male reproductive system
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
gonads
testes
produce gametes (sperm) and testosterone
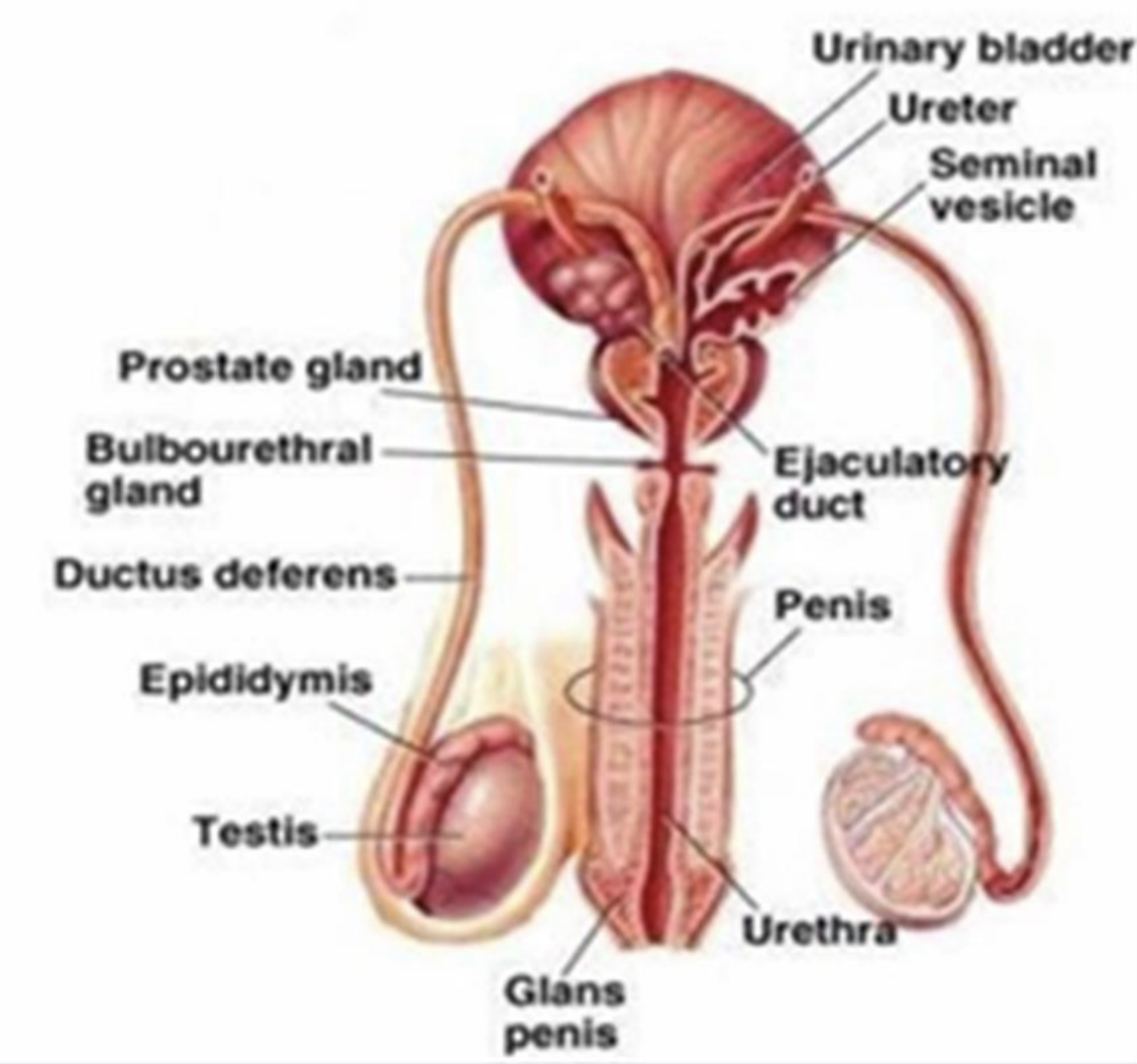
secondary sex organs
aid in the formation semen (seminal fluid) and the transport of semen
epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands and penis
testes
location
a. outside pelvic cavity
within scrotal sac (scrotum)
function
a. production of sperm
b. production of testosterone
structure
small, oval
surrounded by CT
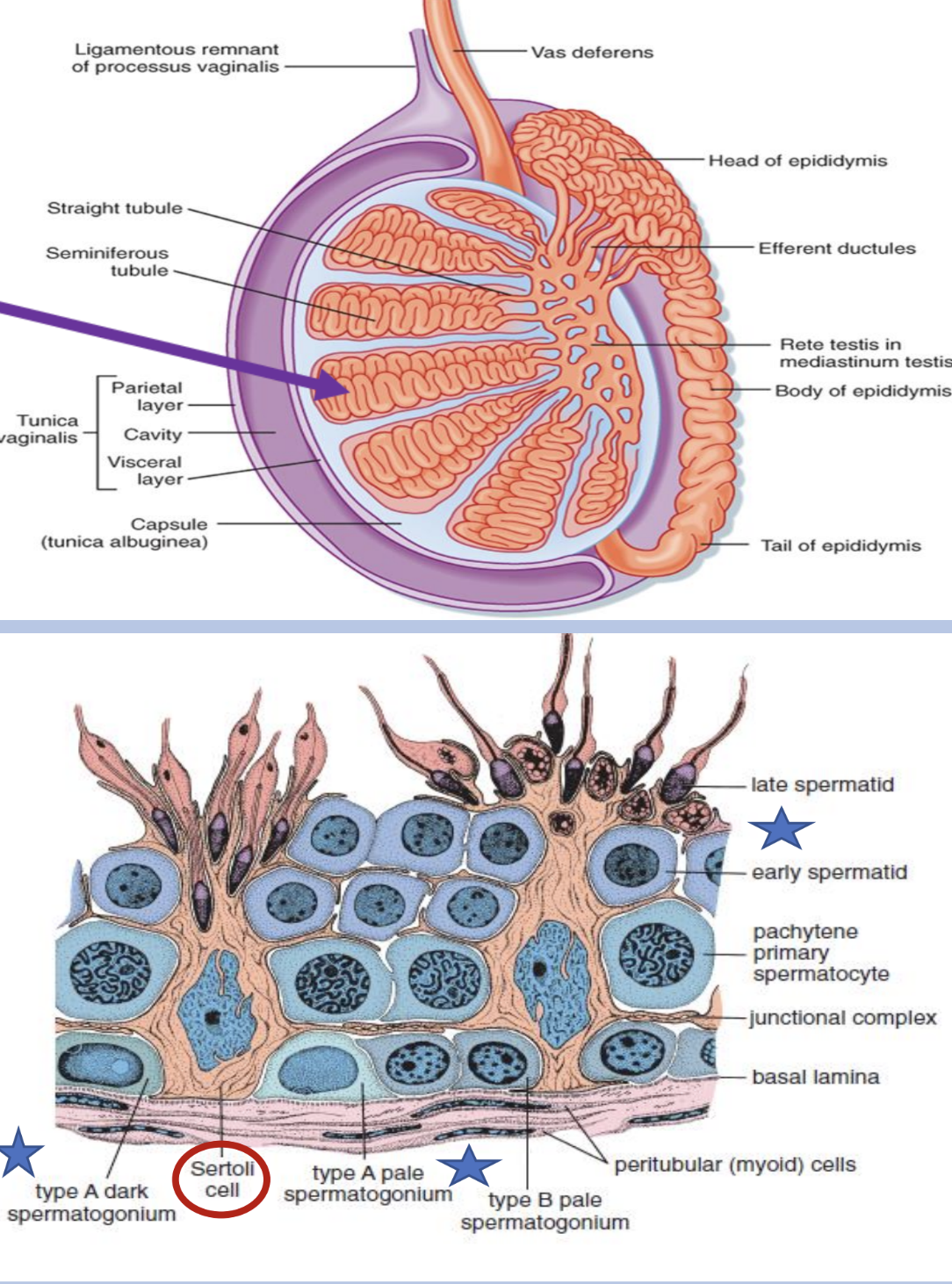
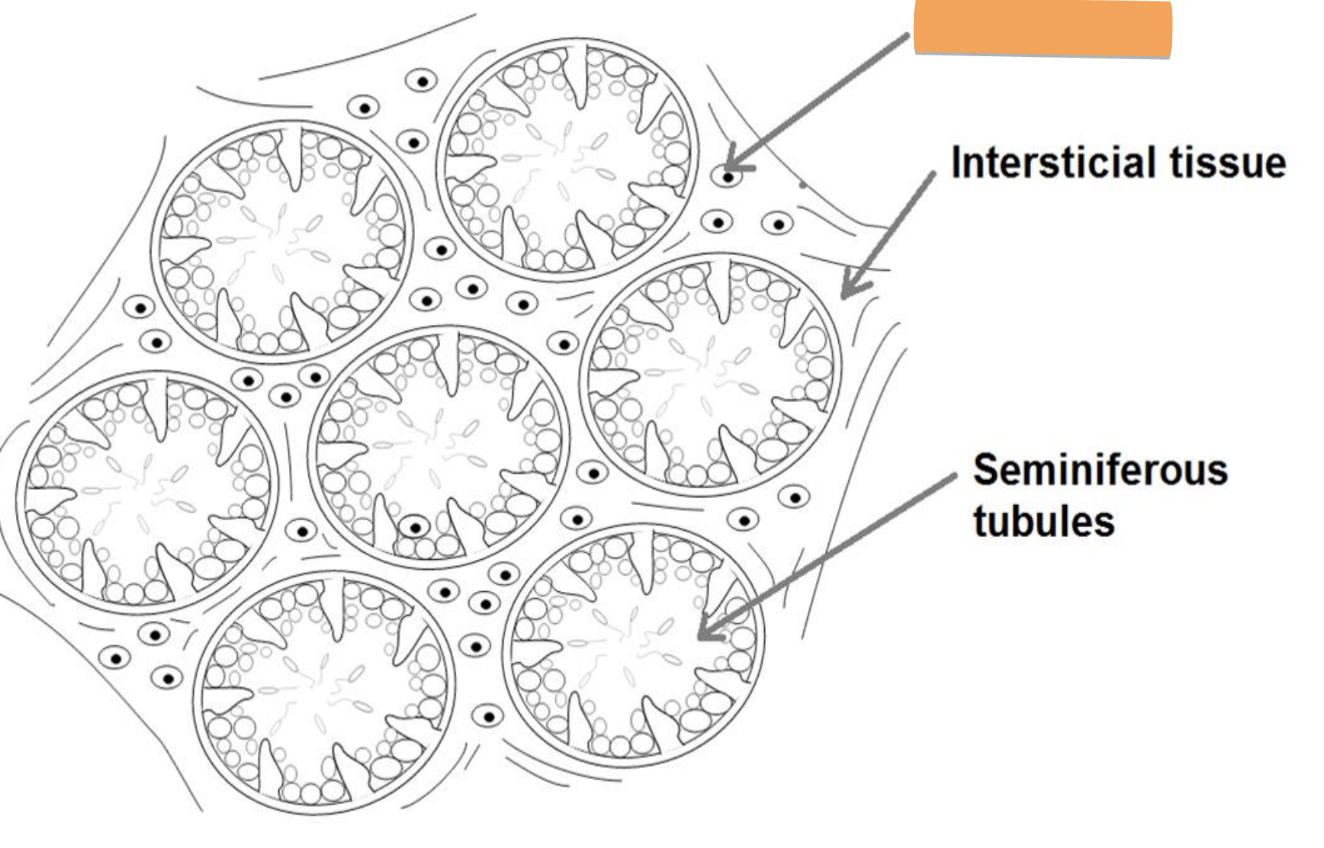
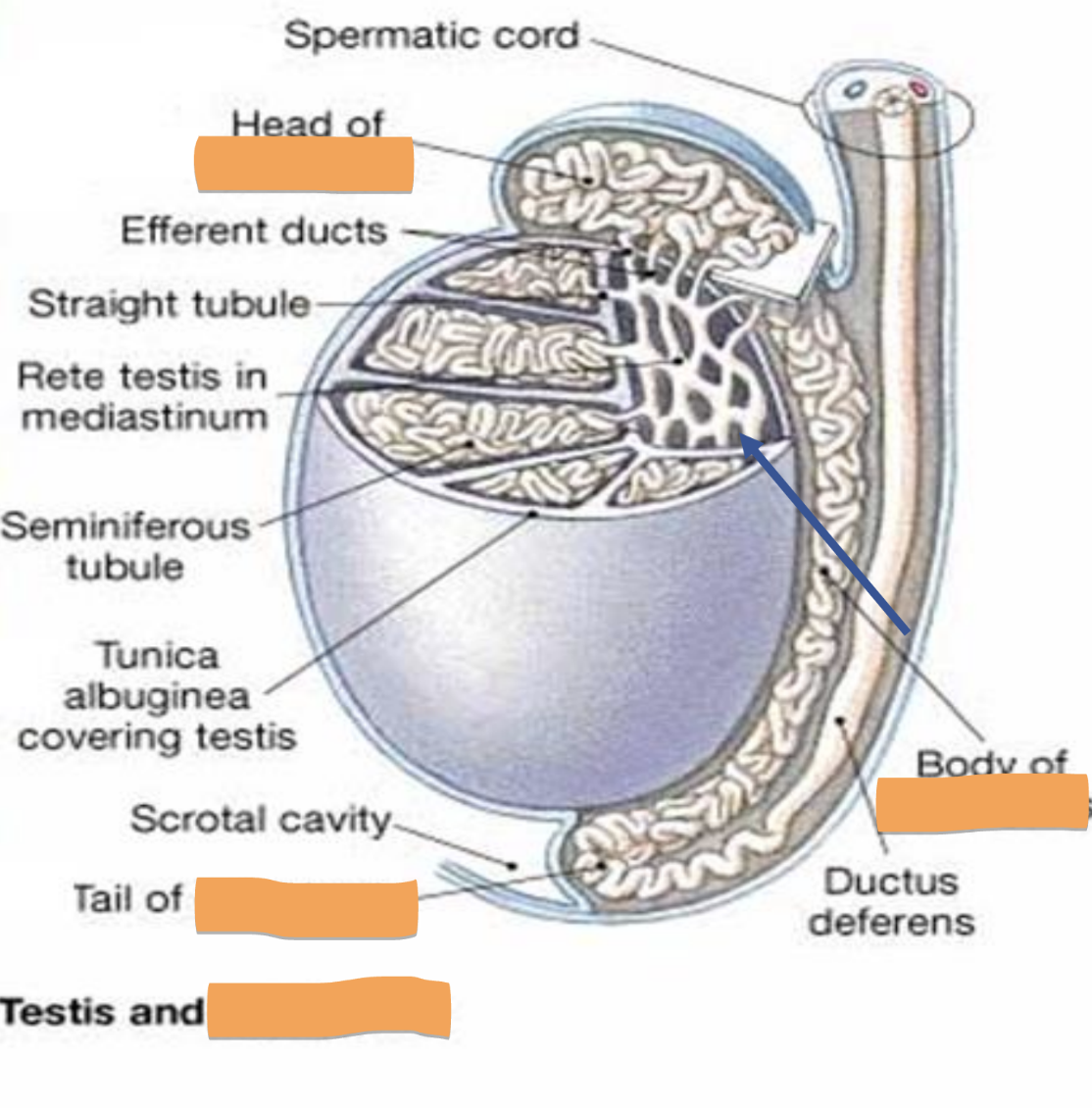
seminiferous tubules
inside testes
functional unit
a. site of sperm production (thousands/sec)
