Organic Chemistry (Functional Groups)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Halogen Atoms (F, Cl, Br, I)
Formula = R - F (-Cl, -Br, -I)
Prefix(Always Substituent): (halo-) eg.(chloro, bromo, fluoro, iodo)
(number required for carbon chain location) eg.( 3-chloropropane)
Properties:
- High Dispersion Forces > Higher Bboiling temperatures than alkanes,
- not sufficiently polar to dissolve in water,
- Neutral (pH = 7).

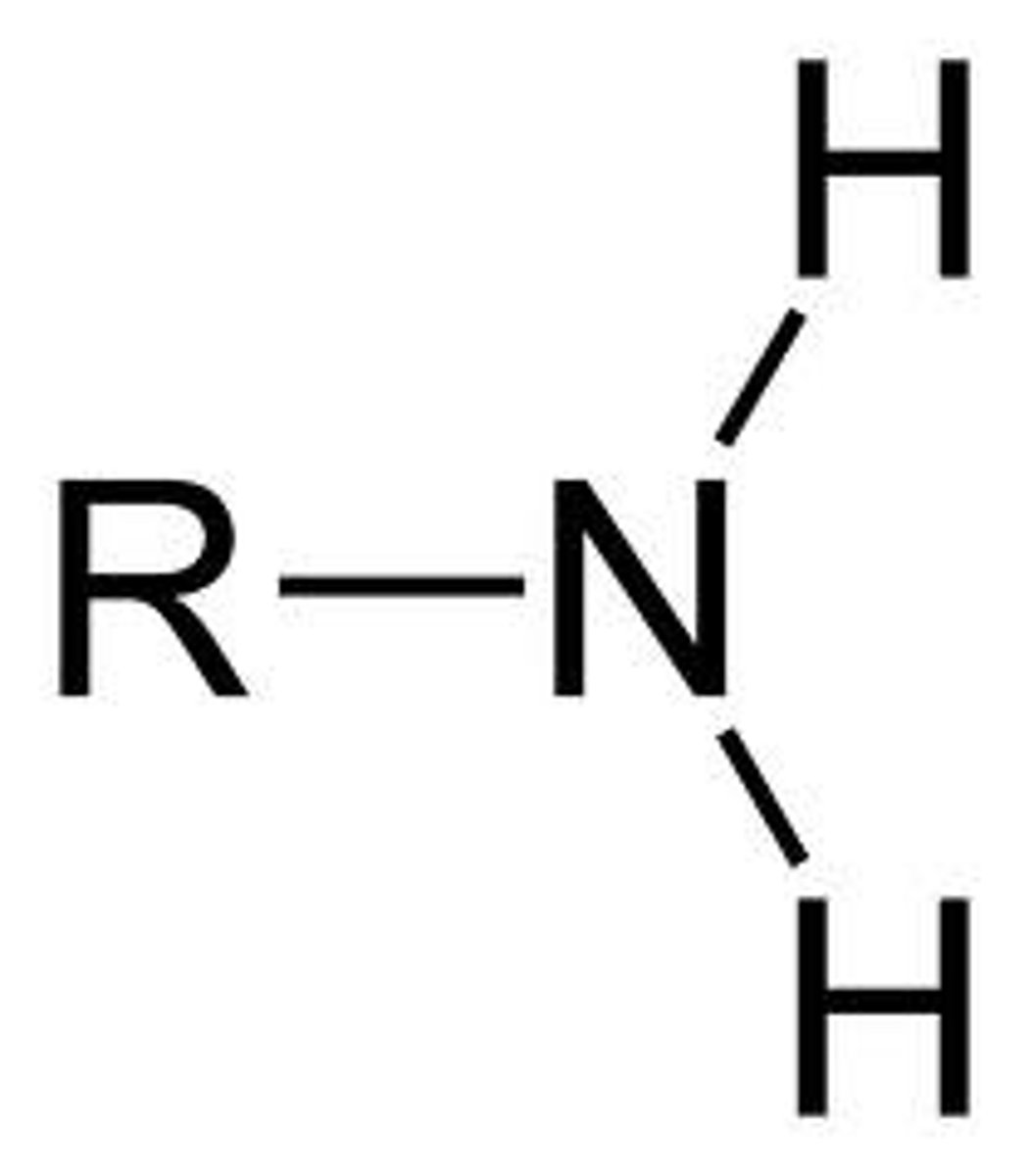
Amino(s)
Formula = R - NH2
Suffix(Primary): (-amine) eg.(propan-2-amine)
Prefix(Substituent): (amino-) eg.(3-amino-butan-2-one(Ketone as primary))
(number required for carbon chain location) eg.(propan-2-amine)
Properties:
- Hydrogen bonds > Higher boiling temperatures than alkanes,
- moderately polar > small amines able to dissolve in water,
