Clinical Pathophysiology Exam 2
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
1
New cards
Hypoxemia
Abnormal low amount of O2 in blood
2
New cards
Hypoxia
Decreased oxygen at the tissue level
3
New cards
Hypercapnia
Abnormal high amount of CO2 in the blood
4
New cards
Hypoventilation
Decreased rate and depth of respirations
5
New cards
Hyperventilation
Increased rate and depth of respirations
6
New cards
Labored Respirations
General term for slow, deliberate breathing associated with airway obstruction
7
New cards
Tachypnea
Fast respiratory rate
8
New cards
Bradypnea
Slow respiratory rate
9
New cards
Normal V/Q ratio
0\.8
10
New cards
Shunting
Blood is flowing but there is no ventilation because alveoli is blocked by something like a mucous plug
11
New cards
Dead Space
Alveoli is getting ventilated but there is a blood clot that is blocking perfusion
12
New cards
No ventilation but positive perfusion
Shunting
13
New cards
Positive ventilation but no perfusion
Dead Space
14
New cards
Normal arterial blood pH range
7\.35 - 7.45
15
New cards
What is pH?
Indirect measurement of hydrogen ion (H+) concentration (acid).
16
New cards
What is PaO2?
Refers to pressure of dissolved oxygen in the arterial blood.
17
New cards
Normal PaO2 arterial range
80 - 100mmHg
18
New cards
What is PaCO2?
Refers to the pressure of dissolved carbon dioxide gas.
Think Respiratory!
Think Respiratory!
19
New cards
Normal PaCO2 arterial range
35 - 45mmHg
20
New cards
What is HCO3?
The body’s main bicarbonate.
Regulated by the kidneys.
Regulated by the kidneys.
21
New cards
Normal HCO3 arterial range
22 - 26mEq/L
22
New cards
What does the Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve respresent?
Hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen or how readily hemoglobin picks up oxygen in the lungs and releases it into the tissues.
23
New cards
Left shift in the Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
Oxygen does not readily dissociate into the tissues, oxygen likes to stay with hemoglobin.
At risk for tissue hypoxia which can then lead to tissue ischemia and tissue necrosis.
At risk for tissue hypoxia which can then lead to tissue ischemia and tissue necrosis.
24
New cards
Right shift in the Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
Decreased hemoglobin affinity to oxygen. Bohr Effect makes it hard for oxygen to bind to hemoglobin in the lungs.
This is an association problem that can cause sickle cell anemia.
This is an association problem that can cause sickle cell anemia.
25
New cards
Patho of Respiratory Acidosis
Carbonic acid excess, increased retention of CO2
26
New cards
Etiologies of Respiratory Acidosis
Hypoventilation
Respiratory depression from diseases, poisons, anesthetics
Airway obstruction
Alveolar-capillary blockage
Inadequate mechanical ventilation
Inadequate chest expansion
Respiratory depression from diseases, poisons, anesthetics
Airway obstruction
Alveolar-capillary blockage
Inadequate mechanical ventilation
Inadequate chest expansion
27
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Acidosis
Respiratory: First increased then decreased
Neurological: Headaches, tremors, lethargy, disorientation, muscle twitching
Complications: Convulsions, arrhythmias, coma
Neurological: Headaches, tremors, lethargy, disorientation, muscle twitching
Complications: Convulsions, arrhythmias, coma
28
New cards
How does the body try to compensate during Respiratory Acidosis?
Kidneys excrete H+ and reabsorb HCO3 to get pH up
Risk for hypokalemia
Risk for hypokalemia
29
New cards
Patho of Respiratory Alkalosis
Carbonic acid effect
30
New cards
Etiologies of Respiratory Alkalosis
Hyperventilation
Hypoxemia
Fear
Pain
Anxiety
Exercise
Brain Injury
Hypoxemia
Fear
Pain
Anxiety
Exercise
Brain Injury
31
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Alkalosis
Respiratory: Hyperventilation/tachypnea (then decreased respirations to compensate)
Neurological: Dizziness, confusion, muscle cramps, tetany
Complications: Dysrhythmias, convulsions, coma
Neurological: Dizziness, confusion, muscle cramps, tetany
Complications: Dysrhythmias, convulsions, coma
32
New cards
How does the body try to compensate during Respiratory Alkalosis?
