Electricity and Magnetism
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Fundamental Forces in Nature
Which of the four fundamental forces in nature has infinite range but is the weakest?
Gravitational force.
Fundamental Forces in Nature
Which force has an infinite range and is stronger than gravity?
Electromagnetic force.
Fundamental Forces in Nature
Which fundamental force is the strongest but acts only over a short range?
Strong nuclear force.
Fundamental Forces in Nature
Which force is weaker than the strong nuclear and electromagnetic forces but stronger than gravity?
Weak nuclear force.
Fundamental Forces in Nature
Which of the four fundamental forces is the most noticeable in daily life?
Electromagnetic force.
Static Electricity
How is static electrical charge created?
When insulators (or conductors insulated from Earth) are subjected to friction.
Static Electricity
What are the two types of static electrical charge?
Positive and negative charge.
Static Electricity
What determines the type of charge acquired?
The material of the rod and the cloth.
Static Electricity
What charge does a polythene rod acquire when rubbed with a cloth?
Negative charge.
Induced Charges
What charge does a polythene rod acquire when rubbed with a cloth?
Negative charge.
Induced charges
Which charges are able to move?
Only negative charges.
Induced Charges
What happens to electrons in the paper when a positively charged rod approaches?
They are attracted towards the rod, inducing charge on the paper.
Induced Charges
Why does the paper stick to the positive rod?
The negative side of the paper is attracted to the positive rod.
Field Lines and Patterns
How do two charged bodies interact with each other without direct contact?
They exert equal and opposite forces on each other.
Field Lines and Patterns
What is the path that a free positive test charge follows called?
A field line or a line of force.
Field Lines and Patterns
What is the convention for field line direction?
Field lines move away from a positive charge and towards a negative charge.
Field Lines and Patterns:
Can field lines cross each other?
No, field lines never cross each other
Current Electricity - Potential Difference
What are the units for potential difference?
Volt (V).
Current Electricity - Potential Difference
Why does an electrical current flow?
Because of a difference in electrical potential
Current Electricity - Potential Difference
In which direction does electrical current flow?
From points at a higher potential to points at a lower potential.
Current Electricity - Potential Difference
What causes the two terminals of a conventional battery to be at different electrical potentials?
The action of chemicals inside the battery.
Current Electricity - Potential Difference
What are the two different electrical potentials in a battery called?
Positive (+ve) and negative (-ve).
Current Electricity - Potential Difference
Do volts flow?
No, volts do not flow
Current Electricity - Current
What is the definition of current?
The flow of charged particles
Current Electricity - Current
What are the units for current?
Amperes (A).
Current Electricity - Current
What is the equation for current?
Current = charge ÷ time (I = Q/t).
Current Electricity - Current
What are the units of charge?
Coulombs.
Coloumb’s Law
What does Coulomb’s Law describe?
The force between two charged objects.
Coloumb’s Law
How does the force between two charges change as their separation distance increases?
The force decreases.
Coloumb’s Law
What happens to the force if the magnitude of the charges increases?
The force increases.
Coloumb’s Law
What type of force acts between like charges?
A repulsive force.
Coloumb’s Law
What type of force acts between opposite charges?
An attractive force.
Coloumb’s Law
What is the equation for Coulomb’s Law?
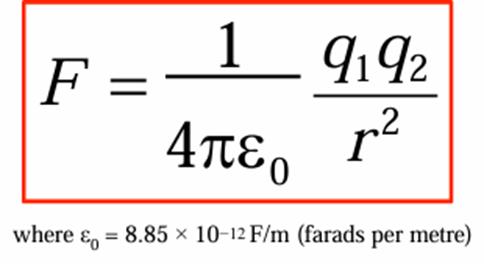
Coloumb’s law:
How does Coulomb’s force compare to gravitational force at the atomic scale?
Coulomb’s force is much stronger than gravitational force.
Resistance & Conductance
What does a conductor do to the flow of current?
It tries to impede the flow of current unless it’s a superconductor
Resistance & Conductance
What is the equation for resistance?
R = V/I
where ( V ) is voltage and ( I ) is current.
Resistance & Conductance
What is the unit for resistance?
Ohm (Ω)
Resistance & Conductance
What happens to resistance if the length of a conductor is doubled?
The resistance also doubles.
Resistance & Conductance
How is resistance calculated in terms of resistivity?