- Basic (pH > 7)
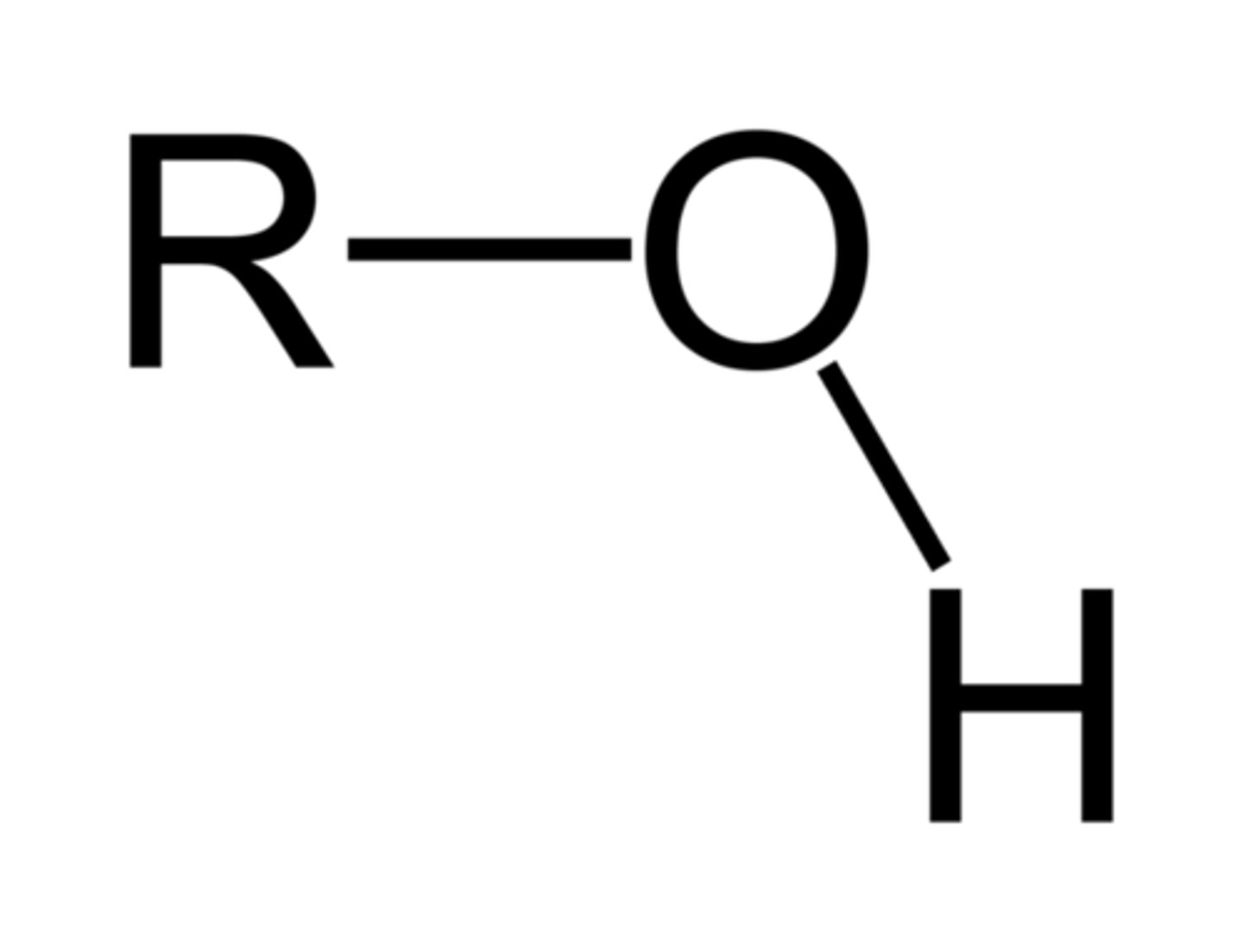
Hydroxy/Hydroxyl- (alcohol)
Formula = R - OH
Suffix(Primary): (-ol) eg.(ethanol)
Prefix(Substituent): (hydroxy-) eg.( 3-hydroxybutanone(Ketone as primary))
(number required for carbon chain location) eg.(hexan-3-ol)
Properties:
- Hydrogen Bonds > Higher boiling temperatures than alkanes,
- polar > able to dissolve in water (as long as hydrocarbon is not too large compared to amount of hydroxyl groups),
