GY 101 Test 1 University of Alabama MD Islam (Jacob's version)
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Earths 4 spheres
atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, biosphere
Biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere - INTERACT WITH ALL OTHER SPHERES
Map Distortion
a change in the shape, size, or position of a place when it is shown on a map
equator
An imaginary circle around the middle of the earth, halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole - divides earth into 2 hemispheres
east and west hemisphere
The Prime Meridian separates the earth into what two hemispheres?
Prime Meridian
0 degrees longitude
Northeast Hemisphere
+ +
southeast hemisphere
- +
southwest hemisphere
- -
northwest hemisphere
+ -
latitude
known as parallels, run in the east-west direction, measure distance north-south of the equator, never intersect, not equal length
longitude
known as meridians, run in a north-south direction, measure distance east or west of prime meridian, farthest apart at the equator and meet at poles, cross equator at right angles, equal length
maximum latitude
90 degrees north or south
maximum longitude
180 degrees
Tropic of Cancer
23.5 degrees North
Tropic of Capricorn
23.5 degrees south
equator degrees
0
Anartic Circle
66.5 degrees South
arctic circle
66.5 degrees North
North Pole
90 degrees north
South Pole
90 degrees south
great circle
line that equally divides the earth into the hemispheres (only longitude and equator can give us a great circle) all latitude can give us is small circles.
great circle route
Shortest route between any two places on the planet
small circle
continuous line that forms a circle smaller than the equator
world time zones
24
move east to west
lose an hour
move west to east
gain an hour
What does polarity give us on Earth?
gives us seasons
What is the June solstice? Also, what latitude is the sun directly over?
June 21-22, start of summer in Northern Hemispheres and start of winter in Southern Hemisphere - southern hemisphere farthest away from the sun. Sun is directly over the tropic of cancer.
What is the winter solstice? What latitude is the sun directly over?
December 22 - Northern Hemisphere farthest away from the sun. The sun is directly over the tropic of Capricorn.
What is the fall equinox? What latitude is the sun directly over?
September 22 with an equal number of hours of daylight and darkness (12 hours of each). Sun is directly over the equator.
spring equinox
March 20th or 21st when both hemispheres recieve 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness. Sun is directly over the equator.