R = resistivity x L/A
where ( L ) is length, and ( A ) is cross-sectional area.
Resistance & Conductance
What are practical applications of measuring resistivity?
Geological and archaeological surveys.
Electron Drift in Materials
What is the typical electron drift speed in metals?
About 1mm per second.
Electron Drift in Materials
What causes resistance in metals?
Electron collisions with the metal lattice.
Electron Drift in Materials
How does temperature affect resistance?
As temperature increases, resistance increases.
Ohms Law & Power
What is Ohm’s Law?
I = V/R
where ( I ) is current, ( V ) is voltage, and ( R ) is resistance.
Ohms Law & Power
What is the formula for electrical power?
A: ( P = V x I ) or ( P = I^2 x R ).
Ohms Law & Power
What is the unit of power?
Watt (W) or J/s
Magnetism
Where were the first magnetic phenomena observed?
In fragments of magnetized iron ore near ancient Magnesia (now Manisa).
Magnetism
What are the three elements capable of being permanent magnets?
Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt.
Magnetism
How can metal be ‘frozen’ into alignment to create a magnet?
By heating it in the presence of a strong magnet.
Visualizing magnetic fields
What happens when opposite magnetic poles come close?
They attract.
Visualizing magnetic fields
What happens when like magnetic poles come close?
They repel.
The Tesla
What is the SI unit of magnetic flux density?
Tesla (T) or 10,000 Gauss (old unit)
Electromagnetism & The Earth’s Magnetic Field
What generates Earth's magnetic field? What intensity is it?
Interaction between inner and outer cores (hot fluid inside) and electric fields
6× 10-5 tesla.
Electromagnetism & The Earth’s Magnetic Field
What geological process helps scientists understand planetary formation?
Palaeomagnetism—decoding locked-in magnetic signals in minerals.
Electromagnetism & The Earth’s Magnetic Field
What rule summarizes the relationship between current direction and magnetic field direction?
The Right-Hand Rule.
Electromagnetism & The Earth’s Magnetic Field
What happens during a geomagnetic flip? What could this cause?
The North Pole becomes the South Pole and vice versa.
Cause disruption of communication systems and power grids; produce multiple north and south poles causing birds, whales and other migratory animals that use the field to establish a sense of direction to encounter problems with their direction.
Magnetic Materials - Ferromagnetic
What is a ferromagnetic material?
A material that is strongly magnetized in the same direction as an applied magnetic field
Magnetic Materials - Ferromagnetic
What happens when a ferromagnetic material is heated?
It loses its magnetism and becomes paramagnetic.
Magnetic Materials - Ferromagnetic
Do ferromagnetic materials retain their magnetism after the field is removed?
Yes, they remain magnetized.
Magnetic Materials - Ferromagnetic
What elements are ferromagnetic?
Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt.
Magnetic Materials - Paramagnetic:
What happens to a paramagnetic material when a magnetic field is removed?
It loses its magnetism.
Magnetic Materials - Paramagnetic
What causes paramagnetism?
Randomly oriented magnetic moments that align weakly with an applied field
Magnetic Materials - Paramagnetic
Give examples of paramagnetic materials.
Oxygen, Magnesium, and Aluminium.
Magnetic Materials - Diamagentic
How does a diamagnetic material behave in a magnetic field?
It creates an induced field in the opposite direction and is repelled.
Magnetic Materials - Diamagentic
Do diamagnetic materials have permanent magnetic dipoles?
No, permanent dipoles are absent in diamagnetic materials.
Magnetic Materials - Diamagentic
Give examples of diamagnetic materials.
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, and Sodium.
Resistors in Series
What happens to total resistance when resistors are connected in series?
The total resistance increases because resistances add up
Resistors in Series
What is the formula for total resistance in a series circuit?
R = R1 + R2 + R3
Resistors in Series
How does current behave in a series circuit?
The same current flows through all components
Resistors in Series
How does voltage behave across resistors in a series circuit?
The voltage is divided among the resistors depending on their resistance
Resistors in Parallel
What happens to total resistance when resistors are connected in parallel?
The total resistance decreases because multiple paths allow current to flow
Resistors in Parallel
What is the formula for total resistance in a parallel circuit?
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
Resistors in Parallel
How does voltage behave in a parallel circuit?
The voltage across all parallel resistors is the same.
Resistors in Parallel
How does current behave in a parallel circuit?
The total current is the sum of the currents flowing through each branch.