- Neutral (pH = 7).
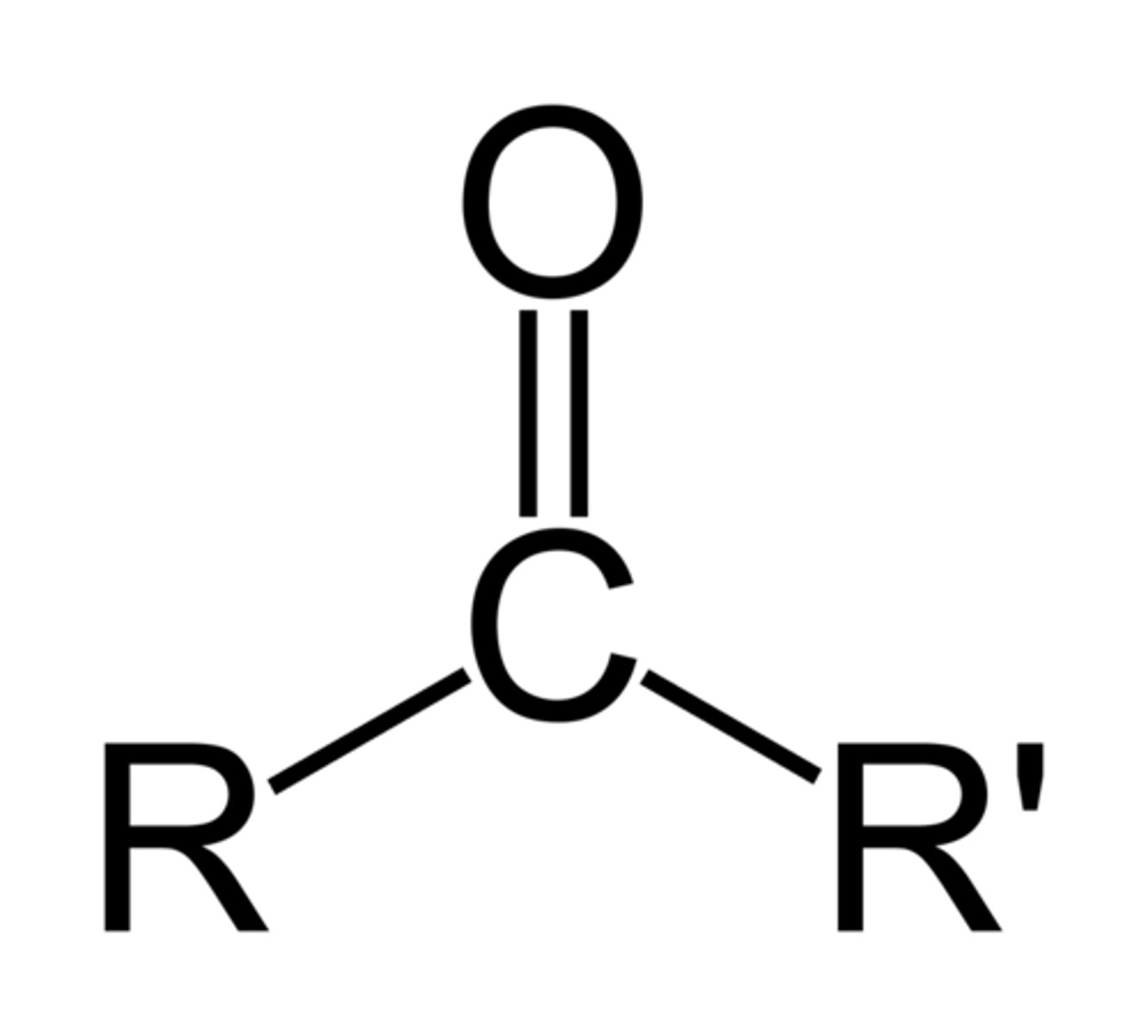
Ketone(s)
Formula: R1 - C(=O) - R2
Suffix(Primary): (-one) eg. (propan-2-one)
(number required for carbon chain location)
Properties:
- Higher boiling temperatures than alkanes, but lower than alcohols due to not having intermolecular hydrogen bonds,
- can be dissolved in water easily due to bonding with hydrogen in water.