equinox
both hemispheres are equally far from the sun. Both hemispheres have 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness.
closed system
matter cannot go out or into the system - energy free to pass
open system
matter can go in and out of a system - energy is free to pass
positive relationship
increase in variables 1 and 2. As one goes up, the other goes up. If one goes down, the other goes down.
negative relationship
increase in variable 1 and decrease in variable 2. As one goes up, the other goes down
graphic scale
consists of a bar line marked to show distance on Earth's surface
verbal scale
description of scale using words "one inch equal four miles"
representative fraction
The scale of a map represented as a ratio or fraction, such as 1:1,000,000
small scale
1:2,000,000 (whole map)
large scale
1:200 (tuscaloosa)
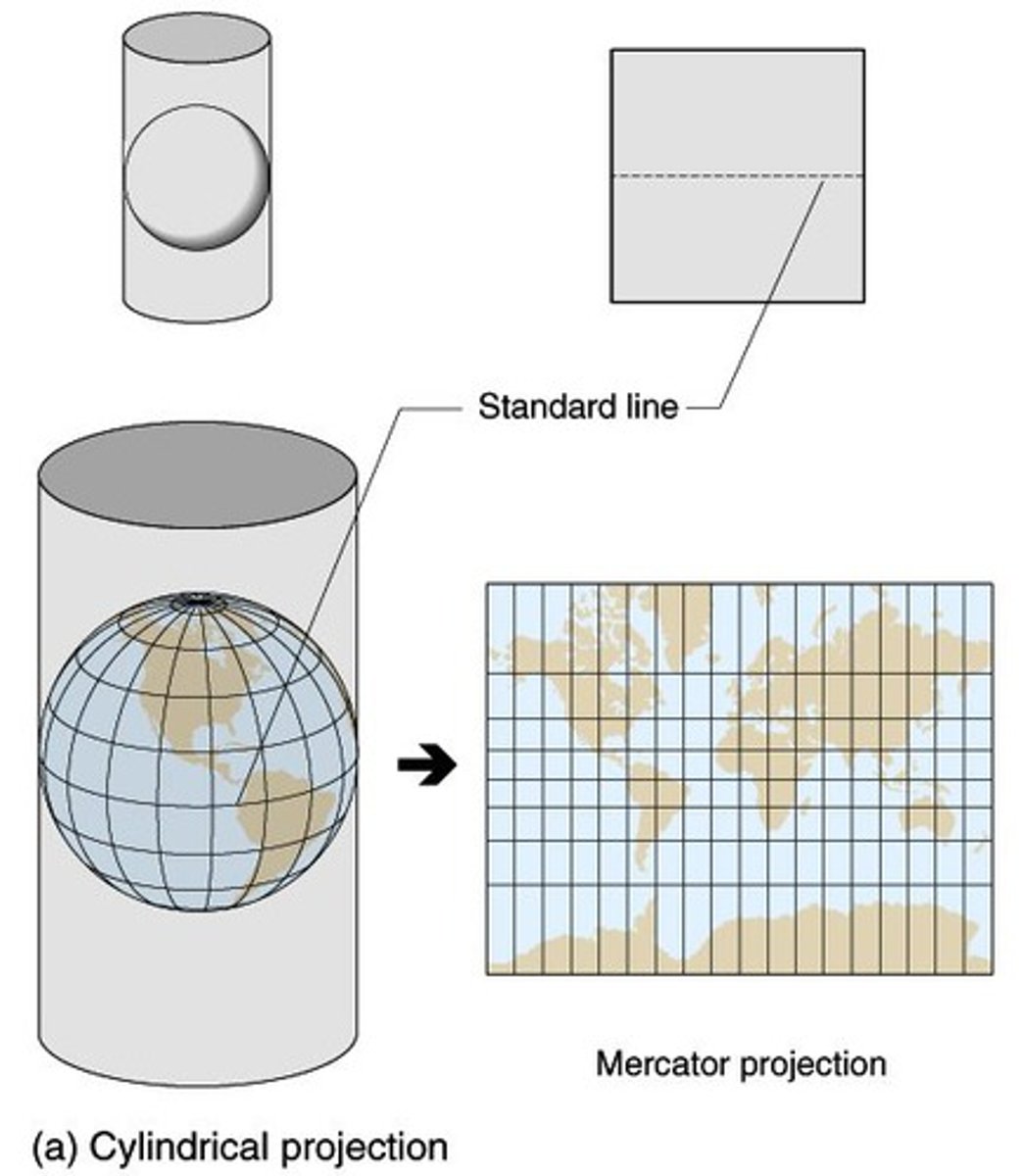
projection
to minimize distortion
cylindrical projection
a map projection that is made by moving the surface features of the globe onto a cylinder. (Good for low latitude representation)
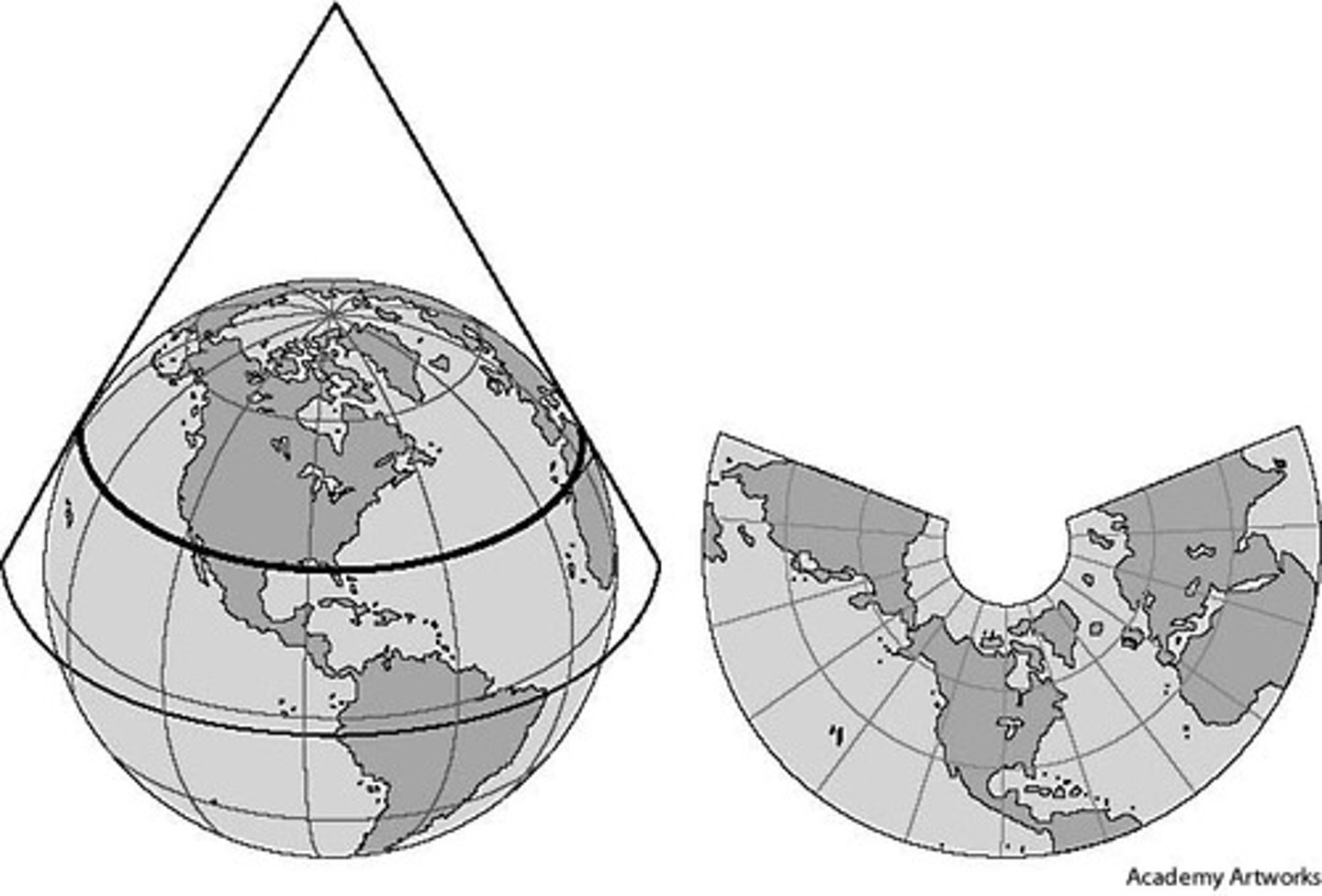
conic projection
a map created by projecting an image of Earth onto a cone placed over part of an Earth model. (Good for mid-latitude representation.
