1. Hepatic lesions caused by circulatory disorders. Nonviral inflammatory diseases of the liver. Drug hepatopathies
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Weight of liver?
1100-1300g
Subgroups of hepatic lesions caused by circulatory disorders?
- Impaired blood into the liver
- Impaired blood flow through the liver
- Impaired blood flow out of the liver
Impaired blood flow into the liver?
- Hepatic artery infarct
- Portal vein obstruction and thrombosis
Why are infarcts to the liver rare?
Because of the dual blood supply
- retrograde arterial flow through the accessory vessels and portal venous supply is enough
Hepatic artery infarct?
Rare
- interruption of the main hepatic artery wont cause ischaemic necrosis
Which scenarios can cause extrahepatic portal vein obstruction?
- Pancreatitis, which cause a thrombosis in the splenic vein that moves into the portal vein
- Thrombogenic disease
- Postsurgical thrombosis
- Cirrhosis
How can cirrhosis cause portal vein obstructions?
Does not obstruct directly, but slows down the blood flow which increase the risk for thrombus formation
Symptoms of portal vein obstruction?
- Abdominal pain
- Ascites
- Portal hypertension
What will an obstruction of the portal vein lead to in the liver?
Infarct of Zahn
Infarct of Zahn?
Sharply demarcated area of red-blue discoloration
- no necrosis but congestion in the sinusoids and atrophy of hepatocytes
Impaired blood flow through the liver?
- Nutmeg liver
- Central haemorrhagic necrosis
What is nutmeg liver?
Chronic passive congestion of liver
- due to right-sided heart failure
What is central haemorrhagic necrosis?
death of liver cells near central vein
due to: toxins; alcohol, drugs or due to acute right sided HF
Hepatic vein outflow obstructions?
- Hepatic vein thrombosis
- Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
Another name for hepatic vein thrombosis?
Budd-Chiari syndrome
What does hepatic vein thrombosis cause?
Congestion of the liver
- Hepatomegaly
- Ascites
- Portal hypertension
Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome is caused by?
Caused by damage to the sinusoidal epithelium
- most commonly due to chemotherapy or radiation
What will happen to the sinusoidal epithelium in sinusoidal obstruction syndrome?
The damaged endothelium cells will slough and form thrombi
- which block the sinusoidal flow
Non-viral inflammatory diseases of the liver?
- Neonatal hepatitis
- Cholangitis
- Liver abscess
- Echinococcus cyst in the liver
What is neonatal hepatitis?
A group of disorders in neonates, which are characterized by;
- hepatocellular dysfunctions
- cholestasis
- conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
What can cause neonatal hepatitis?
- TORCH infections
- Metabolic causes
- Bile duct anomalies
- Progressive familiar intrahepatic cholestasis
Morphology of neonatal hepatitis?
- Balloonisation or focal necrosis of hepatocytes
- Multinucleated hepatocytes
- Lymphocytic infiltration
- Proliferation of bile ducts
What is progressive familiar intrahepatic cholestasis?
Condition which cause cholestasis due to defects in the biliary epithelial transporters
Examples of metabolic causes?
- Fructosaemia
- Galactosemia
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
What is cholangitis?
Inflammation in the biliary tree
Causes of cholangitis?
Usually caused by anything that can obstruct the bile flow
- choledoclithiasis
- surgery of the biliary tree
- tumors
- acute pancreatitis
Stasis = good place for bacteria to grow
Where does the bacteria enter in cholangitis?
Usually enter the biliary tract via the Sphincter of Oddi rather than the blood
- results in an ascending cholangitis
What are usually the pathogens in cholangitis?
