Computer Programming - Module 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
a machine that performs a variety of tasks according to specific instructions. It is a programmable electronic device, which accepts data or information via an input device, and its processor manipulates the information at high speed according to a program.
Computer
is the tangible part of the computer. It is composed of electronic and mechanical parts.
Hardware
The processor is the “brain” of the computer. It contains millions of extremely tiny electrical parts. It does the fundamental computing within the system. Examples of processors are Pentium, Athlon and SPARC.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The memory is where data and instructions needed by the CPU to do its appointed tasks can be found. It is divided into several storage locations that have corresponding addresses. The CPU accesses the memory with the use of these addresses.
Memory
The main memory is very closely connected to the processor. It is used to hold programs and data, that the processor is actively working with. It is not used for long term storage.
Main Memory / Random Access Memory (RAM)
is connected to main memory. It is used to hold programs and data for long term use.
Secondary Memory
allows a computer system to interact with the outside world by moving data into and out of the system.
Input / Output Devices
is the program that a computer uses in order to function. It is kept on some hardware device like a hard disk, but it itself is intangible. The data that the computer uses can be anything that a program needs. A Program acts like instructions for the processor.
Software
Programs that are needed to keep all the hardware and software systems running together smoothly
System Programs
Programs that people use to get their work done
Application Programs
These are used to enhance the performance of the Computer System.
Utility Programs
is a standardized communication technique for expressing instructions to a computer. Like human languages, each language has its own syntax and grammar.
Programming Language
also called machine code, low-level language, in binary form which a particular computer can execute directly.
Machine Language
is a low-level programming language.
Assembly Language
are machine independent. Design to be used by human or Programming style and context is easier to learn and implement. C/C++ and Java are examples.
High-Level Languages
is used for system programming, designed to write system software and low level tasks, like memory and process management.
System Language
is an extremely high level and powerful language. Used to write scripts containing series of commands, which are interpreted one at a time at runtime.
Scripting Language
allow the user to create illustrations to describe various processes, manipulating graphical elements rather than typing textual commands.
Visual Languages
is the style or way of programming. A program can feature multiple paradigms.
Programming Paradigms
Approach with an explicit sequence of commands that update state.
Imperative
Done with specifying the result you want, not how to get it.
Declarative
Programming with clean, goto-free, nested control structures.
Structured
Is an Imperative programming with procedure calls.
Procedural
Using function calls that avoid any global state.
Functional (Applicative)
Uses no variables at all.
Functional level (Combinator)
Defines objects that send messages to each other. Objects have their own internal (encapsulated) state and public interfaces. can be Class-based and Prototype-based
Object-Oriented
Programming with emitters and listeners of asynchronous actions.
Event-driveb
Programming processes communicating with each other over predefined channels.
Flow-driven
Specifies a set of facts and rules. An engine infers the answers to questions.
Logic (Rule-based)
Specifies a set of constraints. An engine finds the values that meet the constraints.
Constraint
Programming cross-cutting concerns applied transparently.
Aspect-Oriented
Programming by manipulating the program elements themselves.
Reflective
Programming with powerful array operators that usually make loops unnecessary.
Array
An algorithm is a clear, step-by-step guide to solving a problem. It can be written in human language, shown as a flowchart, or expressed as pseudocode.