- Acidic(More than aldehydes) (pH < 7)
Aldehydes
Formula: R - CH = O
Suffix(Primary): (-al) eg. (butanal)
(number never required as carboxy is always C1) eg.(pentanal, NOT pentan-1-al acid)
Properties:
- Carbonyl(Ketone group) with a hydrogen,
- slightly polar,
- Slightly Acidic (pH < 7)
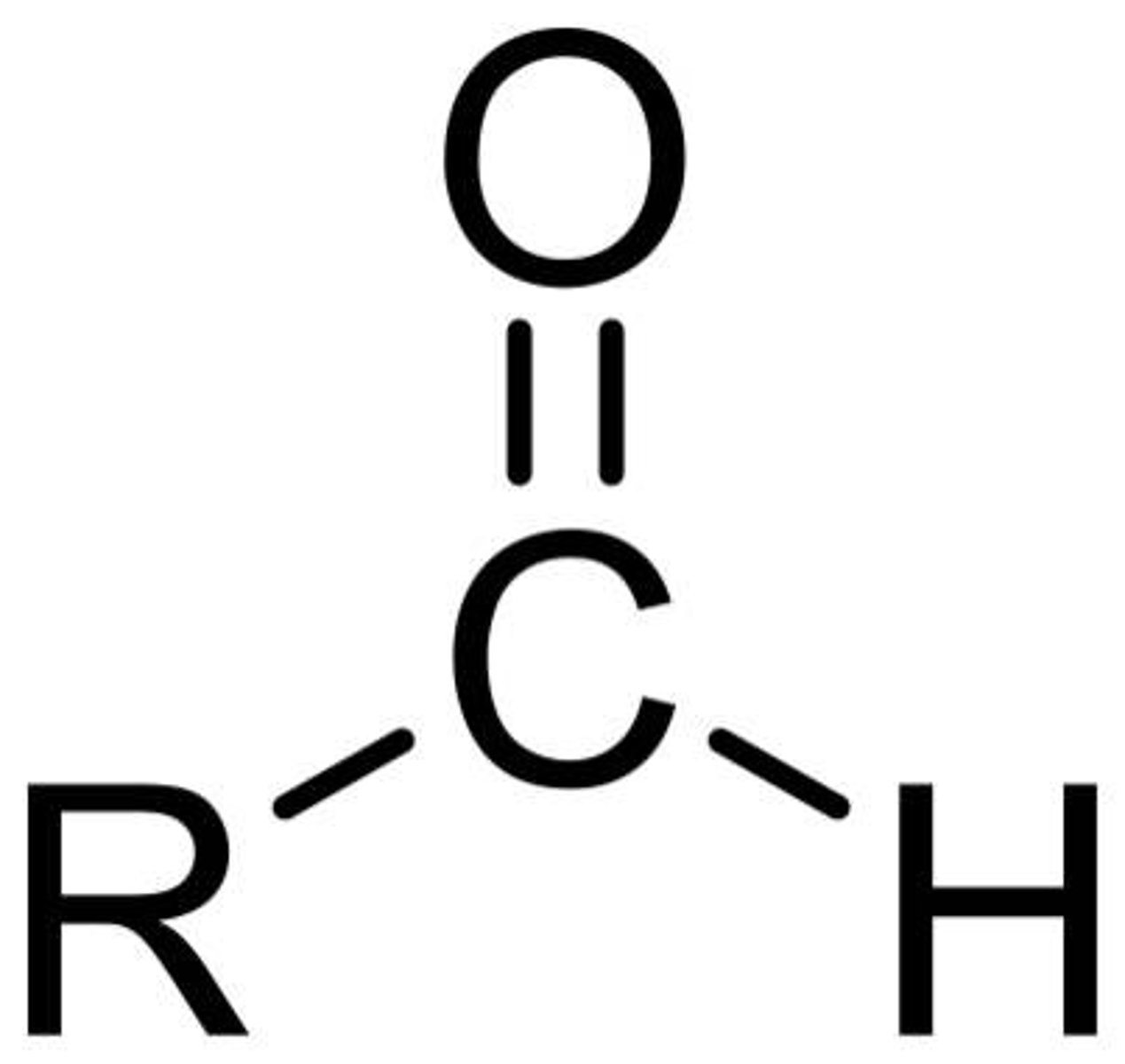
Nitrile
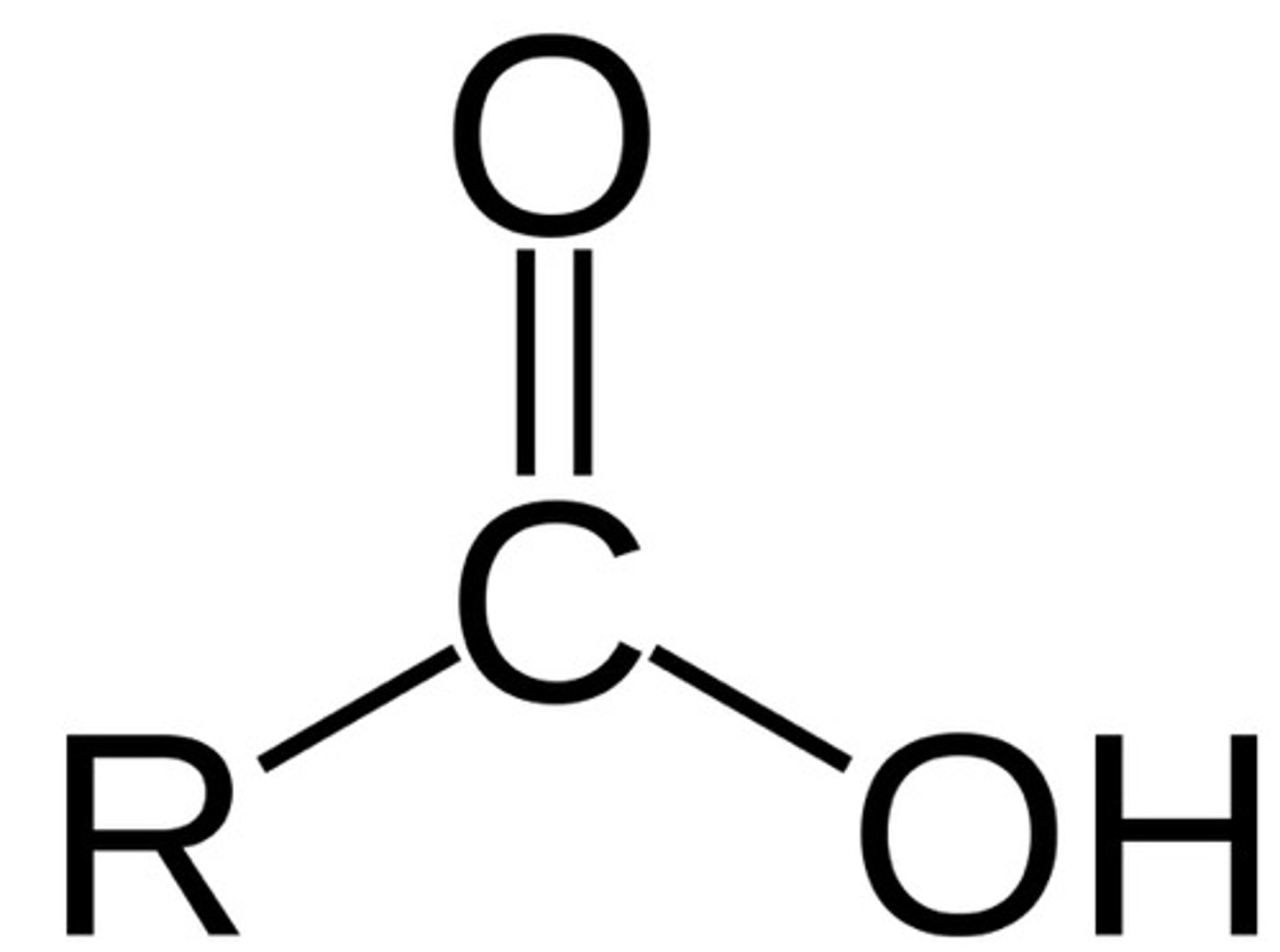
Carboxy (Carboxylic acids)
Formula: R - O(O)=O
Suffix(Primary): (-oic acid) eg. (propanoic acid)
Prefix(Substituent, Rarely): (carboxy) eg.(2-carboxyfuran)
(number never required as carboxy is always C1) eg.(ethanoic acid, NOT ethan-1-oic acid)
Properties:
- Hydrogen Bonds > Higher boiling temperatures are much higher then alkanes,
- Polar > able to dissolve in water (as long as hydrocarbon is not too large,
- Acidic (pH < 7).