b. spermatogonia — sperm in various stages of development
c. sertoli cells — “nurse cells” line tubules and produce nutrients required to maintain developing sperm
leydig
in testes
produce and secrete testosterone
responding to LH — luteinizing hormone → production of testosterone
mature sperm
in testes
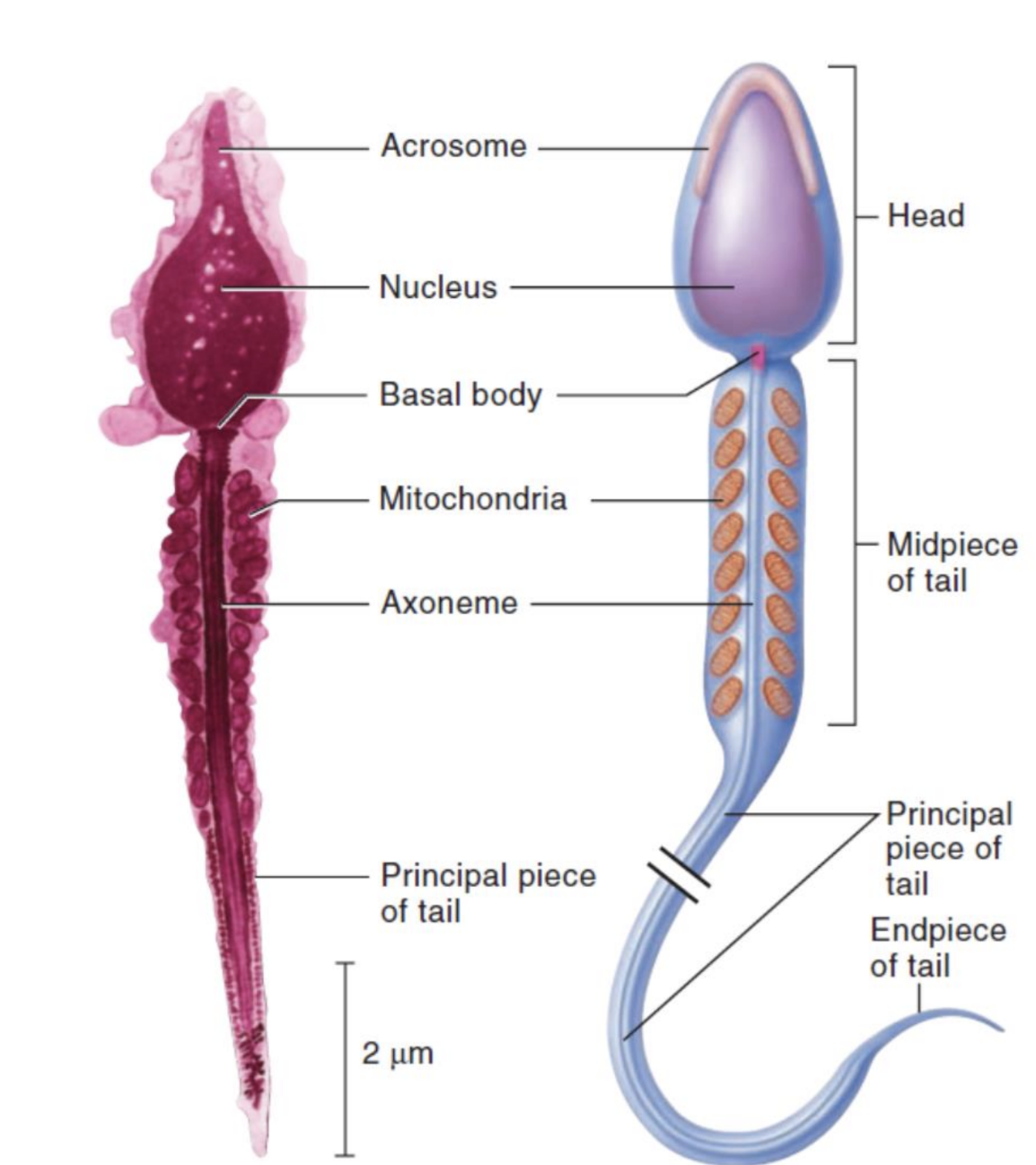
a. structure
head, body, tail
acrosome—located at tip of head, contains enzymes which help penetrate ovum
23 chromosomes (22 autosomes, 1 sex chromosome (allosome)) X or Y
b. life expectancy
48-72 hours after ejaculation at body temperature
c. ejaculate
approximately 50-150 million per milliliter
only 200-400 reach the ovum
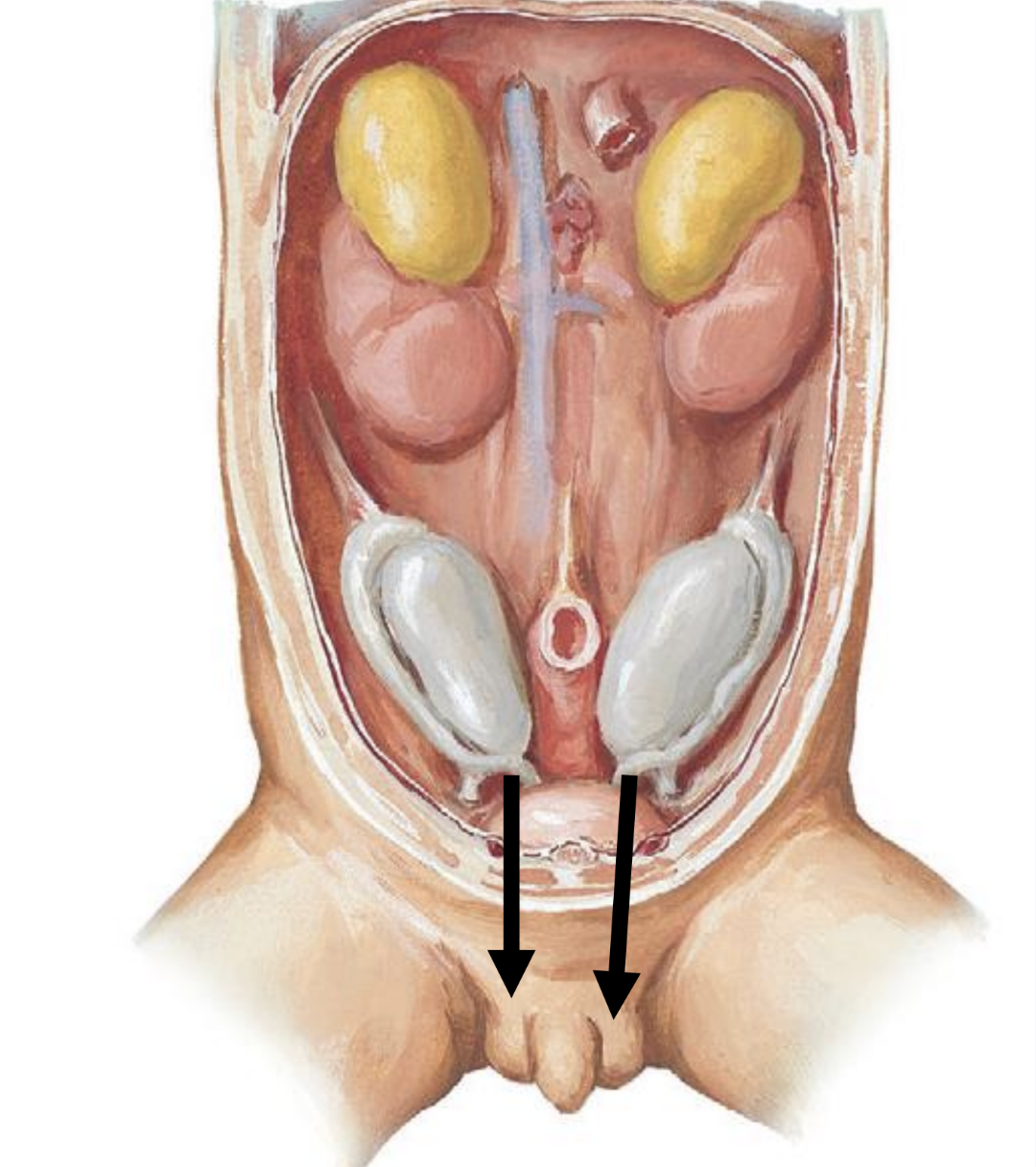