Algorithm
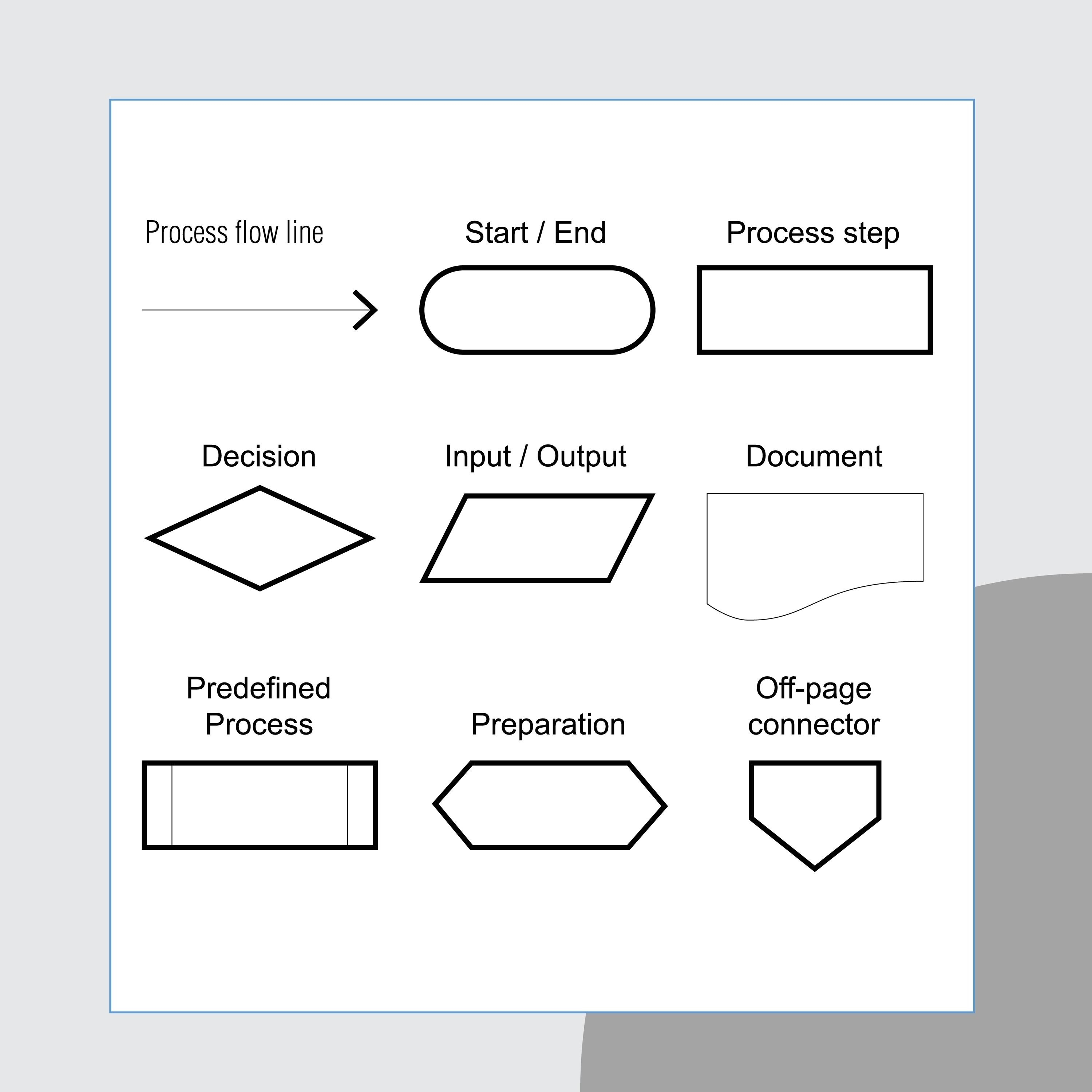
is a design tool that uses graphics to show the logic of a solution. It displays concepts in English or mathematical notation, not in programming language commands.
Flowchart
The symbol represents a process, which is an