azimuthal projection
A map projection in which the plane is the most developable surface. (Good for high latitude representation)
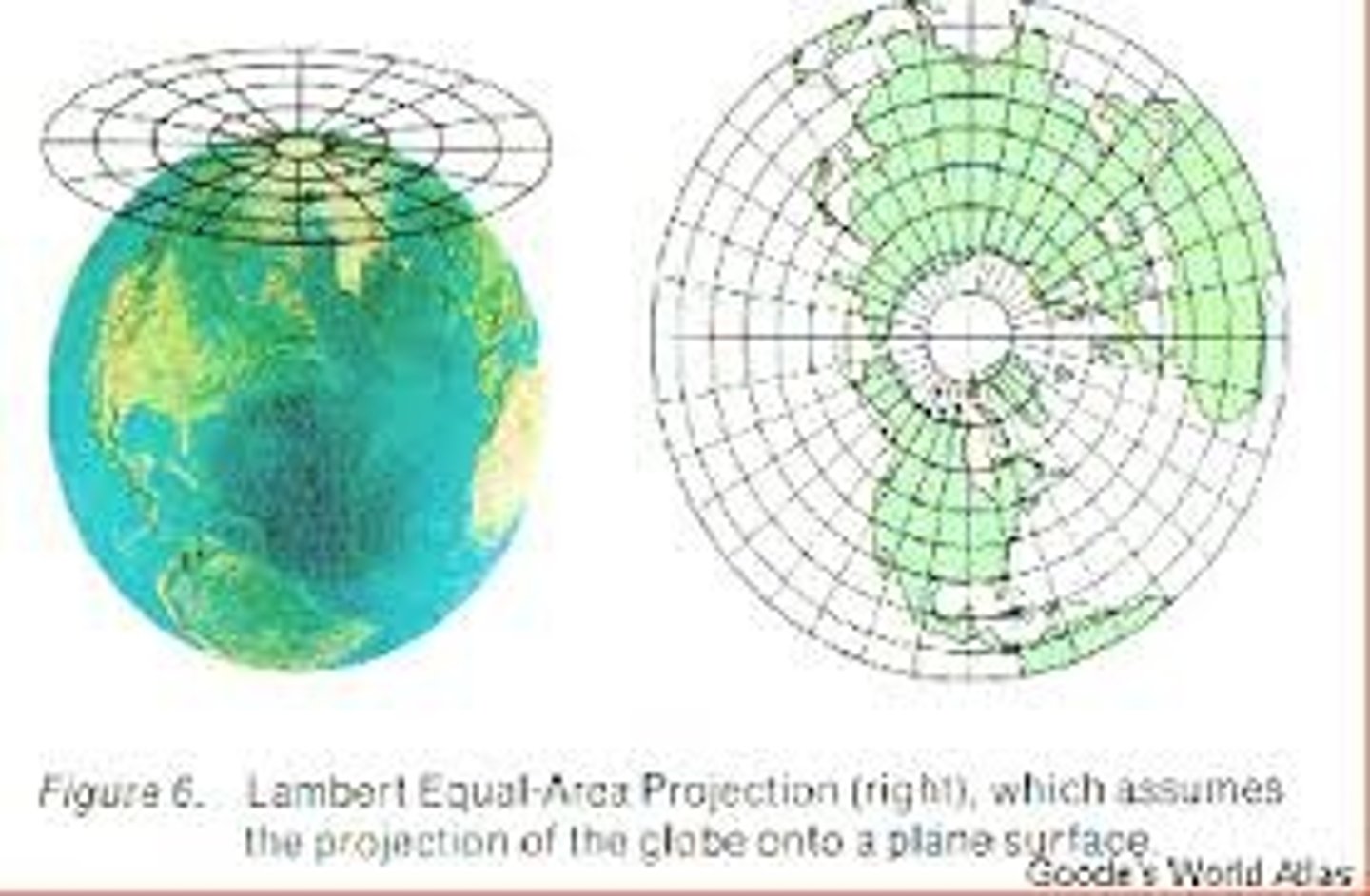
distortion on map examples
relative size of regions, the shape of regions, directions, distances, and remote sensing
photographic imaging system
real photo
non photographic imaging systems
radar
atmosphere uniform gas
oxygen, nitrogen, and a little argon
variable gas
water vapor and carbon dioxide
atmosphere variable gas
water vapor, carbon dioxide, some carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide
exosphere
The outer layer of the thermosphere, extending outward into space.
thermosphere
The uppermost layer (4th) of the atmosphere, in which the temperature increases as altitude increases. Aurora-Burolious happens here.
mesosphere
3rd layer of the atmosphere, where as altitude increases, the temperature decreases.
stratosphere
1) 2nd layer of atmosphere 2) location of ozone layer; 3) absorbs 95% of Ultraviolet radiation; 4) temperature increases with altitude increase.
ozone layer (what gas makes it up? Why important?)
O3 absorbs UV radiation coming from the sun
trophosphere
1) first layer of atmosphere off ground. Every atmospheric reaction happens here. Gets colder the more altitude increases.