development of the testes
testes develop in abdomen and descend into scrotal sac through the inguinal canal at the 28th week of gestation
the inguinal canal is a passageway through lower abdominal wall that connecting the abdomen to the scrotal sac
if the testes don’t descend by age 5 they are surgically placed in scrotal sac
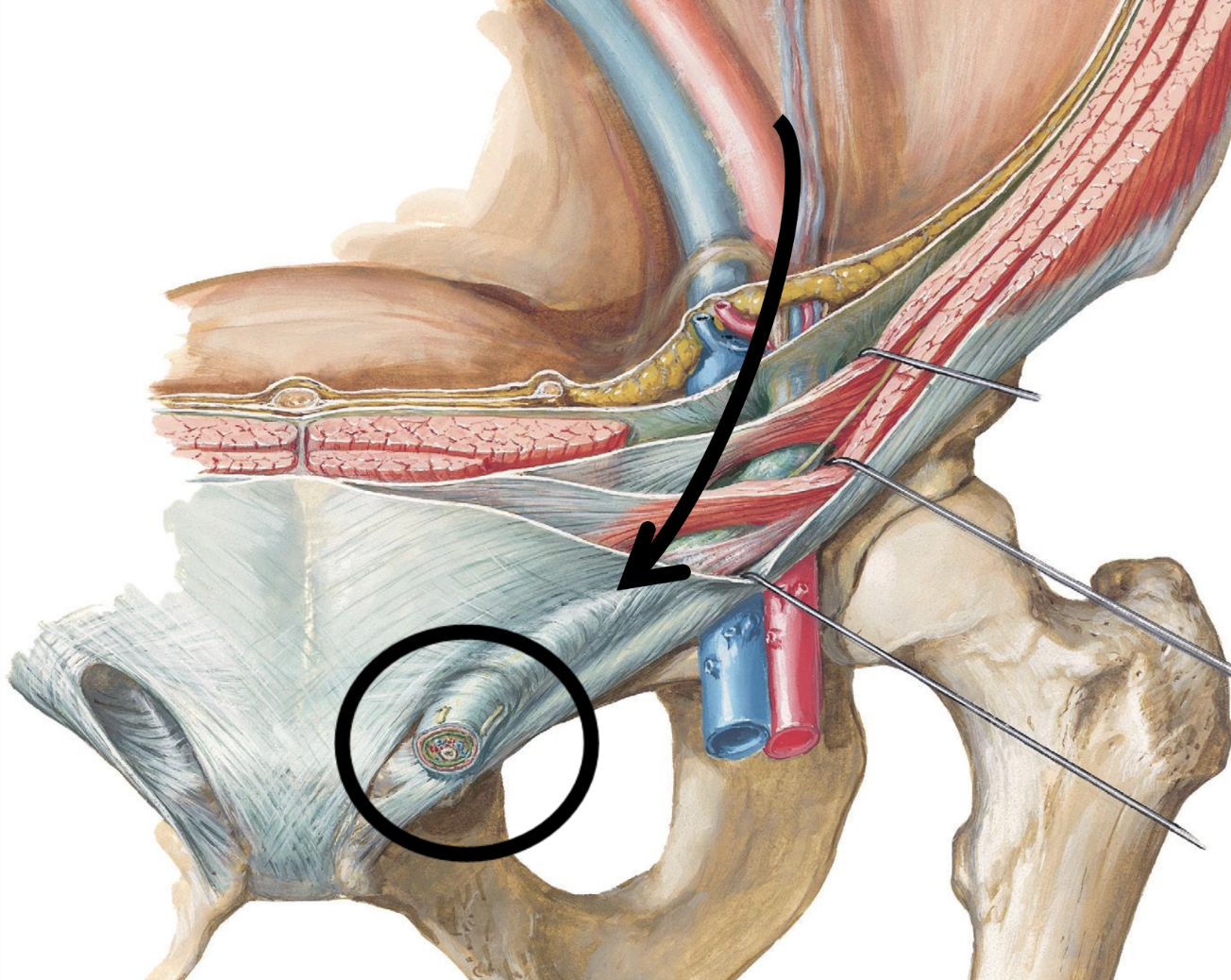
inguinal canal
passageway through the abdominal wall allowing for the passage of the testes and the spermatic cord into scrotal sac
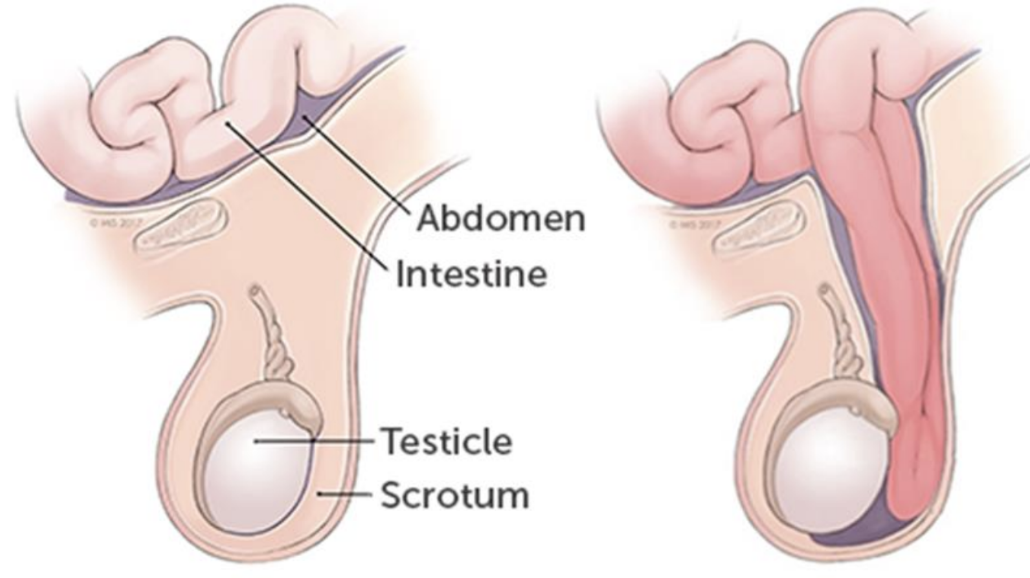
inguinal hernia
refers to the defect in the abdominal wall which allows portions of intestine to pass through the inguinal canal and enter scrotal sac
