LS4004 Human Physiology - Renal Physiology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Kidneys main 6 jobs
-blood composition regulation
-urine production/ waste removal
-production of hormones
-regulation of plamsa ph
-regulation of ions
-extracellular blood volume, blood pressure control
medulla of kidney
inner portion of kidney, composed of collecting tubules that empty into the renal pelvis
Uterer
Tubes tha carries urine from kidney to bladder
Urethra
Muscular tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body
Bladder
stores urine
High functional redundancy
A lot of the nephrons can fail before function is affected
Why is high functional redundancy bad?
Problems may not be detected until irreverable damahe has been done to the nephrons
kidney is concave or convex
concave
kidney is facing or away from spine
facing spine
normal osmolaroty
300osm
Thirst
Kidney controls thirst to keep blood around 290 Osm
Blood too acidic
Remove H+
Blood too alkaline
Remove HCO3 -
Why is the kidney so important?
Disturbances in blood volume or blood composition cause SERIOUS MEDICAL PROBLEMS!
An effect of low blood pressure
-no blood flow to organs
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
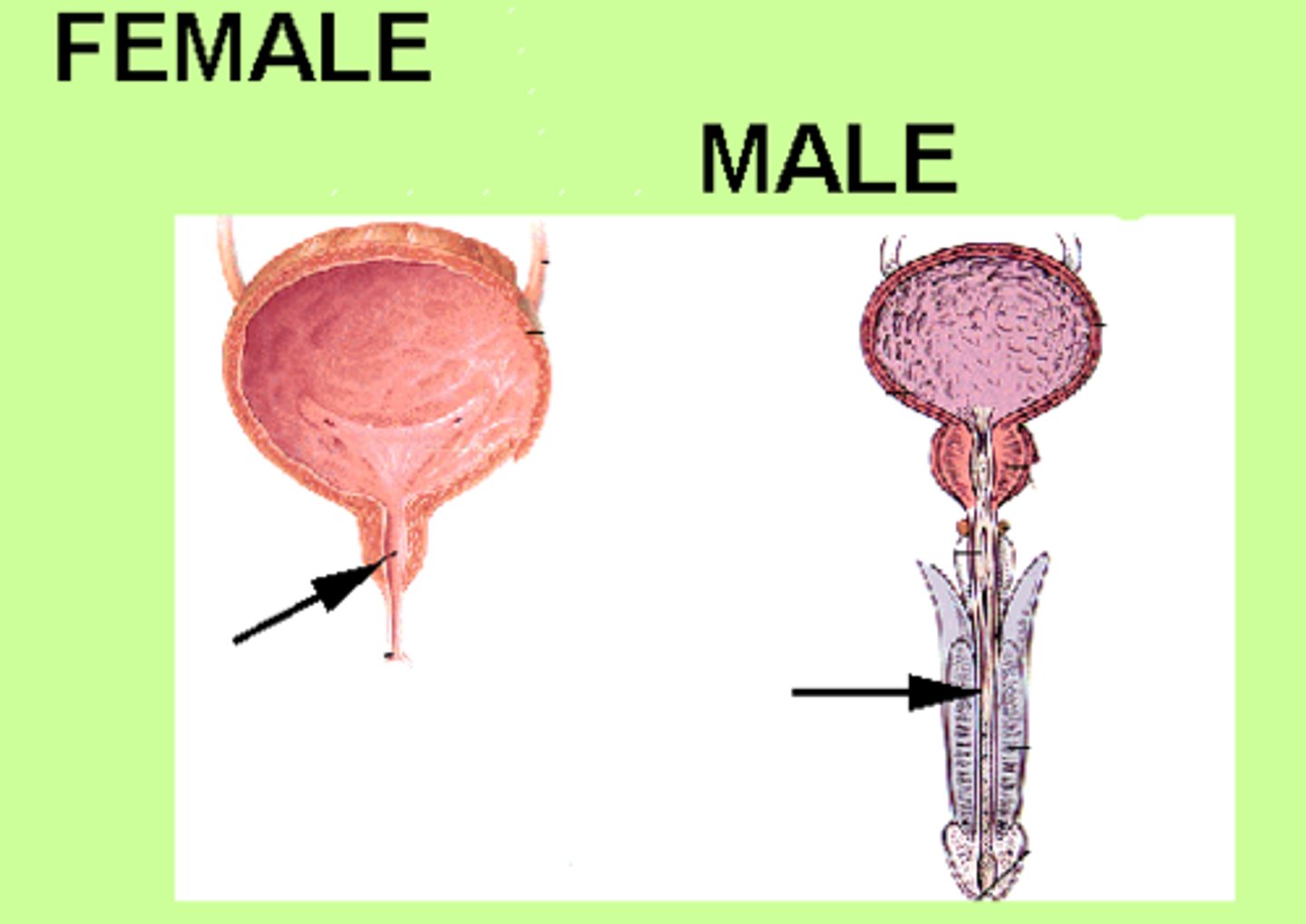
why are UTI chances higher for women?