Kidneys reabsorb H+ and excrete HCO3 to get pH down
33
New cards
Patho and Etiologies of Metabolic Acidosis
Increase in Acid: Inadequate elimination of H+ ions (Renal Disease), and excess production of H+ ions (DKA)
Decrease in Base: Inadequate production of HCO3 (Renal Disease), and excess elimination of HCO3 (diarrhea)
Decrease in Base: Inadequate production of HCO3 (Renal Disease), and excess elimination of HCO3 (diarrhea)
34
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Metabolic Acidosis
Respiratory: Tachypnea
Neurological: Headache, confusion, lethargy (potassium shifts)
Complications: Coma, ventricular dysrhythmias, hyperkalemia
Neurological: Headache, confusion, lethargy (potassium shifts)
Complications: Coma, ventricular dysrhythmias, hyperkalemia
35
New cards
What does the body try to do to compensate during Metabolic Acidosis?
Lungs eliminate CO2 (Kussmaul)
Kidneys reabsorb HCO3 and excrete H+
Kidneys reabsorb HCO3 and excrete H+
36
New cards
Patho and Etiologies of Metabolic Alkalosis
Increase in Base: Ingesting bicarb
Decrease in Acid: NGT suctioning, vomiting
Decrease in Acid: NGT suctioning, vomiting
37
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Metabolic Alkalosis
Respiratory: Hypoventilation to retain CO2
CNS: Skeletal muscle weakness, confusion, muscle cramps
Cardiac: Tachycardia
Complications: Dysrhythmias, convulsions, hypokalemia
CNS: Skeletal muscle weakness, confusion, muscle cramps
Cardiac: Tachycardia
Complications: Dysrhythmias, convulsions, hypokalemia
38
New cards
What does the body try to do to compensate during Metabolic Alkalosis?
Lungs retain CO2 (slow breathing)
Kidneys reabsorb H+ and excrete HCO3
Kidneys reabsorb H+ and excrete HCO3
39
New cards
What is Asthma?
Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
40
New cards
Patho of Asthma
Immune activation of IgE, mast cell degranulation, chemotactic mediators, leukotrienes and histamine, inflammatory response, vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, bronchospasm, vascular congestion, bronchial hyperresponsiveness
41
New cards
Etiologies of Asthma
Allergen
Irritant exposure
Risk Factors: Obesity, GERD, chronic viral infection
Irritant exposure
Risk Factors: Obesity, GERD, chronic viral infection
42
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Asthma
Expiratory wheezing
Dyspnea
Chest tightness
Non-productive cough (the body’s way of trying to open up the airway)
Tachypnea
Tachycardia
Dyspnea
Chest tightness
Non-productive cough (the body’s way of trying to open up the airway)
Tachypnea
Tachycardia
43
New cards
Complications of Asthma
Hypoxemia
Status asthmaticus → severe bronchoconstriction
High risk for developing COPD
Status asthmaticus → severe bronchoconstriction
High risk for developing COPD
44
New cards
What is Chronic Bronchitis?
Chronic inflammatory response from inspired irritants
45
New cards
Patho of Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic inflammation of airway, increase mucous production from goblet cell hyperplasia and hypertrophy, impaired ciliary function, hypertrophy and narrowing of airways, airway obstruction
46
New cards
Etiologies of Chronic Bronchitis
History of smoking
Occupation exposure to toxins
Disrupted lung growth
Occupation exposure to toxins
Disrupted lung growth
47
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Chronic Bronchitis
Productive cough (smoker’s cough, wet sounding)
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Cyanosis
Polycythemia (increase in red blood cells)
Cor Pulmonale (can lead to right sided heart failure, right ventricular enlargement)
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Cyanosis
Polycythemia (increase in red blood cells)
Cor Pulmonale (can lead to right sided heart failure, right ventricular enlargement)
48
New cards
Complications of Chronic Bronchitis
Pulmonary Hypertension
Right sided heart failure
Cor Pulmonale
Right sided heart failure
Cor Pulmonale
49
New cards
What is a Pulmonary Edema?