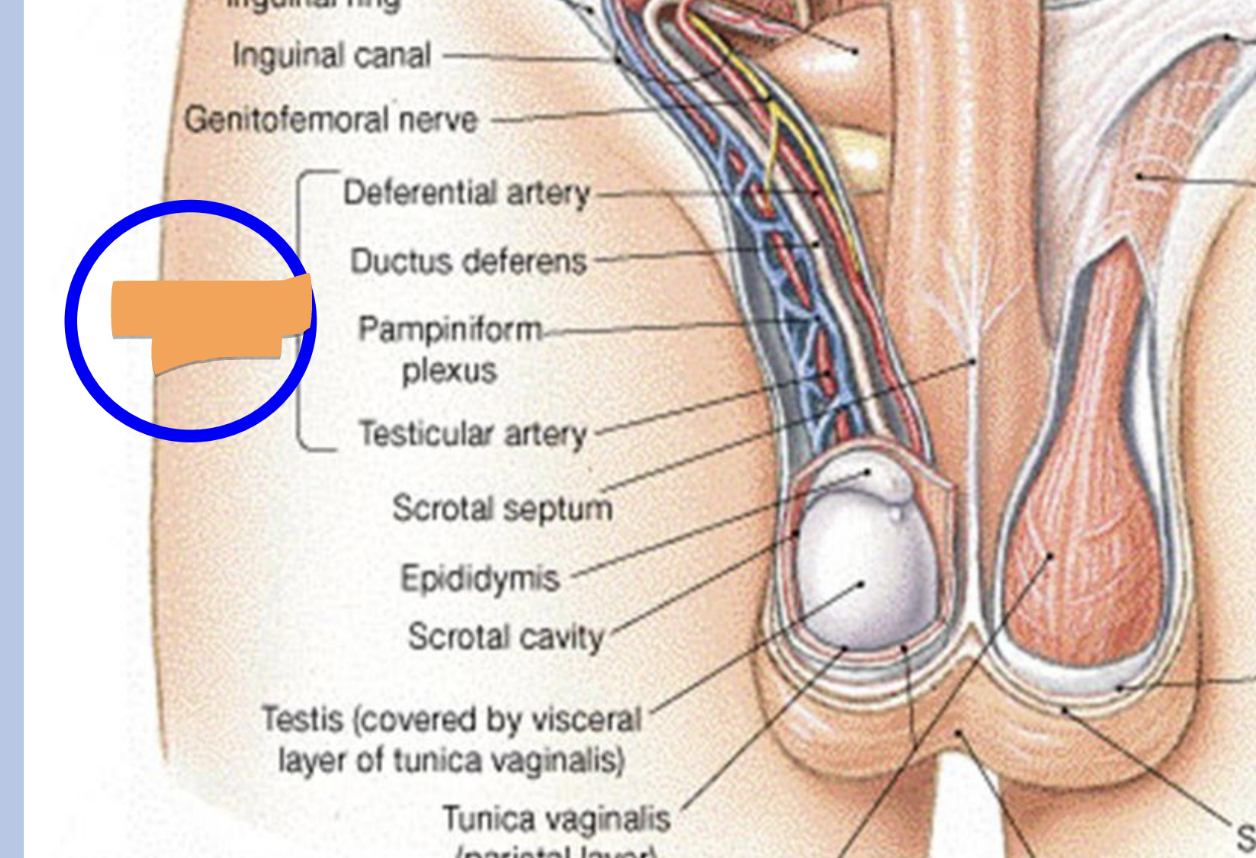
spermatic cord
“life-line”
CT sheath containing:
vas deferens
testicular artery
pampiniform plexus of veins
nerve
lymphatics
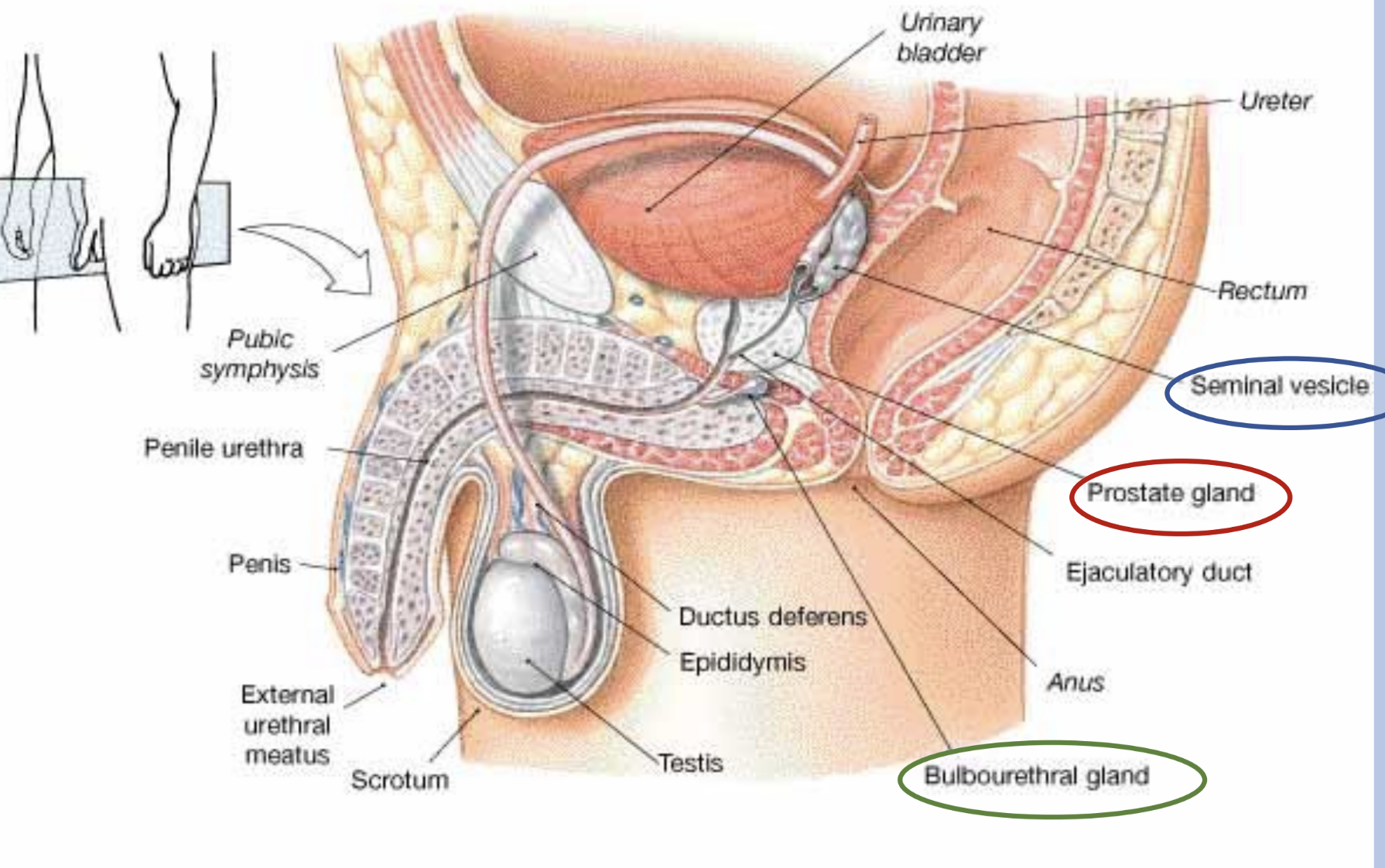
epididymis and vas deferens
the tubules or ducts in the testes which transmit sperm
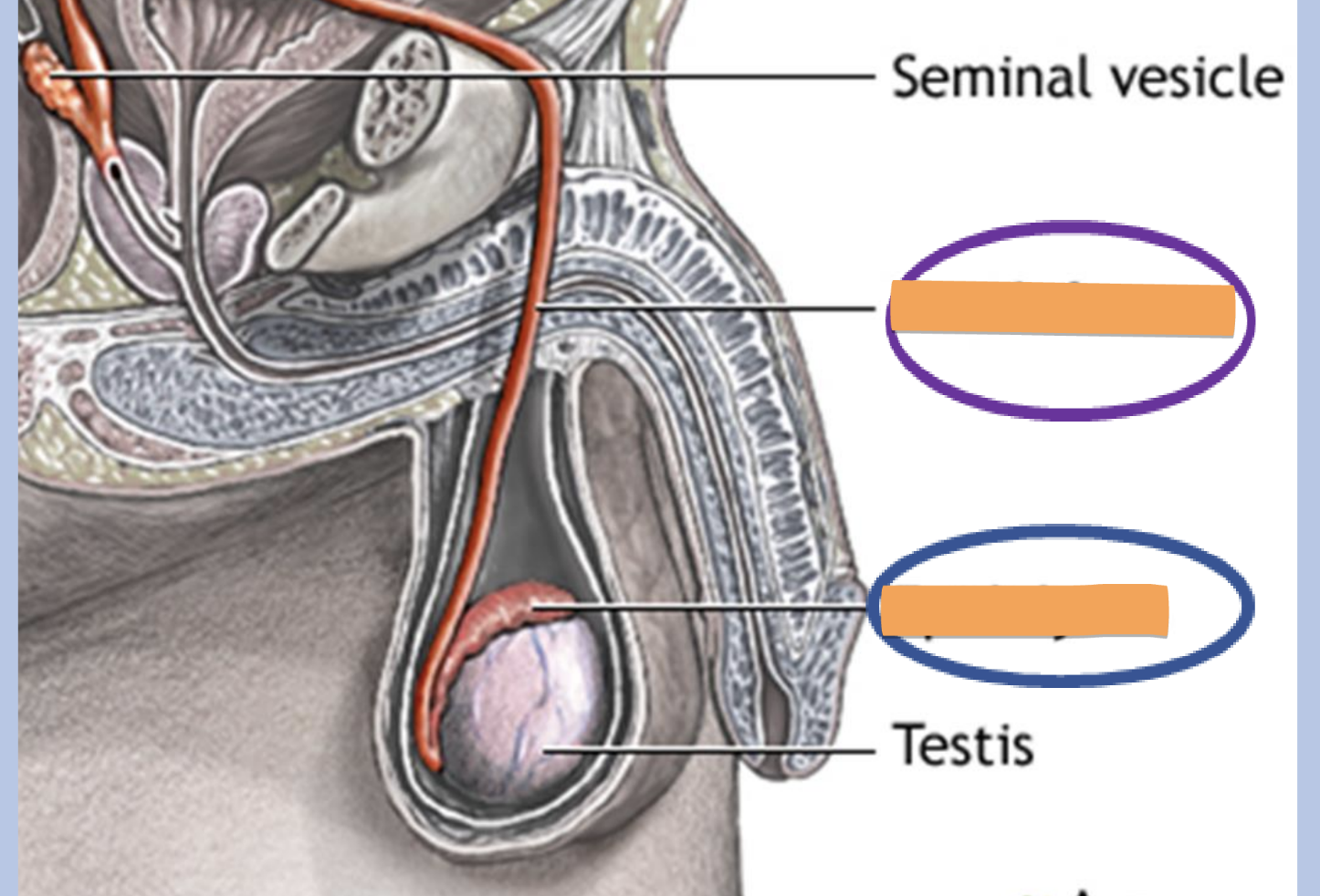
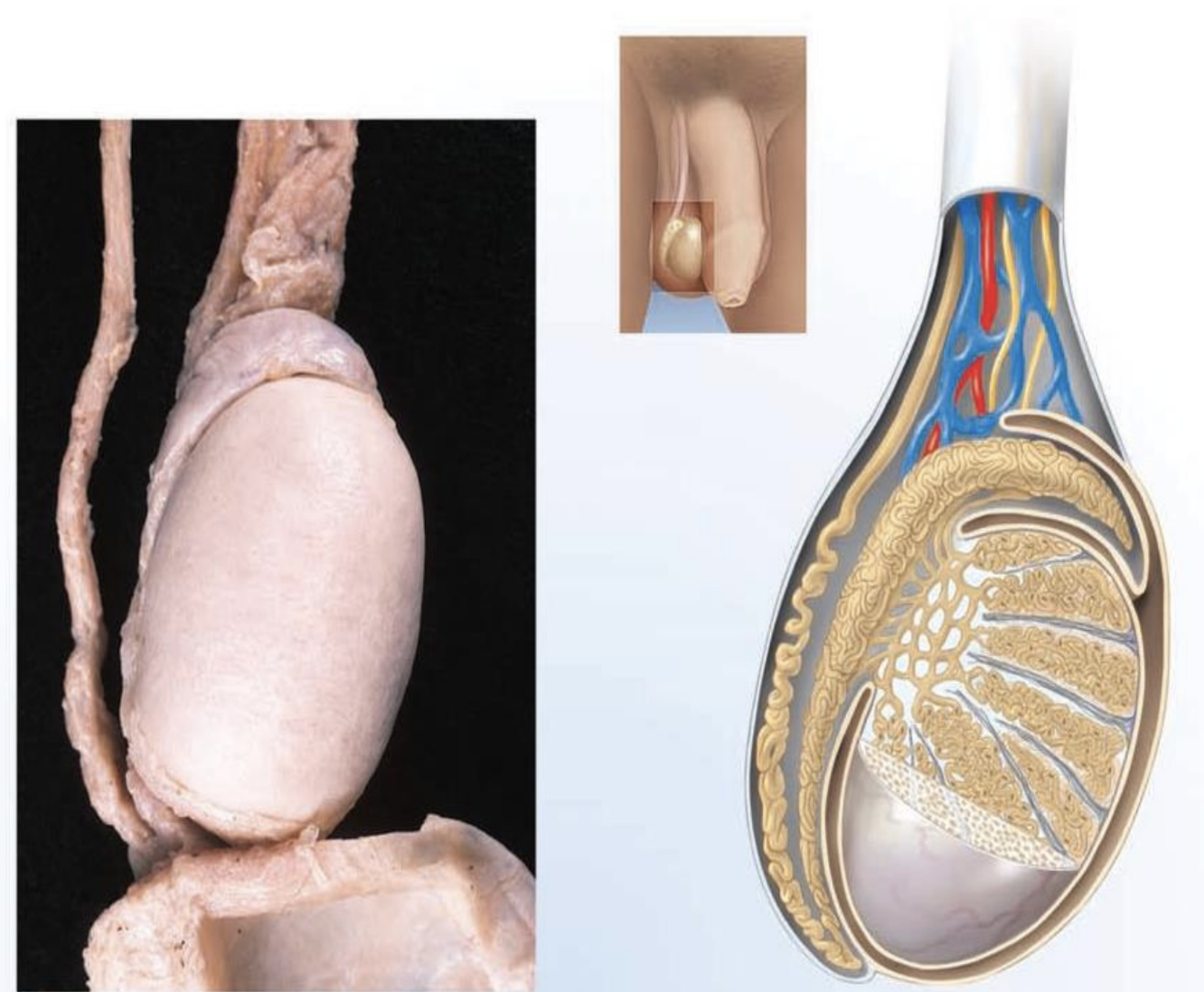
epididymis
location
attached to the posterior surface of the testes
structure
a. coiled tube (17 feet long)
b. contains millions of sperm in their final stage of development
function
stores sperm
transports sperm from testes to the ductus deferens
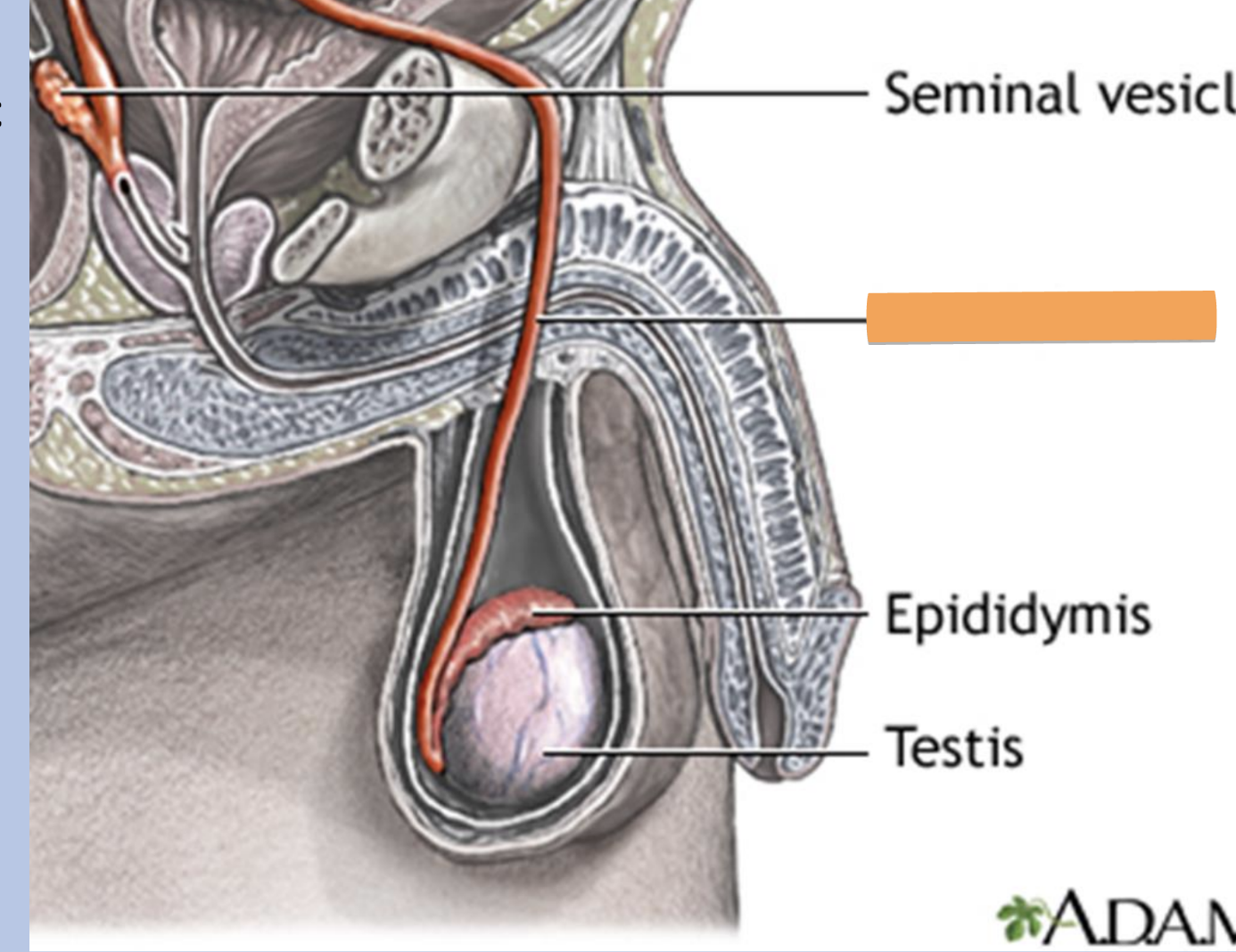
ductus deferens
also called vas deferens
location