operation or group of operations that changes the value, form, or location of data. It also functions as the default symbol when no other symbol is available.
Process Symbol
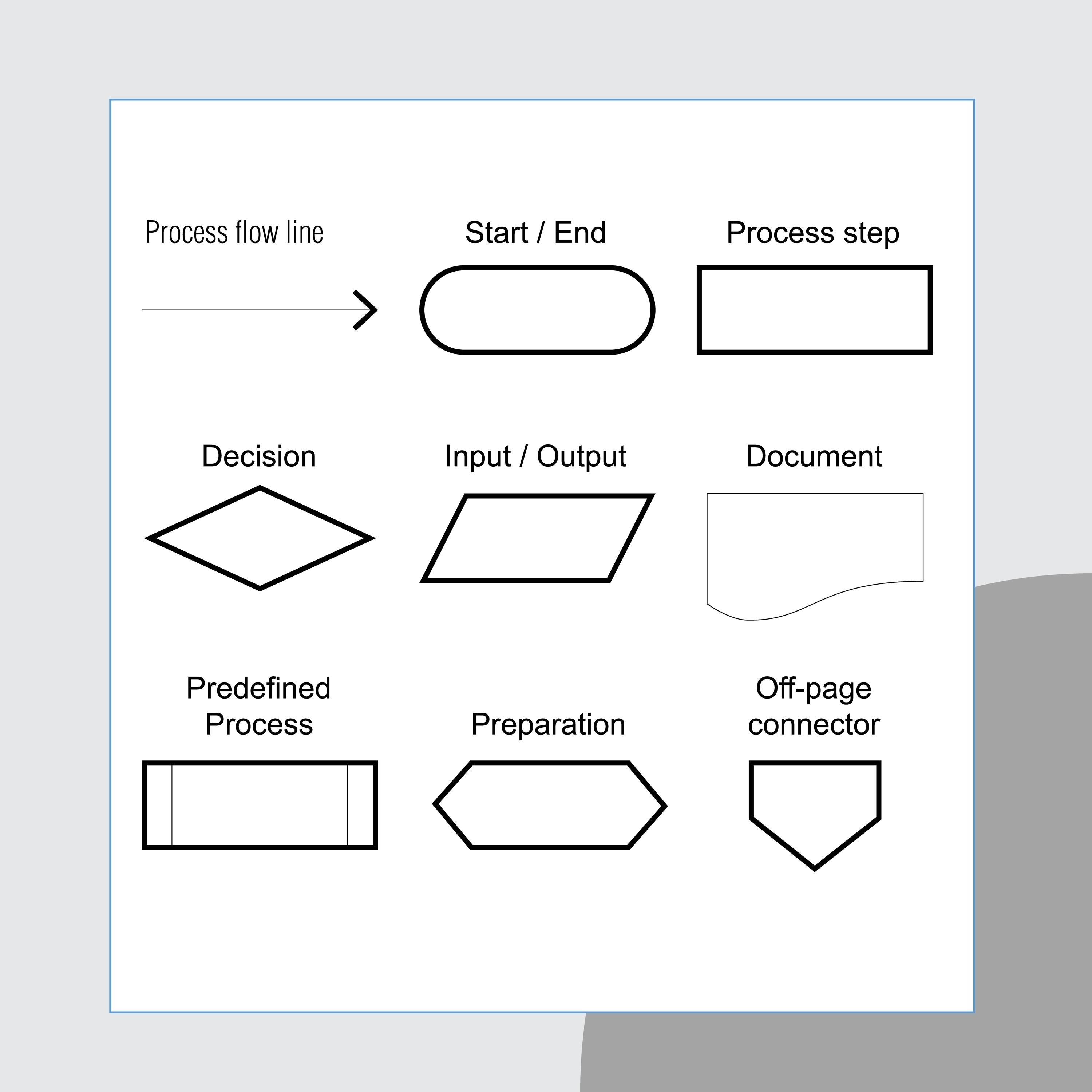
Represents an I/O function, which makes data available for processing (input) or displaying (output)of processed information.
Input/Output (I/O) Symbol
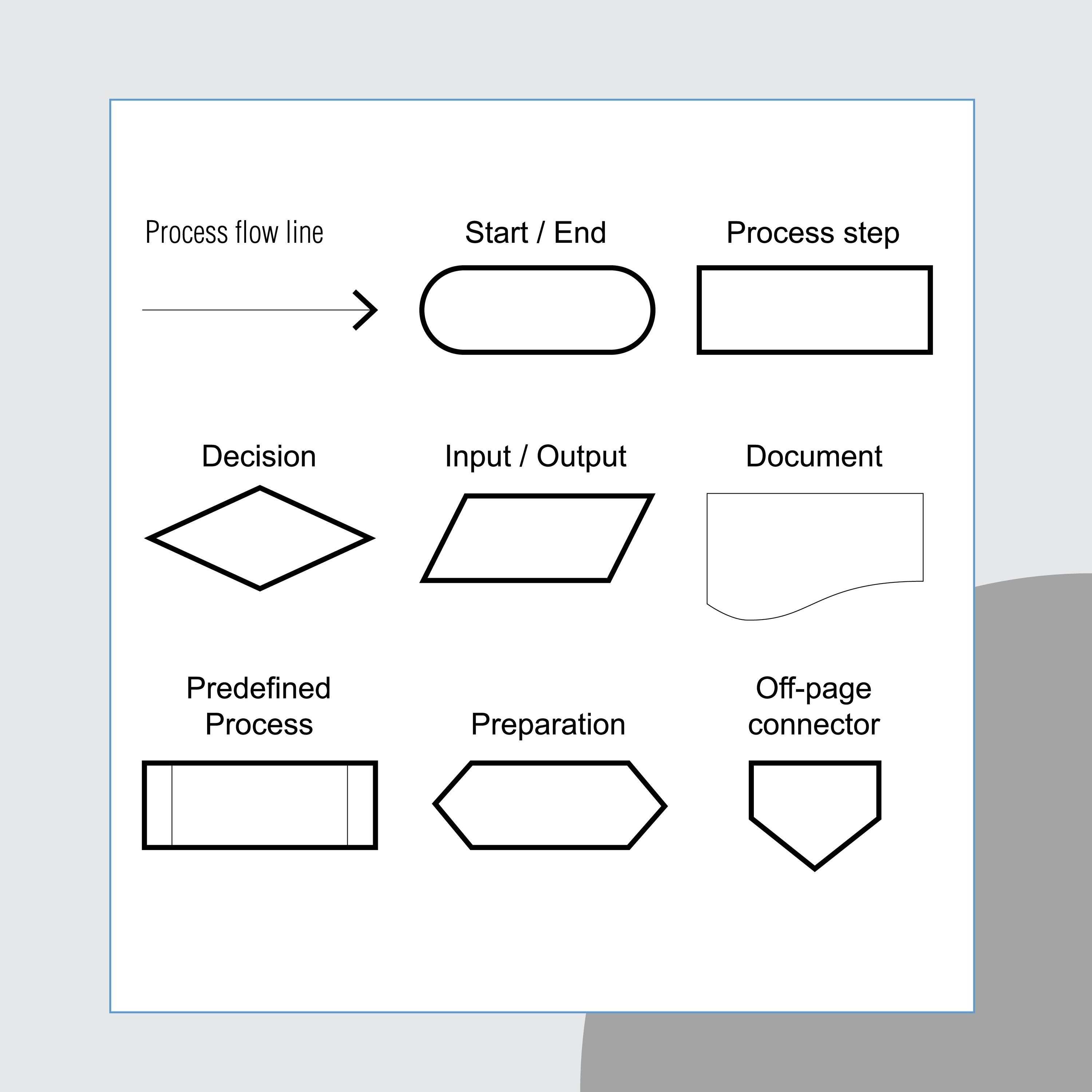
represents the sequence of information and operations. It connects other symbols in a flowchart, and you only need arrowheads for right-to-left or bottom-to-top flows.