Excess fluid in the lungs
50
New cards
Patho of a Pulmonary Edema
Increased left atrial pressure, increased pulmonary hydrostatic capillary pressure → edema
Injury to capillary endothelium, increased capillary permeability → edema
Blockage of lymph vessels, inability to remove fluid from interstitial space → edema
Injury to capillary endothelium, increased capillary permeability → edema
Blockage of lymph vessels, inability to remove fluid from interstitial space → edema
51
New cards
Etiologies of a Pulmonary Edema
Left sided heart failure (MOST COMMON CAUSE)
Capillary endothelium injury, alveolar capillary membrane damage
Lymph vessel blockage (tumor or scar tissue)
Capillary endothelium injury, alveolar capillary membrane damage
Lymph vessel blockage (tumor or scar tissue)
52
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of a Pulmonary Edema
Dyspnea at rest
Anxiety
Inspiratory crackles
Tachycardia
Disorientation and confusion (from lack of oxygen to the brain and buildup of CO2)
Pink frothy sputum (from irritation)
Hypoxemia
Anxiety
Inspiratory crackles
Tachycardia
Disorientation and confusion (from lack of oxygen to the brain and buildup of CO2)
Pink frothy sputum (from irritation)
Hypoxemia
53
New cards
What is a Pulmonary Embolism?
Occlusion of a portion of the pulmonary vascular bed by a thrombus, embolus, tissue fragment, lipids, or an air bubble.
54
New cards
Patho of a Pulmonary Embolism
Virchow triad, thrombus formation, embolus, occlusion, hypoxic vasoconstriction, pulmonary edema and atelectasis
55
New cards
Etiologies of a Pulmonary Embolism
DVT: Deep vein thrombosis
Virchow Triad: Venous stasis, hyper-coagulability, and injuries to the endothelial cells that line the vessels
Virchow Triad: Venous stasis, hyper-coagulability, and injuries to the endothelial cells that line the vessels
56
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of a Pulmonary Embolism
Sudden onset of pleuritic pain
Dyspnea
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Fever
Present grey in color
Most of the time, O2 stat is less than 90%
Dyspnea
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Fever
Present grey in color
Most of the time, O2 stat is less than 90%
57
New cards
Complications of a Pulmonary Embolism
Cor Pulmonale
Pulmonary Infarction
Pulmonary Infarction
58
New cards
What is Atelectasis?
Collapse of lung tissue
59
New cards
Patho of Atelectasis
Alveoli lack full inflation, buildup of secretions, collapse of alveoli, reduced gas exchange
60
New cards
Etiologies of Atelectasis
Obstruction of airway (by something like a mucous plug or food)
Hypoventilation from pain (inadequate surfactant production)
Compression of the lung or bronchi (by tumors, aneurysms, or enlarged lymph nodes)
Hypoventilation from pain (inadequate surfactant production)
Compression of the lung or bronchi (by tumors, aneurysms, or enlarged lymph nodes)
61
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Atelectasis
Dyspnea
Diminished breath sounds on that side
Productive cough (from secretions)
Fever (from inflammation and possible infections from the secretions)
Leukocytosis
Diminished breath sounds on that side
Productive cough (from secretions)
Fever (from inflammation and possible infections from the secretions)
Leukocytosis
62
New cards
Complications of Atelectasis
Can lead to pneumonia and hypoxemia
63
New cards
What is Emphysema?
Abnormal permanent enlargement of the gas-exchange airways after exposure to irritants.
64
New cards
Patho of Emphysema
Inflammation of airway epithelium (from smoking) or inherited alpha antitrypsin deficiency, bronchiole wall collapse, destruction of alveolar walls, loss of elastic recoil, air trapping, bullous bleb formation, decreased gas exchange
65
New cards
Etiologies of Emphysema
History of smoking
Alpha antitrypsin deficiency (inherited disorder)
Occupation exposure
Alpha antitrypsin deficiency (inherited disorder)
Occupation exposure
66
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Emphysema
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Barrel Chest
Club fingers
Use of accessory muscles
Wheezing
Barrel Chest
Club fingers
Use of accessory muscles
67
New cards
Complications of Emphysema
Cor pulmonale
68
New cards
Modifiable Risk Factors of Hypertension
High sodium diet
Glucose intolerance
Anemia
Obesity
Smoking
Heavy alcohol use
Glucose intolerance
Anemia
Obesity
Smoking
Heavy alcohol use
69
New cards
Non-modifiable Risk Factors of Hypertension
Family history
Advancing age
Gender: females over age 55 and males over age 74
Black Race
Advancing age
Gender: females over age 55 and males over age 74
Black Race
70
New cards
CAD Modifiable Risk Factors
Dyslipidemia
Hypertension
Cigarette smoking
Diabetes Mellitus
Obesity/sedentary lifestyle
Atherogenic diet (high fat and meat)
Hypertension
Cigarette smoking
Diabetes Mellitus
Obesity/sedentary lifestyle
Atherogenic diet (high fat and meat)
71
New cards
CAD Non-modifiable Risk Factors
Increased age
Family history
Gender
Family history
Gender
72
New cards
What is Myocardial Ischemia?