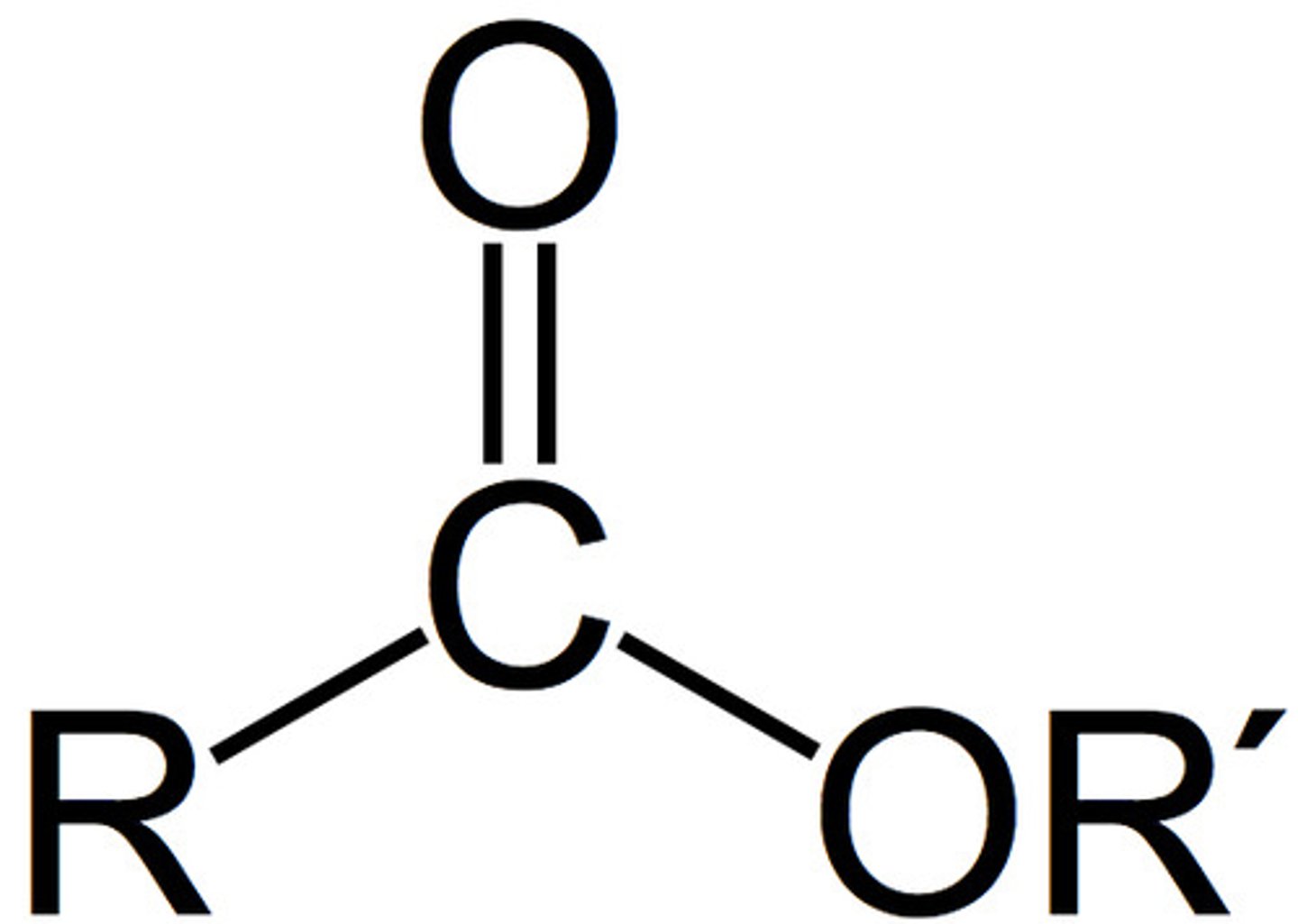
Ester(s)
Carboxy Group reacted with a hydroxy group , byproduct of water, hence Condensation.
