Competency Review Advanced Micro 3
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards

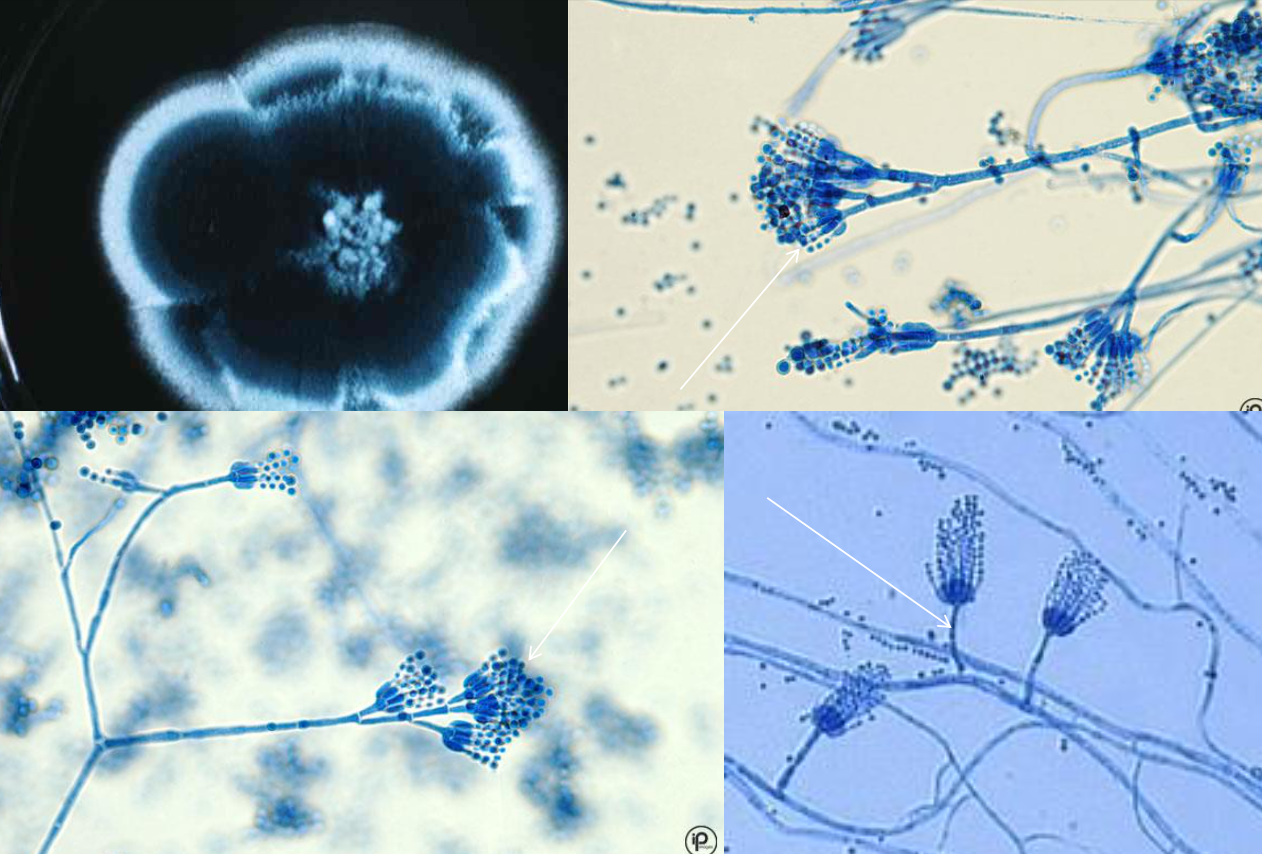
Colony and microscopic morphology of: Penicillium
Microscopic: Septate hyphae, branched conidiophores with 2 branches, flask shaped phialides with chains of round conidia - brush like
Colony: flat, powdery, blue green with white edge
Colony: flat, powdery, blue green with white edge
2
New cards
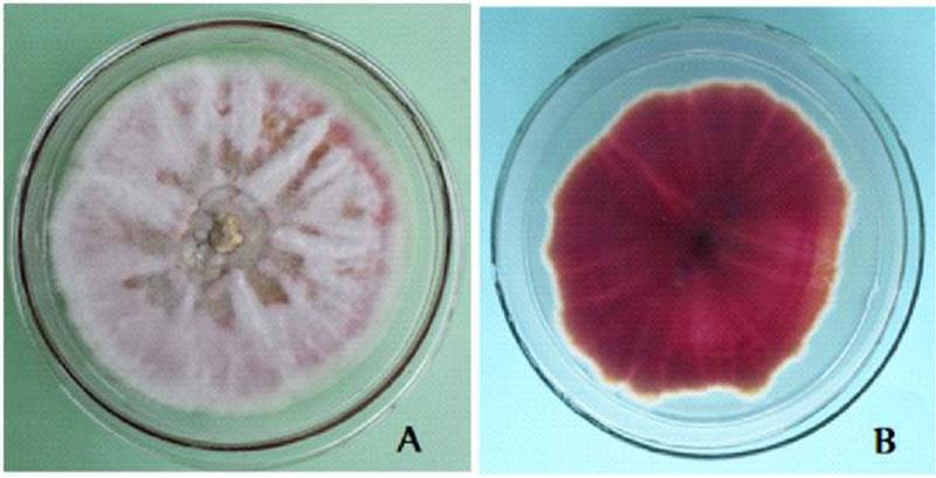
Colony and microscopic morphology of: Fusarium,
Microscopic: septet hyphae, large multi-celled sickle shaped macroconidia on simple conidiophores. small 1-2 celled tear-drop shaped microconidia