The urethra is closer to the bladder in females, men have a penis between them, women only have a short distance
chain from blood to micturition
blood to nephron, becomes urine, to the ureter, to the bladder, to urethra, expulsion, process of micturition
medical term for unrination
micturition
what bacteria is most common in UTI cases
E.Coli is 80% of UTI cases
Renal arteries
give blood to kidney (Away from heart)
Renal Veins
feeds used deoxygenated blood into the inferior cava
Kidneys recieves ?% of cardiac output
20-25%
How does the blood move through the body via kidneys
The oxydenated blood in the body travels (from the aorta) around unfiltered just giving out oxyen and travelling back to the heart.
The unflitered oxgenated blood travels from the aorta to the renak atery, which goes tpo the kidney, which used the oxygen and filters to blood, the feeds the deoxygenated blood and flows out urine.
afferent arterioles
renal artery spilts and spilts until the afferent arterioles which - carry blood unto the glomerulus (that blood gives the oxydgen needed for filtration)
efferent arterioles
small artery that carry blood away from the glomerulus after filtation has occured, this splits into the peritubular carpillaries
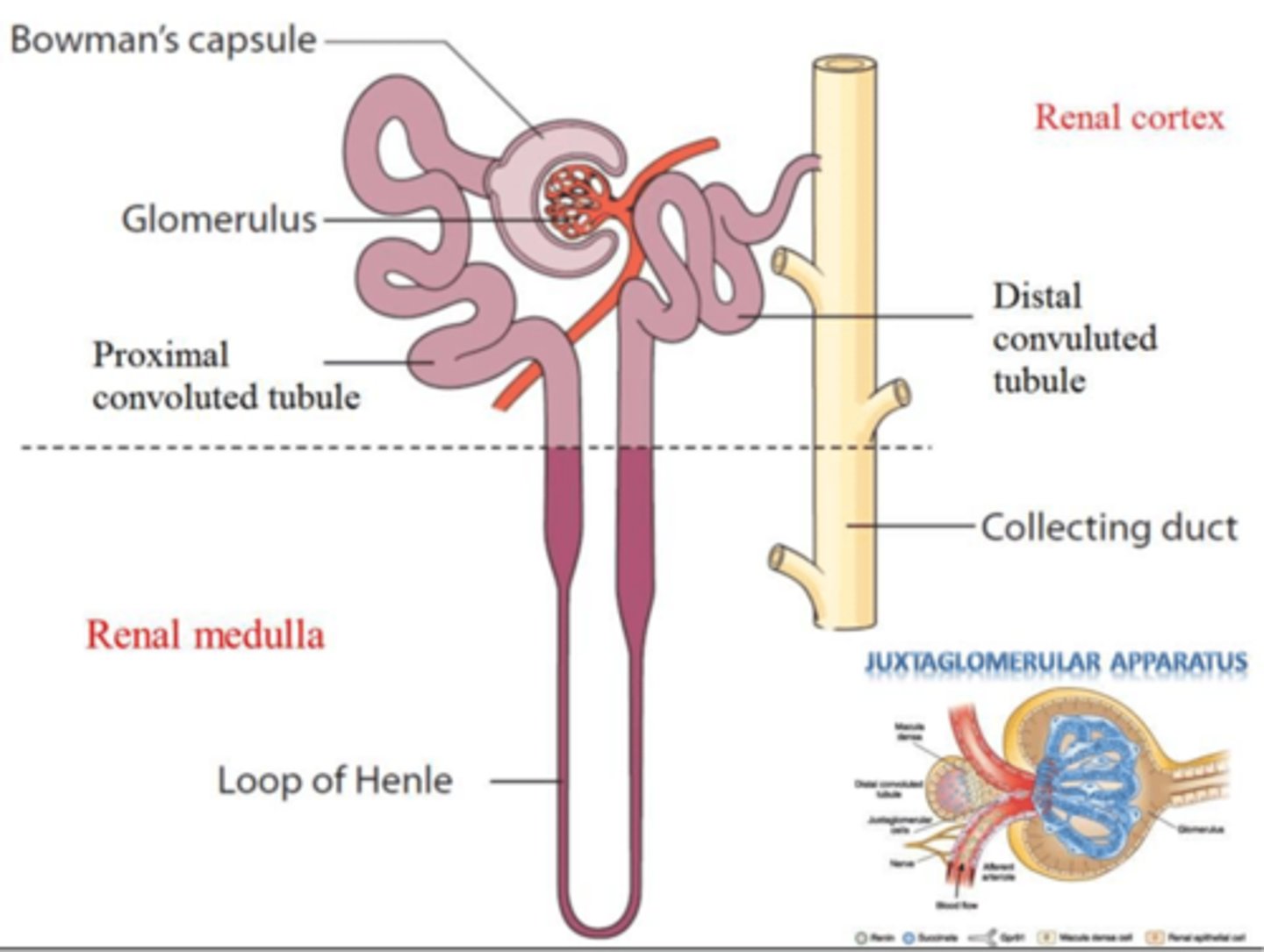
Bowman's capsule
cup-shaped strucutre of the nephron of a kidney which encloses the glomerulus and which filtration takes place.
peritubular capillaries
The network of tiny blood vessels that surrounds the proximal and distal tubules in the kidney