Flowline Symbol
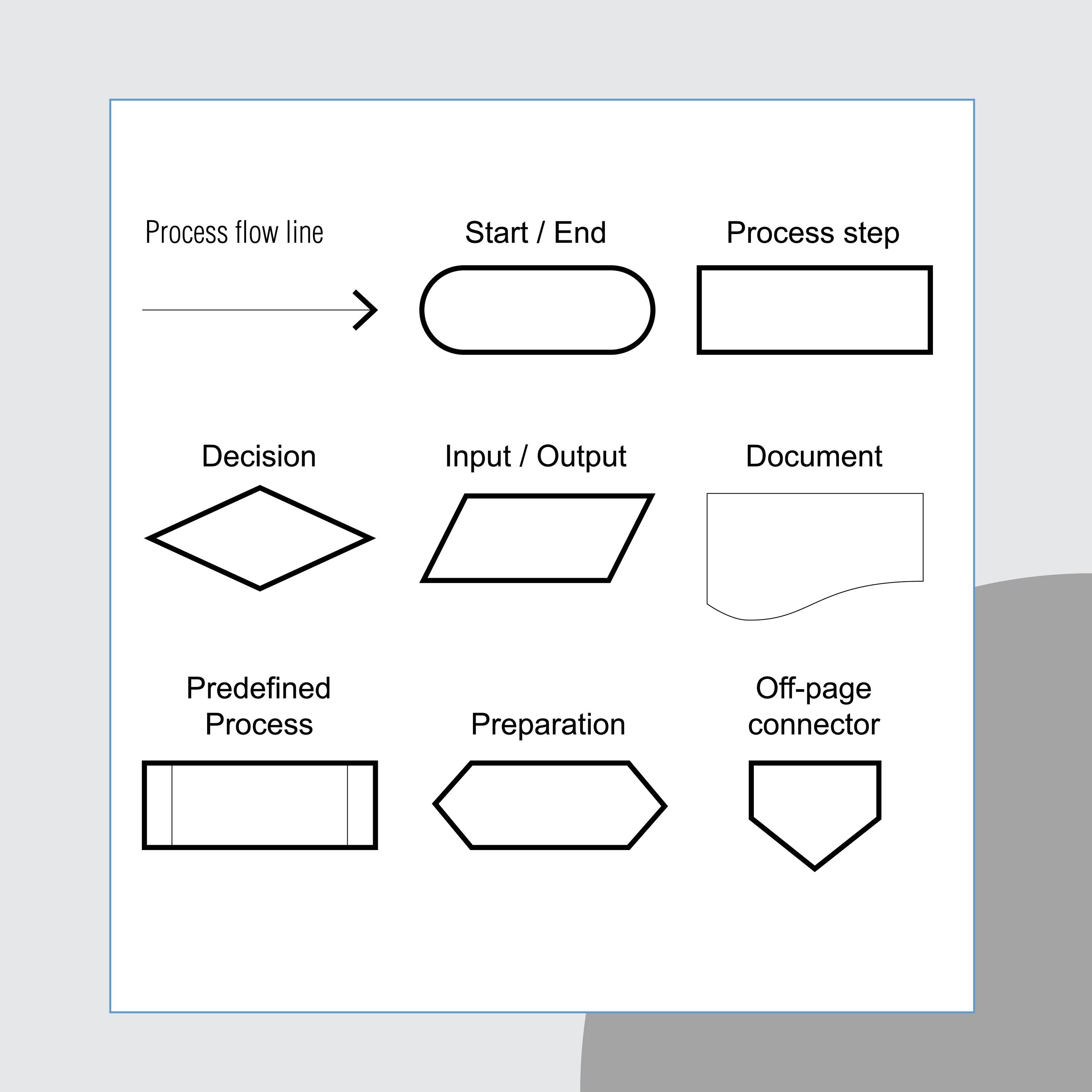
This symbol represents an annotation or comment, used to add descriptive or explanatory notes for clarification. It can be placed on either the left or right side of a flowchart.
Annotation Symbol