Colony: flat, pink to violet with light edge
Colony: flat, pink to violet with light edge

3
New cards
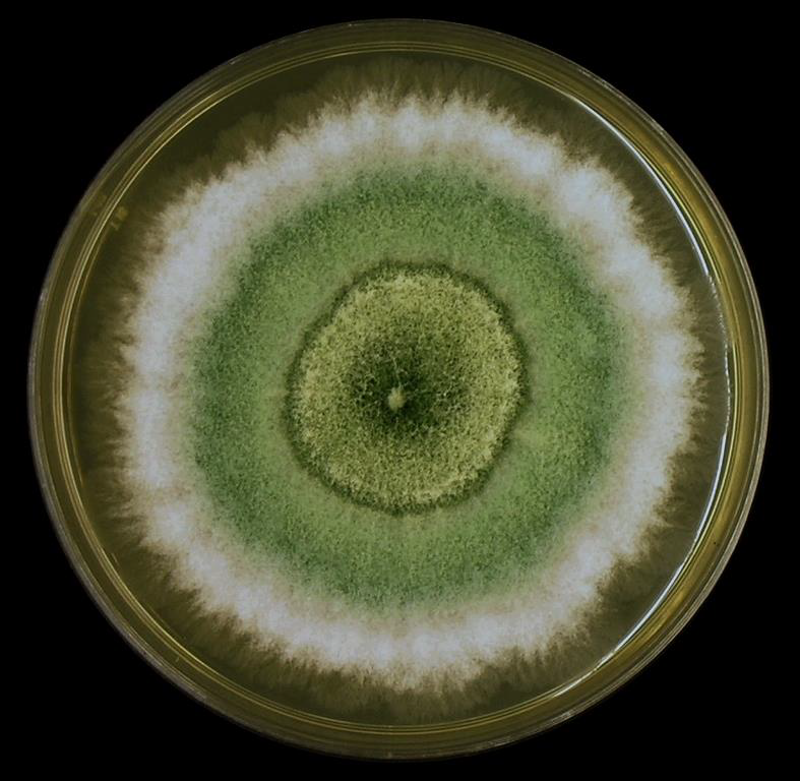

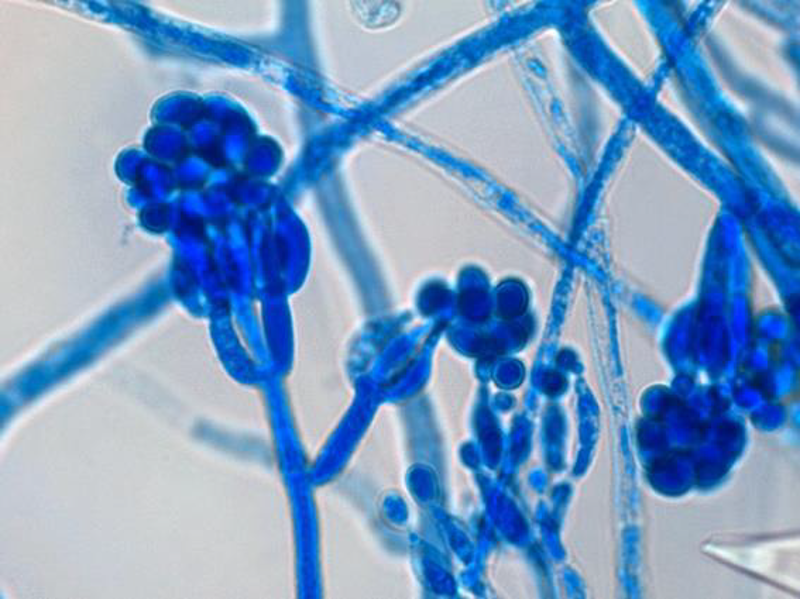
Colony and microscopic morphology of: Gliocladium
Microscopic: Branching conidiophores with flask-shaped phialides like penicillium, microconidia cluster in ball like a golf ball
Colony: White at first, center becomes dark green, reverse: white
Colony: White at first, center becomes dark green, reverse: white
4
New cards
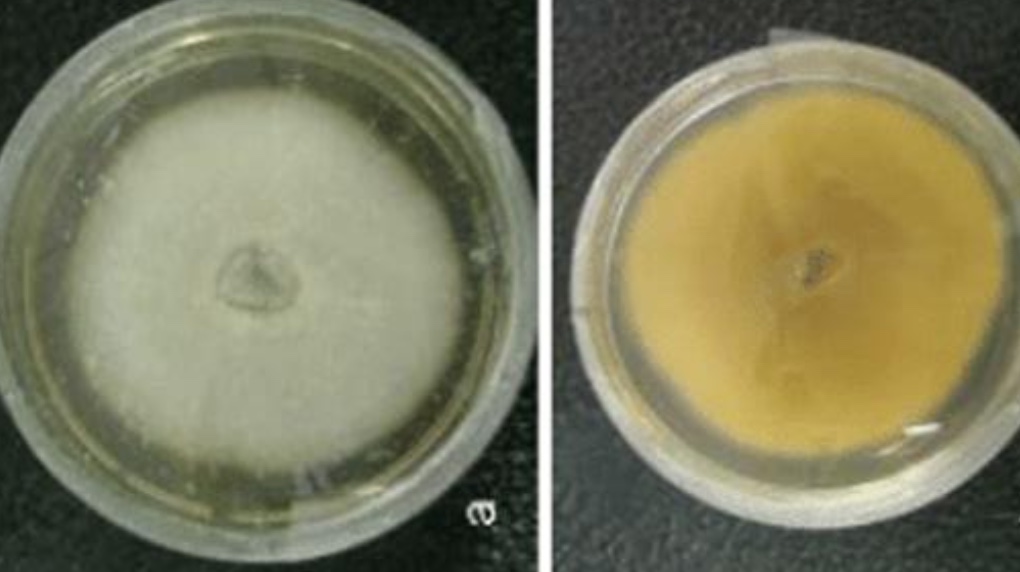
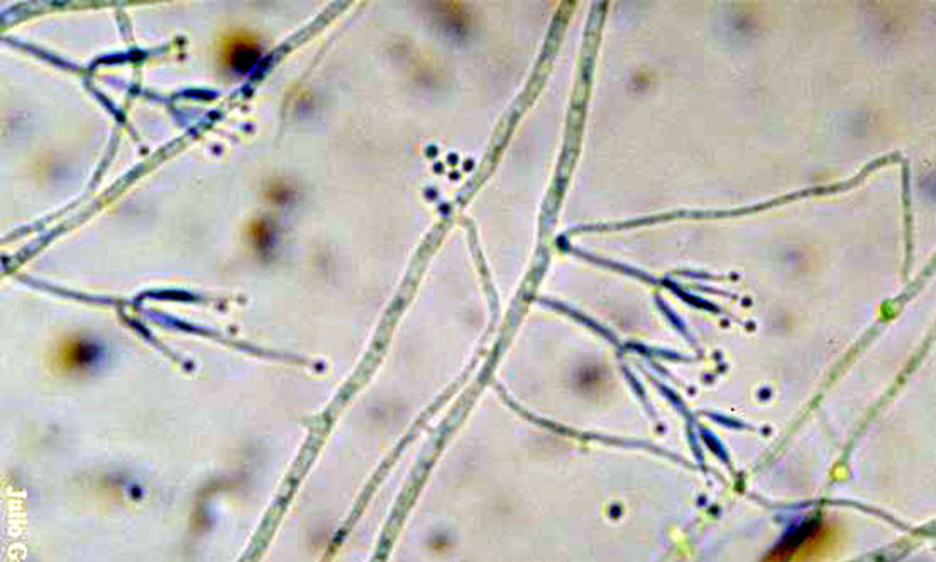