Promixal convoluted tubule
Tubule that comes from the glomerulus, before the loop of Henle
Responsible for isosmotic reabsorption of water and nutrients
distal convoluted tubule
Between the loop of Henle and the collecting duct; Selective reabsorption and secretion occur here, most notably to regulate reabsorption of water and sodium
Loop of Henle
section of the nephron tubule that is responsible for conserving water and minimizing the volume of the filtrate
juxtamedullary nephrons
Nephrons that dip into the medula. they have longer loops of henle
cortex of kidney
outer layer of kidney that contains nephrons
Vasa recta
peritubular capillaries that serve juxtamedullary nephrons
peritubular capillaries merge into
venules, to veins, to the renal vein
tubules of the kidney
passageways, epithelial cells, tight junctions, selective permulability for ions
Bowman's Capsule
a hollow, ball shaped structure,
consuists of 2 layers
1) podocytes - footlike cells that wrap around the glomular carpillaries, cutting small gaps in the them, allowing the passage of filtrate
2) Parietal Layer- simple sqaumous layer of epilial cells that provide structural support
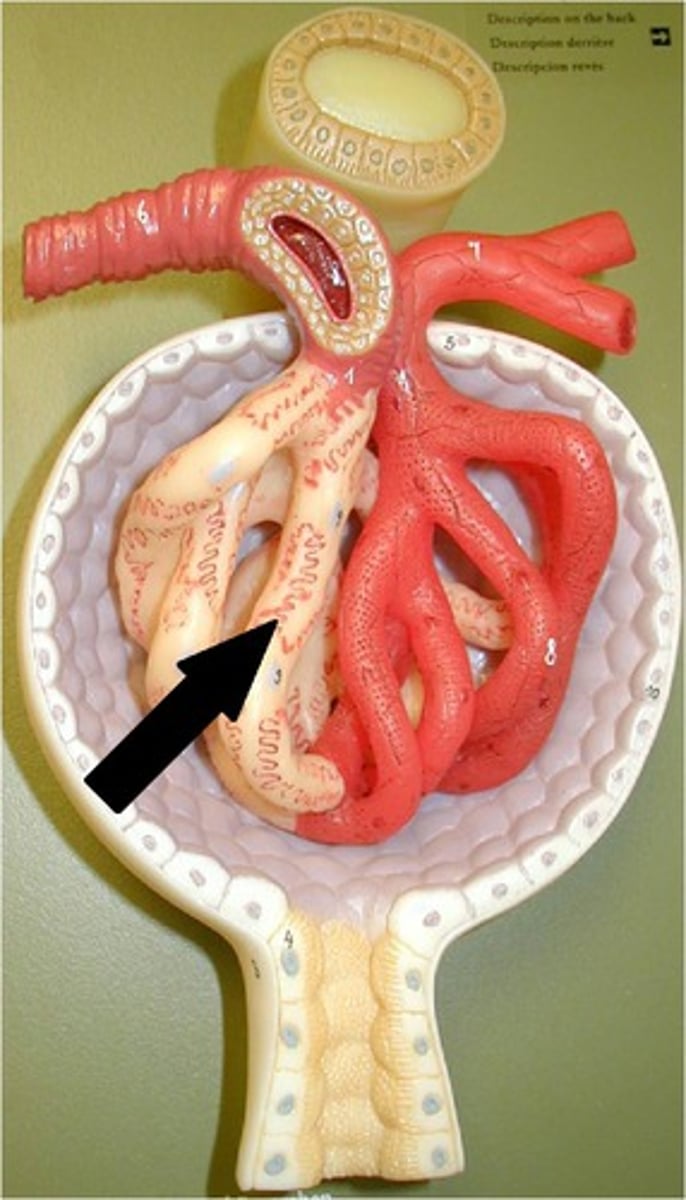
glomerulus
The ball of capillaries at the beginning of the nephron where blood filtration takes place.
what % of the nephrons dip into the medula?
Only 20%
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
The aff-erent arteriole and loop of Henle
The Afferent artoerole does parachute sinalling (letting out hormones that act of nearby cells) with the distal convuled tubule to:
Control salt levels
Regulate blood flow
water reabsorption
Where is the ascending limb of the loop of henle?
The loop of Henle loops back on itself so that acending limb is between the afferent and efferent arterioles
what ans where is reabsorbtion
movement of sunstances from the kidney tubule to blood vessels
pertibular carpillaires
what is secretion
movement og molecules from blood vessels back into the kidney tubules
why does secretion occur?
some molecules were too big to enter tubule at glomerulus
Total pressure in nepron
10mmHg
Carpillary ONCOTIC [colloid] Pressure
Pulling force from proteins in water/blood plasma, keeping water in the capillaries [prevents leaking]
-30mmHg
Carpillary pressure
Blood prshing against the walls of the [any] capillary in the body
affected by the body
the capillary pressure provides the concentration gradient for diffusion to occur for the exchange of substances
Glomeular Hydrostatic pressure
Capillary pressure localised to the glomelular carpillairies
Driving force for filtration, drives substajnces out ofthe carpillaries [FILTRATION]
controlled by kidney
glomerular filtration rate
volume of fluid filtered from the glomeruli of the kidneys into the renal tubules per unit of time
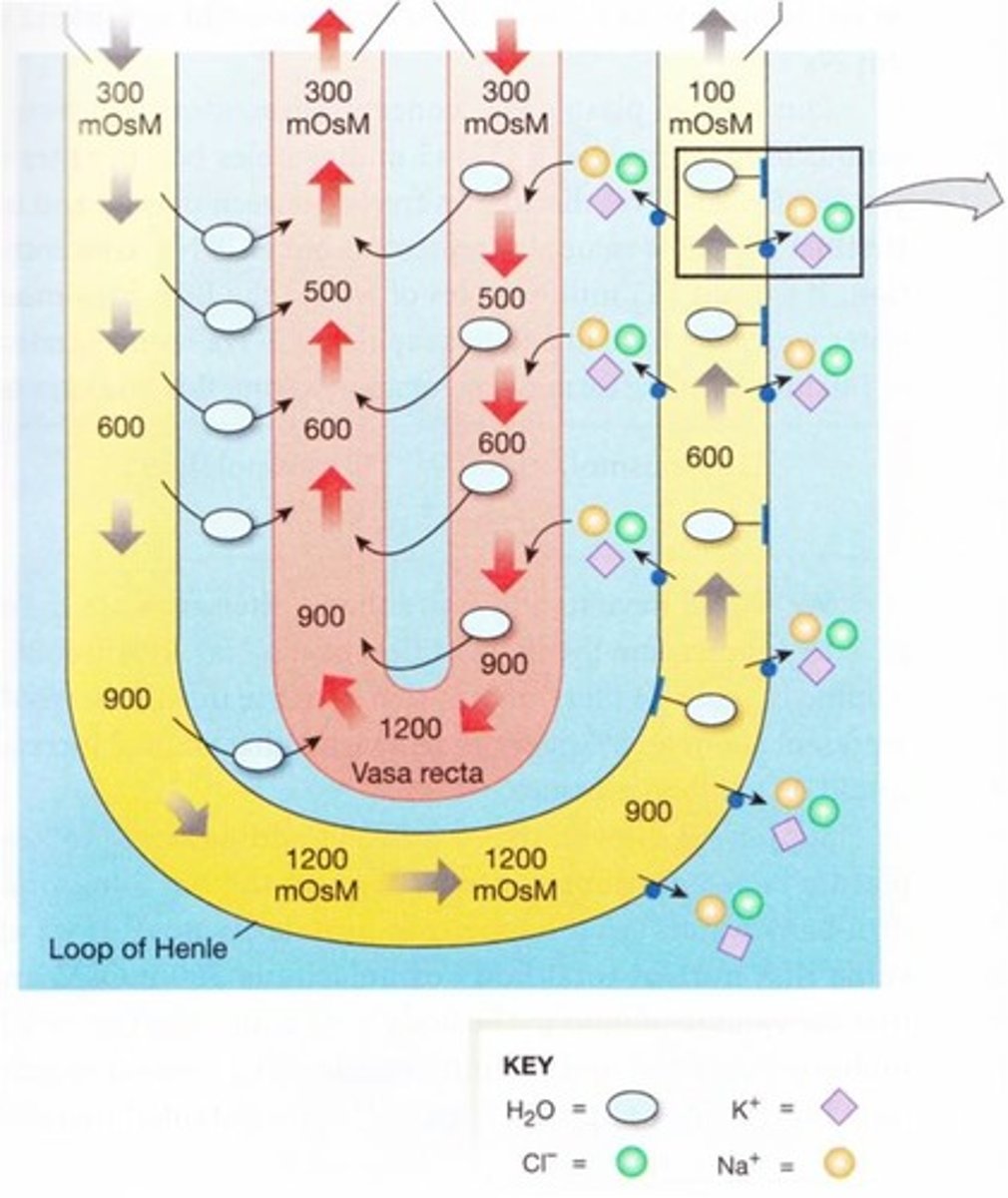
Countercurrent multipication mechanism
DESCENDING LIMB:
water leaves PASSIVELY to help equilibriate molarity with interstitial fluid
ACENDING LIMB:
sodium pumped out to decrease molarity. Has to have 200OsM diffrernce with interstitial fluid.