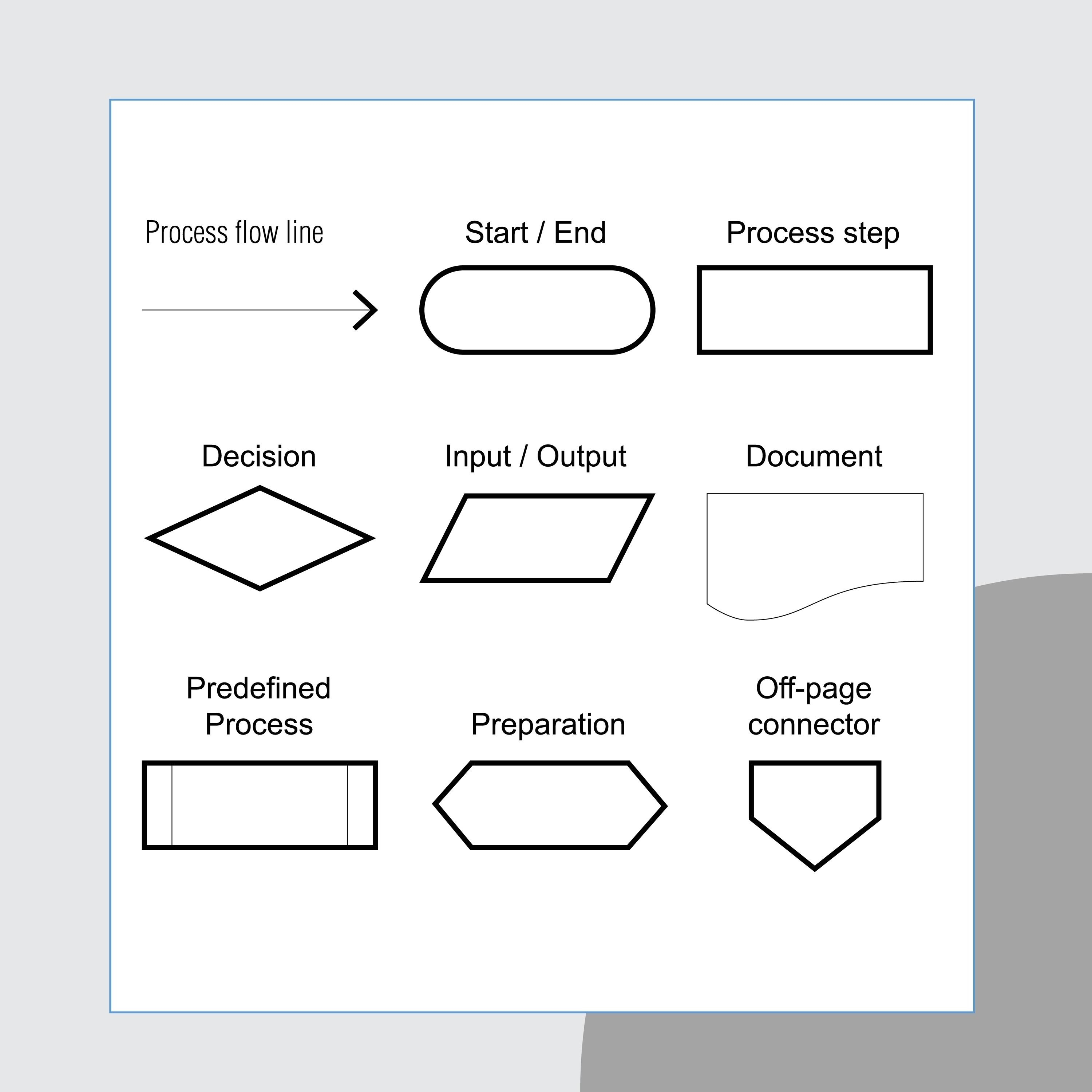
Represents a decision that determines which of a number of alternative paths is to be followed.
Decision Symbol
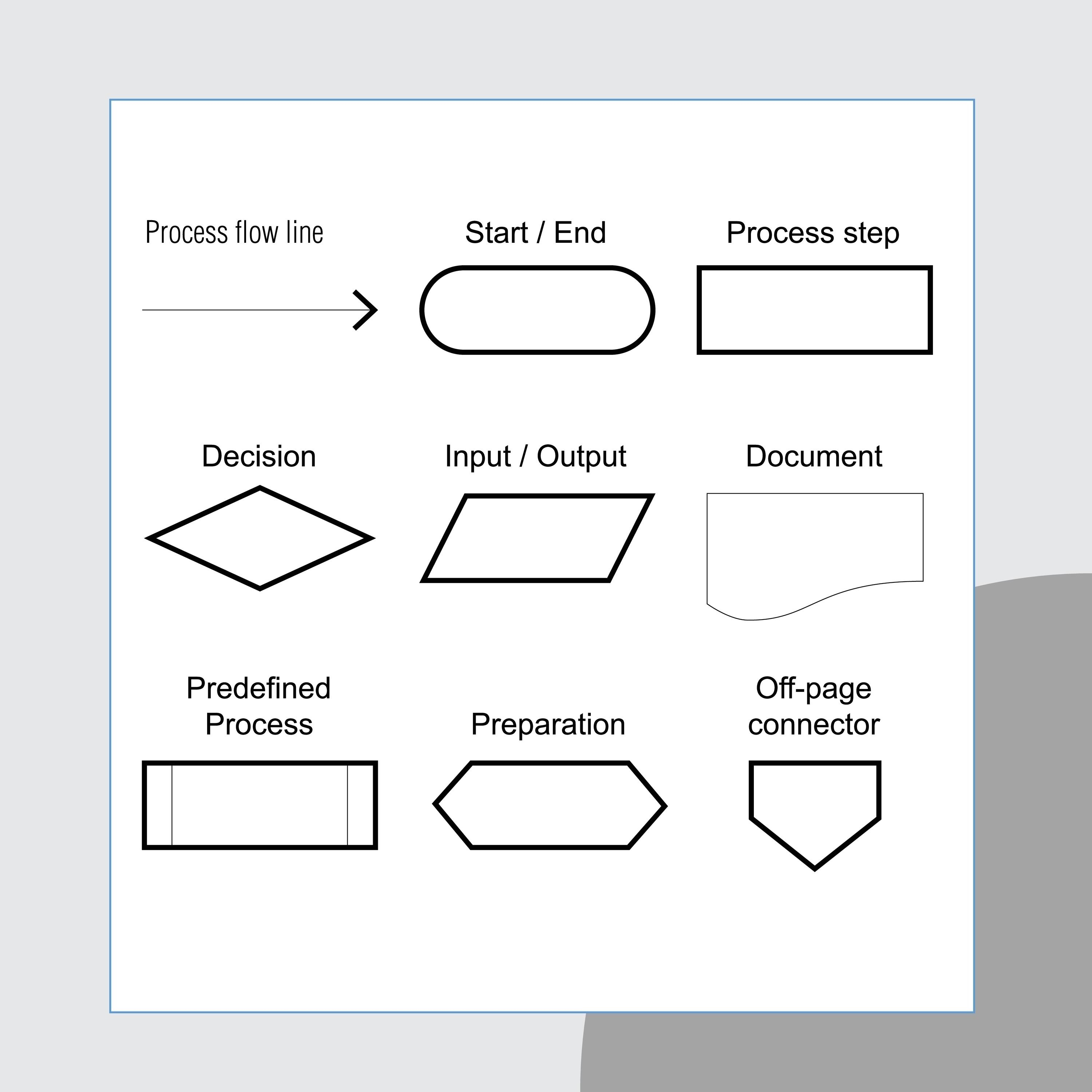
Represents the beginning, the end, or a point of interruption or delay in a program.