Colony and microscopic morphology of: Paecilomyces
Microscopic: branching conidiophores with flask-like phialides in pairs or brush-like groups, long chains of oval microconidia, resembling penicillium
Colony: yellowish brown, pink, white with reverse off-white, light yellow, pale brown
Colony: yellowish brown, pink, white with reverse off-white, light yellow, pale brown
5
New cards
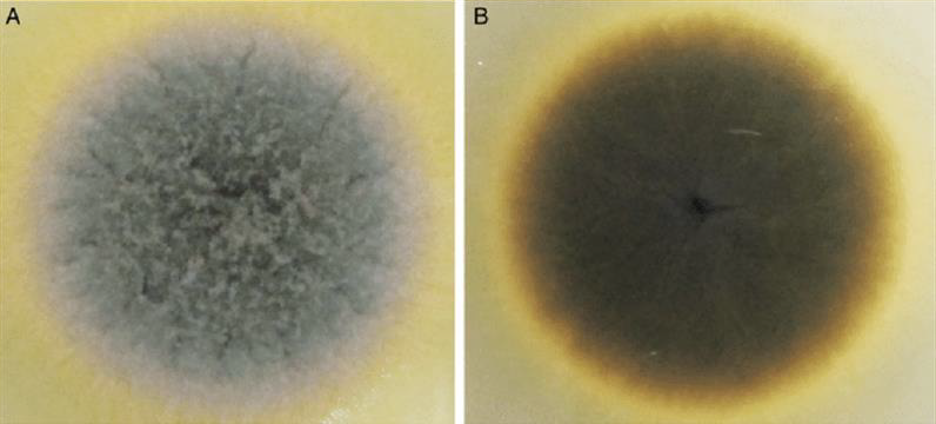
Colony and microscopic morphology of: Bipolaris
Microscopic: elongated conidiophores, oblong conidia with 3 to 5 separation
Colony: Gray, brown, or black with brown. Reverse black.