Local or temporary deprivation of the coronary blood supply
73
New cards
Patho of Myocardial Ischemia
Myocardial O2 deficit from decreased blood supply, impaired pumping, glucose deprivation = anaerobic takeover, decreased cardiac output, blood flow restored
74
New cards
Etiologies of Myocardial Ischemia
Uncontrolled atherosclerosis
Coronary Spasm
Anemia
Coronary Spasm
Anemia
75
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Myocardial Ischemia
Stable Angina: Chest pain with exercise or stress relieved by rest, uncontrolled atherosclerosis
Prinzmental Angina: Chest pain unpredictable, not related to exercise or stress, vasospasm of coronary artery.
Silent Ischemia: No chest pain but fatigue, dyspnea, uneasy feeling, slight disorientation, sometimes feel “butterfly in the chest”, left ventricular sympathetic intervention
Prinzmental Angina: Chest pain unpredictable, not related to exercise or stress, vasospasm of coronary artery.
Silent Ischemia: No chest pain but fatigue, dyspnea, uneasy feeling, slight disorientation, sometimes feel “butterfly in the chest”, left ventricular sympathetic intervention
76
New cards
What is Artherosclerosis?
A form of arteriosclerosis, tends to develop in medium and large sized arteries.
77
New cards
Patho of Artherosclerosis
Injury and inflammation of endothelium, cellular proliferation, macrophages migration, LDL oxidation, fatty streak, fibrous plaque, complicated plaque
78
New cards
Etiologies of Atherosclerosis
Smoking
Diabetes
Hypertension
Hyperlipidemia
Obesity
Diabetes
Hypertension
Hyperlipidemia
Obesity
79
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Atherosclerosis
Initially asymptomatic
Angina
TIA (transient ischemic attacks)
Intermittent claudication
Angina
TIA (transient ischemic attacks)
Intermittent claudication
80
New cards
Patho of Left Sided Heart Failure
Decreased contractility causes SV to fall and LVEDV increases → Dilation
Aortic pressure falls and systemic arterial pressure drops, baroreceptors sense a drop, activates SNS and ADH released, increase in preload and afterload
Kidneys sense a drop in blood flow, activation of RAAS, increase PVR, increase in preload and afterload
Elevated hydrostatic pressure into pulmonary system, pulmonary edema
Aortic pressure falls and systemic arterial pressure drops, baroreceptors sense a drop, activates SNS and ADH released, increase in preload and afterload
Kidneys sense a drop in blood flow, activation of RAAS, increase PVR, increase in preload and afterload
Elevated hydrostatic pressure into pulmonary system, pulmonary edema
81
New cards
Etiologies of Left Sided Heart Failure
CAD (coronary artery disease)
Myocardial infarction (remodeling)
HTN; Pulmonary HTN
Valve disease
CKD (chronic kidney disease)
Anemia
Hyperthyroidism
Myocardial infarction (remodeling)
HTN; Pulmonary HTN
Valve disease
CKD (chronic kidney disease)
Anemia
Hyperthyroidism
82
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Left Sided Heart Failure
Dyspnea
Orthopnea
Frothy Sputum (pink tinged)
Fatigue
Decreased urinary output
Edema
Abnormal heart sounds (S3 gallop)
Pulmonary congestion (crackles)
Orthopnea
Frothy Sputum (pink tinged)
Fatigue
Decreased urinary output
Edema
Abnormal heart sounds (S3 gallop)
Pulmonary congestion (crackles)
83
New cards
Patho of Right Sided Heart Failure
Increased pulmonary vascular resistance, increased force of RV contraction, increased RV O2 demand and RV enlargement and increase in RV preload
Decrease O2 supply, RV hypoxia, decreased force of RV contraction, increased RV and RA preload, peripheral edema
Decrease O2 supply, RV hypoxia, decreased force of RV contraction, increased RV and RA preload, peripheral edema
84
New cards
Etiologies of Right Sided Heart Failure
Left sided heart failure
Increased pulmonary vascular resistance (cause RV to work against the resistance)
ARDS
COPD
Increased pulmonary vascular resistance (cause RV to work against the resistance)
ARDS
COPD
85
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Right Sided Heart Failure
Peripheral edema
Ascites
JVD
Hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver)
Nocturia
Weight Gain
Ascites
JVD
Hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver)
Nocturia
Weight Gain
86
New cards
What is Pericarditis?
