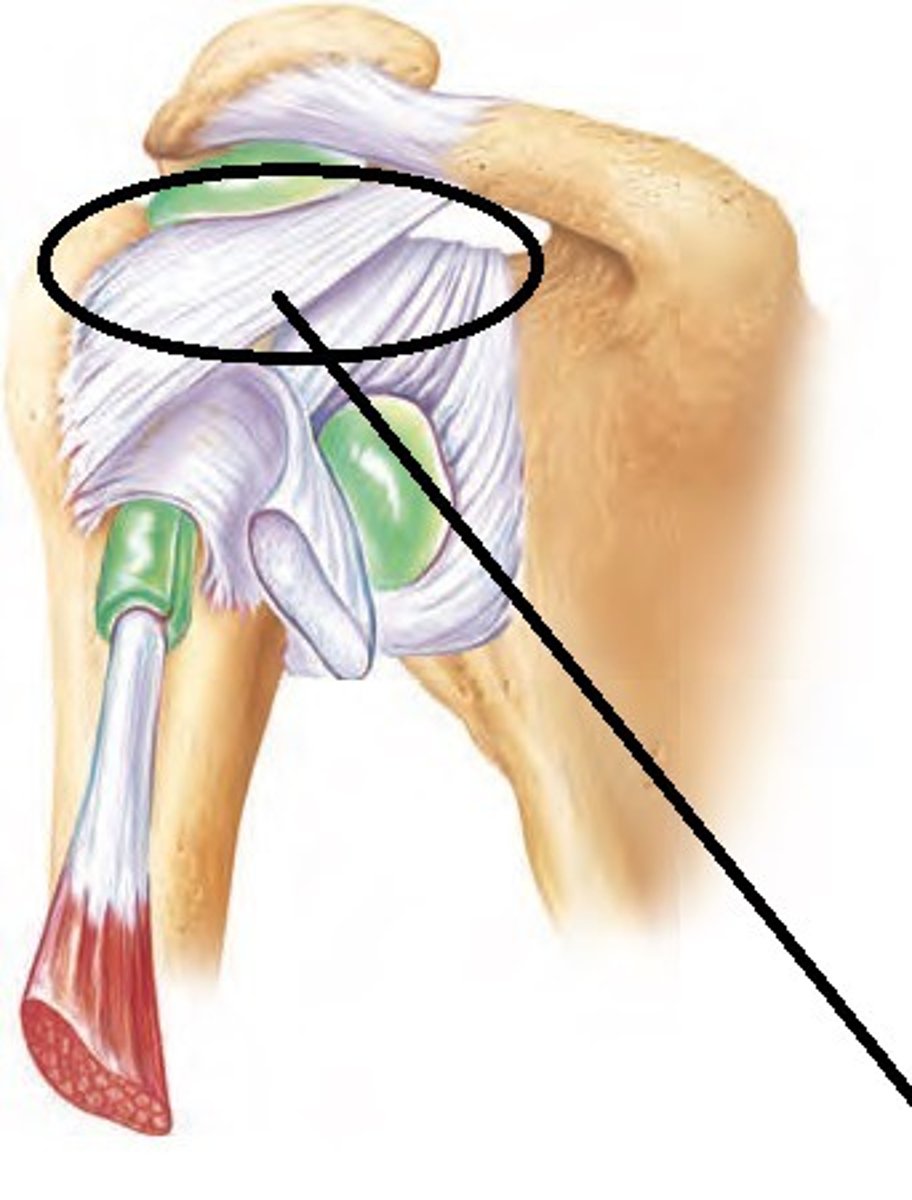
glenohumeral ligament