a. passes from scrotal sac (outside pelvic cavity)
b. travels within the spermatic cord to enter the pelvis
structure
fibromuscular tube
function
transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
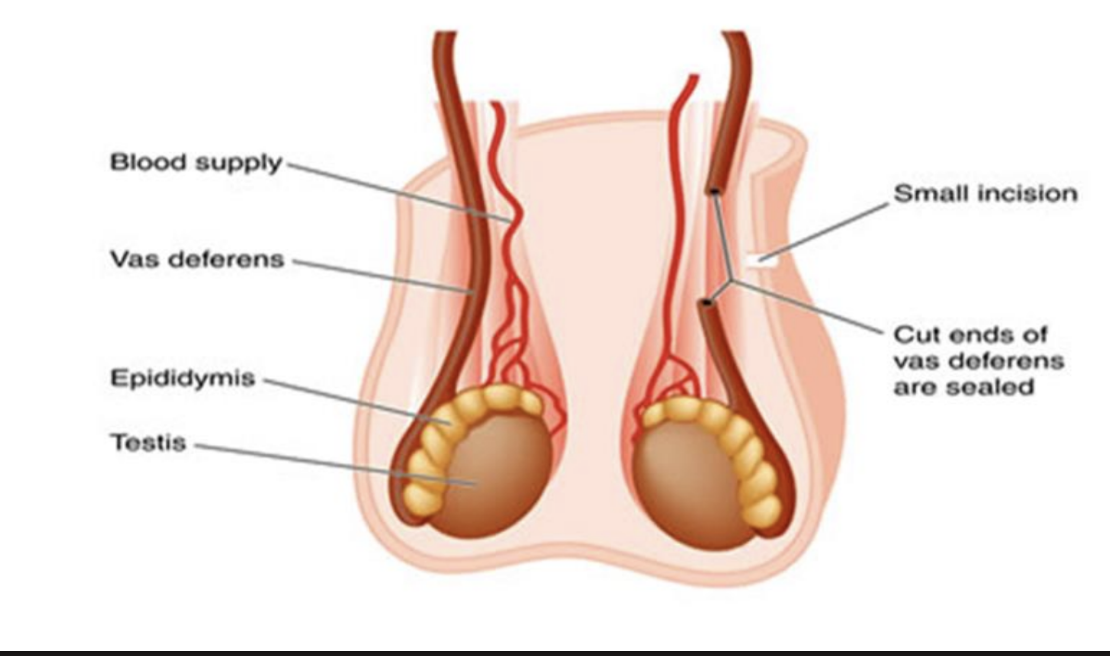
vasectomy
cutting and ligating ductus (vas) deferens
prevents sperm from passing through this tube and entering urethra
ejaculation continues as before, but semen contains no sperm
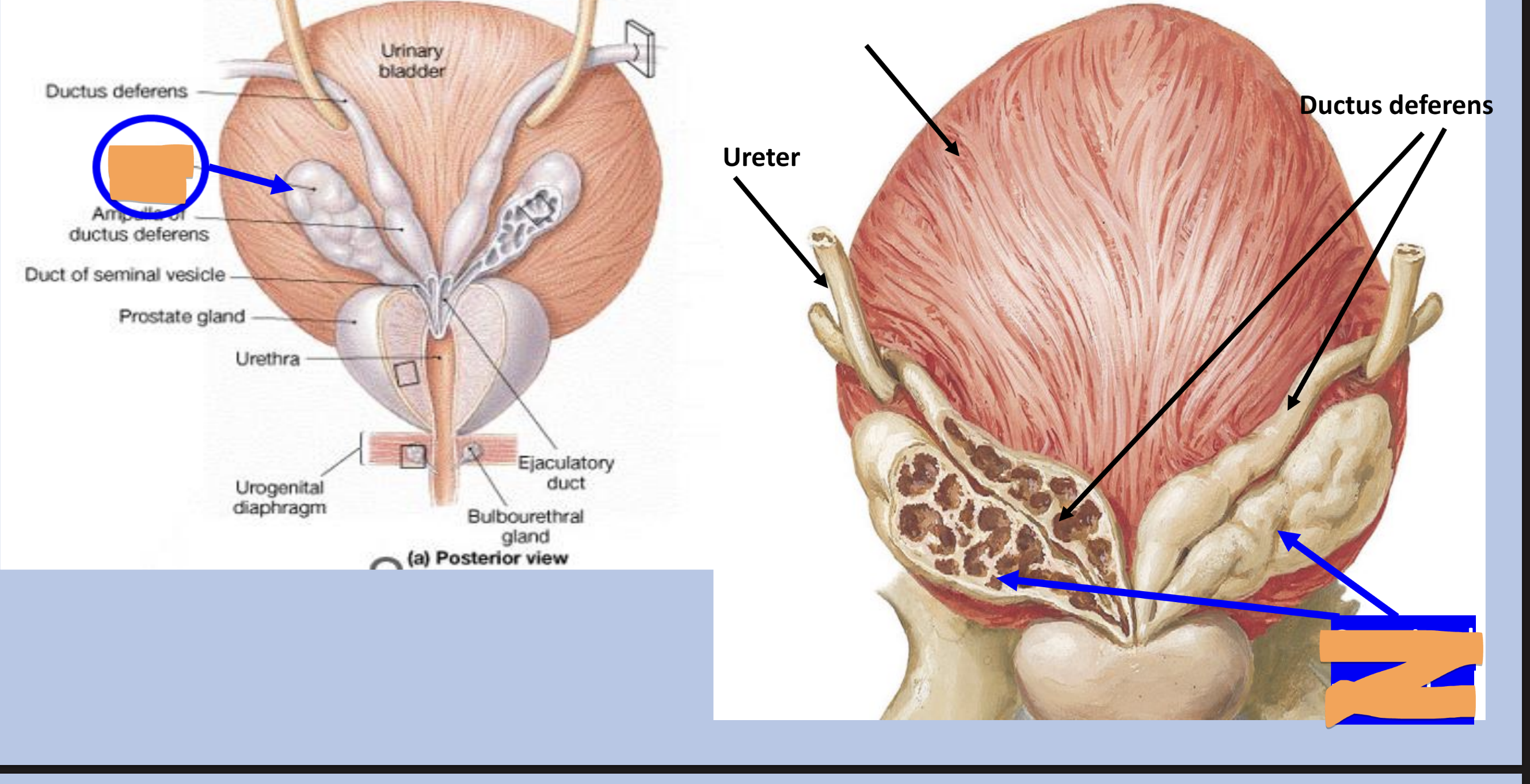
ejaculatory duct
formed by union of ductus deferens and the duct of seminal vesicles
passes through prostate gland to join the prostatic urethra
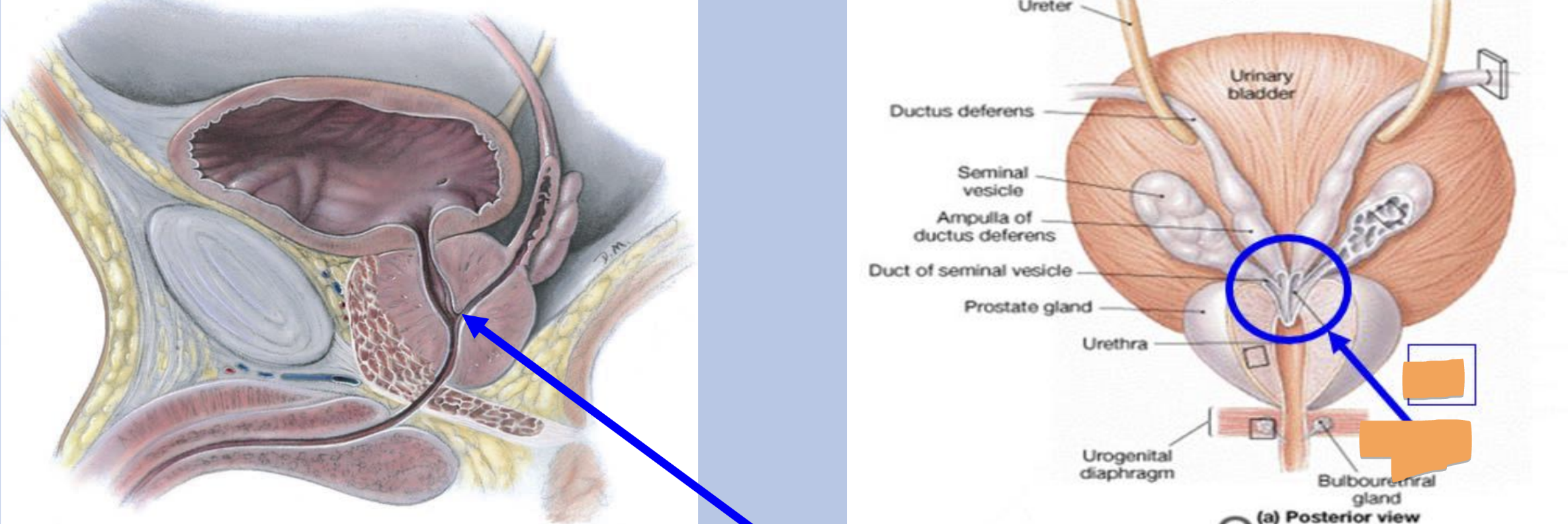
accessory glands
produce seminal fluid
seminal vesicles
prostate gland