COUNTERCURRENT MULTIPLICATION
NAME ORIGIN
COUNTERCURRENT: descending, then ascending
MULTIPLICATION:
molarity increases [multiplies] as you go further
RAAS
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Angiotensin --Renin--> Angiotensin I --ACE--> Angiotensin II -------> Aldosterone
renin
Realeased by the blood when Kidney detects low blood Pressure or low sodium levels
aldosterone
HORMONE
works in kidney
increases sodium reabsorption to increase blood sodium
increased water reabsorption to increase blood volume- blood presure
angiotensin
Angiotensin - found in lungs
Angiotensin I - substrate for ACE [angiotenin converting molecule{found in the lungs}]
Angiotensin II - POTENT vasoCONSTRICTOR [increases blood pressure even before aldosterone]
ADH
antidiuretic hormone
diuresis
increased formation and secretion of urine
Naturesis
increased urinary excretion of Na
Diruetics
Drugs that promotes diuresis (above phsiologic levels)
Direct and Indirect effects of diuretics
DIRECT:
works on nephrons
affects ion pumps, receptors, enzymes
INDIRECT:
increased plasma volume
increased kidney blood flow
increased water retention
NEED TO REDO
COUNERCURRENT MULTIPLICATION
PULLING FORCES AND PRESSURE
PORTAL SYSTEM
THIRST
osmoticc diuretics
PROMOTOE DIURESIS BY CREATING A AN OSMOTIC GRADIENT IN THE KINDEY TUBULES
Symptoms of UTI
Pain from urination, increased urination
Glomerulus function
filtration of blood
What and where is filtatrion
movemnet of substances from blood vessel to tubule
only in bowmans capsule