Articles of the Constitution
5.0(1)Studied by 22 people
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nikith with like 10 questions
Last updated 12:44 PM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Article 1
Establishes the Legislative Branch

2
New cards
Article 2
Establishes the Executive Branch

3
New cards
Article 3
Establishes the Judicial Branch

4
New cards
Article 4
explains the relationships between the states
5
New cards
Article 5
explains the process for amending the constitution
6
New cards
Article 6
discusses the Law of the land, supremacy of the Constitution
7
New cards
Article 7
explains the conditions for Ratification of the Constitution

8
New cards
Preamble
"We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America."

9
New cards
Ratify an Amendment
3/4 of state legislatures must approve the amendment

10
New cards
Amendment- Propose
2/3 House of Rep and Senate must vote

11
New cards
Term of office - Senate
6 years

12
New cards
Term of office - House of Representatives
2 years

13
New cards
Term of office - President
4 years

14
New cards
Most important federal court
The Supreme Court

15
New cards
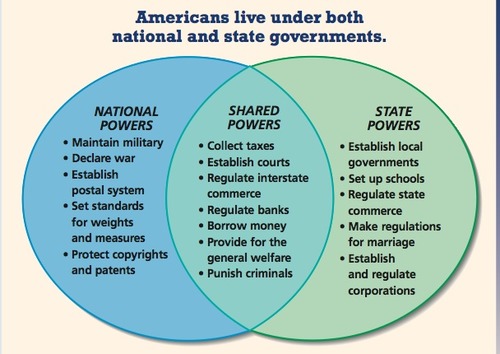
Federalism
division of power between the states and the national governments
16
New cards
Each state has how many senators?
2