- E. Coli
- Klebsiella
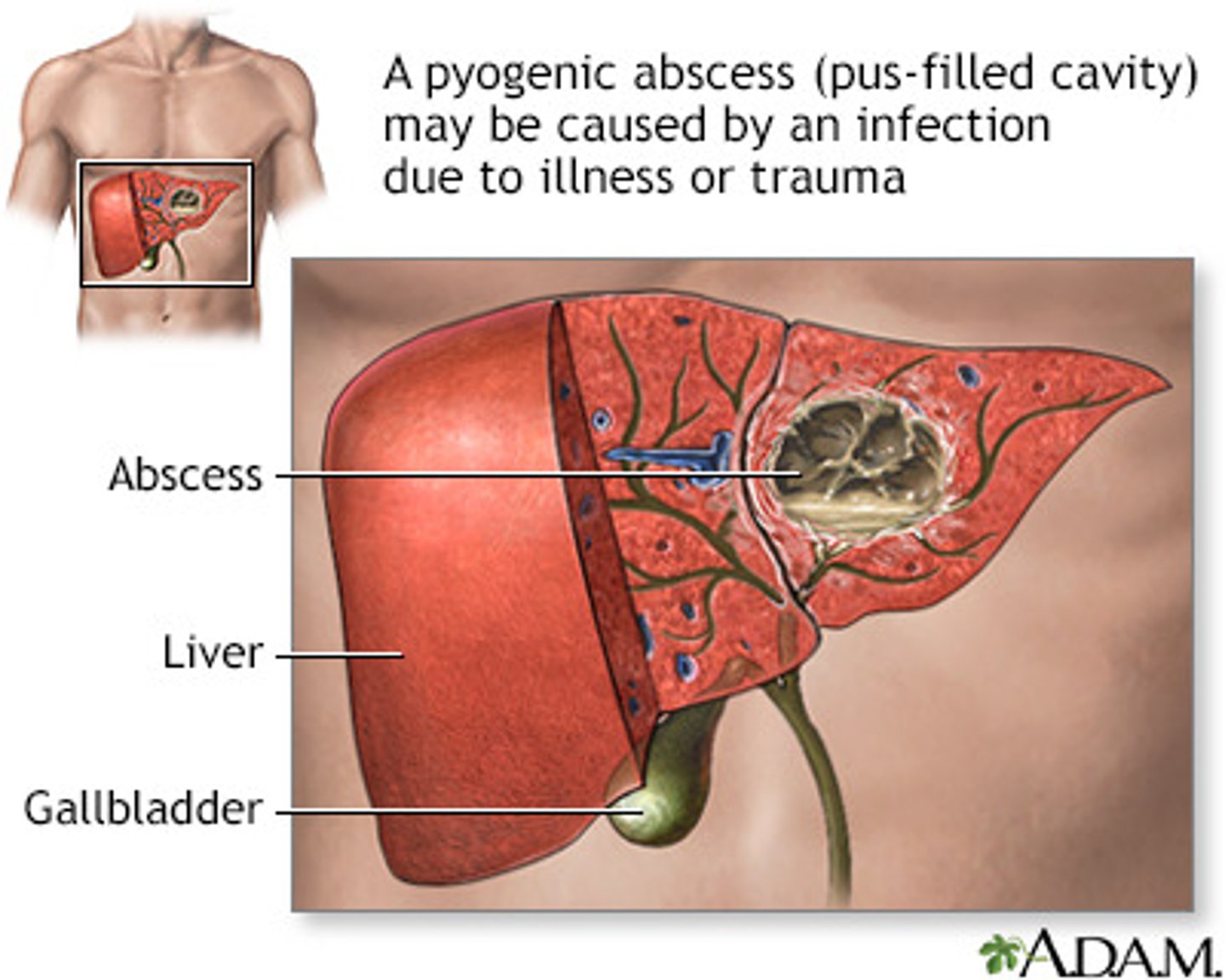
What usually cause liver abscesses in the western world? where does it come from?
Bacterial infection;
- Ascending infections from the biliary tract
- Spreading of bacteria from GI through portal vein
- Systemic bacteraemia
Morphology of liver abscesses?
Pyogenic abscess
- liquefactive necrosis with neutrophil infiltration
Echinococcus cysts in the liver?
Cysts in the liver that develops as a consequence of consuming something contaminated by Echinococcal tapeworms eggs
What happens after consuming Echinoccocal tapeworm eggs?
The eggs hatch in the intestines and the adult tapeworms penetrate the intestinal wall
- often end up in the liver, where they die and form a hydatid cyst
Drug hepatopathies?
Drugs are an important cause of liver damage
How can we classify the drugs that cause liver damage?
- Direct hepatotoxic substances
- Indirect hepatotoxic substances
Direct hepatotoxic substances?
Their metabolites cause direct damage to the liver
- their toxicity is dose dependent
Some examples of direct hepatotoxic substances?
- Anabolic steroids
- Paracetamol
- Contraceptives
Indirect hepatotoxic substances?
Can cause damage because their substances can serve as haptens, initiating and immune reaction
- can also alter the metabolism of the liver
- their toxicity is not dose dependent, so its hard to predict the dose and how an individual will react to the drug
Some examples of indirect hepatotoxic substances?
- Anabolic steroids
- Contraceptives
- Antibiotics