Colony: Gray, brown, or black with brown. Reverse black.
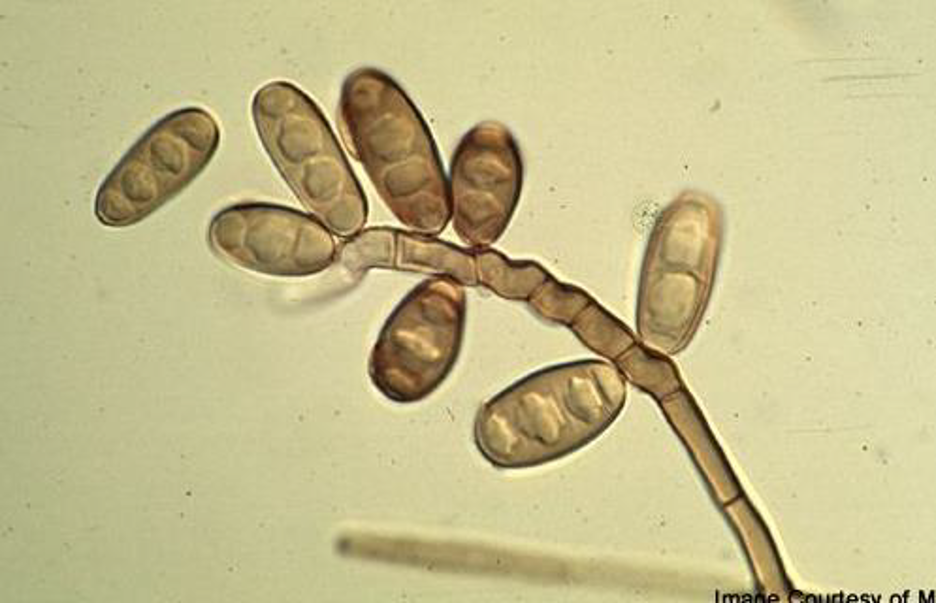
6
New cards
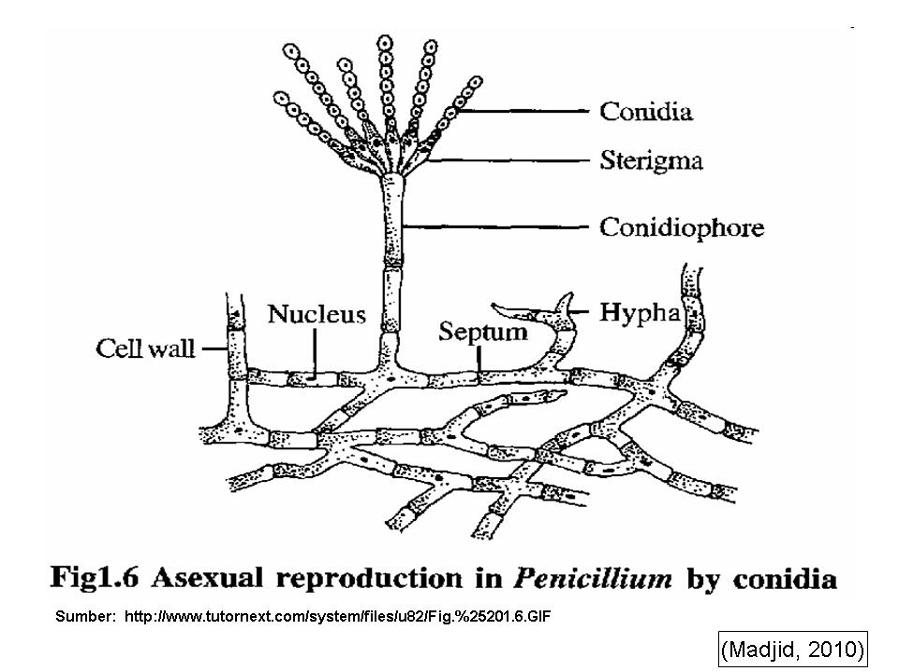
Know the names of the structures found in Penicillium
Septate hyphae, branched conidiophores w/ secondary branches, flask shaped phialides w/ chains of round conidia
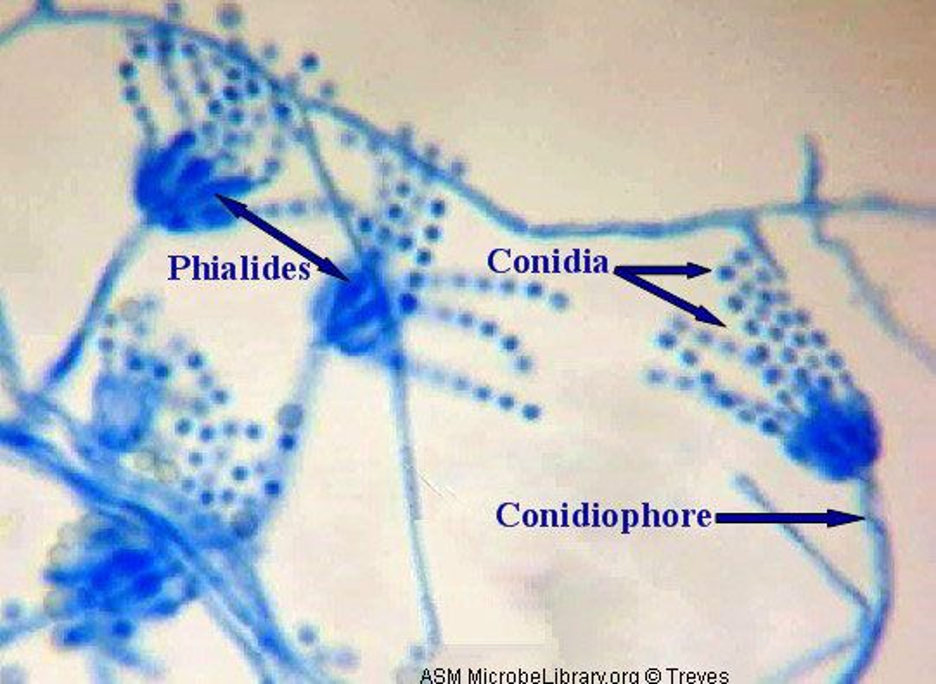
7
New cards
Know the names of the structures found in Fusarium
Septate hyphae, large multi-celled sickle-shaped macroconidia on simple conidiophores, small 1-2 celled tear-drop-shaped microconidia