elements of weather and climate
temperature, moisture, pressure, wind
attenuation
depletion of solar energy
beam spreading
The way a light beam covers a larger area when it hits a surface at an angle
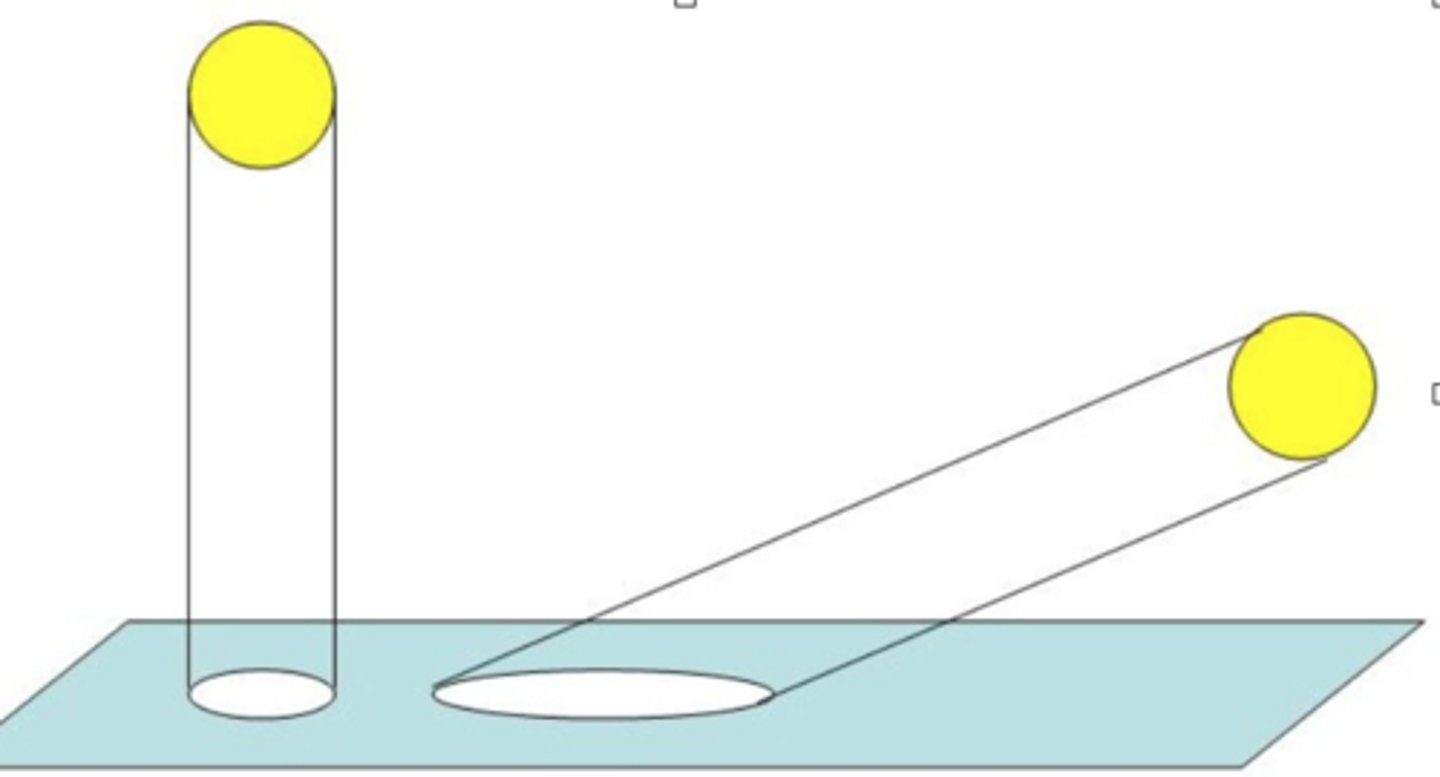
shortwave radiation
hot bodies (ex: the sun)
longwave radiation
cool bodies (ex: the earth)
absorption
the process or action by which one thing absorbs or is absorbed by another
reflection
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a surface through which it cannot pass.
tranmission
heat that that pass through air or some other median like liquid or solids
scattering
reflection of light in all directions
advection
horizontal movement of heat in air
convection
Vertical movement of heat. Process by which, in a fluid being heated, the warmer part of the mass will rise and the cooler portions will sink.
