ch 5: personality disposition over time - stability, change & coherence
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what are the key parts of personality development?
stability (over time)
rank order
mean level stability
personality coherence
analyzing stability & change
population
group differences
individual differences
what is stability in infancy: temperament?
temperament: early differences in emotionality, behaviour, and arousability
stable and early individual differences
more stability over shorter intervals
stability increases with maturity
what is stability in childhood: activity level?
block & block longitudinal study: assessed activity level via actometer & teacher ratings
main findings:
results from both measures positively correlate (validity)
results from same measure at different times correlated (stability)
activity was relatively stable, with more stability over shorter intervals
what is stability in childhood: aggression among males?
bullying & related outcomes later in life
different rater identified same youth as “bullies“
at 24yo, 65% of “bullies“ had felony convictions
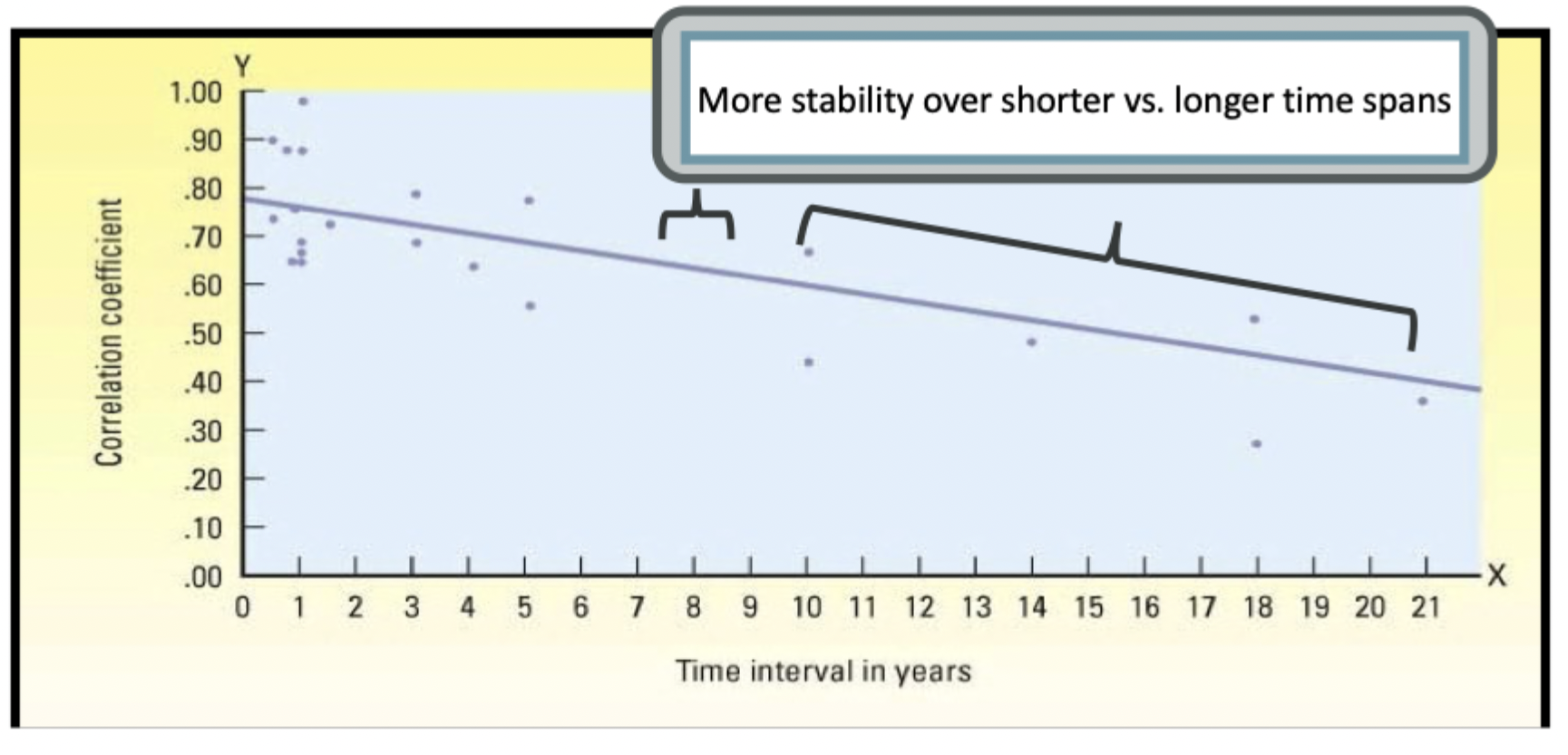
what is stability in adulthood: big 5?
big 5 are relatively stable in adulthood - especially after 50 years of age
but, openess, extraversion, neuroticism decline slightly until the age 50
what is change in adolescence: self-esteem?
boys tend to increase slightly in self-esteem; girls tend to decrease slightly
what is change in adulthood: ambition in business settings?
ambition declined in group of managerial candidates (sample = men)
increases in autonomy, dominance, leadership, motivation
→ results due to men becoming more realistic about limits in promotion
what is change in adulthood: independence among women?
divorced mothers, non-mothers, working mothers
almost all increased in levels of independence
stay-at-home mom had no increases in independence (important to examine subgroups)
what is change over time: cohort effects?
personality change due to social times of individuals
what are predicting outcomes: marital dissatisfaction?
predictors of marital dissatisfaction/divorce
neuroticism of either spouse
husband’s lack of impulse control
neuroticism of both + husband’s lack of impulse control
what are predicting outcomes: alcohol and emotional difficulties?
higher neuroticism (observer ratings) → emotional difficulties & alcoholism
higher neuroticism & lower impulse control → alcoholism
what are predicting outcomes: health and longevity?
better health + life longevity
high conscientiousness
high extraversion
low hostility
what are predicting outcomes: schizophreniform disorder?
schizophreniform disorder
involves schizophrenia symptoms:
hallucinations delusion, disorganized speech and behaviour, negative symptoms (e.g. flat affect)
lasts 1-6 months but not uncommon to later have a diagnosis of schizophrenia
*many of the above symptoms relate to personality (e.g. ways of thinking, feeling) & personality disorders
what are the findings in schizophreniform?
longitudinal study predicting symptoms from age 11-26
findings
for those with “high“ symptoms at 11 yo
25% had a diagnosis of schizophreniform disorder at age 26
70% had at least one symptom (but no diagnosis) at age 26
90% had impaired functioning at age 26