An acute inflammation of the pericardium after an MI.
87
New cards
Etiologies of Pericarditis
Idiopathic
Viral
Autoimmune
Post MI
Viral
Autoimmune
Post MI
88
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Pericarditis
Fever
Tachycardia
Chest pain
Pericardial friction rub
Hypotension
ECG changes
Tachycardia
Chest pain
Pericardial friction rub
Hypotension
ECG changes
89
New cards
What is HTN?
(Hypertension) Consistent elevation of systemic arterial blood pressure
90
New cards
Patho of HTN
Dysfunction of SNS, RAAS, or natriuretic hormones, vasoconstriction, renal Na+ and H2O retention, increased peripheral resistance, increased blood volume, sustained HTN
91
New cards
Risk Factors/Etiologies of HTN
Primary: 92% - 95% of cases, gradual development, idiopathic
Secondary: Underlying disorders like kidney disease, thyroid problems, and some endocrine problems
Secondary: Underlying disorders like kidney disease, thyroid problems, and some endocrine problems
92
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of HTN
Headache (most common)
Fatigue
Impaired Vision
Decreased urine output
Dizziness
Epistaxis (nose bleeds)
Flushed Face
Fatigue
Impaired Vision
Decreased urine output
Dizziness
Epistaxis (nose bleeds)
Flushed Face
93
New cards
What is a Myocardial Infarction?
Death of cells in the myocardium, related to prolonged or severe ischemia lasting longer than 20 minutes.
Non-STEMI: Not full thickness, not as bad, easier to recover from
STEMI: Full thickness (transmural)
Non-STEMI: Not full thickness, not as bad, easier to recover from
STEMI: Full thickness (transmural)
94
New cards
Patho of Myocardial Infarction
O2 deprivation for longer than 20 minutes from obstruction of a coronary artery, cellular loss of K+, Ca+, Mg+, decreased pumping ability, loss of contractility
Angiotensin 2 released, peripheral vasoconstriction fluid retention, increased myocardial work
Catecholamine release, coronary artery spasm
Angiotensin 2 released, peripheral vasoconstriction fluid retention, increased myocardial work
Catecholamine release, coronary artery spasm
95
New cards
Etiologies of Myocardial Infarction
Uncontrolled atherosclerosis
CAD
Renal Disease
Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes
CAD
Renal Disease
Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes
96
New cards
Clinical Manifestations of Myocardial Infarction
Sudden severe chest pain (for women it can radiate to the jaw and down the arm)
Nausea and vomiting
Diaphoresis
Cool clammy skin
Elevated troponins, CK - MB (creatine kinase, myocardial bands)
EKG changes
Nausea and vomiting
Diaphoresis
Cool clammy skin
Elevated troponins, CK - MB (creatine kinase, myocardial bands)
EKG changes
97
New cards
Complications of Myocardial Infarction
Sudden cardiac arrest due to ischemia, left ventricular dysfunction, and electrical instability
Cardiogenic shock
Pericarditis
Pericardial Tamponade
Cardiogenic shock
Pericarditis
Pericardial Tamponade
98
New cards
What is posturing
An abnormal motor response to a painful stimuli
99
New cards
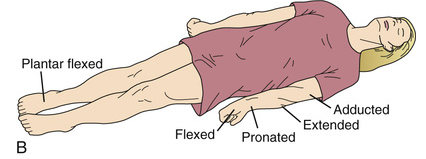
Decorticate
Flexion of arm, wrists, and fingers with adduction in the upper extremity and extension, internal rotation, and plantar flexion of lower extremity.
100
New cards
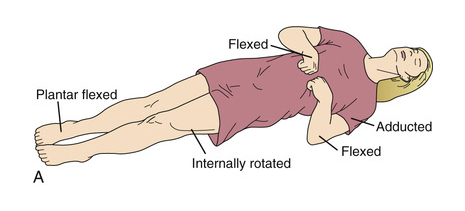
Decerebrate
Indicative of a more severe brain injury.
Opisthotonos (hyperextension of vertebral column) with clenching of teeth, extension, abduction, and hyperpronation of arms with extension of lower extremities.
Opisthotonos (hyperextension of vertebral column) with clenching of teeth, extension, abduction, and hyperpronation of arms with extension of lower extremities.