Terminal Symbol
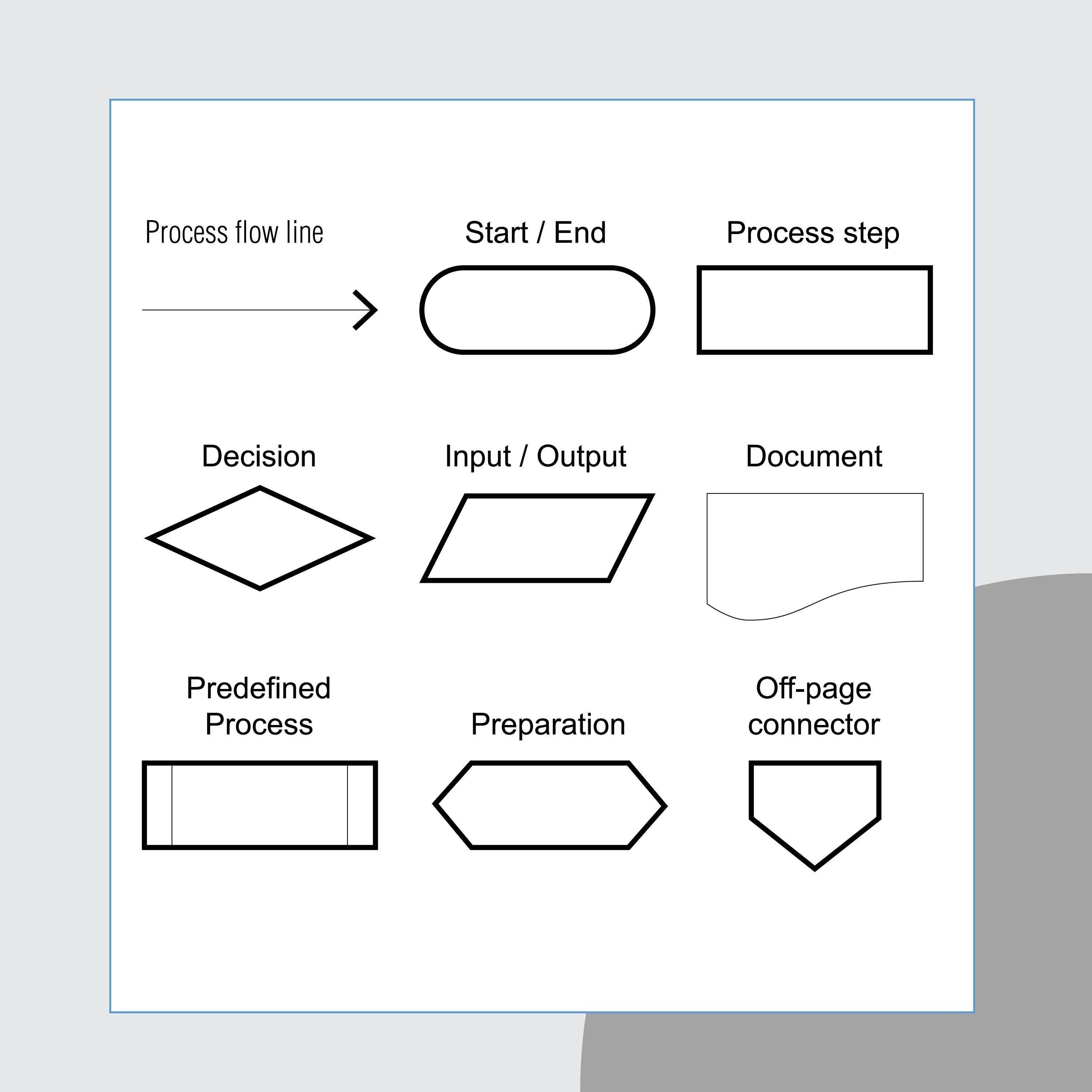
Represents any entry from, or exit to, another part of the flowchart. Also serves as an off-page connector.