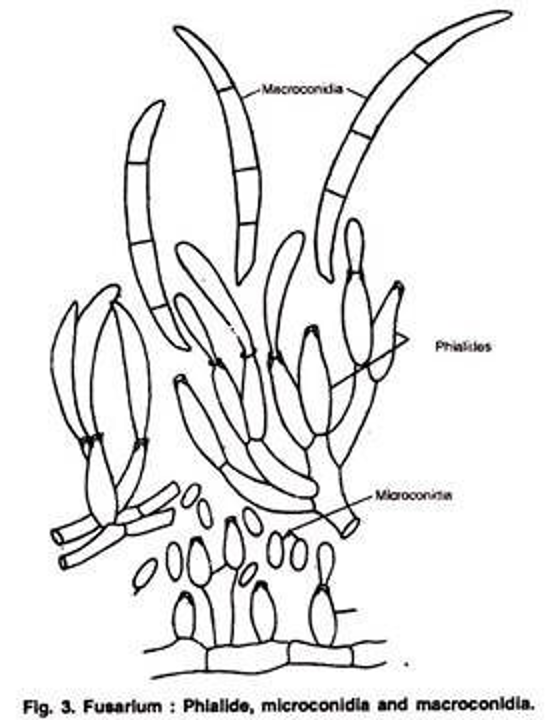
8
New cards
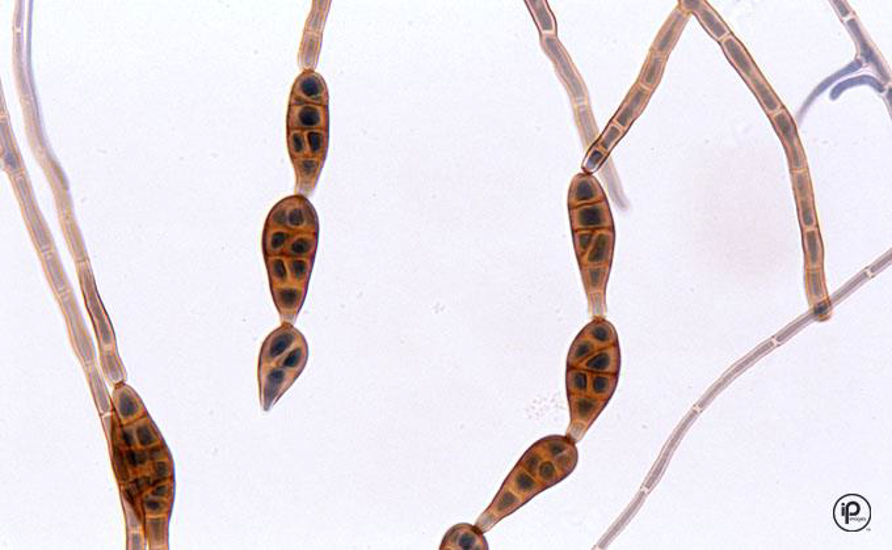

Microscopic morphology of: Alternaria
septate hyphae and dark
large conidia, club shaped
large conidia, club shaped
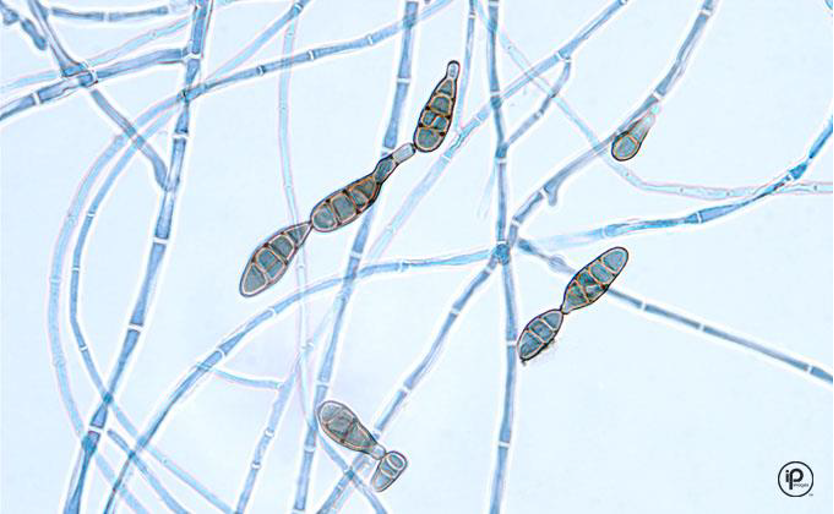
9
New cards
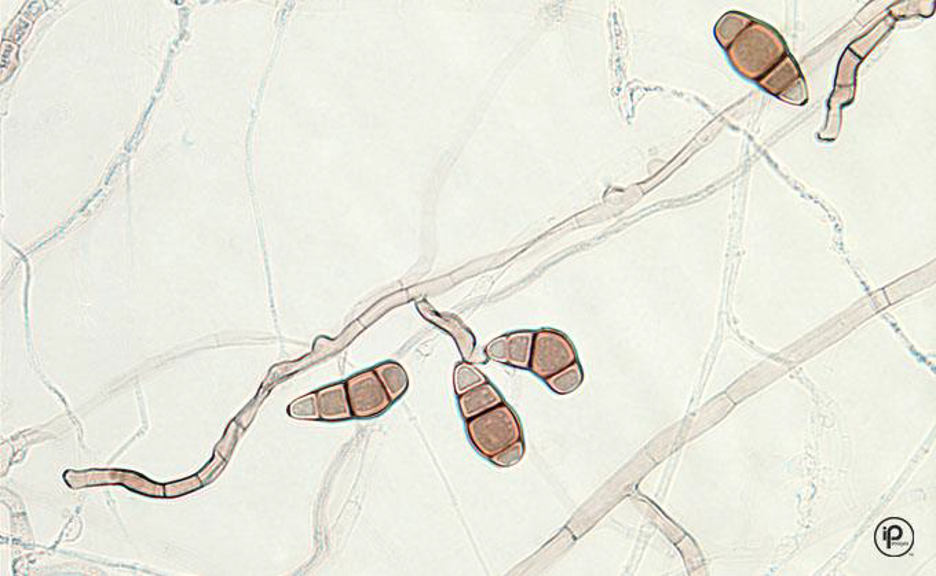
Microscopic morphology of: Curvularia
Septate hyphae
Large conidia with up to 4 cells
central cell swollen - curved
Large conidia with up to 4 cells
central cell swollen - curved
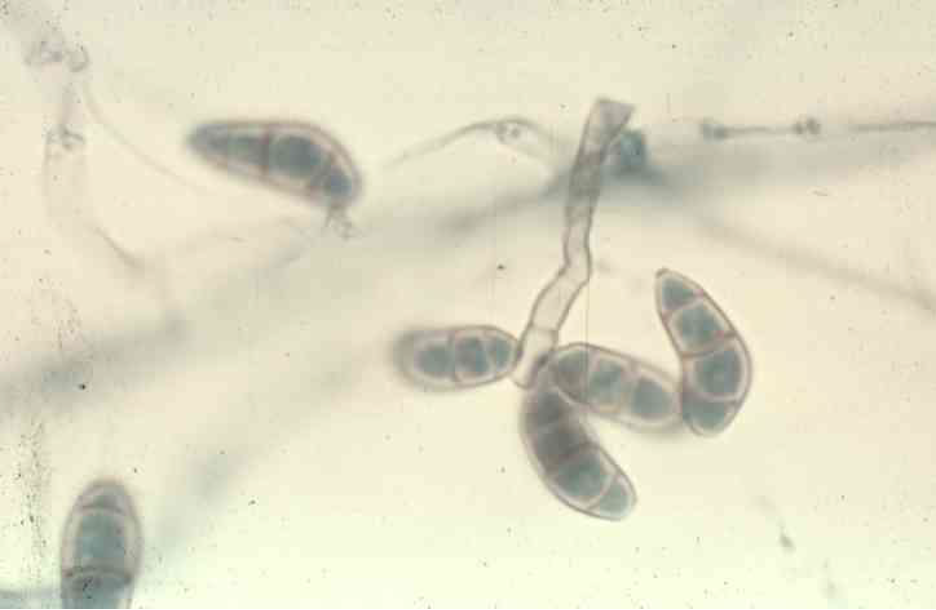
10
New cards
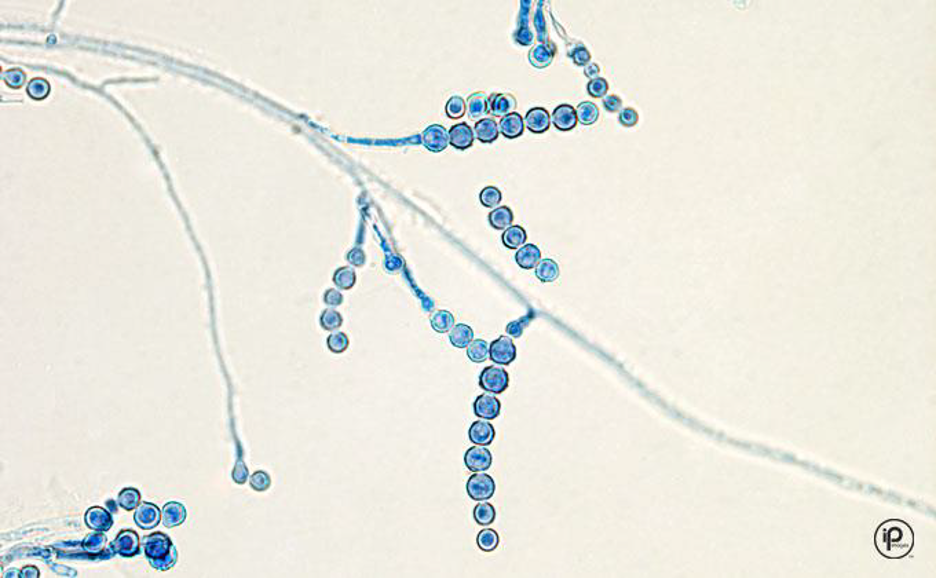