17
New cards
Each state has how many members of the House of Representatives
depends on the state's population
18
New cards
Republicanism
A form of government in which people elect representatives to create and enforce laws
19
New cards
Limited Government
The idea that certain restrictions should be placed on government to protect the natural rights of citizens.
20
New cards
Checks and Balances
A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power
21
New cards
Separation of Powers
Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive applying and enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law
22
New cards
Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.
23
New cards
Individual Rights
Basic liberties and rights of all citizens are guaranteed in the Bill of Rights.
24
New cards
1st Amendment
Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Assembly, and Petition
25
New cards
2nd Amendment
Right to bear arms
26
New cards
3rd Amendment
No quartering of soldiers
27
New cards
4th Amendment
Protection against Unreasonable Search and Seizure
28
New cards
5th Amendment
The Right to Remain Silent, no Double Jeopardy, right to due process
29
New cards
6th Amendment
The right to a Speedy Trial by jury, representation by an attorney for an accused person
30
New cards
7th Amendment
Right to a trial by jury in civil cases
31
New cards
8th Amendment
No cruel or unusual punishment
32
New cards
9th Amendment
Citizens entitled to rights not listed in the Constitution
33
New cards
10th Amendment
Powers not given to federal government go to people and States
34
New cards
John Locke
English philosopher who advocated the idea of a "social contract" in which government powers are derived from the consent of the governed and in which the government serves the people; also said people have natural rights to life, liberty and property.
35
New cards
Unalienable Rights
LIFE, LIBERTY, and the PURSUIT OF HAPPINESS - rights that cannot be taken away by the government
36
New cards
3/5 Compromise
the decision at the Constitutional convention to count slaves as 3/5 of a person for the purpose of deciding the population and determining how many seats each state would have in Congress
37
New cards
The Great Compromise
Compromise made by Constitutional Convention in which states would have equal representation in one house of the legislature and representation based on population in the other house
38
New cards
Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the Constitution
39
New cards
U.S. Constitution (1787)
Replaced the Articles of Confederation and established a functioning government. Established (1) federalist system, (2) separation of powers, (3) checks and balances, (4) Bill of Rights.
40
New cards
Who wrote the constitution
James Madison
41
New cards
When was it written
September 17, 1787
42
New cards
When was it ratified
March 9, 1789
43
New cards
Amendment 11
Prevents federal courts from hearing states get sued
44
New cards
Amendment 12
refined the process whereby a President and a Vice President are elected by the Electoral College
45
New cards
Amendment 15
Africans can vote
46
New cards
Amendment 16
Gave power for the federal government to collect income tax
47
New cards
Amendment 17
The Senate of the United States shall be composed of two Senators from each State, elected by the people thereof, for six years; and each Senator shall have one vote. (Senators are now voted by people)
48
New cards
Amendment 19
Women get vote
49
New cards
Amendment 20
push back the start date to early January in order to shorten the “lame duck” session in election years
50
New cards
Amendment 22
No person shall be elected to the office of the President more than twice
51
New cards
Amendment 23
District of Columbia vote now for president because electoral college act as a state
52
New cards
Amendment 24
Prohibits poll tax in elections
53
New cards
Amendment 25
Vice president became president bc president no longer here, congress confirmed new VP
54
New cards
Amendment 26
Voting age is now 18
55
New cards
Amendment 27
Any paycheck raises for congress will take into affect after elections
56
New cards
When did the 3/5 compromise take place?
1787 constitutional convention, by James Wilson
57
New cards
When did the constitutional convention occur?
May 25, 1787 – Sep 17, 1787
58
New cards
Who created the first 10 amendments?
James Madison
59
New cards
Who is the father of the constitution?
James Madison
60
New cards
What branch can IMPEACH?
legislative branch
61
New cards
What is impeachment?
The accusation of a president, judge, or supreme court justice.
62
New cards
What is the JUDICIAL branch?
A branch that interprets the Constitution and decides whether or not a law is unconstitutional.
63
New cards
Who can veto? What does that do?
The bill passed to the president doesn't become a law if this is done.
64
New cards
What is the EXECUTIVE branch?
A branch that is responsible for enforcing the laws of the land, and responsible for military.
65
New cards
How many essays in the federalists papers?
85
66
New cards
Who wrote the federalist papers?
John Jay, James Madison, and Alexander Hamilton
67
New cards
When were the federalist papers written?
October 1787 and May **1788**
68
New cards
The _____________ must turn over all evidence and witnesses so defendant may be prepared
prosecution
69
New cards
If defendant doesn’t show for court, the _________ keeps the bail and issues another warrant for arrest
court
70
New cards
What is Criminal Procedure
Deals with the set of rules governing the series of proceedings through which the government enforces substantive criminal law.
71
New cards
The Articles of Confederation was the U.S.' first:
constitution
72
New cards
Under the Articles of Confederation, which government had the power to tax?
state
73
New cards
Why were the articles of confederation replaced by the constitution?
to make a more powerful central government while letting people have freedom
74
New cards
When were the articles of confederation ratified?
March 1st, 1781
75
New cards
Leader of the House of Representatives?
Speaker of the House
76
New cards
How many electoral votes must you get to win a presidential election?
270
77
New cards
How many electors in the electoral collage?
538
78
New cards
How many judges normally sit on the appellate court?
3
79
New cards
What branch is the supreme court part of?
Judicial
80
New cards
Who (or what group) must approve the newly picked judges?
The senate
81
New cards
Who picks federal judges?
The president
82
New cards
The supreme court has a chief justice and:
8 associate justices
83
New cards
The president must have lived in the US for at least:
14 years
84
New cards
Who writes tax bills?
HR
85
New cards
The constitution forbids what bill?
A bill of attainder
86
New cards
Who prints money?
congress
87
New cards
How many amendments were added by 1791?
10 (although 12 were proposed)
88
New cards
Where did the constitutional convention meet?
PHILADELPHIA
89
New cards
How many people signed the constitution?
39
90
New cards
who was the first speaker of the house of representatives
Frederick A.C. Muhlenberg
91
New cards
First Vice president?
John Adams (technically Aaron Burr was the first ELECTED one)
92
New cards
who was the first chief justice of the supreme court?
John Jay
93
New cards
One of the main authors for the declaration of independence:
Thomas Jefferson
94
New cards
What is the division of the government into 3 branches called?
The Separation of Powers
95
New cards
A person must be brought before the judge, and stated what his reason for arrest is: Habeas Corpus
Article 1, Section 9
96
New cards
Someone can not be punished for something they did before a law is passed.
Ex post facto
97
New cards
What an example of due process?
A fair trial
98
New cards
The president can limit the power of congress using a ________.
Veto
99
New cards
3 types of federal courts:
Supreme Court, Us District Courts, Circuit court of appeals.
100
New cards
What evidence is needed in order to prove treason?
2 witnesses must testify in open court or the accused person must admit guilt.