Connector Symbol
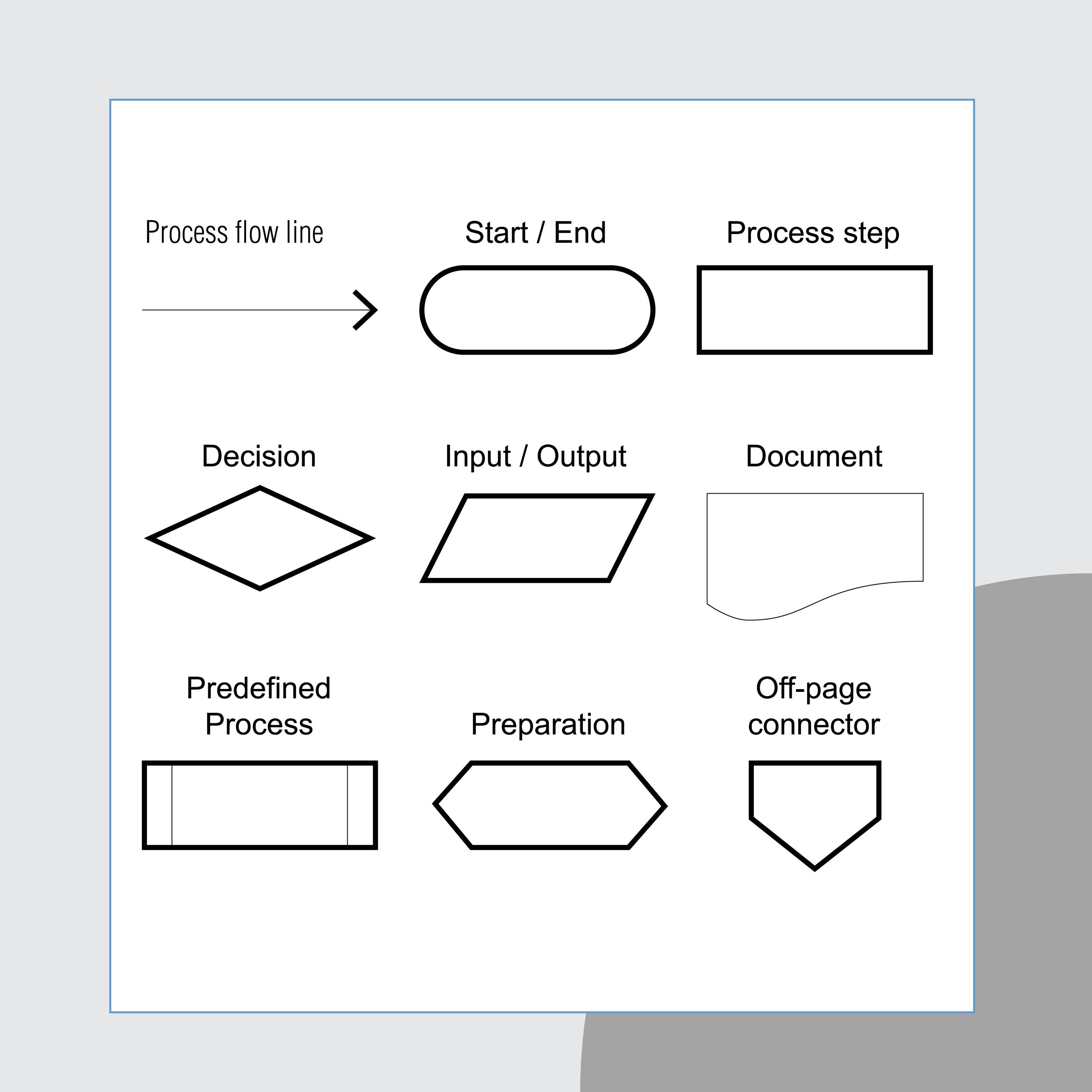
Represents a named process consisting of one or more operations or program steps that are specified elsewhere.
Predefined Process Symbol