conduction
of heat through a solid object
the gas law
when air is compressed its temperature will increase - when air expands its temperature will decrease
adiabatic processes
Cooling happens through expansion (no heat is added)
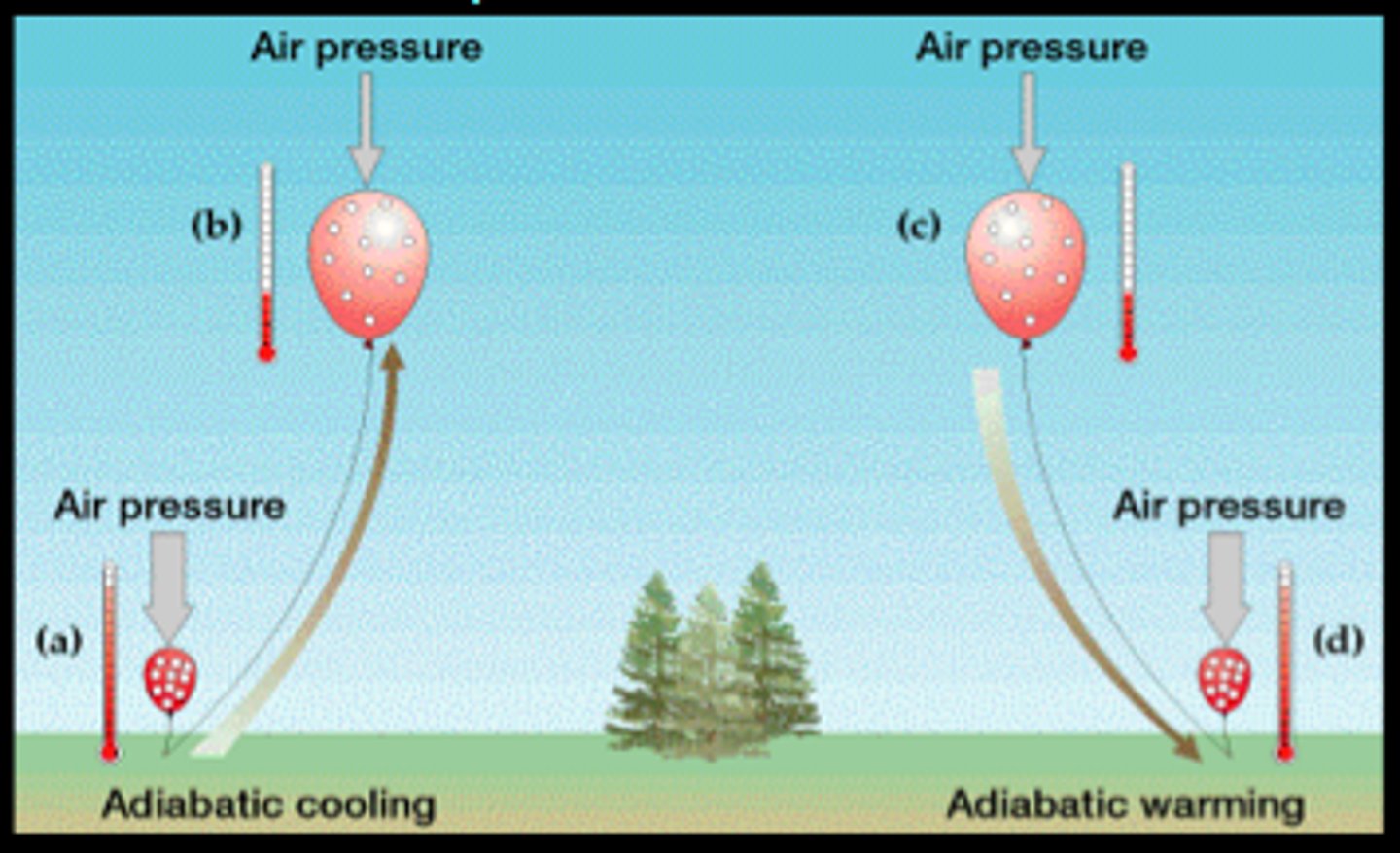
water example: loss of heat
dew forming on blades of grass (condesnation) and snowflake formation (deposition)
sensible heat
when an object is heated its temperature rises as heat is added (an increase in heat)
latent heat
heat loss or gained through a change in the state of water - the heat you need to change the state of matter
water example: addition of heat
evaporation of water and melting ice
melting
cooling process for the environment (ice absorbs energy from the environment and melts)`
freezing
cooling process or water to solid
evaporation
The change of state from a liquid to a gas
condensation
Gas to liquid - warming
sublimation
solid to gas - cooling

deposition
gas to solid - cooling

solid
ice
liquid
water
gas
water vapor
Incoming solar radiation is reflected by what?
reflected by the atmosphere, clouds, surface and absorbed by clouds, and surface
surplus
extra
deficit
A deficiency or lack of something
reasons for unequal heating
1) latitudinal differences 2) length of the day 3)atmospheric obstructions
melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. 32 degrees F or 0 degrees C
boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas. 212 degrees F or 100 degrees C
subsolar point
The point on the Earth where the Sun angle is 90° and solar radiation strikes the surface most directly at any given point in time. Produces no shadows too.