Microscopic morphology of: Scopulariopsis
short conidiophores with round, rough chains of conidia
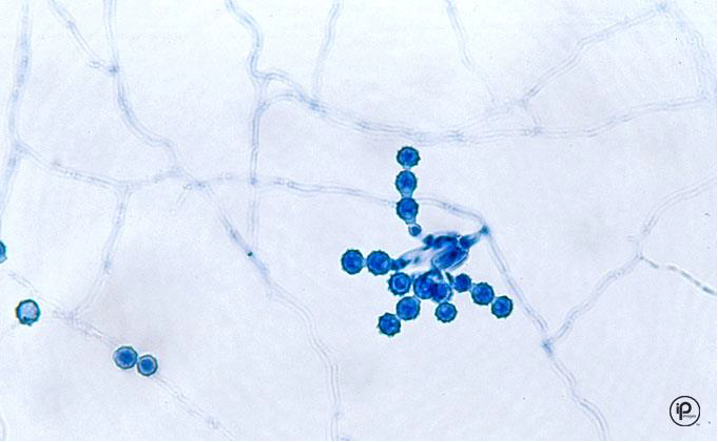
11
New cards
Gram stain results for: Bacillus anthracis
Gram Positive Rod
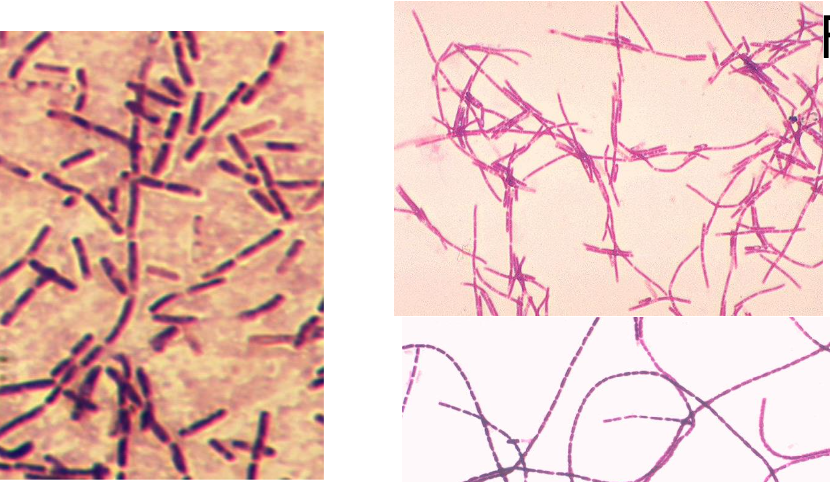
12
New cards
Gram stain results for: Francisella tularensis
Tiny Gram Negative Coccobacillus
13
New cards
Gram stain results for: Yersinia pestis
Gram Negative Rods - may be bipolar stained

14
New cards
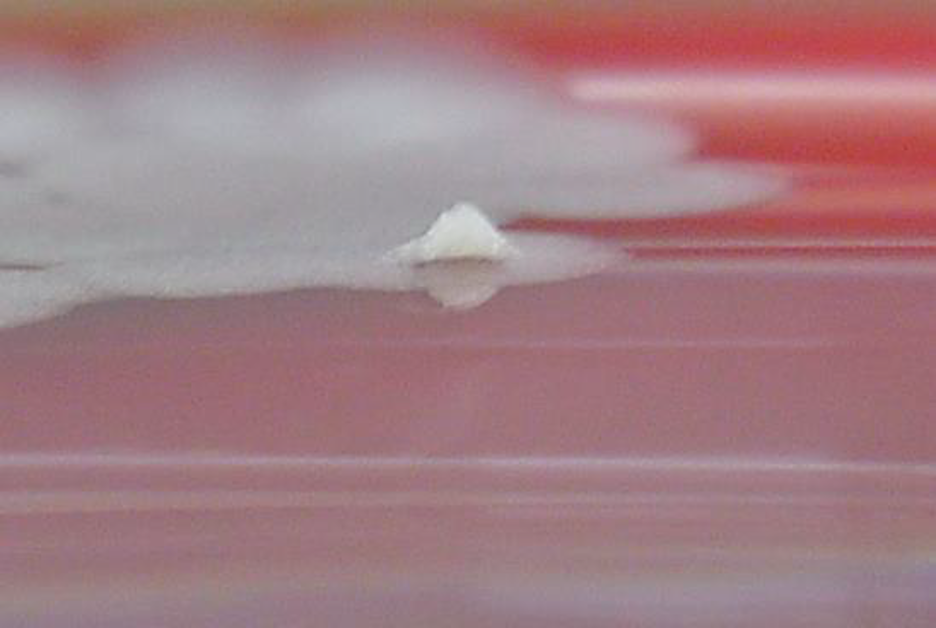

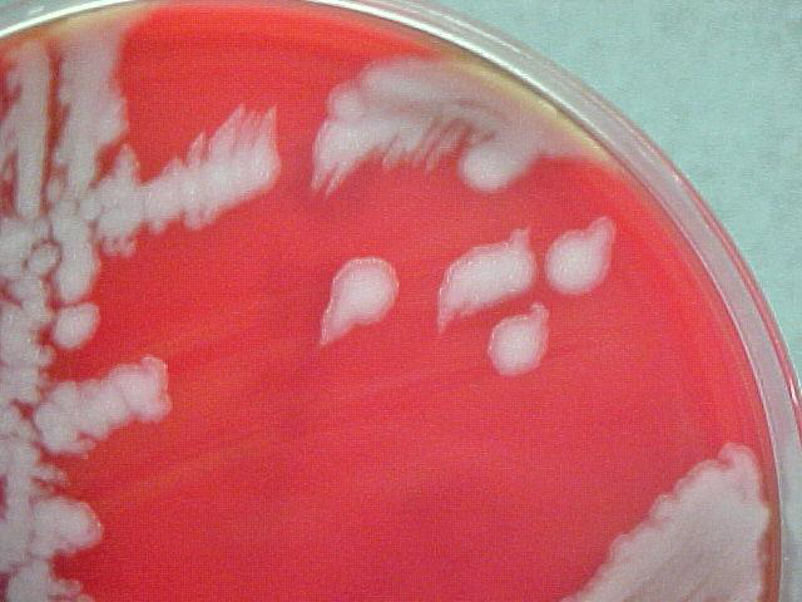
The colony morphology of Bacillus anthracis
Aerobic, 4-8hr growth
No growth on MacConkey (GPR)
Flat colonies with irregular edges
Non-hemolytic on BAP
Sticky colonies
No growth on MacConkey (GPR)
Flat colonies with irregular edges
Non-hemolytic on BAP
Sticky colonies
15
New cards
Which of these are you most likely to come across in the southwest?
Yersinia pestis (plague)
16
New cards
Know the diseases caused by each organism: Bacillus Anthracis
Anthrax
17
New cards
Know the diseases caused by each organism: Francisella Tularensis
Tularemia
18
New cards
Know the diseases caused by each organism: Yersinia pestis
Plague
19
New cards
Things to consider determining if you have a bioterrorism organism
Patient history/travel history
Symptoms
Gram stain results
- GP, small GNC, faintly staining GNR
Growth and/or no growth on routine culture plates
- Slow growth on blood agar plate
- Slow or no growth on MacConkey plate
Symptoms
Gram stain results
- GP, small GNC, faintly staining GNR
Growth and/or no growth on routine culture plates
- Slow growth on blood agar plate
- Slow or no growth on MacConkey plate