Formula R1 - C(O-R2)=O
Name:(alkyl+oate) eg.(propyl-ethanoate (from Propan-1-ol and ethanoic acid)
(number not needed)
Properties:
- Low Boiling points compared to alcohols and carboxylic acids due to a lack of hydrogen bonds (only dipole-dipole and dispersion forces),
- low solubility,
Neutral (pH = 7)
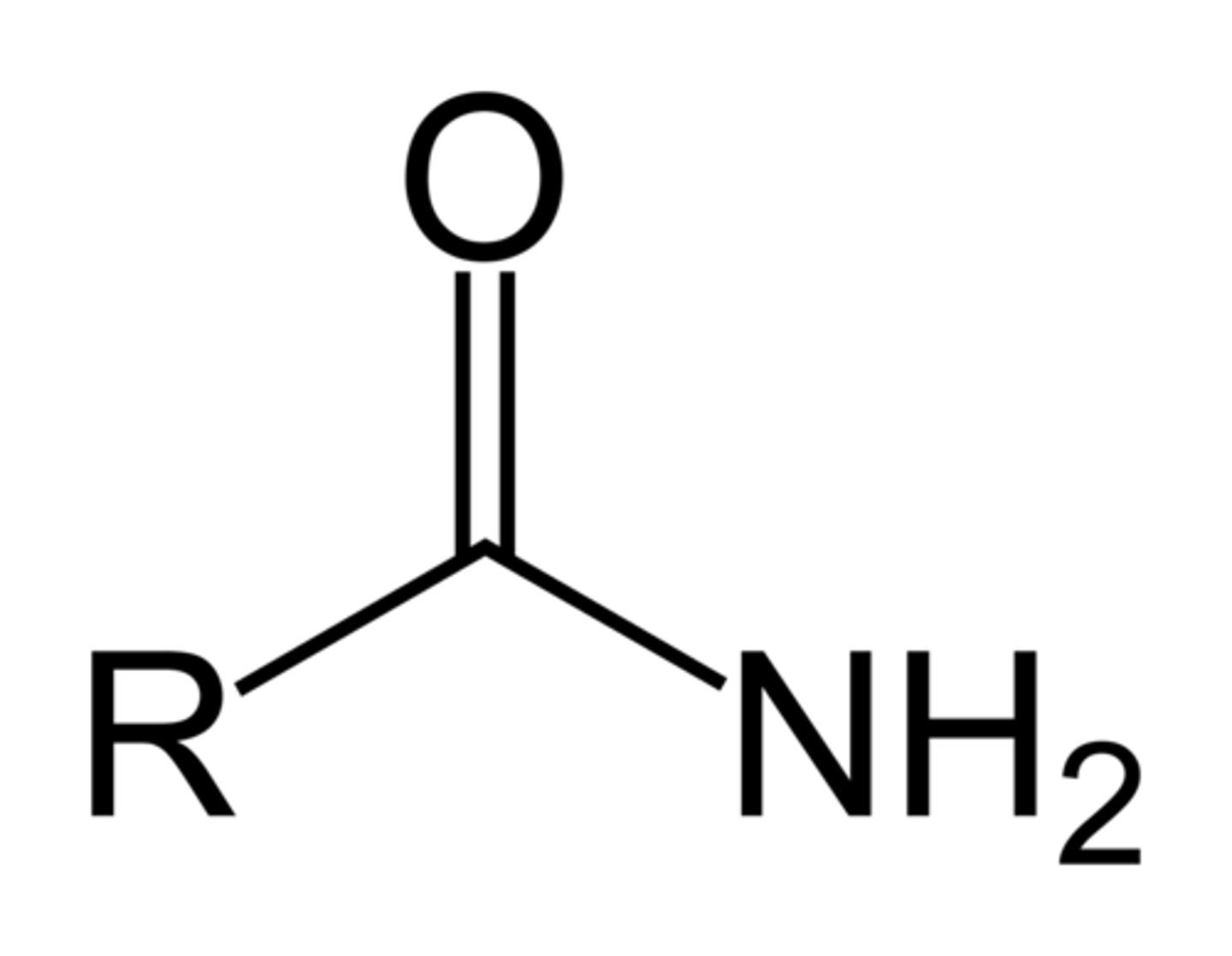
(Primary) Amide(s)
Formula: R - C(=O) - NH2
Suffix(Primary): (-amide) eg.(propanamide)
Prefix(Substituent): (carbamoyl-) eg.(carbamoyl ethanoic acid)
(number never required as carboxy is always C1) eg.(pentanamide, NOT pentan-1-amide)
Properties:
- Hydrogen Bonds > High boiling temperatures,
- polar > able to be dissolved in water,
- Neutral (pH = 7)