What are the two ways that the solar rays' intensity is depleted?
1) Atmosphere absorbs it. 2)Sun's energy isn't as direct, and the sun's ray intensity decreases
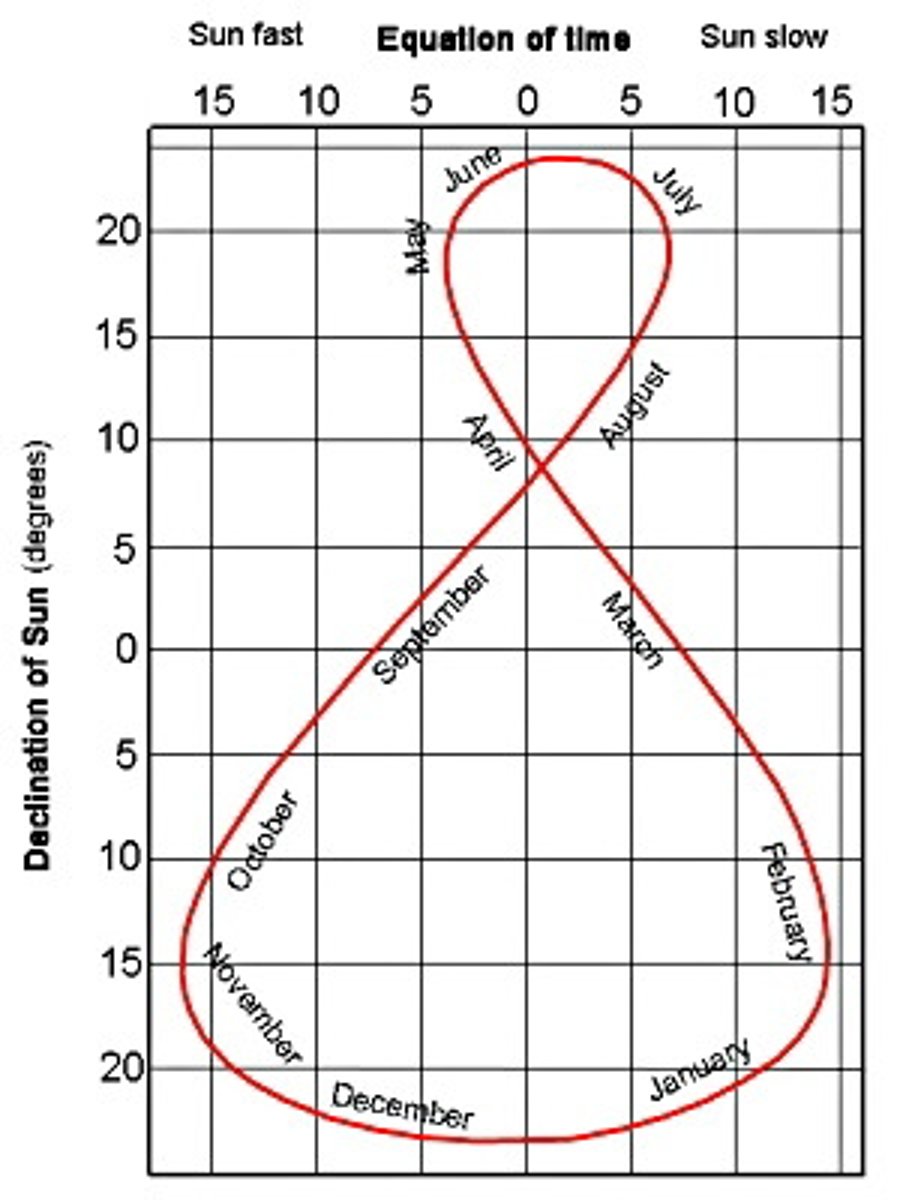
declination
the latitude on Earth at which the noon sun is directly overhead
analemma
shows the declination of sun throught-out the year
What is the coldest time of day?
Right before sunrise
What is the hottest time within a typical day?
3 PM ish
What are the two main processes of heat transfer on earth?
1) Ocean circulation (currents) 2) Atmospheric Circulation
Perihelion
Earth's orbital point nearest to the sun.
Aphelion
Earth's orbital point furthest from the sun.