bulbourethral glands/cowper glands
seminal vesicles
location
posterior to the bladder near its base
structure
glandular organs
contain smooth muscle which contracts to release fluid from the glands
function
produce an alkaline secretion rich in fructose (sugar) used to provide energy for sperm (makes up 60% of seminal fluid)
secrete prostaglandins that are capable of causing uterine contractions to help sperm move through this organ
prostate gland
location
just inferior to the neck of the bladder
surrounds the first portion of the urethra (prostatic urethra)
structure
size and shape of a chestnut
function
secretes an alkaline fluid which contains enzymes
helps to neutralize acidic environment of vagina (30% of semen)
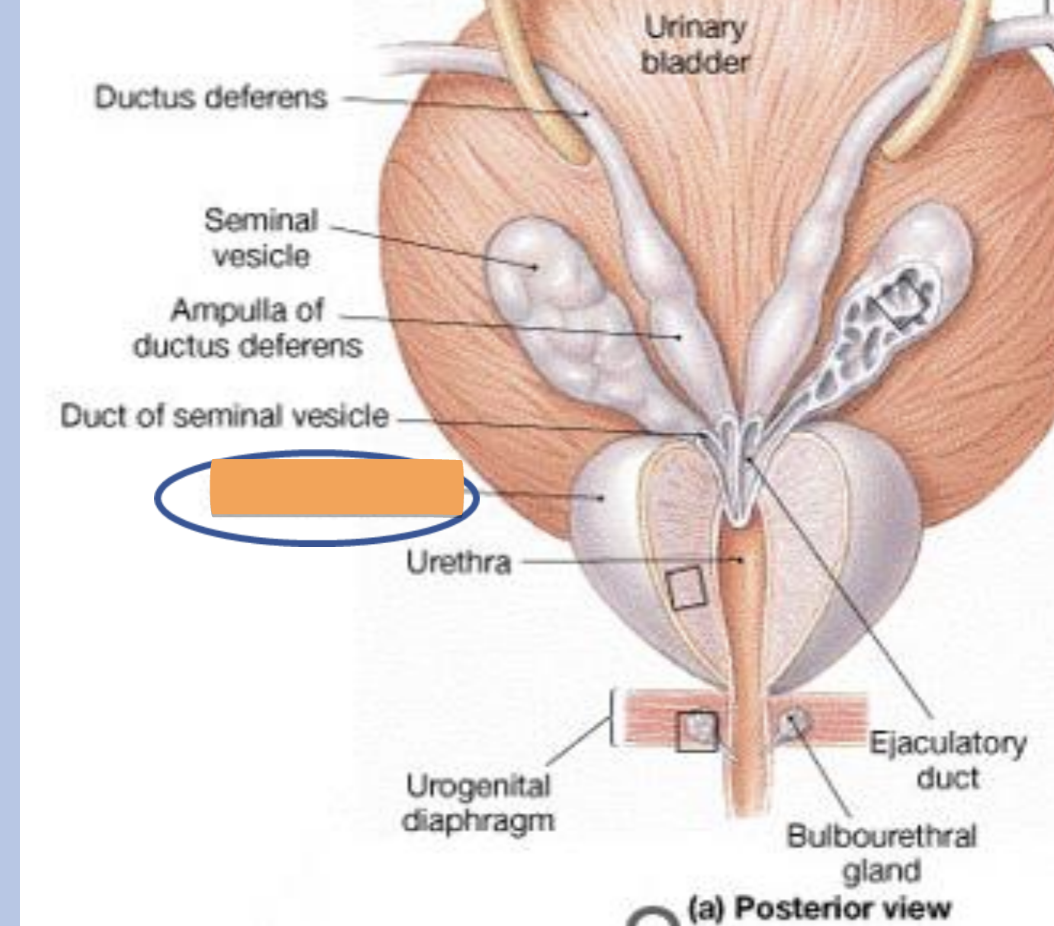
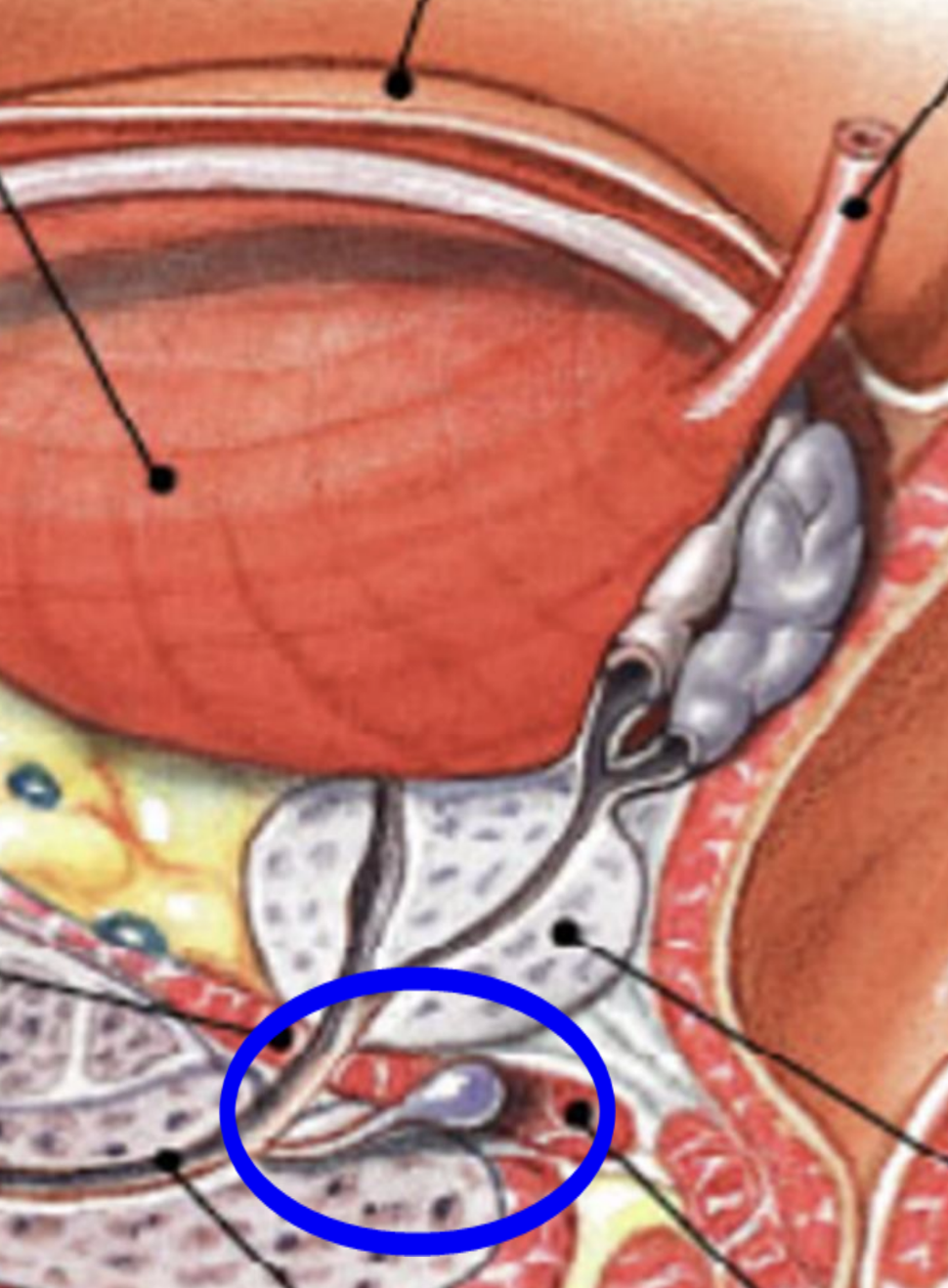
bulbourethral (cowper’s) glands
location
muscular layer of the pelvic floor
structure
small glands with a duct opening into the urethra
function
secrete a mucous-like fluid which lubricates the urethra
scrotum
location
somewhat posterior to the penis
structure
sac-like structure covered by fascia (CT) and skin
contains muscle fibers (cremaster muscle)
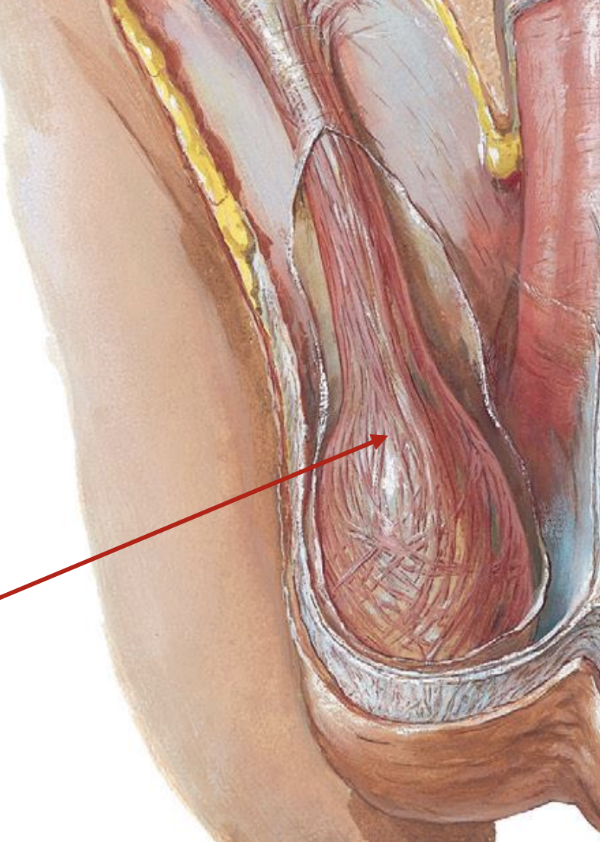
scrotum function
supports and protects testes
helps to regulate the position of the testes and thereby regulate their temperature
optimum temp for sperm production is 95 F
a. when cold:
cremaster muscle contracts and pulls testes up towards warm body wall
b. when hot:
skin is more flaccid & loose
cremaster muscles relax allowing testes to be further away from body wall
penis
structure
shaft
contains highly vascular tissue
composed of sponge-like = erectile tissue
glans
- expanded, terminal position
- contains opening of urethra
- foreskin - retractable portion of skin (removed during circumcision)contains penile urethra - passageway for both sperm and urine
erection
under parasympathetic control
occurs when vascular spaces become engorged with blood and blood is not permitted to drain
erectile tissue becomes rigid
ejaculation
under sympathetic control
affects smooth muscle of the glands and vessels of the reproductive system